CN115485856A - 半导体装置 - Google Patents
半导体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115485856A CN115485856A CN202180029678.0A CN202180029678A CN115485856A CN 115485856 A CN115485856 A CN 115485856A CN 202180029678 A CN202180029678 A CN 202180029678A CN 115485856 A CN115485856 A CN 115485856A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- gate
- trench
- semiconductor device
- drift
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 89
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 250
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 108091006146 Channels Proteins 0.000 description 41
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 33
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 18
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 12
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 108090000699 N-Type Calcium Channels Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004129 N-Type Calcium Channels Human genes 0.000 description 2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010075750 P-Type Calcium Channels Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/10—Modifications for increasing the maximum permissible switched voltage
- H03K17/102—Modifications for increasing the maximum permissible switched voltage in field-effect transistor switches
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1095—Body region, i.e. base region, of DMOS transistors or IGBTs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/06—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration
- H01L27/0611—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration integrated circuits having a two-dimensional layout of components without a common active region
- H01L27/0617—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration integrated circuits having a two-dimensional layout of components without a common active region comprising components of the field-effect type
- H01L27/0629—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration integrated circuits having a two-dimensional layout of components without a common active region comprising components of the field-effect type in combination with diodes, or resistors, or capacitors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
- H01L29/0623—Buried supplementary region, e.g. buried guard ring
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1066—Gate region of field-effect devices with PN junction gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/16—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L29/1608—Silicon carbide
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7811—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with an edge termination structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7813—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with trench gate electrode, e.g. UMOS transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/80—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by a PN or other rectifying junction gate, i.e. potential-jump barrier
- H01L29/808—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by a PN or other rectifying junction gate, i.e. potential-jump barrier with a PN junction gate, e.g. PN homojunction gate
- H01L29/8083—Vertical transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/16—Modifications for eliminating interference voltages or currents
- H03K17/161—Modifications for eliminating interference voltages or currents in field-effect transistor switches
- H03K17/162—Modifications for eliminating interference voltages or currents in field-effect transistor switches without feedback from the output circuit to the control circuit
- H03K17/163—Soft switching
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/51—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used
- H03K17/56—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used by the use, as active elements, of semiconductor devices
- H03K17/687—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used by the use, as active elements, of semiconductor devices the devices being field-effect transistors
- H03K17/6871—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used by the use, as active elements, of semiconductor devices the devices being field-effect transistors the output circuit comprising more than one controlled field-effect transistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/06—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration
- H01L27/07—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration the components having an active region in common
- H01L27/0705—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration the components having an active region in common comprising components of the field effect type
- H01L27/0727—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration the components having an active region in common comprising components of the field effect type in combination with diodes, or capacitors or resistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/063—Reduced surface field [RESURF] pn-junction structures
- H01L29/0634—Multiple reduced surface field (multi-RESURF) structures, e.g. double RESURF, charge compensation, cool, superjunction (SJ), 3D-RESURF, composite buffer (CB) structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/0048—Circuits or arrangements for reducing losses
- H02M1/0051—Diode reverse recovery losses
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M1/00—Details of apparatus for conversion
- H02M1/08—Circuits specially adapted for the generation of control voltages for semiconductor devices incorporated in static converters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M7/00—Conversion of ac power input into dc power output; Conversion of dc power input into ac power output
- H02M7/003—Constructional details, e.g. physical layout, assembly, wiring or busbar connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M7/00—Conversion of ac power input into dc power output; Conversion of dc power input into ac power output
- H02M7/42—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal
- H02M7/44—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters
- H02M7/48—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M7/53—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M7/537—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters
- H02M7/5387—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters in a bridge configuration
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P27/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage
- H02P27/04—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage
- H02P27/06—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/51—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used
- H03K17/56—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used by the use, as active elements, of semiconductor devices
- H03K17/687—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used by the use, as active elements, of semiconductor devices the devices being field-effect transistors
- H03K2017/6875—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking characterised by the components used by the use, as active elements, of semiconductor devices the devices being field-effect transistors using self-conductive, depletion FETs
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
- Junction Field-Effect Transistors (AREA)
Abstract
具备:第1导电型的漂移层(212);第2导电型的沟道层(213),配置在漂移层(212)上;沟槽栅构造,具有配置在以将沟道层(213)贯通而达到漂移层(212)的方式形成的沟槽(214)的壁面上的栅极绝缘膜(215)和配置在栅极绝缘膜(215)上的栅极电极(23);第1导电型的源极层(216),在沟道层(213)的表层部中以与沟槽(214)相接的方式形成,杂质浓度比漂移层(212)高;以及第1导电型的漏极层(211),隔着漂移层(212)而配置在与沟道层(213)相反的一侧。并且,沟槽(214)中的达到漂移层(212)的部分的整个区域被第2导电型的阱层(223)覆盖。阱层(223)与沟道层(213)相连。
Description
关联申请的相互参照
本申请基于2020年4月22日提出的日本专利申请第2020-76334号,这里通过参照而引用其记载内容。
技术领域
本发明涉及具有沟槽栅构造的MOSFET(Metal Oxide Semiconductor FieldEffect Transistor的简称)的半导体装置。
背景技术
以往,提出了具有沟槽栅构造的MOSFET的半导体装置。具体而言,该半导体装置的MOSFET采用构成N-型的漂移层的半导体衬底而构成。并且,半导体衬底在一面侧形成有沟道层,并且以将沟道层贯通而达到漂移层的方式形成有多个沟槽。另外,各沟槽以将半导体衬底的面方向上的一个方向作为长度方向的方式延伸设置。并且,通过在各沟槽中依次形成栅极绝缘膜及栅极电极而构成沟槽栅构造。
在沟道层的表层部,以与沟槽相接的方式形成有N+型的源极区域。在半导体衬底的另一面侧形成有N+型的漏极层。
在这样的MOSFET中,构成有包含沟道层和漂移层及漏极层的寄生二极管(以下也简称作二极管)。并且,在二极管的恢复动作时,如果在沟槽的底部发生电场集中,则通过动态雪崩产生空穴从而恢复损耗容易增加。因此,例如在非专利文献1中,记载了以将沟槽中的向漂移层突出的部分的一部分覆盖的方式配置P型的杂质层的结构。
现有技术文献
非专利文献
非专利文献1:Y.Fukui,K.Sugawara,R.Tanaka,H.Koketsu,H.Hatta,Y.Miyata,H.Suzuki,K.Taguchi,Y.Kagawa,S.Tomohisa,N.Miura,Effects of Grounding BottomOxide Protection Layer in Trench Gate SiC MOSFET by Tilted Al Implantation,International Conference on Silicon Carbide and Related Materials 2019
发明内容
但是,在这样的半导体装置中,也有可能不能充分地减小恢复损耗。
本发明的目的在于,提供能够充分地减小恢复损耗的半导体装置。
根据本发明的一技术方案,半导体装置的MOSFET具备:第1导电型的漂移层;第2导电型的沟道层,配置在漂移层上;沟槽栅构造,具有配置在以将沟道层贯通而达到漂移层的方式形成的沟槽的壁面上的栅极绝缘膜和配置在栅极绝缘膜上的栅极电极;第1导电型的源极层,在沟道层的表层部中以与沟槽相接的方式形成,杂质浓度比漂移层高;第1导电型的漏极层,隔着漂移层而配置在与沟道层相反的一侧;源极电极,与沟道层及源极层电连接;以及漏极电极,与漏极层电连接;沟槽中的达到漂移层的部分的整个区域被第2导电型的阱层覆盖;阱层与沟道层相连。
由此,沟槽中的向漂移层突出的部分的整个区域被阱层覆盖。因此,能够抑制在沟槽的底部发生电场集中的情况,能够抑制通过动态雪崩而产生空穴的情况。因而,能够减小恢复损耗。
另外,对各构成要素等赋予的带括号的标号表示该构成要素等与后述的实施方式中记载的具体构成要素等的对应关系的一例。
附图说明
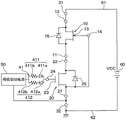
图1是第1实施方式的半导体装置的电路图。
图2是形成JFET的第1半导体芯片的平面图。
图3是图2中的区域III的放大图。
图4是沿着图3中的IV-IV线的剖视图。
图5是沿着图3中的V-V线的剖视图。
图6是沿着图3中的VI-VI线的剖视图。
图7是形成MOSFET的第2半导体芯片的平面图。
图8是沿着图7中的VIII-VIII线的剖视图。
图9是沿着图7中的IX-IX线的剖视图。
图10是表示关于面密度比与导通电压及恢复损耗之间的关系的模拟结果的图。
图11是第2实施方式的第2半导体芯片的剖视图。
图12是第3实施方式的半导体装置的电路图。
图13是利用图12所示的半导体装置构成的逆变器(inverter)的电路图。
图14是图13中的U层的电路图。
具体实施方式
以下,基于附图对本发明的实施方式进行说明。另外,在以下各实施方式中,对于彼此相同或等同的部分赋予相同的标号而进行说明。
(第1实施方式)
参照附图对第1实施方式进行说明。首先,对本实施方式的半导体装置的电路结构进行说明。如图1所示,本实施方式的半导体装置具有常导通(normally on)型的结型FET(Field Effect Transistor:以下简称作JFET)10和常截止(normally off)型的MOSFET20。并且,半导体装置将JFET10和MOSFET20级联连接而构成。另外,在本实施方式中,JFET10及MOSFET20分别为N沟道型。
JFET10具有源极电极11、漏极电极12、栅极层(即栅极电极)13,具体结构后述。MOSFET20具有源极电极21、漏极电极22及栅极电极23,具体结构后述。
并且,JFET10及MOSFET20中,JFET10的源极电极11和MOSFET20的漏极电极22电连接。此外,JFET10的漏极电极12与第1端子31连接,MOSFET20的源极电极21与第2端子32连接。
MOSFET20的栅极电极23经由栅极焊盘24及调整电阻41而与栅极驱动电路50连接。JFET10的栅极层13经由栅极焊盘14而与MOSFET20的源极电极21电连接。
此外,在本实施方式中,在JFET10的漏极电极12与源极电极11之间连接着二极管15。在本实施方式中,JFET10如图4所示那样在N型的沟道层114内形成有P型的体(body)层115,具体后述。并且,二极管15包括该体层115而构成。该二极管15成为阴极与漏极电极12电连接、阳极与源极电极11电连接的状态。
此外,在MOSFET20的漏极电极22与源极电极21之间连接着二极管25。该二极管25是在MOSFET20的结构上形成的寄生二极管,阴极与漏极电极22电连接,阳极与源极电极21电连接。
以上是本实施方式的半导体装置的电路结构。并且,这样的半导体装置如以下那样使用,即:第1端子31与从电源60施加电压Vcc的电源线61连接,第2端子32与地线62连接。
接着,对JFET10及MOSFET20的具体结构进行说明。首先,对JFET10的结构进行说明。JFET10如图2所示,形成于第1半导体芯片100。
第1半导体芯片100如图2及图3所示那样,平面形状为矩形,具有单元区域101以及将单元区域101包围的外周区域102,所述单元区域101具有内缘单元区域101a和将内缘单元区域101a包围的外缘单元区域101b。并且,JFET10形成在单元区域101。
具体而言,第1半导体芯片100如图4~图6所示,具备半导体衬底110,该半导体衬底110具有由N++型的碳化硅(以下称作SiC)衬底构成的漏极层111。并且,漏极层111上配置有杂质浓度比漏极层111低的N+型的缓冲层112,在缓冲层112上配置有杂质浓度比缓冲层112低的N-型的漂移层113。另外,缓冲层112及漂移层113通过在构成漏极层111的SiC衬底上使SiC的外延膜成长而构成。
并且,在单元区域101,在半导体衬底110的一面110a侧形成有沟道层114、栅极层13、体层115及源极层116。具体而言,在单元区域101,在漂移层113上配置有杂质浓度比漂移层113高的N型的沟道层114。另外,沟道层114例如通过使SiC的外延膜成长而构成。并且,半导体衬底110的一面110a包括沟道层114的表面而构成。
在沟道层114中,形成有杂质浓度比沟道层114高的P+型的栅极层13及P+型的体层115。在本实施方式中,栅极层13及体层115杂质浓度彼此相等,并且从半导体衬底110的一面110a(即,沟道层114的表面)沿着深度方向形成。但是,在本实施方式中,体层115比栅极层13形成得更深。即,体层115是比栅极层13更向漏极层111侧突出的结构。
此外,栅极层13及体层115沿着半导体衬底110的面方向上的一个方向延伸设置,在该面方向上的与延伸设置方向正交的方向上交替地配置。即,在图4中,栅极层13及体层115沿着纸面垂直方向延伸设置,在沿着纸面左右方向相互离开的状态下交替地配置。另外,半导体衬底110的深度方向换言之也可以说是漏极层111、漂移层113、沟道层114的层叠方向。此外,栅极层13及体层115例如通过离子注入或使SiC的埋入外延膜成长而构成。
在本实施方式中,如图3、图5、图6所示,栅极层13从内缘单元区域101a延伸设置到外缘单元区域101b。并且,栅极层13通过使位于外缘单元区域101b中的延伸设置方向的两端部环绕而被做成环状构造,被做成环状构造的部分被相互连接。因此,图4中的体层115也可以说配置在被做成环状构造的栅极层13的内缘侧的区域。
另外,在本实施方式中,如图3、图5图6所示,体层115还形成在外缘单元区域101b,如后述那样,与形成于外周区域102的多个保护环121中的1个连接。
此外,如图4所示,在沟道层114的表层部,以与体层115相接的方式形成有杂质浓度比沟道层114高的N+型的源极层116。另外,源极层116例如通过离子注入而构成。
并且,如图3、图5及图6所示,在半导体衬底110上,在外缘单元区域101b中形成有栅极焊盘14和与该栅极焊盘14及栅极层13电连接的栅极布线118。另外,在第1半导体芯片100,虽然没有特别图示,但还形成有温度感测部或电流感测部等。并且,在外缘单元区域101b,还形成有与这些各种感测部电连接的焊盘16及未图示的布线。
此外,如图4~图6所示,在半导体衬底110的一面110a上,以将栅极布线118覆盖的方式形成有层间绝缘膜119。另外,层间绝缘膜119形成在单元区域101及外周区域102。并且,在层间绝缘膜119,在单元区域101中形成有使沟道层114、体层115及源极层116露出的接触孔119a。在层间绝缘膜119上,形成有经由接触孔119a而与源极层116及体层115电连接的源极电极11。
在半导体衬底110的另一面110b侧,形成有与漏极层111电连接的漏极电极12。
外周区域102如图5及图6所示,通过形成将相当于单元区域101的沟道层114的部分除去的凹部120而被做成台面(mesa)构造。并且,在外周区域102,形成有将单元区域101包围的被做成多重环构造的多个保护环121。另外,在本实施方式中,多个保护环121中的最靠单元区域101侧的1个与形成在外缘单元区域101b中的体层115电连接,但也可以不电连接。
以上是本实施方式的第1半导体芯片100的结构。另外,在本实施方式的第1半导体芯片100中,N-型、N型、N+型、N++型相当于第1导电型,P型、P+型相当于第2导电型。此外,在本实施方式中,如上述那样,包含漏极层111、缓冲层112、漂移层113、沟道层114、体层115、源极层116、栅极层13而构成半导体衬底110。并且,在本实施方式中,如上述那样,漏极层111由SiC衬底构成,缓冲层112、漂移层113、沟道层114等通过使SiC的外延膜成长而构成。因此,本实施方式的第1半导体芯片100也可以说是SiC半导体装置。此外,在本实施方式中,第1半导体芯片100形成有P型的体层115。并且,图1中的二极管15起因于体层115而构成。
接着,对MOSFET20的结构进行说明。MOSFET20如图7所示,形成于第2半导体芯片200。
第2半导体芯片200,平面形状为矩形,具有单元区域201及将单元区域201包围的外周区域202。并且,MOSFET20形成在单元区域201。
具体而言,第2半导体芯片200如图8及图9所示,具备半导体衬底210,该半导体衬底210具有由N+型的硅(以下称作Si)衬底构成的漏极层211。在漏极层211上,配置有杂质浓度比漏极层211低的N型的漂移层212。并且,在单元区域201中,在漂移层212上配置有杂质浓度比漂移层212高的P型的沟道层213。
此外,在半导体衬底210,以将沟道层213贯通而达到漂移层212的方式形成有多个沟槽214,通过该沟槽214将沟道层213分离为多个。在本实施方式中,多个沟槽214沿着半导体衬底210的一面210a的面方向中的一个方向(即,图8中纸面进深方向)以等间隔形成为条状。另外,也可以将多个沟槽214通过将前端部环绕而做成环状构造。
此外,各沟槽214内被以将各沟槽214的壁面覆盖的方式形成的栅极绝缘膜215和形成在该栅极绝缘膜215之上的由多晶硅等构成的栅极电极23填埋。由此,构成沟槽栅构造。
并且,在沟道层213中,形成有N+型的源极层216和被源极层216夹着的P+型的接触层217。源极层216杂质浓度比漂移层212高,在沟道层213内终止,并且以与沟槽214的侧面相接的方式形成。接触层217杂质浓度比沟道层213高,与源极层216同样,以在沟道层213内终止的方式形成。
更详细地讲,源极层216在沟槽214间的区域沿着沟槽214的长度方向以与沟槽214的侧面相接的方式以棒状延伸设置,成为在沟槽214的前端的内侧终止的构造。此外,接触层217被2个源极层216夹着而沿着沟槽214的长度方向(即源极层216)以棒状延伸设置。另外,本实施方式的接触层217以半导体衬底210的一面210a为基准形成得比源极层216深。
在沟道层213(即,半导体衬底210的一面210a)上,形成有层间绝缘膜218。另外,该层间绝缘膜218如图9所示也形成在外周区域202。在层间绝缘膜218,形成有使源极层216的一部分及接触层217露出的接触孔218a。在层间绝缘膜218上,形成有经由接触孔218a而与源极层216及接触层217电连接的源极电极21。
在半导体衬底210的另一面210b侧,形成有与漏极层211电连接的漏极电极22。
此外,在外周区域202,如图7所示,形成有栅极焊盘24及未图示的栅极布线等。并且,栅极布线在与图8及图9不同的截面中适当地与栅极电极23电连接。另外,在第2半导体芯片200,虽然没有特别图示,但还形成有温度感测部及电流感测部等。并且,在外周区域202,还形成有与这些各种感测部电连接的焊盘26及未图示的布线。
进而,在外周区域202,为了实现耐压提高,在单元区域201侧的内缘部形成有P型的深层220,并且,在比深层220靠外缘部侧,作为多重环构造而形成有多个P型的保护环221。另外,本实施方式的深层220与沟道层213相连,并且形成至比沟道层213深的位置。此外,在外周区域202,形成有将层间绝缘膜218覆盖的保护膜222,在保护膜222,形成有使源极电极21露出的开口部222a。另外,MOSFET20通过如上述那样构成,构成由沟道层213和漂移层212及漏极层211构成的图1的二极管25。
并且,本实施方式的MOSFET20,在漂移层212中的与沟槽214相接的部分的整个区域中形成有沿着沟槽214的壁面的P型的阱层223。换言之,沟槽214中的向漂移层212突出的部分成为整个区域被阱层223覆盖的状态。另外,阱层223以与沟道层213相连的方式形成。
由此,在MOSFET20中的二极管25的恢复时,能够通过阱层223抑制在沟槽214的底部发生电场集中的情况,能够抑制通过动态雪崩产生空穴的情况。因而,能够减小恢复损耗。
另外,在形成沟槽214之后,在形成栅极绝缘膜215、栅极电极23等之前,通过将硼等杂质对于沟槽214的壁面进行离子注入而形成这样的阱层223。
这里,上述那样的MOSFET20,通过对栅极电极23施加规定的栅极电压,在沟道层213及阱层223中的与沟槽214相接的部分形成作为沟道发挥功能的反型层而成为导通状态。该情况下,如果阱层223的杂质面密度过高,则有可能在阱层223中不适当地形成沟道从而导通电压增加。
因此,本发明的发明人还对于阱层223的杂质面密度相对于漂移层212的杂质面密度的面密度比(以下也简称作面密度比)与导通电压及恢复损耗之间的关系进行专门研究,得到了图10所示的结果。另外,在图10中,将恢复损耗用Err表示,将导通电压用RonA表示。此外,面密度比是阱层223的杂质面密度/漂移层212的杂质面密度。
如图10所示,确认到恢复损耗由于阱层223的形成而下降。具体而言,确认到恢复损耗急剧地下降直到面密度比成为3.0×10-5。并且,确认到恢复损耗当面密度比成为3.0×10-5以上时大致一定。
另一方面,确认到导通电压直到面密度比为4.0×10-5为止是大致一定的。并且,确认到当面密度比大于4.0×10-5时导通电压逐渐增加。该情况下,导通电压中的斜率最小的部分的切线S1与斜率最大的部分的切线S2的交点成为面密度比为2.0×10-4的部分。因此,可以说,当面密度比大于2.0×10-4,则导通电压急剧地变大。
因而,在本实施方式中,面密度比被设为3.0×10-5以上、2.0×10-4以下。由此,能够减小恢复损耗并且抑制导通电压的增加。该情况下,优选的是,面密度比为3.0×10-5以上、4.0×10-5以下。由此,能够减小恢复损耗并且充分地抑制导通电压的增加。
以上是本实施方式的第2半导体芯片200的结构。另外,在本实施方式的第2半导体芯片200中,N型、N-型、N+型、N++型相当于第1导电型,P型、P+型相当于第2导电型。此外,在本实施方式中,如上述那样,包括漏极层211、漂移层212、沟道层213、源极层216、接触层217及阱层223而构成半导体衬底210。进而,在本实施方式中,如上述那样使用Si衬底构成第2半导体芯片200。因此,第2半导体芯片200也可以说是Si半导体装置。
并且,虽然没有特别图示,将这些形成于第1半导体芯片100的JFET10与形成于第2半导体芯片200的MOSFET20以级联连接的方式电连接而构成本实施方式的半导体装置。
接着,对上述半导体装置的基本动作进行说明。另外,本实施方式的半导体装置由于具有常截止的MOSFET20,所以整体为常截止而进行动作。
首先,为了使半导体装置进行开关导通(switching on)动作而成为导通状态,从栅极驱动电路50对MOSFET20的栅极电极23施加阈值电压以上的栅极电压。由此,常截止型的MOSFET20成为导通状态。此外,JFET10的栅极层13与第2端子32连接。因此,关于常导通型的JFET10,栅极层13与源极电极11的电位差大致为零,成为导通状态。因而,在第1端子31与第2端子32之间流过电流,半导体装置最终成为导通状态。
接着,为了使半导体装置进行开关断开(switching off)动作而成为截止状态,使施加在MOSFET20的栅极电极23上的栅极电压比阈值电压小(例如设为0V)。由此,常截止型的MOSFET20成为截止状态。此外,由于MOSFET20成为截止状态,MOSFET20的漏极电极22和与其连接的JFET10的源极电极11的电压上升,在该源极电极11与连接于第2端子32的JFET10的栅极层13之间产生电位差。并且,源极电极11与栅极层13之间的电位差达到阈值,从而沟道消失,JFET10成为截止状态。由此,在第1端子31与第2端子32之间不再流过电流,半导体装置最终成为截止状态。
根据以上说明的本实施方式,MOSFET20成为沟槽214中的向漂移层212突出的部分的整个区域被阱层223覆盖的状态。因此,能够抑制在沟槽214的底部发生电场集中的情况,能够抑制通过动态雪崩产生空穴的情况。因而,能够减小恢复损耗。
此外,MOSFET20的面密度比被设为3.0×10-5以上、2.0×10-4以下。由此,能够减小恢复损耗并且抑制导通电压的增加。该情况下,优选的是,将面密度比设为3.0×10-5以上、4.0×10-5以下。由此,能够减小恢复损耗并且充分地抑制导通电压的增加。
进而,本实施方式的JFET10的体层115比栅极层13深。因此,电场强度在体层115的底部侧容易比栅极层13的底部侧变高。因而,当发生了浪涌时,在体层115的底部侧的区域容易发生击穿,浪涌电流容易向体层115流入。由此,栅极布线118熔断从而还能够抑制半导体装置的损坏,能够实现浪涌耐受性的提高。
(第2实施方式)
对第2实施方式进行说明。本实施方式相对于第1实施方式,在漂移层212中构成了超结(以下也简称作SJ)构造。其他与第1实施方式是同样的,所以这里省略说明。
在本实施方式中,如图11所示,在漏极211层上形成有N型的缓冲层224。并且,在缓冲层224上,形成有作为漂移层212的N型柱(column)区域212a及P型柱区域212b以构成SJ构造。在本实施方式中,这些N型柱区域212a及P型柱区域212b在与半导体衬底210的面方向平行的一个方向(即图11中纸面垂直方向)上延伸设置。此外,这些N型柱区域212a及P型柱区域212b在与该一个方向正交的方向(即图11中纸面左右方向)上反复排列。更详细地讲,这些N型柱区域212a及P型柱区域212b沿着沟槽214的延伸设置方向形成,并且沿着沟槽214的排列方向反复排列。并且,P型柱区域212b与沟道层213连接。
如以上说明的那样,对于具有SJ构造的半导体装置也能够应用上述第1实施方式。
(第3实施方式)
对第3实施方式进行说明。本实施方式使用第1实施方式的半导体装置构成了逆变器。其他与第1实施方式是同样的,所以这里省略说明。
在本实施方式中,如图12所示,将调整电阻41做成以下结构。即,调整电阻41具有串联连接着第1二极管411a和第1电阻411b的第1电阻电路411、以及串联连接着第2二极管412a和第2电阻412b的第2电阻电路412。并且,第1电阻电路411及第2电阻电路412并联地配置,以将第1二极管411a的阴极及第2二极管412a的阳极分别与MOSFET20的栅极电极23连接。
在本实施方式中,MOSFET20的栅极电极23和栅极驱动电路50经由这样的调整电阻41连接。因此,MOSFET20在进行开关导通动作的情况和进行开关断开动作的情况下,通过不同的电阻电路来调整开关速度。
具体而言,MOSFET20的栅极电极23在进行开关导通动作时成为经由第1电阻电路411而与栅极驱动电路50连接的状态。即,第1电阻电路411作为MOSFET20的开关导通动作用的速度调整电阻发挥功能。此外,MOSFET20的栅极电极23在进行开关断开动作时成为经由第2电阻电路412而与栅极驱动电路50连接的状态。即,第2电阻电路412作为MOSFET20的开关断开动作用的速度调整电阻发挥功能。因此,通过调整各电阻电路411、412的电阻值,能够适当调整MOSFET20的开关速度。
以上是本实施方式的半导体装置的结构。这样的半导体装置例如如图13所示,被用作将三相马达驱动的逆变器的开关元件。
即,如图13所示,逆变器成为在被施加来自电源600的电压Vcc的电源线610与被接地的地线620之间具备U相、V相、W相的3个电路的结构。并且,各层分别与栅极驱动电路50及三相马达M连接。以下,参照图14对U层的详细结构进行说明。另外,V层、W层的详细结构与U层相同,所以省略。
如图14所示,U层为具备两个图12所示的半导体装置的结构。并且,U层的上侧臂UA中的JFET10的漏极电极12经由第1端子31而与电源线610连接。U层的下侧臂LA中的MOSFET20的源极电极21经由第2端子32而与地线620连接。此外,上侧臂UA中的MOSFET20的源极电极21与下侧臂LA中的JFET10的漏极电极12电连接。即,上侧臂UA的第2端子32与下侧臂LA的第1端子31电连接。并且,上侧臂UA的第2端子32和下侧臂LA的第1端子31之间与三相马达M连接。此外,关于上侧臂UA及下侧臂LA中的各MOSFET20,各个MOSFET20中的栅极电极23与栅极驱动电路50连接。
这样,还能够将本实施方式的半导体装置用作逆变器的开关元件。
(其他实施方式)
对本发明依据实施方式进行了记述,但应理解的是本发明并不限定于该实施方式及构造。本发明也包含各种各样的变形例及等价范围内的变形。除此以外,各种各样的组合及形态、进而在它们中仅包含一要素、其以上或其以下的其他组合及形态也落入在本发明的范畴及思想范围中。
例如,在上述各实施方式中,也可以将第1导电型设为P型,将第2导电型设为N型。即,也可以将JFET10及MOSFET20做成P沟道型。
此外,在上述各实施方式中,对将JFET10和MOSFET20级联连接的半导体装置进行了说明。但是,半导体装置也可以做成不具备JFET10而仅具有沟槽栅构造的MOSFET20的结构。
进而,在上述各实施方式中,也可以将栅极层13及体层115设为相同的深度。此外,使体层115的底部侧相比于栅极层13的底部侧而言电场强度变高的结构能够适当变更。例如,也可以通过将体层115的底部做成尖细形状、或使体层115的宽度比栅极层13的宽度窄,做成体层115的底部侧相比于栅极层13的底部侧而言电场强度容易变高的结构。
并且,在上述各实施方式中,JFET10也可以使用硅衬底构成,也可以使用其他化合物半导体衬底等构成。同样,MOSFET20也可以使用SiC衬底构成,也可以使用其他化合物半导体衬底构成。
进而,在上述第1、第3实施方式中,MOSFET20中的漂移层212也可以为了能够实现高耐压而使得杂质浓度从漏极层211侧朝向沟道层213侧逐渐下降。
并且,也可以将上述各实施方式适当组合。例如,也可以将上述第2实施方式与上述第3实施方式组合,使用具有SJ构造的MOSFET20构成逆变器。此外,也可以将组合了上述各实施方式的形态彼此进一步组合。
Claims (4)
1.一种半导体装置,具有沟槽栅构造的MOSFET,其特征在于,
上述MOSFET具备:
第1导电型的漂移层(212);
第2导电型的沟道层(213),配置在上述漂移层上;
上述沟槽栅构造,具有配置在以将上述沟道层贯通而达到上述漂移层的方式形成的沟槽(214)的壁面上的栅极绝缘膜(215)、和配置在上述栅极绝缘膜上的栅极电极(23);
第1导电型的源极层(216),在上述沟道层的表层部中以与上述沟槽相接的方式形成,杂质浓度比上述漂移层高;
第1导电型的漏极层(211),隔着上述漂移层而配置在与上述沟道层相反的一侧;
源极电极(21),与上述沟道层及上述源极层电连接;以及
漏极电极(22),与上述漏极层电连接;
上述沟槽中的达到上述漂移层的部分的整个区域被第2导电型的阱层(223)覆盖;
上述阱层与上述沟道层相连。
2.如权利要求1所述的半导体装置,其特征在于,
具备具有源极电极(11)、漏极电极(12)、栅极电极(13)的结型FET;
上述结型FET的源极电极和上述MOSFET的漏极电极被电连接,从而上述MOSFET和上述结型FET被级联连接。
3.如权利要求1或2所述的半导体装置,其特征在于,
上述阱层的杂质面密度相对于上述漂移层的杂质面密度的面密度比为3.0×10-5以上且2.0×10-4以下。
4.如权利要求3所述的半导体装置,其特征在于,
上述面密度比为3.0×10-5以上且4.0×10-5以下。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020-076334 | 2020-04-22 | ||
| JP2020076334A JP7207361B2 (ja) | 2020-04-22 | 2020-04-22 | 半導体装置 |
| PCT/JP2021/016068 WO2021215445A1 (ja) | 2020-04-22 | 2021-04-20 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115485856A true CN115485856A (zh) | 2022-12-16 |
Family
ID=78269100
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202180029678.0A Pending CN115485856A (zh) | 2020-04-22 | 2021-04-20 | 半导体装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20230038806A1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP7207361B2 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN115485856A (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2021215445A1 (zh) |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012169384A (ja) | 2011-02-11 | 2012-09-06 | Denso Corp | 炭化珪素半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP5717661B2 (ja) | 2011-03-10 | 2015-05-13 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置とその製造方法 |
| JP5724997B2 (ja) | 2012-12-07 | 2015-05-27 | 株式会社デンソー | スーパージャンクション構造の縦型mosfetを有する半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6769458B2 (ja) | 2017-07-26 | 2020-10-14 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
-
2020
- 2020-04-22 JP JP2020076334A patent/JP7207361B2/ja active Active
-
2021
- 2021-04-20 WO PCT/JP2021/016068 patent/WO2021215445A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2021-04-20 CN CN202180029678.0A patent/CN115485856A/zh active Pending
-
2022
- 2022-10-19 US US17/969,023 patent/US20230038806A1/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021174835A (ja) | 2021-11-01 |
| JP7207361B2 (ja) | 2023-01-18 |
| WO2021215445A1 (ja) | 2021-10-28 |
| US20230038806A1 (en) | 2023-02-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10229993B2 (en) | LDMOS transistors including resurf layers and stepped-gates, and associated systems and methods | |
| US10192978B2 (en) | Semiconductor apparatus | |
| JP4761644B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2003298053A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| US9620595B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US10490655B2 (en) | Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) with high avalanche withstand | |
| CN111201611A (zh) | 具有高dv/dt能力的功率开关装置及制造这种装置的方法 | |
| US6534828B1 (en) | Integrated circuit device including a deep well region and associated methods | |
| JP2019186312A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US10211331B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| CN109585562B (zh) | 具有阴极短路结构的双向功率mosfet结构 | |
| JP2010147188A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2024015431A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2009512207A (ja) | パワー半導体デバイス | |
| JP4569105B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US20230042174A1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| CN115485856A (zh) | 半导体装置 | |
| CN112219277A (zh) | 具有温度传感器的功率半导体器件 | |
| EP3608961A1 (en) | Electronic circuit with a transistor device and a level shifter | |
| JP6789177B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US9905686B2 (en) | Insulated gate bipolar transistor with improved on/off resistance | |
| JP2021034528A (ja) | スイッチング素子 | |
| US11710734B2 (en) | Cascode-connected JFET-MOSFET semiconductor device | |
| WO2023053439A1 (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| JP2013069801A (ja) | 半導体装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |