EP0304513B1 - Dispositif d'éclairage à basse tension - Google Patents
Dispositif d'éclairage à basse tension Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0304513B1 EP0304513B1 EP87119214A EP87119214A EP0304513B1 EP 0304513 B1 EP0304513 B1 EP 0304513B1 EP 87119214 A EP87119214 A EP 87119214A EP 87119214 A EP87119214 A EP 87119214A EP 0304513 B1 EP0304513 B1 EP 0304513B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- bars
- low
- lighting system
- contact
- voltage lighting
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R25/00—Coupling parts adapted for simultaneous co-operation with two or more identical counterparts, e.g. for distributing energy to two or more circuits
- H01R25/14—Rails or bus-bars constructed so that the counterparts can be connected thereto at any point along their length
- H01R25/142—Their counterparts
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21V—FUNCTIONAL FEATURES OR DETAILS OF LIGHTING DEVICES OR SYSTEMS THEREOF; STRUCTURAL COMBINATIONS OF LIGHTING DEVICES WITH OTHER ARTICLES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F21V21/00—Supporting, suspending, or attaching arrangements for lighting devices; Hand grips
- F21V21/34—Supporting elements displaceable along a guiding element
- F21V21/35—Supporting elements displaceable along a guiding element with direct electrical contact between the supporting element and electric conductors running along the guiding element
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21V—FUNCTIONAL FEATURES OR DETAILS OF LIGHTING DEVICES OR SYSTEMS THEREOF; STRUCTURAL COMBINATIONS OF LIGHTING DEVICES WITH OTHER ARTICLES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F21V21/00—Supporting, suspending, or attaching arrangements for lighting devices; Hand grips
- F21V21/14—Adjustable mountings
- F21V21/30—Pivoted housings or frames
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/62—Means for facilitating engagement or disengagement of coupling parts or for holding them in engagement
- H01R13/6205—Two-part coupling devices held in engagement by a magnet
Definitions
- the invention relates to a low-voltage lighting system consisting of at least one busbar that can be fastened to the ground and lighting bodies that can be fastened to it by means of adapters, the busbar consisting of at least two rods made of magnetic material which are arranged parallel to one another and have different electrical potential and are separated from one another by an insulating layer are and are held together by this.
- Lighting systems which have busbars which are arranged parallel to one another and are separated from one another by an insulating layer, the rods being embedded in this insulating layer over a large part of their circumference. Only two surfaces of the rods, which are opposite each other by 180 degrees, are free of the insulation. This results in a busbar of approximately circular cross section. Since the contact surfaces of the two rods lie diametrically opposite one another, the adapters for fastening the lighting fixtures to the busbar are designed in the form of a clamp. The clamp legs touching the contact surfaces serve to establish the electrical contact from the busbar to the lighting fixture. The production of such busbars is complex since the rods have to be cast into the insulation material.
- the clamp legs are pressed against the contact surfaces of the busbar with the aid of a spring. Since the lighting systems according to the invention should be variable in the arrangement of the lighting fixtures on the rails, it is necessary that the lighting fixtures can be moved quickly and easily on the rail.
- the clamp adapters have the disadvantage that the material of the clamp spring becomes fatigued when the lighting fixtures are frequently moved, and thus a firm hold on the rail is no longer guaranteed.
- the production of the clip adapter is complex. Inevitably, these adapters require a construction whose transverse expansion is significantly larger than the conductor rail diameter. If the premises to be illuminated require that several busbars are arranged closely next to one another, the distance between individual busbars is limited by the expansion of the brackets in order to avoid short circuits.
- the previously known system has the disadvantage that the busbars are limited to two current-carrying rods united in them.
- the busbars are limited to two current-carrying rods united in them.
- French patent FR-A-1 400 179 also discloses a low-voltage lighting system with stainless steel busbars attached to the base and adapters for the lighting fixtures held magnetically thereon, in which the adapters consist of permanent magnetic material and two parallel to one another in one plane have arranged, electrically conductive contact surfaces which are placed directly on the parallel surfaces of the busbars and are thereby mechanically and electrically connected.
- the invention is therefore based on the object of providing a low-voltage lighting system of the type mentioned at the outset which is simple to produce, allows the adapters to be connected in more than one direction and in which the busbar is not limited to two current-carrying rods.
- the invention consists in that the insulating layer between the mutually facing surfaces of the neighboring Rods connects them to each other to form a busbar and the contact surfaces of the adapters are separated from one another by an electrically non-conductive permanent magnet and fastened to it.
- the bars are largely exposed and are only separated from the insulating layer on the surfaces of adjacent bars facing one another.
- the insulating layer can e.g. B. be an adhesive tape, so that the insulating layer also causes the cohesion of the rods in the busbar.
- the contact surfaces of the busbar lie next to one another in one plane, adapters with contact surfaces likewise lying in one plane can be used.
- the contact surfaces are attached to a permanent magnet arranged between them, so that the contact surfaces also become magnetic.
- the busbars according to the invention also offer the advantage that contact surfaces are present both on the top and on the bottom of the busbar. If the busbar is attached at a sufficient distance from the surface, e.g. B. by hanging the track from the ceiling, lighting fixtures can be attached to it both on the lower and on the upper side. The lighting fixtures can be directed in such a way that some of them illuminate the surface and thus generate indirect lighting and another part of the lighting fixtures is directed directly into the room as a spotlight. Because the adapters have a transverse extent which corresponds approximately to the distance between the longitudinal axes of the rods, the distances between individual busbars are minimally small. In addition, the manufacture of the adapter according to the invention and the manufacture of the busbars are considerably simplified.
- the rods can be rectangular in cross section, for. B. be square, which makes the production of the busbars from such rods even easier.
- each facing sides of the rods are flattened and serve as fastening surfaces for the insulating layer.
- Claim 6 has a further advantageous feature of the adapter according to the invention. This makes it possible to quickly and easily separate the lighting fixture from the adapter and the free one Use the adapter as a fastening element for the busbars on the surface.
- the feature of claim 7 offers the advantage of being able to detach the lighting fixtures quickly and easily from the line elements which are attached to the adapter and to replace them with a different type of lighting fixture.
- busbars according to the invention is given by the feature of claim 8. If the insulating layer on both sides of the busbar protrudes beyond the plane formed by the contact surfaces of adjacent rods, rotation of the contact surfaces of the adapters in this plane cannot lead to a short circuit, since the web-shaped design of the insulating layer prevents the contact surfaces of the adapter from twisting the contact surfaces of the conductor rail.
- the features of claim 10 provide a magnetic adapter which is provided for fastening the busbars to the substrate, a wall or a ceiling. Its structure is identical to that of the lighting fixture adapter. As already stated above, the magnetic adapters are designed in such a way that they can be used either as a fastening element for the lighting fixtures or as a fastening element for the busbars themselves.
- An alternative fastening option is given by claim 11.
- About 2 cm long sleeves are attached to the outer bars of the busbar and z. B. attached with grub screws to the bars.
- Two opposite sleeves are on a z. B. cube-shaped base, e.g. B. made of plastic, screwed tight.
- the base On its surface facing away from the busbar, the base has a blind hole into which the bolt of a screw is inserted, which is anchored to the base.
- a further hole is made in the side of the base, which opens into the blind hole.
- the bore has a Internal thread into which a grub screw can be screwed, which presses against the screw bolt when it is tightened and holds it in place.
- a socket for connecting the power supply lines can be attached to each of the sleeves.
- the lighting system according to the invention is not limited to busbars with only two rods combined to form a busbar.
- the busbar consists of three rods arranged parallel to each other, with adjacent rods having different electrical potentials.
- the insulating layer is arranged between two rods in such a way that the contact surfaces of the three rods arranged parallel to one another lie in one plane.
- the middle rod is preferably the neutral conductor, while the outer rods represent the phases.
- the features of claim 13 provide a further busbar in which a total of eight rods are combined to form a busbar which is approximately square in cross section. Three adjacent bars form the sides of the square. The spaces between the bars are one insulating mass filled. If square bars are used to form the busbar, two adjacent bars can be connected to one another with the aid of an insulating adhesive.
- the insulation body is advantageously designed as an extrusion part, so that the rods can be introduced into channels provided for this purpose. With the aid of such a rail, it is possible to implement a four-phase system, the rods enclosed by two outer rods being used as neutral conductors and the outer rods attached to the edges representing the four phases.
- the rods can, for. B. consist of a steel tube of small diameter, which has a core made of a non-ferrous metal, for. B. surrounds copper or aluminum.
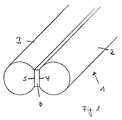
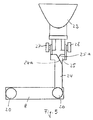
- a conductor rail (1) is shown in broken representation, which consists of two round steels (2 and 3), which have flat surfaces (4 and 5) on their mutually facing sides.
- the flat sides (4 and 5) of the rods (2 and 3) are attached to an insulating adhesive tape (6) which separates and insulates the rods (2 and 3) along their entire length.
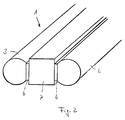
- FIG. 2 shows a further embodiment of a busbar according to the invention in a broken view.
- This consists of three parallel bars (2, 3 and 7).
- the rods (2 and 3) are designed as in Fig. 1, while the intermediate rod is rectangular in cross section.
- the rods are connected to one another along their entire length by an insulating adhesive layer (6).
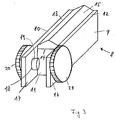
- FIG. 3 shows a magnetic adapter (8) according to the invention. It consists of two steel sheets (9 and 10) which are arranged parallel to one another and are rectangular in outline and which are separated from one another by means of a magnet (11) which consists of a non-conductive material are separated.
- the steel sheets (9 and 10) are attached to the opposite side surfaces of the magnet (11), for. B. glued.
- the contact surfaces (12 and 13) that make contact with the busbar (1) protrude beyond the upper edge (14) of the magnet (11).
- the magnet (11) On its surface facing the busbar, the magnet (11) has a roof-shaped web (15) which is also made of non-conductive material. It is used so that when an adapter (8) is rotated on a busbar according to FIGS.
- the contact surfaces (12 and 13) are lifted off the contact surfaces of the busbar (1), thus preventing a short circuit.
- the steel sheets (9 and 10) are extended beyond the front edge of the magnet (11).
- the extensions (16 and 17) are provided with bores (18) through which the screw bolt (19) of screws (20 and 21) can be inserted.
- the screws (20 and 21) are used to fasten conductor elements, not shown, which are connected to a lighting fixture, also not shown.
- FIG. 4 shows a busbar (1) in which the insulating layer (6) is extended beyond the contact surfaces of the rods (2 and 3) in the form of a web.
- an adapter (8) is used, as is shown in FIG. 3.
- the roof-shaped web is here (15) omitted.
- the web (22) extends approximately to the surface of the magnet (11). This also prevents a short circuit when the adapter (8) is rotated on the busbar, since the web causes the contact surfaces (12 and 13) of the adapter (8) to lift off.
- An adapter (8) with a connected lighting fixture (23) is arranged on the busbar (1). With the aid of the screws (20 and 21), a conductor element (24 and 25) is fastened to the projecting ends (16 and 17) of the steel sheets (9 and 10). They are constructed identically and consist of a metal sheet which has an approximately L-shaped outline, the end of the larger leg of the L being bent by 90 degrees.
- the L-shaped conductor elements (24, 25) have a chamfer (24 a, 25 a) at the transition from the vertical to the horizontal L-leg. These bevels are necessary so that when the lighting fixture (23) is pivoted about an axis that leads through the screw axis of the screws (27 and 28), no short circuit can occur.
- fastenings for the lighting fixture (23) in the form of screws (27 and 28) are provided, which at the same time the electrical Form contact between the conductor elements (24 and 25) and the connections of the lighting fixture (23).
- lighting fixtures (23) can be arranged at both ends of the adapter (8).
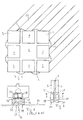
- busbars according to the invention are shown. They have a square cross section, each side of the square consisting of three bars (2, 3, 7), between which an insulation body (6) is arranged.
- the insulation body (6) can consist of adhesive tapes which combine the bars to form the busbar.
- the insulation body it is also possible to design the insulation body as an extruded plastic profile, as is generally provided for busbars consisting of round bars. The rods are pushed into the extruded profile from one side and can also be glued to it.
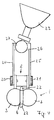
- the base (34) With the help of the screws (33), the base (34) is firmly connected to the sleeves (30).
- a blind hole (not shown) is made in the surface (35) of the base (34) opposite the busbar.
- the screw bolt of a merely indicated wood screw (36) is inserted in this blind hole.
- the wood screw (36) is previously in the underground (37), for. B. wall pegged.
- the base (34) with the blind hole is pushed onto the screw bolt of the screw (36).
- the bore also has an internal thread into which a grub screw can be screwed, which, when the base (34) is placed on the wood screw, rests against the screw bolt of the wood screw (36) presses and the base is fixed on the surface.
- the sleeves can have not shown, but only indicated connection sockets for the power supply.
- the sleeves (30) can be attached at any point on the busbar. There they can be attached to the base using the base (34). However, they can also serve as connecting elements of two aligned busbars without the base. In addition, it is possible to use the sleeves (30), for. B. hanging from the ceiling. It is also possible to connect two sleeves (30) aligned with one another with the aid of a flexible intermediate piece. In this way, two busbars can be attached to each other so that they can be offset from each other by any angle.
- a lighting system is constructed as follows: Adapters (8) which are aligned with one another in the longitudinal direction are fastened to a wall or a ceiling. Busbars (1) are attached to these adapters (8). The power connections of the low-voltage voltage source are at two ends (16 and 17) of one of the adapters, e.g. B. with the screws (20 and 21). On the side of the The busbar (1) is fitted with an adapter (8) equipped with a lighting fixture (23), so that the circuit is closed. Several such rails can be arranged on the ceiling or on the wall, and the lighting elements can be moved on the conductor rails in order to produce a wide variety of lighting configurations.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Non-Portable Lighting Devices Or Systems Thereof (AREA)
Claims (13)
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension constitué par au moins un rail conducteur de courant (1) pouvant être fixé en sous-sol et des corps d'éclairage (23) pouvant être fixés sur celui-ci au moyen d'adaptateurs (8), le rail conducteur de courant (1) étant constitué par au moins deux baguettes (2, 3, 7) disposées de façon parallèle entre elles, situées à un potentiel électrique différent en un matériau magnétique, et qui sont séparées par une couche isolante (6), et les faces de contact des baguettes (2, 3, 7) sont juxtaposées dans un même plan et les adaptateurs (8) présentent deux faces de contact (12, 13) conductrices magnétiquement et éléctriquement parallèles entre elles dans un même plan, faces de contact (12, 13) qui sont destinées à prélever le courant des phases de contact avoisinantes (2, 3, 7), dispositif caractérisé en ce que la couche isolants (6) entre les faces dirigées l'une vers l'autre (4, 5) des baguettes avoisinantes (2, 3, 7) relie celles-ci entre elles au rail conducteur de courant (1), et en ce que les faces de contact (12, 13) des adaptateurs (8) sont séparées par des aimants permanents (11) non conducteurs électriquement et sont fixées sur celui-ci.
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon le revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que la couche isolante (6) est une bande adhésive.
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que les tiges basse tension (2, 3, 7) présentent une section transversale rectangulaire.
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que les tiges (2, 3, 7) sont des tiges rondes en acier, les côtés (4, 5) des tiges (2, 3, 7) dirigés l'un vers l'autre comportant respectivement un méplat.
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon l'une des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisé en ce que l'aimant (11) est de conception parallélépipédique et en ce que sur les duex faces longitudinales opposées de parallélépipède est respectivement fixés une tôle d'acier (9, 10) dont le bord dirigé ver le rail conducteur de courant (1) fait saillie par la surface (14) formée par les côtés longitudinaux du parallélépipède, et forme une face de contact (12, 13) moyennant quoi un élément conducteur (24, 25) menant respectivement au corps d'éclairage (23) peut être fixé sur l'une des extrémités de la tôle d'acier (16, 17).
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon le revendication 5, caractérisé en ce que les extrémités (16, 17) des tôles d'acier (9, 10) font saillie ou dessus des aimants disposés entre celles-ci (11) dans la direction longitudinale, moyennant quoi les éléments conducteurs (24, 25) sont fixés sur les extrémités (16, 17) des tôles d'acier (9, 10) à l'aide de vis (20, 21).
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon la revendication 5 ou 6, caractérisé en ce que les éléments conducteurs (24, 25) peuvent être fixés à l'aide de vis (27, 28) sur le corps d'éclairage (23).
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon une ou plusieurs des revendications 1 à 7, caractérisé en ce que la couche isolante (6) entre les baguettes (2, 3, 7) fait saillie sur le plan formé par les côtés supérieurs des baguettes (2, 3, 7) en alignement réciproque en configuration d'aile (22).
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon une ou plusieurs des revendications 1 à 7, caractérisé en ce que sur l'aiment (11) entre les faces de contact (12, 13) des tôles d'acier (9, 10) est disposée une aile (15) faisant saillie à travers le plan formé par les faces de contact.
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon une ou plusieurs des revendications 1 à 9, caractérisé en as que les rails conducteurs de courant (1) peuvent être fixés sur des adaptateurs magnétiques (8) qui sont constitués par deux tôles d'acier de configuration rectangulaire (9, 10), qui fixent les faces longitudinales opposées entre elles d'un aimant permanent (11) parallélépipédique, ce en quoi les bords longitudinaux (12, 13) des tôles d'acier (9, 10) s'étendent parallèlement aux bords longitudinaux de l'aimant (11) et établissent le contact électrique et le contact magnétique entre les tôles d'acier (9, 10) et les baguettes (2, 3, 7) du rail conducteur de courant (1).
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon une ou plusieurs des revendications 1 à 9, caractérisé en ce que les gaines (30) enserrant partiellement la périphérie des barres extérieures (2, 3) sont enfichables par paire en opposition et peuvent être fixées sur les barres (2, 3) ce en quoi une paire de gaines (30) peut être fixés chaque fois sur un socle (34) qui est monté en sous-sol (37).
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon une ou plusieurs des revendications 1 à 11, caractérisé en ce que le rail conducteur de courant (1) est constitué par trois barres (2, 3, 7) disposées parallèlement entre elles, ce en quoi les barres respectivement contigües (2, 7, 3, 7) se trouvent à un potentiel électrique différent.
- Dispositif d'éclairage basse tension selon une ou plusieurs des revendications 1 à 11, caractérisé en ce que le rail conducteur de courant (1) est constitué par huit barres (2, 3, 7) disposées parallèlement entre elles, moyennant quoi la section tranversale du rail conducteur de courant (1) est sensiblement carrée et les côtés du carré sont respectivement formés par trois barres (2, 3, 7).
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE8711458U DE8711458U1 (de) | 1987-08-24 | 1987-08-24 | Magnetadapter für Stromschiene in Niedervolttechnik |
| DE8711457U DE8711457U1 (de) | 1987-08-24 | 1987-08-24 | Stromschiene in Niedervolttechnik für Magnetadapterleuchten |
| DE8711458U | 1987-08-24 | ||
| DE8711457U | 1987-08-24 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0304513A2 EP0304513A2 (fr) | 1989-03-01 |
| EP0304513A3 EP0304513A3 (en) | 1990-02-28 |
| EP0304513B1 true EP0304513B1 (fr) | 1995-03-08 |
Family
ID=25952001
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP87119214A Expired - Lifetime EP0304513B1 (fr) | 1987-08-24 | 1987-12-24 | Dispositif d'éclairage à basse tension |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0304513B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3751145D1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE29514672U1 (de) * | 1995-09-13 | 1995-12-07 | LTS Licht & Leuchten GmbH, 88069 Tettnang | Stromleitersystem |
| WO2007145446A2 (fr) * | 2006-06-14 | 2007-12-21 | Kyung-Ho Yang | Appareil d'éclairage utilisant un aimant |
| US7402045B2 (en) * | 2006-09-20 | 2008-07-22 | United Technologies Corporation | Electrical interconnection having magnetic conductive elements |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1400179A (fr) * | 1963-07-03 | 1965-05-21 | Philips Nv | Perfectionnements aux fixations d'appareils électriques |
| FR1600124A (fr) * | 1968-12-30 | 1970-07-20 |
-
1987
- 1987-12-24 EP EP87119214A patent/EP0304513B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1987-12-24 DE DE3751145T patent/DE3751145D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0304513A2 (fr) | 1989-03-01 |
| DE3751145D1 (de) | 1995-04-13 |
| EP0304513A3 (en) | 1990-02-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1284033B1 (fr) | Systeme a rail conducteur | |
| EP1117162B1 (fr) | Système de barres omnibus et ensemble de connexions pour connecter les barres aux bornes d'un appareil d'installation | |
| EP1284034B1 (fr) | Systeme de barre omnibus | |
| EP1016821A1 (fr) | Chemin d' éclairage avec un profil support fixable à un mur ou à un plafond | |
| EP1284035B1 (fr) | Systeme de rails conducteurs | |
| EP1994614B1 (fr) | Construction a cadre pour une armoire electrique, armoire electrique et kit pour l'armoire electrique | |
| DE69905932T2 (de) | Stromschiene für eine elektrische energieverteilung | |
| DE4124066C2 (de) | Elektrisches Leuchtensystem | |
| EP0466043B1 (fr) | Installation de distribution comprenant au moins deux rangées d'appareils électriques de type étroit | |
| DE4312617A1 (de) | Elektrisches Schaltfeld, insbesondere für Mittelspannungsanlagen | |
| EP0304513B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'éclairage à basse tension | |
| EP1927172A1 (fr) | Ensemble barre collectrice pour une installation de distribution electrique | |
| DE29814339U1 (de) | Leuchtensystem | |
| DE9215527U1 (de) | Verbindungsstück für Stromschienen | |
| DE202006020037U1 (de) | Rahmenkonstruktion für einen Schaltschrank, Schaltschrank und Bausatz für den Schaltschrank | |
| DE19706865C2 (de) | Adapter für Stromschienen | |
| DE2304639C3 (de) | Fassungsanordnung für elektrische Steckerkupplungen | |
| DE3811459A1 (de) | Bausatz fuer ein sammelschienensystem | |
| DE3806241A1 (de) | Installationseinrichtung fuer niedervolt-leuchten | |
| DE2316590B2 (de) | Verbindungseinheit für elektrische Installationen | |
| DE69312907T2 (de) | Stromschienensystem | |
| DE8910975U1 (de) | Elektrisches Vorschaltgerät für Leuchtstofflampen | |
| DE19750100A1 (de) | Verbindungsvorrichtung | |
| AT356213B (de) | Einrichtung zum formschluessigen verbund einer montageschiene mit einem leuchtenbalken einer leuchtstofflampenleuchte | |
| DE2005953B2 (de) | Anschlußeinheit für den elektrischen Anschluß von Beleuchtungskörpern |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): DE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): DE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19900526 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19930120 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3751145 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19950413 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20010928 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020702 |