CN1129016C - 用于多光纤光缆或单光纤光缆连接器的定位组件 - Google Patents
用于多光纤光缆或单光纤光缆连接器的定位组件 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1129016C CN1129016C CN96180202A CN96180202A CN1129016C CN 1129016 C CN1129016 C CN 1129016C CN 96180202 A CN96180202 A CN 96180202A CN 96180202 A CN96180202 A CN 96180202A CN 1129016 C CN1129016 C CN 1129016C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- connector
- opening
- positioning component
- optical fiber
- optical
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4249—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details comprising arrays of active devices and fibres
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/36—Mechanical coupling means
- G02B6/38—Mechanical coupling means having fibre to fibre mating means
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/36—Mechanical coupling means
- G02B6/38—Mechanical coupling means having fibre to fibre mating means
- G02B6/3807—Dismountable connectors, i.e. comprising plugs
- G02B6/3873—Connectors using guide surfaces for aligning ferrule ends, e.g. tubes, sleeves, V-grooves, rods, pins, balls
- G02B6/3885—Multicore or multichannel optical connectors, i.e. one single ferrule containing more than one fibre, e.g. ribbon type
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4219—Mechanical fixtures for holding or positioning the elements relative to each other in the couplings; Alignment methods for the elements, e.g. measuring or observing methods especially used therefor
- G02B6/4228—Passive alignment, i.e. without a detection of the degree of coupling or the position of the elements
- G02B6/423—Passive alignment, i.e. without a detection of the degree of coupling or the position of the elements using guiding surfaces for the alignment
- G02B6/4231—Passive alignment, i.e. without a detection of the degree of coupling or the position of the elements using guiding surfaces for the alignment with intermediate elements, e.g. rods and balls, between the elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4219—Mechanical fixtures for holding or positioning the elements relative to each other in the couplings; Alignment methods for the elements, e.g. measuring or observing methods especially used therefor
- G02B6/4236—Fixing or mounting methods of the aligned elements
- G02B6/424—Mounting of the optical light guide
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4219—Mechanical fixtures for holding or positioning the elements relative to each other in the couplings; Alignment methods for the elements, e.g. measuring or observing methods especially used therefor
- G02B6/4236—Fixing or mounting methods of the aligned elements
- G02B6/424—Mounting of the optical light guide
- G02B6/4243—Mounting of the optical light guide into a groove
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4219—Mechanical fixtures for holding or positioning the elements relative to each other in the couplings; Alignment methods for the elements, e.g. measuring or observing methods especially used therefor
- G02B6/4236—Fixing or mounting methods of the aligned elements
- G02B6/4244—Mounting of the optical elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4256—Details of housings
- G02B6/4257—Details of housings having a supporting carrier or a mounting substrate or a mounting plate
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4256—Details of housings
- G02B6/426—Details of housings mounting, engaging or coupling of the package to a board, a frame or a panel
- G02B6/4261—Packages with mounting structures to be pluggable or detachable, e.g. having latches or rails
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/36—Mechanical coupling means
- G02B6/38—Mechanical coupling means having fibre to fibre mating means
- G02B6/3807—Dismountable connectors, i.e. comprising plugs
- G02B6/3833—Details of mounting fibres in ferrules; Assembly methods; Manufacture
- G02B6/3834—Means for centering or aligning the light guide within the ferrule
- G02B6/3838—Means for centering or aligning the light guide within the ferrule using grooves for light guides
- G02B6/3839—Means for centering or aligning the light guide within the ferrule using grooves for light guides for a plurality of light guides
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/36—Mechanical coupling means
- G02B6/38—Mechanical coupling means having fibre to fibre mating means
- G02B6/3807—Dismountable connectors, i.e. comprising plugs
- G02B6/3833—Details of mounting fibres in ferrules; Assembly methods; Manufacture
- G02B6/3855—Details of mounting fibres in ferrules; Assembly methods; Manufacture characterised by the method of anchoring or fixing the fibre within the ferrule
- G02B6/3858—Clamping, i.e. with only elastic deformation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/36—Mechanical coupling means
- G02B6/38—Mechanical coupling means having fibre to fibre mating means
- G02B6/3807—Dismountable connectors, i.e. comprising plugs
- G02B6/3873—Connectors using guide surfaces for aligning ferrule ends, e.g. tubes, sleeves, V-grooves, rods, pins, balls
- G02B6/3882—Connectors using guide surfaces for aligning ferrule ends, e.g. tubes, sleeves, V-grooves, rods, pins, balls using rods, pins or balls to align a pair of ferrule ends
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4201—Packages, e.g. shape, construction, internal or external details
- G02B6/4219—Mechanical fixtures for holding or positioning the elements relative to each other in the couplings; Alignment methods for the elements, e.g. measuring or observing methods especially used therefor
- G02B6/422—Active alignment, i.e. moving the elements in response to the detected degree of coupling or position of the elements
- G02B6/4221—Active alignment, i.e. moving the elements in response to the detected degree of coupling or position of the elements involving a visual detection of the position of the elements, e.g. by using a microscope or a camera
- G02B6/4224—Active alignment, i.e. moving the elements in response to the detected degree of coupling or position of the elements involving a visual detection of the position of the elements, e.g. by using a microscope or a camera using visual alignment markings, e.g. index methods
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/42—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements
- G02B6/4292—Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements the light guide being disconnectable from the opto-electronic element, e.g. mutually self aligning arrangements
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Mechanical Coupling Of Light Guides (AREA)
Abstract
本发明提供一种精密的光缆连接器(10),该连接器用于使一对光缆的末端对正并连接起来。连接器(10)有一个光纤定位块(12),该定位块有光纤接收面(14)及连接器衔接表面(18)。在连接器的衔接表面上提供第一和第二开口(44,46)。提供一个定位球(62)并使该定位球保持在第一开口(44)内。定位球(62)用于使连接器(10)与另一个同样的连接器对正,尤其是使安装在连接器定位组件上的光纤对正。
Description
本发明所属技术领域
本发明涉及光纤连接器。具体地说,本发明涉及一种用于光纤连接器的带定位球的定位组件,该定位球将保持在光纤定位块的一个面上,用于定位目的。
本发明的背景技术
众所周知,光缆是用于传输光学信号的。光缆的使用通常受到远程中继设施的限制,在这种场合改进的光纤传输特性已被证明需要提高制造和安装这些设施的成本和难度。随着对通信媒体的需求持续增加,将光缆用于跨越较短距离传输信号或局域设备互连网的优势也持续增长。大多数研制工作致力于提供实际的低耗损的玻璃材料及生产玻璃光纤光缆(如带状光缆)的制造技术。显然,如果在实际的信号传输及处理系统中使用光缆,则必须提供用于光缆的连接与分离的实用的连接器。
与研制实用的光纤连接器密切相关的问题是连接器的光学传输效率。影响连接器光学传输效率的各种因素包括对接点的间隙和不同轴导致的横向错位。
已经研制了数种有助于带状光缆连接的光学连接器。在授权给Maekawa等人的美国专利第5,315,678号和授权给Sizier II等人的美国专利5,430,819中都介绍了销式连接器。在819号和678号两份专利中都展示并介绍了用定位销使连接器定位的方法。使用定位销时遇到的数个问题可借助使用定位球得到缓解。首先,公差要求严格的精密的定位销难于制造,因此价格昂贵。相比之下,众所周知滚珠轴承制造技术能够以相当低的成本制造出公差要求严格的精密的球体。其次,不论选用何种材料,小型定位销既不坚固也不耐用;脆性的定位销容易折断,而韧性的定位销容易弯曲。而球体依靠其对称的形状既不容易折断,也不会弯曲。第三,使用两个或多个定位销的定位部件在机械上过度地制约定位,而且需要严格控制各个定位销插座的角取向、定位和延伸段截面直径以及各定位销的直径和平直度,以避免降低定位质量的装配误差。相比之下,使用球体定位仅仅取决于球体直径和球座的精确定位,从而消除了过度的制约和产生装配误差的可能。
授权给Deacon的美国专利第4,087,155号揭示了一种不使用定位销使一对单纤对准的方法。具体地说,Deacon的155号专利揭示一种使一对单光纤耦合的连接器,它利用三个等直径球体在彼此之间定义一个三尖瓣形的间隙,单根光纤就插在这个间隙之中。这些球体围绕在光纤周围,使光纤保持在连接器中心,该连接器有圆形的卡箍以卡位这些球体。在按轴向对接的关系安装第二个类似的连接器时,连接器中的球体彼此巢套,以使两根光纤对准。为了依此方式使单根光纤适当地对准,使这些等直径球体围绕着单根光纤的周界是必不可少的。遗憾的是,在Deacon的155号专利中介绍的技术不能应用于多纤光缆,如带状光缆。
虽然有为单纤光缆和多纤光缆两者设计的连接器,但仍然需要耐用的、精密的、便宜的且容易制造的光学连接器,它们将使两个邻接的连接器中的多条光纤精确对准。
本发明的简要说明
本发明提供适合一对多纤光缆或单纤光缆末端对正和连接的光缆连接器使用的精密的定位组件。该定位组件将与诸如光纤应变消除元件及连接器锁定元件之类的连接器辅助零件组合,以形成完整的光纤连接器。该定位组件有光纤定位块,在光纤定位块上有光纤接收面及连接器衔接表面。在连接器衔接表面上提供第一开口和第二个开口。在第一个开口中有与该开口紧配合的定位球,该定位球适合使该连接器与另一个同样的连接器对正,尤其适合使连接器中安装的光纤对正。
本发明还提供一种光缆连接器定位组件,该定位组件有一个固定零件,适合将来自光缆的每条光纤固定在定位组件上。定位组件有光纤定位块,在该定位块上有光纤接收面及连接器衔接表面。在光纤接收面上形成一导槽,在导槽内形成至少一个定位槽。固定零件的尺寸使它固定在导槽内,以使每条光纤都保持在定位槽内。在连接器衔接表面上有第一开口和第二开口。在第一开口中有与该开口紧配合的定位球,该定位球适合使该连接器与另一个同样的连接器对正,尤其适合使连接器中安装的光纤对正。
还揭示了一种将这种连接器定位组件安装到带状光缆上的方法。提供一对定位组件并按面对面的排列方式放置。定位组件借助定距零件适当地隔开。将一段光缆放在定位组件的顶部,非必选地借助除去一部分或全部光缆和光纤的涂覆物质使该段光缆插在定位组件中。然后,安装固定零件,使来自光缆的每条光纤都保持在定位组件的定位槽内。随后将介于定位组件之间的光缆锯开或切断。最后对末端进行任何必要的处理或平整。
具体说来,本发明提供了一种光缆连接器定位组件(80),该组件包括:
一个光纤定位块(82),在该定位块上有用于承接来自光缆(16)的至少一条光纤的光纤接收面(84)和连接器衔接表面(86);
第一及第二开口(92,90),这两个开口均在连接器衔接表面(86)上形成,其中的第一开口(92)具有d3的深度,第二开口(90)为筒状;以及
一定位球(94),其半径为R,该定位球保持在第一开口中,其中R>d3,,第二开口(90)的尺寸大于定位球(94)的直径。
本发明还提供了一种光缆连接器定位组件(10),包括:
一个光纤定位块(12),在该定位块上有用于承接来自光缆(16)的至少一条光纤的光纤接收面(14)和连接器衔接表面(18);
第一及第二开口(44,46),这两个开口均在连接器衔接表面(18)上形成;以及
一定位球(62),该定位球保持在第一开口中,其特征在于,
该组件进一步包括与第一开口相邻的第一对突出物(48)以及与第二开口相邻的第二对突出物(49),这两对突出物均从连接器衔接表面凸起;第二开口的大小允许滑动地承接保持在将与该光缆连接器配对的另一个连接器定位组件中的定位球;定位球保持在第一对突出物之间;以及,第一开口的大小允许第二对突出物插入,而第二开口的大小允许第一对突出物插入。
进一步地,本发明还提供了一种在连续光缆(72)上装配至少一对光学连接器定位组件(10)的方法,其中连接器定位组件(10)包括:
一个光纤定位块(12),在该定位块上有用于承接来自光缆(16)的至少一条光纤的光纤接收面(14)和连接器衔接表面(18);
第一及第二开口(44,46),这两个开口均在连接器衔接表面(18)上形成;以及
一定位球(62),该定位球保持在第一开口中,其特征在于,
该组件进一步包括与第一开口相邻的第一对突出物(48)以及与第二开口相邻的第二对突出物(49),这两对突出物均从连接器衔接表面凸起;第二开口的大小允许滑动地承接保持在将与该光缆连接器配对的另一个连接器定位组件中的定位球;定位球保持在第一对突出物之间;以及,第一开口的大小允许第二对突出物插入,而第二开口的大小允许第一对突出物插入;
该方法包括以下步骤:
将至少一对连接器定位组件(10)按面对面排列放置;
将定距零件(71)置于至少一对连接器定位组件(10)的连接器衔接表面(18)之间;
将连续光缆(72)平放在连接器定位组件(10)上,使光缆(72)中各条未经涂覆的光纤逐一放在定位槽(28)的每个槽中;
安装固定零件(32),以使光缆保持在定位槽(28)中;以及
在连接器定位组件(10)之间切断光缆(72)。
附图的简要说明
图1是依据本发明的光缆连接器定位组件的透视图。
图2是图1中定位组件的主视图。
图3a是依据本发明的一对定位组件在连接前的透视图。
图3b是图3a所示的定位组件已被连接起来的透视图。
图4a-d说明将许多依据本发明的定位组件与多纤光缆装配起来的装配办法。
图5a-c说明在光缆末端安装一个依据本发明的定位组件的装配办法。
图6是在本发明的另一个实施方案中定位组件的透视图。
图7是沿图6的7-7线截取的剖视图。
图8是沿图6的8-8线截取的剖视图。
本发明的详细描述
图1说明依据本发明的一个实施方案的光缆连接器定位组件10。该定位组件10具有光纤定位块12,该光纤定位块具有前缘13、后缘15、嵌入光缆16的光纤接收面14、与另一个同样的连接器定位组件的连接器衔接表面邻接的连接器衔接表面18、后面19(在图3a中给出)、第一侧面21及第二侧面23(未示出)。光缆16由一根或多根单根光纤17组成,而且在优先的实施方案中,每根光纤大体上按平面取向一根挨一根地放置,以形成带状光缆。
光纤接收面14包含在光纤定位块12上形成的导槽20。导槽包含第一和第二导槽锁紧唇22和24,以及一个导槽底26。锁紧唇22、24从前缘13至后缘15向外形成一个角度,以形成梯形导槽。具体地说,随着锁紧唇24自前缘13向后缘15延伸,它朝第一侧面21形成一个角度。随着锁紧唇22自前缘13向后缘15延伸,它朝侧面23形成一个角度。此外,锁紧唇22和24自顶部向底部倾斜,以形成一锁定机构。优先的是锁紧唇22、24由顶部唇边22a、24a分别对应于底部唇边22b、24b构成。锁紧唇22、24的倾斜角度大约是30°,以致底部唇边22b、24b分别比顶部唇边22a、24a更接近侧缘23、21。应当注意不脱离本发明精神或范围可以使用较大的或较小的倾斜角。
在导槽底部26形成一个或多个定位槽28,以容纳来自光缆16的每根光纤17。在优先的实施方案中定位槽28被描绘成V型槽,但是,在不脱离本发明精神及范围的条件下,也可以使用其他截面形状的凹槽,如矩形槽、U型槽或半圆型槽。在导槽底部26还形成容纳光缆外壳的导槽30。在正常操作中,光纤光缆16被部分剥皮露出每根光纤17,以便放入定位槽28。剥掉一段光缆外壳以及非必选地剥掉在每根光纤17周围的任何涂层,被剥掉的距离至少等于定位槽28长度。借助提供容纳光缆外壳的导槽30,每根光纤17在光纤定位块12的整个宽度上自始至终可以保持基本平坦的通道。
在优先的实施方案中,连接器衔接表面18与光纤接收面14是彼此垂直的平面。为了减少光纤内的光线逆反射,连接器衔接表面18的平面可以偏离光纤接收面14的垂面几度(优先是6°至9°),而且在某些情况下还是有利的。在不脱离本发明精神和范围的条件下,光纤接收面可以向上或向下偏离水平面。换言之,光纤接收面14与连接器衔接表面之间的角度可以在81°至99°的范围内。
本发明的光纤可以是单模的或多模的玻璃光纤或塑料光纤。多模的玻璃光纤通常具有在50至100微米范围内的芯纤直径。单模光纤具有较小的芯纤直径。因为多模光纤具有较大的芯纤直径,所以它提供比单模光纤宽松的对正公差。
提供有前缘34、后缘36及侧缘38、40的燕尾形固定零件32,以便将光缆16固定在导槽20中,尤其是将每条光纤17固定在定位槽28内。在固定零件32上提供组装掣输器42,以帮助安装固定零件。在本发明的实施方案中,燕尾形零件32呈梯形,前缘34比后缘36短。侧缘38和40尺寸基本相同。燕尾形固定零件32的尺寸和形状大体上与导槽20一致,而且其尺寸允许它按滑动配合安装在导槽锁紧唇22和24之下。固定零件32前缘34的宽度大于前缘13处的顶部唇边22a和24a之间的距离、小于底部唇边22b和24b之间的距离,后缘36的宽度大于后缘15处的顶部唇边22a和24a之间的距离、小于底部唇边22b和24b之间的距离。固定零件32的高度小于自导槽底部26至顶部唇边22a、24a的垂直距离。固定零件32的高度大约是2mm,但在不脱离本发明精神及范围的条件下,可以使用较大的或较小的高度。固定零件32的大小是使前缘34比前缘13处的导槽20宽,以保证在固定零件32安装在导槽20中时,前缘34不超过前缘13和禁止它与对接的连接器紧密衔接。
在优先的实施方案中,光纤定位块12及固定零件32用陶瓷材料模塑而成。但是用塑料、玻璃、金属或任何已知的其他连接块材料制造光纤定位块12也是可能的。在优先的实施方案中借助使用可模塑物质,可以将光纤定位块12作为整体单元迅速而简便地制造。例如,在优先的实施方案中,可以借助模塑法轻易地形成定位槽28,不必加工导槽20。
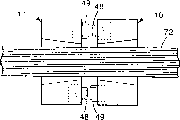
连接器衔接表面18包含第一开口44和第二开口46。提供铸塑成型的突出物48、49,它们从光纤定位块12凸起,基本上彼此平行,而且非必选地垂直于连接器衔接表面18。突出物48、49分别与开口44、46相邻,而且作为光纤定位块12的一部分整体模塑成型。在优先的实施方案中,铸塑成型突出物48、49从衔接表面18伸出的高度大约是定位球62直径的1/2,下面将更详细地介绍。如图1所示,突出物48、49分别具有圆形的内表面50、51和外表面52、53。圆形的内表面50、51适合容纳定位球,而外表面52、53适合在开口44、46内形成动配合,下面将详细介绍。
在图2中可以更详细地看到开口44、46。如图所示,开口44、46的形状基本相同,但开口46相对于开口44旋转90度。这样做的目的在阅读下文后就变得明朗起来。开口44包括圆柱形主承接孔54和一对间隙孔56。开口46包括圆柱形主承接孔58及一对间隙孔60。圆柱形主承接孔54、58的直径分别为d1和d2,分别用带箭头的符号57和59表示。直径d1、d2分别与铸塑成型突出物48、49的间距对应。在本发明优先的实施方案中,圆柱形孔58的直径d2稍大于圆柱型孔54的直径d1,因此突出物49之间的距离稍大于突出物48之间的距离。在优先的实施方案中,直径d1和d2之间的差异在几微米的数量级上。精确的尺寸将取决于光纤的类型和选定的连接器材料。
如图2所示,间隙孔56及铸塑成型突出物48基本上在圆柱形主孔54周围。同样地,铸塑成型突出物49及间隙孔60基本上在圆柱形主孔58的周围。间隙孔56、60的形状本质上分别与铸塑成型突出物48、49相同,而且它们的深度足以完全容纳该突出物。重要的是间隙孔56、60的深度至少与铸塑成型突出物48、49一样,以便在两个连接器相连时,它们的衔接表面18可以彼此接触,从而使每个连接器上安装的光纤末端紧贴在一起。
为了插入介于铸塑成型突出物48之间的开口44,提供精密的定位球62。提供精密的定位球62是为了使定位槽28中的光纤17与另一个同样的连接器中的光纤对正,下面将进一步介绍。球62是高精度的钢制滚珠,但在不脱离本发明精神或范围的条件下,也可以由其他具有滚珠精度的材料制成,诸如碳化钨、陶瓷、其他金属、或液晶聚合物之类的塑料。在优先的实施方案中,球62具有约2mm的直径,而且直径公差大约是±0.5微米。重要的是公差将依据定位球的材料而变化。虽然公差范围对本发明的适当操作极为重要,但是应当认识到在不脱离本发明的精神或范围的条件下,可以使用较大或较小的直径。
如上所述,圆柱形主孔54的直径d1以及突出物48相应的间距均稍小于孔58的直径d2。这是为了使球62紧密地保持在孔54中。铸塑成型突出物49是这样设计的,使其间距(d2)允许球62在其间轻松地滑动。如果球62被插进开口46,它将不密合于其中而是掉出来。突出物48、49的间距公差再一次取决于所用材料。在优先的实施方案中,采用陶瓷制作光纤定位块,包括突出物。在这种情况下,突出物48的间距公差大约为±2-3微米(与定位球形成静配合),而突出物49的间距公差大约是±0-2微米(与定位球形成动配合)。如果突出物采用塑料制作,则突出物48间距的公差大约为±50微米,对于突出物49也是大约±50微米。
重要的是应当注意:在这个实施方案中,球62并非必须在突出物48之间的孔54中的任何特定的深度或位置。球62可以保持在突出物48之间但在孔54的外面,它也可以一半在孔54内、另一半在孔外,或完全位于孔内,或在其间的任何位置,都不会改变本发明的对正能力。还应当注意,如果需要,在不脱离本发明的精神或范围的前提下可以将球62粘接在突出物48之间。此外,应当注意圆柱形孔54和58完全可能具有相同的尺寸,以致两个孔均允许定位球62在其中滑动。尽管这个实施方案在连接器尚未组装起来时不能阻止球62从孔中掉出来,但是在决定将球嵌入哪个孔时该实施方案提供附加的自由度。
图3a及3b说明两个依据本发明制造的连接器定位组件被精确地装配起来。图示的连接器定位组件10有借助固定零件32保持在定位槽28中的带状光缆16。如图所示,球62已经插入两个连接器定位组件10的承接孔54。铸塑成型的突出物48提供紧配合,使球62保持在孔54中。在装配连接器定位组件时,铸塑成型突出物48插在间隙孔60中,而突出物49插在间隙孔56中,在突出物49和球62插在间隙孔56中时,突出物49的圆形内表面51与球62形成滑动配合。象图3b那样连接时,带状光缆16中的每条光纤17都精确地对正,而连接器定位组件受到限制不能多向移动。
本发明还提供一种使连接器定位组件10与带状光缆的组装自动化的方法。这种方法用图4a-b予以说明。如图所示,提供一对连接器定位组件10,并将它们按面对面排列放置。在优先的实施方案中,提供定距零件71以使两个连接器定位组件10隔开适当的距离。本发明的定距零件71是用完就扔的定距器,它使定位组件的间距大约为0.015英寸(0.038cm),但在不脱离本发明精神或范围的条件下可以选择较大或较小的距离。定距器71优先用塑料制成,但也可以使用任何其他适当的间隔材料。连接器定位组件10还可以在不脱离本发明精神或范围的前提下借助某种箝位机构就地固定。
一旦将两个连接器定位组件适当地隔开,从连续滚筒或类似连续供应源提供一段带状光缆72。将带状光缆放在连接器定位组件10上,使每根光纤位于各个定位槽28中,随后将固定零件32安装到两个定位组件10上,使带状光缆紧贴在连接器定位组件上。此时,将带状光缆72在定距器71的位置锯断或切断。最后,对光纤末端进行必要的处理或平整。上述方法还可以同样地用于将一个连接器安装到一段带状光缆的末端。
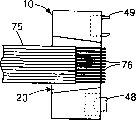
本发明的连接器定位组件非常适合于快速的现场安装。这种人工现场安装方法用图5a-c予以说明。在现场技术人员首先沿着带状光缆75的长度确定需要连接器10的位置。然后,在这个点将光缆切断。然后,将光纤周围的绝缘涂层剥掉,以暴露出每根光纤76。随后,将每根光纤直接放在定位组件的定位槽28上方。接下来,将固定零件32滑插到定位组件的导槽20中,使光纤76紧贴在定位槽28中。将光纤伸出连接器衔接表面18的部分切除,最后,进行必要的整理或平整。
本发明第一个替代实施方案用图6予以说明。图6说明一对即将结合在一起的定位组件80。定位组件80包括光纤定位块82,该定位块上有光纤接收表面84和连接器衔接表面86,该表面与另一个同样的连接器的连接器衔接表面邻接。在这个实施方案中,光纤定位块82是用陶瓷或玻璃模塑成型的。在光纤接收面84上形成许多定位槽88,以保持来自光缆的每根光纤。借助任何已知的固定方法(诸如粘胶带或粘合剂)将光纤保持在定位槽88中。
连接器衔接表面86包含第一开口92和第二开口90。开口90、92分别与通孔90a、92a相连,这两个通孔贯穿定位组件80的长度,并分别在后开口90b、92b终止。通孔90a、92a和后开口90b、92b在图7和图8中可以看得更清楚。开口90的尺寸能容纳绝大部分定位球94,下面将详细介绍。开口92包括倒角93,其尺寸适合在其内部容纳和固定定位球94的一部分。
倒角93在图7中可以看得更清楚。如图所示,倒角93可以容纳不足半个定位球94。具体地说,倒角93的深度d3(用95表示)小于定位球94的半径R(用97表示)。在优先的替代实施方案中,定位球的直径d4(用99表示)大约为2mm,因此其半径大约为1mm。因此,深度d3(95)小于大约1mm,在大约0.5至0.7mm范围内。球94一旦坐进倒角93,就通过后开口92b导入粘合剂,以便将球94固定在开口92中。应当注意可能有的定位组件没有贯穿定位组件长度的通孔90a、92a。粘合剂可以直接涂在倒角93上,随后将球94放进去,只要均匀地涂粘合剂,定位球94就能精确地坐在倒角93中。
现在参照图8,更详细地说明开口90。开口90的尺寸稍大于99所示的直径d4。这允许定位球94滑动地装进开口90。如图8所示,后开口90b和通孔90a大于开口90。这是为了减少需要机械加工的面积。加工精度是使光纤对正的关键,因此开口90的机械加工公差非常严格,在4或5微米的数量级上。由于通孔90a和后开口90b大于开口90,所以机床只需加工较小的表面积。
提供适合嵌入开口92的精密的定位球94。球94是为了精确地对正一对连接器定位组件80、并依次精确地对正固定在该定位组件上的光缆中的每条光纤而提供的。对于使用单模光纤的应用,球94是公差在±0.5微米范围内的精密的钢制滚珠,对于使用多模光纤的应用,公差在±2微米的范围内。在不脱离本发明精神或范围的前提下,球94也可以用具有滚珠轴承精度的其他材料制成,诸如碳化钨、陶瓷、其他金属或液晶聚合物之类的塑料。如上所述,球94被粘合在开口92中。可以用粘接剂或低熔点陶瓷密封玻璃实现粘接,其中所述密封玻璃可以在适度的高温下流动,随后在冷却时将陶瓷的或玻璃的光纤定位块80与定位球94粘接到一起。在不脱离本发明精神或范围的前提下,也可以使用其他的粘合剂。
Claims (14)
1.一种光缆连接器定位组件(80),该组件包括:
一个光纤定位块(82),在该定位块上有用于承接来自光缆(16)的至少一条光纤的光纤接收面(84)和连接器衔接表面(86);
第一及第二开口(92,90),这两个开口均在连接器衔接表面(86)上形成,其中的第一开口(92)具有d3的深度,第二开口(90)为筒状;以及
一定位球(94),其半径为R,该定位球保持在第一开口中,其中R>d3,第二开口(90)的尺寸大于定位球(94)的直径。
2.根据权利要求1所述的连接器定位组件,其中所述的光纤接收面包括至少一个定位槽(28),以保持至少一条来自光缆的光纤。
3.根据权利要求1所述的连接器定位组件,其中第二开口的大小允许滑动地承接保持在将与该光缆连接器配对的另一个连接器定位组件中的定位球。
4.根据权利要求1所述的连接器定位组件,其中定位球靠紧配合固定在第一开口内。
5.根据权利要求1所述的连接器定位组件,其中该定位球被粘接在第一开口内。
6.根据权利要求1所述的连接器定位组件,其中第一和第二开口分别与第一和第二通孔相连,而且第一及第二通孔贯穿光纤定位块的宽度。
7.一种光缆连接器定位组件(10)包括:
一个光纤定位块(12),在该定位块上有用于承接来自光缆(16)的至少一条光纤的光纤接收面(14)和连接器衔接表面(18);
第一及第二开口(44,46),这两个开口均在连接器衔接表面(18)上形成;以及
一定位球(62),该定位球保持在第一开口中,其特征在于,
该组件进一步包括与第一开口相邻的第一对突出物(48)以及与第二开口相邻的第二对突出物(49),这两对突出物均从连接器衔接表面凸起;第二开口的大小允许滑动地承接保持在将与该光缆连接器配对的另一个连接器定位组件中的定位球;定位球保持在第一对突出物之间;以及,第一开口的大小允许第二对突出物插入,而第二开口的大小允许第一对突出物插入。
8.根据权利要求7所述的连接器定位组件,其中定位球与第二对突出物形成滑动配合。
9.根据权利要求7所述的光缆连接器定位组件(10),该组件包括:
导槽(20),该导槽在光纤接收面上形成;
至少一个定位槽(28),该定位槽在导槽(20)中形成;以及
固定零件(32),该固定零件的尺寸使它固定在导槽(20)内,以便将至少一条光纤固定在至少一个定位槽(28)中。
10.根据权利要求9所述的连接器定位组件,其中的导槽包括导槽表面(26)和第一锁紧唇和第二锁紧唇(22、24),而锁紧唇(22、24)又包括顶部唇边和底部唇边(22a、24a、22b、24b),其中顶部唇边相距的距离为第一距离,底部唇边相距的距离为第二距离,顶部唇边与导槽表面(26)相距的距离为第三距离,而且该锁紧唇自顶部唇边至底部唇边向内倾斜,以致顶部唇边之间的第一距离小于底部唇边之间的第二距离。
11.根据权利要求10所述的连接器定位组件,其中该固定零件的厚度小于顶部唇边至导槽表面的第三距离。
12.根据权利要求11所述的连接器定位组件,其中当固定零件插入导槽时,该固定零件借助第一和第二锁紧唇保持在导槽中。
13.根据权利要求7所述的连接器定位组件,其中该连接器衔接表面与光纤接收面形成一个角度,该角度在81°-99°范围内。
14.一种在连续光缆(72)上装配至少一对光学连接器定位组件(10)的方法,其中连接器定位组件(10)包括:
一个光纤定位块(12),在该定位块上有用于承接来自光缆(16)的至少一条光纤的光纤接收面(14)和连接器衔接表面(18);
第一及第二开口(44,46),这两个开口均在连接器衔接表面(18)上形成;以及
一定位球(62),该定位球保持在第一开口中,其特征在于,
该组件进一步包括与第一开口相邻的第一对突出物(48)以及与第二开口相邻的第二对突出物(49),这两对突出物均从连接器衔接表面凸起;第二开口的大小允许滑动地承接保持在将与该光缆连接器配对的另一个连接器定位组件中的定位球;定位球保持在第一对突出物之间;以及,第一开口的大小允许第二对突出物插入,而第二开口的大小允许第一对突出物插入;
该方法包括以下步骤:
将至少一对连接器定位组件(10)按面对面排列放置;
将定距零件(71)置于至少一对连接器定位组件(10)的连接器衔接表面(18)之间;
将连续光缆(72)平放在连接器定位组件(10)上,使光缆(72)中各条未经涂覆的光纤逐一放在定位槽(28)的每个槽中;
安装固定零件(32),以使光缆保持在定位槽(28)中;以及
在连接器定位组件(10)之间切断光缆(72)。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US08/614,412 US5778123A (en) | 1996-03-12 | 1996-03-12 | Alignment assembly for multifiber or single fiber optical cable connector |
| US08/614,412 | 1996-03-12 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1214122A CN1214122A (zh) | 1999-04-14 |
| CN1129016C true CN1129016C (zh) | 2003-11-26 |
Family
ID=24461155
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN96180202A Expired - Fee Related CN1129016C (zh) | 1996-03-12 | 1996-10-07 | 用于多光纤光缆或单光纤光缆连接器的定位组件 |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US5778123A (zh) |
| EP (3) | EP1028336A3 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP2000505208A (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR19990087648A (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1129016C (zh) |
| DE (1) | DE69618668T2 (zh) |
| HK (1) | HK1019169A1 (zh) |
| TW (1) | TW381186B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO1997034179A1 (zh) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI422887B (zh) * | 2005-09-12 | 2014-01-11 | Stratos Int Inc | 光電連接器 |
| TWI561877B (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2016-12-11 | Hon Hai Prec Ind Co Ltd | Photoelectric transmitting module and optical fiber connector thereof |
Families Citing this family (68)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5920670A (en) * | 1996-06-07 | 1999-07-06 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Multiple alignment connector ferrule |
| US5778123A (en) * | 1996-03-12 | 1998-07-07 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Alignment assembly for multifiber or single fiber optical cable connector |
| US6805493B2 (en) | 1996-03-12 | 2004-10-19 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Optical connector assembly using partial large diameter alignment features |
| US5940562A (en) * | 1996-03-12 | 1999-08-17 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Stubless optoelectronic device receptacle |
| US6318902B1 (en) | 1996-03-12 | 2001-11-20 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Optical connector assembly using partial large diameter alignment features |
| EP0938003A1 (en) * | 1998-02-24 | 1999-08-25 | Jds Fitel Inc. | Tunable multiple fiber optical connector |
| JPH11344640A (ja) * | 1998-03-31 | 1999-12-14 | Ngk Insulators Ltd | ガラス基板及びその2段階成形方法 |
| JPH11281823A (ja) * | 1998-03-31 | 1999-10-15 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 光ファイバの整列方法及び光ファイバアレイ装置 |
| CA2336388C (en) | 1998-07-02 | 2008-09-09 | Tyco Electronics Logistics Ag | Ferrule for a pluggable optical connection |
| FR2786881B1 (fr) * | 1998-12-03 | 2002-08-16 | Socapex Amphenol | Connecteur optique hermaphrodite |
| US6332052B1 (en) * | 2000-02-28 | 2001-12-18 | Corning Cable Systems Llc | Optical fiber ribbon cables with controlled bending behavior |
| US6798933B2 (en) * | 2000-04-14 | 2004-09-28 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Fiber optic array switch |
| US6826324B2 (en) * | 2000-04-13 | 2004-11-30 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical waveguide switch |
| US6832016B2 (en) * | 2000-04-13 | 2004-12-14 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Fiber array switch having micromachined front face with roller balls |
| US6842552B1 (en) | 2000-04-13 | 2005-01-11 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical waveguide switch |
| US6633691B2 (en) * | 2000-05-02 | 2003-10-14 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical waveguide switch having stepped waveguide holding member |
| US6748131B2 (en) * | 2000-05-19 | 2004-06-08 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical waveguide devices and methods of fabricating the same |
| US6434315B1 (en) * | 2000-06-23 | 2002-08-13 | Molex Incorporated | Fiber optic connector |
| US6434316B1 (en) * | 2000-06-23 | 2002-08-13 | Molex Incorporated | Fiber optic connector |
| US6870981B2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2005-03-22 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical switch and method for making |
| US6853764B2 (en) * | 2000-08-28 | 2005-02-08 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical switch assembly and method for making |
| US6798968B2 (en) * | 2000-09-21 | 2004-09-28 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Fiber array with support post |
| US6526205B1 (en) * | 2000-10-13 | 2003-02-25 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Method and apparatus for the passive alignment of optical components |
| US6520686B1 (en) | 2000-11-09 | 2003-02-18 | Teradyne, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for forming a fiber optic connection |
| US6799897B2 (en) | 2000-11-16 | 2004-10-05 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical connector system |
| US6810162B2 (en) * | 2000-12-20 | 2004-10-26 | Shipley Company, L.L.C. | Optical switch assembly with flex plate and method for making |
| US6527457B2 (en) | 2001-02-01 | 2003-03-04 | International Business Machines Corporation | Optical fiber guide module and a method for making the same |
| JP2002328251A (ja) * | 2001-02-28 | 2002-11-15 | Asahi Glass Co Ltd | 樹脂製光ファイバの接合法 |
| US6623177B1 (en) | 2001-07-09 | 2003-09-23 | Emc Corporation | Systems and methods for providing fiber optic communications between circuit boards |
| US20030086661A1 (en) * | 2001-11-02 | 2003-05-08 | Boudreau Robert A. | Silicon waferboard |
| EP1442475A4 (en) * | 2001-11-08 | 2005-12-21 | Shipley Co Llc | FIBER OPTIC CLOSURE |
| US6839935B2 (en) * | 2002-05-29 | 2005-01-11 | Teradyne, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for cleaning optical connectors |
| US6957920B2 (en) | 2002-06-24 | 2005-10-25 | Corning Cable Systems Llc | Ferrule assembly having highly protruding optical fibers and an associated fabrication method |
| US6762941B2 (en) | 2002-07-15 | 2004-07-13 | Teradyne, Inc. | Techniques for connecting a set of connecting elements using an improved latching apparatus |
| US6832858B2 (en) * | 2002-09-13 | 2004-12-21 | Teradyne, Inc. | Techniques for forming fiber optic connections in a modularized manner |
| US7042562B2 (en) * | 2002-12-26 | 2006-05-09 | Amphenol Corp. | Systems and methods for inspecting an optical interface |
| JP2005352453A (ja) * | 2004-05-12 | 2005-12-22 | Nec Corp | 光ファイバ部品及び光導波路モジュール並びにこれらの製造方法 |
| KR101119780B1 (ko) * | 2005-06-30 | 2012-03-23 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | 플라즈마 화학증착장치 |
| WO2007009491A1 (de) * | 2005-07-15 | 2007-01-25 | Diamond Sa | Optischer mehrfaser-steckeranschluss |
| US7515782B2 (en) * | 2006-03-17 | 2009-04-07 | Zhang Boying B | Two-channel, dual-mode, fiber optic rotary joint |
| JP4901654B2 (ja) * | 2007-09-03 | 2012-03-21 | 株式会社フジクラ | 光コネクタ |
| US20090196563A1 (en) * | 2008-02-01 | 2009-08-06 | Mullsteff David M | Multi-Fiber Optical Patch Cord Breakout Assembly |
| KR101394844B1 (ko) * | 2008-05-09 | 2014-05-14 | 휴렛-팩커드 디벨롭먼트 컴퍼니, 엘.피. | 근접 자유 공간 광학적 상호접속부 |
| US20100067852A1 (en) * | 2008-09-18 | 2010-03-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for assembling a furrule for an optical wave guide connector, ferrule, wave guide ribbon and tool for assembling the ferrule |
| US8580162B2 (en) * | 2009-03-17 | 2013-11-12 | Adc Telecommunications, Inc. | Method of directly molding ferrule on fiber optic cable |
| US8408816B2 (en) | 2010-03-18 | 2013-04-02 | Fujikura Ltd. | Optical connector |
| US8529138B2 (en) * | 2010-07-15 | 2013-09-10 | Tyco Electronics Corporation | Ferrule for optical transports |
| JP2013533515A (ja) * | 2010-07-30 | 2013-08-22 | コーニング ケーブル システムズ リミテッド ライアビリティ カンパニー | 相補嵌合ジオメトリを備えたフェルール及び関連光ファイバコネクタ |
| US10401572B2 (en) * | 2010-07-30 | 2019-09-03 | Corning Optical Communications, Llc | Fiber optic connectors including ferrules with complementary mating geometry and related fiber optic connectors |
| US9529159B2 (en) * | 2010-07-30 | 2016-12-27 | Corning Optical Communications LLC | Ferrules with complementary mating geometry and related fiber optic connectors |
| US8585300B2 (en) * | 2011-02-09 | 2013-11-19 | Tyco Electronics Nederland Bv | Ferrule with alignment pin channels |
| TWM450737U (zh) * | 2011-06-14 | 2013-04-11 | Molex Inc | 光纖組件 |
| US10215926B2 (en) | 2011-12-14 | 2019-02-26 | Commscope Technologies Llc | Multi-fiber fiber optic connection system with flexible, insertable pins |
| WO2013155337A1 (en) * | 2012-04-11 | 2013-10-17 | Nanoprecision Products, Inc. | Hermetic optical fiber alignment assembly having integrated optical element |
| US9897764B2 (en) | 2012-09-28 | 2018-02-20 | Commscope Technologies Llc | Molded ferrules for optical fibers |
| JP2014106409A (ja) * | 2012-11-28 | 2014-06-09 | International Business Maschines Corporation | 複数積層の光導波路コネクタ |
| CN104678504B (zh) * | 2013-11-30 | 2018-07-27 | 内蒙古炎林通讯技术有限公司 | 光纤连接器 |
| JP6459334B2 (ja) | 2014-09-18 | 2019-01-30 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | フェルール及び光接続構造 |
| WO2016087449A1 (en) | 2014-12-01 | 2016-06-09 | Commscope Asia Holdings B.V. | Multi-fiber optic connector with pivotally-aligned ferrule |
| WO2016205201A1 (en) | 2015-06-19 | 2016-12-22 | Commscope Technologies Llc | Fiber optic connector ferrule with improved alignment mechanism |
| CN108139548B (zh) * | 2015-10-12 | 2020-11-20 | 3M创新有限公司 | 光学套管 |
| WO2018186037A1 (ja) * | 2017-04-04 | 2018-10-11 | Tdk株式会社 | 光ファイバ部材及び光ファイバ保持具 |
| CN107577014B (zh) * | 2017-09-11 | 2019-06-28 | 武汉福地科技有限公司 | 一种具有收发一体功能的光纤阵列连接设备 |
| CN113710738A (zh) | 2019-03-20 | 2021-11-26 | 提克纳有限责任公司 | 用于相机模块的致动器组件 |
| US11086200B2 (en) | 2019-03-20 | 2021-08-10 | Ticona Llc | Polymer composition for use in a camera module |
| WO2020235041A1 (ja) * | 2019-05-22 | 2020-11-26 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 導波路接続構造、導波路チップ、コネクタ、および導波路接続部品の製造方法、ならびに導波路接続方法 |
| US10942316B1 (en) * | 2019-10-31 | 2021-03-09 | Alliance Fiber Optic Products, Inc. | FAU connectors and assemblies employing pin-to-pin alignment |
| KR20240087345A (ko) | 2022-12-12 | 2024-06-19 | 주식회사 에이티솔루션 | 광섬유 케이블 커넥터 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3409641A1 (de) * | 1984-03-16 | 1985-09-19 | Standard Elektrik Lorenz Ag, 7000 Stuttgart | Steckverbindung fuer lichtwellenleiter |
| US5315678A (en) * | 1992-03-30 | 1994-05-24 | Nippon Telegraph & Telephone Corporation | Optical fiber connector |
| US5430819A (en) * | 1993-12-21 | 1995-07-04 | At&T Corp. | Multiple optical fiber connector and method of making same |
Family Cites Families (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3871935A (en) * | 1974-03-14 | 1975-03-18 | Bell Telephone Labor Inc | Method of encapsulating and terminating the fibers of an optical fiber ribbon |
| US4037902A (en) * | 1976-03-16 | 1977-07-26 | Tesco Engineering Company | Hermaphroditic multiple connector plug |
| US4094580A (en) * | 1976-12-27 | 1978-06-13 | Bell Telephone Laboratories, Incorporated | Hermaphrodite optical fiber connector |
| US4116532A (en) * | 1977-01-05 | 1978-09-26 | Bell Telephone Laboratories, Incorporated | Fiber positioning and connection method and apparatus |
| US4087155A (en) * | 1977-03-23 | 1978-05-02 | International Telephone & Telegraph Corporation | Single optical fiber connector utilizing spherical alignment elements |
| GB1600272A (en) * | 1977-05-02 | 1981-10-14 | Plessey Co Ltd | Optical fibre connectors |
| US4279466A (en) * | 1978-02-21 | 1981-07-21 | Bunker Ramo Corporation | Hermaphroditic fiber optic connector |
| US4184742A (en) * | 1978-10-26 | 1980-01-22 | International Telephone And Telegraph Corporation | Hermaphroditic fiber optic connector |
| US4712861A (en) * | 1985-02-07 | 1987-12-15 | Northern Telecom Limited | Two-channel hermaphroditic fiber connector |
| US4737118A (en) * | 1985-12-20 | 1988-04-12 | Amp Incorporated | Hermaphroditic flat cable connector |
| US4953944A (en) * | 1988-10-12 | 1990-09-04 | Hughes Aircraft Company | Multi-channel hermaphroditic lens type fiber optic connector |
| US5183409A (en) * | 1991-04-15 | 1993-02-02 | Eric Clever | Hermaphroditic multiple contact connector |
| AU635172B2 (en) * | 1991-05-13 | 1993-03-11 | Nippon Telegraph & Telephone Corporation | Multifiber optical connector plug with low reflection and low insertion loss |
| US5121457A (en) * | 1991-05-21 | 1992-06-09 | Gte Laboratories Incorporated | Method for coupling laser array to optical fiber array |
| US5123073A (en) * | 1991-05-31 | 1992-06-16 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Precision optical fiber connector |
| AU649162B2 (en) * | 1991-08-17 | 1994-05-12 | Nippon Telegraph & Telephone Corporation | Optical connector |
| US5151964A (en) * | 1991-09-06 | 1992-09-29 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Wedge-actuated multiple optical fiber splice |
| JPH0743455B2 (ja) * | 1991-09-24 | 1995-05-15 | 株式会社精工技研 | リボン光ファイバ・コネクタ |
| US5257332A (en) * | 1992-09-04 | 1993-10-26 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Optical fiber expanded beam coupler |
| EP0609841B1 (en) * | 1993-02-02 | 1999-10-06 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Optical connector ferrule filled with adhesive |
| JPH06337328A (ja) * | 1993-03-29 | 1994-12-06 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | 光コネクタ |
| JPH0720340A (ja) * | 1993-06-28 | 1995-01-24 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | 光ファイバブロックアレイ及びその製造方法 |
| US5333225A (en) * | 1993-08-03 | 1994-07-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Substrate-embedded pluggable receptacles for connecting clustered optical cables to a module |
| JP3256922B2 (ja) * | 1994-10-13 | 2002-02-18 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | 光コネクタ |
| US5727097A (en) * | 1996-06-07 | 1998-03-10 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Pull-proof fiber optic array connector |
| US5778123A (en) * | 1996-03-12 | 1998-07-07 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Alignment assembly for multifiber or single fiber optical cable connector |
-
1996
- 1996-03-12 US US08/614,412 patent/US5778123A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1996-10-07 KR KR1019980707105A patent/KR19990087648A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1996-10-07 DE DE69618668T patent/DE69618668T2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1996-10-07 EP EP00111353A patent/EP1028336A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1996-10-07 WO PCT/US1996/016052 patent/WO1997034179A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1996-10-07 CN CN96180202A patent/CN1129016C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1996-10-07 EP EP00111351A patent/EP1028335A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1996-10-07 EP EP96934091A patent/EP0886797B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1996-10-07 JP JP9511495A patent/JP2000505208A/ja not_active Withdrawn
-
1997
- 1997-02-14 TW TW086101690A patent/TW381186B/zh active
- 1997-10-20 US US08/953,950 patent/US5845028A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1999
- 1999-10-04 HK HK99104305A patent/HK1019169A1/xx not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3409641A1 (de) * | 1984-03-16 | 1985-09-19 | Standard Elektrik Lorenz Ag, 7000 Stuttgart | Steckverbindung fuer lichtwellenleiter |
| US5315678A (en) * | 1992-03-30 | 1994-05-24 | Nippon Telegraph & Telephone Corporation | Optical fiber connector |
| US5430819A (en) * | 1993-12-21 | 1995-07-04 | At&T Corp. | Multiple optical fiber connector and method of making same |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI422887B (zh) * | 2005-09-12 | 2014-01-11 | Stratos Int Inc | 光電連接器 |
| TWI561877B (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2016-12-11 | Hon Hai Prec Ind Co Ltd | Photoelectric transmitting module and optical fiber connector thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1028335A3 (en) | 2000-09-06 |
| US5845028A (en) | 1998-12-01 |
| DE69618668D1 (de) | 2002-02-28 |
| US5778123A (en) | 1998-07-07 |
| EP1028335A2 (en) | 2000-08-16 |
| HK1019169A1 (en) | 2000-01-14 |
| EP1028336A2 (en) | 2000-08-16 |
| TW381186B (en) | 2000-02-01 |
| DE69618668T2 (de) | 2002-08-14 |
| WO1997034179A1 (en) | 1997-09-18 |
| JP2000505208A (ja) | 2000-04-25 |
| CN1214122A (zh) | 1999-04-14 |
| EP0886797B1 (en) | 2002-01-02 |
| KR19990087648A (ko) | 1999-12-27 |
| EP0886797A1 (en) | 1998-12-30 |
| EP1028336A3 (en) | 2000-09-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1129016C (zh) | 用于多光纤光缆或单光纤光缆连接器的定位组件 | |
| CN1129015C (zh) | 制作光纤连接器套箍用的夹紧装置 | |
| CN103597393B (zh) | 横向插入光纤的套管组件 | |
| CN1192268C (zh) | 光纤连接器 | |
| US7566175B2 (en) | Ferrule for optical fiber connector | |
| CN101806940B (zh) | 一种光纤现场连接器 | |
| CN1134688C (zh) | 制作光纤连接器套箍的方法 | |
| US4738508A (en) | Terminated optical fiber and methods of making | |
| CN1091523C (zh) | 光学接头 | |
| EP0327267B1 (en) | Optical fiber connector and methods of making | |
| CN1019148B (zh) | 光纤连接器及其连接方法 | |
| CN103562767A (zh) | 用于多芯光纤电缆的多光纤连接器 | |
| CN1220015A (zh) | 光电子装置插座及其制造方法 | |
| JP2013238692A (ja) | マルチコアファイバコネクタの製造方法、マルチコアファイバの回転装置 | |
| CN1373376A (zh) | 连接塑料光纤的方法 | |
| CN104635304A (zh) | 光纤连接器插芯及其制造方法、光纤连接器 | |
| CN1134686C (zh) | 光纤连接器套箍 | |
| JPS61502638A (ja) | 複数チャネル光学回転ジョイント | |
| CN1735825A (zh) | 具有多根光纤的装置 | |
| CN1209559A (zh) | 光缆的连接器套箍中的对准系统 | |
| CN1879044A (zh) | 一种光学纤维连接件 | |
| CN1412585A (zh) | 光耦合模块 | |
| JPH0361916A (ja) | 光多心コネクタ | |
| US7274845B2 (en) | Low-cost method and apparatus for establishing fiber optic connections | |
| CN213717980U (zh) | 一种易于观察的光路显示器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C19 | Lapse of patent right due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |