EP0188932B1 - Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Eliminieren einer Flüssigkeit aus einem Material insbesondere erhalten durch ein Papiermacherverfahren - Google Patents
Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Eliminieren einer Flüssigkeit aus einem Material insbesondere erhalten durch ein Papiermacherverfahren Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0188932B1 EP0188932B1 EP85402383A EP85402383A EP0188932B1 EP 0188932 B1 EP0188932 B1 EP 0188932B1 EP 85402383 A EP85402383 A EP 85402383A EP 85402383 A EP85402383 A EP 85402383A EP 0188932 B1 EP0188932 B1 EP 0188932B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- liquid
- layer
- evaporation
- cloth
- fabric
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 76
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 23
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title claims description 7
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 claims description 59
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 235000019441 ethanol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 10
- 229920003043 Cellulose fiber Polymers 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 claims 6
- 238000010924 continuous production Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 abstract description 14
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 14
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 abstract description 9
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 description 5
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000010802 sludge Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- -1 isopropyl alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 210000003127 knee Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008961 swelling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000018747 cerebellar ataxia with neuropathy and bilateral vestibular areflexia syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001873 dinitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003337 fertilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008246 gaseous mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010445 mica Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052618 mica group Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D21—PAPER-MAKING; PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE
- D21F—PAPER-MAKING MACHINES; METHODS OF PRODUCING PAPER THEREON
- D21F9/00—Complete machines for making continuous webs of paper
- D21F9/003—Complete machines for making continuous webs of paper of the twin-wire type
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D21—PAPER-MAKING; PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE
- D21F—PAPER-MAKING MACHINES; METHODS OF PRODUCING PAPER THEREON
- D21F11/00—Processes for making continuous lengths of paper, or of cardboard, or of wet web for fibre board production, on paper-making machines
- D21F11/14—Making cellulose wadding, filter or blotting paper
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D21—PAPER-MAKING; PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE
- D21F—PAPER-MAKING MACHINES; METHODS OF PRODUCING PAPER THEREON
- D21F9/00—Complete machines for making continuous webs of paper
- D21F9/02—Complete machines for making continuous webs of paper of the Fourdrinier type
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F26—DRYING
- F26B—DRYING SOLID MATERIALS OR OBJECTS BY REMOVING LIQUID THEREFROM
- F26B7/00—Drying solid materials or objects by processes using a combination of processes not covered by a single one of groups F26B3/00 and F26B5/00
Definitions
- the present invention relates to the removal of at least part of the liquid from a layer obtained by deposition according to a papermaking process as described in the first part of claim 1.
- the removal of the liquid portion of a layer having a low solids content is a problem encountered in various industries. This can be the elimination of water from the sludge, for example sludge obtained in treatment plants or sludge which one wishes to recover in particular as a fertilizer.
- paper is meant according to the invention any material based on cellulosic fibers, in the form of a mattress or sheets.
- the liquid is removed first by draining by gravity and / or by suction through the porous fabric, then by a spin by pressing between fabrics and / or rollers, this operation being able to take place on the first fabric, that is to say the fabric for forming the layer, or on one or more other fabrics succeeding it.
- the fibrous mat leaves the last cloth on which it was placed so that it can be heated, for example by contact with hot cylinders, so that another part of the liquid which it contains is eliminated by evaporation.
- Patent publication GB-A-2 047 396 thus describes a device for drying a Slurry by draining with suction followed by evaporation of the water.
- the invention provides a new process for the continuous elimination of at least part of the liquid from a layer based on cellulosic fibers obtained by continuous deposition on a mobile, porous support, of a liquid composition having a low dry matter (solid) content, i.e. less than about 10% by weight.
- the liquid is at least partially removed from the layer by draining by gravity and / or if necessary by suction, associated with wringing by pressing, and by evaporation, all of these operations then being carried out.
- the layer is placed on the same fabric porous to the liquid which is the support for forming the layer, therefore without transfer from one support to another support, the evaporation of the liquid from the layer placed on its formation support, being obtained by passing a gas flow through the layer and said support.
- the method according to the invention makes it possible to continuously and rapidly eliminate a quantity of liquid which can bring the cellulosic layer to solids concentrations of between 30 and 100% approximately, without said layer leaving the formation support, and this at starting from a liquid composition, with a dryness of less than approximately 10% and preferably less than 1%.
- the gas flow can be a flow of air, nitrogen, or another gas, depending in particular on the nature of the liquid to be eliminated, as described in more detail below.
- a second fabric or strip which takes the layer to be treated sandwiched between itself and the fabric used for the assembly. of treatment.
- the layer to be treated is sandwiched between the two fabrics during only part of the milking liquid elimination.
- the second fabric is used during essentially all of the liquid removal treatment.
- the use or not of a second porous fabric at one or more locations, or over essentially the whole extent of the treatment is dictated by the nature of the layer to be treated, that is to say in particular its composition, its resistance mechanical in the running direction, and also the liquid to be eliminated.
- spin is meant according to the invention all operations tending to exert pressure on the layer to extract liquid therefrom.
- the spin can also be variable depending on the material of the layer to be treated. It can vary in intensity and / or by the means used to achieve it. It can vary according to its location and also according to the mechanical properties of the layer to be treated and this at a determined location. It can also be progressive in intensity.
- the method according to the invention applies to the elimination of a liquid which may be water or any other diluent allowing the formation of the cellulosic layer on a porous formation support, for example an alcohol or a mixture of 'Alcohols chosen in particular from methyl, ethyl and isopropyl alcohols.
- a liquid which may be water or any other diluent allowing the formation of the cellulosic layer on a porous formation support, for example an alcohol or a mixture of 'Alcohols chosen in particular from methyl, ethyl and isopropyl alcohols.
- the invention applies in particular and with advantage to very fragile layers which have very little resistance mechanical in the running direction, and in particular those which are not self-supporting.
- the invention applies in particular to the manufacture of paper of very low grammage which cannot be obtained without risk of rupture on a conventional paper manufacturing line requiring a high speed transfer of the fibrous layer of the forming fabric. to the cylinders for spinning.
- the invention therefore advantageously applies to the manufacture of paper with a grammage of less than approximately 30 g.
- the water-miscible liquid is generally an alcohol such as methyl, ethyl or isopropyl alcohol, so that the elimination of the liquid according to the invention consists in eliminating this alcohol.
- the evaporation of the liquid from the layer supported by the porous fabric by passing a flow of gas through the layer can use a flow of hot air or, in a variant, a flow of nitrogen.
- the treatment station for evaporation is advantageously placed in a closed enclosure in the case where the liquid to be removed from the layer is an organic liquid, in particular to avoid nuisances.
- all the operations for removing the liquid can if necessary take place under a nitrogen atmosphere.
- the invention also applies to the elimination of the liquid contained in superimposed layers obtained by several simultaneous or successive jets.
- the invention also relates to a device for removing the liquid part of a layer obtained continuously by depositing a very diluted composition on a mobile support.
- the device according to the invention comprises a mobile, continuous support canvas, porous to the liquid to be eliminated, extending over the entire extent of the device, means for depositing the liquid composition based on cellulosic fibers on the canvas. porous, these means being placed in the upstream part of the device, means for eliminating part of the liquid by spinning, means creating a gas flow through the support fabric to eliminate another part of the liquid by evaporation, all of these means being arranged above and / or below the porous fabric supporting the cast layer, the porous fabric having characteristics such that it allows drainage, spinning, heating, etc.
- the device can also include, to accentuate the spin, very varied pressing means, known in particular in the paper industry, for example one or more pairs of cylinders between which the layer to be treated is pressed, one or more knee pads, etc. ..
- the latter further comprises an upper strip or fabric which, associated with the lower casting fabric, takes the layer to be sandwiched at least at one of the locations for the elimination of the liquid.
- this second strip maintains the layer to be sandwiched preferably from its formation or just after, until the end of the treatment.
- the assembly When the device is used to remove an organic liquid, such as an alcohol, the assembly can be placed in an enclosure under an inert atmosphere with respect to the liquid to be removed from the layer.
- an organic liquid such as an alcohol
- the means for eliminating the liquid by evaporation are advantageously means creating a gas flow passing through the layer.
- These means may include suction boxes and blowing boxes associated therewith, being arranged opposite the suction boxes on either side of the porous conveyor fabric.
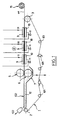
- the device shown in FIG. 1 comprises a continuous support fabric 1, kept taut, between rollers 101 and in particular its upper part between an upstream roller 2 and a downstream roller 3.
- a box of head 4 extends transversely above the fabric 1.
- the device comprises located further downstream a press consisting of two rollers 5 and 6 arranged on either side of the conveyor fabric. Under the upper part of the conveyor belt is placed a tank 7 for recovering the liquid eliminated by wringing and pressing.
- the device Downstream of the press, the device comprises means 8 for removing the liquid by evaporation.
- These means are here a succession of blower boxes 9 and suction 10 a gas flow, arranged above and below the conveyor fabric.
- the operation of the device is described in relation to the manufacture of paper with a grammage of 10 g / m 2 .
- the aqueous paper composition 102 having a concentration of approximately 0.2% in dry matter is brought to the headbox from where it is poured to form a liquid layer of uniform thickness on the conveyor fabric 1.
- part of the water 12 is removed by drainage, passing by gravity through the porous fabric 1. Another part of the water is removed by wringing at the time of pressing between the two rollers 5 and 6
- the water which passes through the porous fabric 1 is recovered in the tank 7.
- an additional quantity of water is entrained in the form of vapor 13 by the flow of hot air.
- the sheet of paper 14 is removed from the canvas to be wound in a reel 15 and stored.
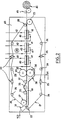
- the device shown in Figure 2 is used for the manufacture of a superabsorbent layer based on grafted cellulosic fibers.
- This device comprises a continuous support fabric 21, the upper part of which is kept tensioned between rollers, in particular an upstream roller 22 and a downstream roller 23. Rollers 24, 25 some of which 25, with adjustable position, act on the lower part of the canvas and allow it to be stretched correctly.
- a second porous fabric 26 is disposed above the first fabric, in parallel, being stretched between rollers, in particular an upstream roller 27 and a downstream roller 28. Rollers 29, 30 some of which 30, with adjustable position, correctly tension the fabric 26.
- a headbox 31 extends transversely above the lower conveyor fabric, upstream of the roller 27.
- the device also comprises a press 32, consisting of two rollers 33 and 34, arranged on either side of the two canvases. Between the roller 27 and the press 32, three rollers 35, 36 and 37 constitute a toggle for the two fabrics. Under the upper part of the lower conveyor fabric 21, a tank 38 is arranged for recovering the liquid eliminated by draining and spinning. Downstream of the press 32 the device comprises means 39 for removing the liquid by evaporation. These means are boxes blowing 40 and sucking 41 a gas flow, arranged above and below the two fabrics. On each other side of the two fabrics, there is a suction box facing each blowing fan. These boxes are supplied with nitrogen 42.
- the entire device is described in connection with the manufacture of a sheet of superabsorbent cellulosic material.
- a liquid composition 103 containing modified cellulose fibers to which a polymer is chemically bonded in the form of an alkali metal salt originating from a polymerizable olefinically unsaturated monomer, in a mixture of ethyl alcohol and ammonia, the concentration of dry matter being about 0.3%, is brought to the headbox from where it is sheeted on the conveyor fabric 21.
- the liquid layer is entrained by said fabric and it is sandwiched between this fabric 21 and the upper fabric 26.
- Part of the liquid 44 is removed by draining and wringing through the lower fabric 21 and is recovered in the tank 38, under the fabric 21 to then be recycled. Spinning is accentuated as the knee switch passes.
- the layer still sandwiched between the two fabrics then passes between the two rollers of the press, which further completes the spin.
- the layer then passes between the blower and suction boxes.
- a stream of nitrogen 42 passing through the upper fabric eliminates an additional part of the liquid by evaporation in contact with the stream 42.
- the nitrogen gas stream charged with the gaseous mixture 47 of alcohol and ammonia passes through the lower fabric , passes into the suction boxes and is sent to an annex device, not shown, for the recovery of vapors.
- the layer still maintained between the two fabrics is dry. After the upper fabric is detached from the fibrous layer, the latter leaves the lower fabric to be wound up using a winding device 45 on a spool 46.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Paper (AREA)
- External Artificial Organs (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Treatments For Attaching Organic Compounds To Fibrous Goods (AREA)
- Spinning Methods And Devices For Manufacturing Artificial Fibers (AREA)
- Chemical Or Physical Treatment Of Fibers (AREA)
- Apparatus For Making Beverages (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Water Treatment By Sorption (AREA)
- Physical Or Chemical Processes And Apparatus (AREA)
- Treatment Of Sludge (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT85402383T ATE44784T1 (de) | 1984-12-17 | 1985-12-03 | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum eliminieren einer fluessigkeit aus einem material insbesondere erhalten durch ein papiermacherverfahren. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8419245A FR2574829B1 (fr) | 1984-12-17 | 1984-12-17 | Procede et dispositif pour l'elimination du liquide d'une couche obtenue notamment par un procede papetier |
| FR8419245 | 1984-12-17 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0188932A1 EP0188932A1 (de) | 1986-07-30 |
| EP0188932B1 true EP0188932B1 (de) | 1989-07-19 |
Family
ID=9310659
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP85402383A Expired EP0188932B1 (de) | 1984-12-17 | 1985-12-03 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Eliminieren einer Flüssigkeit aus einem Material insbesondere erhalten durch ein Papiermacherverfahren |
Country Status (12)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4808266A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0188932B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS61146400A (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE44784T1 (de) |
| BR (1) | BR8506319A (de) |
| DE (1) | DE3571663D1 (de) |
| DK (1) | DK583185A (de) |
| ES (1) | ES8606558A1 (de) |
| FI (1) | FI854983A (de) |
| FR (1) | FR2574829B1 (de) |
| NO (1) | NO167163C (de) |
| PT (1) | PT81678B (de) |
Families Citing this family (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT392304B (de) * | 1989-06-09 | 1991-03-11 | Andritz Ag Maschf | Vorrichtung zur behandlung, insbesondere entwaesserung, von stoffbahnen |
| AT394739B (de) * | 1989-06-09 | 1992-06-10 | Andritz Ag Maschf | Vorrichtung zur entwaesserung einer zellstoffbahn bzw. einer materialbahn fuer eine pappenerzeugung |
| JPH0445898A (ja) * | 1990-06-14 | 1992-02-14 | Yukimasa Sato | 汚泥やスラッジ等の脱水装置及びその脱水方法 |
| US5225042A (en) * | 1991-12-02 | 1993-07-06 | Beloit Technologies, Inc. | Twin wire paper forming section with heated air pressure domes |
| GB2269602A (en) * | 1992-08-13 | 1994-02-16 | Courtaulds Plc | Absorbent nonwoven fabric |
| US5667636A (en) * | 1993-03-24 | 1997-09-16 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Method for making smooth uncreped throughdried sheets |
| US5399412A (en) * | 1993-05-21 | 1995-03-21 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Uncreped throughdried towels and wipers having high strength and absorbency |
| US5607551A (en) * | 1993-06-24 | 1997-03-04 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Soft tissue |
| DE19654200A1 (de) | 1996-12-23 | 1998-06-25 | Voith Sulzer Papiermasch Gmbh | Naßpresse |
| US6423183B1 (en) | 1997-12-24 | 2002-07-23 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Paper products and a method for applying a dye to cellulosic fibers |
| DE19820585A1 (de) * | 1998-05-08 | 1999-11-11 | Voith Sulzer Papiertech Patent | Auftragsverfahren und -vorrichtung |
| US6375799B1 (en) * | 1999-01-28 | 2002-04-23 | Voith Sulzer Papiertechnik Patent Gmbh | Process and apparatus for producing a fibrous material web |
| US6379498B1 (en) * | 2000-02-28 | 2002-04-30 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Method for adding an adsorbable chemical additive to pulp during the pulp processing and products made by said method |
| US6749721B2 (en) * | 2000-12-22 | 2004-06-15 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Process for incorporating poorly substantive paper modifying agents into a paper sheet via wet end addition |
| US7749356B2 (en) * | 2001-03-07 | 2010-07-06 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Method for using water insoluble chemical additives with pulp and products made by said method |
| US6582560B2 (en) * | 2001-03-07 | 2003-06-24 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Method for using water insoluble chemical additives with pulp and products made by said method |
| US6736935B2 (en) * | 2002-06-27 | 2004-05-18 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Drying process having a profile leveling intermediate and final drying stages |
| US6916402B2 (en) * | 2002-12-23 | 2005-07-12 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Process for bonding chemical additives on to substrates containing cellulosic materials and products thereof |
| US7670459B2 (en) * | 2004-12-29 | 2010-03-02 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Soft and durable tissue products containing a softening agent |
| US7749355B2 (en) * | 2005-09-16 | 2010-07-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Tissue paper |
| US7744723B2 (en) * | 2006-05-03 | 2010-06-29 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fibrous structure product with high softness |
| US20070256802A1 (en) * | 2006-05-03 | 2007-11-08 | Jeffrey Glen Sheehan | Fibrous structure product with high bulk |
| CN103534411A (zh) * | 2011-03-25 | 2014-01-22 | 纳瑙佩颇公司 | 用于造纸的挥发性解胶剂配方 |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA787649A (en) * | 1968-06-18 | Porrmann Herbert | Manufacture of non-woven fabrics | |
| GB246048A (en) * | 1925-08-10 | 1926-01-21 | Drying Systems Inc | Improvements in paper making processes |
| US1881404A (en) * | 1931-03-16 | 1932-10-04 | Kellogg Hadley Corp | Box board machine |
| US2753766A (en) * | 1951-12-29 | 1956-07-10 | Forming Machine Company Of Ame | Positive pressure machine for forming continuous strips of fibrous materials |
| US3533725A (en) * | 1954-07-23 | 1970-10-13 | Tee Pak Inc | Wood fibers with polymer deposited therein |
| US2929448A (en) * | 1958-06-16 | 1960-03-22 | West Virginia Pulp & Paper Co | Single stage continuous paper making process and apparatus |
| US3117907A (en) * | 1958-10-01 | 1964-01-14 | Mycalex Corp Of America | Apparatus for making reconstituted synthetic mica sheet |
| DE1445353B2 (de) * | 1961-07-15 | 1970-06-04 | Deutsche Gold- u. Silber-Scheideanstalt, vorm. Roessler, 6OOO Frankfurt | Verfahren zur Verbindung von thermoplastischen Vinylpolymerisatsn mit Fasern zu Vliesen |
| NL130162C (de) * | 1962-08-06 | |||
| NL132533C (de) * | 1962-09-24 | |||
| US3370935A (en) * | 1962-09-24 | 1968-02-27 | Tee Pak Inc | Soil additive composition containing hydrolyzed graft polymer |
| US3301746A (en) * | 1964-04-13 | 1967-01-31 | Procter & Gamble | Process for forming absorbent paper by imprinting a fabric knuckle pattern thereon prior to drying and paper thereof |
| FR1473842A (fr) * | 1965-04-13 | 1967-03-24 | Procter & Gamble | Papier bouffant et son procédé de fabrication |
| DE1511186A1 (de) * | 1965-12-27 | 1970-04-02 | Anglo Paper Prod Ltd | Papierbahnfoerdervorrichtung |
| US3542640A (en) * | 1967-03-23 | 1970-11-24 | Procter & Gamble | Method for drying a wet foam containing cellulosic fibers |
| AT327670B (de) * | 1970-10-30 | 1976-02-10 | Arledter Hanns F Dr Ing | Entwasserungseinrichtung fur eine doppelsieb-papiermaschine |
| US3826711A (en) * | 1972-04-17 | 1974-07-30 | Buckeye Cellulose Corp | Sheeted cellulose derivative fibers |
| GB1389992A (en) * | 1973-04-19 | 1975-04-09 | Valmet Oy | Machine for making tissue paper |
| US4102737A (en) * | 1977-05-16 | 1978-07-25 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Process and apparatus for forming a paper web having improved bulk and absorptive capacity |
| GB2047396B (en) * | 1979-03-29 | 1983-08-03 | Casburt Ltd | Drying slurries |
-
1984
- 1984-12-17 FR FR8419245A patent/FR2574829B1/fr not_active Expired
-
1985
- 1985-12-03 DE DE8585402383T patent/DE3571663D1/de not_active Expired
- 1985-12-03 AT AT85402383T patent/ATE44784T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1985-12-03 EP EP85402383A patent/EP0188932B1/de not_active Expired
- 1985-12-06 ES ES549663A patent/ES8606558A1/es not_active Expired
- 1985-12-14 JP JP60280227A patent/JPS61146400A/ja active Pending
- 1985-12-16 DK DK583185A patent/DK583185A/da not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1985-12-16 FI FI854983A patent/FI854983A/fi not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1985-12-16 NO NO855054A patent/NO167163C/no unknown
- 1985-12-16 PT PT81678A patent/PT81678B/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1985-12-16 BR BR8506319A patent/BR8506319A/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
-
1987
- 1987-05-12 US US07/051,218 patent/US4808266A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FI854983A0 (fi) | 1985-12-16 |
| ATE44784T1 (de) | 1989-08-15 |
| DE3571663D1 (en) | 1989-08-24 |
| ES549663A0 (es) | 1986-04-16 |
| PT81678A (fr) | 1986-01-01 |
| FR2574829B1 (fr) | 1987-01-09 |
| US4808266A (en) | 1989-02-28 |
| PT81678B (pt) | 1987-10-20 |
| NO167163C (no) | 1991-10-09 |
| DK583185A (da) | 1986-06-18 |
| DK583185D0 (da) | 1985-12-16 |
| JPS61146400A (ja) | 1986-07-04 |
| FI854983A (fi) | 1986-06-18 |
| EP0188932A1 (de) | 1986-07-30 |
| NO855054L (no) | 1986-06-18 |
| BR8506319A (pt) | 1986-08-26 |
| FR2574829A1 (fr) | 1986-06-20 |
| ES8606558A1 (es) | 1986-04-16 |
| NO167163B (no) | 1991-07-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0188932B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Eliminieren einer Flüssigkeit aus einem Material insbesondere erhalten durch ein Papiermacherverfahren | |
| FR2474883A1 (fr) | Machine a tamisage | |
| CH629268A5 (fr) | Toile de sechage pour machine de fabrication du papier. | |
| EP0772705B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur herstellung von vliesstoffen wovon die kohäsion durch flüssigkeitsstrahl hergestellt ist | |
| CH620577A5 (de) | ||
| FR2649017A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de traitement d'un melange liquide-matiere fibreuse, en particulier de cellulose | |
| FR2643397A1 (fr) | Machine a papier a deux filtres | |
| FR2529922A1 (fr) | Procede et equipement pour le traitement par compression d'une bande continue de fibres et en particulier une bande continue de papier ou de carton | |
| FR2513672A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de formation d'une bande de papier dans une machine a papier | |
| JPH02269893A (ja) | 抄紙機のプレス装置 | |
| FR2481328A1 (fr) | Procede pour fabriquer un article en tissu ouate crepe | |
| JP2000256982A (ja) | 抄紙機におけるテール紙の通紙方法とその装置 | |
| FR2477596A1 (fr) | Presse a deux feutres sans fin et procede pour enlever de l'eau d'une bande fibreuse telle que du papier | |
| FR2786509A1 (fr) | Appareil et procede pour essorer une nappe de papier | |
| FR2478491A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif pour couvrir une feuille avec une composition de revetement | |
| FR2733522A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de fabrication d'une feuille de papier avec presechage par air traversant | |
| BE411709A (de) | ||
| BE547824A (de) | ||
| JPH11513313A (ja) | 濃縮機プレス | |
| BE627767A (de) | ||
| BE531035A (de) | ||
| JPS5922838B2 (ja) | 抄紙機における脱水圧搾部 | |
| BE540012A (de) | ||
| BE715908A (de) | ||
| BE410445A (de) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19861229 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19880524 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 44784 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19890815 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3571663 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19890824 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19920904 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19920924 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19920924 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19921012 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19921104 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19921228 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19921231 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19930206 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19931203 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19931203 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19931204 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19931231 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19931231 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19931231 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: LA CELLULOSE DU PIN Effective date: 19931231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19940701 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19931203 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19940831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19940901 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 85402383.5 Effective date: 19940710 |