EP1316629A1 - Disque de support et roulement pour un rotor de filature - Google Patents
Disque de support et roulement pour un rotor de filature Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1316629A1 EP1316629A1 EP02025441A EP02025441A EP1316629A1 EP 1316629 A1 EP1316629 A1 EP 1316629A1 EP 02025441 A EP02025441 A EP 02025441A EP 02025441 A EP02025441 A EP 02025441A EP 1316629 A1 EP1316629 A1 EP 1316629A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- tread
- rotor
- nanoparticles
- support
- support disc
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01H—SPINNING OR TWISTING
- D01H4/00—Open-end spinning machines or arrangements for imparting twist to independently moving fibres separated from slivers; Piecing arrangements therefor; Covering endless core threads with fibres by open-end spinning techniques
- D01H4/04—Open-end spinning machines or arrangements for imparting twist to independently moving fibres separated from slivers; Piecing arrangements therefor; Covering endless core threads with fibres by open-end spinning techniques imparting twist by contact of fibres with a running surface
- D01H4/08—Rotor spinning, i.e. the running surface being provided by a rotor
- D01H4/10—Rotors
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01H—SPINNING OR TWISTING
- D01H4/00—Open-end spinning machines or arrangements for imparting twist to independently moving fibres separated from slivers; Piecing arrangements therefor; Covering endless core threads with fibres by open-end spinning techniques
- D01H4/04—Open-end spinning machines or arrangements for imparting twist to independently moving fibres separated from slivers; Piecing arrangements therefor; Covering endless core threads with fibres by open-end spinning techniques imparting twist by contact of fibres with a running surface
- D01H4/08—Rotor spinning, i.e. the running surface being provided by a rotor
- D01H4/12—Rotor bearings; Arrangements for driving or stopping
Definitions
- the object of the present invention relates to a support disc for a bearing of a spinning rotor according to the preamble of claim 1 and a bearing for a spinning rotor according to claim 16 and one A rotor for an open-end spinning device according to claim 16.
- a support disc which to remove deposits to reduce the rotor shaft of the spinning rotor, with a tread is provided, which has a cleaning groove.
- the tread of the support disks should thus be prevented Deposits on the rotor shaft.
- the support discs made of a plastic form, which has a relatively small electrical resistance. Thereby electrostatic charges on the support disks are to be avoided become. The dirt particles get through these electrostatic charges on the running surface of the support disc as a result of electrostatic charging. This results as a result of friction with the surrounding air, because the support disks rotate at high speeds during operation.
- the support disc of DE 198 24 286 A1 therefore requires to prevent Deposits take special measures on their constructive design and material composition of the tread. This includes the contribution a cleaning groove and on the other hand a certain material for the tread the support disc to the electrical properties required there to achieve. Ultimately, the expert is not free to choose the Material of the support disc covering, just like the constructive one Design of the tread of the support disc.
- the object of the present invention is a support disk and a bearing for an open-end spinning rotor, each propose the problems solve the state of the art.
- the present one suggests Invention before a spinning rotor, which is particularly suitable with the support disks and a bearing according to the present invention to cooperate and the less to deposit in the area with the it interacts with the support disks, tends.
- the additives are designed according to the invention such that they are the recording of dirt on the tread of the tread. That is, the deposition the dirt on the support disc is due to the invention Additions made much more difficult and sometimes even completely prevented.
- the adhesive Forces that are responsible for dirt particles adhering to the Can store tread in the long term, are the inventive Design reduced so much that the desired effect occurs.
- the addition is in molded the tread of the support disc, i.e. that for example components of the additive together with the polymeric material on the Base body of the support disc are applied.
- This has the advantage that Machining of the support disc and wear of the tread are not included lead that the tread is without the additive according to the invention, because the essential part of the tread according to the invention the addition in itself contains.
- This can advantageously be designed in such a way that the addition however, it is not included where there is tread and base touch so as not to endanger a secure connection.
- the addition is applied to the tread of the tread.
- This application on the The surface of the tread is the same as for a surface coating.
- the top layer of the tread equipped with an additive according to the invention so that the surface of the tread on the tread according to the characteristics of the addition is trained.
- the surface of the tread is advantageous Use of a dirt-repellent additive is also dirt-repellent.
- the whole does not need to be beneficial Tread be provided with the addition, but only the relevant one Rotor shaft cooperating surface of the tread of the tread. This makes it possible to design the whole thing more cost-effectively, as if the entire covering is soaked with the additive.
- the layer is advantageously so thin that the mechanical properties of the material, the surface structure and the elasticity of the tread are not negative to be influenced.
- the addition is a Plastic, since plastics in particular are endowed with properties, with the help of a dirt-repellent or dirt-resistant Tread on the support disc is made possible.
- PTFE polytetrafluoroethylene
- a further development of the invention is the addition of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which is a particularly effective and versatile material for one Additive according to the invention is.
- PTFE polytetrafluoroethylene
- silicone can also be used
- an addition made of a plastic in particular also PTFE, can be combined with other additives so that other properties, in addition to the property of dirt repellency, in the tread of the tread can be implemented.
- a lacquer or Film is formed on the tread of the tread of the support disc.
- Additives can be added to the paint, for example be integrated from a plastic, which is a particularly good dirt-repellent Have an effect, while at the same time components may be included, which ensure wear resistance.
- nanoparticles with the help of different properties of Surface can be realized in a simple manner, at the same time due to the specific properties of the nanoparticles the surface the tread of the support disc according to the invention designed to be dirt-repellent.
- the nanoparticles can consist of different materials. According to the invention, an easy-to-clean can thus be particularly effective - Surface are created.
- Nanoparticles are structural units and measure the size of particles in nanometers because of their tiny size is. Thus, nanoparticles according to the invention can have a size of have only 100 nm.
- the nanoparticles of the additive at least partially produced using the so-called sol-gel process Service.
- the nanoparticles are inside a liquid eliminated, with a fixed and preferred size he follows.
- Nanoparticles produced by evaporation with finely focused laser beams are produced that can not be produced by the gel-sol process are.
- nanoparticles made of different materials i.e. also that they have different properties in the coating of the Can represent treads of the support disc.
- nanoparticles can be used, which are different were manufactured.
- the nanoparticles are formed at least partially from an organic material, which in particular can be used to achieve properties on the tread, by the specific material properties of the organic material, for example, a plastic.
- the Nanoparticles at least partially made of an inorganic material, whereby in addition to the property that the support disc covering with a coating can be equipped that is particularly dirt-repellent, At the same time, a coating can be realized that goes beyond that is particularly wear-resistant and has other advantageous properties.
- the nanoparticles as the basis for the formation of the Surface of the tread is advantageously allows the properties of the To design the surface freely, i.e. without the material of the support disc in must be changed to a particular extent, since with the help of the nanoparticles other required properties of the surface are also realized at the same time can be.
- a surface can also be obtained with it For example, is antistatic. The necessary property remains, for example the elasticity and damping properties of the tread the support disc. With the help of the invention can now support disc coverings can be realized, the positive properties of different Unite materials.
- the tread of the tread is with a dirt-repellent additive equipped, thus it is advantageously achieved that storage is created which allows the rotor shaft of the spinning rotor not to Debris comes into contact with the bearings of the State of the art on the support disc and fix the property have to pass from the support disc to the rotor shaft and this to be coated with a layer of dirt.
- the configuration according to the invention the surface of the tread of the support disc ensures that the Storage also copes with an application where large dirt and Amounts of dust accumulate that would otherwise lead to difficulties.
- the storage is advantageous according to the invention with one or more Support discs equipped with the features of the invention described above have.
- a rotor for an open-end spinning device proposed, the rotor shaft at least in the area, with which he interacts with a support disc with a coating is provided, the adherence of deposits, in particular Dirt, difficult.
- a rotor according to the invention can a storage are operated, in which the support discs according to State of the art, but are also particularly advantageous Storage according to the invention, wherein the tread of the support disks Storage is equipped with the properties as described above.
- the rotor is provided with a coating, which are at least partially applied to the surface of the rotor shaft Nanoparticles exist.
- This type of design can the rotor shaft can be provided with a coating that ensures that dirt particles do not stick to the surface of the rotor shaft can.
- a coating is a particularly advantageous further development provided with nanoparticles, these in addition to the property
- To repel dirt is also a wear protection for the rotor shaft form. So substances can be used for the nanoparticles that result in a particularly wear-resistant coating.
- the rotor shaft can advantageously be provided with nanoparticles be as described in the dependent claims and the same As in the case of the coating in the support disk according to the invention, it has an effect.
- the rotor shaft has a particularly advantageous effect if At the same time, the properties are dirt-repellent and wear-resistant become. Nanoparticles are particularly suitable for this. To be a special one To achieve wear resistance, nanoparticles are also particularly cheap can be used from a hard material, for example carbides such as silicon carbide.
- the nanoparticles are also especially in the recesses of the surface structure can be deposited, whereby they are particularly protected against wear, so that the coated Component can lose the desired properties less easily. Further advantageous embodiments of the invention are described in the subclaims.
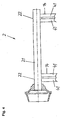
- FIG. 1 shows a basic illustration of a bearing for an open-end spinning rotor, as they are often used on open-end spinning machines comes.
- the bearing 1 essentially consists of a bearing block 11, which carries the support disc bearings 12.
- the support disc bearings 12 each store one Shaft 13, which in turn has a press fit with one at each of its ends Support disc 14 is connected.
- the support disks 14 each form two pairs of support disks, so that two wedge gaps 141 arise.
- the support disks 14 carry the rotor shaft 21 of the open-end spinning rotor 2.
- the open-end spinning rotor 2 for example, via a tangential belt (see Figure 2) driven, it rolls in the wedge gap 141 on the support disks 14 from. This causes them to rotate.
- the support washers 14 are each provided with a cooling groove 3, which ensures that the in the tread 4 of the support disc 14 heat generated during operation can be dissipated more easily.
- the resulting 4 support disks 14 in the tread Warmth is not only due to the flexing work on the tread 41 of the support disk 4 rolling rotor shaft 21, but also generated by the inclination of the shafts 13.
- the waves 13 that the Wear support discs 4 are not formed parallel to each other, but skewed so that on the rotor shaft 21 through the support disks 4th an axial thrust is exerted.
- This is based on one in a known manner Axial bearing 101.
- This can be designed as a track bearing, for example be, or, as indicated in the embodiment of Figure 1, in shape of an aerostatic thrust bearing.
- Figure 2 shows a partial front view of a bearing of an open-end spinning rotor 2.
- the rotor shaft 21 is radial in wedge gaps 141 of two pairs supported by support disks 14.
- the cut of Figure 2 is laid out that the section through the rotor shaft 21, which hatches accordingly is shown, is laid.
- the other components are with dash-dotted lines shown.
- the rotor shaft 21 is supported by a tangential belt 5 runs in one direction through the spinning machine, driven. All open-end spinning rotors on one machine side are Spinning machine driven.
- the tangential belt 5 is in the range of each Spinning rotor 2 loaded with a pressure roller 51, which is free around an axis rotatably arranged and by means of a load spring, not shown is pressed against the tangential belt 5.
- the support disks 14 are in known manner slightly skewed to each other, so that in connection with the direction of rotation of the tangential belt on the rotor shaft 21 against an axial bearing (see Figure 1) an axial thrust is achieved.
- an axial thrust is achieved.
- the open-end spinning rotor maintains its operating position in the axial direction.
- the spinning process for open-end rotor spinning is known to the person skilled in the art and need not be explained here. In those places (compare Figure 1) on which the surface 22 of the rotor shaft 21 with the Treads 41 of the support discs 14 comes into contact, the rotor shaft tends 21 for pollution, primarily from the treads 41 of the Support discs 14 originates.
- the tread 41 advantageously all support disks 14 are equipped with an additive, which prevents the tread 41 from picking up dirt. Because this is especially harmful because not only the tread 4 on his Tread 41 dirty, but also this dirt to the Surface 22 of the rotor shaft 21 transmits where these dirt particles lock and form a hard and irregular surface.
- the addition of the tread can be similar to a surface coating on the tread 41 of the tread 4 of the support disk 14 be applied by a coating process.
- Another one Embodiment of the invention is the addition according to the invention in Tread 4 of the support disc 12 is molded in, i.e. already during production the support discs 14 contains the material of the covering, which is the tread 4 forms the additive according to the invention. This can also be advantageous only be molded in a thin outer layer of the tread 4 or also in the entire radial thickness of the tread 4 of the support disk 14.
- the addition is a plastic in the embodiment of Figure 1, especially polytetrafluoroethylene or silicone, which is particularly simply insert into the tread 4 or apply to the surface to let.
- plastics especially polytetrafluoroethylene or silicone, which is particularly simply insert into the tread 4 or apply to the surface to let.
- they are inexpensive and offer sufficient sure guarantee that no dirt particles on the tread 41 of the tread 4 are added. As a result, neither will Dirt on the rotor shaft 21, which cooperates with such support disks, transfer.
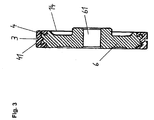
- Figure 3 shows a section through a support disc 14 with a circumferential Cooling groove 3 in the tread 4, the tread on its outer circumference 41 forms.
- the support disc consists of a base body 6, for example is designed as an aluminum injection molded part.
- the support disc 14 has in the middle of a bore 61, through which it on the shaft 13 of a support disc bearing 12 (see Figure 1) is attached by means of a press fit.
- the area of the transition between base body 6 and tread 4 is the outer circumference of the base body 6 designed in a special way, so that a ensures better adhesion between base body 6 and tread 4 can be.
- the known basic bodies are designed so that in the area of a central Cooling groove 3 has a sufficient thickness of the tread 4.
- the tread 41 of the tread 4 of the support disk 14 is according to the invention equipped with an additive that prevents dirt from entering the tread 41 of the tread 4 prevented, at least greatly reduced.
- the addition is in the embodiment of Figure 3 according to the invention in the form of the tread 41 applied nanoparticles formed over a Adhesive is applied to the tread 41 of the tread 4.
- the tread 4 with Nanoparticles is coated, is guaranteed according to their property, that dirt does not adhere to the surface of the tread 41 stay. This is a transfer of dirt from the support disc 14 to a cooperating with this spinning rotor or its rotor shaft 21 (see Figure 1) severely restricted, respectively does not take place.
- FIG. 4 shows a spinning rotor designed according to the further invention 2 with its rotor shaft 21.
- the invention it is provided, at least at those points on the surface 22 of the rotor shaft 21 which are associated with the running surfaces 41 of the support disks 14 come into contact, a coating that prevent deposits from adhering.
- This Coating is according to the invention as on the surface of the rotor shaft applied nanoparticles formed In the representation of FIG. 4, the nanoparticles cannot be represented in detail since they are tiny Size are.
- the entire surface 22 of the rotor shaft 21 with an inventive Be provided not only those parts of the coating Surface that are in contact with the support disks 14.
- the nanoparticles with which the rotor shaft 21 of the spinning rotor 2 is coated is advantageously made of a hard material, in the embodiment of Figure 4 made of silicon carbide, which in addition to the invention dirt-repellent effect at the same time a surface is created which is wear resistant.
- a hard material in the embodiment of Figure 4 made of silicon carbide, which in addition to the invention dirt-repellent effect at the same time a surface is created which is wear resistant.
- other hard materials can also be used Form of nanoparticles can be used according to the invention.
- the surfaces of the running surfaces 41 of the support disks 14 are in the exemplary embodiment of Figure 4, different from that described above according to the invention designed support disc 14, not with a coating provided, especially for rotor bearings that are less dusty Stand atmosphere, a spinning rotor designed according to the invention are sufficient can to prevent this in the area in which it is connected to the treads 41 of support disks worked together, not dirty.
- a spinning rotor designed according to the invention are sufficient can to prevent this in the area in which it is connected to the treads 41 of support disks worked together, not dirty.
- the treads 41 of the support plates 14 according to the invention relating to the support disks. Then it is guaranteed that even under the toughest conditions, no pollution of the rotor shaft 21 takes place.
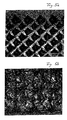
- the rotor shaft 21 is shown in FIG Invention in the area where he cooperates with the support discs on his Provide the surface with a structure.
- This can, for example be a corrugation that can be cut into the Surface of the rotor shaft was stamped. Tools can also be used with diamond-embossed surfaces.
- Such a designed surface of the rotor shaft according to the invention is in figure 5a in the form of a micrograph, greatly enlarged.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10159693 | 2001-11-29 | ||
| DE10159693 | 2001-11-29 | ||
| DE10237007 | 2002-08-13 | ||
| DE10237007A DE10237007A1 (de) | 2001-11-29 | 2002-08-13 | Stützscheibe und Lagerung für einen Spinnrotor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1316629A1 true EP1316629A1 (fr) | 2003-06-04 |
Family
ID=26010715
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02025441A Withdrawn EP1316629A1 (fr) | 2001-11-29 | 2002-11-15 | Disque de support et roulement pour un rotor de filature |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1316629A1 (fr) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100554538C (zh) * | 2004-01-19 | 2009-10-28 | 里特机械公司 | 精梳机棉网引导装置 |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3050056C1 (de) * | 1979-11-22 | 1988-06-16 | Glyco Metall Werke | Zwei- oder Mehrschicht-Verbundwerkstoff und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| DE4227909A1 (de) * | 1992-08-22 | 1994-02-24 | Glyco Metall Werke | Metall-Kunststoff-Verbundlagerwerkstoff sowie Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung |
| US5517814A (en) * | 1993-10-14 | 1996-05-21 | Fritz Stahlecker | Supporting disk for a supporting disk bearing arrangement of an open-end spinning rotor |
| EP0794273A1 (fr) * | 1996-03-05 | 1997-09-10 | Rieter Ingolstadt Spinnereimaschinenbau AG | Métier à filer à bout libre |
| US5992137A (en) * | 1998-04-23 | 1999-11-30 | Spindelfabrik, Suessen, Schurr, Stahlecker & Grill Gmbh | Supporting disc for a supporting disc bearing of open-end spinning rotors and process of making same |
| EP0960963A2 (fr) * | 1998-05-29 | 1999-12-01 | Rieter Ingolstadt Spinnereimaschinenbau AG | Palier à disques d'appui de rotor de filage avec extremité ouverte |
| US6106936A (en) * | 1995-07-08 | 2000-08-22 | Glyco-Metall-Werke, Glyco B.V. & Co. Kg | Overlay material for plain bearing comprising filled fluorothermoplastic material |
| EP1096045A1 (fr) * | 1999-10-26 | 2001-05-02 | Rieter Ingolstadt Spinnereimaschinenbau AG | Palier pour un rotor de filage dans un métier à filer à bout libre |
| DE10055443A1 (de) * | 2000-11-09 | 2002-05-29 | Wacker Chemie Gmbh | Beschichtete Rotorwelle für einen Spinnrotor zum Offenend-Spinnen |
-
2002
- 2002-11-15 EP EP02025441A patent/EP1316629A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3050056C1 (de) * | 1979-11-22 | 1988-06-16 | Glyco Metall Werke | Zwei- oder Mehrschicht-Verbundwerkstoff und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| DE4227909A1 (de) * | 1992-08-22 | 1994-02-24 | Glyco Metall Werke | Metall-Kunststoff-Verbundlagerwerkstoff sowie Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung |
| US5517814A (en) * | 1993-10-14 | 1996-05-21 | Fritz Stahlecker | Supporting disk for a supporting disk bearing arrangement of an open-end spinning rotor |
| US6106936A (en) * | 1995-07-08 | 2000-08-22 | Glyco-Metall-Werke, Glyco B.V. & Co. Kg | Overlay material for plain bearing comprising filled fluorothermoplastic material |
| EP0794273A1 (fr) * | 1996-03-05 | 1997-09-10 | Rieter Ingolstadt Spinnereimaschinenbau AG | Métier à filer à bout libre |
| US5992137A (en) * | 1998-04-23 | 1999-11-30 | Spindelfabrik, Suessen, Schurr, Stahlecker & Grill Gmbh | Supporting disc for a supporting disc bearing of open-end spinning rotors and process of making same |
| EP0960963A2 (fr) * | 1998-05-29 | 1999-12-01 | Rieter Ingolstadt Spinnereimaschinenbau AG | Palier à disques d'appui de rotor de filage avec extremité ouverte |
| EP1096045A1 (fr) * | 1999-10-26 | 2001-05-02 | Rieter Ingolstadt Spinnereimaschinenbau AG | Palier pour un rotor de filage dans un métier à filer à bout libre |
| DE10055443A1 (de) * | 2000-11-09 | 2002-05-29 | Wacker Chemie Gmbh | Beschichtete Rotorwelle für einen Spinnrotor zum Offenend-Spinnen |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100554538C (zh) * | 2004-01-19 | 2009-10-28 | 里特机械公司 | 精梳机棉网引导装置 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE2015545C2 (de) | Folie für ein hydro- oder pneumodynamisches Folienlager | |
| AT406141B (de) | Vorrichtung zum reinigen und schmieren von antriebsketten, insbesondere von motorrädern | |
| DE102009039279A1 (de) | Dichtungsvorrichtung | |
| DE212018000105U1 (de) | Gewebereinigungsvorrichtung für Song-Brokat | |
| DE3111894A1 (de) | "saugwalze zum foerdern einer materialbahn und eine derartige saugwalze enthaltende anordnung" | |
| DE102013225996A1 (de) | Kunststoff-Wälzlagerkäfig für ein Axiallager und Axiallager | |
| DE3009810A1 (de) | Dichtung | |
| DE10145610A1 (de) | Schneidgarnitur einer Kettensäge | |
| DE69407011T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Dichtung für Wälzlager, Dichtung für Wälzlager und mit einer solchen Dichtung versehenes Wälzlager | |
| DE19824286A1 (de) | Lagerung für einen Offenend-Spinnrotor mittels Stützscheiben | |
| WO2018054416A1 (fr) | Joint d'étanchéité pour palier de roue avec joint de pré-étanchéité intégré | |
| DE2061462B2 (fr) | ||
| EP3464888A1 (fr) | Couronne d'orientation pour éoliennes, pale de rotor et éolienne ainsi équipée | |
| DE10237007A1 (de) | Stützscheibe und Lagerung für einen Spinnrotor | |
| EP1316629A1 (fr) | Disque de support et roulement pour un rotor de filature | |
| EP1146152B1 (fr) | Disque de support comportant une couche en caoutchouc pour un palier à disques supportant un rotor à filature | |
| DE2713464C3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von Wellpappe | |
| DE4443103B4 (de) | Reibfläche einer für den Einsatz in einer Riemenspanneinrichtung vorgesehenen Reibscheibe | |
| DE2706760A1 (de) | Beweglicher abgriff fuer potentiometer | |
| DE102005036690B4 (de) | Verbundmaterial für Gleitanwendungen | |
| DE3012916C2 (de) | Labyrinthwellendichtung | |
| EP0656434B1 (fr) | Rouleau de pression pour une machine de préparation à la filature | |
| EP0968771B1 (fr) | Procédé et appareil pour appliquer une force à un object sans le toucher | |
| DE3734410C2 (de) | Dichtscheibe und mit dieser ausgerüstetes Linearlager | |
| DE19818125B4 (de) | Stützscheibe für eine Stützscheibenlagerung von Offenend-Spinnrotoren |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20030617 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT CH DE IT LI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20040922 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20050203 |