EP0091047B1 - Vergaserkraftstoff - Google Patents
Vergaserkraftstoff Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0091047B1 EP0091047B1 EP83103030A EP83103030A EP0091047B1 EP 0091047 B1 EP0091047 B1 EP 0091047B1 EP 83103030 A EP83103030 A EP 83103030A EP 83103030 A EP83103030 A EP 83103030A EP 0091047 B1 EP0091047 B1 EP 0091047B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- phenol
- oil
- gasoline
- extraction
- boiling
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/04—Liquid carbonaceous fuels essentially based on blends of hydrocarbons
- C10L1/06—Liquid carbonaceous fuels essentially based on blends of hydrocarbons for spark ignition
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10G—CRACKING HYDROCARBON OILS; PRODUCTION OF LIQUID HYDROCARBON MIXTURES, e.g. BY DESTRUCTIVE HYDROGENATION, OLIGOMERISATION, POLYMERISATION; RECOVERY OF HYDROCARBON OILS FROM OIL-SHALE, OIL-SAND, OR GASES; REFINING MIXTURES MAINLY CONSISTING OF HYDROCARBONS; REFORMING OF NAPHTHA; MINERAL WAXES
- C10G19/00—Refining hydrocarbon oils in the absence of hydrogen, by alkaline treatment
- C10G19/02—Refining hydrocarbon oils in the absence of hydrogen, by alkaline treatment with aqueous alkaline solutions
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for producing a low-benzene, environmentally friendly gasoline from light coal oil.
- the conversion of coal to gasoline (gasoline) is preferably done in two stages. In the first stage, the bottom phase, the coal is converted into an intermediate product (medium oil and crude gasoline) in the presence of finely divided catalysts using hydrogen under suitable pressure and temperature, which is then converted into gasoline fuel in subsequent stages using further catalysts.
- Carburetor fuels obtained in this way are highly aromatic because of the molecular structure of the coal from condensed aromatics.
- the benzene content in particular is between 10 and 20% by weight. This high benzene content is undesirable because of the toxic properties of benzene.
- the benzene content in carburetor fuels is or is being striven for.
- the benzene content in gasoline in the Federal Republic of Germany should be limited to 5 percent by weight.
- the invention has for its object to produce a low-benzol gasifier fuel from light coal oil, which is independent of the availability of low-benzol admixture components.
- a core fraction of the boiling point 145-185 ° C. is distilled off from the crude light coal oil.
- the fraction contains the majority of the phenol contained in the coal oil.
- the phenol can be separated from this core fraction and extracted by extraction with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution or sodium phenolate solution, preferably in a three-stage mixer-settler extractor.
- the remaining phenol-free raffinate of the core fraction is mixed with the portion of light coal oil, boiling up to 145 ° C, and by refining z.
- B pressure 60 bar, temperature 410 ° C load 1.5 kg oil / kg cat. H) prepared for reformer application specification. Reforming (e.g. pressure 15 bar, temperature 480 ° C, load 1.5 kg oil / kg cat. H) results in a low-gasoline gasoline fuel with a high octane number.
- the benzene content of the reformate is reduced to approximately 5% by weight and the process stages of refining and reformer are relieved in terms of quantity.
- the phenol is not converted into worthless water and benzene by the hydrogenation reactions or, depending on the degree of hydrogenation, into cyclohexane, valuable hydrogen is saved in this stage.
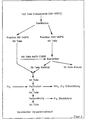
- FIG. 1 shows the procedure of the method according to the invention.
- Examples 1 to 3 give experimental data on how the benzene content is reduced in the process according to the invention, the quantity of product flow in the refining and in the reformer is relieved and how the hydrogen consumption is reduced for the hydrogenating removal of the phenols while simultaneously hydrogenating the benzene to cyclohexane.
- a core fraction in the boiling range 145-185 ° C. which contains the majority of the phenol present in the light coal oil, are distilled off from 100 parts of crude light coal oil by refractionation.
- This core fraction is de-phenolized by 3-stage extraction with 69 parts of 12% aqueous NaOH in a mixer-settler extractor and the fraction freed from phenol is then mixed again with the light coal oil (boiling point - 145 ° C).
- the phenol-free light coal oil is processed by refining and reforming on gasoline. The procedure described lowers the benzene content of the gasoline fuel to 2.6% by weight. If the light coal oil is not de-phenolic before processing in the refiner and reformer, the benzene content in the gasoline is 17.1% by weight.
- 100 parts of light coal oil which contain 16% by weight of phenol, are broken down into two fractions - boiling from the beginning of boiling to 145 ° C, 55 parts or 45 parts from 145 to 185 ° C.
- the phenol is enriched to 35% by weight.
- the feed oil for the refiner / reformer still contains 0.8% by weight of phenol. Due to the extraction of the phenol, only 84 parts of the original 100 parts of light coal oil have to be processed in the refiner / reformer, ie this system is relieved in terms of quantity.
- the hydrogen consumption in refining is reduced by 130 I / kg feed oil compared to processing of the crude, non-de-phenolic light coal oil, since the phenol has been removed and thus the hydrogen requirement for the hydrogenating phenol removal is eliminated.
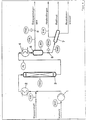
- a 3-stage mixer-settling extraction apparatus is used to remove phenols from light coal oil using aqueous sodium hydroxide solution.
- stage I fresh sodium hydroxide solution is introduced into the mixer zone by means of a metering pump and pre-extracted light coal oil via a forced flow in stage 11.
- stage II the simply pre-extracted light coal oil from stage 111 is extracted with the stage 1 extract, which is partially loaded with phenols.
- stage III the raw coal light oil is conveyed by means of a metering pump and pre-extracted with the extract (phenol-containing sodium hydroxide solution) from the first two stages.
- the lighter, organic phase is led to stage 11.
- the heavy phase is removed from the process as a phenol-containing extract to recover the phenols.
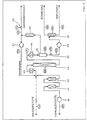
- the light coal oil to be refined is introduced into the reaction system by means of a metering pump 1.
- Compressed make-up hydrogen is metered in before the preheater 2, in which the components are heated to a temperature slightly below the reaction temperature.
- the implementation takes place in a fixed bed reactor, which is electrically heated by a heating jacket with several control loops.
- On the catalytic converter all organic sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen compounds contained in the oil are converted into hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, water and hydrocarbons, and gaseous decomposition products are also formed.
- the product stream leaving the reactor is separated into gas and liquid phases in high-pressure separator 5.
- the gas phase is expanded via a gas expansion valve 8. It mainly consists of excess hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide and small amounts of C i -C 4 gases.
- the liquid phase flows through an expansion valve 6 into a water-oil separating container 7.
- the raffinate separates from the water of reaction due to the density differences, and also small amounts of dissolved gases are released as stripping gas.
- the system according to FIG. 4 includes control loops with mass measurement WIR, volume measurement FIR, pressure measurement PI, temperature measurement TIRC, maintenance LIRC and pressure control PRC. Since, when the refined light coal oil is reformed, the reformer contact is quickly deactivated by oxygen and excessive water vapor partial pressure, the feed oil according to FIG. 5 is pumped through a deoxidizer 11 and dryer 12 by means of a pump 10. Subsequently, compressed hydrogen is added before a preheater 13, which heats the mixture to the reaction temperature. The following fixed bed reactor 14 must be heated from the outside to maintain the reaction. In the reforming, aromatics are formed from paraffinic and naphthenic hydrocarbons with the evolution of hydrogen.
- the oil After expansion, the oil is pumped into a stabilizing column 18 by means of expansion valve 17, in which low-boiling hydrocarbons are removed by distillation.
- the associated pump is designated 19.
- the distillation sump is the aromatic-rich reformate.
- the gaseous phase from the high-pressure separator is freed of organic constituents under system pressure in a gas scrubber and gas dryer 20 and is returned as a cycle gas by means of a cycle gas compressor 21.
- the hydrogen formed during the reforming leaves the process via a valve 22 as excess gas.
- control devices belonging to the system according to FIG. 5 have the same designations as the control devices according to FIG. 4.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Production Of Liquid Hydrocarbon Mixture For Refining Petroleum (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE3213220 | 1982-04-08 | ||
| DE19823213220 DE3213220A1 (de) | 1982-04-08 | 1982-04-08 | Vergaserkraftstoff |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0091047A2 EP0091047A2 (de) | 1983-10-12 |
| EP0091047A3 EP0091047A3 (en) | 1985-01-09 |
| EP0091047B1 true EP0091047B1 (de) | 1987-03-04 |
Family
ID=6160604
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP83103030A Expired EP0091047B1 (de) | 1982-04-08 | 1983-03-26 | Vergaserkraftstoff |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0091047B1 (member.php) |
| AU (1) | AU556607B2 (member.php) |
| CA (1) | CA1206908A (member.php) |
| DE (2) | DE3213220A1 (member.php) |
| IN (1) | IN158910B (member.php) |
| NZ (1) | NZ203807A (member.php) |
| SU (1) | SU1172452A3 (member.php) |
| ZA (1) | ZA832467B (member.php) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3410455A1 (de) * | 1984-03-22 | 1985-10-03 | Ruhrkohle Ag, 4300 Essen | Verfahren zur herstellung eines vergaserkraftstoffes aus kohleleichtoel |
| CN101429449B (zh) * | 2007-11-09 | 2012-10-10 | 丁冉峰 | 一种催化烃重组制备高质量汽油的设备及其方法 |
| CN101429446B (zh) * | 2007-11-09 | 2012-10-10 | 丁冉峰 | 一种催化烃重组制备高质量汽油的设备及其方法 |
| CN101475835B (zh) * | 2009-01-22 | 2012-09-05 | 北京金伟晖工程技术有限公司 | 一种组分炼油烃重组后加氢制备高质量汽油的系统和方法 |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB107454A (en) * | 1916-07-31 | 1917-07-05 | George Edward Heyl | Improvements in Liquid Fuels. |
| US4319981A (en) * | 1980-11-12 | 1982-03-16 | The United States Of America As Represented By The United States Department Of Energy | Process for preparing a liquid fuel composition |
-
1982
- 1982-04-08 DE DE19823213220 patent/DE3213220A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1983
- 1983-03-26 EP EP83103030A patent/EP0091047B1/de not_active Expired
- 1983-03-26 DE DE8383103030T patent/DE3370022D1/de not_active Expired
- 1983-03-31 AU AU13094/83A patent/AU556607B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1983-04-06 NZ NZ203807A patent/NZ203807A/en unknown
- 1983-04-07 SU SU833582281A patent/SU1172452A3/ru active
- 1983-04-07 IN IN234/DEL/83A patent/IN158910B/en unknown
- 1983-04-07 CA CA000425386A patent/CA1206908A/en not_active Expired
- 1983-04-08 ZA ZA832467A patent/ZA832467B/xx unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3370022D1 (en) | 1987-04-09 |
| EP0091047A2 (de) | 1983-10-12 |
| DE3213220A1 (de) | 1983-10-13 |
| CA1206908A (en) | 1986-07-02 |
| AU1309483A (en) | 1983-10-13 |
| EP0091047A3 (en) | 1985-01-09 |
| NZ203807A (en) | 1986-02-21 |
| AU556607B2 (en) | 1986-11-13 |
| SU1172452A3 (ru) | 1985-08-07 |
| IN158910B (member.php) | 1987-02-14 |
| ZA832467B (en) | 1983-12-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69328029T2 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von hochreinem benzol durch extraktivdestillation | |
| US3105095A (en) | Process of liquefaction of lignin | |
| US2662843A (en) | Shale oil refining | |
| US8197678B2 (en) | Refining coal-derived liquid from coal gasification, coking and other coal processing operations | |
| DE60208420T2 (de) | Schwefel-entfernungsverfahren | |
| EP0091047B1 (de) | Vergaserkraftstoff | |
| US4761222A (en) | Method for separating normally liquid organic compounds | |
| US3974073A (en) | Coal liquefaction | |
| US2645655A (en) | Recovery and purification of oil soluble oxygenated compounds | |
| US1844362A (en) | Process of producing an antiknock compound | |
| DE2612449A1 (de) | Verfahren zur entfernung von schwefelverbindungen aus kohlenwasserstoffeinsatzprodukten | |
| US4382855A (en) | Process for removal of hydroxy- and/or mercapto-substituted hydrocarbons from coal liquids | |
| DE1270017B (de) | Verfahren zur Gewinnung von hochgereinigtem Benzol | |
| US2754248A (en) | Refining hydrocarbon oils with sulfur dioxide | |
| US5964987A (en) | Neutral oil removal from natural cresylic acid mixtures | |
| US2719106A (en) | Champagnat | |
| DE3022158C2 (de) | Verfahren zur hydrierenden Kohleverflüssigung | |
| US2356980A (en) | Toluene sweetening | |
| DE1272921B (de) | Verfahren zur katalytischen Hochdruckhydrierung eines im wesentlichen mehrkernige aromatische Kohlenwasserstoffe enthaltenden Ausgangsmaterials in zwei Stufen | |
| US3017346A (en) | Solvent extraction process using dimethyl hydrogen phosphite | |
| US2953523A (en) | Chemical process | |
| US2754252A (en) | Refining hydrocarbon oils with bf3 and perfluoroalkanoic acid | |
| EP0155456B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Vergaser-Kraftstoffes aus Kohleleichtöl | |
| US2257547A (en) | Solvent treating mineral oils | |
| US2240727A (en) | Extraction of phenolic compounds from mineral oils |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE DE FR GB IT NL |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19830928 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: VEBA OEL AG Owner name: RUHRKOHLE AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE DE FR GB IT NL |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): BE DE FR GB IT NL |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3370022 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19870409 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19930911 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19941201 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19950317 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19960331 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19960507 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19961129 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19970213 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19970331 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: VEBA OEL A.G. Effective date: 19970331 Owner name: RUHRKOHLE A.G. Effective date: 19970331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19971001 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19971001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980326 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19980326 |