CN1220522A - 维特比译码装置及维特比译码方法 - Google Patents
维特比译码装置及维特比译码方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1220522A CN1220522A CN98125339A CN98125339A CN1220522A CN 1220522 A CN1220522 A CN 1220522A CN 98125339 A CN98125339 A CN 98125339A CN 98125339 A CN98125339 A CN 98125339A CN 1220522 A CN1220522 A CN 1220522A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- state
- termination
- path
- register
- decoding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/03—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words
- H03M13/23—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words using convolutional codes, e.g. unit memory codes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/65—Purpose and implementation aspects
- H03M13/6577—Representation or format of variables, register sizes or word-lengths and quantization
- H03M13/6583—Normalization other than scaling, e.g. by subtraction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/37—Decoding methods or techniques, not specific to the particular type of coding provided for in groups H03M13/03 - H03M13/35
- H03M13/39—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes
- H03M13/41—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors
- H03M13/4107—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors implementing add, compare, select [ACS] operations
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/37—Decoding methods or techniques, not specific to the particular type of coding provided for in groups H03M13/03 - H03M13/35
- H03M13/39—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes
- H03M13/41—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors
- H03M13/4123—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors implementing the return to a predetermined state
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/37—Decoding methods or techniques, not specific to the particular type of coding provided for in groups H03M13/03 - H03M13/35
- H03M13/39—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes
- H03M13/41—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors
- H03M13/4161—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors implementing path management
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/37—Decoding methods or techniques, not specific to the particular type of coding provided for in groups H03M13/03 - H03M13/35
- H03M13/39—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes
- H03M13/41—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors
- H03M13/4161—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors implementing path management
- H03M13/4169—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors implementing path management using traceback
- H03M13/4176—Sequence estimation, i.e. using statistical methods for the reconstruction of the original codes using the Viterbi algorithm or Viterbi processors implementing path management using traceback using a plurality of RAMs, e.g. for carrying out a plurality of traceback implementations simultaneously
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Probability & Statistics with Applications (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Error Detection And Correction (AREA)
- Detection And Correction Of Errors (AREA)
- Compression Of Band Width Or Redundancy In Fax (AREA)
Abstract
除了存储单元序列之外设置一个与分割长度一样长的寄存器序列,相应于每个状态排列。与状态00相应的寄存器序列中各级的选择器的输出被输入到寄存器序列中的一个寄存器1021中和选择器中。将前级寄存器的输出分别输入到那三个选择器中。在终止接收字以及其他情形下,这三个选择器根据控制电路的控制将输出切换到后级。从而,在终止接收字时,原样传送存储在寄存器序列中的信息。利用这种操作,在终止接收字时能对到达状态00的路径进行译码。
Description
本发明涉及在对例如使用在卫星广播等中的卷积编码进行最大似然译码的方法中所使用的维特比译码装置以及维特比译码方法。
作为对卷积编码的译码方法之一,维特比译码方法是公知的。维特比译码方法是对于卷积编码的最大似然译码方法,借助这种方法,通过从发送方的编码器能够形成的编码序列中选择一个与接收的编码序列最接近的序列(后文中将这样的一个序列称为最大似然路径),进行错误校正。也就是,使用发送方编码器根据编码方法形成的变换图(后文中称为格子),作为先决条件。例如,从变换图中能够产生的变换中,将其与接收编码序列的汉明间距最短的路径选择为最大似然路径。
用于执行维特比译码方法的维特比译码装置包括:一个分支尺度计算电路,用于计算一个分支尺度,即到达格子中每个状态的路径与根据时钟收到的编码序列之间的汉明间距;一个ACS电路,用于根据分支尺度计算状态尺度,比较状态尺度的值,并且选择最大似然路径;一个正规化电路,用于正规化状态尺度的值;一个状态尺度存储电路,用于存储状态尺度的值;以及一个路径存储器电路,用于根据ACS的选择结果形成译码数据。
在该例中,作为路径存储器电路,有两种电路,一种是执行寄存器变换方法以便通过使用寄存器序列来传送路径选择内容的电路,一种是用于执行通过使用RAM来存储路径选择内容、跟踪存储内容和从而译码的方法的电路。下面来描述这两种方法。
在寄存器变换方法中,该方法一般使用在维特比译码装置中,包括一个选择器和一个寄存器的每个存储单元被设置在路径存储器电路的格子上,根据从ACS电路输出的路径选择信息传送寄存器的内容。通过从最后级的存储单元的输出中选择最大似然状态的输出,选择最大似然路径的信息并且输出译码数据。
尽管这种寄存器变换方法具有这样的优点:可以执行高速操作,但是有一个缺点:当分割长度增加时,电路规模变得很大。特别是,因为最近几年已经出现了分割长度超过100的应用,所以电路规模的扩大成为一个严重的问题。
最近几年中,通过使用RAM(随机存取存储器)存储路径信息以及跟踪存储信息的方法已得到广泛研究。下文中将这种方法称为反向跟踪方法。
作为终止卷积编码的一种方法,已经知道了终止。当所终止的积卷编码是维特比译码的时,通过从全部为0的状态反向跟踪一条路径进行译码而获得最大似然路径。在迄今使用的维特比译码装置中,当连续收到终止的卷积编码时,在许多情况下由正常操作执行译码。
在这种译码方法中,存在一个问题,在终止卷积编码之后继续输入下一个卷积编码时,不能执行严格的最大似然译码,因此恐怕产生译码错误。因为这个问题是进行维特比译码时未考虑终止间隔的观点引起的,所以这个问题也存在于前述寄存器变换方法和反向跟踪方法中。
考虑到这种情况提出了本发明。因此,本发明的一个目的在于提供一种维特比译码装置和维特比译码方法,它们即使对于终止的卷积编码也能够执行严格的最大似然译码。
为实现上述目的,本发明提供一种维特比译码装置,用于连续接收终止的卷积编码,包括终止状态路径译码装置,用于对一条到达将被终止的状态的路径进行确定地译码。
本发明还提供一种维特比译码方法,连续地接收终止卷积编码,包括一个终止状态路径译码步骤,对到达将被终止的状态的路径进行确定地译码。
根据上述的本发明,因为到达将被终止的状态的路径能够被确定地译码,所以对于终止的卷积编码能够执行最大似然译码。
通过以下结合附图进行的详细描述,本发明的上述及其他目的、特征和优点将会更加明显。
图1是用于说明本发明的一个实施方式的总体结构的框图;
图2是用于说明约束长度等于3的情形下变换图的框图;
图3是用于说明常规使用的一般装置中的状态尺度存储电路的框图;
图4是用于说明寄存器变换方法中路径存储器的存储单元的示意图;
图5是用于说明寄存器变换方法中路径存储器的存储单元设置的示意图;
图6是用于说明终止的示意图;
图7是示出约束长度为3的卷积编码器例子的示意图;
图8A和图8B是用于说明常规使用的维特比译码装置中终止和译码错误时刻的格子的示意图;
图9是用于说明本发明第一实施方式中路径存储器电路的框图;
图10是用于说明本发明第二实施方式中路径存储器电路的框图;
图11是用于说明反向跟踪方法中跟踪原理的示意图;
图12是用于说明反向跟踪方法中跟踪方法的示意图;
图13是用于说明已经常规使用的一般反向跟踪方法中每个RAM作用的示意图;
图14是用于说明常规使用的一般反向跟踪方法中的存储器操作的框图;
图15是用于说明本发明第三实施方式中路径存储器电路的框图;
图16是用于说明本发明第四实施方式中路径存储器电路的框图;
图17是用于说明状态00开始的路径尺度的示意图。
下面结合附图描述本发明第一个实施方式。首先,参照图1描述本发明的第一实施方式的总体结构。本发明的第一实施方式包括:一个分支尺度计算电路701;一个ACS电路702;一个正规化电路703;一个状态尺度存储电路704;以及一个路径存储器电路705。当从发送方输入经过发送路径接收的数据时,从可以由发送方的编码器形成的编码序列中选择一个最大似然路径,并且根据选择内容形成译码数据。
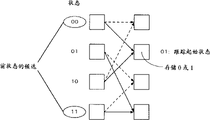
也就是说,例如,使用由发送方的编码器根据编码方法形成的如图2中所示的变换图(后文中称为格子),作为先决条件,并且例如,从能够在变换图中产生的变换中,将其与接收编码序列的汉明间距为最小的路径选择为最大似然路径。
当输入接收数据信号S701时,分支尺度计算电路701计算接收数据的分支尺度,并且输出一个计算结果,作为分支尺度信号S702。根据分支尺度信号S702和从状态尺度存储电路704输入的状态尺度信号S705,ACS电路702将分支尺度和状态尺度加到连结某个状态的两个路径中的每一个上,比较它们的加法值,根据比较结果选择具有较高似然的加法值,并将其设定为新的状态尺度。
如此选择的内容作为路径选择信息S706得以输出,将具有最小状态尺度的状态号码作为最大似然状态信号S707进行输出,将新获得的状态尺度作为新的状态尺度信号S703进行输出。
现在以约束长度为3这种情形为例描述选择路径的方法。图2的格子示出具有四个状态00、01、10和11以及约束长度等3情形下的格子的例子。箭头指示每个时隙能够产生的路径。与译码数据“0”相应的路径由虚线所示。与译码数据“1”相应的路径由实线所示。两条连接的路径存在于每个时隙的所有状态中。因此,对于连接某个状态的两条路径中的每一条,将接收信号与该路径之间的汉明间距(分支尺度)与到目前为止的分支尺度的累加和(状态尺度)相加并且比较加法结果,根据比较结果选择具有较高似然的值。
正规化电路703使用一个方法进行正规化,从而从ACS电路702等所输出的新状态尺度信号S703中减去最小状态尺度,将经过正规化的值设定到预置范围内的一个值,并且作为正规化状态尺度信号S704进行输出。状态尺度存储电路704对从正规化电路703输出的正规化状态尺度信号S704进行存储,并且作为状态尺度信号S705将其返回到ACS电路702。图3示出状态尺度存储电路704的结构例子。假设存储电路704具有四个寄存器,相应于图2格子中的四个状态。尽管四个寄存器中的每一个是一个图3所示的5位寄存器,但是也可以使用其他位数的寄存器。
因此,在说明本发明第一实施方式中的路径存储器电路705之前,为了便于理解,现在说明为了实现寄存器变换方法的一般路径存储器电路的结构。图5示出的路径存储器电路结构中,每个存储单元包括图4所示的选择器和寄存器,按照图2所示的格子排列。在图5中,存储单元由MS表示。在上述结构中,通过根据从ACS电路702输出的路径选择信息传送寄存器的内容,将与每个状态的存活路径相应的信息保留在每个存储单元的寄存器中。因此,实现了使用图2所示的格子作为先决条件的译码,也就是在具有四个状态且约束长度为3分割长度为4的情形下实现寄存器变换方法的译码。
在这种一般路径存储器电路中,存在一个问题,即在连续收到终止的卷积编码时不能进行严格的最大似然译码。下面详细说明这个问题。为了终止对卷积编码的编码,在输入了所有信息位之后,向编码器输入数0(约束长度-1)的方法是已知的(见图6)。如上所述在预定时间点将编码器的状态全都设为0的过程称为“终止”。在开始编码之后在结束终止之前的时间数称为“终止长度”。
在对终止的卷积编码进行维特比译码的情形下,通过从全部为0的状态反向跟踪路径进行译码,能够获得最大似然路径。然而,在实际维特比译码装置中,在连续收到终止的卷积编码的情形下,通常利用普通操作进行译码。
然而,在这种译码方法中,当在终止卷积编码之后连续输入下一卷积编码时,存在一种不能进行严格的最大似然译码的情况。下面描述这种情况。在使用图7所示的约束长度为3的卷积编码器的情形下,现有考虑在编码终止之后顺序执行下一编码的情形。这种情形中格子的例子示于图8A。图8A示出在从全部为0的状态反向跟踪路径而对终止间隔之后的编码进行译码从而获得最大似然路径的情形下所跟踪的格子。
现在考虑正确路径是全部为0的路径(图8B中的Pr)的情形。在这种情形下,如果不考虑终止进行译码,则恐怕对图8B所示的错误路径Pe进行译码。这是因为对于错误路径Pe,因为与全部为0的路径Pr的汉明距离小,为6,所以被错误地设置为译码结果的概率相当高。
现在,假设对错误路径Pe错误地进行了译码,即使忽略了执行终止时间隔中的译码位,在与发送信息有关的信息位中也包括一位错误。因为这个路径在固有的终止格子中并不存在,如果考虑到终止间隔进行严格的最大似然译码,则不产生这种译码错误。
图9示出在上述情况下考虑到终止间隔时进行最大似然译码的本发明第一实施方式中路径存储器电路705的结构。除了与每个状态相应设置的分割长度一样多的存储单元序列,路径存储器电路705还具有一个寄存器序列102和一个根据终止信息控制寄存器序列102的控制电路101。
即,在与状态00相应的寄存器序列中第一级、第二级、第三级和第四级的选择器的输出分别输入到寄存器序列102中的寄存器1021和选择器1022、1024和1026。前一级的寄存器1021、1023和1025的输出分别输入到选择器1022、1024和1026。每个选择器1022、1024和1026输出一个数据,该数据响应于控制电路101的命令输入到后一级的寄存器。
通过根据从ACS电路702输入的每个状态的路径选择信息进行传送,将与每个状态的存活路径相应的信息存储到寄存器中。在终止接收字之前的间隔中,通过从最后级输出中选择最大似然状态的输出,选择与最大似然路径相应的信息,并且输出译码数据。在这个间隔中,例如,从控制电路向寄存器序列102输出“1”,还将与状态0相应的译码字存储到寄存器序列102中。
另一方面,当终止接收字时,将从控制电路101到寄存器序列102的信号例如切换为“0”,从而允许原样传送存储在寄存器序列102中的信息。利用最后级的选择电路103,作为译码字原样输出寄存器序列102的输出。利用这种操作,在终止接收字时可以对到达状态00的路径进行译码。
在输出寄存器102内容时的间隔内,其他四个寄存器序列中的每一个重新开始相应于后继卷积编码的普通变换,将操作返回到普通译码,同时输出寄存器序列102的所有内容,将控制电路101的信号切换为“0”。在上述本发明的第一实施方式中,即使在连续输入终止的卷积编码的情形下,在继续译码操作的同时可以对到达即将终止状态的路径进行译码。因此,也可以对终止编码进行严格的最大似然译码,能够改进译码错误率。
现在描述具有与本发明第一实施方式不同结构的路径存储器电路805的本发明第二实施方式。图10示出本发明第二实施方式中路径存储器电路805的结构。当进行约束长度为3分割长度为4的译码时,路径存储器电路805具有即使对于终止的接收字也进行严格的最大似然译码的功能。
在路径存储器电路805中,在与每个状态相应设置的分割长度一样多的存储单元的序列中,输入到与状态00相应的寄存器序列203中每个存储单元的选择器的信号受到控制电路的控制。即,设置了选择器204、205、206和207,将路径选择信息和“0”输入到这些选择器中。响应于控制电路201的命令,每个选择器204至207向寄存器序列203中的每个存储单元的选择器输入路径选择信息与“0”中的一个,作为控制信号。
以下操作是利用这种结构实现的。即,在终止接收字之前的间隔中,作为控制信号向状态00的寄存器序列203给出路径选择信息,并且进行普通寄存器变换。在最后级的输出中,通过选择最大似然状态的输出,选择与最大似然路径相应的信息,并且输出译码数据。另一方面,在终止接收字的时钟,进行控制,使得选择器204至207给出“0”,作为状态00的寄存器序列203的控制信号。原样传送这个时钟的存储内容。
在下一时钟,选择器204将路径选择信息给到第一级的存储单元的选择器,选择205至207将“0”给到第二至最后一级的存储单元的选择器。又在下一时钟,选择器204和205将路径选择信息给到直到第二级的存储单元的选择器。选择器206和207将“0”给到第三至最后一级的存储单元的选择器。以类似于上述的方式,控制信号被顺序切换与分割长度相应的信号次数。在终止时,直至完成输出状态00的寄存器序列中所存储的译码字,最后级的选择电路202产生状态00的输出,作为译码数据。
在完成输出状态00的寄存器序列中所存储的译码字之前的时间周期内,路径存储器执行后续输入的卷积编码的普通操作。因此,在结束终止编码的译码的同时,可以将操作返回到普通译码。
如上所述,同样在本发明的第二实施方式中,即使连续输入终止的卷积编码,在继续译码操作的同时也可能对到达即将终止状态的路径进行译码。
以上本发明的第一和第二实施方式与作为先决条件的寄存器变换方法相关。在连续输入终止的卷积编码的情形下能够产生的译码错误也同样成为维特比译码装置在执行反向跟踪方法时的问题。因此,现在描述为了解决反向跟踪方法中的这一问题的本发明的第三实施方式。为了便于理解,首先描述迄今已被使用的一般反向跟踪方法。
现在以约束长度等于3这种情形为例描述反向跟踪方法中的主要跟踪操作。在图11中,考虑从状态01跟踪的情形。具有变换到状态01的可能性的状态为状态00和状态10。当选择了状态00侧的路径时,已经将“0”存储到了路径存储器中。当选择了状态10侧的路径时,已经将“1”(即先前状态的最高有效位)存储到了路径存储器中。
甚至在从任何状态变换的情形下,输入为1,将其表示为状态01的最低有效位。通过以上描述,足以如下执行跟踪操作。即,如图12所示,用于开始跟踪的跟踪起始状态的最低有效位被用作译码位。通过新增加路径存储器中的这一位,作为跟踪起始状态的最高有效位到第二最低位范围的最高有效位,形成后序跟踪到跟踪起始状态的下一跟踪状态的号码。通过这种操作,能够从具有最小状态尺度的状态跟踪所选择的路径。
为了使维特比译码装置高速工作,必须每个时钟仅执行一次对RAM的访问。现在描述这种情形,其中使用了具有四个单端口存储器的路径存储器电路,以便通过一次访问对每个RAM进行译码。在以下描述中,将编码的约束长度为3分割长度为4作为先决条件。在这种情形下所使用的路径存储器电路,是一个具有四个单端口RAM的路径存储器电路,每个RAM具有与状态数一样多的位数(该情形下为4位)以及与分割长度一般多的字数(该情形下为4个字)。
每个时钟,从ACS电路702向路径存储器电路输入与状态数一样多的路径选择信息。对于四个RAM,与分割长度相应的每个时钟(该情形下为四个时钟)对以下四个作用(1)至(4)顺序切换(参见图13)。根据这种操作的对四个RAM中的每一个的操作的例子示于图14。
(1)顺序写入路径选择信息。
(2)根据写入的路径选择信息顺序执行跟踪。不进行译码。
(3)无访问。
(4)从(2)中的跟踪结果顺序执行跟踪,并且输出译码位。
反向跟踪方法进行的译码是利用路径存储器电路的结构和操作实现的。
现有描述在如上所述的进行反向跟踪方法的维特比译码装置中,为了解决与卷积编码的终止有关的前述问题的本发明的第三实施方式。图15示出本发明第三实施方式中的路径存储器电路905的结构。路径存储器电路905是一种利用反向跟踪方法进行译码的路径存储器电路,在对约束长度为3终止长度为16的编码进行(分割长度)=(终止长度/4)=4的译码时的情形下,使用了四个四位四字的单端口RAM。现在假设将路径选择信息写入RAM的起始时间点与编码的起始时间点匹配。
对于RAM 30、31、32和33,写入ACS电路输入的路径选择信息S302和读出存储的路径选择信息是响应于控制电路301形成的控制信号S303进行的,并且将读取的路径选择信息S304、S305、S306和S307输入到控制电路301中。在类似于常规的方式,通过切换以下作用执行接收字终止之前的存储器操作:
(1)顺序写入路径选择信息。
(2)根据写入的路径选择信息顺序执行跟踪。不进行译码。
(3)无访问。
(4)从(2)中的跟踪结果顺序执行跟踪,并且输出译码位。
在对终止间隔进行译码时,执行作用(4)的RAM从状态00而不是从(2)的跟踪结果开始跟踪,并且进行译码。因此,控制电路301根据终止信号S301切换每个RAM的操作。因为编码的起始时间点与写入RAM的起始时间点匹配,并且存在一种关系使得分割长度等于终止长度的1/4,所以完成终止的时序与开始跟踪的时序吻合。即使在对终止的间隔进行译码期间,也执行部分(2)的跟踪,以对下一间隔进行译码。因此,在结束终止编码的译码的同时,可以将操作返回到普通译码操作。
(4)中跟踪所译码的信号S308被输入到一个输出缓冲器302,并且根据固有时间序列的顺序重新安排。此后,作为译码位信号S309进行输出。如上所述,同样在本发明的第三实施方式中,即使连续输入终止的卷积编码,在继续译码操作的同时也可能对到达即将终止状态的路径进行译码。
本发明的前述第一、第二和第三实施方式目的在于解决与路径存储器电路中的终止有关的问题。另一方面,现在描述能够解决与状态尺寸存储电路中的终止有关的问题的本发明的第四实施方式。本发明第四实施方式的整体结构与上述本发明的第一实施方式等类似。本发明第四实施方式中的状态尺度存储电路1004的结构示于图16。状态尺度存储电路1004是在对约束长度为3的编码进行译码时设置分支尺度为4位及状态尺度为5位的情形下的状态尺度的存储电路。
在用于存储到达状态00、01、10和11的路径的状态尺度的四个寄存器的前级,设置了选择器401、402、403和404。从正规化电路向每个选择器输入正规化的状态尺度的值。还将0值输入到与状态00相应的寄存器401中。还将值31(由5位表示的最大值)输入到与其他状态相应的选择器402至404。将终止信息输入到选择器401至404,并且每个选择器根据终止信息输出状态尺度以及值0和31中的一个。对值31进行剪取,使得状态尺度在ACS电路702中不溢出。
在状态尺度存储电路1004中,在终止接收字之前的时间周期内,选择器401至404分别向后一级的寄存器输出状态尺度值。这样,进行普通译码操作,使得顺序更新状态尺度,并且输出分割长度之前的译码数据。另一方面,当终止接收字时,每个选择器向后一级的每个寄存器输出除了状态尺度值之外的值。
因此,状态00的状态尺度被初始化为0,其他状态的状态尺度被初始化为31。因为每个时钟的分支尺度由四位组成,如图17所示,所以周期P51和P52中的分支尺度值等于或小于15(由4位表示的最大值),在新卷积编码开始之后的两个时钟中的一个时间周期内(即周期P51和P52之后),用作为起始点的状态00中的路径的尺度数等于或小于30。这样,确定选择了状态00的路径。
即使以类似于普通译码操作的方式执行后续操作,并且利用相应于分割长度的间隔进行反向跟踪而执行译码,对于进行终止时的时序的译码,也能够从经过状态00的路径中确定地选择最大似然路径。甚至在上述本发明的第四实施方式中,当同样连续输入终止的卷积编码时,在继续译码操作的同时也能够对到达即将终止状态的路径进行译码。
尽管已经相对于约束长度为3分割长度为4的情形描述了上述本发明的第一实施方式和其他实施方式,但是本发明能够适用于约束长度和分割长度为任意值的情形。
如上所述,本发明目的在于在考虑到接收字的终止间隔时进行维特比译码。所以,可以对终止的卷积编码进行最大似然译码。
在参照附图描述了本发明的具体的较佳实施方式之后,应理解到本发明不限于那些具体的实施方式,本领域内熟练的技术人员可以做出各改变和修改,而不背离如权利要求书限定的本发明的范围和实质。
Claims (10)
1.用于连续接收终止的卷积编码的维特比译码装置,包括:
终止状态路径译码装置,用于对到达即将终止状态的路径进行确定地译码。
2.根据权利要求1的装置,其中
执行寄存器变换方法的路径存储器具有一个与分割长度一样长的寄存器序列,并且
与即将终止状态相应的译码字存储在所述寄存器序列中,并且在终止时,顺序输出存储在所述寄存器序列中的所述译码字。
3.根据权利要求1的装置,其中
进一步将用于对与即将终止状态相应的所述寄存器序列中的每个存储单元的选择信息进行控制的控制电路增加到路径存储器中,以执行寄存器变换方法,并且
在利用所述控制电路的操作终止时,原样输出与即将终止状态相应的译码字。
4.根据权利要求1的装置,包括
一个路径存储器,用于执行反向跟踪方法,
并且其中通过将分割长度设定为终止长度的m/n,m和n是整数,
在终止时从即将终止的状态开始跟踪。
5.根据权利要求1的装置,其中在终止时通过将终止状态之外的状态的状态尺度设定为一个足够大的值,
对通过即将终止状态的路径进行确定地译码。
6.用于连续接收终止的卷积编码的维特比译码方法,包括:
终止状态路径译码步骤:对到达即将终止状态的路径进行确定地译码。
7.根据权利要求6的方法,其中当利用寄存器变换方法进行译码时,所述维特比译码方法还包括:
一个存储步骤:将与即将终止状态相应的译码字存储到与分割长度一样长的被增加到路径存储器的寄存器序列中,以便执行寄存器变换方法;以及
一个输出步骤:在终止时,顺序输出存储在所述寄存器序列中的所述译码字。
8.根据权利要求6的方法,其中当利用寄存器变换方法进行译码时,所述维特比译码方法还包括:
一个控制步骤:对与即将终止状态相应的寄存器序列中的每个存储单元的选择信息进行控制;以及
一个输出步骤:在利用所述控制步骤终止时,原样输出与即将终止状态相应的译码字。
9.根据权利要求6的方法,其中当利用反向跟踪方法进行译码时,所述维特比译码方法还包括:
一个将截断长度设定为所述分割长度的终止长度的m/n的步骤,m和n整数;以及
一个在终止时从即将终止状态开始跟踪的步骤。
10.根据权利要求6的方法,还包括:
一个在终止时将终止状态之外的状态的状态尺度设定为足够大的值的步骤;以及
一个对通过即将终止状态的路径进行确定地译码的步骤。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP351434/97 | 1997-12-19 | ||
| JP35143497A JP3900637B2 (ja) | 1997-12-19 | 1997-12-19 | ビタビ復号装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1220522A true CN1220522A (zh) | 1999-06-23 |
Family
ID=18417266
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN98125339A Pending CN1220522A (zh) | 1997-12-19 | 1998-12-18 | 维特比译码装置及维特比译码方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6748034B2 (zh) |
| EP (2) | EP2053750A1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP3900637B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR100538730B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1220522A (zh) |
| MY (1) | MY119831A (zh) |
Families Citing this family (159)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7225393B2 (en) | 1999-10-01 | 2007-05-29 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Viterbi decoder and Viterbi decoding method |
| US6654929B1 (en) * | 1999-10-01 | 2003-11-25 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Viterbi decoder and Viterbi decoding method |
| JP3613134B2 (ja) * | 2000-05-12 | 2005-01-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | 高速ターボデコーダ |
| JP3532884B2 (ja) * | 2001-05-18 | 2004-05-31 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | ビタビ復号器 |
| AUPR679201A0 (en) * | 2001-08-03 | 2001-08-30 | Lucent Technologies Inc. | Path metric normalization of add-compare-select processing |
| WO2005117272A1 (ja) | 2004-05-27 | 2005-12-08 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | ビタビ復号装置、およびビタビ復号方法 |
| JP4840651B2 (ja) * | 2006-07-27 | 2011-12-21 | ソニー株式会社 | 復号装置および復号方法 |
| US7801200B2 (en) * | 2006-07-31 | 2010-09-21 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for code dependency reduction |
| US7802163B2 (en) * | 2006-07-31 | 2010-09-21 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for code based error reduction |
| US7779331B2 (en) | 2006-07-31 | 2010-08-17 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for tri-column code based error reduction |
| JP4666646B2 (ja) * | 2006-08-24 | 2011-04-06 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 軟判定ビタビ復号装置および方法、復号装置および方法 |
| US7673224B2 (en) * | 2006-09-12 | 2010-03-02 | Agere Systems Inc. | Low power viterbi decoder using a novel register-exchange architecture |
| US7971125B2 (en) * | 2007-01-08 | 2011-06-28 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for prioritizing error correction data |
| US8359522B2 (en) | 2007-05-01 | 2013-01-22 | Texas A&M University System | Low density parity check decoder for regular LDPC codes |
| US7930621B2 (en) * | 2007-06-01 | 2011-04-19 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for LDPC decoding with post processing |
| US8196002B2 (en) * | 2007-06-01 | 2012-06-05 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for joint LDPC encoding and decoding |
| US7876862B2 (en) | 2007-07-16 | 2011-01-25 | Agere Systems Inc. | Conditionally input saturated Viterbi detector |
| WO2009041979A1 (en) * | 2007-09-28 | 2009-04-02 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for reduced complexity data processing |
| US8161348B2 (en) * | 2008-02-05 | 2012-04-17 | Agere Systems Inc. | Systems and methods for low cost LDPC decoding |
| US8245104B2 (en) | 2008-05-02 | 2012-08-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for queue based data detection and decoding |
| EP2191569B1 (en) * | 2008-05-19 | 2018-11-21 | Avago Technologies General IP (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for mitigating latency in a data detector feedback loop |
| US8660220B2 (en) * | 2008-09-05 | 2014-02-25 | Lsi Corporation | Reduced frequency data processing using a matched filter set front end |
| US8245120B2 (en) * | 2008-09-17 | 2012-08-14 | Lsi Corporation | Power reduced queue based data detection and decoding systems and methods for using such |
| WO2010059264A1 (en) * | 2008-11-20 | 2010-05-27 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for noise reduced data detection |
| US7990642B2 (en) * | 2009-04-17 | 2011-08-02 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for storage channel testing |
| KR20120012960A (ko) | 2009-04-28 | 2012-02-13 | 엘에스아이 코포레이션 | 판독된 데이터 처리 시스템의 동적 스케일링을 위한 시스템 및 방법 |
| US8443267B2 (en) * | 2009-04-28 | 2013-05-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for hard decision assisted decoding |
| US8250434B2 (en) * | 2009-06-18 | 2012-08-21 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for codec usage control during storage pre-read |
| US8352841B2 (en) | 2009-06-24 | 2013-01-08 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for out of order Y-sample memory management |
| US8312343B2 (en) * | 2009-07-28 | 2012-11-13 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for re-using decoding parity in a detector circuit |
| US8458553B2 (en) | 2009-07-28 | 2013-06-04 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for utilizing circulant parity in a data processing system |
| US8250431B2 (en) * | 2009-07-30 | 2012-08-21 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for phase dependent data detection in iterative decoding |
| US8321746B2 (en) | 2009-07-30 | 2012-11-27 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for quasi-cyclic LDPC code production and decoding |
| US8565811B2 (en) * | 2009-08-04 | 2013-10-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Software-defined radio using multi-core processor |
| US8266505B2 (en) * | 2009-08-12 | 2012-09-11 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for retimed virtual data processing |
| US8176404B2 (en) * | 2009-09-09 | 2012-05-08 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for stepped data retry in a storage system |
| US9753884B2 (en) * | 2009-09-30 | 2017-09-05 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Radio-control board for software-defined radio platform |
| US8627189B2 (en) * | 2009-12-03 | 2014-01-07 | Microsoft Corporation | High performance digital signal processing in software radios |
| US20110136439A1 (en) * | 2009-12-04 | 2011-06-09 | Microsoft Corporation | Analyzing Wireless Technologies Based On Software-Defined Radio |
| US8688873B2 (en) | 2009-12-31 | 2014-04-01 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for monitoring out of order data decoding |
| US8683306B2 (en) * | 2010-01-04 | 2014-03-25 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for data detection including dynamic scaling |
| US8578253B2 (en) | 2010-01-04 | 2013-11-05 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for updating detector parameters in a data processing circuit |
| US8743936B2 (en) * | 2010-01-05 | 2014-06-03 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for determining noise components in a signal set |
| US9343082B2 (en) | 2010-03-30 | 2016-05-17 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for detecting head contact |
| US8161351B2 (en) | 2010-03-30 | 2012-04-17 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for efficient data storage |
| US8418019B2 (en) | 2010-04-19 | 2013-04-09 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for dynamic scaling in a data decoding system |
| US8443249B2 (en) | 2010-04-26 | 2013-05-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for low density parity check data encoding |
| US8527831B2 (en) | 2010-04-26 | 2013-09-03 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for low density parity check data decoding |
| US8381074B1 (en) | 2010-05-21 | 2013-02-19 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for utilizing a centralized queue based data processing circuit |
| US8381071B1 (en) | 2010-05-21 | 2013-02-19 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for decoder sharing between data sets |
| US8208213B2 (en) | 2010-06-02 | 2012-06-26 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for hybrid algorithm gain adaptation |
| US8773794B2 (en) | 2010-09-13 | 2014-07-08 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for block-wise inter-track interference compensation |
| US8295001B2 (en) | 2010-09-21 | 2012-10-23 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for low latency noise cancellation |
| US9219469B2 (en) | 2010-09-21 | 2015-12-22 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for filter constraint estimation |
| US8560930B2 (en) | 2010-10-11 | 2013-10-15 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for multi-level quasi-cyclic low density parity check codes |
| US8661071B2 (en) | 2010-10-11 | 2014-02-25 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for partially conditioned noise predictive equalization |
| US8443250B2 (en) | 2010-10-11 | 2013-05-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for error correction using irregular low density parity check codes |
| US8385014B2 (en) | 2010-10-11 | 2013-02-26 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for identifying potential media failure |
| US8750447B2 (en) | 2010-11-02 | 2014-06-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for variable thresholding in a pattern detector |
| US8667039B2 (en) | 2010-11-17 | 2014-03-04 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for variance dependent normalization for branch metric calculation |
| US8566379B2 (en) | 2010-11-17 | 2013-10-22 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for self tuning target adaptation |
| US8810940B2 (en) | 2011-02-07 | 2014-08-19 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for off track error recovery |
| US8699167B2 (en) | 2011-02-16 | 2014-04-15 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for data detection using distance based tuning |
| US8446683B2 (en) | 2011-02-22 | 2013-05-21 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for data pre-coding calibration |
| US8693120B2 (en) | 2011-03-17 | 2014-04-08 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for sample averaging in data processing |
| US8854753B2 (en) | 2011-03-17 | 2014-10-07 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for auto scaling in a data processing system |
| US8611033B2 (en) | 2011-04-15 | 2013-12-17 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for selective decoder input data processing |
| US8887034B2 (en) | 2011-04-15 | 2014-11-11 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for short media defect detection |
| US8670955B2 (en) | 2011-04-15 | 2014-03-11 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for reliability assisted noise predictive filtering |
| EP2705631B1 (en) | 2011-05-04 | 2022-07-27 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC | Spectrum allocation for base station |
| US8566665B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2013-10-22 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for error correction using low density parity check codes using multiple layer check equations |
| US8560929B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2013-10-15 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for non-binary decoding |
| US8499231B2 (en) | 2011-06-24 | 2013-07-30 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for reduced format non-binary decoding |
| US8862972B2 (en) | 2011-06-29 | 2014-10-14 | Lsi Corporation | Low latency multi-detector noise cancellation |
| US8595576B2 (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2013-11-26 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for evaluating and debugging LDPC iterative decoders |
| US8650451B2 (en) | 2011-06-30 | 2014-02-11 | Lsi Corporation | Stochastic stream decoding of binary LDPC codes |
| US8566666B2 (en) | 2011-07-11 | 2013-10-22 | Lsi Corporation | Min-sum based non-binary LDPC decoder |
| US8879182B2 (en) | 2011-07-19 | 2014-11-04 | Lsi Corporation | Storage media inter-track interference cancellation |
| US8830613B2 (en) | 2011-07-19 | 2014-09-09 | Lsi Corporation | Storage media inter-track interference cancellation |
| US8819527B2 (en) | 2011-07-19 | 2014-08-26 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for mitigating stubborn errors in a data processing system |
| US8539328B2 (en) | 2011-08-19 | 2013-09-17 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for noise injection driven parameter selection |
| US8854754B2 (en) | 2011-08-19 | 2014-10-07 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for local iteration adjustment |
| US9026572B2 (en) | 2011-08-29 | 2015-05-05 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for anti-causal noise predictive filtering in a data channel |
| US8656249B2 (en) | 2011-09-07 | 2014-02-18 | Lsi Corporation | Multi-level LDPC layer decoder |
| US8756478B2 (en) | 2011-09-07 | 2014-06-17 | Lsi Corporation | Multi-level LDPC layer decoder |
| US8661324B2 (en) | 2011-09-08 | 2014-02-25 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for non-binary decoding biasing control |
| US8681441B2 (en) | 2011-09-08 | 2014-03-25 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for generating predictable degradation bias |
| US8850276B2 (en) | 2011-09-22 | 2014-09-30 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for efficient data shuffling in a data processing system |
| US8767333B2 (en) | 2011-09-22 | 2014-07-01 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for pattern dependent target adaptation |
| US8578241B2 (en) | 2011-10-10 | 2013-11-05 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for parity sharing data processing |
| US8689062B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2014-04-01 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for parameter selection using reliability information |
| US8479086B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2013-07-02 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for efficient parameter modification |
| US8862960B2 (en) | 2011-10-10 | 2014-10-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for parity shared data encoding |
| US8996597B2 (en) | 2011-10-12 | 2015-03-31 | Lsi Corporation | Nyquist constrained digital finite impulse response filter |
| US8707144B2 (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2014-04-22 | Lsi Corporation | LDPC decoder with targeted symbol flipping |
| US8604960B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-12-10 | Lsi Corporation | Oversampled data processing circuit with multiple detectors |
| US8527858B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-09-03 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for selective decode algorithm modification |
| US8443271B1 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2013-05-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for dual process data decoding |
| US8683309B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2014-03-25 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for ambiguity based decode algorithm modification |
| US8989286B2 (en) | 2011-11-10 | 2015-03-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Mapping a transmission stream in a virtual baseband to a physical baseband with equalization |
| US8751913B2 (en) | 2011-11-14 | 2014-06-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for reduced power multi-layer data decoding |
| US8531320B2 (en) | 2011-11-14 | 2013-09-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for memory efficient data decoding |
| US8760991B2 (en) | 2011-11-14 | 2014-06-24 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for post processing gain correction |
| US8700981B2 (en) | 2011-11-14 | 2014-04-15 | Lsi Corporation | Low latency enumeration endec |
| US8719686B2 (en) | 2011-11-22 | 2014-05-06 | Lsi Corporation | Probability-based multi-level LDPC decoder |
| US8631300B2 (en) | 2011-12-12 | 2014-01-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for scalable data processing shut down |
| US8625221B2 (en) | 2011-12-15 | 2014-01-07 | Lsi Corporation | Detector pruning control system |
| US8819515B2 (en) | 2011-12-30 | 2014-08-26 | Lsi Corporation | Mixed domain FFT-based non-binary LDPC decoder |
| US8707123B2 (en) | 2011-12-30 | 2014-04-22 | Lsi Corporation | Variable barrel shifter |
| US8751889B2 (en) | 2012-01-31 | 2014-06-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for multi-pass alternate decoding |
| US8850295B2 (en) | 2012-02-01 | 2014-09-30 | Lsi Corporation | Symbol flipping data processor |
| US8775896B2 (en) | 2012-02-09 | 2014-07-08 | Lsi Corporation | Non-binary LDPC decoder with low latency scheduling |
| US8749907B2 (en) | 2012-02-14 | 2014-06-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for adaptive decoder message scaling |
| US8782486B2 (en) | 2012-03-05 | 2014-07-15 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for multi-matrix data processing |
| US8610608B2 (en) | 2012-03-08 | 2013-12-17 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for reduced latency loop correction |
| US8731115B2 (en) | 2012-03-08 | 2014-05-20 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for data processing including pre-equalizer noise suppression |
| US8873182B2 (en) | 2012-03-09 | 2014-10-28 | Lsi Corporation | Multi-path data processing system |
| US8977937B2 (en) | 2012-03-16 | 2015-03-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for compression driven variable rate decoding in a data processing system |
| US9043684B2 (en) | 2012-03-22 | 2015-05-26 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for variable redundancy data protection |
| US9230596B2 (en) | 2012-03-22 | 2016-01-05 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for variable rate coding in a data processing system |
| US8612826B2 (en) | 2012-05-17 | 2013-12-17 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for non-binary LDPC encoding |
| US8880986B2 (en) | 2012-05-30 | 2014-11-04 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for improved data detection processing |
| US9019647B2 (en) | 2012-08-28 | 2015-04-28 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for conditional positive feedback data decoding |
| US8930780B2 (en) | 2012-08-28 | 2015-01-06 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for non-zero syndrome based processing |
| US8751915B2 (en) | 2012-08-28 | 2014-06-10 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for selectable positive feedback data processing |
| US9324372B2 (en) | 2012-08-28 | 2016-04-26 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for local iteration randomization in a data decoder |
| US8949702B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2015-02-03 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for detector side trapping set mitigation |
| US9112531B2 (en) | 2012-10-15 | 2015-08-18 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for enhanced local iteration randomization in a data decoder |
| US8634152B1 (en) | 2012-10-15 | 2014-01-21 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for throughput enhanced data detection in a data processing circuit |
| US9048870B2 (en) | 2012-11-19 | 2015-06-02 | Lsi Corporation | Low density parity check decoder with flexible saturation |
| US9130589B2 (en) | 2012-12-19 | 2015-09-08 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Low density parity check decoder with dynamic scaling |
| US8929009B2 (en) | 2012-12-19 | 2015-01-06 | Lsi Corporation | Irregular low density parity check decoder with low syndrome error handling |
| US8773791B1 (en) | 2013-01-14 | 2014-07-08 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for X-sample based noise cancellation |
| US9003263B2 (en) | 2013-01-15 | 2015-04-07 | Lsi Corporation | Encoder and decoder generation by state-splitting of directed graph |
| US9009557B2 (en) | 2013-01-21 | 2015-04-14 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for reusing a layered decoder to yield a non-layered result |
| US8885276B2 (en) | 2013-02-14 | 2014-11-11 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for shared layer data decoding |
| US8930792B2 (en) | 2013-02-14 | 2015-01-06 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for distributed low density parity check decoding |
| US9214959B2 (en) | 2013-02-19 | 2015-12-15 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for skip layer data decoding |
| US9048873B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2015-06-02 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for multi-stage encoding of concatenated low density parity check codes |
| US8797668B1 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2014-08-05 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for penalty based multi-variant encoding |
| US9048874B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2015-06-02 | Lsi Corporation | Min-sum based hybrid non-binary low density parity check decoder |
| US9281843B2 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2016-03-08 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for reduced constraint code data processing |
| US9048867B2 (en) | 2013-05-21 | 2015-06-02 | Lsi Corporation | Shift register-based layered low density parity check decoder |
| US9274889B2 (en) | 2013-05-29 | 2016-03-01 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for data processing using global iteration result reuse |
| US8959414B2 (en) | 2013-06-13 | 2015-02-17 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for hybrid layer data decoding |
| US8917466B1 (en) | 2013-07-17 | 2014-12-23 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for governing in-flight data sets in a data processing system |
| US8817404B1 (en) | 2013-07-18 | 2014-08-26 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for data processing control |
| US8908307B1 (en) | 2013-08-23 | 2014-12-09 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for hard disk drive region based data encoding |
| US9196299B2 (en) | 2013-08-23 | 2015-11-24 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for enhanced data encoding and decoding |
| US9047882B2 (en) | 2013-08-30 | 2015-06-02 | Lsi Corporation | Systems and methods for multi-level encoding and decoding |
| US9129651B2 (en) | 2013-08-30 | 2015-09-08 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Array-reader based magnetic recording systems with quadrature amplitude modulation |
| US9298720B2 (en) | 2013-09-17 | 2016-03-29 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for fragmented data recovery |
| CN104518801A (zh) | 2013-09-29 | 2015-04-15 | Lsi公司 | 非二进制的分层低密度奇偶校验解码器 |
| US9219503B2 (en) | 2013-10-16 | 2015-12-22 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for multi-algorithm concatenation encoding and decoding |
| US9323606B2 (en) | 2013-11-21 | 2016-04-26 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods for FAID follower decoding |
| US9130599B2 (en) | 2013-12-24 | 2015-09-08 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Systems and methods of converting detector output to multi-level soft information |
| RU2014104571A (ru) | 2014-02-10 | 2015-08-20 | ЭлЭсАй Корпорейшн | Системы и способы для эффективного с точки зрения площади кодирования данных |
| US9378765B2 (en) | 2014-04-03 | 2016-06-28 | Seagate Technology Llc | Systems and methods for differential message scaling in a decoding process |
| US9419656B2 (en) * | 2014-07-29 | 2016-08-16 | Intel IP Corporation | Decoder and method for decoding an encoded sequence of bits |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US477636A (en) * | 1892-06-28 | blodgett | ||
| CA1260143A (en) * | 1986-02-24 | 1989-09-26 | Atsushi Yamashita | Path trace viterbi decoder |
| GB2309867A (en) * | 1996-01-30 | 1997-08-06 | Sony Corp | Reliability data in decoding apparatus |
| JPH09266448A (ja) * | 1996-03-28 | 1997-10-07 | Sony Corp | ビタビ復号化装置およびビタビ復号化方法 |
| US5878098A (en) * | 1996-06-27 | 1999-03-02 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for rate determination in a communication system |
| DE69719141T2 (de) * | 1996-10-15 | 2003-07-24 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Vorrichtung zur Zurückverfolgung des Pfades in einem Viterbi Dekodierer |
| WO1998018209A1 (fr) * | 1996-10-24 | 1998-04-30 | Sony Corporation | Dispositif et appareil de decodage de viterbi |
-
1997
- 1997-12-19 JP JP35143497A patent/JP3900637B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1998
- 1998-12-15 MY MYPI98005661A patent/MY119831A/en unknown
- 1998-12-17 EP EP09001553A patent/EP2053750A1/en not_active Ceased
- 1998-12-17 EP EP98124034A patent/EP0924863A3/en not_active Ceased
- 1998-12-17 US US09/215,452 patent/US6748034B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1998-12-18 KR KR1019980056323A patent/KR100538730B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-12-18 CN CN98125339A patent/CN1220522A/zh active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0924863A2 (en) | 1999-06-23 |
| JP3900637B2 (ja) | 2007-04-04 |
| EP0924863A3 (en) | 2004-06-09 |
| US6748034B2 (en) | 2004-06-08 |
| KR19990063227A (ko) | 1999-07-26 |
| JPH11186919A (ja) | 1999-07-09 |
| US20030108128A1 (en) | 2003-06-12 |
| EP2053750A1 (en) | 2009-04-29 |
| MY119831A (en) | 2005-07-29 |
| KR100538730B1 (ko) | 2006-02-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1220522A (zh) | 维特比译码装置及维特比译码方法 | |
| CN1130028C (zh) | 维特比译码装置及维特比译码方法 | |
| US7765457B2 (en) | Parallel convolutional encoder | |
| CN101777924B (zh) | 一种Turbo码译码方法和装置 | |
| CN100508440C (zh) | 接收移动无线信号时的译码及循环冗余校验的并行处理的方法和装置 | |
| AU7778400A (en) | Interleaver and method for interleaving an input data bit sequence using a codedstoring of symbol and additional information | |
| CN101969311B (zh) | 一种高速并行分段交错维特比译码方法 | |
| CN1853350A (zh) | 用于移动通信系统的维特比/涡轮联合译码器 | |
| US7340669B2 (en) | Memory efficient streamlined transmitter with a multiple instance hybrid ARQ | |
| EP0819341B1 (en) | Multiport ram for use within a viterbi decoder | |
| WO2016127853A1 (zh) | 一种基于扩展汉明码的二维乘积码编码装置及编码方法 | |
| CN1830151A (zh) | 维特比解码器 | |
| CN1249588C (zh) | 公用存储器设备及其控制方法 | |
| CN201018490Y (zh) | TD-SCDMA/3G硬核turbo译码器 | |
| US7035356B1 (en) | Efficient method for traceback decoding of trellis (Viterbi) codes | |
| CN1614898B (zh) | Turbo码编码器及其编码方法 | |
| CN111900999B (zh) | 一种面向卫星非连续通信的高性能极化编码方法及编码器 | |
| US6408418B1 (en) | Reduced-state device and method for decoding data | |
| JP2002271209A (ja) | ターボ符号器およびターボ復号器 | |
| CN1176541C (zh) | 用于提高乘积码译码速度的方法及译码装置 | |
| CN1251464C (zh) | 信息处理系统 | |
| CN102282771B (zh) | 解码方法 | |
| RU196572U1 (ru) | Функциональный прототип на программируемой логической интегральной схеме цифровой сверхбольшой интегральной схемы для радиосистем | |
| CN100444524C (zh) | 用于通信系统中编码数据位的方法、设备和系统 | |
| SU1587644A1 (ru) | Устройство дл декодировани двоичных блочных кодов, согласованных с многопозиционными сигналами |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C01 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application (patent law 1993) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |