EP0182736A2 - Kuppelkontaktstück zum Verbinden runder elektrischer Leiter - Google Patents
Kuppelkontaktstück zum Verbinden runder elektrischer Leiter Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0182736A2 EP0182736A2 EP85730142A EP85730142A EP0182736A2 EP 0182736 A2 EP0182736 A2 EP 0182736A2 EP 85730142 A EP85730142 A EP 85730142A EP 85730142 A EP85730142 A EP 85730142A EP 0182736 A2 EP0182736 A2 EP 0182736A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- lamellae
- thin
- contact piece
- walled
- cylindrical housing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 12
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 241000446313 Lamella Species 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910000906 Bronze Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010974 bronze Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- KUNSUQLRTQLHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N copper tin Chemical compound [Cu].[Sn] KUNSUQLRTQLHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H1/00—Contacts
- H01H1/12—Contacts characterised by the manner in which co-operating contacts engage
- H01H1/36—Contacts characterised by the manner in which co-operating contacts engage by sliding
- H01H1/38—Plug-and-socket contacts
- H01H1/385—Contact arrangements for high voltage gas blast circuit breakers
Definitions
- the invention relates to a coupling contact piece for connecting round electrical conductors, in particular for detachable plug connections on metal-encapsulated, compressed gas-insulated high-voltage switchgear, with a plurality of elongated trapezoidal contact lamellae which are arranged on the circumference of the conductor to be connected and by leaf springs which are parallel to the lamellae on the outside thereof. are pressed against the conductor, the leaf springs being fixed in a groove in the blunt side of the lamellae and supported against a cylindrical housing containing the lamellae, which contains at least one longitudinally extending intermediate wall projecting between two lamellae.
- Such a dome contact piece is known from DE-PS 11 60 914. It has the advantage of simple manufacture and easy assembly of its components, which can be done in particular by means of automatic machines. The force exerted on each lamella by the leaf springs also results in an even contact pressure.
- the selectable number of contact lamellae is limited by the fact that they should have a width of 6 to 10 mm on the blunt side, because if the width is too small, a lateral tilting of the lamellae can occur under certain circumstances, whereby the contact pressure is released would. Although this can be avoided by means of solid partition walls which guide the lamellae, the tubular housing loses its simple inner cylindrical shape, which makes its manufacture more difficult.
- the invention has for its object to enable the simple manufacture of the housing of such a dome contact piece despite the presence of an axially extending partition between the fins.
- the dome contact piece of the type described above is designed according to the invention in such a way that the cylindrical housing surrounding the lamellae is formed from a strip of thin-walled sheet metal bent into a cylinder, the width of which approximately corresponds to the length of the lamellae, one of the axially extending edges is bent radially inwards at a height selected less than the height of the lamellae and that this thin-walled cylindrical housing lies in a thicker-walled cylindrical outer housing of the dome contact piece.
- the partition is therefore not rigidly connected to the cylindrical outer housing, but is arranged on a separate thin-walled cylindrical housing. Since this thin-walled cylindrical housing is formed from a strip of thin-walled sheet metal bent into a cylinder, the intermediate wall is obtained in the simplest manner by bending one of the axially extending edges radially inwards. The height of the bent part is chosen to be smaller than the slat height. This partition protrudes between two fins and results in good guiding and fixing of the fins in terms of both their circumferential and longitudinal directions. The contact pressures of the lamellae created by the leaf springs, on the other hand, are absorbed by the thick-walled outer housing.
- the other axially extending edge of the thin-walled cylindrical housing forms a narrow gap to the bent edge, which is smaller than the distance between the lamella side surface and the groove for receiving the leaf spring.
- the bent inner cylindrical housing is advantageously made of a non-magnetic sheet with high mechanical strength and hard surface, such as. B. bronze or brass. This prevents the leaf springs from being pressed into the sheet, which would reduce the contact pressure.
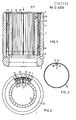
- FIG. 1 shows a longitudinal section through a dome contact piece designed according to the invention.
- FIG. 2 shows, partially in section, a view of an end face of the dome contact piece, viewed in the direction of the arrow drawn in FIG. 1.
- Figure 3 shows the inner cylindrical housing on a smaller scale.
- the dome contact piece 1 for the connection of two round conductors of a compressed gas-insulated metal encapsulated high-voltage switchgear has a thick-walled outer housing 2, which has a substantially cylindrical shape.
- the front outer edges 3 as well as the edges 4 next to a constriction 5 for receiving a safety spring, not shown, are greatly rounded, so that the outer housing 2 also acts as a shield controlling the electrical field in the course of the conductor connection.
- the inner diameter 6 in the area of the constriction 5 is smaller than the inner diameter 7 for receiving the lamellae 8, so that a paragraph 9 forms between the two, on which the lamellae 8 abut one side.
- Each lamella 8 is trapezoidal.
- the pointed side 10 of the lamella 8 forms the contact surface with the conductors (not shown) to be connected.
- the blunt side facing the outer housing 2 contains a central groove 11, which is laterally spaced 12 from the slat side surface 13.
- a leaf spring 14 is arranged, which supports the lamella 8 with respect to the outer housing 2 and thus causes the contact pressure of the lamella 8.
- the leaf spring 14 does not abut the inner bore 15 of the outer housing 2, but a thin-walled cylindrical housing 16 is inserted into this.
- This thin-walled cylindrical housing 16 is formed from a strip of thin-walled bronze sheet bent into a cylinder.
- the width of the sheet approximately corresponds to the length of the lamellae 8.
- One of the axially extending edges 17 of the sheet is bent radially inward at a height 19 selected less than the lamella height 18.
- this bent edge 17 forms an intermediate wall 20 which projects between two lamellae 8.
- the other, not bent, axially extending edge 21 of the thin-walled cylindrical housing 16 forms a narrow gap 22 to the bent edge 17, which is smaller than the distance 12 between the lamella side surface 13 and the groove 11 for receiving the leaf spring 14
- Leaf springs 14 each on the inner surface of the thin-walled cylindrical housing 16, so that the same contact pressure is ensured along the entire circumference of the dome contact piece 1.
- the thin-walled housing 16 absorbs the contact force itself, but transmits it directly to the outer housing 2.
- the assembly of the dome contact piece 1 is very simple. First, the thin-walled cylindrical housing 16 is inserted into the inner bore 15 of the outer housing 2 until it comes to rest on the paragraph 9. Then the individual slats 8 are inserted from the side and also reach paragraph 9 to the system. Now the leaf springs 14 are inserted into each groove 11 of the slats 8. Finally, in front of the end face of the thin-walled cylindrical housing 16, the leaf springs 14 and the lamellae 8, a disk 23 is placed for axial securing, which is fixed at some points in the outer housing 2 by caulking.
- the intermediate wall 20 of the cylindrical housing 16 projecting between two lamellae 8 provides precise lateral guidance and fixing of the lamellae 8, so that they are prevented from tilting in a simple manner, which leads to a reduction in the current carrying capacity would lead.
Landscapes
- Coupling Device And Connection With Printed Circuit (AREA)
- Springs (AREA)
- Arc-Extinguishing Devices That Are Switches (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft ein Kuppelkontaktstück zum Verbinden runder elektrischer Leiter, insbesondere für lösbare Steckverbindungen an metallgekapselten, druckgasisolierten Hochspannungsschaltanlgen, mit mehreren länglichen trapezförmigen Kontaktlamellen, die am Umfang der zu verbindenden Leiter angeordnet sind und durch Blattfedern, die parallel zu den Lamellen auf deren Außenseite liegen, gegen die Leiter gedrückt werden, wobei die Blattfedern in einer Nut in der stumpfen Seite der Lamellen festgelegt sind und sich gegen ein die Lamellen enthaltendes zylindrisches Gehäuse abstützen, daß zumindest eine in Längsrichtung verlaufende, zwischen zwei Lamellen ragende Zwischenwand enthält.
- Ein derartiges Kuppelkontaktstück ist aus der DE-PS 11 60 914 bekannt. Es hat den Vorteil einer einfachen Fertigung und einer leichten Montage seiner Bestandteile, die insbesondere mittels Automaten erfolgen kann. Der durch die Blattfedern auf jede einzelne Lamelle ausgeübte Kraft ergibt außerdem einen gleichmäßigen Kontaktdruck. Bei diesem bekannten Kuppelkontaktstück ist aber die wählbare Zahl der Kontaktlamellen dadurch begrenzt, daß diese an der stumpfen Seite eine Breite von 6 bis 10 mm aufweisen sollen, weil sonst bei zu geringer Breite unter Umständen ein seitliches Kippen der Lamellen auftreten kann, wodurch der Kontaktdruck aufgehoben würde. Dies kann zwar durch feste Zwischenwände vermieden werden, welche die Lamellen führen, dadurch verliert aber das rohrförmige Gehäuse seine einfache innere zylindrische Form, was seine Herstellung erschwert.
- Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, die einfache Fertigung des Gehäuses eines derartigen Kuppelkontaktstückes trotz des Vorhandenseins einer axial verlaufenden Zwischenwand zwischen den Lamellen zu ermöglichen.
- Zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe ist gemäß der Erfindung das Kuppelkontaktstück der eingangs beschriebenen Art so ausgebildet, daß das die Lamellen umgebende zylindrische Gehäuse aus einem zu einem Zylinder gebogenen Streifen dünnwandigen Bleches gebildet ist, dessen Breite angenähert der Länge der Lamellen entspricht, wobei eine der axialverlaufenden Kanten in einer kleiner als die Lamellenhöhe gewählten Höhe radial nach innen abgebogen ist und daß dieses dünnwandige zylindrische Gehäuse in einem dickerwandigen zylindrischen Außengehäuses des Kuppelkontaktstückes liegt.
- Die Zwischenwand ist also nicht starr mit dem zylindrischen Außengehäuse verbunden, sondern ist an einem gesonderten dünnwandigen zylindrischen Gehäuse angeordnet. Da dieses dünnwandige zylindrische Gehäuse aus einem zu einem Zylinder gebogenen Streifen dünnwandigen Bleches gebildet ist, ergibt sich die Zwischenwand in einfachster Weise durch Abbiegen einer der axial verlaufenden Kanten radial nach innen. Die Höhe des abgebogenen Teils ist kleiner als die Lamellenhöhe gewählt. Diese Zwischenwand ragt zwischen zwei Lamellen hinein und ergibt eine gute Führung und Festlegung der Lamellen sowohl hinsichtlich ihrer Umfangs- als auch ihre Längsrichtung. Die durch die Blattfedern erzeugten Kontaktdrücke der Lamellen werden dagegen von dem dickerwandigen Außengehäuse aufgenommen.
- Nicht nur die Herstellung dieses inneren zylindrischen Gehäuses mit der Zwischenwand ist einfach, sondern auch seine Montage, da die so gebildete zylindrische Hülse von einer Stirnseite her von außen in das zylindrische Außengehäuse geschoben wird.
- Es empfiehlt sich, daß die andere axial verlaufende Kante des dünnwandigen zylindrischen Gehäuses zu der abgebogenen Kante einen engen Spalt bildet, der kleiner ist als der Abstand zwischen der Lamellenseitenfläche und der Nut zur Aufnahme der Blattfeder. Dadurch haben alle auf die Lamellen drückenden Blattfedern die gleiche Auflagefläche auf der Innenfläche des gebogenen Bleches, so daß der Kontaktdruck über den Umfang gleichmäßig ist.
- Mit Vorteil wird das abgebogene innere zylindrische Gehäuse aus einem unmagnetischen Blech mit hoher mechanischer Festigkeit und harter Oberfläche hergstellt, wie z. B. Bronze oder Messing. Dadurch wird ein Eindrücken der Blattfedern in das Blech vermieden, was eine Verringerung des Kontaktdruckes bewirken würde.
- Im folgenden sei die Erfindunq noch anhand des in den Figuren 1 bis 3 dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiels näher erläutert. Die Figur 1 zeigt einen Längsschnitt durch ein gemäß der Erfindunq ausgebildetes Kuppelkontaktstück. In Figur 2 ist, teilweise geschnitten, eine Ansicht auf eine Stirnseite des Kuppelkontaktstückes dargestellt, in Richtung des bei Figur 1 gezeichneten Pfeiles gesehen. Figur 3 zeigt in kleinerem Maßstab das innnere zylindrische Gehäuse.
- Das Kuppelkontaktstück 1 für die Verbindung zweier runder Leiter einer druckgasisolierten metallgekapselten Hochspannungschaltanlage besitzt ein dickwandiges Außengehäuses 2, das im wesentlichen eine zylindrische Form hat. Die stirnseitigen Außenkanten 3 ebenso wie die Kanten 4 neben einer Einschnürung 5 zur Aufnahme einer nicht dargestellten Sicherungsfeder sind stark abgerundet, so daß das Außengehäuse 2 gleichzeitig als eine das elektrische Feld steuernde Abschirmung im Zuge der Leiterverbindung wirkt. Der Innendurchmesser 6 im Bereich der Einschnürung 5 ist kleiner als der Innendurchmesser 7 zur Aufnahme der Lamellen 8, so daß sich zwischen beiden ein Absatz 9 bildet, an dem die Lamellen 8 einseitig anliegen.
- Jede Lamelle 8 ist trapezförmig ausgebildet. Die spitze Seite 10 der Lamelle 8 bildet die Kontaktfläche zu den nicht dargestellten zu verbindenden Leitern. Die dem Außengehäuse 2 zugewandte stumpfe Seite enthält eine mittige Nut 11, die jeweils seitlich einen Abstand 12 zur Lamellenseitenfläche 13 aufweist. In dieser Nut 11 ist jeweils eine Blattfeder 14 angeordnet, welche die Lamelle 8 gegenüber dem Außengehäuse 2 abstützt und somit den Kontaktdruck der Lamelle 8 hervorruft.
- Die Blattfeder 14 liegt aber nicht an der Innenbohrung 15 des Außengehäuses 2 an, sondern in diese ist ein dünnwandiges zylindrisches Gehäuse 16 eingeschoben. Dieses dünnwandige zylindrische Gehäuse 16 ist aus einem zu einem Zylinder gebogenen Streifen dünnwandiges Bronzebleches gebildet.
- Die Breite des Bleches entspricht angenähert der Länge der Lamellen 8. Eine der axial verlaufenden Kanten 17 des Bleches ist in einer kleiner als die Lamellenhöhe 18 gewählten Höhe 19 radial nach innen abgebogen. Dadurch bildet diese abgebogene Kante 17 eine Zwischenwand 20, die zwischen zwei Lamellen 8 hineinragt. Die andere, nicht abgebogene, axial verlaufende Kante 21 des dünnwandigen zylindrischen Gehäuses 16 bildet einen engen Spalt 22 zu der abgebogenen Kante 17, der kleiner ist als der Abstand 12 zwischen der Lamellenseitenfläche 13 und der Nut 11 zur Aufnahme der Blattfeder 14. Dadurch liegen alle Blattfedern 14 jeweils auf der Innenfläche des dünnwandigen zylindrischen Gehäuses 16, so daß der gleiche Kontaktdruck entlang des gesamten Umfanges des Kuppelkontaktstückes 1 gewährleistet ist. Das dünnwandige Gehäuse 16 nimmt die Kontaktkraft micht selbst auf, sondern überträgt sie unmittelbar auf das Außengehäuse 2.
- Die Montage des Kuppelkontaktstückes 1 ist sehr einfach. Zunächst wird das dünnwandige zylindrische Gehäuse 16 in die Innenbohrung 15 des Außengehäuses 2 eingeschoben, bis es an den Absatz 9 zur Anlage gelangt. Danach werden die einzelnen Lamellen 8 von der Seite her eingeschoben und gelangen ebenfalls an den Absatz 9 zur Anlage. Jetzt werden in jede Nut 11 der Lamellen 8 die Blattfedern 14 eingeschoben. Schließlich wird vor die Stirnseite des dünnwandigen zylindrischen Gehäuses 16, der Blattfedern 14 und der Lamellen 8 eine Scheibe 23 zur axialen Sicherung gelegt, die an einigen Stellen in dem Außengehäuse 2 durch Verstemmen festgelegt wird.
- Bei diesem gemäß der Erfindung ausgebildeten Kuppelkontaktstück ist durch die zwischen zwei Lamellen 8 hineinragende Zwischenwand 20 des zylindrischen Gehäuses 16 eine genaue seitliche Führung und Festlegung der Lamellen 8 gegeben, so daß diese auf einfache Weise an einem Kippen gehindert sind, was zu einer Minderung der Stromtragfähigkeit führen würde.
Claims (4)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE8431557U | 1984-10-25 | ||
| DE8431557U DE8431557U1 (de) | 1984-10-25 | 1984-10-25 | Kuppelkontaktstück zum Verbinden runder elektrischer Leiter |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0182736A2 true EP0182736A2 (de) | 1986-05-28 |
| EP0182736A3 EP0182736A3 (en) | 1986-06-04 |
| EP0182736B1 EP0182736B1 (de) | 1988-06-15 |
Family
ID=6772126
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP85730142A Expired EP0182736B1 (de) | 1984-10-25 | 1985-10-16 | Kuppelkontaktstück zum Verbinden runder elektrischer Leiter |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0182736B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS61104569A (de) |
| DE (2) | DE8431557U1 (de) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0789424A3 (de) * | 1996-02-08 | 1998-11-11 | Asea Brown Boveri Ag | Verbindungselement für zwei Abschnitte eines hochspannungsführenden Stromleiters |
| EP3748780A1 (de) * | 2019-06-05 | 2020-12-09 | Tyco Electronics UK Ltd | Kontaktklemme |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5714516B2 (ja) * | 2012-01-23 | 2015-05-07 | サンコール株式会社 | 電気コネクタ |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1160914B (de) * | 1961-11-24 | 1964-01-09 | Siemens Ag | Kuppelkontaktstueck |
| GB1070033A (en) * | 1964-06-24 | 1967-05-24 | Pyle National Co | Improvements in or relating to electrical contacts |
| CH474876A (de) * | 1968-11-05 | 1969-06-30 | Bbc Brown Boveri & Cie | Elektrische Kontaktanordnung |
| US3713075A (en) * | 1971-04-26 | 1973-01-23 | Ite Imperial Corp | Dielectric shield for plug-in contacts |
-
1984
- 1984-10-25 DE DE8431557U patent/DE8431557U1/de not_active Expired
-
1985
- 1985-10-16 EP EP85730142A patent/EP0182736B1/de not_active Expired
- 1985-10-16 DE DE8585730142T patent/DE3563402D1/de not_active Expired
- 1985-10-22 JP JP60236253A patent/JPS61104569A/ja active Granted
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0789424A3 (de) * | 1996-02-08 | 1998-11-11 | Asea Brown Boveri Ag | Verbindungselement für zwei Abschnitte eines hochspannungsführenden Stromleiters |
| EP3748780A1 (de) * | 2019-06-05 | 2020-12-09 | Tyco Electronics UK Ltd | Kontaktklemme |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3563402D1 (en) | 1988-07-21 |
| JPH0313709B2 (de) | 1991-02-25 |
| JPS61104569A (ja) | 1986-05-22 |
| EP0182736A3 (en) | 1986-06-04 |
| DE8431557U1 (de) | 1985-03-21 |
| EP0182736B1 (de) | 1988-06-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE2651108C3 (de) | Elektrische Kontaktvorrichtung | |
| DE2615996C2 (de) | Einstückig aus Metallblech gestanzte und geformte elektrische Anschlußklemme | |
| DE3722069C2 (de) | ||
| DE2338056B2 (de) | Elektrische Anschlußklemme | |
| DE9311781U1 (de) | Kabelstecker für vieladrige Kabel | |
| DE2449042A1 (de) | Elektrischer verbinder | |
| DE69603318T2 (de) | Vorrichtung für elektrische Kontakte mit Isolationsverschiebung | |
| DD269496A5 (de) | Schneidklemm-huelsenkontakt | |
| DE69523729T2 (de) | Schneidklemmverbinder | |
| EP0182736B1 (de) | Kuppelkontaktstück zum Verbinden runder elektrischer Leiter | |
| EP0308819A2 (de) | Elektromagnetisches Relais | |
| DE29705134U1 (de) | Steckerbuchse | |
| DE4320539C2 (de) | Leitungsdraht-Verbindungsklemme | |
| EP0226907A2 (de) | Relais | |
| DE3625864A1 (de) | Elektrische kontaktvorrichtung | |
| DE2438234C3 (de) | Elektrodenbaugruppe für Mehrstrahlerzeugersysteme und Verfahren zum Betrieb dieser Baugruppe | |
| DE2936616C2 (de) | Verbinder für zwei Koaxialkabelenden | |
| EP3869621B1 (de) | Anschlussklemme | |
| DE69103372T2 (de) | Spulenkörper mit winkelrechten Anschlussstiften. | |
| EP0210126B1 (de) | Kuppelkontakstück für eine Steckverbindung zwischen zwei zylindrischen Leitern einer gekapselten, drukgasisolierten Hochspannungsschaltanlage. | |
| DE2304639B2 (de) | Fassungsanordnung für elektrische Steckerkupplungen | |
| DE19539958B4 (de) | Kontakt | |
| DE4225544C1 (de) | Kabelsteckverbinder für Flachbandkabel | |
| DE9304392U1 (de) | Kontaktelement mit Schneidklemm- und Crimpanschluß | |
| DE1160914B (de) | Kuppelkontaktstueck |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB LI NL SE |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB LI NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19860626 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19870929 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB LI NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3563402 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19880721 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 85730142.8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19980909 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19981027 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19981030 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19991016 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19991030 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000501 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19991016 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 85730142.8 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20000501 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20031029 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20031217 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20040114 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20041031 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20041031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050503 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050630 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |