EP1533262B1 - Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn - Google Patents
Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1533262B1 EP1533262B1 EP03405823A EP03405823A EP1533262B1 EP 1533262 B1 EP1533262 B1 EP 1533262B1 EP 03405823 A EP03405823 A EP 03405823A EP 03405823 A EP03405823 A EP 03405823A EP 1533262 B1 EP1533262 B1 EP 1533262B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- web
- winding core
- winding
- gel
- water
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 34
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 34
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 17
- 239000000123 paper Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004115 Sodium Silicate Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000010338 boric acid Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium silicate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-][Si]([O-])=O NTHWMYGWWRZVTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052911 sodium silicate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010980 cellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000019794 sodium silicate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 claims 1
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000002985 plastic film Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 229920006255 plastic film Polymers 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000002390 adhesive tape Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003349 gelling agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002261 Corn starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000663 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004354 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002153 Hydroxypropyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008120 corn starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940099112 cornstarch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021485 fumed silica Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019447 hydroxyethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001863 hydroxypropyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010977 hydroxypropyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012785 packaging film Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006280 packaging film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001592 potato starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940116317 potato starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- -1 rice starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940100486 rice starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940100445 wheat starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H19/00—Changing the web roll
- B65H19/22—Changing the web roll in winding mechanisms or in connection with winding operations
- B65H19/28—Attaching the leading end of the web to the replacement web-roll core or spindle
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2301/00—Handling processes for sheets or webs
- B65H2301/40—Type of handling process
- B65H2301/41—Winding, unwinding
- B65H2301/414—Winding
- B65H2301/41419—Starting winding process
- B65H2301/41423—Starting winding process involving liquid, e.g. wetting core by water
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for winding a material web according to the preamble of claim 1.
- the present invention is based on the object in a method of the type mentioned to set the adhesion between the material web and the winding core so that it generates during winding during the first one to two complete revolutions of the winding core sufficient adhesive force between the material web and lateral surface.
- the adhesive force should drop sharply in a relatively short time, so that the material web unwinds easily from the core during subsequent processing.
- the use of a gel greatly reduces the mobility of the water bound in it. This effect leads to the formation of a stress in the interface between the gel and the material web or the lateral surface of the winding core and thus to an instantaneous adhesion between the material web and the lateral surface.
- the migration of the water from the gel into the winding core or into the material web begins and the adhesive force between the material web and the lateral surface decreases continuously.
- At least one region of the winding core which forms the lateral surface preferably consists of cardboard or paper.
- a hollow cylinder made of cardboard has proven.
- the material web consists for example of a film of plastic, metal, paper or of a multilayer film of at least two layers of said materials.
- the chemical composition of the gelling agent is of minor importance for the process according to the invention.
- the sole purpose of the gel is to reduce the mobility of the water during the first phase of winding a web.
- gel formers for example, fumed silica, sodium silicate and boric acid, gelatin, celluloses such as pure cellulose powder, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, etc. and starches such as corn starch, rice starch, potato starch or wheat starch can be used.
- a gel that is as firm as possible ie a gel whose water content is smaller than its maximum possible water content, is used.
- the webs of material wound with the method according to the invention can be automatically and uninterruptedly hung together in a continuous further processing.
- a particular area of application of the method according to the invention relates to the winding up of material webs which are cut from a material strip in a cutting device.
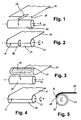
- an end 11 of a material web 10 is fastened by means of an adhesive tape 16 to the cylindrical jacket surface 14 of a winding core 12 with a cylindrical or rotational axis s.
- the adhesive force of the adhesive tape 16 is dependent on its length.
- the adhesive force to the lateral surface 14 of the winding core 12 may be so large that the material web does not readily dissolve during subsequent unwinding of the lateral surface, which can lead to problems especially in Autosplicing machines.
- a gel 18 is applied to the water-based on the winding core 12 side facing the web 10 and the gel with the 18th provided end 11 is applied to the cylindrical surface 14 of the winding core 12.
- the winding core 12 is, for example, a hollow cylinder made of cardboard and the material web is e.g. an 80 ⁇ m thick packaging film made of an aluminum / plastic composite material.
- the water-based gel contains, for example, a mixture of sodium silicate and boric acid as gelling agent.
- the resulting adhesion between web 10 and winding core 12 is sufficiently high that the web is taken during the first revolution of the winding core 12 of this.
- the water migrates completely over time in the winding core 12 and the adhesive force decreases continuously.
- the adhesive force is practically zero and the end 11 of the material web 10 firmly adhering during winding is easily detached from the lateral surface 14 of the winding core 12.
Landscapes
- Storage Of Web-Like Or Filamentary Materials (AREA)
- Replacement Of Web Rolls (AREA)
- Winding Of Webs (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft ein Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn nach dem Oberbegriff von Anspruch 1.
- Ein derartiges Verfahren ist beispielsweise aus US-A-3 951 890 bekannt.
- Bei bekannten Rollenschneidmaschinen wird ein von einer Bandrolle abgewickeltes Band in einer Schneideinrichtung zu Streifen oder Materialbahnen aufgeteilt. Diese Materialbahnen werden nachfolgend auf Wickelkerne gewickelt. Sobald eine Rolle ihren vorbestimmten Durchmesser erreicht hat, wird die Materialbahn von einer Bedienperson an der Maschine von der vollen Rolle abgetrennt und das neue Ende mit Hilfe eines Klebbandes an der Oberfläche eines leeren Wickelkerns fixiert. Dieses Klebband kann bei der Weiterverarbeitung der Materialbahnen auf Maschinen, bei denen eine neue Materialbahn automatisch und unterbrechungsfrei an das Ende einer abgewickelten Materialbahn angehängt wird, zu Problemen führen. Wenn beispielsweise das Klebband zu lang ist, kann es vorkommen, dass sich die Materialbahn nach vollständiger Abwicklung nicht vom Wickelkern löst, was zu einem Anhalten der Maschine und damit zu einem unerwünschten Betriebsunterbruch führt.
- Der vorliegenden Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, bei einem Verfahren der eingangs genannten Art die Haftung zwischen Materialbahn und Wickelkern so einzustellen, dass sie beim Aufwickeln während den ersten eins bis zwei vollständigen Umdrehungen des Wickelkerns eine ausreichende Haftkraft zwischen Materialbahn und Mantelfläche erzeugt. Die Haftkraft soll in verhältnismässig kurzer Zeit stark absinken, so dass sich bei der späteren Weiterverarbeitung die Materialbahn beim Abwickeln problemlos vom Kern löst.
- Zur erfindungsgemässen Lösung der Aufgabe führt ein Verfahren mit den Merkmalen von Anspruch 1.
- Durch die Verwendung eines Gels wird die Beweglichkeit des in diesem gebundenen Wassers stark vermindert. Dieser Effekt führt zum Aufbau einer Spannung in der Grenzfläche zwischen dem Gel und der Materialbahn bzw. der Mantelfläche des Wickelkerns und damit zu einer augenblicklichen Haftung zwischen Materialbahn und Mantelfläche. Als Folge der Wasser absorbierenden Eigenschaften des Wickelkerns bzw. der Materialbahn beginnt die Migration des Wassers aus dem Gel in den Wickelkern bzw. in die Materialbahn und die Haftkraft zwischen Materialbahn und Mantelfläche nimmt kontinuierlich ab.
- Bevorzugt besteht zumindest ein die Mantelfläche bildender Bereich des Wickelkerns aus Karton oder aus Papier. Als besonders zweckmässig hat sich ein aus Karton gefertigter Hohlzylinder erwiesen.
- Die Materialbahn besteht beispielsweise aus einer Folie aus Kunststoff, Metall, Papier oder aus einer mehrschichtigen Folie aus wenigstens zwei Schichten der genannten Materialien.
- Die chemische Zusammensetzung des Gelbildners ist für das erfindungsgemässe Verfahren von untergeordneter Bedeutung. Wie oben erwähnt, hat das Gel nur die Aufgabe, während der ersten Phase des Aufwickelns einer Materialbahn die Mobilität des Wassers herabzusetzen. Als Gelbildner kann beispielsweise hochdisperses Siliziumoxid, Natriumsilikat und Borsäure, Gelatine, Cellulosen wie reines Cellulosepulver, Hydroxyethylcellulose, Hydroxypropylcellulose, etc. und Stärken wie beispielsweise Maisstärke, Reisstärke, Kartoffelstärke oder Weizenstärke eingesetzt werden.
- Verwendet wird ein möglichst festes Gel, d. h. ein Gel, dessen Wassergehalt kleiner ist als sein maximal möglicher Wassergehalt.
- Die mit dem erfindungsgemässen Verfahren gewickelten Materialbahnen können bei einer kontinuierlichen Weiterverarbeitung automatisch und unterbrechungsfrei aneinandergehängt werden.
- Ein besonderer Anwendungsbereich des erfindungsgemässen Verfahrens betrifft die Aufwicklung von Materialbahnen, die in einer Schneideinrichtung aus einem Materialband geschnitten werden.
- Weitere Vorteile, Merkmale und Einzelheiten der Erfindung ergeben sich aus der nachfolgenden Beschreibung bevorzugter Ausführungsbeispiele sowie anhand der Zeichnung; diese zeigt schematisch in
- Fig. 1 und 2 die Befestigung einer Materialbahn auf einem Wickelkern nach dem Stand der Technik;
- Fig. 3 und 4 die Befestigung einer Materialbahn an einen Wickelkern mit einem Gel auf Wasserbasis;
- Fig. 5 einen Querschnitt durch einen Wickelkern mit an dessen Mantelfläche haftender Materialbahn.
- In dem in Fig. 1 gezeigtem Beispiel nach dem Stand der Technik wird ein Ende 11 einer Materialbahn 10 mittels eines Klebbandes 16 an der zylindrischen Mantelfläche 14 eines Wickelkerns 12 mit Zylinder- oder Rotationsachse s befestigt. Es ist ohne weiteres verständlich, dass die Haftkraft des Klebbandes 16 von dessen Länge abhängig ist. Je nach Länge und Art des Klebbandes16 kann die Haftkraft zur Mantelfläche 14 des Wickelkerns 12 so gross sein, dass sich die Materialbahn beim späteren Abwickeln nicht ohne weiteres von der Mantelfläche löst, was vor allem bei Autosplicing-Maschinen zu Problemen führen kann.
- In den Fig. 3 und 4 wird ein Gel 18 auf Wasserbasis auf die dem Wickelkern 12 zugewandte Seite der Materialbahn 10 aufgetragen und das mit dem Gel 18 versehene Ende 11 wird an die zylindrische Mantelfläche 14 des Wickelkerns 12 angelegt.
- Der Wickelkern 12 ist beispielsweise ein Hohlzylinder aus Karton und die Materialbahn z.B. eine 80 µm dicke Verpackungsfolie aus einem Aluminium/Kunststoff-Verbundmaterial. Das Gel auf Wasserbasis enthält beispielsweise eine Mischung von Natriumsilikat und Borsäure als Gelbildner.
- Die auf diese Weise entstehende Haftkraft zwischen Materialbahn 10 und Wickelkern 12 ist ausreichend hoch, dass die Materialbahn während der ersten Umdrehung des Wickelkerns 12 von diesem mitgenommen wird. Das Wasser migriert mit der Zeit vollständig in den Wickelkern 12 und die Haftkraft nimmt kontinuierlich ab. Beim späteren Abwickeln der Materialbahn ist die Haftkraft praktisch Null und das beim Aufwickeln fest haftende Ende 11 der Materialbahn 10 löst sich problemlos von der Mantelfläche14 des Wickelkerns 12.
Claims (7)
- Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn (10) auf einen Wickelkern (12) mit zylindrischer Mantelfläche (14), wobei die Materialbahn (10) und/oder der Wickelkern (12) Wasser absorbierende Eigenschaften aufweist, bei welchem Verfahren ein Ende (11) der Materialbahn (10) über ein auf das Ende (11) der Materialbahn (10) und/oder die Mantelfläche (14) aufgetragenes Gel (18) auf Wasserbasis mit der Mantelfläche (14) des Wickelkerns (12) lösbar haftend verbunden und die Materialbahn durch Rotation des Wickelkerns (12) um seine Zylinderachse (s) aufgewickelt wird,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
dass der Wassergehalt des Gels (18) kleiner ist als sein maximal möglicher Wassergehalt. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zumindest ein die Mantelfläche (14) bildender Bereich des Wickelkerns (12) aus Karton oder Papier besteht.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Wickelkern (12) ein aus Karton gefertigter Hohlzylinder ist.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Materialbahn (10) aus einer Folie aus Kunststoff, Metall, Papier oder aus einer mehrschichtigen Folie aus wenigstens zwei Schichten der genannten Materialien besteht.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass als Gelbildner hochdisperses Siliziumdioxid, Natriumsilikat und Borsäure, Gelatine, Cellulose oder Stärke eingesetzt wird.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Materialbahn (10) ein Streifen eines in einer Schneideinrichtung zu Streifen geschnittenen Materialbandes ist.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die auf die Wickelkerne (12) gewickelten Materialbahnen (10) bei einer kontinuierlichen Weiterverarbeitung automatisch und unterbrechungsfrei aneinander gehängt werden.
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE50306861T DE50306861D1 (de) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn |
| ES03405823T ES2281616T3 (es) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Procedimiento para el arrollamiento de una banda de material. |
| SI200330823T SI1533262T1 (sl) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Postopek navijanja traka materiala |
| DK03405823T DK1533262T3 (da) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Fremgangsmåde til opvikling af en materialebane |
| PT03405823T PT1533262E (pt) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | ''processo para enrolar uma fita de material'' |
| EP03405823A EP1533262B1 (de) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn |
| AT03405823T ATE357397T1 (de) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Verfahren zum wickeln einer materialbahn |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03405823A EP1533262B1 (de) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1533262A1 EP1533262A1 (de) | 2005-05-25 |
| EP1533262B1 true EP1533262B1 (de) | 2007-03-21 |
Family
ID=34429623
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03405823A Expired - Lifetime EP1533262B1 (de) | 2003-11-19 | 2003-11-19 | Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1533262B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE357397T1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE50306861D1 (de) |
| DK (1) | DK1533262T3 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2281616T3 (de) |
| PT (1) | PT1533262E (de) |
| SI (1) | SI1533262T1 (de) |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3951890A (en) * | 1974-07-22 | 1976-04-20 | Unitech Chemical Inc. | Tail control and transfer adhesives for rolled paper products |
| US5646090A (en) * | 1995-04-06 | 1997-07-08 | Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. | Thermal transfer image-receiving sheet |
| AT406255B (de) * | 1998-01-13 | 2000-03-27 | Andritz Patentverwaltung | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum wechseln von rollen bei papiermaschinen |
| US6705560B1 (en) * | 2000-11-28 | 2004-03-16 | Metso Paper Karlstad Aktiebolg (Ab) | Method for winding a tissue web in a reel-up in a paper machine |
| CA2417294C (en) * | 2002-02-25 | 2011-04-12 | Tesa Ag | Producing a roll of a flat web material |
-
2003
- 2003-11-19 DK DK03405823T patent/DK1533262T3/da active
- 2003-11-19 AT AT03405823T patent/ATE357397T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2003-11-19 SI SI200330823T patent/SI1533262T1/sl unknown
- 2003-11-19 DE DE50306861T patent/DE50306861D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-11-19 ES ES03405823T patent/ES2281616T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-11-19 PT PT03405823T patent/PT1533262E/pt unknown
- 2003-11-19 EP EP03405823A patent/EP1533262B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE50306861D1 (de) | 2007-05-03 |
| EP1533262A1 (de) | 2005-05-25 |
| ATE357397T1 (de) | 2007-04-15 |
| ES2281616T3 (es) | 2007-10-01 |
| DK1533262T3 (da) | 2007-07-30 |
| SI1533262T1 (sl) | 2007-08-31 |
| PT1533262E (pt) | 2007-06-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5323981A (en) | Splicer tape system | |
| DE3876437T2 (de) | Abdeckband und herstellungsverfahren von rollen dieses bandes. | |
| DE2319542A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur alternierenden abgabe einzelner bahnabschnitte | |
| DE60124850T2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Verpacken von Papierbahnrollen und Rollverpackung | |
| EP0970904A1 (de) | Klebeband und seine Verwendung | |
| DE10058956A1 (de) | Klebeband | |
| EP3946918A1 (de) | Herstellen von trinkhalmen aus papier | |
| EP2742105B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines klebebands mit überstehendem liner | |
| EP1104795A2 (de) | Klebeband | |
| DE3743656C2 (de) | ||
| WO2003024850A1 (de) | Klebeband für den fliegenden rollenwechsel | |
| EP1533262B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Wickeln einer Materialbahn | |
| EP0683122B1 (de) | Klebemittel zum Verbinden von auf angetriebenen Rollen gewickelten Materialbahnen | |
| DE3228255T1 (de) | Automatische bandwickelvorrichtung | |
| EP1046602B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Splice-Vorbereitung | |
| EP2641471B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur beschichtung eines raffbaren innenbeschichteten gewürzschlauchs | |
| DE2953552C1 (de) | Wickelpackung und Verfahren zur Herstellung derselben | |
| EP1340703B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Rolle eines Flachbahnmaterials | |
| DE60225882T2 (de) | Aufzeichnungspapierrolle | |
| EP0399488B1 (de) | Hülsenförmiger Wickelkern für dünnes bahnförmiges Wickelgut | |
| DE19652448C1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Verpacken einer Materialbahnrolle mit einer Verpackungsbahn | |
| DE102005004109B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines flachen Umwickelungsmaterials | |
| EP1645533A1 (de) | Klebeband zur Herstellung einer Verbindung bei einem statischen Rollenwechsel | |
| DE102022125313B4 (de) | Verfahren zum Verlegen einer Dehnmessfaser | |
| EP3719092B1 (de) | Klebeband und flachbahnmaterial mit einem derartigen klebeband |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20051125 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE SI SK |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE SI SK |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20070321 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50306861 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20070503 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20070606 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: EP Ref document number: 20070401916 Country of ref document: GR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2281616 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20071227 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HU Ref legal event code: AG4A Ref document number: E002823 Country of ref document: HU |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20081125 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20081104 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20081125 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: EE Payment date: 20081105 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: IE Payment date: 20081125 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: LU Payment date: 20081204 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: MC Payment date: 20081103 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20081124 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20081103 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20081126 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20081128 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20081031 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: SK Payment date: 20081103 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20081125 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20081128 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: BG Payment date: 20081127 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: CY Payment date: 20081112 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20081117 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20081223 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20081128 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: GR Payment date: 20081127 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: SI Payment date: 20081118 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20090128 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Payment date: 20081113 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: MM4A Free format text: LAPSE DUE TO NON-PAYMENT OF FEES Effective date: 20100519 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: ALCAN TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT LTD. Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: V1 Effective date: 20100601 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20091119 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: FAILURE TO ELECT DOMICILE IN THE NATIONAL COUNTRY Effective date: 20100531 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091120 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100519 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SK Ref legal event code: MM4A Ref document number: E 1952 Country of ref document: SK Effective date: 20091119 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: EE Ref legal event code: MM4A Ref document number: E001214 Country of ref document: EE Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20100730 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SI Ref legal event code: KO00 Effective date: 20100825 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100602 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100601 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100601 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091120 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20100421 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20110301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091119 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091120 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20091120 |