EP1479636A1 - Buffer that can create a safety inspection zone for elevators - Google Patents
Buffer that can create a safety inspection zone for elevators Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1479636A1 EP1479636A1 EP04011503A EP04011503A EP1479636A1 EP 1479636 A1 EP1479636 A1 EP 1479636A1 EP 04011503 A EP04011503 A EP 04011503A EP 04011503 A EP04011503 A EP 04011503A EP 1479636 A1 EP1479636 A1 EP 1479636A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- elevator car
- counterweight
- elevator
- movable means
- buffer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/28—Buffer-stops for cars, cages, or skips
- B66B5/288—Buffer-stops for cars, cages, or skips with maintenance features
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/0043—Devices enhancing safety during maintenance
- B66B5/005—Safety of maintenance personnel
Definitions
- the invention relates to an elevator system with a Buffers to create a protection zone.
- a procedure for Creating a protection zone is another object of the Invention.
- Elevator systems are usually with one or more Buffers provided on the floor of an elevator shaft are arranged to the elevator car when driving over the lowest stop position in the elevator train compartment in Downward direction and / or when driving over the top one Stop position in the elevator train bay in the upward direction Stop traversing a given distance.
- This Buffers are usually located below the elevator car and / or the counterweight.
- the shaft head can be arranged above the elevator car.
- the shaft head or the shaft floor can therefore only be used for other purposes to a limited extent.
- at Lift systems without a pit are one of them Standard arrangement of the buffers not possible, because below there is little space in the elevator car.
- a protection zone in the area of the shaft head To be able to create, the elevator car has according to the PCT Patent application for a device on the roof of the Elevator car is attached. This device can be folded up and drives against the shaft ceiling. So becomes a protection zone at the top of the shaft created.
- This PCT patent application is next Considered the state of the art.
- the present invention has for its object a To provide a solution that makes it possible, if necessary a protection zone at the bottom or at the top of one To create elevator shaft.
- the elevator installation according to the invention has a buffer on, the movable means that are in the orbit of the Elevator car can be moved into it, and movable means, which can be moved into the path of the counterweight, includes.
- the movable means in the web of the elevator car are movable, and the movable means in the Path of the counterweight can be moved into it realized, for example, as a single movable part that can be moved between different layers, that it is in both the elevator car train and in the path of the counterweight can be brought. It is also possible the movable means that in the orbit of the Elevator car can be moved in, and the movable Means that move into the path of the counterweight are, each by different, independently to realize moving parts. For example, a first movable part can be arranged on the buffer so that it can be moved into the path of the elevator car, and a second movable part could be arranged on the buffer be that it can move into the path of the counterweight is.
- the movable means can in one Be brought in the position in which they are are arranged that the elevator car and / or that Counterweight with the movable means in one mechanical contact can be brought. It will allows you to choose the Elevator car or the counterweight in a first or in a second predetermined distance above a floor can be supported. The specified first distance and the predetermined second distance can be different, depending on the arrangement and shape of the buffer or the movable Medium. The elevator car and the counterweight can are therefore supported at different heights.
- the movable means are in a normal position the movable means are not in the path of the elevator car and the counterweight. Consequently, the space available for the Elevator car is accessible when restricted movable means are brought into the operating position. Because either the elevator car or the Counterweight each at a predetermined distance can be supported on a floor, the track that the Can drive through elevator car, shortened at both ends. Thus, shelters at both ends of the web are Elevator car created.
- Another embodiment of the buffer according to the invention comprises a buffering element arranged in such a way that it protrudes into the elevator car path when the movable means are brought into the normal position, wherein the buffering element is designed such that the elevator car with the buffering element in one mechanical contact and at a third distance is supported above the ground, which is less than that first predetermined distance.
- This embodiment is also usable as overrun protection, which the elevator car at Driving over a lowest stop position in the downward direction brakes and stops.
- An embodiment of the buffer according to the invention can have a buffering element arranged in this way is that when the movable means are brought into the normal position, wherein the buffering element is designed such that the counterweight with the buffering element in one mechanical contact and at a fourth distance is supported above the ground, which is less than that second predetermined distance.
- This buffer can be used as Overrun protection can be used by the mechanical contact with the counterweight the counterweight decelerates and stops in the downward direction and thus the Elevator car when driving over a top stop position decelerates in the upward direction and stops.
- the buffer can be developed in such a way that a buffering element in the lanes of the elevator car and the Counterweight protrudes when the movable means in the Are brought to normal position.
- This embodiment has the advantage that with a single buffer - depending on the choice of position of the movable means - the elevator car and / or that Counterweight in at least two different ways Distances above a floor can be supported.
- On such buffers can be suitably dimensioned in one pitless elevator system against overrun protection Driving over a lowest stopping position of the elevator car in the downward direction and against driving over a top one Stop position of the elevator car in the upward direction guarantee and additionally - with a suitable Position of the movable means - the creation of temporary Shelters below and above the elevator car enable.
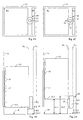
- FIGS. 1A to 1F show a first embodiment of an elevator installation with a buffer 10, according to the invention, in different schematic views and in different states.
- the buffer 10 shown is a buffer for supporting an elevator car 15 above the floor 18 of an elevator shaft 11.
- the elevator car 15 is counterbalanced by means of a suspension element 23.1, for example one or more ropes and / or one or more belts 23 that the elevator car 15 and the counterweight 23 can be moved up and down along the paths V K and V G in the elevator shaft 11.
- the counterweight, the suspension element, the traction sheave for the suspension element, the drive for the traction sheave, the guide rails for the elevator car 15 and the counterweight and the other usual elements of an elevator installation are not shown in FIGS. 1A to 1D.
- the buffer 10 has an elongated extension substantially parallel to the tracks V K or V G of the elevator car 15 or the counterweight 23. It comprises a lower base element 12 and a slimmer upper part 13.
- the buffer further comprises movable means 14 and 14.1 which can be moved out of the upper part 13, as indicated in FIGS. 1C, 1D and 1E.
- a drive device (not shown) is provided which allows the means 14 or 14.1 to be moved between different positions.
- a control device (not shown), which acts on the drive device, allows the positioning of the means 14 or 14.1 to be checked and monitored.
- FIGS. 1A and 1C show the projection K1 of the floor 15.1 of the elevator car 15 and the projection G1 of the underside 23.2 of the counterweight 23, each projected onto the shaft floor, shown.
- the projections K1 and G1 are shown with dashed lines in the areas in which they overlap with the base 12.1 of the base element 12 on the shaft bottom 18.
- the movable means 14 and 14.1 are asymmetrical in the embodiment shown.
- the left trapezoidal part 14 protrudes laterally out of the upper part 13 than the right trapezoidal part 14.1.
- the movable means 14 and 14.1 can be moved at different heights above the shaft floor 18 by the tracks V K and V G :
- An upper part of the movable means 14 is at a height Z1.1 and an upper part of the movable means 14.1 is arranged at a height Z1.2, Z1.2 being larger than Z1.1 (FIGS. 1D and 1E).
- the buffer 10 is shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B in a so-called normal state.
- the movable means 14 and 14.1 are located outside the tracks V K and V G.
- the respective positions which the movable means 14 and 14.1 assume in the normal state of the buffer are referred to below as the normal position.
- the elevator car 15 can move to the landing door 17 of the lower floor without making mechanical contact with the buffer 10.
- the cabin door 16 and the shaft door 17 can be used to get in and out.
- 1C, 1D and 1E show the buffer 10 in a so-called operating state.
- the movable means 14 When the buffer is in use, the movable means 14 is brought into the path V K and / or the movable means 14.1 is brought into the path V G , ie the movable means 14 and / or the movable means 14.1 are in their respective positions of use. If the movable means 14 is in its operating position, the elevator car 15 can be brought into mechanical contact with the means. If the movable means 14.1 is in its operating position, the counterweight 23 can be brought into mechanical contact with the means 14.1.
- the buffer 10 with the movable means 14 and 14.1 is so designed and arranged that also a mechanical Contact with the counterweight 23 takes place when the movable Means 14.1 in its operating position and the buffer 10 is thus brought into the operational state and that Counterweight 23 the predetermined distance Z1.2 with respect to Bottom 18 falls below.
- the counterweight 23 is in the Figures 1A to 1D not visible because it is at the top Is at the shaft end when the elevator car 15 is on lower shaft end.
- a protection zone in the Area of the lower shaft end can be created.
- the buffer 10 is removed from the Normal state converted to the operational state, whereby the happens by moving the movable means 14 from the top Part 13 is moved out.
- the elevator car 15 can now be moved down until it is on the movable means 14 attaches and from the buffer 10 at a distance Z1.1 with respect to Bottom 18 is supported. This way is below the Elevator car 15 created a protection zone.
- the landing door 17 is arranged such that a person enters the protection zone enter through an opening in the shaft door 17 and / or can leave.
- the distance Z1.1 ensures sufficient distance from the floor 18 to a safe and enable trouble-free working in the protection zone.
- the buffer 10 can also create a temporary protection zone in the Area of the upper shaft end.
- Fig. 1E In this figure is a schematic Longitudinal section through the entire elevator shaft 11 shown.
- the elevator shaft 11 has four or more than four Floors. At the level of each of the floors a shaft door 17 indicated.
- the counterweight 23 moves in the opposite direction to that Elevator cabin 15.
- the elevator cabin is at the top
- the counterweight 23 is on lower shaft end.
- Around a protection zone at the top Creating the end of the shaft becomes the counterweight to it prevented from falling below the distance Z1.2 to the floor 18.
- the elevator car 15 is also fixed in one given distance to the shaft head. Thereby there is a protection zone at the top of the shaft.
- the Base element 12 also acts as a buffering element.
- the base element 12 takes the kinetic Energy of the elevator car 15 or the kinetic energy of the counterweight 23 and brakes the elevator car 15 or the counterweight 23 when the elevator car 15 and / or the counterweight 23 in mechanical contact with the buffer 10. This applies both in the event that the elevator car 15 and / or the counterweight 23 directly on the base element 12, as well in the event that the elevator car 15 or Counterweight 23 on the movable means 14 and 14.1 put on.
- the elevator car 15 In the event that the lowest stopping position is overrun the elevator car 15 comes down, sets a lower one Edge of the elevator car 15 on the base element 12, as shown in Fig. 1B. That as a buffering element acting base element 12 takes the kinetic energy of the Elevator car 15 and brakes the car 15 until this comes to a stop.
- the Buffer 10 both for creating protection zones and as Overrun protection serve.
- Figures 1A to 1F stands out in that they are not just running over the lowest stop position of the elevator car 15 down prevented, but also that the top one is run over Holding position of the elevator car 15 intercepted upwards becomes.
- This "emergency" is shown in Fig. 1F.
- FIG. 1F In this figure is a schematic longitudinal section through the entire elevator shaft 11 shown.
- the buffer 10 is in the normal state.
- a run over the top one Stop position of the elevator car 15 is now up stopped by the counterweight 23 in mechanical Interaction with the base element 12 of the buffer 10 occurs.
- the elevator cars 15 thereon prevented from driving further up.
- the drive unit the elevator system in or immediately below the Socket element 12 sit.
- Base element in the top view (Fig. 1A and 1B) different out.
- the base element 12 does not necessarily have to protrude into the tracks V K or V G if the buffer 10 is to be used exclusively as a device for creating protective spaces and is also not intended to serve as an overrun protection for the elevator car.
- the elevator car 15 and the counterweight 23 could not be brought into mechanical contact with the buffer 10 if the movable means 14 and 14.1 assume the normal position.
- overrun protection could be implemented by installing additional buffers in the elevator shaft 11, which act separately on the elevator car 15 and / or the counterweight 23 and whose dimensions are matched to the position of the lowest and / or the top stop position of the elevator car 15 become.
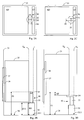
- FIGS. 2A to 2D show - as a second embodiment of the invention - an elevator installation with a buffer 30 in different schematic views and in different states.
- the buffer 30 shown is a buffer for supporting an elevator car 35 above a floor 38 of an elevator shaft 31.
- the buffer serves as overrun protection and as a means of creating a temporary protection zone.
- the elevator car 35 is connected to a counterweight such that the elevator car 35 can be moved up and down along a path V K and the counterweight along a path V G in the elevator shaft 31.
- the counterweight, the suspension element for the elevator car 35 and the counterweight, the traction sheave, the guide rails and the other usual elements of an elevator installation are not shown in FIGS. 2A to 2D.
- the buffer 30 has an elongated extension substantially parallel to the paths V K and V G of the elevator car 35 and the counterweight.
- the buffer 30 is designed and arranged such that it projects at least partially into the path V K of the elevator car and into the path V G of the counterweight.
- the buffer 30 includes a lower, as a strong damper designed base element 32 and a slimmer upper Part 33, which is designed as a weak damper.
- the Buffer 30 includes movable means 34 that are on top Part 33 sit and between different positions can be rotated as in Figures 2B and 2D indicated.
- the movable means 34 are shown in FIG Embodiment executed symmetrically, i.e. they protrude same parts on both sides over the upper part 33 out.
- the buffer 30 is shown in FIGS. 2A and 2B in a so-called normal state.
- the movable means 34 are in their normal position, ie they do not protrude into the paths V K or V G.
- FIGS. 2C and 2D show the buffer 30 in a so-called operating state. In this case, the movable means 34 are in their operating position, ie they protrude into the paths V K or V G.
- the buffer 30 is located at least partially between the web V K of the elevator car 35 and the web V G of the counterweight. 2A and 2C, the projection K3 of the elevator car 35 and the projection G3 of the counterweight, each projected onto the shaft floor, are shown.
- the projections K3 and G3 are shown in dashed lines in the areas in which they overlap with the base 32.1 of the base element 32 on the shaft bottom 38.
- Elevator car 35 When in use, there is mechanical contact Elevator car 35 with the movable means 34 of the buffer 30 as soon as the elevator car 35 has a first predetermined one Distance Z3 with respect to the floor 38 falls below. In the shown embodiment sits with the elevator car 35 a lower edge on the movable means 34, such as shown in Fig. 2D. This can, if necessary, in the area a temporary protection zone at the bottom of the shaft be created.
- the buffer 30 with the movable means 34 is like this designed and arranged that in use also a mechanical contact with the counterweight occurs when that Counterweight the predetermined distance Z3 with respect to the Bottom 38 falls below.
- the counterweight is in the Figures 2A to 2D not visible because it is on the top
- the shaft end is when the elevator car 35 is at lower shaft end.
- FIG. 2B shows the buffer 30 in the normal state. Since the upper part 33 of the buffer 30 is not in the path of the Elevator car protrudes, the elevator car 35 can Approach landing door 37 of the lower floor without one to establish mechanical contact with the buffer 30. In the in Fig. 2B situation can get on or off through the cabin door 36 and the shaft door 37, when the elevator car is at the lowest stopping position on occupies the lowest floor.
- Elevator car 35 If the lowest stopping position is overrun the elevator car 35 downwards (not in FIGS. 2A to 2D), then there is a mechanical contact of the Elevator car 35 with the designed as a strong damper Base element 32 of the buffer 30 as soon as the elevator car 35 a predetermined distance Z3.1 with respect to the floor 38 below. In the embodiment shown, the Elevator car 35 then with a lower edge on the Base element 32. This means that in an "emergency" Elevator car 35 are braked and stopped.
- the buffer 30 is transferred from the normal state to the operating state, this being done by moving the movable means 34 about an axis of rotation which is oriented essentially parallel to the path V K of the elevator car 35 or to the path V G of the counterweight, be rotated.
- the respective position of the movable means is controlled by means of a drive and a control device acting on the drive.
- the drive and the control device are not shown in the figures.
- the elevator car 35 can be moved downwards until it touches the movable means 34. In this way, a protection zone is created below the elevator car 35.
- a shaft door 37 is arranged such that a person can enter and / or leave the protection zone through an opening in the shaft door 37.
- the distance Z3 ensures sufficient distance from the floor 38 to enable safe and problem-free work in the protection zone.
- Elevator system with shaft pit acts and since that Base element 32 has an elongated extent H3 at any time a flat protection zone was created, in which the Elevator car 35 can not penetrate. Even if through an error or the necessary due to incorrect operation A change to the operational state has not taken place Person in the pit should not be crushed as always a minimum distance due to the height H3 of the base element 32 is preserved.
- the base element 32 and / or the upper part 33 have an extension in the direction of the path V K or V G depending on their mechanical load.
- the load dependency of this extension essentially determines the ability of the base element 32 or of the upper part 33 to brake and stop the elevator car or the counterweight when it hits the buffer 30.
- the extent of the buffer 30 in the direction of the path V K is shown reduced by a distance ⁇ Z in comparison to the distance Z3 in FIG. 2D.
- the extent of the buffer 30 in the direction of the path V G is reduced to a height below the distance Z3 if the counterweight loads the buffer 30.
- the buffer 30 can also create a temporary protection zone in the region of the upper shaft end. However, this state is not shown in FIGS. 2A to 2D.
- the movable means 34 are moved into the path V G of the counterweight and the counterweight is supported by the buffer 30 as soon as the counterweight falls below the distance Z3 to the floor 38.
- the elevator car 35 is also held at a fixed predetermined distance from the shaft head. This creates a protection zone at the top of the shaft.
- FIGS 3A to 3D show - as a third Embodiment of the invention - an elevator system with a buffer 40 in various schematic views and in different states. It is the shown buffer 40 around a buffer to support a Elevator car 45 over a floor 48 of an elevator shaft 41.
- the buffer serves as overrun protection and means for Create a temporary protection zone in a pitless one Elevator system, i.e. in an elevator system where the lowest holding level of the elevator car in such a way short distance above the ground that there is no space for a pit.
- the elevator car 45 is so connected to a counterweight that the Elevator car 45 and the counterweight along tracks in the Elevator shaft 41 can be moved up and down.
- the Counterweight, the suspension element for the elevator car 45 and the counterweight, the traction sheave, the guide rails and are the other common elements of an elevator system not shown in Figures 3A to 3D.
- the buffer 40 has an elongated extension substantially parallel to the Paths of the elevator car 45 and the counterweight.
- the Buffer 40 is designed and arranged so that it depends on Condition at least partially in the path of the elevator car and protrudes into the path of the counterweight.
- the buffer 40 includes a lower, as a strong damper designed base element 43 and movable means 44, the sit on the base element 43 and can be rotated, as indicated in Figures 3C and 3D.
- the moveable Means 44 are in the embodiment shown symmetrical, i.e. they protrude in equal parts on both sides beyond the base element 43.
- the Movable means 44 include dampers 44.1, which in Recesses of the movable means 44 sit.
- the buffer 40 is in one in FIGS. 3A and 3B so-called normal state shown.
- the movable means 44 and 44.1 in their Normal position, i.e. they do not protrude into the path of the Elevator car 45 and the counterweight.
- Figures 3C and 3D is the buffer 40 in a so-called Operating condition shown.
- the movable means 44 and 44.1 in their operating position, i.e. they protrude into the path of the elevator car 45 and the Counterweight.
- the buffer 40 is at least partly between the elevator car track and the track of the counterweight. Illustrative is in the figures 3A and 3C the projection K4 of the floor 45.2 of the Elevator car 45 and the projection G4 the bottom of the Counterweight shown.
- Elevator car 45 When in use, there is mechanical contact Elevator car 45 with the damper 44.1 of the buffer 40, as soon as the elevator car 45 a first predetermined distance Z4 falls below with respect to the bottom 48. In the shown embodiment sits the elevator car 45 a lower edge on the damper 44.1, as in Fig. 3D shown.
- the buffer 40 is therefore eccentrically loaded. If necessary, this can be done in the lower area A temporary protection zone will be created at the shaft.
- the buffer 40 with the movable means 44, 44.1 is so designed and arranged that in use also a mechanical contact with the counterweight occurs when that Counterweight the predetermined distance Z4 with respect to the Bottom 48 falls below.
- the counterweight is in the Figures 3A to 3D are not visible because it is at the top Is at the shaft end when the elevator car 45 is at lower shaft end.
- the buffer 40 is shown in the normal state. Since in the normal state the movable means 44, 44.1 of the Buffer 40 not in the path of the bottom 45.2 of the Elevator car 45 protrude, the elevator car 45 can Approach landing door 47 of the lower floor without one establish mechanical contact with the buffer 40. It is noted that in the condition shown Distance D between one at the elevator car 45 attached angle 45.1 (buffer stop) and the movable Means 44.1 exist. In the situation shown in Fig. 3B can an entry or exit through the cabin door 46 and the Landing door 47 take place.
- FIGS. 3A and 3C are each with dashed lines a projection K4.1 of the angle 45.1 and a projection G4.1 of said angle or protruding element on the counterweight, respectively projected onto the shaft floor, shown.
- the buffer 40 is removed from the Normal state converted to the operational state, whereby the happens by moving the movable means 44 into the tracks of the floor 45.2 of the elevator car 45 or the underside the counterweight are rotated (Fig. 3C and 3D).
- the necessary change can be made, for example, by a (Key) switch or triggered electronically become.
- the Elevator car 45 slowly moves down until it is on the Damper 44.1 touches down. A person can enter the protection zone enter through an opening in the landing door 47 and / or leave.
- the distance Z4 ensures sufficient Distance from the ground 48 to a safe and easy To enable work in the protection zone.
- a temporary buffer can also be created using the same buffer 40 Protection zone created in the area of the upper shaft end become. However, this state is not shown in FIGS. 3A shown to 3D.
- the counterweight is prevented from the Distance between Z4 and floor 48 is less.
- the elevator car 45 at a fixed distance from the shaft head held. This creates a protection zone at the top Shaft end.
- the Elevator car and the counterweight are not on the same Supported.
- the embodiments according to FIG. 2A-2D and 3A-3D can be modified accordingly by an appropriate adaptation of the forms of the movable means 34 and 44 and 44.1.
- the buffer can be a Have damping characteristics that are specific to the application is adjusted.
- Damper 44.1 used which is a slightly damped Put on the elevator car 35 or the counterweight allow the movable means 44 when a protection zone to be created.
- the movable means 44 are so spared in operation. If the elevator car and / or that Counterweight at high speed on each Impact buffers - especially when driving over the bottom or top stop position of the elevator car on the other hand - then the damping characteristics come the base elements 12, 32 or 43 are used.
- the buffers according to the invention can be prepared using special agents be equipped with an asymmetrical load allow without the buffer "buckling” or "evading".
- the buffer can be wholly or partially with a surrounded by a corset-like element or by special means be led to due to the eccentric To compensate for bending moments occurring in the buffer load.
- the buffer completely between the elevator car and the counterweight arranged (see for example Fig. 3A).
- the buffer element be arranged entirely or partially under the counterweight and acts directly on the counterweight. A movable one The buffer element then acts as required accordingly to the elevator car.
- the cross section of the buffer can be chosen arbitrarily.
- Buffers 10 and 30 are generally round Cross section parallel to the floor of the elevator shaft.
- buffer 40 has 43 in the lower region, for example a square cross section.
- a movement of the movable Buffer means electro-magnetic, hydraulic, pneumatic, manual, or by means of a servomotor respectively.
- a pit set used that a drive / converter unit, a Speed limiter, an attachment for the Includes guide rails and the buffer. Thereby Installation in the elevator shaft is noticeably easier.
- the present invention is also suitable for use in an elevator system in backpack disposition.
- the invention is particularly for use in Suitable elevator systems that have little or no Have pit and headroom heights.
- the movable means 14, 14.1, 34, 44 and 44.1 can in Modified the scope of the invention in various ways become. They can be replaced by funds that come from a basic position can be folded out, swung out, slidable and / or rotatable and each in Paths of the elevator car and / or the counterweight are movable to the elevator car and / or that Counterweight at a distance above the ground support.
- the movable means can by a suitable Arrangement can also be designed so that the elevator car and the counterweight at different heights can be supported. They can be multi-part or too be designed in one piece.
Landscapes
- Maintenance And Inspection Apparatuses For Elevators (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Gegenstand der Erfindung ist eine Aufzugsanlage mit einem Puffer zum Schaffen einer Schutzzone. Ein Verfahren zum Schaffen einer Schutzzone ist ein weiterer Gegenstand der Erfindung.The invention relates to an elevator system with a Buffers to create a protection zone. A procedure for Creating a protection zone is another object of the Invention.
Aufzugsanlagen sind üblicherweise mit einem oder mehreren Puffern versehen, die am Schachtboden eines Aufzugsschachts angeordnet sind, um die Aufzugskabine beim Überfahren der untersten Halteposition im Aufzugzugsachacht in Abwärtsrichtung und/oder beim Überfahren der obersten Halteposition im Aufzugzugsachacht in Aufwärtsrichtung nach Durchlaufen einer vorgegebenen Wegstrecke zu stoppen. Diese Puffer sitzen in der Regel unterhalb der Aufzugskabine und/oder dem Gegengewicht.Elevator systems are usually with one or more Buffers provided on the floor of an elevator shaft are arranged to the elevator car when driving over the lowest stop position in the elevator train compartment in Downward direction and / or when driving over the top one Stop position in the elevator train bay in the upward direction Stop traversing a given distance. This Buffers are usually located below the elevator car and / or the counterweight.
Um ein Überfahren einer obersten Halteposition im Aufzugsschacht nach oben spätestens nach Durchlaufen einer vorgegeben Wegstrecke zu verhindern, können Puffer auch am Schachtkopf oberhalb der Aufzugskabine angeordnet werden. Dadurch, dass solche Puffer am Schachtboden bzw. Schachtkopf unmittelbar unterhalb bzw. oberhalb der Aufzugskabine angeordnet werden müssen, ergibt sich ein gewisser Platzbedarf. Der Schachtkopf oder der Schachtboden kann daher nur bedingt anderweitig genutzt werden. Bei Aufzugsanlagen ohne Schachtgrube ist eine solche Standardanordnung der Puffer nicht möglich, da unterhalb der Aufzugskabine wenig Platz vorhanden ist.To pass a top stop position in the Elevator shaft upwards at the latest after passing through one buffers can also prevent the specified distance The shaft head can be arranged above the elevator car. The fact that such buffers on the shaft floor or Shaft head immediately below or above the There must be an elevator car certain space requirements. The shaft head or the shaft floor can therefore only be used for other purposes to a limited extent. at Lift systems without a pit are one of them Standard arrangement of the buffers not possible, because below there is little space in the elevator car.
In der PCT Patentanmeldung WO 00/64798-A1 ist eine Aufzugsanlage mit einem Aufzugsschacht, einer vertikal bewegbaren Aufzugskabine mit Gegengewicht und mit Puffern beschrieben, wobei die Puffer sich nicht unterhalb der Aufzugskabine, sondern neben der Aufzugskabine am Schachtboden befinden. Die Aufzugskabine ist mit Winkeln versehen, die auf die Puffer auftreffen, falls es zu einer Überfahrsituation kommt, d.h. falls die Aufzugskabine die unterste Halteposition am untersten Stockwerk nach unten überfährt. Dadurch wird die Aufzugskabine abgebremst und in einer kurzen Distanz oberhalb des Schachtbodens gestoppt. Ein Überfahrschutz gegen ein Überfahren der obersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine nach oben ist in dieser PCT Patentanmeldung nicht vorgeschlagen. Die Aufzugsanlage weist einen grubenlosen Schacht auf. Eine Möglichkeit, temporäre Schutzzonen für die Durchführung von Wartungsund Reparaturarbeiten im Aufzugschacht am Schachtboden und/oder am Schachtkopf zu schaffen, ist nicht offenbart.In PCT patent application WO 00/64798-A1 there is one Elevator system with one elevator shaft, one vertically movable elevator car with counterweight and with buffers described, the buffers are not below the Elevator car, but next to the elevator car on Pit floor. The elevator car is with angles provided that hit the buffers, if there is a Crossing situation comes, i.e. if the elevator car does lowest stop position on the lowest floor down overruns. As a result, the elevator car is braked and in stopped a short distance above the shaft floor. Overrun protection against overriding the top one Stop position of the elevator car is in this PCT Patent application not proposed. The elevator system has a pit without a pit. A possibility, Temporary protection zones for carrying out maintenance and Repair work in the elevator shaft on the shaft floor and / or to create on the shaft head is not disclosed.
Häufig ist aus baulichen oder anderen Gründen zu wenig Platz für eine konventionelle Aufzugsanlage mit Schachtgrube und Schachtkopf vorhanden. Insbesondere bei dem nachträglichen Einbau oder Anbau einer Aufzugsanlage in ein bereits existierendes Gebäude kommen vermehrt Aufzugschächte ohne Schachtgrube und ohne Schachtkopf zum Einsatz. Bei derartigen Aufzugschächten, aber auch bei konventionellen Aufzugsschächten gibt es Situationen, in denen es notwendig ist, eine Schutzzone am oberen oder unteren Schachtende zu schaffen. Dies ist zum Beispiel der Fall, wenn die Aufzugsanlage gewartet oder kontrolliert werden soll und zu diesem Zweck ein Monteur in den Schacht einsteigen muss.Often there is too little for structural or other reasons Space for a conventional elevator system with Shaft pit and shaft head available. Especially at the subsequent installation or addition of an elevator system in an existing building is increasingly coming Elevator shafts without shaft pit and without shaft head for Commitment. With such elevator shafts, but also with There are situations in conventional elevator shafts who need a protection zone at the top or to create the lower shaft end. For example, this is the Case when the elevator system is serviced or checked should be and for this purpose a fitter in the shaft must get in.
Es ist wichtig, dass ein System zum Schaffen einer solchen temporären Schutzzone sicher ist. Hierzu gibt es verschiedene Lösungsvorschläge. Ein weiteres Kriterium sind die Kosten und der Platzbedarf für ein solches System. Auch die einfache Kontrolle und Wartung eines Systems zum Schaffen einer temporären Schutzzone ist wichtig. Der Aufwand bei der Montage und das anfängliche Ausrichten aller Teile eines solchen Systems ist ein weiteres Kriterium, das zu berücksichtigen ist.It is important to have a system to create one temporary protection zone is safe. There is different solutions. Another criteria are the cost and space requirements for such a system. Also the simple control and maintenance of a system for It is important to create a temporary protection zone. The Assembly effort and initial alignment all parts of such a system is another Criterion to take into account.
In der Europäischen Patentanmeldung EP 0 725 033-A1 ist eine Aufzugsanlage mit einem Aufzugsschacht und einer vertikal bewegbaren Aufzugskabine mit Gegengewicht beschrieben. Am Schachtboden ist eine Aufsetzeinrichtung vorgesehen, die einen Schwenkpuffer umfasst, der in den Fahrweg der Aufzugskabine geschwenkt werden kann. Dadurch kann im Bedarfsfalle eine Schutzzone am Schachtboden geschaffen werden. Als besondere Ausführungsform wird eine Kombination eines Schachtpuffers, der ausserhalb einer Bahn einer Aufzugskabine aufgestellt ist, mit einem starren Schwenkhebel, der in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine schwenkbar ist, vorgeschlagen. Damit kann die Aufzugskabine bei einem Aufprall auf den Schwenkhebel durch den Schachtpuffer abgebremst werden und auf einer Höhe oberhalb des Schachtbodens gestützt werden, die oberhalb der untersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine liegt.In European patent application EP 0 725 033-A1 an elevator system with an elevator shaft and one vertically movable elevator car with counterweight described. There is an attachment device on the shaft floor provided, which comprises a swivel buffer, which in the Travel path of the elevator car can be pivoted. Thereby can create a protection zone on the shaft floor if necessary be created. As a special embodiment, a Combination of a shaft buffer that is outside of one Track of an elevator car is set up with a rigid one Swivel lever that swivels into the path of the elevator car is suggested. So that the elevator car at one Impact on the swivel lever through the shaft buffer be braked and at a height above the Shaft bottom are supported, the top of the bottom Stop position of the elevator car is.
Es ist ein Nachteil dieser Ausführungsform, dass sie zwar zum Schaffen einer Schutzzone am Schachtboden geeignet ist, allerdings keine Möglichkeit bietet, ein Überfahren der untersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine im Aufzugzugsachacht in Abwärtsrichtung nach Durchlaufen einer vorgegebenen Wegstrecke zu stoppen. Eine Möglichkeit, eine Schutzzone am Schachtkopf zu schaffen, ist auch nicht vorgesehen. It is a disadvantage of this embodiment that it does is suitable for creating a protection zone on the shaft floor, but does not offer a possibility to run over the lowest stopping position of the elevator car in Lift train shaft in the downward direction after passing through one stop the specified distance. One way, one It is also not possible to create a protection zone on the shaft head intended.
In der PCT Patentanmeldung WO 02/051737-A1 ist eine Aufzugsanlage mit einem Aufzugsschacht, einer vertikal bewegbaren Aufzugskabine mit Gegengewicht und einer bewegbaren Stützvorrichtung beschrieben. Die Stützvorrichtung ist exzentrisch am Schachtboden zwischen der Aufzugskabine und dem Gegengewicht angeordnet und kann bei Bedarf in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine bewegt werden. Die Stützvorrichtung umfasst eine Platte, die am Schachtboden klappbar angelenkt ist. Im Bedarfsfall wird diese Platte leicht in Richtung der Aufzugskabine geklappt. An der Aufzugskabine befinden sich Puffer, die auf die Platte auftreffen und die Aufzugskabine in einem vorgegebenen Abstand zum Schachtboden halten. Dadurch kann im Bedarfsfalle eine Schutzzone am Schachtboden geschaffen werden. Um eine Schutzzone im Bereich des Schachtkopfes schaffen zu können, weist die Aufzugskabine gemäss der PCT Patentanmeldung eine Vorrichtung auf, die am Dach der Aufzugskabine befestigt ist. Diese Vorrichtung kann hochgeklappt werden und fährt gegen die Schachtdecke. So wird eine Schutzzone am oberen Ende des Schachtes geschaffen. Diese PCT Patentanmeldung wird als nächster Stand der Technik betrachtet.In PCT patent application WO 02/051737-A1 there is one Elevator system with one elevator shaft, one vertically movable elevator car with counterweight and one movable support device described. The Support device is eccentric on the bottom of the shaft the elevator car and the counterweight arranged and can can be moved into the elevator car if necessary. The Support device includes a plate on the bottom of the shaft is hinged hinged. If necessary, this plate easily folded towards the elevator car. At the Elevator cabs have buffers on the plate hit and the elevator car in a predetermined Keep a distance from the shaft floor. This allows in If necessary, a protection zone is created on the shaft floor become. A protection zone in the area of the shaft head To be able to create, the elevator car has according to the PCT Patent application for a device on the roof of the Elevator car is attached. This device can be folded up and drives against the shaft ceiling. So becomes a protection zone at the top of the shaft created. This PCT patent application is next Considered the state of the art.
Es ist ein Nachteil dieser Ausführungsform, dass zum Schaffen einer Schutzzone am Schachtkopf eine Vorrichtung notwendig ist, die auf der Aufzugskabine sitzt. Dadurch erhöht sich die zu beschleunigende und zu bewegende Masse.It is a disadvantage of this embodiment that Create a protection zone on the head of a device is necessary, which sits on the elevator car. Thereby the mass to be accelerated and moved increases.
Der vorliegenden Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Lösung bereit zu stellen, die es ermöglicht, bei Bedarf eine Schutzzone am unteren oder am oberen Ende eines Aufzugsschachts zu schaffen. The present invention has for its object a To provide a solution that makes it possible, if necessary a protection zone at the bottom or at the top of one To create elevator shaft.
Die Lösung dieser Aufgabe erfolgt erfindungsgemäss durch
die Merkmale des Anspruchs 1 und die Merkmale des
Verfahrensanspruchs 14.According to the invention, this object is achieved by
the features of
Vorteilhafte Weiterbildungen der erfindungsgemässen
Aufzugsanlage sind durch die abhängigen Ansprüche 2 bis 13
definiert. Eine Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemässen
Verfahrens ist in Anspruch 15 angegeben.Advantageous developments of the inventive
Elevator systems are defined by the dependent claims 2 to 13
Are defined. A further development of the invention
The method is specified in
Die Aufzugsanlage gemäss der Erfindung weist einen Puffer auf, der bewegbare Mittel, die in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine hineinbewegbar sind, und bewegbare Mittel, die in die Bahn des Gegengewichts hineinbewegbar sind, umfasst.The elevator installation according to the invention has a buffer on, the movable means that are in the orbit of the Elevator car can be moved into it, and movable means, which can be moved into the path of the counterweight, includes.
Die bewegbare Mittel, die in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine hineinbewegbar sind, und die bewegbaren Mittel, die in die Bahn des Gegengewichts hineinbewegbar sind, können beispielsweise als ein einziges bewegbares Teil realisiert sein, das so zwischen verschiedenen Lagen bewegbar ist, dass es sowohl in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine als auch in die Bahn des Gegengewicht gebracht werden kann. Es ist auch möglich, die bewegbaren Mittel, die in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine hineinbewegbar sind, und die bewegbaren Mittel, die in die Bahn des Gegengewichts hineinbewegbar sind, jeweils durch verschiedene, unabhängig voneinander bewegbare Teile zu realisieren. Beispielsweise könnte ein erstes bewegbares Teil so am Puffer angeordnet sein, dass es in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine hineinbewegbar ist, und ein zweites bewegbares Teil könnte so am Puffer angeordnet sein, dass es in die Bahn des Gegengewichts hineinbewegbar ist. The movable means in the web of the elevator car are movable, and the movable means in the Path of the counterweight can be moved into it realized, for example, as a single movable part that can be moved between different layers, that it is in both the elevator car train and in the path of the counterweight can be brought. It is also possible the movable means that in the orbit of the Elevator car can be moved in, and the movable Means that move into the path of the counterweight are, each by different, independently to realize moving parts. For example, a first movable part can be arranged on the buffer so that it can be moved into the path of the elevator car, and a second movable part could be arranged on the buffer be that it can move into the path of the counterweight is.
Folglich können die bewegbaren Mittel in eine Einsatzstellung gebracht werden, in der sie derart angeordnet sind, dass die Aufzugskabine und/oder das Gegengewicht mit den bewegbaren Mitteln in einen mechanischen Kontakt bringbar sind. Dadurch wird es ermöglicht, dass mit einem einzigen Puffer wahlweise die Aufzugskabine bzw. das Gegengewicht in einer ersten bzw. in einer zweiten vorgegebenen Distanz oberhalb eines Bodens abgestützt werden kann. Die vorgegebene erste Distanz und die vorgegebene zweite Distanz können unterschiedlich sein, je nach Anordnung und Form des Puffers bzw. der bewegbaren Mittel. Die Aufzugskabine und das Gegengewicht können demnach in unterschiedlichen Höhen gestützt werden.Consequently, the movable means can in one Be brought in the position in which they are are arranged that the elevator car and / or that Counterweight with the movable means in one mechanical contact can be brought. It will allows you to choose the Elevator car or the counterweight in a first or in a second predetermined distance above a floor can be supported. The specified first distance and the predetermined second distance can be different, depending on the arrangement and shape of the buffer or the movable Medium. The elevator car and the counterweight can are therefore supported at different heights.
In einer Normalstellung der bewegbaren Mittel befinden sich die bewegbaren Mittel nicht in den Bahnen der Aufzugskabine und des Gegengewichts. Folglich wird der Raum, der für die Aufzugskabine zugänglich ist, eingeschränkt, wenn die bewegbaren Mittel in die Einsatzstellung gebracht sind. Dadurch, dass wahlweise die Aufzugskabine oder das Gegengewicht jeweils in einer vorgegebenen Distanz über einem Boden gestützt werden können, wird die Bahn, die die Aufzugskabine durchfahren kann, an beiden Enden verkürzt. Somit werden Schutzräume an beiden Enden der Bahn der Aufzugskabine geschaffen.The movable means are in a normal position the movable means are not in the path of the elevator car and the counterweight. Consequently, the space available for the Elevator car is accessible when restricted movable means are brought into the operating position. Because either the elevator car or the Counterweight each at a predetermined distance can be supported on a floor, the track that the Can drive through elevator car, shortened at both ends. Thus, shelters at both ends of the web are Elevator car created.
Eine weitere Ausführungsform des erfindungsgemässen Puffers umfasst ein pufferndes Element, das derart angeordnet ist, dass es in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine ragt, wenn die bewegbaren Mittel in die Normalstellung gebracht sind, wobei das puffernde Element derart ausgebildet ist, dass die Aufzugskabine mit dem puffernden Element in einen mechanischen Kontakt bringbar und auf einer dritten Distanz über dem Boden stützbar ist, welche geringer ist als die erste vorgegebene Distanz. Diese Ausführungsform ist auch als Überfahrschutz verwendbar, der die Aufzugskabine beim Überfahren einer untersten Halteposition in Abwärtsrichtung abbremst und stoppt.Another embodiment of the buffer according to the invention comprises a buffering element arranged in such a way that it protrudes into the elevator car path when the movable means are brought into the normal position, wherein the buffering element is designed such that the elevator car with the buffering element in one mechanical contact and at a third distance is supported above the ground, which is less than that first predetermined distance. This embodiment is also usable as overrun protection, which the elevator car at Driving over a lowest stop position in the downward direction brakes and stops.
Eine Ausführungsform des erfindungsgemässen Puffers kann ein pufferndes Element aufweisen, das derart angeordnet ist, dass es in die Bahn des Gegengewichts ragt, wenn die bewegbaren Mittel in die Normalstellung gebracht sind, wobei das puffernde Element derart ausgebildet ist, dass das Gegengewicht mit dem puffernden Element in einen mechanischen Kontakt bringbar und auf einer vierten Distanz über dem Boden stützbar ist, welche geringer ist als die zweite vorgegebene Distanz. Dieser Puffer kann als Überfahrschutz eingesetzt werden, der durch den mechanischen Kontakt mit dem Gegengewicht das Gegengewicht in Abwärtsrichtung abbremst und stoppt und damit die Aufzugskabine beim Überfahren einer obersten Halteposition in Aufwärtsrichtung abbremst und stoppt.An embodiment of the buffer according to the invention can have a buffering element arranged in this way is that when the movable means are brought into the normal position, wherein the buffering element is designed such that the counterweight with the buffering element in one mechanical contact and at a fourth distance is supported above the ground, which is less than that second predetermined distance. This buffer can be used as Overrun protection can be used by the mechanical contact with the counterweight the counterweight decelerates and stops in the downward direction and thus the Elevator car when driving over a top stop position decelerates in the upward direction and stops.
Der Puffer kann derart weitergebildet werden, dass ein pufferndes Element in die Bahnen der Aufzugskabine und des Gegengewichts ragt, wenn die bewegbaren Mittel in die Normalstellung gebracht sind. Somit kann allein durch die Wahl der Anordnung eines einzigen Puffers die Aufzugskabine daran gehindert werden, eine unterste Halteposition nach unten und eine oberste Halteposition nach oben zu überfahren.The buffer can be developed in such a way that a buffering element in the lanes of the elevator car and the Counterweight protrudes when the movable means in the Are brought to normal position. Thus, only through the Choice of the arrangement of a single buffer the elevator car be prevented from moving to a lowest stop position down and a top stop position up run over.
Diese Ausführungsform bringt den Vorteil mit sich, dass mit einem einzigen Puffer - je nach Wahl der Stellung der bewegbaren Mittel - die Aufzugskabine und/oder das Gegengewicht jeweils in mindestens zwei verschiedenen Distanzen oberhalb eines Bodens gestützt werden können. Ein solcher Puffer kann - geeignet dimensioniert - in einer grubenlosen Aufzugsanlage einen Überfahrschutz gegen das Überfahren einer untersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine in Abwärtsrichtung und gegen das Überfahren einer obersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine in Aufwärtsrichtung gewährleisten und zusätzlich - bei einer geeigneten Stellung der bewegbaren Mittel - die Schaffung temporärer Schutzräume unterhalb und oberhalb der Aufzugskabine ermöglichen.This embodiment has the advantage that with a single buffer - depending on the choice of position of the movable means - the elevator car and / or that Counterweight in at least two different ways Distances above a floor can be supported. On such buffers can be suitably dimensioned in one pitless elevator system against overrun protection Driving over a lowest stopping position of the elevator car in the downward direction and against driving over a top one Stop position of the elevator car in the upward direction guarantee and additionally - with a suitable Position of the movable means - the creation of temporary Shelters below and above the elevator car enable.
Einzelheiten und Vorteile der Erfindung werden im Folgenden anhand von Ausführungsbeispielen und mit Bezug auf die schematischen Zeichnungen beschrieben. Es zeigen:
- Fig. 1A
- eine schematische Draufsicht einer ersten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in einem Normalzustand;
- Fig. 1B
- eine schematische Seitenansicht der ersten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Normalzustand;
- Fig. 1C
- eine schematische Draufsicht der ersten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in einem Einsatzzustand;
- Fig. 1D
- eine schematische Seitenansicht der ersten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Einsatzzustand, wobei eine temporäre Schutzzone geschaffen ist;
- Fig. 1E
- eine schematische Seitenansicht eines gesamten Aufzugsschachts mit der ersten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Einsatzzustand, wobei ein Gegengewicht auf dem Puffer aufsitzt und eine Schutzzone am oberen Schachtende geschaffen ist;
- Fig. 1F
- eine schematische Seitenansicht des Aufzugsschachts mit der ersten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Normalzustand, wobei ein Gegengewicht auf dem Puffer aufsitzt und ein Überfahren einer obersten Halteposition nach oben verhindert ist;
- Fig. 2A
- eine schematische Draufsicht einer zweiten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in einem Normalzustand;
- Fig. 2B
- eine schematische Seitenansicht der zweiten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Normalzustand;
- Fig. 2C
- eine schematische Draufsicht der zweiten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in einem Einsatzzustand;
- Fig. 2D
- eine schematische Seitenansicht der zweiten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Einsatzzustand, wobei eine temporäre Schutzzone am Schachtboden geschaffen ist;
- Fig. 3A
- eine schematische Draufsicht einer dritten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in einem Normalzustand;
- Fig. 3B
- eine schematische Seitenansicht der dritten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Normalzustand, wobei die nach unten über eine unterste Haltposition hinaus fahrende Aufzugskabine gestoppt wird;
- Fig. 3C
- eine schematische Draufsicht der dritten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in einem Einsatzzustand;
- Fig. 3D
- eine schematische Seitenansicht der dritten Ausführungsform eines Puffers gemäss Erfindung, in dem Einsatzzustand, wobei eine temporäre Schutzzone geschaffen ist.
- Fig. 1A
- a schematic plan view of a first embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in a normal state;
- Figure 1B
- is a schematic side view of the first embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the normal state;
- 1C
- a schematic plan view of the first embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in an operating state;
- Figure 1D
- is a schematic side view of the first embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the operating state, wherein a temporary protection zone is created;
- Figure 1E
- is a schematic side view of an entire elevator shaft with the first embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the operating state, wherein a counterweight sits on the buffer and a protection zone is created at the upper end of the shaft;
- Figure 1F
- is a schematic side view of the elevator shaft with the first embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the normal state, wherein a counterweight is seated on the buffer and a top stop position is prevented from being passed over;
- Figure 2A
- a schematic plan view of a second embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in a normal state;
- Figure 2B
- is a schematic side view of the second embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the normal state;
- Figure 2C
- a schematic plan view of the second embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in an operating state;
- Figure 2D
- is a schematic side view of the second embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the operating state, wherein a temporary protection zone is created on the shaft bottom;
- Figure 3A
- a schematic plan view of a third embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in a normal state;
- Figure 3B
- is a schematic side view of the third embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the normal state, wherein the elevator car moving downward beyond a lowest stop position is stopped;
- Figure 3C
- a schematic plan view of the third embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in an operating state;
- Fig. 3D
- is a schematic side view of the third embodiment of a buffer according to the invention, in the operating state, a temporary protection zone being created.
Die Figuren 1A bis 1F zeigen eine erste Ausführungsform
einer Aufzugsanlage mit einem Puffer 10, gemäss Erfindung,
in verschiedenen schematischen Ansichten und in
verschiedenen Zuständen. Es handelt sich bei dem gezeigten
Puffer 10 um einen Puffer zum Stützen einer Aufzugskabine
15 über dem Boden 18 eines Aufzugsschachts 11. Die
Aufzugskabine 15 ist mittels eines Tragmittels 23.1,
beispielsweise einem oder mehren Seilen und/oder einem oder
mehreren Riemen, so mit einem Gegengewicht 23 verbunden,
dass die Aufzugskabine 15 und das Gegengewicht 23 längs
Bahnen VK bzw. VG in dem Aufzugsschacht 11 auf- und
abbewegbar sind. Das Gegengewicht, das Tragmittel, die
Treibscheibe für das Tragmittel, der Antrieb für die
Treibscheibe, die Führungsschienen für die Aufzugskabine 15
und das Gegengewicht und die anderen üblichen Elemente
einer Aufzugsanlage sind nicht in den Figuren 1A bis 1D
gezeigt.FIGS. 1A to 1F show a first embodiment of an elevator installation with a
Der Puffer 10 hat eine längliche Ausdehnung im wesentlichen
parallel zu den Bahnen VK bzw. VG der Aufzugskabine 15 bzw.
des Gegengewichts 23. Er umfasst ein unteres Sockelelement
12 und einen schlankeren oberen Teil 13. Der Puffer umfasst
weiterhin bewegbare Mittel 14 und 14.1, die aus dem oberen
Teil 13 herausbewegt werden können, wie in den Figuren 1C,
1D und 1E angedeutet. Zusätzlich ist eine (nicht
dargestellte) Antriebsvorrichtung vorgesehen, die es
erlaubt, die Mittel 14 bzw. 14.1 jeweils zwischen
verschiedenen Stellungen zu bewegen. Eine (nicht
dargestellte) Steuervorrichtung, die auf die
Antriebseinrichtung einwirkt, erlaubt es, die
Positionierung der Mittel 14 bzw. 14.1 zu kontrollieren und
zu überwachen.The
Die Bahnen VK und VG sind in Fig. 1B und 1D-1F durch
gestrichelte Linien angedeutet. Der Puffer 10 befindet sich
zumindest teilweise zwischen der Bahn VK der Aufzugskabine
15 und der Bahn VG des Gegengewichts 23. Zur
Veranschaulichung ist in den Fig. 1A und 1C die Projektion
K1 des Bodens 15.1 der Aufzugskabine 15 und die Projektion
G1 der Unterseite 23.2 des Gegengewichts 23, jeweils
projiziert auf den Schachtboden, gezeigt. Die Projektionen
K1 und G1 sind in den Bereichen, in denen sie mit der
Grundfläche 12.1 des Sockelelements 12 am Schachtboden 18
überlappen, mit gestrichelten Linien dargestellt.The tracks V K and V G are indicated in FIGS. 1B and 1D-1F by dashed lines. The
Die bewegbaren Mittel 14 und 14.1 sind bei der gezeigten
Ausführungsform unsymmetrisch ausgeführt. Das linke
trapezförmige Teil 14 ragt seitlich weiter aus dem oberen
Teil 13 heraus als das rechte trapezförmige Teil 14.1.
Weiterhin können die bewegbaren Mittel 14 bzw. 14.1 in
unterschiedlichen Höhen oberhalb des Schachtbodens 18 durch
die Bahnen VK bzw. VG bewegt werden: Ein oberer Teil des
bewegbaren Mittels 14 ist in einer Höhe Z1.1 und ein oberer
Teil des bewegbaren Mittels 14.1 ist in einer Höhe Z1.2
angeordnet, wobei Z1.2 grösser ist als Z1.1 (Fig. 1D und
1E).The movable means 14 and 14.1 are asymmetrical in the embodiment shown. The left
Der Puffer 10 ist in den Figuren 1A und 1B in einem
sogenannten Normalzustand gezeigt. Im Normalzustand des
Puffers befinden sich die bewegbaren Mittel 14 und 14.1
ausserhalb der Bahnen VK bzw. VG. Die jeweiligen
Stellungen, die die bewegbaren Mittel 14 und 14.1 im
Normalzustand des Puffers einnehmen, werden im Folgenden
Normalstellung genannt.The
Da im Normalzustand des Puffers 10 der obere Teil 13 des
Puffers 10 nicht in die Bahn VK der Aufzugskabine 15 ragt,
kann die Aufzugskabine 15 die Schachttüre 17 des unteren
Stockwerks anfahren, ohne einen mechanischen Kontakt mit
dem Puffer 10 herzustellen. In der in Fig. 1B gezeigten
Situation kann ein Zu- bzw. Ausstieg durch die Kabinentüre
16 und die Schachttüre 17 erfolgen.Since, in the normal state of the
In den Figuren 1C, 1D und 1E ist der Puffer 10 in einem
sogenannten Einsatzzustand dargestellt. In einem
Einsatzzustand des Puffers ist das bewegliche Mittel 14 in
die Bahn VK und/oder das bewegliche Mittel 14.1 in die Bahn
VG gebracht, d.h. das bewegliche Mittel 14 und/oder das
bewegliche Mittel 14.1 befinden sich in ihrer jeweiligen
Einsatzstellung. Ist das bewegliche Mittel 14 in seiner
Einsatzstellung, so ist die Aufzugskabine 15 mit dem Mittel
in einen mechanischen Kontakt bringbar. Ist das bewegliche
Mittel 14.1 in seiner Einsatzstellung, so ist die
Gegengewicht 23 mit dem Mittel 14.1 in einen mechanischen
Kontakt bringbar.1C, 1D and 1E show the
Wenn das bewegbare Mittel 14 in seine Einsatzstellung
gebracht ist und sich somit der Puffer 10 im Einsatzzustand
befindet, dann erfolgt ein mechanischer Kontakt der
Aufzugskabine 15 mit dem bewegbaren Mittel 14 des Puffers
10, sobald die Aufzugskabine 15 eine erste vorgegebene
Distanz, im vorliegenden Fall die Distanz Z1.1, bezüglich
des Bodens 18 unterschreitet. Bei der gezeigten
Ausführungsform sitzt die Aufzugskabine 15 mit einer
unteren Kante auf dem bewegbaren Mittel 14 auf, wie in Fig.
1D gezeigt.When the
Der Puffer 10 mit den bewegbaren Mitteln 14 und 14.1 ist so
ausgelegt und angeordnet, dass auch ein mechanischer
Kontakt mit dem Gegengewicht 23 erfolgt, wenn das bewegbare
Mittel 14.1 in seine Einsatzstellung und der Puffer 10
somit in den Einsatzzustand gebracht ist und das
Gegengewicht 23 die vorgegebene Distanz Z1.2 bezüglich des
Bodens 18 unterschreitet. Das Gegengewicht 23 ist in den
Figuren 1A bis 1D nicht sichtbar, da es sich am oberen
Schachtende befindet, wenn sich die Aufzugskabine 15 am
unteren Schachtende befindet.The
Da es sich bei dem Aufzugsschacht 11 um einen Schacht ohne
Schachtgrube handelt, muss bei Bedarf eine Schutzzone im
Bereich des unteren Schachtendes geschaffen werden können.
Zum Schaffen der Schutzzone wird der Puffer 10 vom
Normalzustand in den Einsatzzustand überführt, wobei das
geschieht, indem das bewegbare Mittel 14 aus dem oberen
Teil 13 herausbewegt wird. Die Aufzugskabine 15 kann nun
nach unten bewegt werden, bis sie auf dem bewegbaren Mittel
14 aufsetzt und vom Puffer 10 im Abstand Z1.1 bezüglich des
Bodens 18 gestützt wird. Auf diese Weise ist unterhalb der
Aufzugskabine 15 eine Schutzzone geschaffen. Die Schachttür
17 ist derart angeordnet, dass eine Person die Schutzzone
durch eine Öffnung der Schachttüre 17 hindurch betreten
und/oder verlassen kann. Der Abstand Z1.1 gewährleistet
genügend Abstand zum Boden 18, um eine sicheres und
problemloses Arbeiten in der Schutzzone zu ermöglichen. Since the
Durch den Puffer 10 kann auch eine temporäre Schutzzone im
Bereich des oberen Schachtendes geschaffen werden. Das ist
in Fig. 1E gezeigt. In dieser Figur ist ein schematischer
Längsschnitt durch den gesamten Aufzugsschacht 11 gezeigt.
Der Aufzugsschacht 11 hat vier oder mehr als vier
Stockwerke. Auf der Höhe eines jeden der Stockwerke ist
eine Schachttüre 17 angedeutet. In dem Aufzugsschacht 11
bewegt sich das Gegengewicht 23 gegenläufig zu der
Aufzugskabine 15. Befindet sich die Aufzugskabine am oberen
Schachtende, so befindet sich das Gegengewicht 23 am
unteren Schachtende. Um eine Schutzzone am oberen
Schachtende zu schaffen, wird das Gegengewicht daran
gehindert, den Abstand Z1.2 zum Boden 18 zu unterschreiten.
Sobald das Gegengewicht 23 auf dem bewegbaren Mittels 14.1
aufsitzt, wird auch die Aufzugskabine 15 in einem fest
vorgegebenen Abstand zum Schachtkopf gehalten. Dadurch
ergibt sich eine Schutzzone am oberen Schachtende.The
Es ist möglich, den Puffer 10 so auszuführen, dass das
Sockelelement 12 auch als pufferndes Element wirkt. In
diesem Fall nimmt das Sockelelement 12 die kinetische
Energie der Aufzugskabine 15 bzw. die kinetische Energie
des Gegengewichts 23 auf und bremst die Aufzugskabine 15
bzw. das Gegengewicht 23 ab, wenn die Aufzugskabine 15
und/oder das Gegengewicht 23 in mechanischen Kontakt mit
dem Puffer 10 geraten. Dies gilt sowohl für den Fall, dass
die Aufzugskabine 15 und/oder das Gegengewicht 23
unmittelbar auf das Sockelelement 12 aufsetzten, als auch
für den Fall, dass die Aufzugskabine 15 bzw. das
Gegengewicht 23 auf das bewegbare Mittel 14 bzw. 14.1
aufsetzen. It is possible to make the
Falls es zu einem Überfahren der untersten Halteposition
der Aufzugskabine 15 nach unten kommt, setzt eine untere
Kante der Aufzugskabine 15 auf dem Sockelelement 12 auf,
wie Fig. 1B zu entnehmen ist. Das als pufferndes Element
wirkende Sockelelement 12 nimmt die kinetische Energie der
Aufzugskabine 15 auf und bremst die Kabine 15, bis diese
zum Stoppen kommt. In dieser Ausführungsform kann also der
Puffer 10 sowohl zum Schaffen von Schutzzonen als auch als
Überfahrschutz dienen.In the event that the lowest stopping position is overrun
the
Die Ausführungsform der Figuren 1A bis 1F zeichnet sich
dadurch aus, dass sie nicht nur ein Überfahren der
untersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 15 nach unten
verhindert, sondern dass auch ein Überfahren der obersten
Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 15 nach oben abgefangen
wird. Dieser "Notfall" ist in Fig. 1F dargestellt. In
dieser Figur ist ein schematischer Längsschnitt durch den
gesamten Aufzugsschacht 11 gezeigt. Der Puffer 10 ist in
den Normalzustand versetzt. Ein Überfahren der obersten
Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 15 nach oben wird nun
dadurch gestoppt, dass das Gegengewicht 23 in mechanische
Wechselwirkung mit dem Sockelelement 12 des Puffers 10
tritt. Durch das Abbremsen und Stoppen des Gegengewichts 23
durch den Puffer 10 wird die Aufzugskabinen 15 daran
gehindert, weiter nach oben zu fahren.The embodiment of Figures 1A to 1F stands out
in that they are not just running over the
lowest stop position of the
In einer anderen Ausführungsform kann die Antriebseinheit
der Aufzugsanlage in dem oder unmittelbar unter dem
Sockelelement 12 sitzen. In diesem Fall sähe das
Sockelelement in der Draufsicht (Fig. 1A und 1B) anders
aus. Beispielsweise wäre in diesem Fall die von der
Antriebseinheit angetriebene Treibscheibe für die Tragseile
an dem Sockelelement 12 angeordnet. In another embodiment, the drive unit
the elevator system in or immediately below the
Es ist ein Vorteil der vorliegenden Erfindung, dass sie mit möglichst wenigen Elementen und bei geringem Platzbedarf verschiedene Funktionen bereitstellt.It is an advantage of the present invention that it can be used as few elements as possible and with a small footprint provides various functions.
Das Sockelelement 12 muss nicht unbedingt in die Bahnen VK
bzw. VG ragen, falls der Puffer 10 ausschliesslich als
Vorrichtung zum Schaffen von Schützräumen verwendet werden
soll und nicht zusätzlich als Überfahrschutz für die
Aufzugskabine dienen soll. In diesem Fall könnten die
Aufzugskabine 15 und das Gegengewicht 23 nicht mit dem
Puffer 10 in einen mechanischen Kontakt gebracht werden,
wenn die bewegbaren Mittel 14 und 14.1 die Normalstellung
einnehmen. In diesem Fall könnte ein Überfahrschutz
realisiert werden, indem zusätzliche Puffer, die separat
auf die Aufzugskabine 15 und/oder das Gegengewicht 23
wirken und deren Abmessungen auf die Lage der untersten
und/oder der obersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 15
abgestimmt sind, im Aufzugsschacht 11 installiert werden.The
Die Figuren 2A bis 2D zeigen - als eine zweite
Ausführungsform der Erfindung - eine Aufzugsanlage mit
einem Puffer 30 in verschiedenen schematischen Ansichten
und in verschiedenen Zuständen. Es handelt sich bei dem
gezeigten Puffer 30 um einen Puffer zum Stützen einer
Aufzugskabine 35 über einem Boden 38 eines Aufzugsschachts
31. Der Puffer dient als Überfahrschutz und als Mittel zum
Schaffen einer temporären Schutzzone. Die Aufzugskabine 35
ist so mit einem Gegengewicht verbunden, dass die
Aufzugskabine 35 längs einer Bahne VK und das Gegengewicht
längs einer Bahn VG in dem Aufzugsschacht 31 auf- und
abbewegbar sind. Das Gegengewicht, das Tragmittel für die
Aufzugskabine 35 und das Gegengewicht, die Treibscheibe,
die Führungsschienen und die anderen üblichen Elemente
einer Aufzugsanlage sind nicht in den Figuren 2A bis 2D
gezeigt. Der Puffer 30 hat eine längliche Ausdehnung im
wesentlichen parallel zu den Bahnen VK und VG der
Aufzugskabine 35 und des Gegengewichts. Der Puffer 30 ist
so ausgeführt und angeordnet, dass er zumindest teilweise
in die Bahn VK der Aufzugskabine und in die Bahn VG des
Gegengewichts hineinragt.FIGS. 2A to 2D show - as a second embodiment of the invention - an elevator installation with a
Der Puffer 30 umfasst ein unteres, als starker Dämpfer
ausgelegtes Sockelelement 32 und einen schlankeren oberen
Teil 33, der als schwacher Dämpfer ausgelegt ist. Der
Puffer 30 umfasst bewegbare Mittel 34, die auf dem oberen
Teil 33 sitzen und zwischen verschiedenen Stellungen
gedreht werden können, wie in den Figuren 2B und 2D
angedeutet. Die bewegbaren Mittel 34 sind bei der gezeigten
Ausführungsform symmetrisch ausgeführt, d.h. sie ragen zu
gleichen Teilen auf beiden Seiten über das obere Teil 33
hinaus.The
Der Puffer 30 ist in den Figuren 2A und 2B in einem
sogenannten Normalzustand gezeigt. In diesem Fall befinden
sich die bewegbaren Mittel 34 in ihrer Normalstellung, d.h.
sie ragen nicht in die Bahnen VK bzw. VG. In den Figuren 2C
und 2D ist der Puffer 30 in einem sogenannten
Einsatzzustand dargestellt. In diesem Fall befinden sich
die bewegbaren Mittel 34 in ihrer Einsatzstellung, d.h. sie
ragen in die Bahnen VK bzw. VG. Der Puffer 30 befindet sich
zumindest teilweise zwischen der Bahn VK der Aufzugskabine
35 und der Bahn VG des Gegengewichts. Zur Veranschaulichung
ist in den Figuren 2A und 2C die Projektion K3 der
Aufzugskabine 35 und die Projektion G3 des Gegengewichts,
jeweils projiziert auf den Schachtboden, gezeigt. Die
Projektionen K3 und G3 sind in den Bereichen, in denen Sie
mit der Grundfläche 32.1 des Sockelelements 32 am
Schachtboden 38 überlappen, mit gestrichelten Linien
dargestellt.The
Im Einsatzzustand erfolgt ein mechanischer Kontakt der
Aufzugskabine 35 mit den bewegbaren Mitteln 34 des Puffers
30, sobald die Aufzugskabine 35 eine erste vorgegebene
Distanz Z3 bezüglich des Bodens 38 unterschreitet. Bei der
gezeigten Ausführungsform sitzt die Aufzugskabine 35 mit
einer unteren Kante auf dem bewegbaren Mittel 34 auf, wie
in Fig. 2D gezeigt. Dadurch kann im Bedarfsfalle im Bereich
des unteren Schachtendes eine temporäre Schutzzone
geschaffen werden.When in use, there is mechanical
Der Puffer 30 mit den bewegbaren Mitteln 34 ist so
ausgelegt und angeordnet, dass im Einsatzzustand auch ein
mechanischer Kontakt mit dem Gegengewicht erfolgt, wenn das
Gegengewicht die vorgegebene Distanz Z3 bezüglich des
Bodens 38 unterschreitet. Das Gegengewicht ist in den
Figuren 2A bis 2D nicht sichtbar, da es sich am oberen
Schachtende befindet wenn sich die Aufzugskabine 35 am
unteren Schachtende befindet.The
In der Fig. 2B ist der Puffer 30 im Normalzustand gezeigt.
Da der obere Teil 33 des Puffers 30 nicht in die Bahn der
Aufzugskabine ragt, kann die Aufzugskabine 35 die
Schachttüre 37 des unteren Stockwerks anfahren, ohne einen
mechanischen Kontakt mit dem Puffer 30 herzustellen. In der
in Fig. 2B gezeigten Situation kann ein Zu- bzw. Ausstieg
durch die Kabinentüre 36 und die Schachttüre 37 erfolgen,
wenn die Aufzugskabine die unterste Halteposition am
untersten Stockwerk einnimmt. 2B shows the
Kommt es nun zu einem Überfahren untersten Halteposition
der Aufzugskabine 35 nach unten (nicht in den Figuren 2A
bis 2D gezeigt), so erfolgt ein mechanischer Kontakt der
Aufzugskabine 35 mit dem als starker Dämpfer ausgelegten
Sockelelement 32 des Puffers 30, sobald die Aufzugskabine
35 eine vorgegebene Distanz Z3.1 bezüglich des Bodens 38
unterschreitet. Bei der gezeigten Ausführungsform sitzt die
Aufzugskabine 35 dann mit einer unteren Kante auf dem
Sockelelement 32 auf. Dadurch kann im "Notfall" die
Aufzugskabine 35 abgebremst und gestoppt werden.If the lowest stopping position is overrun
the
Zum Schaffen einer Schutzzone wird der Puffer 30 vom
Normalzustand in den Einsatzzustand überführt, wobei das
geschieht, indem die bewegbaren Mittel 34 um eine
Drehachse, die im wesentlichen parallel zur Bahn VK der
Aufzugskabine 35 bzw. zur Bahn VG des Gegengewichts
ausgerichtet ist, gedreht werden. Die jeweilige Stellung
der bewegbaren Mittel wird mittels eines Antriebs und einer
auf den Antrieb wirkenden Steuervorrichtung kontrolliert.
Der Antrieb und die Steuervorrichtung sind in den Figuren
nicht dargestellt. Die Aufzugskabine 35 kann nach unten
bewegt werden, bis sie auf den bewegbaren Mitteln 34
aufsetzt. Auf diese Weise wird unterhalb der Aufzugskabine
35 eine Schutzzone geschaffen. Eine Schachttür 37 ist
derart angeordnet, dass eine Person die Schutzzone durch
eine Öffnung der Schachttüre 37 hindurch betreten und/oder
verlassen kann. Der Abstand Z3 gewährleistet genügend
Abstand zum Boden 38, um eine sicheres und problemloses
Arbeiten in der Schutzzone zu ermöglichen.To create a protective zone, the
Da es sich in der gezeigten Ausführungsform um eine
Aufzugsanlage mit Schachtgrube handelt und da das
Sockelelement 32 eine längliche Ausdehnung H3 hat, wird
jederzeit eine flache Schutzzone geschaffen, in die die
Aufzugskabine 35 nicht eindringen kann. Selbst wenn durch
einen Fehler oder durch eine Fehlbedienung die notwendige
Umstellung in den Einsatzzustand nicht erfolgt, kann eine
Person in der Schachtgrube nicht erdrückt werden, da stets
ein Mindestabstand durch die Höhe H3 des Sockelelements 32
gewahrt wird.Since it is in the embodiment shown
Elevator system with shaft pit acts and since that
Das Sockelelement 32 und/oder der obere Teil 33 weisen eine
von ihrer mechanischen Belastung abhängige Erstreckung in
Richtung der Bahn VK bzw. VG auf. Die Lastabhängigkeit
dieser Erstreckung bestimmt wesentlich das Vermögen des
Sockelelements 32 bzw. des oberen Teils 33, die
Aufzugskabine bzw. das Gegengewicht beim Auftreffen auf den
Puffer 30 zu bremsen und zu stoppen. Um die Belastung des
Puffers 30 durch die Aufzugskabine 35 anzudeuten, ist in
Fig. 2D die Erstreckung des Puffers 30 in Richtung der Bahn
VK um eine Strecke ΔZ im Vergleich zur Distanz Z3 reduziert
dargestellt. Analog wird die Erstreckung des Puffers 30 in
Richtung der Bahn VG auf eine Höhe unterhalb der Distanz Z3
reduziert, wenn dass Gegengewicht den Puffer 30 belastet.The
Durch den Puffer 30 kann auch eine temporäre Schutzzone im
Bereich des oberen Schachtendes geschaffen werden. Dieser
Zustand ist jedoch nicht in den Figuren 2A bis 2D gezeigt.
Um eine Schutzzone am oberen Schachtende zu schaffen,
werden die bewegbaren Mittel 34 in die Bahn VG des
Gegengewichts bewegt und das Gegengewicht durch den Puffer
30 gestützt, sobald das Gegengewicht den Abstand Z3 zum
Boden 38 unterschreitet. Sobald das Gegengewicht auf der
rechten Seite der bewegbaren Mittel 34 aufsitzt, wird auch
die Aufzugskabine 35 in einem fest vorgegebenen Abstand zum
Schachtkopf gehalten. Dadurch ergibt sich eine Schutzzone
am oberen Schachtende.The
Die Figuren 3A bis 3D zeigen - als eine dritte
Ausführungsform der Erfindung - eine Aufzugsanlage mit
einem Puffer 40 in verschiedenen schematischen Ansichten
und in verschiedenen Zuständen. Es handelt sich bei dem
gezeigten Puffer 40 um einen Puffer zum Stützen einer
Aufzugskabine 45 über einem Boden 48 eines Aufzugsschachts
41. Der Puffer dient als Überfahrschutz und Mittel zum
Schaffen einer temporären Schutzzone in einer grubenlosen
Aufzugsanlage, d.h. in einer Aufzugsanlage, bei der das
unterste Halteniveau der Aufzugskabine in einer derart
kurzen Distanz oberhalb des Bodens liegt, dass kein Platz
für eine Schachtgrube vorhanden ist. Die Aufzugskabine 45
ist so mit einem Gegengewicht verbunden, dass die
Aufzugskabine 45 und das Gegengewicht längs Bahnen in dem
Aufzugsschacht 41 auf- und abbewegbar sind. Das
Gegengewicht, das Tragmittel für die Aufzugskabine 45 und
das Gegengewicht, die Treibscheibe, die Führungsschienen
und die anderen üblichen Elemente einer Aufzugsanlage sind
nicht in den Figuren 3A bis 3D gezeigt. Der Puffer 40 hat
eine längliche Ausdehnung im wesentlichen parallel zu den
Bahnen der Aufzugskabine 45 und des Gegengewichts. Der
Puffer 40 ist so ausgeführt und angeordnet, dass er je nach
Zustand zumindest teilweise in die Bahn der Aufzugskabine
und in die Bahn des Gegengewichts hineinragt.Figures 3A to 3D show - as a third
Embodiment of the invention - an elevator system with
a
Der Puffer 40 umfasst ein unteres, als starker Dämpfer
ausgelegtes Sockelelement 43 und bewegbare Mittel 44, die
auf dem Sockelelement 43 sitzen und gedreht werden können,
wie in den Figuren 3C und 3D angedeutet. Die bewegbaren
Mittel 44 sind bei der gezeigten Ausführungsform
symmetrisch ausgeführt, d.h. sie ragen zu gleichen Teilen
auf beiden Seiten über das Sockelelement 43 hinaus. Die
bewegbaren Mittel 44 umfassen Dämpfer 44.1, die in
Ausnehmungen der bewegbaren Mittel 44 sitzen.The
Der Puffer 40 ist in den Figuren 3A und 3B in einem
sogenannten Normalzustand gezeigt. In diesem Fall befinden
sich die bewegbaren Mittel 44 und 44.1 in ihrer
Normalstellung, d.h. sie ragen nicht in die Bahnen der
Aufzugskabine 45 und des Gegengewichts. In den Figuren 3C
und 3D ist der Puffer 40 in einem sogenannten
Einsatzzustand dargestellt. In diesem Fall befinden sich
die bewegbaren Mittel 44 und 44.1 in ihrer Einsatzstellung,
d.h. sie ragen in die Bahnen der Aufzugskabine 45 und des
Gegengewichts. Der Puffer 40 befindet sich zumindest
teilweise zwischen der Bahn der Aufzugskabine und der Bahn
des Gegengewichts. Zur Veranschaulichung ist in den Figuren
3A und 3C die Projektion K4 des Bodens 45.2 der
Aufzugskabine 45 und die Projektion G4 der Unterseite des
Gegengewichts gezeigt.The
Im Einsatzzustand erfolgt ein mechanischer Kontakt der
Aufzugskabine 45 mit dem Dämpfer 44.1 des Puffers 40,
sobald die Aufzugskabine 45 eine erste vorgegebene Distanz
Z4 bezüglich des Bodens 48 unterschreitet. Bei der
gezeigten Ausführungsform sitzt die Aufzugskabine 45 mit
einer unteren Kante auf den Dämpfer 44.1 auf, wie in Fig.
3D gezeigt. Der Puffer 40 wird also exzentrisch belastet.
Dadurch kann im Bedarfsfalle im Bereich des unteren
Schachtendes eine temporäre Schutzzone geschaffen werden.When in use, there is mechanical
Der Puffer 40 mit den bewegbaren Mitteln 44, 44.1 ist so
ausgelegt und angeordnet, dass im Einsatzzustand auch ein
mechanischer Kontakt mit dem Gegengewicht erfolgt, wenn das
Gegengewicht die vorgegebene Distanz Z4 bezüglich des
Bodens 48 unterschreitet. Das Gegengewicht ist in den
Figuren 3A bis 3D nicht sichtbar, da es sich am oberen
Schachtende befindet, wenn sich die Aufzugskabine 45 am
unteren Schachtende befindet.The
In der Fig. 3B ist der Puffer 40 im Normalzustand gezeigt.
Da in Normalzustand die bewegbaren Mittel 44, 44.1 des
Puffers 40 nicht in die Bahn des Bodens 45.2 der
Aufzugskabine 45 ragen, kann die Aufzugskabine 45 die
Schachttüre 47 des unteren Stockwerks anfahren, ohne einen
mechanischen Kontakt mit dem Puffer 40 herzustellen. Es ist
darauf hingewiesen, dass in dem gezeigten Zustand ein
Abstand D zwischen einem an der Aufzugskabine 45
befestigten Winkel 45.1 (Pufferanschlag) und dem bewegbaren
Mittel 44.1 besteht. In der in Fig. 3B gezeigten Situation
kann ein Zu- bzw. Ausstieg durch die Kabinentüre 46 und die
Schachttüre 47 erfolgen.3B, the
Kommt es nun zu einem Überfahren der untersten
Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 45 nach unten (nicht in den
Figuren 3A bis 3D gezeigt), so erfolgt ein mechanischer
Kontakt des Winkels 45.1, der an der Aufzugskabine 45
befestigt ist, mit dem Mittel 44 bzw. dem als starker
Dämpfer ausgelegten Sockelelement 43 des Puffers 40.
Dadurch kann im "Notfall" die Aufzugskabine 45 abgebremst
und gestoppt werden. Es ist angemerkt, dass beim Überfahren
der untersten Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 45 die
Dämpfer 44.1 nicht zum Einsatz kommen, da der Winkel 45.1
direkten Kontakt mit dem Mittel 44 herstellt. Der Puffer 40
wird also in einem solchen "Notfall" mittig belastet. If the bottom one is run over
Stop position of the
Wenn die bewegbaren Mittel 44 und 44.1 die Normalstellung
einnehmen, dann wird ein Überfahren der obersten
Halteposition der Aufzugskabine 45 nach oben dadurch
verhindert, dass ein Winkel oder ein anderes
hervorstehendes Element an der der Schachttür 47
zugewandten Seite des Gegengewichts einen Kontakt mit dem
bewegbaren Mittel 44 des Puffers 40 herstellt. Auch dies
führt zu einer mittigen Belastung des Puffers 40.When the
Zur Veranschaulichung sind in Fig. 3A und 3C jeweils mit gestrichelten Linien eine Projektion K4.1 des Winkels 45.1 und eine Projektion G4.1 des genannten Winkels bzw. des hervorstehenden Elements am Gegengewicht, jeweils projiziert auf den Schachtboden, dargestellt.For illustration, FIGS. 3A and 3C are each with dashed lines a projection K4.1 of the angle 45.1 and a projection G4.1 of said angle or protruding element on the counterweight, respectively projected onto the shaft floor, shown.
Zum Schaffen einer Schutzzone wird der Puffer 40 vom
Normalzustand in den Einsatzzustand überführt, wobei das
geschieht, indem die bewegbaren Mittel 44 in die Bahnen
des Bodens 45.2 der Aufzugskabine 45 bzw. der Unterseite
des Gegengewichts gedreht werden (Fig. 3C und 3D). Die
notwendige Umstellung kann zum Beispiel durch einen
(Schlüssel-)Schalter oder elektronisch gesteuert ausgelöst
werden. Um die temporäre Schutzzone zu schaffen, wird die
Aufzugskabine 45 langsam nach unten bewegt, bis sie auf dem
Dämpfer 44.1 aufsetzt. Eine Person kann die Schutzzone
durch eine Öffnung der Schachttüre 47 hindurch betreten
und/oder verlassen. Der Abstand Z4 gewährleistet genügend
Abstand zum Boden 48, um eine sicheres und problemloses
Arbeiten in der Schutzzone zu ermöglichen.To create a protection zone, the
Durch denselben Puffer 40 kann auch eine temporäre
Schutzzone im Bereich des oberen Schachtendes geschaffen
werden. Dieser Zustand ist jedoch nicht in den Figuren 3A
bis 3D gezeigt. Um eine Schutzzone am oberen Schachtende zu
schaffen, wird das Gegengewicht daran gehindert, den
Abstand Z4 zum Boden 48 zu unterschreiten. Sobald das
Gegengewicht auf dem Dämpfer 44.1 auf der rechten Seite des
bewegbaren Mittels 44 aufsitzt, wird auch die Aufzugskabine
45 in einem fest vorgegebenen Abstand zum Schachtkopf
gehalten. Dadurch ergibt sich eine Schutzzone am oberen
Schachtende.A temporary buffer can also be created using the
Wie in den Figuren 1D und 1E angedeutet, müssen die
Aufzugskabine und das Gegengewicht nicht auf der gleichen
Höhe abgestützt werden. Die Ausführungsformen gemäss Fig.
2A-2D und 3A-3D können entsprechend abgeändert werden durch
eine geeignete Anpassung der Formen der bewegbaren Mittel
34 und 44 bzw. 44.1.As indicated in Figures 1D and 1E, the
Elevator car and the counterweight are not on the same
Supported. The embodiments according to FIG.
2A-2D and 3A-3D can be modified accordingly by
an appropriate adaptation of the forms of the
Der Puffer kann gemäss Erfindung eine
Dämpfungscharakteristik haben, die dem Einsatzfall speziell
angepasst ist. Bei der dritten Ausführungsform werden
Dämpfer 44.1 eingesetzt, die ein leicht gedämpftes
Aufsetzen der Aufzugskabine 35 oder des Gegengewichts auf
den bewegbaren Mitteln 44 ermöglichen, wenn eine Schutzzone
geschaffen werden soll. Die bewegbaren Mittel 44 werden so
im Betrieb geschont. Falls die Aufzugskabine und/oder das
Gegengewicht mit hoher Geschwindigkeit auf den jeweiligen
Puffer auftreffen - insbesondere beim Überfahren über die
unterste bzw. die oberste Halteposition der Aufzugskabine
hinaus - dann kommen dagegen die Dämpfungscharakteristiken
der Sockelelemente 12, 32 oder 43 zum Einsatz.According to the invention, the buffer can be a
Have damping characteristics that are specific to the application
is adjusted. In the third embodiment
Damper 44.1 used, which is a slightly damped
Put on the
Die erfindungsgemässen Puffer können mit speziellen Mitteln ausgestattet sein, die eine unsymmetrische Belastung zulassen, ohne das der Puffer "einknickt" oder "ausweicht". The buffers according to the invention can be prepared using special agents be equipped with an asymmetrical load allow without the buffer "buckling" or "evading".
Hierzu kann der Puffer ganz oder teilweise mit einem korsettartigen Element umgeben oder durch spezielle Mittel geführt sein, um die aufgrund der exzentrischen Pufferbelastung auftretenden Biegemomente auszugleichen.For this purpose, the buffer can be wholly or partially with a surrounded by a corset-like element or by special means be led to due to the eccentric To compensate for bending moments occurring in the buffer load.
Bei einem Teil der Ausführungsformen ist der Puffer komplett zwischen der Aufzugskabine und dem Gegengewicht angeordnet (siehe zum Beispiel Fig. 3A).In part of the embodiments is the buffer completely between the elevator car and the counterweight arranged (see for example Fig. 3A).
Bei einer weiteren Ausführungsform kann das Pufferelement ganz oder teilweise unter dem Gegengewicht angeordnet sein und wirkt direkt auf das Gegengewicht. Ein bewegbares Mittel des Pufferelements wirkt dann bei Bedarf entsprechend auf die Aufzugskabine.In a further embodiment, the buffer element be arranged entirely or partially under the counterweight and acts directly on the counterweight. A movable one The buffer element then acts as required accordingly to the elevator car.
Der Querschnitt des Puffer kann beliebig gewählt werden.
Die Puffer 10 und 30 haben einen im wesentlichen runden
Querschnitt parallel zum Boden des Aufzugsschachts. Der
Puffer 40 dagegen hat zum Beispiel im unteren Bereich 43
einen quadratischen Querschnitt.The cross section of the buffer can be chosen arbitrarily.
Je nach Ausführungsform kann eine Bewegung der bewegbaren Mittel des Puffers elektro-magnetisch, hydraulisch , pneumatisch, manuell, oder mittels eines Stellmotors erfolgen.Depending on the embodiment, a movement of the movable Buffer means electro-magnetic, hydraulic, pneumatic, manual, or by means of a servomotor respectively.
In einer weiteren Ausführungsform wird ein Grubenset verwendet, das eine Antriebs-/Umrichtereinheit, einen Geschwindigkeitsbegrenzer, eine Befestigung für die Führungsschienen und den Puffer umfasst. Dadurch vereinfacht sich die Montage im Aufzugsschacht merklich. In a further embodiment, a pit set used that a drive / converter unit, a Speed limiter, an attachment for the Includes guide rails and the buffer. Thereby Installation in the elevator shaft is noticeably easier.
Die vorliegende Erfindung eignet sich auch für den Einsatz in einer Aufzugsanlage in Rucksackdisposition.The present invention is also suitable for use in an elevator system in backpack disposition.
Durch die spezielle Anordnung und Ausführung des Puffers ergibt sich ein reduzierter Platzbedarf im Vergleich zu konventionellen Lösungen.Due to the special arrangement and design of the buffer there is a reduced space requirement compared to conventional solutions.
Die Erfindung ist besonders für den Einsatz in Aufzugsanlagen geeignet, die keine oder nur geringe Schachtgruben- und Schachtkopfhöhenmasse haben.The invention is particularly for use in Suitable elevator systems that have little or no Have pit and headroom heights.
Es ist ein Vorteil der Erfindung, dass Vorschriften für die Erfüllung des Personenschutzes eingehalten und die Baukosten bzw. Anlagekosten, je nach Ausführungsform, erheblich reduziert werden können.It is an advantage of the invention that regulations for the Compliance with personal protection and the Construction costs or plant costs, depending on the design, can be significantly reduced.
Die bewegbaren Mittel 14, 14.1, 34, 44 und 44.1 können im Rahmen der Erfindung auf verschiedene Weise modifiziert werden. Sie können durch Mittel ersetzt werden, die aus einer Grundstellung ausklappbar, ausschwenkbar, herausschiebbar und/oder herausdrehbar und jeweils in Bahnen der Aufzugskabine und/oder des Gegengewichts bewegbar sind, um die Aufzugskabine und/oder das Gegengewicht in einem Abstand oberhalb des Bodens zu stützen. Die bewegbaren Mittel können durch eine geeignete Anordnung auch so ausgelegt werden, dass die Aufzugskabine und das Gegengewicht jeweils in unterschiedlichen Höhen gestützt werden können. Sie können mehrteilig oder auch einstückig ausgelegt sein.The movable means 14, 14.1, 34, 44 and 44.1 can in Modified the scope of the invention in various ways become. They can be replaced by funds that come from a basic position can be folded out, swung out, slidable and / or rotatable and each in Paths of the elevator car and / or the counterweight are movable to the elevator car and / or that Counterweight at a distance above the ground support. The movable means can by a suitable Arrangement can also be designed so that the elevator car and the counterweight at different heights can be supported. They can be multi-part or too be designed in one piece.
Claims (15)
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Puffer (10, 30, 40) bewegbare Mittel (14, 14.1, 34, 44, 44.1), die in die Bahn (VK) der Aufzugskabine (15, 35, 45) hineinbewegbar sind,
und bewegbare Mittel (14.1, 34, 44, 44.1), die in die Bahn (VG) des Gegengewichts (23) hineinbewegbar sind, umfasst.Elevator system with a buffer (10, 30, 40) for creating at least one protection zone, the elevator system comprising an elevator car (15, 35, 45) and a counterweight (23) for the elevator car and the elevator car (15, 35, 45) and the counterweight (23) can be moved along tracks (V K , V G ),
characterized in that the buffer (10, 30, 40) movable means (14, 14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) which can be moved into the path (V K ) of the elevator car (15, 35, 45),
and movable means (14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) which can be moved into the path (V G ) of the counterweight (23).
die bewegbaren Mittel (14, 34, 44, 44.1) in eine Einsatzstellung bringbar sind, in welcher sie derart angeordnet sind, dass
ein mechanischer Kontakt zwischen den bewegbaren Mitteln (14, 34, 44, 44.1) und der Aufzugskabine (15, 35, 45) erfolgt, wenn die Aufzugskabine (15, 35, 45) eine erste vorgegebene Distanz (Z1.1, Z3, Z4) bezüglich eines Bodens (18, 38, 48) unterschreitet, und/oder dass
ein mechanischer Kontakt zwischen den bewegbaren Mitteln (14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) und dem Gegengewicht (23) erfolgt, wenn das Gegengewicht (23) eine zweite vorgegebene Distanz (Z1.2, Z3, Z4) bezüglich eines Bodens (18, 38, 48) unterschreitet. Elevator system according to claim 1, characterized in that
the movable means (14, 34, 44, 44.1) can be brought into an operating position in which they are arranged such that
A mechanical contact between the movable means (14, 34, 44, 44.1) and the elevator car (15, 35, 45) takes place when the elevator car (15, 35, 45) has a first predetermined distance (Z1.1, Z3, Z4 ) with respect to a floor (18, 38, 48), and / or that
A mechanical contact between the movable means (14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) and the counterweight (23) takes place when the counterweight (23) is a second predetermined distance (Z1.2, Z3, Z4) with respect to a floor (18, 38 , 48) falls below.
dass kein mechanischer Kontakt zwischen den bewegbaren Mitteln (14, 34, 44, 44.1) und der Aufzugskabine (45) erfolgt, wenn die Aufzugskabine (15, 35, 45) die erste vorgegebene Distanz (Z1.1, Z3, Z4) bezüglich eines Bodens (18, 38, 48) unterschreitet, und dass
kein mechanischer Kontakt zwischen den bewegbaren Mitteln (14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) und dem Gegengewicht (23) erfolgt, wenn das Gegengewicht (23) die zweite vorgegebene Distanz (Z1.2, Z3, Z4) bezüglich des Bodens (18, 38, 48) unterschreitet.Elevator system according to claims 2 and 3, characterized in that the movable means (14, 14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) can be brought into a normal position in which they are arranged in such a way that
that there is no mechanical contact between the movable means (14, 34, 44, 44.1) and the elevator car (45) when the elevator car (15, 35, 45) is the first predetermined distance (Z1.1, Z3, Z4) with respect to a Boden (18, 38, 48) falls below and that
there is no mechanical contact between the movable means (14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) and the counterweight (23) when the counterweight (23) is the second predetermined distance (Z1.2, Z3, Z4) with respect to the floor (18, 38 , 48) falls below.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Puffer (10, 30, 40) eine geeignete Dämpfungscharakteristik aufweist, um bei einem Erfolgen eines mechanischen Kontakts mit der Aufzugskabine (15, 35, 45) oder mit dem Gegengewicht (23) ein weiches Aufsetzen zu ermöglichen
und/oder
dass sich mindestens ein oberer Teil (13, 33, 43) des Puffers (10, 30, 40) zwischen einer Flächenprojektion (K1, K3, K4) der Aufzugskabine (15, 35, 45) und einer Flächenprojektion (G1, G3, G4) des Gegengewichts (23) befindet
und/oder dass es sich bei den bewegbaren Mitteln (14, 14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) um ausklappbare Mittel,
schwenkbare Mittel, schiebbare Mittel oder drehbare Mittel handelt.Elevator installation according to one of claims 1 to 7,
characterized in that the buffer (10, 30, 40) has a suitable damping characteristic in order to enable a soft touchdown when mechanical contact with the elevator car (15, 35, 45) or with the counterweight (23) is achieved
and or
that at least an upper part (13, 33, 43) of the buffer (10, 30, 40) is between a surface projection (K1, K3, K4) of the elevator car (15, 35, 45) and a surface projection (G1, G3, G4 ) of the counterweight (23)
and / or that the movable means (14, 14.1, 34, 44, 44.1) are fold-out means,
pivoting means, sliding means or rotating means.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04011503A EP1479636A1 (en) | 2003-05-21 | 2004-05-14 | Buffer that can create a safety inspection zone for elevators |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03405352 | 2003-05-21 | ||
| EP03405352 | 2003-05-21 | ||
| EP04011503A EP1479636A1 (en) | 2003-05-21 | 2004-05-14 | Buffer that can create a safety inspection zone for elevators |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1479636A1 true EP1479636A1 (en) | 2004-11-24 |
Family
ID=33099719
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04011503A Withdrawn EP1479636A1 (en) | 2003-05-21 | 2004-05-14 | Buffer that can create a safety inspection zone for elevators |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1479636A1 (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1674416A1 (en) * | 2004-12-23 | 2006-06-28 | ThyssenKrupp Aufzugswerke GmbH | Elevator and elevator car |
| WO2008002300A1 (en) * | 2006-06-26 | 2008-01-03 | Otis Elevator Company | Retractable stop for maintaining overhead clearance above an elevator car |
| EP1908720A1 (en) | 2006-10-06 | 2008-04-09 | Inventio Ag | Elevator pit barrier |
| US8807289B2 (en) | 2006-10-06 | 2014-08-19 | Inventio Ag | Elevator pit barrier |
| DE102017004719A1 (en) * | 2017-05-16 | 2018-11-22 | Michael Geisenhofer | Device for a secured area in a hoistway |
| CN110510542A (en) * | 2019-09-29 | 2019-11-29 | 山东富士制御电梯有限公司 | A kind of guide rail-type lifting platform falling proof device |
| CN111295351A (en) * | 2017-10-31 | 2020-06-16 | 因温特奥股份公司 | Device for performing maintenance work in an elevator shaft |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05201647A (en) * | 1992-01-28 | 1993-08-10 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Elevator device |
| EP0725033A1 (en) * | 1995-01-31 | 1996-08-07 | Inventio Ag | Temporary securing of a working space |
| JPH09227046A (en) * | 1996-02-26 | 1997-09-02 | Mitsubishi Denki Bill Techno Service Kk | Car stopper device for elevator device |
| EP1052212A1 (en) * | 1999-05-14 | 2000-11-15 | Inventio Ag | Device for carrying out work in an elevator shaft |
-
2004
- 2004-05-14 EP EP04011503A patent/EP1479636A1/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05201647A (en) * | 1992-01-28 | 1993-08-10 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Elevator device |
| EP0725033A1 (en) * | 1995-01-31 | 1996-08-07 | Inventio Ag | Temporary securing of a working space |
| JPH09227046A (en) * | 1996-02-26 | 1997-09-02 | Mitsubishi Denki Bill Techno Service Kk | Car stopper device for elevator device |
| EP1052212A1 (en) * | 1999-05-14 | 2000-11-15 | Inventio Ag | Device for carrying out work in an elevator shaft |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| PATENT ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN vol. 017, no. 641 (M - 1516) 29 November 1993 (1993-11-29) * |
| PATENT ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN vol. 1998, no. 01 30 January 1998 (1998-01-30) * |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1674416A1 (en) * | 2004-12-23 | 2006-06-28 | ThyssenKrupp Aufzugswerke GmbH | Elevator and elevator car |
| WO2008002300A1 (en) * | 2006-06-26 | 2008-01-03 | Otis Elevator Company | Retractable stop for maintaining overhead clearance above an elevator car |
| US8028808B2 (en) | 2006-06-26 | 2011-10-04 | Otis Elevator Company | Retractable stop for maintaining overhead clearance above an elevator car |
| EP1908720A1 (en) | 2006-10-06 | 2008-04-09 | Inventio Ag | Elevator pit barrier |
| US8807289B2 (en) | 2006-10-06 | 2014-08-19 | Inventio Ag | Elevator pit barrier |
| DE102017004719A1 (en) * | 2017-05-16 | 2018-11-22 | Michael Geisenhofer | Device for a secured area in a hoistway |
| CN111295351A (en) * | 2017-10-31 | 2020-06-16 | 因温特奥股份公司 | Device for performing maintenance work in an elevator shaft |
| CN110510542A (en) * | 2019-09-29 | 2019-11-29 | 山东富士制御电梯有限公司 | A kind of guide rail-type lifting platform falling proof device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2219985B1 (en) | Lift system with lift cars which can move vertically and horizontally | |
| DE69203697T2 (en) | Double-sided safety gear. | |
| EP2398729B1 (en) | Elevator system having a multi-deck vehicle | |
| EP2585395B1 (en) | Elevator system | |
| DE69000686T2 (en) | CAR PARK SYSTEM FOR INDIVIDUAL AND AUTOMATIC PARKING IN THE URBAN AREA. | |
| EP1693331A1 (en) | Elevator system with several shafts and with elevator cars that can be coupled and uncoupled from the selected drive system. | |
| WO2009077397A1 (en) | Ascension brake for two elevator bodies moving independently of one another | |
| EP2346771A1 (en) | Modernization method for elevator systems | |
| EP2512969A1 (en) | Double-decker lift installation | |
| DE69417686T2 (en) | Stage step for an escalator | |
| DE112015005891T5 (en) | winder | |
| EP1479636A1 (en) | Buffer that can create a safety inspection zone for elevators | |
| DE102017004719A1 (en) | Device for a secured area in a hoistway | |
| EP1999043B1 (en) | Workpiece support system | |
| EP3931141B1 (en) | Elevator system | |
| DE19752232C2 (en) | Rope elevator with concrete base protruding into the elevator shaft | |
| EP1479637B1 (en) | Buffer and elevator using such a buffer | |
| EP2468674A1 (en) | Lift facility with double decker | |
| EP3645443B1 (en) | Elevator system | |
| DE102016007070A1 (en) | Safety catch for lifting device | |
| WO2011107390A1 (en) | Method for the energy-saving operation of an elevator system and corresponding elevator system | |
| EP2050706B1 (en) | Holding device | |
| EP3924285B1 (en) | Elevator system | |
| WO2022144174A1 (en) | Maintenance device for a vehicle and method for operating a maintenance device | |
| DE102017110275A1 (en) | Elevator system with two shafts |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL HR LT LV MK |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20050509 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HK Ref legal event code: DE Ref document number: 1071122 Country of ref document: HK |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20070724 |
|
| R17C | First examination report despatched (corrected) |
Effective date: 20080724 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: HK Ref legal event code: WD Ref document number: 1071122 Country of ref document: HK |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Effective date: 20170406 |