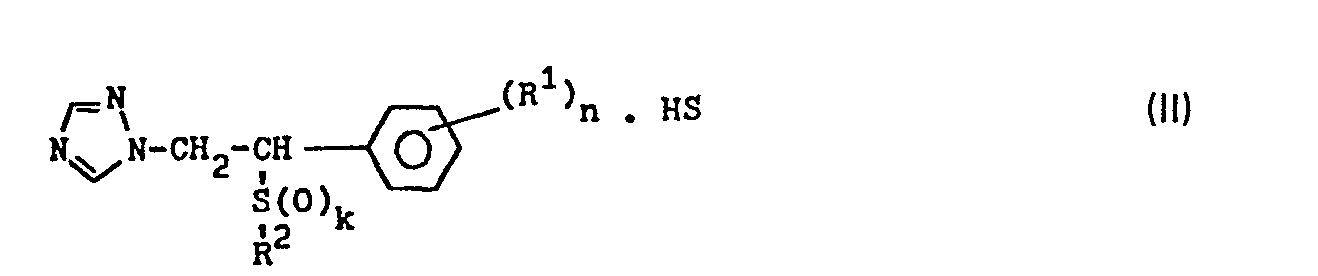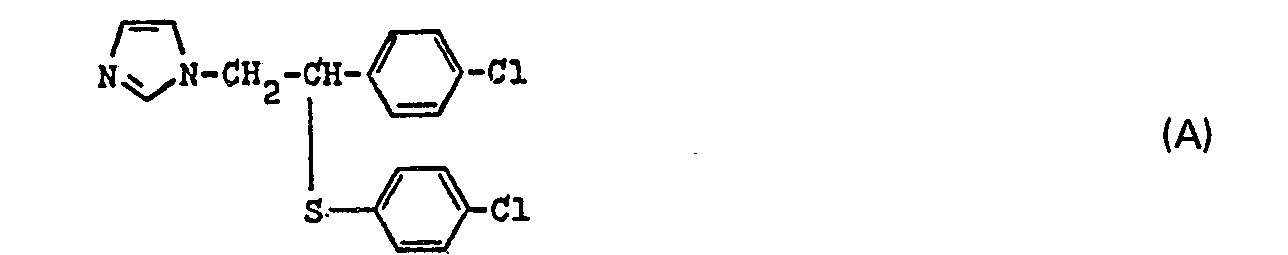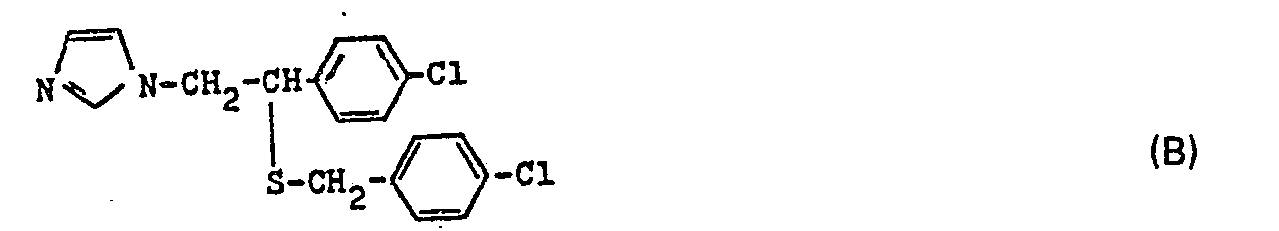EP0000112B1 - Triazolsubstituierte Schwefelverbindungen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie ihre Verwendung als Fungizide - Google Patents
Triazolsubstituierte Schwefelverbindungen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie ihre Verwendung als Fungizide Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0000112B1 EP0000112B1 EP78100044A EP78100044A EP0000112B1 EP 0000112 B1 EP0000112 B1 EP 0000112B1 EP 78100044 A EP78100044 A EP 78100044A EP 78100044 A EP78100044 A EP 78100044A EP 0000112 B1 EP0000112 B1 EP 0000112B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- triazole
- ethyl
- parts
- dichlorophenyl
- carbon atoms
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- -1 Triazol-substituted sulphur Chemical class 0.000 title claims description 30
- 239000000417 fungicide Substances 0.000 title claims description 12
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title description 4
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 16
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 claims description 12
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000000855 fungicidal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims 4
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 claims 3
- 125000001246 bromo group Chemical group Br* 0.000 claims 2
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 claims 2
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 22
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 19
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 18
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 125000004201 2,4-dichlorophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C(Cl)C([H])=C1Cl 0.000 description 11
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 9
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 9
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 8
- 240000005979 Hordeum vulgare Species 0.000 description 7
- 235000007340 Hordeum vulgare Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 6
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(III) oxide Inorganic materials O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 6
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 241001480061 Blumeria graminis Species 0.000 description 5
- 241000221785 Erysiphales Species 0.000 description 5
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 5
- WBIQQQGBSDOWNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1S(O)(=O)=O WBIQQQGBSDOWNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 235000007319 Avena orientalis Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 244000075850 Avena orientalis Species 0.000 description 4
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241000209140 Triticum Species 0.000 description 4
- 235000021307 Triticum Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000013339 cereals Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 244000038559 crop plants Species 0.000 description 4
- 229940060296 dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 4
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 4
- UENGBOCGGKLVJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)ethanone Chemical compound FC1=CC=C(C(=O)CCl)C(F)=C1 UENGBOCGGKLVJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic anhydride Chemical compound CC(=O)OC(C)=O WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241001295925 Gegenes Species 0.000 description 3
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 3
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 244000046052 Phaseolus vulgaris Species 0.000 description 3
- 235000010627 Phaseolus vulgaris Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 3
- CODNYICXDISAEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine monochloride Chemical compound BrCl CODNYICXDISAEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004359 castor oil Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000019438 castor oil Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000012990 dithiocarbamate Substances 0.000 description 3
- ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N glycerol triricinoleate Natural products CCCCCC[C@@H](O)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@@H](O)CCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@H](O)CCCCCC ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- IXCSERBJSXMMFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen chloride Substances Cl.Cl IXCSERBJSXMMFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910000041 hydrogen chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229920005610 lignin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 3
- XEPBBUCQCXXTGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-dimethyl-n-phenylfuran-3-carboxamide Chemical compound O1C(C)=CC(C(=O)NC=2C=CC=CC=2)=C1C XEPBBUCQCXXTGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YTOPFCCWCSOHFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dimethyl-4-tridecylmorpholine Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCN1CC(C)OC(C)C1 YTOPFCCWCSOHFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UPTVJAJPBGIRLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(trichloromethylsulfanyl)-3a,4,5,7a-tetrahydroisoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1CC=CC2C(=O)N(SC(Cl)(Cl)Cl)C(=O)C21 UPTVJAJPBGIRLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Methylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1S(O)(=O)=O LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FSCWZHGZWWDELK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-5-ethenyl-5-methyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione Chemical compound O=C1C(C)(C=C)OC(=O)N1C1=CC(Cl)=CC(Cl)=C1 FSCWZHGZWWDELK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azaniumyl-2-hydroxypropanoate Chemical compound NCC(O)C(O)=O BMYNFMYTOJXKLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OOTHTARUZHONSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(2-chlorophenyl)hydrazinylidene]-3-methyl-1,2-oxazol-5-one Chemical compound CC1=NOC(=O)C1=NNC1=CC=CC=C1Cl OOTHTARUZHONSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZXOZSQDJJNBRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-chlorobenzenethiol Chemical compound SC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 VZXOZSQDJJNBRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000895502 Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici Species 0.000 description 2
- 240000004244 Cucurbita moschata Species 0.000 description 2
- NDUPDOJHUQKPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dalapon Chemical compound CC(Cl)(Cl)C(O)=O NDUPDOJHUQKPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000221787 Erysiphe Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000510928 Erysiphe necator Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000896222 Erysiphe polygoni Species 0.000 description 2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001732 Lignosulfonate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001337928 Podosphaera leucotricha Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000896203 Podosphaera pannosa Species 0.000 description 2
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical compound [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfurous acid Chemical compound OS(O)=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001807 Urea-formaldehyde Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 150000008052 alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000012211 aluminium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- IMHBYKMAHXWHRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N anilazine Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1NC1=NC(Cl)=NC(Cl)=N1 IMHBYKMAHXWHRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NBNTWDUNCHRWMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(4-chlorophenyl)-pyridin-3-ylmethanol Chemical compound C=1C=C(Cl)C=CC=1C(C=1C=NC=CC=1)(O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 NBNTWDUNCHRWMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WQAQPCDUOCURKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N butanethiol Chemical compound CCCCS WQAQPCDUOCURKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 159000000007 calcium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- TWFZGCMQGLPBSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbendazim Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(NC(=O)OC)=NC2=C1 TWFZGCMQGLPBSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940125904 compound 1 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940126214 compound 3 Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1 JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CJHXCRMKMMBYJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethirimol Chemical compound CCCCC1=C(C)NC(N(C)C)=NC1=O CJHXCRMKMMBYJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- JMXKCYUTURMERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodemorph Chemical compound C1C(C)OC(C)CN1C1CCCCCCCCCCC1 JMXKCYUTURMERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 2
- CKAPSXZOOQJIBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexachlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1Cl CKAPSXZOOQJIBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical compound I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940071870 hydroiodic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutanol Chemical compound CC(C)CO ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052943 magnesium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000019341 magnesium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010446 mineral oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- OYRIKLVYHTWHCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-cyclohexyl-2,5-dimethylfuran-3-carboxamide Chemical compound O1C(C)=CC(C(=O)NC2CCCCC2)=C1C OYRIKLVYHTWHCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000006072 paste Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003032 phytopathogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- MCJGNVYPOGVAJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinolin-8-ol Chemical compound C1=CN=C2C(O)=CC=CC2=C1 MCJGNVYPOGVAJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012312 sodium hydride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000104 sodium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium hydroxide Inorganic materials [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrachloromethane Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)Cl VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGHREAKMXXNCOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiophanate-methyl Chemical compound COC(=O)NC(=S)NC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=S)NC(=O)OC QGHREAKMXXNCOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KUAZQDVKQLNFPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiram Chemical compound CN(C)C(=S)SSC(=S)N(C)C KUAZQDVKQLNFPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960002447 thiram Drugs 0.000 description 2
- YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichloroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- WHOZNOZYMBRCBL-OUKQBFOZSA-N (2E)-2-Tetradecenal Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCC\C=C\C=O WHOZNOZYMBRCBL-OUKQBFOZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GKQXPTHQTXCXEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-chlorophenyl)methanethiol Chemical compound SCC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 GKQXPTHQTXCXEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GJJSIBHNXGFVAA-FOCLMDBBSA-N (E)-3-(dinitromethyl)-4-methyl-2-phenyldec-2-enoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(C)C(\C([N+]([O-])=O)[N+]([O-])=O)=C(/C(O)=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 GJJSIBHNXGFVAA-FOCLMDBBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YIKWKLYQRFRGPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-dodecylguanidine acetate Chemical compound CC(O)=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCN=C(N)N YIKWKLYQRFRGPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IUWQJWIKCTXFIT-PJQLUOCWSA-N 2,3-dinitrooctan-2-yl (e)-2-phenylbut-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCCCC([N+]([O-])=O)C(C)([N+]([O-])=O)OC(=O)C(=C\C)\C1=CC=CC=C1 IUWQJWIKCTXFIT-PJQLUOCWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CWOLHXOFHDPLQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-heptadecyl-4,5-dihydroimidazol-1-yl)acetic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC1=NCCN1CC(O)=O CWOLHXOFHDPLQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NFAOATPOYUWEHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(6-methylheptyl)phenol Chemical compound CC(C)CCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1O NFAOATPOYUWEHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYELSNVLZVIGTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-[2-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-ylamino)pyrimidin-5-yl]-5-ethylpyrazol-1-yl]-1-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)ethanone Chemical compound C1C(CC2=CC=CC=C12)NC1=NC=C(C=N1)C=1C=NN(C=1CC)CC(=O)N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2 FYELSNVLZVIGTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YAUCKEPYKXHCFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-carbamothioylsulfanylethyl carbamodithioate;manganese Chemical compound [Mn].NC(=S)SCCSC(N)=S YAUCKEPYKXHCFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JMZRZEXRYJUHEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-carbamothioylsulfanylethyl carbamodithioate;zinc Chemical compound [Zn].NC(=S)SCCSC(N)=S JMZRZEXRYJUHEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZRDUSMYWDRPZRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-sec-butyl-4,6-dinitrophenyl 3-methylbut-2-enoate Chemical compound CCC(C)C1=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1OC(=O)C=C(C)C ZRDUSMYWDRPZRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SLRMQYXOBQWXCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2154-56-5 Chemical compound [CH2]C1=CC=CC=C1 SLRMQYXOBQWXCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BMZQYRRBCSGPRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3,3-trichloro-n-[4-(3,3,3-trichloropropanoylamino)piperazin-1-yl]propanamide Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)CC(=O)NN1CCN(NC(=O)CC(Cl)(Cl)Cl)CC1 BMZQYRRBCSGPRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006275 3-bromophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(Br)=C([H])C(*)=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- ZOYYBCOPCZOTAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-sulfanylidene-2-(trichloromethyl)isoindol-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=S)N(C(Cl)(Cl)Cl)C(=O)C2=C1 ZOYYBCOPCZOTAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CDIJOYCNNFLOAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(trichloromethylsulfanyl)isoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)SC1=CC=CC2=C1C(=O)NC2=O CDIJOYCNNFLOAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWSWPOJRYCYBRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4h-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium;chloride Chemical compound Cl.C=1N=CNN=1 BWSWPOJRYCYBRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005725 8-Hydroxyquinoline Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005995 Aluminium silicate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000235349 Ascomycota Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000221198 Basidiomycota Species 0.000 description 1
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bisulfite Chemical compound OS([O-])=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- JOIQIUVYCDOANM-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCC(C)C1=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1C(=C(C)C)C(O)=O Chemical compound CCC(C)C1=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1C(=C(C)C)C(O)=O JOIQIUVYCDOANM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- REEFSLKDEDEWAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloraniformethan Chemical compound ClC1=CC=C(NC(NC=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl)C=C1Cl REEFSLKDEDEWAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 240000007154 Coffea arabica Species 0.000 description 1
- 229910021592 Copper(II) chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 240000008067 Cucumis sativus Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000009849 Cucumis sativus Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cyclohexane Chemical compound C1CCCCC1 XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dihydrogen disulfide Chemical compound SS BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HDWLUGYOLUHEMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dinobuton Chemical compound CCC(C)C1=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1OC(=O)OC(C)C HDWLUGYOLUHEMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTDRLOKFLJJHTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Furmecyclox Chemical compound C1=C(C)OC(C)=C1C(=O)N(OC)C1CCCCC1 QTDRLOKFLJJHTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000068988 Glycine max Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000010469 Glycine max Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- DYMNZCGFRHLNMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glyodin Chemical compound CC(O)=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC1=NCCN1 DYMNZCGFRHLNMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000219146 Gossypium Species 0.000 description 1
- 244000070406 Malus silvestris Species 0.000 description 1
- MZNCVTCEYXDDIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Mebenil Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 MZNCVTCEYXDDIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LSDPWZHWYPCBBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanethiol Chemical compound SC LSDPWZHWYPCBBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000896238 Oidium Species 0.000 description 1
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000005662 Paraffin oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000221300 Puccinia Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001123561 Puccinia coronata Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001123569 Puccinia recondita Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000004789 Rosa xanthina Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241000109329 Rosa xanthina Species 0.000 description 1
- 240000000111 Saccharum officinarum Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007201 Saccharum officinarum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 241000209056 Secale Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007238 Secale cereale Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 240000008042 Zea mays Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000005824 Zea mays ssp. parviglumis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000002017 Zea mays subsp mays Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N [C]1=CC=CC=C1 Chemical compound [C]1=CC=CC=C1 CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DODVABAEAOOKOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N [carbamimidoyl(dodecyl)amino] acetate Chemical compound C(C)(=O)ON(C(=N)N)CCCCCCCCCCCC DODVABAEAOOKOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000008055 alkyl aryl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940045714 alkyl sulfonate alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001450 anions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000021016 apples Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002969 artificial stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000005228 aryl sulfonate group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- LJOZMWRYMKECFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N benodanil Chemical compound IC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 LJOZMWRYMKECFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RIOXQFHNBCKOKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benomyl Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(C(=O)NCCCC)C(NC(=O)OC)=NC2=C1 RIOXQFHNBCKOKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DKVNPHBNOWQYFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbamodithioic acid Chemical compound NC(S)=S DKVNPHBNOWQYFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CSNJTIWCTNEOSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbamothioylsulfanyl carbamodithioate Chemical compound NC(=S)SSC(N)=S CSNJTIWCTNEOSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GYSSRZJIHXQEHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N carboxin Chemical compound S1CCOC(C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 GYSSRZJIHXQEHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1 MVPPADPHJFYWMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000008422 chlorobenzenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000016213 coffee Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000013353 coffee beverage Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000013066 combination product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940127555 combination product Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940125782 compound 2 Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000001879 copper Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L copper(II) chloride Substances Cl[Cu]Cl ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 235000005822 corn Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanol Chemical compound OC1CCCCC1 HPXRVTGHNJAIIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000004659 dithiocarbamates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013399 edible fruits Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- KQTVWCSONPJJPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N etridiazole Chemical compound CCOC1=NC(C(Cl)(Cl)Cl)=NS1 KQTVWCSONPJJPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002191 fatty alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003337 fertilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035784 germination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003630 growth substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000004009 herbicide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000003898 horticulture Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002917 insecticide Substances 0.000 description 1
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical group II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N kaolin Chemical compound O.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=O NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940074355 nitric acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000002828 nitro derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid group Chemical group C(CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC)(=O)O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- AMEKQAFGQBKLKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxycarboxin Chemical compound O=S1(=O)CCOC(C)=C1C(=O)NC1=CC=CC=C1 AMEKQAFGQBKLKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003540 oxyquinoline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940044654 phenolsulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960004838 phosphoric acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 231100000208 phytotoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000000885 phytotoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000021110 pickles Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- KNCYXPMJDCCGSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N piperidine-2,6-dione Chemical compound O=C1CCCC(=O)N1 KNCYXPMJDCCGSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000151 polyglycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000010695 polyglycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- ODGAOXROABLFNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N polynoxylin Chemical compound O=C.NC(N)=O ODGAOXROABLFNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012047 saturated solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium carbonate Substances [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002689 soil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003457 sulfones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003464 sulfur compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940032330 sulfuric acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- YFNCATAIYKQPOO-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiophanate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)NC(=S)NC1=CC=CC=C1NC(=S)NC(=O)OCC YFNCATAIYKQPOO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011135 tin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000009827 uniform distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000013311 vegetables Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
- DUBNHZYBDBBJHD-UHFFFAOYSA-L ziram Chemical compound [Zn+2].CN(C)C([S-])=S.CN(C)C([S-])=S DUBNHZYBDBBJHD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D231/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings
- C07D231/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D231/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D231/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/64—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/647—Triazoles; Hydrogenated triazoles
- A01N43/653—1,2,4-Triazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,4-triazoles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D233/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D233/54—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D233/56—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms or radicals containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms, attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D249/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D249/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms not condensed with other rings
- C07D249/08—1,2,4-Triazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,4-triazoles
Definitions
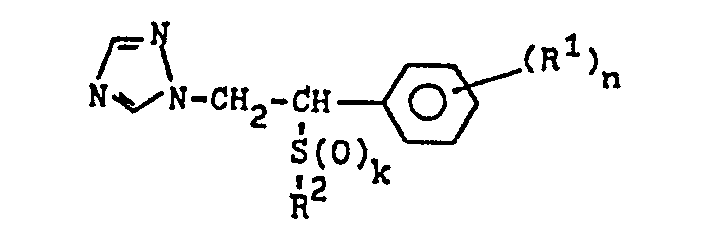
- the invention relates to valuable triazole-substituted sulfur compounds, their salts and metal complex salts with good fungicidal activity, to processes for their preparation and to fungicides which contain these compounds as active compounds.
- imidazole-substituted sulfur compounds as fungicides for controlling phytopathogenic fungi (DE-OS 25 41 833).
- they often only act against a specific fungus or against a specific class of fungus, or cause damage to the crop plants or, when used as a mordant, cause germination delays and damage caused by emergence, so that their general and broad application are subject to strict limits.
- the salts have the general formula II in which R ', R 2 , n and k have the meanings given above and HS denotes any organic or inorganic acid which, however, must not be phytotoxic at the application rates used and must be able to react with the compounds of the general formula 1 To form salts.
- Particularly suitable acids are sulfuric acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, phosphoric acid, trichloroacetic acid, dichloropropionic acid, oxalic acid, toluenesulfonic acid and dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid.
- the compounds of the general formula II can be prepared by simply adding the acids HS to the compounds of the general formula I, if appropriate in a solvent.
- the metal complex salts have the general formula Ila in which R 1 , R 2 , n and k have the meanings given above, p and q are the numbers 1 to 4, Y ⁇ is an equivalent of an anion of an inorganic or organic acid and Me is a metal from the 1st, 11th and IV. To VIII. Subgroup and from de II. And IV. Main group of the periodic system.
- Such metals are: copper, iron, zinc and tin.
- the metal complex salts can be prepared by reacting a metal salt with a compound of the general formula I in a solvent.
- the compounds of the general formula can be reacted with 2-haloethyl-1,2,4-triazoles of the general formula III in which R 1 and n have the meaning given above and X is chlorine, bromine or iodine, with a mercaptide of the general formula IV in which R 2 has the meaning given above, in a solvent.
- the mercaptide is prepared from the associated mercaptan by reaction with a base before or during the reaction.
- the compounds of general formula I in which k represents the numbers 1 or 2, are converted from compounds of general formula I, in which k represents the number 0, by oxidation with an oxygen-donating reagent according to the customary, generally known methods of oxidizing sulfides Sulfoxides and sulfones manufactured.
- the fungicidal compounds according to the invention are obtained either in the form of the free bases or their salts.
- the salts can be converted to the free bases in the usual manner, e.g. by reaction with alkali such as sodium or potassium hydroxide, sodium or potassium carbonate, ammonia or similar alkalis.
- alkali such as sodium or potassium hydroxide, sodium or potassium carbonate, ammonia or similar alkalis.
- suitable acids e.g.
- inorganic acids such as hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, organic acids such as trichloroacetic acid, dichloropropionic acid, oxalic acid, toluenesulfonic acid or higher alkylbenzenesulfonic acids such as dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid can be converted into the salts which are valuable in terms of application technology.
- Hydrogen chloride is gassed into the extract, 25.9 parts of 1 - [2-butylmercapto-2 - (2,4-dichlorophenyl) - ethyl - (1)] 1,2,4-triazole hydrochloride precipitate out, which after recrystallization from ethyl acetate melt at 143 ° C.
- the triazole-substituted sulfur compounds according to the invention and their salts and metal complex salts are notable for excellent activity against a broad spectrum of phytopathogenic fungi. Some of them are systemically effective and can be used as foliar and soil fungicides, but also as mordants and as technical fungicides.
- the fungicidal compounds are particularly interesting for controlling a large number of fungi on different crop plants.
- crops to mean, in particular, wheat, rye, barley, oats, rice, corn, cotton, soybeans, coffee, sugar cane, fruit and ornamental plants in horticulture, and also vegetables such as cucumbers, beans and pumpkin plants.
- the formulations generally contain between 0.1 and 95% by weight of active compound, preferably between 0.5 and 90%.
- formulations or the ready-to-use preparations produced therefrom, such as solutions, emulsions, suspensions, powders, dusts, pickles, pastes or granules, are used in a known manner.
- the application rates are between 0.01 and 3, but preferably between 0.01 and 1 kg of active ingredient per hectare.
- the agents according to the invention can also be present together with other active ingredients, such as e.g. Herbicides, insecticides, growth regulators and fungicides or also mixed with fertilizers and applied.
- active ingredients such as e.g. Herbicides, insecticides, growth regulators and fungicides or also mixed with fertilizers and applied.
- the fungicidal spectrum of activity is enlarged; a number of these fungicide mixtures also have synergistic effects, i.e. the fungicidal activity of the combination product is greater than that of the added activity of the individual components.
- Leaves of barley seedlings grown in pots are sprayed with aqueous emulsions of 80% (% by weight) active ingredient and 20% emulsifier and, after the spray coating has dried on, are dusted with oidia (spores) of the barley powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis var. Hordei).
- the test plants are then placed in a greenhouse at temperatures between 20 and 22 ° C and 75 to 80% relative humidity. After 10 days, the extent of mildew development is determined.
- Leaves of potted wheat seedlings of the "Jubilar” variety are sprayed with aqueous emulsions of 80% (weight percent) active ingredient and 20% emulsifier and, after the spray coating has dried on, are dusted with oidia (spores) of the powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis var. Tritici).
- the test plants are then placed in a greenhouse at temperatures between 20 and 22 ° C and 75 to 80% relative humidity. The extent of mildew development is determined after 10 days.
- leaves of pots of oat seed of the "Flämings Krone" variety are dusted with spores of the oat crown rust (Puccinia coronata) and placed in a chamber with high atmospheric humidity.
- the infected plants are then sprayed to runoff point with 0.05% (by weight) aqueous spray liquors which contain 80% active ingredient and 20% lignin sulfonate in the dry matter.
- the test plants are grown in the greenhouse at temperatures between 20 and 22 ° C. and 65 to 70% rel. Humidity set up. After 8 days, the extent of the rust fungus development on the leaves is determined.
- active ingredient 2 20 parts by weight of active ingredient 2 are mixed well with 3 parts by weight of the sodium acid of diisobutylnaphthalene-a-sulfonic acid, 17 parts by weight of the sodium salt of lignin sulfonic acid from a sulfite waste liquor and 60 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and ground in a hammer mill.
- a spray liquor is obtained which contains 0.1% by weight of the active ingredient.
- active ingredient 1 40 parts by weight of active ingredient 1 are intimately mixed with 10 parts of sodium salt of a phenolsulfonic acid urea-formaldehyde condensate, 2 parts of silica gel and 48 parts of water. A stable aqueous dispersion is obtained. Dilution with 100,000 parts by weight of water gives an aqueous dispersion which contains 0.04% by weight of active ingredient.
- active ingredient 2 20 parts are intimately mixed with 2 parts of calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts of fatty alcohol polyglycol ether, 2 parts of sodium salt of a phenolsulfonic acid-urea-formaldehyde condensate and 68 parts of a paraffinic mineral oil. A stable oily dispersion is obtained.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Agronomy & Crop Science (AREA)
- Pest Control & Pesticides (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft wertvolle triazolsubstituierte Schwefelverbindungen, ihre Salze und Metallkomplexsalze mit guter fungizider Wirkung sowie Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und Fungizide, die diese Verbindungen als Wirkstoffe enthalten.
- Es ist bekannt, imidazolsubstituierte Schwefelverbindungen als Fungizide zur Bekämpfung pflanzenpathogener Pilze zu verwenden (DE-OS 25 41 833). Sie wirken jedoch häufig nur gegen einen bestimmten Pilz oder nur gegen eine bestimmte Pilzklasse, oder verursachen Schäden an den Kulturpflanzen oder bewirken bei der Verwendung als Beizmittel Keimverzögerungen und Auflaufschäden, so daß ihrer allgemeinen und breiten Anwendung enge Grenzen gesetzt sind.
-
- R' Wasserstoff, Fluor, Chlor, Brom, einen Alkylrest mit 1 bis 5 Kohlenstoffatomen, eine Trifluormethyl-, Phenyl- oder Alkoxygruppe mit 1 bis 3 Kohlenstoffatomen,
- n die Zahlen 1 bis 3 bedeutet, wobei für n gleich 2 oder 3 die Reste R' gleich oder verschieden sein können,
- R2 einen geradkettigen oder verzweigten Alkylrest mit 1 bis 14 Kohlenstoffatomen, der für den Fall des verzweigten Alkylrestes mehr als 2 Kohlenstoffatome enthält, einen Phenylrest der Formel
- R4 Wasserstoff, Fluor, Chlor, Brom, einen Alkylrest mit 1 bis 5 Kohlenstoffatomen, eine Trifluormethyl-, Phenyl- oder Alkoxygruppe mit 1 bis 3 Kohlenstoffatomen,
- R5 Wasserstoff, Fluor, Chlor, Brom, einen Alkylrest mit 1 bis 5 Kohlenstoffatomen, eine Trifluormethyl-, Phenyl- oder Alkoxygruppe mit 1 bis 3 Kohlenstoffatomen,
- m die Zahlen 1 bis 3 bedeutet, wobei für m gleich 2 oder 3 die Reste R4 gleich oder verschieden sein können,
- I die Zahlen 1 bis 3 bedeutet, wobei für 1 gleich 2 oder 3 die Reste R5 gleich oder verschieden sein können und
- k die Zahlen 0, 1 oder 2 bedeutet,
- und ihre Salze und Metallkomplexsalze eine sehr gute fungizide Wirkung besitzen, keine mit den bekannten Wirkstoffen vergleichbaren Schädigungen an Kulturpflanzen hervorrufen und in ihrer ausgezeichneten Wirksamkeit gegen ein breites Spektrum von Pilzen den bekannten Wirkstoffen überlegen sind, wobei ihre gleichzeitige Wirksamkeit sowohl gegen Pilze aus der Klasse der Ascomyceten als auch gegen solche aus der Klasse der Basidiomyceten hervorzuheben ist.
- Die Salze haben die allgemeine Formel II
- Die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel II können durch einfache Addition der Säuren HS an die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel I, gegebenenfalls in einem Lösungsmittel, hergestellt werden.
- Die Metallkomplexsalze haben die allgemeine Formel Ila
- Solche Metalle sind beispielsweise: Kupfer, Eisen, Zink und Zinn.
- Die Metallkomplexsalze können durch Umsetzung eines Metallsalzes mit einer Verbindung der allgemeinen Formel I in einem Lösungsmittel hergestellt werden.
- Die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel lassen sich für den Fall k = 0 durch Umsetzung von 2-Halogenäthyl-1,2,4-triazolen der allgemeinen Formel III
- Die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel III sind bekannt aus der DE-OS 25 47 954.
- Die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel I, in denen k die Zahlen 1 oder 2 darstellt, werden aus Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel I, in denen k die Zahl 0 bedeutet, durch Oxidation mit einem sauerstoffabgebenden Reagens nach den üblichen allgemein bekannten Verfahren der Oxidation von Sulfiden zu Sulfoxiden und Sulfonen hergestellt. Die Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel I, bei denen k = 2 bedeutet, lassen isch auch durch Oxidation der Verbindungen der allgemeinen Formel 1, bei denen k = 1 bedeutet, nach den üblichen Methoden herstellen.
- In Abhängigkeit von den Bedingungen, unter denen die Reaktionen durchgeführt werden, fallen die erfindungsgemäßen fungiziden Verbindungen entweder in Form der freien Basen oder ihrer Salze an. Die Salze können in der üblichen Weise in die freien Basen umgewandelt werden, z.B. durch Umsetzung mit Alkali wie Natrium- oder Kaliumhydroxid, Natrium- oder Kaliumcarbonat, Ammoniak oder ähnlichen Alkalien. Die Verbindungen in Basenform können durch Umsetzung mit geeigneten Säuren, z.B. anorganischen Säuren, wie Salzsäure, Bromwasserstoffsäure, Jodwasserstoffsäure, Schwefelsäure, Salpetersäure, Phosphorsäure, organischen Säuren, wie Trichloressigsäure, Dichlorpropionsäure, Oxalsäure, Toluolsulfonsäure oder höhere Alkylbenzolsulfonsäuren wie Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure in die anwendungstechnisch wertvollen Salze umgewandelt werden.
- Einige charakteristische Beispiele sollen das Herstellungsverfahren erläutern.
- Im folgenden verstehen sich alle Teile als Gewichtsteile und alle Prozente als Gewichtsprozente.
- 21 Teile 4-Chlorthiophenol, 400 Teile Aceton, 20,2 Teile 1 - [2 - (3 - Bromphenyl) - 2 - chloräthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol und 22 Teile Kaliumcarbonat werden unter gutem Rühren 8 Stunden zum Sieden erhitzt. Man engt ein und verrührt den Rückstand mit 200 Teilen Wasser, extrahiert 2 mal mit 150 Teilen Methylenchlorid, wäscht den Extrakt 2 mal mit 50 Teilen Wasser, trocknet mit Magnesiumsulfat, filtriert und dampft ein. Das zurückbleibende ÖI wird in Äthylacetat gelöst und in die Lösung Chlorwasserstoff bis zur Sättigung eingeleitet. Beim Absaugen erhält man 30 teile 1 - [2 - (3 - Bromphenyl) - 2 - (4 - chlorphenylmercapto) - äthyl - (1)J - 1,2,4 - triazolhydrochlorid, das nach dem Umkristallisieren aus Isopropanol bei 172 bis 173°C schmilzt.
- Eine Mischung von 24 Teilen 4-Chlorthiophenol, 22 Teilen 1 - [2 - Chlor - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol, 25 Teilen Kaliumcarbonat und 400 Teilen Aceton wird 12 Stunden unter Luftausschluß zum Sieden erhitzt. Anschließend wird filtriert und das Filtrat eingeengt. Nach dem Umkristallisieren aus Cyclohexan verbleiben 22 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)J - 1,2,4 - triazol vom Schmelzpunkt 72°C.
- Zu einer gut gerührten Suspension von 3,33 Teilen Natriumhydrid in 150 Teilen Tetrahydrofuran gibt man 22,4 Teile 4-Chlorbenzylmercaptan und rührt 1/2 Stunde. Anschließend tropft man 27,5 Teile 1 - [2 - Chlor - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol, gelöst in 40 Teilen Tetrahydrofuran, zu und läßt 2 Tage rühren. Danach werden 10 Teile Wasser zugetropft und die Reaktionsmischung wird eingedampft. Man verrührt den Rückstand mit 200 Teilen Wasser und ebensoviel Essigester, trennt den letzteren ab, wächst ihn mit Wasser, trocknet mit Natriumsulfat, filtriert und leitet Chlorwasserstoff bis zur Sättigung ein. Es fallen 30,6 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorbenzylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazolhydrochlorid aus, die nach dem Umkristallisieren bei 178°C schmelzen.
- 3,33 Teile Natriumhydrid werden in 150 Teilen Tetrahydrofuran suspendiert und mit 12,6 Teilen Butylmercaptan zur Reaktion gebracht. Dann gibt man bei Raumtemperatur 27,5 Teile 1 - [2 - Chlor - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorophenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol, die man zuvor in 50 Teilen Tetrahydrofuran gelöst hat, zu und läßt 3 Tage rühren. Anschließend tropft man 10 Teile Wasser zu, dampft ein, schlämmt mit Wasser auf und extrahiert mit Äthylacetat. In den Extrakt gast man Chlorwasserstoff ein, wobei 25,9 Teile 1 - [2 - Butylmercapto - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] 1,2,4 triazolhydrochlorid ausfallen, die nach dem Umkristallisieren aus Äthylacetat bei 143°C schmelzen.
- 10 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol werden in 100 Teilen Diäthyläther gelöst und mit einer gesättigten Lösung von Oxalsäure in Diäthyläther versetzt. Es fallen 9,5 Teile 1 -[2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazoloxalat mit dem Schmelzpunkt 155°C aus.
- 10 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2.4 - triazol werden in 50 Teilen Eisessig gelöst und bei 10°C mit 2,95 Teilen 30 prozentigem Wasserstoffperoxid versetzt. Nach mehrtägigem Stehen bei Raumtemperatur gießt man auf 500 Teile Wasser, extrahiert die Mischung mit Methylenchlorid, wäscht letzteres mit Wasser, trocknet es mit Magnesiumsulfat und dampft ein. Man erhält 8 Teile 1 - [2 - (2 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazoloxid, die nach dem Umkristallisieren aus Tetrachlormethan bei 127°C schmelzen.
- 10 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol werden in einer Mischung aus 50 Teilen Eisessig und 50 Teilen Acetanhydrid gelöst und mit 9 Teilen 30%igem Wasserstoffperoxid versetzt. Man erwärmt 1 Tag auf 80°C, gießt dann auf 300 Teile Wasser und saugt die ausfallenden Kristalle ab. Man erhält 8,4 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)J - 1,2,4 - triazoldioxid, die nach dem Reinigen bei 145°C schmelzen.
-
-
- Die erfindungsgemäßen triazolsubstituierten Schwefelverbindungen und ihre Salze und Metallkomplexsalze zeichen sich durch eine hervorragende Wirksamkeit gegen ein breites Spektrum von pflanzenpathogenen Pilzen aus. Sie sind zum Teil systemisch wirksam und können als Blatt- und Bodenfungizide, aber auch als Beizmittel sowie als technische Fungizide eingesetzt werden.
- Besonders interessant sind die fungiziden Verbindungen für die Bekämpfung einer Vielzahl von Pilzen an verschiedenen Kulturpflanzen. Unter-Kulturpflanzen verstehen wir in diesem Zusammenhang insbesondere Weizen, Roggen, Gerste, Hafer, Reis, Mais, Baumwolle, Soja, Kaffee, Zuckerrohr, Obst und Zierpflanzen im Gartenbau, sowie Gemüse wie Gurken, Bohnen und Kürbisgewächse.
- Die Verbindungen sind insbesondere geeignet zur Bekämpfung folgender Pflanzenkrankheiten:
- Erysiphe graminis (echter Mehltau) an Getreide,
- Erysiphe cichoriacearum (echter Mehltau) an Kürbisgewächsen,
- Podosphaera leucotricha an Äpfeln,
- Uncinula necator an Reben,
- Erysiphe polygoni an Bohnen,
- Sphaerotheca pannosa an Rosen,
- Puccinia-Arten an Getreide,
- Uromvces-Arten an Bohnen.
- Die erfindungsgemäßen Substanzen können in die üblichen Formulierungen übergeführt werden, wie Lösungen, Emulsionen, Suspensionen, Stäube, Pulver, Pasten und Granulate. Die Anwendungsformen richten sich ganz nach den Verwendungszwecken; sie sollen in jedem Fall eine feine und gleichmäßige Verteilung der wirksamen Substanz gewährleisten. Die Formulierungen werden in bekannter Weise hergestellt, z.B. durch Verstrecken des Wirkstoffs mit Lösungsmitteln und/oder Trägerstoffen, gegebenenfalls under Verwendung von Emulgiermitteln und Dispergiermitteln, wobei im Falle der Benutzung von Wasser als Verdünnungsmittel auch andere organische Lösungsmittel als Hilfslösungsmittel verwendet werden können. Als Hilfsstoffe kommen dafür im wesentlichen in Frage:
- Lösungsmittel wie Aromaten (z.B. Xylol, Benzol), chlorierte Aromaten (z.B. Chlorbenzole), Paraffine (z.B. Erdölfraktionen), Alkohole (z.B. Methanol, Butanol), Amine (z.B. Äthanolamin, Dimethylformamid) und Wasser; Trägerstoffe wie natürliche Gesteinsmehle (z.B. Kaoline, Tonerden, Talkum, Kreide) und synthetische Gesteinsmehle (z.B. hochdisperse Kieselsäure, Silikate); Emulgiermittel wie nichtionogene und anionische Emulgatoren (z.B. Polyoxyäthylen - Fettalkohol - Äther, Alkylsulfonate und Arylsulfonate) und Dispergiermittel, wie Lignin, Sulfitablaugen und Methylcellulose.
- Die Formulierungen enthalten im allgemeinen zwischen 0,1 und 95 Gew.% Wirkstoff, vorzugsweise zwischen 0,5 und 90%.
- Die Formulierungen, bzw. die daraus hergestellten gebrauchsfertigen Zubereitungen, wie Lösungen, Emulsionen, Suspensionen, Pulver, Stäube, Beizen, Pasten oder Granulate werden in bekannter Weise angewendet.
- Die Aufwandmengen liegen nach Art des gewünschten Effektes zwischen 0,01 und 3, vorzugsweise jedoch zwischen 0,01 und 1 kg Wirkstoff pro Hektar.
- Die erfindungsgemäßen Mittel können in diesen Anwendungsformen auch zusammen mit anderen Wirkstoffen vorliegen, wie z.B. Herbiziden, Insektiziden, Wachstumsregulatoren und Fungiziden oder auch mit Düngemitteln vermischt und ausgebracht werden. Beim Vermischen mit Fungiziden. erhält man dabei in vielen Fällen eine Vergrößerung des fungiziden Wirkungsspektrums; bei einer Anzahl dieser Fungizidmischungen treten auch synergistische Effekte auf, d.h. die fungizide Wirksamkeit des Kombinationsproduktes ist größer als die der addierten Wirksamkeiten der Einzelkomponenten.
- Die folgende Liste von Fungiziden, mit denen die erfingungsgemäßen Verbindungen kombiniert werden können, soll die Kombinationsmöglichkeiten erläutern, nicht aber einschränken.
- Fungizide, die mit den erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen kombiniert werden können, sind beispielsweise:
- Dithiocarbamate und deren Derivate, wie
- Ferridimethyldithiocarbamat,
- Zinkdimethyldithiocarbamat,
- Manganäthylenbisdithiocarbamat,
- Mangan-Zink-äthylendiamin-bis-dithiocarbamat,
- Zinkäthylenbisdithiocarbamat,
- Tetramethylthiuramdisulfide,
- Ammoniak-Komplex von Zink-(N,N-äthylen-bis-dithiocarbamat)
- und N,N'-Polyäthylen-bis-(thiocarbamoyi)-disulfid,
- Zink-(N,N'-propylen-bis-dithiocarbamat),
- Ammoniak-Komplex von Zink-(N,N'-propylen-bis-dithiocarbamat)
- und N,N'-Polypropylen-bis-(thiocarbamoyl)-disulfid
- Nitroderivate, wie
- Dinitro-( 1-methylheptyl)-phenylcrotonat,
- 2-sec-Butyl-4,6-dinitrophenyl-3,3-dimethylacrylat,
- 2-sec-Butyl-4,6-dinitrophenyl-isopropylcarbonat;
- heterocyclische Strukturen, wie
- N-Trichlormethylthio-tetrahydrophthalimid,
- N-Trichlormethylthio-phthalimid,
- 2-Heptadecyl-2-imidazolin-acetat,
- 2,4-Dichloro-6-(o-chloranilino)-s-triazin,
- 0,0-Diäthyl-phthalimidophosphonothioat,
- 5-Amino-1-(bis-(dimethylaminol-phosphinyl)-3-phenyl-1,2,4-triazol,
- 5-Äthoxy-3-trichlormethyl-1,2,4-thiadiazol,
- 2,3-Dicyano-1,4-dithiaanthrachinon,
- 2-Thio-1,3-dithio-(4,5-b)-chinoxylin,
- 1-(Butylcarbamoyl)-2-benzimidazol-carbaminsäuremethylester,
- 2-Methoxycarbonylamino-benzimidazol,
- 2-Rhodanmethylthio-benzthiazol,
- 4-(2-Chlorphenylhydrazono)-3-methyl-5-isoxazolon, Pyridin-2-thio-1-oxid,
- 8-Hydroxychinolin bzw. dessen Kupfersalz,
- 2,3-Dihydro-5-carboxanilido-6-methyl-1,4-oxathiin-4,4-dioxid,
- 2,3-Dihydro-5-carboxanilido-6-methyl-1,4-oxathiin,
- 2-(Furyl-(2)-benzimidazol,
- 5-Methyl-5-vinyl-3-(3,5-dichlorphenyl)-2,4-dioxo-1,3-oxazolidin,
- N-Cyclohexyl-2,5-dimethylfuran-3-hydroxamsäuremethylester,
- Piperazin-1,4-diyl-bis-(1-(2,2,2-trichlor-äthyl)-formamid),
- 2-(Thiazolyl-(4)-benzimidazol,
- 5-Butyl-2-dimethylamino-4-hydroxy-6-methyl-pyrimidin,
- Bis-(p-Chlorphenyl)-3-pyridinmethanol,
- 1,2-Bis-(3-äthoxycarbonyl-2-thioureido)-benzol,
- 1,2-Bis-(3-methoxycarbonyl-2-thioureido)-benzol
- und verschiedene Fungizide, wie
- Dodecylguanidinacetat,
- 3-(2-(3,5-Dimethyl-2-oxycyclohexyl)-2-hydroxyäthyl)-glutarimid, Hexachlorbenzol,
- N-Dichlorfluormethylthio-N',N'-dimethyl-N-phenyl-schwefel- säurediamid,
- 2,5-Dimethyl-furan-3-carbonsäureanilid,
- 2,5-Dimethyl-furan-3-carbonsäure-cyclohexylamid,
- 2-Methyl-benzoesäure-anilid,
- 2-Jod-benzoesäure-anilid,
- 1-(3,4-Dichloranilino)-1-formylamino-2,2,2-trichloräthan,
- 2,6-Dimethyl-N-tridecyl-morpholin bzw. dessen Salze,
- 2,6-Dimethyl-N-cyclododecyl-morpholin bzw. dessen Salze.
-
- Blätter von in Töpfen gewachsenen Gerstenkeimlingen werden mit wäßrigen Emulsionen aus 80% (Gew.%) Wirkstoff und 20% Emulgiermittel besprüht und nach dem Antrocknen des Spritzbelages mit Oidien (Sporen) des Gerstenmehltaus (Erysiphe graminis var. hordei) bestäubt. Die Versuchspflanzen werden anschließend im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C und 75 bis 80% relativer Luftfeuchtigkeit aufgestellt. Nach 10 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Mehltaupilzentwicklung ermittelt.
- Blätter von in Töpfen gewachsenen Weizenkeimlingen der Sorte "Jubilar" werden mit wäßrigen Emulsionen aus 80% (Gewichtsprozent) Wirkstoff und 20% Emulgiermittel besprüht und nach dem Antrocknen des Spritzbelages mit Oidien (Sporen) des Weizenmehltaus (Erysiphe graminis var. tritici) bestäubt. Die Versuchspflanzen werden anschließend im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C und 75 bis 80% relativer Luftfeuchtigkeit aufgestellt. Nach 10 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Mehltauentwicklung ermittelt.
- Blätter von in Töpfen gewachsenen Weizensämlingen der Sorte "Caribo" werden mit Sporen des Braunrostes (Puccinia recondita) bestäubt. Danach werden die Töpfe für 24 Stunden bei 20 bis 22°C in eine Kammer mit hoher Luftfeuchtigkeit (90 bis 95%) gestellt. Während dieser Zeit keimen die Sporen aus und die Keimschläuche dringen in das Blattgewebe ein. Die infizierten Pflanzen werden anschließend mit 0,05%, 0,025 und 0,012%igen (Gew.%) wäßrigen Spritzbrühen, die 80% Wirkstoff und 20% Ligninsulfonat in der Trockensubstanz enthalten, tropfnass gespritzt. Nach dem Antrocknen des Spritzbelages werden die Versuchspflanzen im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C und 65 bis 70% relativer Luftfeuchte aufgestellt. Nach 8 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Rostpilzentwicklung auf den Blättern ermittelt.
- In gleicher Weise wie in Beispiel 10 angeführt, werden Blätter von in Töpfen gewachsenen Hafersämlengen der Sorte "Flämings Krone" mit Sporen des Haferkronenrostes (Puccinia coronata) bestäubt und in eine Kammer mit hoher Luftfeuchtigkeit gestellt. Die infizierten Pflanzen werden anschliesend mit 0,05%igen (Gew.%) wäßrigen Spritzbrühen, die 80% Wirkstoff und 20% Ligninsulfonat in der Trockensubstanz enthalten, tropfnaß gespritzt. Nach dem Antrocknen des Spritzbelages werden die Versuchspflanzen im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C und 65 bis 70% rel. Luftfeuchte aufgestellt. Nach 8 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Rostpilzentwicklung auf den Blättern ermittelt.
- 100 g-Proben Gerstensaatgut der Sorte "Asse" werden in Glasflaschen etwa 5 Minuten lang mit jeweils 300 mg (= 0,3 Gew.%) der in der Tabelle angeführten Beizmittel sorgfältig gebeizt. Danach werden jeweils 8 Körner in Töpfe eingelegt und mit Erde bedeckt. Zehn Tage nach dem Auflauf des Getreides werden die Blätter mit Oidium (Konidien) des Gerstenmehltaus (Erysiphe graminis var. hordei) bestäubt. Die Versuchspflanzen werden anschließend im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C rel. Luftfeuchte aufgestellt. Nach weiteren 10 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Mehltaupilzentwicklung auf den Blättern ermittelt.
- Man vermischt 90 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 1 mit 10 Gewichtsteilen N-Methyl-α-pyrrolidon und erhält eine Lösung, die zur Anwendung in Form kleinster Tropfen geeignet ist.
- 20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 2 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 80 Gewichtsteilen Xylol, 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 8 bis 10 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Olsäure-N-monoäthanolamid, 5 Gewichtsteilen Calciumsalz der Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure und 5 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Ausgießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- 20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 3 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 40 Gewichtsteilen Cyclohexanon, 30 Gewichtsteilen Isobutanol, 20 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 7 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Isooctylphenol und 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Eingießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- 20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 1 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 25 Gewichtsteilen Cyclohexanol, 65 Gewichtsteilen einer Mineralölfraktion vom Siedepunkt 210 bis 280°C und 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Athylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Eingießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- 20 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs 2 werden mit 3 Gewichtsteilen des Natriumsaizes der Diisobutylnaphthalin-a-sulfonsäure, 17 Gewichtsteilen des Natriumsalzes einer Ligninsulfonsäure aus einer Sulfit-Ablauge und 60 Gewichtsteilen pulverförmigen Kieselsäuregel gut vermischt und in einer Hammermühle vermahlen. Durch feines Verteilen der Mischung in 20 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine Spritzbrühe, die 0,1 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- 3 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 3 werden mit 97 Gewichtsteilen feinteiligem Kaolin innig vermischt. Man erhält auf diese Weise ein Stäubemittel, das 3 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.
- 30 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 4 werden mit einer Mischung aus 92 Gewichtsteilen pulverförmigem Kieselsäuregel und 8 Gewichtsteilen Paraffinöl, das auf die Oberfläche dieses Kieselsäuregels gesprüht wurde, innig vermischt. Man erhält auf diese Weise eine Aufbereitung des Wirkstoffs mit guter Haftfähigkeit.
- 40 Gewichtstelle des Wirkstoffs 1 werden mit 10 Teilen Natriumsalz eines Phenolsulfonsäureharnstoff-formaldehyd-Kondensats, 2 Teilen Kieselgel und 48 Teilen Wasser innig vermischt. Man erhält eine stabile wäßrige Dispersion. Durch Verdünnen mit 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,04 Gewichtsprozent Wirkstoff enthält.
- 20 Teile des Wirkstoffs 2 werden mit 2 Teilen Calciumsalz der Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure, 8 Teilen Fettalkohol-polyglykoläther, 2 Teilen Natriumsalz eines Phenolsulfonsäure-harnstoff-formaldehyd-Kondensats und 68 Teilen eines paraffinischen Mineralöls innig vermischt. Man erhält eine stabile ölige Dispersion.
- 9,58 Teile 1 - [2 - (4 - Chlorphenylmercapto) - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)] - 1,2,4 - triazol werden in 300 Teilen Äthanol gelöst und tropfenweise mit einer Lösung von 2,2 Teilen hydratwasserhaltigem Kupfer (11) - chlorid in 3 Teilen Wasser versetzt. Nach 20-minutigem führen wird abgesaugt. Man erhält 10 Teile Bis - [1 - (2 - (4 - chlorphenylmercapto - 2 - (2,4 - dichlorphenyl) - äthyl - (1)) - 1,2,4 - triazol] - Kupfer (II) - chlorid vom Schmelzpunkt 196°C.
Claims (17)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE2724684 | 1977-06-01 | ||
| DE19772724684 DE2724684A1 (de) | 1977-06-01 | 1977-06-01 | Triazolsubstituierte schwefelverbindungen |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0000112A1 EP0000112A1 (de) | 1978-12-20 |
| EP0000112B1 true EP0000112B1 (de) | 1981-09-09 |
Family
ID=6010391
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP78100044A Expired EP0000112B1 (de) | 1977-06-01 | 1978-06-01 | Triazolsubstituierte Schwefelverbindungen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie ihre Verwendung als Fungizide |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0000112B1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE2724684A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2928768A1 (de) * | 1979-07-17 | 1981-02-12 | Bayer Ag | 1-(2,4-dichlorphenyl)-1-(2,6- dihalogenbenzylmercapto)-2-(1,2,4- triazol-1-yl)-ethane, verfahren zu ihrer herstellung und ihre verwendung als fungizide |
| DE3108770A1 (de) * | 1981-03-07 | 1982-09-16 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | Triazolylalkyl-thioether, verfahren zu ihrer herstellung sowie ihre verwendung als pflanzenwachstumsregulatoren und fungizide |
| CA1179678A (en) * | 1981-03-27 | 1984-12-18 | Elmar Sturm | Antimicrobial triazole derivatives |
| DE3342310A1 (de) * | 1983-11-23 | 1985-05-30 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | Verwendung von 1-(2,4-dichlorphenyl)-1-(4-chlorbenzylmercapto)-2-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-ethan zur regulierung des pflanzenwachstums |
| GB9125791D0 (en) * | 1991-12-04 | 1992-02-05 | Schering Agrochemicals Ltd | Herbicides |
| CZ88095A3 (en) * | 1992-10-09 | 1995-11-15 | Uniroyal Chemical Ltd | Substituted azole derivatives exhibiting fungicidal activity, process of their preparation, intermediates of such process, fungicidal agent in which said derivatives are comprised and method of controlling phytopathogenic mildews |
| JP4329905B2 (ja) | 2001-12-27 | 2009-09-09 | 第一三共株式会社 | βアミロイド蛋白産生・分泌阻害剤 |
| CA2526487A1 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2005-01-06 | Daiichi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Heterocyclic methyl sulfone derivative |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2645496A1 (de) * | 1976-10-08 | 1978-04-13 | Bayer Ag | (1-phenyl-2-triazolyl-aethyl)-thioaether-derivate, verfahren zu ihrer herstellung und ihre verwendung als fungizide und wachstumsregulatoren |
-
1977
- 1977-06-01 DE DE19772724684 patent/DE2724684A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1978
- 1978-06-01 EP EP78100044A patent/EP0000112B1/de not_active Expired
- 1978-06-01 DE DE7878100044T patent/DE2861048D1/de not_active Expired
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE2724684A1 (de) | 1978-12-14 |
| EP0000112A1 (de) | 1978-12-20 |
| DE2861048D1 (en) | 1981-11-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0000752A2 (de) | Alpha-azolysulfide, -sulfoxide und -sulfone, deren Salze und Metallkomplexe, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung, sowie sie enthaltende Mittel zur Pilzbekämpfung | |
| EP0021345B1 (de) | Alpha-Azolylglykolderivate, ihre Herstellung, sie enthaltende pflanzenwachstumsregulierende Mittel und ihre Verwendung | |
| DE2723942C2 (de) | ω-(1,2,4-Triazol-1-yl) acetophenonoximäther | |
| EP0010723B1 (de) | Imidazol-Kupferkomplexverbindungen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| EP0069330B1 (de) | Pyridincarbinole, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| CH635481A5 (de) | Fungizides mittel. | |
| EP0000112B1 (de) | Triazolsubstituierte Schwefelverbindungen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie ihre Verwendung als Fungizide | |
| EP0025882A1 (de) | N-phenylpropylsubstituierte Azole, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| EP0021327A1 (de) | Neue beta-Triazolylether, ihre Herstellung, sie enthaltende Fungizide, Verfahren zur Bekämpfung von Fungi und zur Herstellung von Fungiziden | |
| CH629079A5 (en) | Fungicide | |
| EP0129211B1 (de) | 2,6-Trans-Dimethylmorpholinderivate und diese enthaltende Fungizide und Verfahren zur Bekämpfung von Pilzen | |
| EP0057362B1 (de) | Dibenzofuranderivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung zur Bekämpfung von Pilzen | |
| EP0010270A1 (de) | Neue alpha-Azolyl-alpha-phenylessigsäurederivate, ihre Herstellung, sie enthaltende Fungizide, Verfahren zur Bekämpfung von Fungi und zur Herstellung von Fungiziden | |
| EP0028363A1 (de) | Entriazole, ihre Herstellung, ihre Verwendung zur Bekämpfung von Fungi und Mittel dafür | |
| EP0002671A1 (de) | Substituierte Triazolylglykoläther, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie ihre Verwendung als Fungizide | |
| EP0057365A2 (de) | Vinylazole, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und ihre Verwendung bei der Bekämpfung von Pilzen | |
| EP0033501A2 (de) | Beta-Imidazolylalkohole, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung, diese enthaltende Fungizide und Verfahren zur Bekämpfung von Pilzen mit ihnen | |
| EP0082400B1 (de) | Fungizide alpha-Azolylglykole | |
| EP0071095B1 (de) | Phenylketenacetale und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| EP0019153A1 (de) | Carbinolether, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| EP0001571B1 (de) | Phenylazophenyloxy-triazolylverbindungen und Fungizide, die diese Verbindungen enthalten | |
| EP0069289B1 (de) | Azolderivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| EP0092674B1 (de) | Triazolverbindungen, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Fungizide | |
| EP0037468A2 (de) | Verfahren zur Bekämpfunng von Pilzen mit Triatolylderivaten | |
| EP0020968A1 (de) | Glykolaldehyd-N,O-acetale, ihre Herstellung und Verwendung als Fungizide |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 2861048 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19811126 |
|
| KL | Correction list |
Free format text: 82/02 TITELBLATT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19820630 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19830524 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19830524 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19830525 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19830531 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19830531 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19830616 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19830630 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19840519 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19840602 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19840630 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19840630 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: BASF A.G. Effective date: 19840601 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19850101 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19850228 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19881117 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 78100044.3 Effective date: 19850612 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |