EP0004875A2 - Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für ein Möbelstück, insbesondere einen Tisch - Google Patents
Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für ein Möbelstück, insbesondere einen Tisch Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0004875A2 EP0004875A2 EP79100844A EP79100844A EP0004875A2 EP 0004875 A2 EP0004875 A2 EP 0004875A2 EP 79100844 A EP79100844 A EP 79100844A EP 79100844 A EP79100844 A EP 79100844A EP 0004875 A2 EP0004875 A2 EP 0004875A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- furniture
- piece
- spindle drive
- drive
- shaft
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A47—FURNITURE; DOMESTIC ARTICLES OR APPLIANCES; COFFEE MILLS; SPICE MILLS; SUCTION CLEANERS IN GENERAL
- A47B—TABLES; DESKS; OFFICE FURNITURE; CABINETS; DRAWERS; GENERAL DETAILS OF FURNITURE
- A47B9/00—Tables with tops of variable height
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A47—FURNITURE; DOMESTIC ARTICLES OR APPLIANCES; COFFEE MILLS; SPICE MILLS; SUCTION CLEANERS IN GENERAL
- A47B—TABLES; DESKS; OFFICE FURNITURE; CABINETS; DRAWERS; GENERAL DETAILS OF FURNITURE
- A47B2200/00—General construction of tables or desks
- A47B2200/0035—Tables or desks with features relating to adjustability or folding
- A47B2200/005—Leg adjustment
- A47B2200/0056—Leg adjustment with a motor, e.g. an electric motor
Definitions
- the invention relates to a lifting and lowering device for a piece of furniture, in particular a table, with a drive acting on a part of the piece of furniture which can be raised and lowered relative to a fixed part.
- Lifting and lowering devices of this type enable furniture to be adjusted to different heights. This is of particular importance for work tables, the height of which has to be adapted to the seat height or body size of a working person.
- lifting and lowering devices are known which work according to various possible principles, but have the disadvantage that they have to be complicated and thus expensive to guide the lifting and lowering part of the piece of furniture on the fixed part without tilting.
- tension elements for example wire cables.
- a device of the type mentioned is designed to solve this problem according to the invention in such a way that a spindle drive acting directly in a punctiform manner on the liftable and lowerable part is provided and that the liftable and lowerable part by means of spaced-apart vertical toothed racks on a common, stationary mounted shaft pinions is guided.
- This device is extremely simple and, as will be shown, can be constructed so that it can also be retrofitted to furniture.
- a spindle drive acting directly on the liftable and lowerable part and on the other hand a guide of the liftable and lowerable part on the fixed part is provided, which ensures a non-positive connection of the racks with one another via the stationary shaft, are tilted at the Lifting and lowering movements excluded.
- the spindle drive ensures a very fine working method, and only a small amount of force is required to operate it, so that, for example, a comparatively small electric motor can be used for this purpose.
- the device can advantageously be further developed in such a way that a guide frame is provided, each having a rack-containing telescopic devices, the fixed telescopic parts of which are connected by a horizontal and parallel to the shaft arranged transverse rail.
- This design results in a very rigid guide structure that can be retrofitted as a unit to a piece of furniture, for example on the underside of a table.
- the two telescopic devices can form table legs or can also be attached to side surfaces or table legs.
- the cross rail increases the stability of the piece of furniture significantly, so that the tilt-free guidance of the lifting and lowering part is also improved.
- the spindle drive can be attached to the cross rail in a simple manner in the last-described development, so that it is included in the lifting and lowering unit.
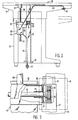
- a work table 10 for example a laboratory table or other equipment table, is shown in a front view, which essentially comprises a table plate 11 which can be raised and lowered, and fixed side parts 12 and 13 which are rigidly connected to one another, for example, by a vertical back plate 14 are.
- the work table 10 contains below the table top 11 a lifting and lowering device which comprises a spindle drive 15, a stationary shaft 16 and two telescopic devices 17 and 18 which are non-positively coupled to this shaft 16.
- the telescopic devices 17 and 18 are connected to the side parts 12 and 13 or fastened to lower cross members 19 and 20 mounted on the side parts 12 and 13.
- the movable elements 21 and 22 of the telescopic devices 17 and 18 are attached to the underside of the table top 11, so that they guide the table top 11 during its lifting and lowering movement in the fixed parts of the telescopic devices 17 and 18. During this movement, tilting of the movable elements 21 and 22 in the telescopic devices 17 and 18 is avoided in that the movable elements 21 and 22 are provided with toothed racks, not shown, which are each guided by a pinion, which is fixed on the shaft 16 . In this way, there is a non-positive coupling of the two movable elements 21 and 22, which in each case ensures corresponding movement lengths during the telescopic movement and thereby makes canting impossible.
- the drive 15 comprises an electric motor 25 which can be reversed with respect to its direction of rotation and which actuates a vertically arranged rotating spindle. This is guided in a sleeve 26 provided in the drive 15 and, by means of its rotary movement, causes a pressure stamp 27 on a thrust rod 28 is more or less far out of the drive 15 or moved into it.
- the pressure stamp 27 can be made of rubber or an elastic plastic, for example, and acts on the table top 11 from below, so that it lifts it or causes it to drop when inserted into the drive 15 due to its own weight.
- the drive 15 is mounted on a cross rail 30 which rigidly connects the two telescopic devices 17 and 18 to one another.
- the drive, the telescopic devices 17 and 18 and the transverse rail 30 thus form a unit which can be mounted on the table 10 in a very simple manner from below.
- the telescopic devices 17 and 18 are only to be connected to the side parts 12 and 13 of the work table 10, and the movable elements 21 and 22 must be fastened to the table top 11. Comparatively weak fastening elements are sufficient for this, since there is no power transmission via the movable elements 21 and 22, but rather they only serve for tilt-free guidance by means of the non-positive coupling realized via the shaft 16.
- the driving force for the lifting movement is transmitted solely to the table top 11 via the pressure stamp 27.
- a connecting cable 40 with a connector 41 for the power supply of the electric motor 25 is also shown.
- an actuating switch 42 can be seen, which is connected to the electric motor 25 via a connecting cable 43 and with two different switching positions enables the electric motor 25 to be actuated in the direction of rotation.
- Fig. 2 shows a sectional view of the lifting and lowering device according to the bleaching direction II indicated in Fig. 1.
- the work table 10 is shown for an uppermost position of the table top 11, the lowest limit position is indicated by dash-dotted lines.
- the view of the Side part 13 shows the telescopic device 17 attached to it and the fastening of the drive 15 by means of two hatch elements 31 and 32, which can be, for example, extended tabs of a mounting bracket 33.
- the tab 31 surrounds the cross rail 30, which has a U-profile and surrounds the shaft 16. It can also be seen that the telescopic device 17 is connected to a lower cross member 19 with the side part 13 of the work table 10.
- the actuation switch 42 for the electric motor 25 of the spindle drive 15 is arranged on the underside of the table top 11 facing a working person near the front edge and is designed as a rocker switch. He T enables a convenient switching on and off of the spindle drive 15 in one or the other possible direction of rotation and thus a very precise adjustment of the height of the table top 11 to the respective requirements.
- the telescopic devices 17 and 18 can be designed in the form of square tubes guided one inside the other. This brings a further improvement in the tilt-free guidance of the table top 11 on the fixed side parts 12 and 13 of the table 10.
- FIG. 3 shows a detail of the lifting and lowering device in accordance with the dash-dotted line in FIG. 1 for better illustration of the guidance of the toothed racks already mentioned, each on a pinion which is fastened on the shaft 16.
- the corresponding part of the lifting and lowering device shown in FIG. 3 is shown partially broken, so that the coupling of a pinion 35 arranged on the shaft 16 to a rack 36 can be seen, which is firmly connected to the movable element 21 of the telescopic device 17 is. It is one on the side part 13 of the Ar beitsticians 10 provided arrangement. This is surrounded by the dash-dotted line G in FIG. 3.
- Fig. 1 shows that a similar unit G is also provided on the side part 12 of the work table 10.
- the pinion 35 is fixed to the shaft 16. This is arranged in a bearing 37, which is shown in FIG. 3 as a simple sleeve and is firmly connected to the cross rail 30.
- the movable element 21 is displaceably guided in the telescopic device 17 in the vertical direction and is provided on its side facing the shaft 16 with a slot, not shown in FIG. 3, which enables movement relative to the shaft 16.
- an arrangement G is provided which is designed analogously to the arrangement of pinion 35 and rack 36 shown in FIG. 3, the two are with the movable elements 21 and 22 the telescopic devices 17 and 18 firmly connected racks non-positively connected to each other via the shaft 16, so that exactly matching lifting and lowering movements of the movable elements 21 and 22 are ensured when the plunger 27 acts on the table top 11 via the push rod 28 or from it Underside is removed.
- the result is a completely trouble-free, low-noise and extremely precise operation of the lifting and lowering device, which is also extremely simple.
- the lifting and lowering device according to the invention thus enables trouble-free guidance of the part moved relative to the fixed part despite the asymmetrical force.
- a device according to the invention can be used wherever the most precise and sensitive way of working is important. For example, use in height-adjustable chairs is also conceivable.
- the device can be used not only with furniture in the narrower sense, but also with all other furnishing or work equipment in which a relatively frequent change in height can be achieved.
Landscapes
- Tables And Desks Characterized By Structural Shape (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für ein Möbelstück, insbesondere einen Tisch, mit einem auf einen relativ zu einem feststehenden Teil heb- und senkbar geführten Teil des Möbelstücks einwirkenden Antrieb.
- Hebe- und Senkvorrichtungen dieser Art ermöglichen eine Einstellung von Möbelstücken in unterschiedliche Höhen. Dies ist von besonderer Bedeutung bei Arbeitstischen, deren Höhe der Sitzhöhe bzw. Körpergröße einer arbeitenden Person anzupassen ist. Es sind hierzu Hebe- und Senkvorrichtungen bekannt, die nach verschiedenen möglichen Prinzipien arbeiten, jedoch den Nachteil haben, daß sie zur verkantungsfreien Führung des heb- und senkbaren Teils des Möbelstücks an dem feststehenden Teil kompliziert und damit kostspielig aufgebaut sein müssen. So ist es beispielsweise bekannt, die vier Beine eines Tisches teleskopartig auszuführen und diese Teleskopvorrichtungen über einen gemeinsamen, auf Zugelemente, beispielsweise Drahtseile,gleichzeitig einwirkenden Kurbeltrieb zu betätigen. Andererseits ist es bekannt, Hebel- und Gelenkvorrichtungen vorzusehen, die direkt auf den heb- und senkbaren Teil einwirken. Solche Vorrichtungen müssen aber entweder an möglichst weit beabstandeten Stellen symmetrisch auf den heb- und senkbaren Teil einwirken oder es müssen besondere aufwendige Führungen für den heb- und senkbaren Teil vorgesehen sein, um während der Hebe- und Senkbewegung eine Verkantung der zueinander bewegten Teile zu vermeiden. Auch derartige Hebel- und Gelenkvorrichtungen sind relativ kompliziert aufgebaut und verursachen insbesondere bei Anordnung an zueinander beabstandeten Stellen einen hohen Aufwand.
- Es ist Aufgabe der Erfindung, eine Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung anzugeben, die möglichst bequem und ohne hohen Kraftaufwand zu bedienen ist, eine sehr feine Höheneinstellung ermöglicht und dabei eine glatte und möglichst geräuschlose Arbeitsweise gewährleistet.
- Eine Vorrichtung eingangs genannter Art ist zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe erfindungsgemäß derart ausgebildet, daß als Antrieb ein auf den heb- und senkbaren Teil direkt punktförmig einwirkender Spindeltrieb vorgesehen ist und daß der heb- und senkbare Teil mittels zueinander beabstandeter vertikaler Zahnstangen an auf einer gemeinsamen, ortsfest gelagerten Welle befestigten Ritzeln geführt ist.
- Diese Vorrichtung ist außerordentlich einfach aufgebaut und läßt sich, wie noch gezeigt wird, so konstruieren, daß sie auch nachträglich an Möbelstücken angebracht werden kann. Dadurch, daß einerseits ein direkt auf den heb-und senkbaren Teil einwirkender Spindeltrieb und andererseits eine Führung des heb- und senkbaren Teils an dem feststehenden Teil vorgesehen ist, die über die ortsfest gelagerte Welle eine kraftschlüssige Verbindung der Zahnstangen miteinander gewährleistet, sind Verkantungen bei der Hebe- und Senkbewegung ausgeschlossen. Der Spindeltrieb gewährleistet dabei eine sehr feine Arbeitsweise, und zu seiner Betätigung ist ein nur geringer Kraftaufwand erforderlich, so daß beispielsweise hierzu ein vergleichsweise kleiner Elektromotor verwendet werden kann.
- Die Vorrichtung kann vorteilhaft derart weiter ausgebildet sein, daß ein Führungsrahmen vorgesehen ist, der jeweils eine Zahnstange enthaltende Teleskopvorrichtungen aufweist, deren ortsfeste Teleskopteile durch eine horizontale und parallel zur Welle angeordnete Querschiene verbunden sind. Durch diese Ausbildung ergibt sich eine sehr starre Führungskonstruktion, die als eine Einheit nachträglich an einem Möbelstück, beispielsweise an der Unterseite eines Tisches, angebracht werden kann. Die beiden Teleskopvorrichtungen können dabei Tischbeine bilden oder auch an Seitenflächen bzw. Tischbeinen angebracht sein. Die Querschiene erhöht dabei die Stabilität des Möbelstücks wesentlich, so daß auch dadurch die verkantungsfreie Führung des heb- und senkbaren Teils verbessert wird.
- Der Spindeltrieb kann bei der zuletzt beschriebenen Weiterbildung in einfacher Weise an der Querschiene befestigt sein, so daß er in die Hebe- und Senkeinheit einbezogen ist.
- Ein Ausführungsbeispiel einer Vorrichtung nach der Erfindung wird im folgenden anhand der Figuren beschrieben. Es zeigen
- Fig. 1 die Vorderansicht eines Arbeitstisches mit einer gegenüber einem feststehenden Teil heb- und senkbaren Tischplatte,
- Fig. 2 eine Schnittansicht der Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung des in Fig. 1 gezeigten Arbeitstisches gemäß der dort angedeuteten Blichrichrichtung II und
- Fig. 3 eine vergrößert dargestellte Einzelheit der Führungsvorrichtung.
- In Fig. 1 ist ein Arbeitstisch 10, beispielsweise ein Labortisch oder ein sonstiger Gerätetisch, in einer Vorderansicht dargestellt, der im wesentlichen eine heb-und senkbare Tischplatte 11 sowie feststehende Seitenteile 12 und 13 umfaßt, die beispielsweise durch eine vertikale Rückplatte 14 miteinander starr verbunden sind. Der Arbeitstisch 10 enthält unterhalb der Tischplatte 11 eine Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung, die einen Spindeltrieb 15, eine ortsfest gelagerte Welle 16 und zwei mit dieser Welle 16 kraftschlüssig gekoppelte Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 umfaßt. Die Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 sind mit den Seitenteilen 12 und 13 verbunden bzw. auf unteren, an den Seitenteilen 12 und 13 montierten Querträgern 19 und 20 befestigt. Die beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22 der Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 sind an der Unterseite der Tischplatte 11 befestigt, so daß sie die Tischplatte 11 bei ihrer Hebe- und Senkbewegung in den feststehenden Teilen der Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 führen. Während dieser Bewegung wird eine Verkantung der beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22 in den Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 dadurch vermieden, daß die beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22 mit nicht dargestellten Zahnstangen versehen sind, die an jeweils einem Ritzel geführt sind, welches auf der Welle 16 befestigt ist. Auf diese Weise ergibt sich eine kraftschlüssige Kopplung der beiden beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22, die jeweils übereinstimmende Bewegungslängen während der Teleskopbewegung gewährleistet und dadurch eine Verkantung unmöglich macht.
- Der Antrieb 15 umfaßt einen hinsichtlich seiner Drehrichtung umsteuerbaren Elektromotor 25, der eine senkrecht angeordnete Drehspindel betätigt. Diese ist in einer im Antrieb 15 vorgesehenen Hülse 26 geführt und bewirkt durch ihre Drehbewegung, daß ein Druckstempel 27 an einer Schubstange 28 mehr oder weniger weit aus dem Antrieb 15 heraus- bzw. in ihn hineinbewegt wird. Der Druckstempel 27 kann beispielsweise aus Gummi oder einem elastischen Kunststoff bestehen und wirkt von unten her auf die Tischplatte 11 ein, so daß er sie anhebt bzw. beim Einschieben in den Antrieb 15 ihr Absenken infolge ihres Eigengewichts bewirkt. Der Antrieb 15 ist an einer Querschiene 30 montiert, die die beiden Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 starr miteinander verbindet. Somit bilden der Antrieb, die Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 und die Querschiene 30 eine Einheit, die an dem Tisch 10 in sehr einfacher Weise von unten her montiert werden kann. Hierzu sind die Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 lediglich mit den Seitenteilen 12 und 13 des Arbeitstisches 10 zu verbinden, und die beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22 müssen an der Tischplatte 11 befestigt werden. Hierzu genügen vergleichsweise schwache Befestigungselemente, denn über die beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22 erfolgt keine Kraftübertragung, sondern sie dienen lediglich der verkantungsfreien Führung mittels der über die Welle 16 verwirklichten kraftschlüssigen Kopplung. Die Antriebskraft für die Hebebewegung wird einzig und allein über den Druckstempel 27 auf die Tischplatte 11 übertragen.
- In Fig. 1 ist ferner ein Anschlußkabel 40 mit einem Anschlußstecker 41 für die Stromversorgung des Elektromotors 25 dargestellt. Außerdem ist ein Betätigungsschalter 42 zu erkennen, der über ein Verbindungskabel 43 mit dem Elektromotor 25 verbunden ist und mit zwei verschiedenen Schaltstellungen eine drehrichtungsabhängige Betätigung des Elektromotors 25 ermöglicht.
- Fig. 2 zeigt eine Schnittdarstellung der Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung gemäß der in Fig. 1 angedeuteten Blichrichtung II. Der Arbeitstisch 10 ist für eine oberste Stellung der Tischplatte 11 dargestellt, die unterste Grenzstellung ist strichpunktiert angedeutet. Die Ansicht des Seitenteils 13 zeigt die daran befestigte Teleskopvorrichtung 17 sowie die Befestigung des Antriebs 15 mittels zweier Hateleelemente 31 und 32, die beispielsweise verlängerte Laschen eines Montageträgers 33 sein können. Die Lasche 31 umgibt die Querschiene 30, die ein U-Profil aufweist und die Welle 16 umgibt. Es ist ferner zu erkennen, daß die Teleskopvorrichtung 17 an einem unteren Querträger 19 mit dem Seitenteil 13 des Arbeitstisches 10 verbunden ist.
- Der Betätigungsschalter 42 für den Elektromotor 25 des Spindeltriebs 15 ist an der einer arbeitenden Person zugewandten Unterseite der Tischplatte 11 nahe der Vorderkante angeordnet und als Wippschalter ausgebildet. Er erT möglicht eine bequeme Ein- und Ausschaltung des Spindeltriebs 15 in der einen oder anderen möglichen Drehrichtung und damit eine sehr genaue Anpassung der Höhe der Tischplatte 11 an die jeweiligen Erfordernisse.
- Wie aus Fig. 1 in Verbindung mit Fig. 2 hervorgeht, können die Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 in Form ineinander geführter Vierkantrohre ausgebildet sein. Dies bringt eine weitere Verbesserung der verkantungsfreien Führung der Tischplatte 11 an den feststehenden Seitenteilen 12 und 13 des Tisches 10.
- Fig. 3 zeigt gemäß der entsprechend bezeichneten strichpunktierten Linie in Fig. 1 eine Einzelheit der Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung zur besseren Darstellung der Führung der bereits genannten Zahnstangen an jeweils einem Ritzel, das auf der Welle 16 befestigt ist. Der entsprechende, in Fig. 3 gezeigte Teil der Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung ist teilweise gebrochen dargestellt, so daß die Kopplung eines auf der Welle 16 angeordneten Ritzels 35 mit einer Zahnstange 36 zu erkennen ist, die mit dem beweglichen Element 21 der Teleskopvorrichtung 17 fest verbunden ist. Es handelt sich hierbei um one am Seitenteil 13 des Arbeitstisches 10 vorgesehene Anordnung. Diese ist in Fig. 3 durch die strichpunktierte Linie G umgeben. Fig. 1 zeigt, daß eine gleichartige Einheit G auch an dem Seitenteil 12 des Arbeitstisches 10 vorgesehen ist.
- Das Ritzel 35 ist mit der Welle 16 fest verbunden. Diese ist in einem Lager 37 angeordnet, das in Fig. 3 als einfache Hülse dargestellt ist und mit der Querschiene 30 fest verbunden ist. Das bewegliche Element 21 ist in der Teleskopvorrichtung 17 in vertikaler Richtung verschiebbar geführt und auf seiner der Welle 16 zugewandten Seite mit einem in Fig. 3 nicht dargestellten Schlitz versehen, der die Bewegung relativ zur Welle 16 ermöglicht.
- Dadurch, daß auf der anderen Seite des Arbeitstisches, d.h. an dem Seitenteil 12, eine Anordnung G vorgesehen ist, die analog der in Fig. 3 gezeigten Anordnung aus Ritzel 35 und Zahnstange 36 ausgebildet ist, sind die beiden mit den beweglichen Elementen 21 und 22 der Teleskopvorrichtungen 17 und 18 fest verbundenen Zahnstangen über die Welle 16 kraftschlüssig miteinander verbunden, so daß exakt übereinstimmende Hebe- und Senkbewegungen der beweglichen Elemente 21 und 22 gewährleistet sind, wenn der Druckstempel 27 über die Schubstange 28 auf die Tischplatte 11 einwirkt bzw. von ihrer Unterseite entfernt wird. Es ergibt sich somit eine völlig störungsfreie, geräuscharme und überaus genaue Arbeitsweise der Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung, die darüber hinaus noch außerordentlich einfach aufgebaut ist. Es sind keine besonderen Erfordernisse hinsichtlich eines genauen Einbaus zu berücksichtigen, und der Ort, an dem der Druckstempel 27 auf die Tischplatte 11 einwirkt, ist völlig unkritisch. Insbesondere ist es möglich, den Druckstempel 27 nicht in der Mitte, sondern auf der einen Seite des Möbelstücks anzuordnen, so daß beispielsweise bei einem Tisch die Beinfreiheit unterhalb der Tischplatte nicht gestört wird. Die Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung nach der Erfindung ermöglicht also trotz asymmetrischer Krafteinwirkung eine störungsfreie Führung des relativ zum feststehenden Teil bewegten Teils.
- Eine Vorrichtung nach der Erfindung kann überall dort eingesetzt werden, wo es auf möglichst genaue und feinfühlige Arbeitsweise ankommt. Beispielsweise ist auch die Verwendung bei höhenverstellbaren Stühlen denkbar. Außerdem kann die Vorrichtung nicht nur bei Möbelstücken im engeren Sinne, sondern auch bei allen anderen Einrichtungs- oder Arbeitsgerätschaften eingesetzt werden, bei denen eine relativ häufige Höhenänderung zu verwirklichen ist.
Claims (9)
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß ein Führungsrahmen (17, 18, 30) vorgesehen ist, der jeweils eine Zahnstange (36) enthaltende Teleskopvorrichtungen (17, 18, 21, 22) aufweist, deren ortsfeste Teleskopteile (17, 18) durch eine horizontal und parallel zur Welle (16) angeordnete Querschiene (30) verbunden sind.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Spindeltrieb (15) an der Querschiene (30) befestigt ist.
daß der Spindeltrieb (15) einen umsteuerbaren Elektromotor (25) als Antriebsvorrichtung aufweist..
daß die Querschiene (30) U-Profil aufweist und die Welle (16) umgibt.
daß der Spindeltrieb (15) eine vertikal nach oben ragende Schubstange (28) aufweist, die über einen elastischen Druckstempel (27) auf den heb- und senkbaren Teil (11) des Möbelstücks (10) einwirkt.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Druckstempel (27) auf die Unterseite einer relativ zu feststehenden Seitenteilen (12, 13) heb-und senkbaren Tischplatte (11) eines Arbeitstisches (10) einwirkt.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß die feststehenden Teile (17, 18) der Teleskopvorrichtungen (17, 18, 21, 22) an den Seitenteilen (12, 13) des Arbeitstisches (10) montiert sind.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Spindeltrieb (15) nahe einem Seitenteil (13) unterhalb der Tischplatte (11) des Arbeitstisches (10) montiert ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19782816849 DE2816849A1 (de) | 1978-04-18 | 1978-04-18 | Hebe- und senkvorrichtung fuer ein moebelstueck, insbesondere einen tisch |
| DE2816849 | 1978-04-18 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0004875A2 true EP0004875A2 (de) | 1979-10-31 |
| EP0004875A3 EP0004875A3 (en) | 1979-11-14 |
| EP0004875B1 EP0004875B1 (de) | 1981-05-13 |
Family
ID=6037328
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP79100844A Expired EP0004875B1 (de) | 1978-04-18 | 1979-03-20 | Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für ein Möbelstück, insbesondere einen Tisch |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0004875B1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE2816849A1 (de) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105725572A (zh) * | 2016-03-03 | 2016-07-06 | 祁旭东 | 一种支架 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0074019A3 (de) * | 1981-09-04 | 1985-11-06 | Asea Ab | Überwachungspult |
| US10034538B1 (en) * | 2017-05-05 | 2018-07-31 | Sauder Woodworking Co. | Height-adjustable work surface assembly |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE508600C (de) * | 1929-04-19 | 1930-09-29 | Arno Doerr | Als Fachgestell verwendbarer Tisch |
| DE930542C (de) * | 1949-06-26 | 1955-07-18 | Friedrich Moerschner | Gebrauchsmoebel, insbesondere Tische und Stuehle bzw. Polstersessel |
| SE360634B (de) * | 1972-02-24 | 1973-10-01 | Linden Alimak Ab |
-
1978
- 1978-04-18 DE DE19782816849 patent/DE2816849A1/de not_active Ceased
-
1979
- 1979-03-20 DE DE7979100844T patent/DE2960337D1/de not_active Expired
- 1979-03-20 EP EP79100844A patent/EP0004875B1/de not_active Expired
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105725572A (zh) * | 2016-03-03 | 2016-07-06 | 祁旭东 | 一种支架 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0004875A3 (en) | 1979-11-14 |
| EP0004875B1 (de) | 1981-05-13 |
| DE2816849A1 (de) | 1979-10-25 |
| DE2960337D1 (en) | 1981-08-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0234008B1 (de) | Präzisionswaage | |
| EP0017765B1 (de) | Hydraulische Hebevorrichtung | |
| DE29500574U1 (de) | Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für Möbelelemente | |
| EP0074019A2 (de) | Überwachungspult | |
| DE9116652U1 (de) | Dachdeckelanordnung für ein Kraftfahrzeug | |
| EP0437283A1 (de) | Fahrzeugschiebedach | |
| EP0401465A2 (de) | Küchenarbeitseinheit | |
| EP0004875B1 (de) | Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für ein Möbelstück, insbesondere einen Tisch | |
| DE2846223A1 (de) | Arbeitstisch | |
| DE1559725B1 (de) | Hebebeschlag fuer den Fluegelrahmen eines Schiebefensters oder einer Schiebetuer | |
| DE3242523C2 (de) | Einrichtung zur Schnellverstellung von Mikroskoptischen | |
| DE1555632A1 (de) | Scheibenfuehrung fuer in den Fensterschacht eines Fahrzeuges versenkbare Schiebefenster | |
| DE19517656C2 (de) | Hebe- und Senkvorrichtung für Möbelelemente | |
| DE3037375A1 (de) | Hoehenverstellbarer objekttraeger | |
| DE202005000589U1 (de) | Hebeschiebeanlage | |
| DE2649868A1 (de) | Zeichentisch fuer hoehenverstellbare zeichenbretter | |
| EP0132448B1 (de) | Tisch mit verstellbarer Tischplatte | |
| DE2952716A1 (de) | Fensterheber, insbesondere fuer kraftfahrzeugfenster | |
| DE2600753A1 (de) | Ausziehtisch, insbesondere hoehenverstellbarer ausziehtisch | |
| DE3025958C2 (de) | Ausziehtisch für Möbel, insbesondere Küchenmöbel | |
| DE212018000408U1 (de) | Einstellvorrichtung | |
| DE29611496U1 (de) | Kombinationsbett | |
| EP1813170B1 (de) | Sitz- oder Liegemöbel | |
| DE1530517C3 (de) | Horizontal und vertikal verstellbarer Sitz, insbesondere für Kraftfahrzeuge | |
| DE9109033U1 (de) | Parallelführungsbeschlag für Türen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 2960337 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19810820 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19890131 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19890331 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19890622 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19900321 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19900331 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19900331 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: NIXDORF COMPUTER A.G. Effective date: 19900331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19901001 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19920228 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19920323 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19920331 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19920521 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CD |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19930320 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19930320 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19931130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19931201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 79100844.4 Effective date: 19910109 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |