WO2021111984A1 - 回路構成体 - Google Patents
回路構成体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021111984A1 WO2021111984A1 PCT/JP2020/044063 JP2020044063W WO2021111984A1 WO 2021111984 A1 WO2021111984 A1 WO 2021111984A1 JP 2020044063 W JP2020044063 W JP 2020044063W WO 2021111984 A1 WO2021111984 A1 WO 2021111984A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- circuit configuration
- relay
- refrigerant
- cooling component
- cooling
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02G—INSTALLATION OF ELECTRIC CABLES OR LINES, OR OF COMBINED OPTICAL AND ELECTRIC CABLES OR LINES
- H02G3/00—Installations of electric cables or lines or protective tubing therefor in or on buildings, equivalent structures or vehicles
- H02G3/02—Details
- H02G3/03—Cooling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K7/00—Constructional details common to different types of electric apparatus
- H05K7/20—Modifications to facilitate cooling, ventilating, or heating
- H05K7/20218—Modifications to facilitate cooling, ventilating, or heating using a liquid coolant without phase change in electronic enclosures
- H05K7/20272—Accessories for moving fluid, for expanding fluid, for connecting fluid conduits, for distributing fluid, for removing gas or for preventing leakage, e.g. pumps, tanks or manifolds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02G—INSTALLATION OF ELECTRIC CABLES OR LINES, OR OF COMBINED OPTICAL AND ELECTRIC CABLES OR LINES
- H02G3/00—Installations of electric cables or lines or protective tubing therefor in or on buildings, equivalent structures or vehicles
- H02G3/02—Details
- H02G3/08—Distribution boxes; Connection or junction boxes
- H02G3/16—Distribution boxes; Connection or junction boxes structurally associated with support for line-connecting terminals within the box
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to a circuit configuration including heat generating parts.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a circuit configuration including a relay that interrupts and interrupts the power supply of a battery to a motor or a generator connected via an inverter as a load on the vehicle side.
- the circuit configuration of the present disclosure includes a heat-generating component that generates heat by energization, an energizing member connected to a connection portion of the heat-generating component, and a cooling component in which a refrigerant is circulated inside and is thermally contacted with the energizing member. It is a circuit configuration including.
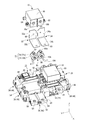
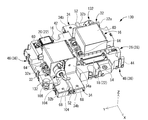
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a circuit configuration according to the first embodiment.
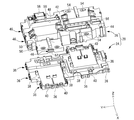
- FIG. 2 is an exploded perspective view of the circuit configuration shown in FIG.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram schematically showing an electrical configuration in a path from a power source to a load in the circuit configuration shown in FIG.
- FIG. 4 is an exploded perspective view of a base member constituting the circuit configuration shown in FIG.
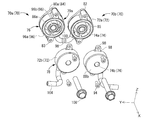
- FIG. 5 is an exploded perspective view of the cooling components constituting the circuit configuration shown in FIG.
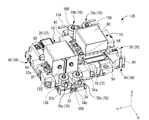
- FIG. 6 is an exploded perspective view showing the cooling component shown in FIG. 5 from another direction.
- FIG. 7 is a perspective view of the circuit configuration according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 8 is a perspective view of the circuit configuration according to the third embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a perspective view of the circuit configuration according to the fourth embodiment.
- the circuit configuration of the present disclosure is (1) A circuit configuration including a heat-generating component that generates heat by energization, an energizing member connected to a connection portion of the heat-generating component, and a cooling component in which a refrigerant is circulated inside and is thermally contacted with the energizing member. is there.
- the cooling component through which the refrigerant flows is in thermal contact with the energizing member directly connected to the connecting portion which is the heat generating portion of the heat generating component. Therefore, the energizing member to which the heat of the heat-generating component is transferred can be positively cooled by the cooling component, and the heat-dissipating path of the heat-generating component is promoted more reliably by a shorter heat transfer path as compared with the conventional structure. The heat dissipation performance can be improved.
- the chassis and the housing itself to which the energizing member such as the bus bar is thermally contacted are at a high temperature exceeding 70 ° C. Compared with the conventional structure, the heat dissipation effect and the cooling effect can be improved.
- the refrigerant flowing through the refrigerant flow path can be any refrigerant that can be used in the vehicle, such as a radiator liquid.
- the thermal contact of the cooling component with the energizing member includes a mode in which the cooling component is directly contacted with the energizing member or indirectly contacted with another member having high thermal conductivity.
- the energizing member is connected to the connecting portion of the heat generating component, the heat of the heat generating component is advantageously transferred, but the energizing member connected to the connecting portion of the heat generating component is of the heat generating component.
- Heat-generating parts include parts that generate heat when energized, such as relays and fuses.
- the cooling component is fastened to the connection portion of the heat generating component via the current-carrying member. Since the cooling component is fastened to the connection part, which is the heat generating part of the heat generating part, together with the energizing member, the separation distance between the heat generating part and the heat radiating part can be almost eliminated, and the heat radiating of the heat generating part can be realized more efficiently. Because it can be done.
- the cooling component has a refrigerant flow path provided with an inlet and an outlet for the refrigerant, and an external refrigerant supply path and a refrigerant discharge path can be connected to the inlet and the outlet.
- An external refrigerant supply / discharge path can be easily connected to the inlet and outlet of the refrigerant flow path provided in the cooling component, and the circulation of the refrigerant in the refrigerant flow path of the cooling component can be easily realized. Because it can be done.
- the cooling component has an annular cylinder body, the inner hole of the annular cylinder body is a fastening component insertion hole, and the annular cylinder bodies are assembled to each other in the axial direction.
- the first part includes an annular first part and an annular second part, the first part has a concave first-flow passage forming portion that opens to an assembly surface to the second part, and the second part is the first part. It has a concave second flow passage forming portion that opens to the assembly surface to one part, and the first part and the second part are in close contact with each other via a sealing member. It is preferable that the refrigerant flow path partitioned by the first flow passage forming portion and the second flow passage forming portion is formed inside the annular cylinder body by being assembled and fixed to each other.
- the fastener insertion hole through which the fastener can be inserted is configured by using the inner hole of the annular cylinder body, and it is possible to provide a compact cooling component that can be fastened by the fastener.
- the refrigerant flow path can be made by bringing the first flow passage forming portion and the second flow passage forming portion that open to each assembly surface of the annular first / second parts close to each other via the sealing member. Since it is partitioned, the cooling component can be formed by a simple molding mold structure.
- one of the first part and the second part in contact with the energizing member is made of a material having higher thermal conductivity than the other part. .. This is because by improving the thermal conductivity of one part in contact with the current-carrying member, it is possible to efficiently improve the heat transfer performance of the cooling part and reduce the cost of the other part.
- the cooling component is fixed to the energizing member in a contact state by using a bolt, and the cooling component has a rotation blocking protrusion that abuts on another member to prevent the cooling component from rotating. It is preferable to do.
- the rotation blocking protrusion of the cooling component comes into contact with another member, excessive rotation of the cooling component can be prevented, so that the bolt can be advantageously fastened between the cooling component and the energizing member.
- the circuit configuration 10 is mounted on a vehicle (not shown) such as an electric vehicle or a hybrid vehicle, and supplies and controls electric power from a power source 12 such as a battery to a load 14 such as a motor (see FIG. 3).
- a power source 12 such as a battery
- a load 14 such as a motor
- the orientation of the circuit configuration 10 when mounted on the vehicle is not limited, but in the following description, the upward direction is the Z direction in FIG. 1, and the front direction is the X direction and the left direction in FIG. Will be described as the Y direction in FIG.
- a reference numeral may be added to only a part of the members, and the reference numeral may be omitted for the other members.
- the circuit configuration 10 includes a circuit configuration 10a provided on the positive electrode side and a circuit configuration 10b provided on the negative electrode side.
- the positive electrode side of the power supply 12 is connected to the input side of the circuit configuration 10a, and the negative electrode side of the power supply 12 is connected to the input side of the circuit configuration 10b.
- the positive electrode side of the load 14 is connected to the output side of the circuit configuration 10a, and the negative electrode side of the load 14 is connected to the output side of the circuit configuration 10b.
- a relay 16 which is a heat generating component for connecting the power supply 12 to the load 14 is connected between the input side and the output side of the circuit structure 10a and the circuit structure 10b, respectively.
- a precharge circuit 22 in which the precharge resistor 18 and the precharge relay 20 are connected in series so as to bypass the relay 16 is connected to the relay 16 that connects the power supply 12 and the positive electrode side of the load 14. ..
- the precharge resistor 18 is connected to the input side of the precharge relay 20.
- the precharge circuit 22 is similarly connected to the relay 16 connecting the power supply 12 and the negative electrode side of the load 14, but in FIG. 3, the precharge circuit 22 is connected to the relay 16 connecting the power supply 12 and the negative electrode side of the load 14.
- the charge circuit 22 is shown by a chain double-dashed line.
- both the relay 16 and the precharge relay 20 are relays that move the contact portion to switch the contact portion ON / OFF while the exciting coil is energized, and ON / OFF control is performed by a control circuit (not shown). ..
- the circuit structure 10a and the circuit structure 10b have substantially the same structure.
- the circuit configuration 10 includes a lower case 24 located below and an upper case 26 located above when mounted on a vehicle.
- the lower case 24 and the upper case 26 constitute an insulating base member 28.
- a bus bar that connects the relay 16 and the precharge circuit 22 and a bus bar that connects the inside of the precharge circuit 22 are housed.
- the base member 28 is provided with two relays 16 and bus bars 32 and 34 as energizing members connected to the connecting portions 30a and 30b of the respective relays 16.
- the lower case 24 is formed by injection molding an insulating synthetic resin into a predetermined shape.
- the synthetic resin constituting the lower case 24 may contain a filler such as glass fiber.
- the lower case 24 has a horizontally long flat shape as a whole (the width dimension in the left-right direction is larger than the width dimension in the front-rear direction).
- a plurality of lower side engaging portions 36 are provided on the outer peripheral surface of the lower case 24.
- the lower side engaging portion 36 engages with the upper side engaging portion 46 provided on the outer peripheral surface of the upper case 26, which will be described later, so that the lower case 24 and the upper case 26 are mutually fixed. ..
- the engagement mode between the lower side engaging portion 36 and the upper side engaging portion 46 is not limited, and for example, uneven fitting or the like can be adopted.
- a relay fixing portion 38 having a substantially square cylinder shape to which the legs 63 of the relays 16 and 16 described later are bolted is provided so as to project upward.
- a bolt insertion portion 40 for connecting an electric wire or the like to the relay 16, the precharge resistor 18, the precharge relay 20, or the like is provided on the upper surface of the lower case 24 . That is, the electric wire and the relay 16 and the like can be electrically connected by inserting the bolt into the bolt insertion portion 40 in a state where the terminal portion provided at the end of the electric wire and the upper case 26 are overlapped with each other.
- a plurality of bolt insertion portions 40 are provided in a substantially square tubular shape.
- the upper case 26 is formed by injection molding an insulating synthetic resin into a predetermined shape.
- the synthetic resin constituting the upper case 26 may contain a filler such as glass fiber.
- the upper case 26 has a substantially box-like shape that opens downward as a whole, and is provided with an upper wall 42 having a shape substantially similar to that of the lower case 24 and a peripheral wall 44 that protrudes downward from the upper wall 42. ing.
- an upper-side engaging portion 46 is provided at a position corresponding to the lower-side engaging portion 36 in the lower case 24 so that the lower-side engaging portion 36 can be engaged with the lower-side engaging portion 36.
- the upper case 26 is formed with a storage recess 48 in which the relay 16 is housed.
- the accommodating recess 48 in which the relay 16 on the positive electrode side is accommodated and the accommodating recess 48 in which the relay 16 on the negative electrode side is accommodated are provided so as to be separated from each other in the left-right direction.
- the bottom surface of the accommodating recess 48 is a substantially flat surface extending on a horizontal plane (a plane extending in a direction orthogonal to the vertical direction), and is provided at a position lower than the upper wall 42.
- mounting surfaces 50 and 50 on which the bus bars 32 and 34 are mounted are provided in front of the storage recess 48 on the left side and behind the storage recess 48 on the right side.
- the mounting surfaces 50 and 50 are provided at positions lower than the bottom surface of the accommodating recess 48.
- a partition wall portion 52 projecting in the vertical direction is formed between the mounting surfaces 50 and 50.
- a through hole 54 penetrating in the vertical direction is formed at a position corresponding to the relay fixing portion 38 and the bolt insertion portion 40 in the lower case 24.
- the upper wall 42 is provided with a precharge resistor mounting portion 56 for mounting the precharge resistor 18 and a precharge relay mounting portion 58 for mounting the precharge relay 20 with an opening upward.
- the relay 16 is a mechanical relay, and ON / OFF control is performed by a control circuit (not shown).
- the relay 16 includes a relay main body 60 having a substantially hollow rectangular parallelepiped shape as a whole, and has a contact portion and a coil portion (not shown) inside the relay main body 60. ..
- the relay 16 on the left side and the relay 16 on the right side have the same structure, and are mounted in a front-rear inverted state. In the following description, the relay 16 on the left side will be described, and the description of the relay 16 on the right side will be omitted. Further, a pair of through holes are formed on the front end surface of the relay main body 60 so as to be separated from each other in the left-right direction, and these through holes form the connection portions 30a and 30b of the relay 16 described above.
- connection portions 30a and 30b When energized, a current flows between the connection portions 30a and 30b via the contact portion of the relay 16, so that heat is generated at the contact portion.
- a partition plate portion 62 projecting forward is formed between the connecting portions 30a and 30b over substantially the entire length of the relay main body 60 in the vertical direction.
- the relay body 60 is provided with a plurality of legs 63 (three in the present embodiment) protruding from both sides in the left-right direction, and the legs 63 are formed with bolt insertion holes.
- the relay 16 is attached to the base member 28 by inserting and fastening the fixing bolt 64 in a state where the through hole 54 provided in the bottom surface of the accommodating recess 48 in the base member 28 and the bolt insertion hole of the leg portion 63 are aligned. It is attached.
- bus bars 32 and 34 are formed by processing a metal plate material, each of which has conductivity. As shown in FIG. 2, each of the bus bars 32 and 34 is formed by bending into a substantially L shape. One side with respect to the bent portion is a substantially rectangular plate-shaped first connecting portion 32a, 34a connected to the connecting portions 30a, 30b of the relay 16. The first connecting portions 32a and 34a have bolt insertion holes 66 penetrating in the front-rear direction, which is the plate thickness direction. The bus bars 32 and 34 are bolted to the connection portions 30a and 30b of the relay 16 so as to be electrically and thermally connected to the connection portions 30a and 30b of the relay 16.
- each of the bus bars 32 and 34 the other side with respect to the bent portion extends forward, and the extended portion is a second connecting portion 32b and 34b having a substantially rectangular plate shape.
- the second connecting portions 32b and 34b have bolt insertion holes 68 penetrating in the vertical direction, which is the plate thickness direction. These bolt insertion holes 68 are aligned with the through holes 54 provided in the mounting surface 50 when the bus bars 32 and 34 are mounted on the mounting surfaces 50 and 50 of the base member 28. There is.
- the electric wire and the bus bar 32 are fastened by superimposing the terminal portions at the ends of the electric wires (not shown) on the second connecting portions 32b and 34b of the bus bars 32 and 34, and inserting and fastening the bolts through the bolt insertion holes 68 and the through holes 54. , 34 are electrically connected.
- the cooling components 70 as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6 are in thermal contact with the bus bars 32 and 34.
- the cooling component 70 of the first embodiment has a cylindrical shape extending in the front-rear direction as a whole, and includes an annular cylinder main body 72 and an inner hole 74 penetrating the inner peripheral side of the annular cylinder main body 72 in the front-rear direction. There is.
- a pair of cooling parts 70, 70 are provided. That is, the first cooling component 70a is attached to the + side connection portion 30a of the relay 16, and the second cooling component 70b is attached to the ⁇ side connection portion 30b of the relay 16. ..
- the first cooling component 70a and the second cooling component 70b have the same structure. Therefore, in the following description, the first cooling component 70a will be described and the second cooling component 70a will be described. The description of the component 70b will be omitted.
- the annular cylinder body 72 of the first cooling component 70a is configured to include a first part 76 and a second part 78 that are connected to each other in the front-rear direction (the central axis direction of the annular cylinder body 72).
- the first part 76 and the second part 78 are assembled so as to overlap the end faces in the front-rear direction. That is, the front end surface of the first part 76 is the assembly surface 79a to the second part 78, and the rear end surface of the second part 78 is the assembly surface 79b to the first part 76.
- the annular cylinder body 72 and the inner hole 74 are separable in the front-rear direction
- the first part 76 is the first annular cylinder body 72a and the first annular cylinder body 72a constituting the rear portion of the annular cylinder body 72 and the inner hole 74. It is provided with a first inner hole 74a.
- the second part 78 includes a second annular cylinder main body 72b and a second inner hole 74b that form a front portion of the annular cylinder main body 72 and the inner hole 74.
- the first part 76 has a substantially bottomed cylinder shape as a whole, and the first annular cylinder main body 72a is provided so as to project forward from the first bottom wall portion 80a having a substantially disk shape.
- the first annular cylinder main body 72a is integrally formed with protrusions 82 and 82 protruding from both sides in the vertical direction.
- the protruding portion 82 has a semicircular or circular cross section, and extends over substantially the entire length of the first part 76 in the front-rear direction. Then, in the first part 76, the outer peripheral surface of the protruding portion 82 and the outer peripheral surface of the non-formed portion of the protruding portion 82 are continuous with a smooth curved surface.
- the protrusion 82 is provided with a bolt hole 83 that opens forward. Further, the shape of the first bottom wall portion 80a substantially corresponds to the shape of the first annular cylinder body 72a, and the width dimension in the vertical direction is larger than the width dimension in the left-right direction, and the width dimension in the vertical direction is larger. Protruding portions 84 and 84 are formed on both sides.
- the radial intermediate portion of the first part 76 has a concave portion that opens to the front end surface (assembly surface 79a).
- the concave portion is an arc-shaped concave portion 85 extending in the circumferential direction.
- it extends with a circumferential dimension of about one circumference. That is, in the first embodiment, the first inner cylinder portion 86a is provided on the inner peripheral side of the first annular cylinder main body 72a, separated in the radial direction.
- a first inner hole 74a is formed on the inner peripheral side of the first inner cylinder portion 86a, and an arc-shaped recess is formed between the first annular cylinder main body 72a and the first inner cylinder portion 86a in the radial direction. 85 is formed.
- the first part 76 has a double tubular structure including a first annular tubular body 72a and a first inner tubular portion 86a, and has a first annular tubular body 72a and a first annular cylinder body 72a on a part of the circumference.
- One inner cylinder portion 86a is connected to each other.
- the second part 78 has a substantially bottomed cylinder shape as a whole, and a second annular cylinder main body 72b is provided so as to project rearward from the second bottom wall portion 80b having a substantially disk shape. There is.
- the second annular cylinder body 72b is integrally formed with protruding portions 88 projecting on both sides in the vertical direction.
- the protruding portion 88 has an outer shape similar to that of the protruding portion 82 in the first part 76.
- the protruding portion 88 does not extend to the total length in the front-rear direction of the second part 78, and is provided at the rear end portion of the second part 78. Then, a bolt hole 90 is formed by penetrating the protruding portion 88 in the front-rear direction.
- the radial intermediate portion of the second part 78 has a concave portion that opens to the rear end surface (assembly surface 79b).
- the concave portion is an arc-shaped concave portion 92 extending in the circumferential direction.
- it extends with a circumferential dimension of about one circumference. That is, in the first embodiment, the second inner cylinder portion 86b is provided on the inner peripheral side of the second annular cylinder main body 72b, separated in the radial direction.
- a second inner hole 74b is formed on the inner peripheral side of the second inner cylinder portion 86b, and an arc-shaped recess is formed between the second annular cylinder main body 72b and the second inner cylinder portion 86b in the radial direction. 92 is formed.
- the second part 78 has a double tubular structure including a second annular tubular body 72b and a second inner tubular portion 86b, and has a second annular tubular body 72b and a second annular cylinder body 72b on a part of the circumference.
- the second inner cylinder portion 86b is connected to each other.
- the protruding portion 82 of the first part 76 and the protruding portion 88 of the second part 78 are also overlapped.
- the bolt hole 83 and the bolt hole 90 communicate with each other.
- the first part 76 and the second part 78 are connected in the front-rear direction by inserting and fastening the fixing bolt 94 from the front through the bolt hole 83 and the bolt hole 90.
- the first annular cylinder main body 72a and the second annular cylinder main body 72b form a continuous annular cylinder main body 72, and the first inner hole 74a and the second inner hole 74b communicate with each other.
- the inner hole 74 is formed. Further, the arcuate recess 85 in the first part 76 and the arcuate recess 92 in the second part 78 communicate with each other in the front-rear direction. The region partitioned by the two arcuate recesses 85 and 92 is the refrigerant flow path 95 through which the refrigerant flows.
- the refrigerant flowing through the refrigerant flow path 95 can be any refrigerant that can be used in the vehicle, such as a radiator liquid.
- the rear end surfaces of the first annular cylinder body 72a and the first inner cylinder portion 86a and the front end surfaces of the second annular cylinder main body 72b and the second inner cylinder portion 86b are overlapped with each other. It has become.
- An O-ring 96 as a sealing member is provided between these overlapping surfaces.
- an outer peripheral side O-ring 96a is provided between the first and second annular cylinder main bodies 72a and 72b, and between the first inner cylinder portion 86a and the second inner cylinder portion 86b.
- the inner peripheral side O-ring 96b is provided.
- the outer and inner O-rings 96a and 96b are compressed in the front-rear direction, so that the assembling surfaces 79a and 79b of the first part 76 and the second part 78 are assembled. Are in close contact with each other to prevent the refrigerant from leaking.
- the first cooling component 70a and the second cooling component 70b having the above structure are provided one on each of the left and right sides of the relay 16. Then, the first cooling component 70a and the second cooling component 70b that are adjacent to each other in the left-right direction are communicated with each other by the tube 98.
- through holes 100 penetrating in the thickness direction are formed in both first annular cylinder bodies 72a and 72a adjacent to each other in the left-right direction.
- through holes 102 penetrating in the thickness direction are formed in both second annular cylinder bodies 72b and 72b adjacent to each other in the left-right direction.
- the tube 104 extending outward is fixed to the opening edge of the through hole 102 by adhesion, welding, or the like, so that both arcuate recesses 92 and 92 (that is, both refrigerant flow paths 95 and 95) pass through the tube 104, respectively. It is communicated to the external space.
- one through hole 102 is used as an inflow port for the refrigerant into the refrigerant flow path 95, and the other through hole 102 is used as an outflow port from the refrigerant flow path 95.
- the tube 104 connected to one of the through holes 102 is used as a refrigerant supply path for supplying the refrigerant from the outside to the refrigerant flow path 95.
- the tube 104 connected to the other through hole 102 (outlet) is used as a refrigerant discharge path for discharging the refrigerant from the refrigerant flow path 95 to the outside.
- the first flow passage forming portion which is opened in the assembling surface 79a to the second part 78 in the first part 76 and forms a part of the refrigerant flow path 95 is formed by the arc-shaped recess 85.
- the second flow passage forming portion that opens to the assembly surface 79b to the first part 76 and forms a part of the refrigerant flow path 95 is formed by the arc-shaped recess 92.
- the cooling parts (first part 76 and second part 78) as described above can be suitably formed by, for example, a hard synthetic resin. Further, of the first part 76 and the second part 78, the one that comes into contact with the bus bars 32 and 34, which are energizing members (the first part 76 in the first embodiment), is preferably a material having high thermal conductivity.
- the lower case 24 and the upper case 26 constituting the base member 28 are prepared.
- a bus bar that connects the relay 16 and the precharge circuit 22 and a bus bar that connects the inside of the precharge circuit 22 are accommodated and arranged with respect to the lower case 24 or the upper case 26.
- the upper case 26 is superposed on the lower case 24 from above, and the lower side engaging portion 36 and the upper side engaging portion 46 are engaged with each other. As a result, the lower case 24 and the upper case 26 are assembled to form the base member 28.
- the relay 16 is arranged in the accommodating recess 48 of the upper case 26, and the relay 16 is fixed to the base member 28 by the fixing bolt 64. Subsequently, bus bars 32 and 34 are arranged for the two relays 16, respectively. In the following description, the relay 16 on the left side will be described.
- first connecting portions 32a and 34a of the bus bars 32 and 34 are overlapped with respect to the connecting portions 30a and 30b of the relay 16 from the front side. Further, the second connecting portions 32b, 34b of the bus bars 32, 34 are overlapped with the mounting surface 50 located on the front side with respect to the bottom surface of the accommodating recess 48 from above.
- the pre-assembled cooling components 70 (first and second cooling components 70a, 70b) are superposed on the front end faces of the relay 16 via the first connecting portions 32a, 34a of the bus bars 32, 34. ..
- Fixing bolts 108 and 108 as fastening parts are inserted into these connecting portions 30a and 30b, bolt insertion holes 66 and 66, and inner holes 74a and 74b for fastening.
- the first and second cooling components 70a and 70b are bolted to the connection portions 30a and 30b of the relay 16 via the bus bars 32 and 34.
- the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are co-tightened by using the fixing bolts 108 and 108 that fix the bus bars 32 and 34 to the relay 16. That is, the fastening component insertion hole through which the fixing bolt 108, which is the fastening component, is inserted in the cooling component 70 is formed by the inner hole 74 of the annular cylinder body 72.
- first and second bottom wall portions 80a and 80b of the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are in direct contact with the bus bars 32 and 34, so that the first and second bottoms are in direct contact with each other.
- the wall portions 80a and 80b are in thermal contact.
- the first and second bottom wall portions 80a and 80b are provided with projecting portions 84 and 84 protruding on both sides in the vertical direction, so that a large contact area with the bus bars 32 and 34 is secured.
- the electric heating efficiency from the bus bars 32 and 34 to the first and second cooling components 70a and 70b is improved.
- bus bars 32 and 34 need only be in thermal contact with the first and second cooling components 70a and 70b, and need not be in direct contact with each other. That is, a member having heat transfer property may be provided between the bus bar and the cooling component, and the bus bar and the cooling component may be indirectly in contact with each other via the member having heat transfer property.
- the rotation blocking protrusion that prevents the cooling component 70 from rotating due to contact with another member in the cooling component 70 is composed of at least one of a protruding portion 82, a protruding portion 88, and a protruding portion 84. Has been done.
- the circuit configuration 10 is assembled by the above process. By superimposing the terminal portions at the ends of the electric wires on the second connecting portions 32b and 34b of the bus bars 32 and 34 and fixing them with bolts, electric power can be supplied to the relay 16 via the bus bars 32 and 34.
- the contact portion inside the relay 16 generates heat when power is supplied to the relay 16, and this heat is generated by the bus bar 32 connected to the relay 16. , 34.
- the cooling components 70 first and second cooling components 70a, 70b
- the refrigerant flow path 95 through which the refrigerant flows inside the cooling components 70.
- the refrigerant flows through the refrigerant flow path 95, so that the bus bars 32 and 34 are efficiently cooled and the heat generated by the relay 16 is eliminated.
- heat dissipation of the heat-generating component can be achieved without increasing the material cost and the processing cost without separately providing a heat-dissipating path or the like.
- the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b together with the bus bars 32 and 34 are fastened together with the relay 16 by bolting. Therefore, the structure of the circuit configuration 10 can be simplified without separately providing the fixing means for the heat generating component and the energizing member and the fixing means for the energizing member and the cooling component. In particular, by setting the heat radiation portion to the fixing bolts 108 and 108 that are directly fixed to the relay 16, heat radiation from the relay 16 can be achieved more efficiently.
- the tube 104 is connected to the inflow port (through hole 102) and the outflow port (through hole 102) of the refrigerant in the first and second cooling components 70a and 70b. It constitutes a refrigerant supply path and a refrigerant discharge path. Thereby, the supply of the refrigerant from the external refrigerant source to the refrigerant flow path 95 and the discharge of the refrigerant from the refrigerant flow path 95 to the external refrigerant source can be more reliably achieved.
- the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b have an annular cylinder body 72 having an inner hole 74 that can be used as a fastening component insertion hole, and the annular cylinder body 72 has an annular cylinder body 72. It is configured by assembling the first part 76 and the second part 78, which are separated from each other. Then, the first flow passage forming portion (arc-shaped recess 85) provided inside the first part 76 and the second flow passage forming portion (arc-shaped recess 92) provided inside the second part 78 are included. A refrigerant flow path 95 is formed.
- the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b which can be fastened by the fastening member and have the refrigerant flow path 95 inside, can be formed by a molding die having a simple structure. Further, since the O-ring 96 (outer peripheral side O-ring 96a and inner peripheral side O-ring 96b) as a sealing member is provided between the assembling surfaces 79a and 79b of the first part 76 and the second part 78, Leakage of the refrigerant from between the assembly surfaces 79a and 79b can also be prevented.
- the inner hole 74 of the annular cylinder body 72 is used as a fastening component insertion hole through which the fixing bolt 108, which is a fastening component, is inserted, a cooling component 70 that can be fastened by the fastening component is provided compactly. can do.
- the first part 76 in contact with the bus bars 32 and 34 is made of a material having higher thermal conductivity.
- the heat generated by the relay 16 is more efficiently transmitted to the first part 76 constituting the cooling component 70 via the bus bars 32 and 34, and the cooling by the cooling component 70 can be more reliably achieved.
- first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are provided with projecting portions 82 and 88 and projecting portions 84 projecting on both sides in the vertical direction, so that the vertical dimension is larger than the horizontal dimension. There is.
- both side portions in the vertical direction of the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are partition plates.
- the circuit configuration 120 shown in FIG. 7 has the same structure as the circuit configuration 10 of the first embodiment as a whole, but is attached with the cooling component 70 (the first cooling component 70a and the second cooling component 70b). The position is different.
- the differences from the circuit configuration 10 of the first embodiment will be described, and the description of the portion having the same structure will be omitted.
- the members or parts substantially the same as those in the first embodiment are designated by the same reference numerals as those in the first embodiment, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
- the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are attached to the second connecting portions 32b and 34b of the bus bars 32 and 34. That is, the through holes 54 provided in the mounting surface 50 of the base member 28, the bolt insertion holes 68 provided in the second connecting portions 32b and 34b, and the first in the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b. And the second inner holes 74a and 74b are aligned respectively. A terminal portion provided on an electric wire terminal (not shown) is interposed between the second connecting portions 32b and 34b and the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b in a state of being aligned with the bolt insertion hole. To. Then, the fixing bolts 108 and 108 are inserted and fastened to the through holes 54, the bolt insertion holes 68 and the first and second inner holes 74a and 74b.
- the first connection portions 32a and 34a of the bus bars 32 and 34 are overlapped with terminal portions at the ends of electric wires (not shown), and the bolt insertion holes 66 and 66 of the first connection portions 32a and 34a and the connection portions 30a of the relay 16 are overlapped. , 30b. Then, bolts 122 and 122 are inserted and fastened to these.
- the heat generated by the relay 16 is transmitted to the bus bars 32 and 34, and the cooling component 70 is in thermal contact with the bus bars 32 and 34. Can dissipate heat.
- the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are fastened together with the bus bars 32 and 34 to the base member 28, and efficient assembly is realized as in the first embodiment. obtain.
- the partition wall portion 52 provided on the base member 28 is located between the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b.
- the protruding portions 82 and 88 and the protruding portions 84 protruding from both sides in the front-rear direction of the first and second cooling parts 70a and 70b are partition walls. It comes into contact with the portion 52 to prevent further rotation. Therefore, also in the second embodiment, the rotation blocking protrusions that prevent the rotation of the first and second cooling components 70a and 70b may be composed of at least one of the protruding portion 82, the protruding portion 88, and the protruding portion 84.
- the circuit configuration 130 shown in FIG. 8 has the same structure as the circuit configuration 10 of the first embodiment as a whole, but the structure of the cooling component 132 is different from that of the circuit configuration 10 of the first embodiment. .. In the following description, the differences from the circuit configuration 10 of the first embodiment will be described, and the description of the portion having the same structure will be omitted.
- the cooling component 132 is in thermal contact with one of the bus bars 32 and 34 (bus bar 32) connected to the connection portions 30a and 30b of the relay 16. Even in the circuit configuration 130 having such a structure, the cooling effect on the heat generation of the relay 16 can be exhibited.
- the cooling component 132 of the third embodiment is also composed of the first part 76 and the second part 78, and the second part 78 is provided with two through holes 102 and 102 with respect to the through holes 102 and 102.
- the tubes 104, 104 constituting the refrigerant supply path and the refrigerant discharge path may be connected. Therefore, the cooling component 132 of the third embodiment is not provided with a tube (98) for connecting the first components (76,76) adjacent to each other in the left-right direction.
- the cooling component 132 may be provided only for one of the relays 16. .. Further, the other bus bar 34 connected to the relay 16 may not be provided with a cooling component, or a conventionally known cooling component may be adopted.
- the circuit configuration 140 shown in FIG. 9 has the same structure as the circuit configuration 130 of the third embodiment as a whole, but the cooling component 132 of the bus bar 32 is similar to the circuit configuration 120 of the second embodiment. It is in thermal contact with the second connection portion 32b.
- the mode in which the cooling component is thermally contacted with the first connection portion of the bus bar as shown in FIG. 8 and the mode in which the cooling component is thermally contacted with the second connection portion of the bus bar as shown in FIG. 9 are combined. It is possible to adopt it. That is, the cooling component 132 may be thermally brought into contact with the first connecting portion 32a of one bus bar 32, and the cooling component 132 may be thermally contacted with the second connecting portion 34b of the other bus bar 34. At that time, these cooling components 132 and 132 may be connected to each other by a tube 98 to form one refrigerant flow path, or may be independent of each other to form separate refrigerant flow paths. ..
- cooling components having the same structure are used as the cooling components adjacent to each other on the left and right, but the shapes and sizes may be different from each other.
- the first parts 76 and 76 of the adjacent cooling parts 70a and 70b are connected to each other by the tube 98, and the second parts 78 and 78 are connected via the tube 104, respectively. It was connected to the outside.
- the second parts may be connected to each other by a tube, the first part may be connected to the outside via a tube, or the first part and the second part may be connected by a tube. May be done.
- the arcuate recess 85 in the first part 76 and the arcuate recess 92 in the second part 78 have substantially the same circumferential length and are provided at positions corresponding to each other.
- the present invention is not limited to this mode, and for example, the circumferential lengths may be different from each other, or the forming positions may be different from each other in the circumferential direction. It suffices if the circumferential recesses to be provided communicate with each other. However, the circumferential recess does not have to be provided in both the first part and the second part, and the opening of the circumferential recess provided in one part may be covered with the other part.
- the cooling components 70 and 132 have a cylindrical main body portion as a whole, but for example, a square tubular main body portion may be provided. In such a case, the corners of the main body may form a rotation blocking protrusion that blocks the rotation of the cooling component.
- the first part 76 and the second part 78 are fixed by fixing bolts 94, but the fixing method of both parts is not limited, and for example, due to adhesion, welding, or unevenness. It may be locked or the like.
- Precharge resistor Precharge circuit 24 Lower case 26 Upper case 28 Base members 30a, 30b Connections 32, 34 Bus bars 32a, 34a First connection 32b, 34b Second connection 36 Lower side engagement 38 Relay fixing part 40
- Bolt insertion part 42 Upper wall 44 Peripheral wall 46 Upper side engaging part 48 Storage recess 50
- Mounting surface 52 Partition wall part 54 Through hole 56
- Precharge resistor mounting part 58
- Precharge relay mounting part 60 Relay body 62 Partition plate Part 63 Leg 64 Fixing bolt 66, 68 Bolt insertion hole 70 Cooling part 70a First cooling part 70b Second cooling part 72 Ring cylinder body 72a First ring cylinder body 72b Second ring cylinder body 74 Inner hole ( Fastener insertion hole) 74a First inner hole 74b Second inner hole 76 First part 78 Second part 79a Assembling surface 79b (to the second part in the first part) 79b (to the first
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Cooling Or The Like Of Electrical Apparatus (AREA)
- Connection Or Junction Boxes (AREA)
Abstract
短い伝熱経路でより確実に発熱部品の放熱を促すことができる新規な構造の回路構成体を開示する。 回路構成体10が、通電により発熱する発熱部品16と、前記発熱部品16の接続部30a,30bに接続される通電部材32,34と、内部に冷媒が流通されて前記通電部材32,34に熱的に接触される冷却部品70を含む。
Description
本開示は、発熱部品を含む回路構成体に関する。
従来から、車両には、リレー等の発熱部品を含む回路構成体が搭載されている。例えば、特許文献1には、車両側の負荷としてインバータを介して接続されるモータや発電機に対して、バッテリーの電力供給を断続するリレーを備えた回路構成体が示されている。
このような回路構成体に用いられるリレー等の発熱部品は、大電流が流れることから、電流量の二乗に比例したジュール熱が発生し、発熱量も大きくなる。そこで、特許文献1では、ケース内に収容されたリレーの接続部とケース外に配置されたバッテリーの接続端子とを接続する通電部材であるバスバーの中間部分を利用して、リレーの放熱を行う構造が提案されている。具体的には、リレーを収容するケース外に延出されたバスバーの中間部において伝熱シートを介してシャーシや電源装置全体を収容する筐体等に当接させることで、リレーで発生した熱をシャーシや筐体に熱伝導して放熱する構造が開示されている。
ところで、リレーとバッテリーを接続する通電部材を構成するバスバーは、大電流に耐え得るように厚さや面積を大きく確保する必要がある。そのため、特許文献1の構造では、大型のバスバーを用いて放熱用の経路を追加する必要があり、材料費や加工費が上昇するという問題があった。また、大型のバスバーを放熱用にケース外に設けられた他部材まで長く引き回す必要があり、リレーの接続部と放熱部分との距離が大きくなることが避けられない。そのため、リレーでの発熱を効率よく放熱できていないという問題も内在していた。
そこで、短い伝熱経路でより確実に発熱部品の放熱を促すことができる新規な構造の回路構成体を開示する。
本開示の回路構成体は、通電により発熱する発熱部品と、前記発熱部品の接続部に接続される通電部材と、内部に冷媒が流通されて前記通電部材に熱的に接触される冷却部品を含む回路構成体である。
本開示によれば、短い伝熱経路でより確実に発熱部品の放熱を促すことができる。
<本開示の実施形態の説明>
最初に、本開示の実施態様を列記して説明する。
本開示の回路構成体は、
(1)通電により発熱する発熱部品と、前記発熱部品の接続部に接続される通電部材と、内部に冷媒が流通されて前記通電部材に熱的に接触される冷却部品を含む回路構成体である。
最初に、本開示の実施態様を列記して説明する。
本開示の回路構成体は、
(1)通電により発熱する発熱部品と、前記発熱部品の接続部に接続される通電部材と、内部に冷媒が流通されて前記通電部材に熱的に接触される冷却部品を含む回路構成体である。
本開示の回路構成体によれば、発熱部品の発熱部位となる接続部に直接接続される通電部材に対して、内部に冷媒が流通される冷却部品が熱的に接触している。そのため、発熱部品の熱が伝熱される通電部材を、冷却部品により積極的に冷却することができ、従来構造に比べて短い伝熱経路でより確実に発熱部品の放熱を促し、回路構成体の放熱性能の向上を図ることができる。
特に、発熱部品の熱が伝熱される通電部材が、冷却部品を流通する冷媒により冷却されることから、バスバー等の通電部材が熱的に接触されるシャシーや筐体自体が70℃を越える高温になる従来構造に比して、放熱効果や冷却効果の向上が図られ得る。
なお、冷媒流路を流通する冷媒は、ラジエター液等の車両内で利用可能な冷媒であれば、何れも採用可能である。また、冷却部品の通電部材への熱的接触は、通電部材へ冷却部品を直接接触させたり、他の熱伝導率の高い部材を介して間接的に接触させる態様を含む。加えて、通電部材は、発熱部品の接続部に接続されているため、発熱部品の熱が有利に伝熱されるものであるが、発熱部品の接続部に接続された通電部材は、発熱部品の接続部と他部材との間の通電用としてのものの他、他部材に接続されず単に放熱用に用いられるものも含まれる。発熱部品には、リレーやヒューズ等の通電により発熱する部品が含まれる。
(2)前記発熱部品の前記接続部に対して、前記冷却部品が前記通電部材を介して締結されていることが好ましい。冷却部品が、発熱部品の発熱部位である接続部に対して通電部材と共に、締結されることから、発熱部品と放熱部位の離隔距離を殆ど無くすことができ、一層効率よく発熱部品の放熱を実現できるからである。
(3)前記冷却部品が、前記冷媒の流入口と流出口を備えた冷媒流路を有しており、前記流入口と前記流出口に外部の冷媒供給路と冷媒排出路が接続可能とされていることが好ましい。冷却部品に設けられた冷媒流路の流入口と排出口に対して、外部の冷媒供給/排出路を容易に接続することができ、冷却部品の冷媒流路内の冷媒の循環を容易に実現できるからである。
(4)上記(3)において、前記冷却部品が、環状筒本体を有し、該環状筒本体の内孔が締結部品挿通孔とされており、前記環状筒本体が、軸方向で相互に組み付けられる環状の第一パーツと環状の第二パーツを含み、前記第一パーツが前記第二パーツへの組付面に開口する凹状の第一流通路形成部を有し、前記第二パーツが前記第一パーツへの組付面に開口する凹状の第二流通路形成部を有し、前記第一パーツと前記第二パーツが、シール部材を介して各前記組付面を密接させた状態で、相互に組み付けられて固定されることにより、前記環状筒本体の内部に前記第一流通路形成部と前記第二流通路形成部により区画された前記冷媒流路が構成されていることが好ましい。
締結部品を挿通可能な締結部品挿通孔が環状筒本体の内孔を利用して構成されており、締結部品による締結が可能な冷却部品をコンパクトに提供することができる。しかも、環状の第一/第ニパーツの各組付面に開口する第一流通路形成部と第二流通路形成部を、各組付面をシール部材を介して密接させることで、冷媒流路が区画されるようになっていることから、簡単な成形型の構造により冷却部品を形成することができる。
(5)上記(4)において、前記第一パーツと前記第二パーツのうち、前記通電部材に接触する一方のパーツが他方のパーツよりも熱伝導性が高い材料で形成されていることが好ましい。通電部材に接触する一方のパーツの熱伝導性を向上させることにより、冷却部品による伝熱性能の向上を効率的に向上させつつ、他方のパーツのコストを抑えることができるからである。
(6)前記冷却部品が、前記通電部材に対してボルトを用いて接触状態に固定されており、前記冷却部品が他部材に当接して前記冷却部品の回転を阻止する回転阻止突部を有していることが好ましい。冷却部品が有する回転阻止突部が他部材に当接することで、冷却部品の過度の回転が阻止できることから、冷却部品と通電部材とのボルト締結を有利に行うことができる。
<本開示の実施形態の詳細>
本開示の回路構成体の具体例を、以下に図面を参照しつつ説明する。なお、本開示は、これらの例示に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
本開示の回路構成体の具体例を、以下に図面を参照しつつ説明する。なお、本開示は、これらの例示に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
<実施形態1>
以下、本開示の実施形態1について、図1から図6を参照しつつ説明する。回路構成体10は、例えば電気自動車やハイブリッド自動車等の車両(図示せず)に搭載され、バッテリー等の電源12からモータ等の負荷14への電力の供給、制御を行う(図3参照)。なお、回路構成体10の車両搭載時の向きは限定されるものではないが、以下の説明において、上方向とは図1中のZ方向、前方向とは図1中のX方向、左方向とは図1中のY方向として説明する。また、複数の同一部材については、一部の部材にのみ符号を付し、他の部材については符号を省略する場合がある。
以下、本開示の実施形態1について、図1から図6を参照しつつ説明する。回路構成体10は、例えば電気自動車やハイブリッド自動車等の車両(図示せず)に搭載され、バッテリー等の電源12からモータ等の負荷14への電力の供給、制御を行う(図3参照)。なお、回路構成体10の車両搭載時の向きは限定されるものではないが、以下の説明において、上方向とは図1中のZ方向、前方向とは図1中のX方向、左方向とは図1中のY方向として説明する。また、複数の同一部材については、一部の部材にのみ符号を付し、他の部材については符号を省略する場合がある。
<回路構成体10の概略的回路構成>
回路構成体10は、図3に示すように、正極側に設けられた回路構成体10aと負極側に設けられた回路構成体10bを備えている。回路構成体10aの入力側には、電源12の正極側が接続されており、回路構成体10bの入力側には、電源12の負極側が接続されている。回路構成体10aの出力側には、負荷14の正極側が接続されており、回路構成体10bの出力側には、負荷14の負極側が接続されている。回路構成体10aと回路構成体10bの入力側と出力側の間にはそれぞれ、電源12を負荷14に接続する発熱部品であるリレー16が接続されている。加えて、電源12と負荷14の正極側を接続するリレー16には、プリチャージ抵抗18およびプリチャージリレー20がリレー16をバイパスするように直列に接続されたプリチャージ回路22が接続されている。
回路構成体10は、図3に示すように、正極側に設けられた回路構成体10aと負極側に設けられた回路構成体10bを備えている。回路構成体10aの入力側には、電源12の正極側が接続されており、回路構成体10bの入力側には、電源12の負極側が接続されている。回路構成体10aの出力側には、負荷14の正極側が接続されており、回路構成体10bの出力側には、負荷14の負極側が接続されている。回路構成体10aと回路構成体10bの入力側と出力側の間にはそれぞれ、電源12を負荷14に接続する発熱部品であるリレー16が接続されている。加えて、電源12と負荷14の正極側を接続するリレー16には、プリチャージ抵抗18およびプリチャージリレー20がリレー16をバイパスするように直列に接続されたプリチャージ回路22が接続されている。
なお、本開示の実施形態1では、図3に示すように、プリチャージ抵抗18は、プリチャージリレー20の入力側に接続されている。電源12と負荷14の負極側を接続するリレー16にも同様にプリチャージ回路22が接続されるが、図3中では、電源12と負荷14の負極側を接続するリレー16に接続されるプリチャージ回路22を二点鎖線で示す。また、リレー16とプリチャージリレー20はいずれも、励磁コイルの通電状態で接点部を移動させて接点部をON/OFFに切り換えるリレーであり、図示しない制御回路によりON/OFF制御がなされている。以上述べてきたように、回路構成体10aと回路構成体10bは略同一構造とされている。
<回路構成体10>
回路構成体10は、例えば図4に示すように、車両搭載時において下方に位置するロアケース24と上方に位置するアッパケース26を備えている。そして、ロアケース24とアッパケース26によって絶縁性のベース部材28が構成されている。ベース部材28の内部にはリレー16とプリチャージ回路22を接続するバスバーやプリチャージ回路22内を接続するバスバーが収容される。また、ベース部材28に対して、2つのリレー16と、それぞれのリレー16の接続部30a,30bに接続された通電部材としてのバスバー32,34が設けられている。
回路構成体10は、例えば図4に示すように、車両搭載時において下方に位置するロアケース24と上方に位置するアッパケース26を備えている。そして、ロアケース24とアッパケース26によって絶縁性のベース部材28が構成されている。ベース部材28の内部にはリレー16とプリチャージ回路22を接続するバスバーやプリチャージ回路22内を接続するバスバーが収容される。また、ベース部材28に対して、2つのリレー16と、それぞれのリレー16の接続部30a,30bに接続された通電部材としてのバスバー32,34が設けられている。
<ロアケース24>
ロアケース24は、絶縁性の合成樹脂を所定の形状に射出成形してなる。ロアケース24を構成する合成樹脂は、ガラスファイバー等のフィラーを含んでいてもよい。ロアケース24は、全体として横長の(左右方向幅寸法が前後方向幅寸法よりも大きい)扁平形状を有している。ロアケース24の外周面には、複数のロア側係合部36が設けられている。ロア側係合部36は、後述するアッパケース26の外周面に設けられたアッパ側係合部46と係合して、ロアケース24とアッパケース26とが相互に固定されるようになっている。なお、ロア側係合部36とアッパ側係合部46との係合態様は限定されるものではなく、例えば凹凸嵌合等が採用され得る。
ロアケース24は、絶縁性の合成樹脂を所定の形状に射出成形してなる。ロアケース24を構成する合成樹脂は、ガラスファイバー等のフィラーを含んでいてもよい。ロアケース24は、全体として横長の(左右方向幅寸法が前後方向幅寸法よりも大きい)扁平形状を有している。ロアケース24の外周面には、複数のロア側係合部36が設けられている。ロア側係合部36は、後述するアッパケース26の外周面に設けられたアッパ側係合部46と係合して、ロアケース24とアッパケース26とが相互に固定されるようになっている。なお、ロア側係合部36とアッパ側係合部46との係合態様は限定されるものではなく、例えば凹凸嵌合等が採用され得る。
ロアケース24の上面には、後述するリレー16,16の脚部63がボルト締結される略角筒形状のリレー固定部38が上方に向かって突出して設けられている。さらに、ロアケース24の上面には、リレー16やプリチャージ抵抗18、プリチャージリレー20等に電線等を接続するためのボルト挿通部40が設けられている。即ち、電線の末端に設けられた端子部とアッパケース26とが重ね合わされた状態でボルト挿通部40にボルトが挿通されることで、電線とリレー16等が電気的に接続され得る。ロアケース24において、ボルト挿通部40は、略角筒形状をもって複数設けられている。
<アッパケース26>
アッパケース26は、絶縁性の合成樹脂を所定の形状に射出成形してなる。アッパケース26を構成する合成樹脂は、ガラスファイバー等のフィラーを含んでいてもよい。アッパケース26は、全体として下方に開口する略箱体形状を有しており、ロアケース24と略同様の形状とされた上壁42と、当該上壁42から下方に突出する周壁44が設けられている。周壁44の下端部において、ロアケース24におけるロア側係合部36と対応する箇所には、アッパ側係合部46が設けられており、ロア側係合部36と係合可能とされている。
アッパケース26は、絶縁性の合成樹脂を所定の形状に射出成形してなる。アッパケース26を構成する合成樹脂は、ガラスファイバー等のフィラーを含んでいてもよい。アッパケース26は、全体として下方に開口する略箱体形状を有しており、ロアケース24と略同様の形状とされた上壁42と、当該上壁42から下方に突出する周壁44が設けられている。周壁44の下端部において、ロアケース24におけるロア側係合部36と対応する箇所には、アッパ側係合部46が設けられており、ロア側係合部36と係合可能とされている。
また、アッパケース26には、リレー16が収容される収容凹部48が形成されている。実施形態1では、正極側のリレー16が収容される収容凹部48と負極側のリレー16が収容される収容凹部48とが相互に左右方向で離隔して設けられている。収容凹部48の底面は、水平平面(上下方向と直交する方向に広がる平面)上に広がる略平坦面とされており、上壁42よりも低い位置に設けられている。さらに、左側の収容凹部48の前方および右側の収容凹部48の後方には、バスバー32,34が載置される載置面50,50が設けられている。載置面50,50は、収容凹部48の底面よりも低い位置に設けられている。これら載置面50,50の間には上下方向に突出する仕切壁部52が形成されている。これにより、リレー16の+側に接続されるバスバー32と-側に接続されるバスバー34とが当接して、電気的な短絡が発生することが防止され得る。
なお、上壁42において、ロアケース24におけるリレー固定部38およびボルト挿通部40と対応する位置には、上下方向で貫通する貫通孔54が形成されている。貫通孔54にボルトを挿通することで、リレー16をボルト締結したり、バスバー32,34と電線等を電気的に接続することが可能とされている。また、上壁42には、プリチャージ抵抗18を装着するためのプリチャージ抵抗装着部56と、プリチャージリレー20を装着するためのプリチャージリレー装着部58が、上方に開口して設けられている。
<リレー16>
リレー16は、機械式のリレーであって、図示しない制御回路によりON/OFF制御がなされている。リレー16は、図2にも示すように、全体として略中空の直方体状とされたリレー本体60を備えており、当該リレー本体60の内部に、図示しない接点部およびコイル部を有している。なお、左側のリレー16と右側のリレー16は同様の構造であり、前後反転した状態で装着される。以下の説明では、左側のリレー16について説明して、右側のリレー16の説明を省略する。また、リレー本体60の前端面には、一対の貫通孔が左右方向で相互に離隔して形成されており、これら貫通孔により前述のリレー16の接続部30a,30bが構成されている。
リレー16は、機械式のリレーであって、図示しない制御回路によりON/OFF制御がなされている。リレー16は、図2にも示すように、全体として略中空の直方体状とされたリレー本体60を備えており、当該リレー本体60の内部に、図示しない接点部およびコイル部を有している。なお、左側のリレー16と右側のリレー16は同様の構造であり、前後反転した状態で装着される。以下の説明では、左側のリレー16について説明して、右側のリレー16の説明を省略する。また、リレー本体60の前端面には、一対の貫通孔が左右方向で相互に離隔して形成されており、これら貫通孔により前述のリレー16の接続部30a,30bが構成されている。
そして、通電時においてリレー16の接点部を介して、接続部30a,30b間に電流が流れることで、接点部において発熱するようになっている。なお、接続部30a,30bの間には、前方に突出する仕切板部62が、リレー本体60の上下方向略全長に亘って形成されている。これにより、+側の接続部30aに接続されるバスバー32と-側の接続部30bに接続されるバスバー34との接触に伴う電気的な短絡が発生しないようになっている。
リレー本体60には、左右方向両側に突出する複数(本実施形態では3個)の脚部63が設けられていると共に、当該脚部63にはボルト挿通孔が形成されている。ベース部材28における収容凹部48の底面に設けられた貫通孔54と脚部63のボルト挿通孔とを位置合わせした状態で固定ボルト64を挿通して締結することで、リレー16がベース部材28に取り付けられている。
<バスバー32,34>
一対のバスバー32,34は、それぞれが導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。各バスバー32,34は、図2にも示されるように、略L字形状に屈曲して形成されている。屈曲部分に対する一方の側がリレー16の接続部30a,30bに接続される略矩形板形状の第一接続部32a,34aとされている。第一接続部32a,34aは、板厚方向である前後方向に貫通するボルト挿通孔66を有している。バスバー32,34は、リレー16の接続部30a,30bに対してボルト締結されることにより、リレー16の接続部30a,30bに対して電気的および熱的に接続されるようになっている。
一対のバスバー32,34は、それぞれが導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。各バスバー32,34は、図2にも示されるように、略L字形状に屈曲して形成されている。屈曲部分に対する一方の側がリレー16の接続部30a,30bに接続される略矩形板形状の第一接続部32a,34aとされている。第一接続部32a,34aは、板厚方向である前後方向に貫通するボルト挿通孔66を有している。バスバー32,34は、リレー16の接続部30a,30bに対してボルト締結されることにより、リレー16の接続部30a,30bに対して電気的および熱的に接続されるようになっている。
また、各バスバー32,34において屈曲部分に対する他方の側は前方に向かって延び出しており、当該延出部分が略矩形板形状の第二接続部32b,34bとされている。第二接続部32b,34bは、板厚方向である上下方向に貫通するボルト挿通孔68を有している。これらのボルト挿通孔68は、ベース部材28の載置面50,50にバスバー32,34を載置した際に、載置面50に設けられた貫通孔54と位置合わせされるようになっている。そして、バスバー32,34の第二接続部32b,34bに図示しない電線末端の端子部等を重ね合わせて、ボルト挿通孔68および貫通孔54にボルトを挿通して締結することで電線とバスバー32,34とが電気的に接続されるようになっている。
<冷却部品70>
バスバー32,34には、図5,6に示される如き冷却部品70が熱的に接触している。実施形態1の冷却部品70は、全体として前後方向に延びる円筒形状とされており、環状筒本体72と、当該環状筒本体72の内周側を前後方向に貫通する内孔74とを備えている。
バスバー32,34には、図5,6に示される如き冷却部品70が熱的に接触している。実施形態1の冷却部品70は、全体として前後方向に延びる円筒形状とされており、環状筒本体72と、当該環状筒本体72の内周側を前後方向に貫通する内孔74とを備えている。
実施形態1では、一対の冷却部品70,70が設けられている。即ち、リレー16における+側の接続部30aに対して第一の冷却部品70aが取り付けられていると共に、リレー16における-側の接続部30bに対して第二の冷却部品70bが取り付けられている。実施形態1では、第一の冷却部品70aと第二の冷却部品70bとが同様の構造とされていることから、以下の説明では、第一の冷却部品70aについて説明して、第二の冷却部品70bについての説明を省略する。
第一の冷却部品70aの環状筒本体72は、前後方向(環状筒本体72の中心軸方向)で相互に連結される第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とを含んで構成されている。実施形態1では、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とが前後方向で端面同士を重ね合わせるように組み付けられている。即ち、第一パーツ76の前端面が第二パーツ78への組付面79aとされていると共に、第二パーツ78の後端面が第一パーツ76への組付面79bとされている。それ故、環状筒本体72および内孔74が前後方向で分離可能とされており、第一パーツ76が、環状筒本体72および内孔74の後方部分を構成する第一の環状筒本体72aおよび第一の内孔74aを備えている。また、第二パーツ78が、環状筒本体72および内孔74の前方部分を構成する第二の環状筒本体72bおよび第二の内孔74bを備えている。
第一パーツ76は、全体として略有底筒形状とされており、略円板形状とされた第一の底壁部80aから前方に向かって第一の環状筒本体72aが突出して設けられている。実施形態1では、第一の環状筒本体72aに、上下方向両側に突出する突出部82,82が一体的に形成されている。この突出部82は、半円形乃至は円形断面を有して、第一パーツ76の前後方向略全長に亘って延びている。そして、第一パーツ76において突出部82の外周面と突出部82の非形成部分の外周面とが滑らかな湾曲面で連続している。なお、突出部82には、前方に開口するボルト穴83が設けられている。また、第一の底壁部80aの形状は、第一の環状筒本体72aの形状に略対応して、左右方向の幅寸法に比して上下方向の幅寸法が大きくされており、上下方向両側に突出部分84,84が形成されている。
さらに、第一パーツ76の径方向中間部分には、前端面(組付面79a)に開口する凹状の部分を有している。実施形態1では、この凹状の部分が、周方向に延びる円弧状凹部85とされている。特に、実施形態1では、略1周の周方向寸法をもって延びている。即ち、実施形態1では、第一の環状筒本体72aの内周側に径方向で離隔して第一の内側筒部86aが設けられている。この第一の内側筒部86aの内周側に第一の内孔74aが形成されていると共に、第一の環状筒本体72aと第一の内側筒部86aとの径方向間に円弧状凹部85が形成されている。
この第一パーツ76は、第一の環状筒本体72aと第一の内側筒部86aとからなる二重筒構造とされていると共に、周上の一部において第一の環状筒本体72aと第一の内側筒部86aとが相互に連結されている。これにより、後述する冷媒が第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b内を流通する際に、冷媒が第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b内で回り込むように流動することができる。それ故、後述する冷媒流路95の長さを十分に確保することができて、冷却効果が安定して発揮され得る。
第二パーツ78は、全体として略有底筒形状とされており、略円板形状とされた第二の底壁部80bから後方に向かって第二の環状筒本体72bが突出して設けられている。第二の環状筒本体72bには、上下方向両側に突出する突出部88が一体的に形成されている。この突出部88は、第一パーツ76における突出部82と同様の外形状とされている。突出部88は、第二パーツ78の前後方向全長までは延びておらず、第二パーツ78の後方端部に設けられている。そして、この突出部88を前後方向で貫通してボルト孔90が形成されている。
第二パーツ78の径方向中間部分には、後端面(組付面79b)に開口する凹状の部分を有している。実施形態1では、この凹状の部分が、周方向に延びる円弧状凹部92とされている。特に、本実施形態1では、略1周の周方向寸法をもって延びている。即ち、実施形態1では、第二の環状筒本体72bの内周側に径方向で離隔して第二の内側筒部86bが設けられている。この第二の内側筒部86bの内周側に第二の内孔74bが形成されていると共に、第二の環状筒本体72bと第二の内側筒部86bとの径方向間に円弧状凹部92が形成されている。
この第二パーツ78は、第二の環状筒本体72bと第二の内側筒部86bとからなる二重筒構造とされていると共に、周上の一部において第二の環状筒本体72bと第二の内側筒部86bとが相互に連結されている。これにより、後述する冷媒が第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b内を流通する際に、冷媒が第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b内で回り込むように流動することができる。それ故、後述する冷媒流路95の長さを十分に確保することができて、冷却効果が安定して発揮され得る。
そして、第一パーツ76の組付面79aと第二パーツ78の組付面79bとを重ね合わせることで、第一パーツ76の突出部82と第二パーツ78の突出部88も重ね合わされて、ボルト穴83とボルト孔90とが相互に連通する。これらボルト穴83およびボルト孔90に前方から固定ボルト94が挿通されて締結されることで、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とが前後方向で連結される。これにより、第一の環状筒本体72aと第二の環状筒本体72bとが連続して環状筒本体72が構成されると共に、第一の内孔74aと第二の内孔74bとが連通して内孔74が構成される。また、第一パーツ76における円弧状凹部85と第二パーツ78における円弧状凹部92とが前後方向で相互に連通するようになっている。そして、これら両円弧状凹部85,92により区画された領域が、冷媒が流通される冷媒流路95とされている。なお、冷媒流路95を流通する冷媒は、ラジエター液等の車両内で利用可能な冷媒であれば、何れも採用可能である。
すなわち、実施形態1では、第一の環状筒本体72aおよび第一の内側筒部86aの後端面と第二の環状筒本体72bおよび第二の内側筒部86bの前端面とが重ね合わされるようになっている。これらの重ね合わせ面間には、シール部材としてのOリング96が設けられている。要するに、第一および第二の環状筒本体72a,72b間には、外周側Oリング96aが設けられていると共に、第一の内側筒部86aと第二の内側筒部86bとの間には、内周側Oリング96bが設けられている。第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とが組み付けられる際に外内のOリング96a,96bが前後方向で圧縮されることにより、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78との組付面79a,79bが相互に密接して、冷媒が漏出しないようにされている。
以上の如き構造とされた第一の冷却部品70aと第二の冷却部品70bとが、リレー16の左右両側で1つずつ設けられている。そして、左右方向で隣り合う第一の冷却部品70aと第二の冷却部品70bが、チューブ98で連通されている。実施形態1では、左右方向で隣り合う両第一の環状筒本体72a,72aに厚さ方向で貫通する貫通孔100が形成されている。貫通孔100の開口縁部にチューブ98が接着や溶着等により固着されることで、円弧状凹部85,85同士(即ち、冷媒流路95,95同士)がチューブ98を介して相互に連通されている。
また、左右方向で隣り合う両第二の環状筒本体72b,72bに厚さ方向で貫通する貫通孔102が形成されている。貫通孔102の開口縁部に外方に延びるチューブ104が接着や溶着等により固着されることで、両円弧状凹部92,92(即ち、両冷媒流路95,95)がそれぞれチューブ104を介して外部空間に連通されている。
これにより、一方の貫通孔102が冷媒流路95へ冷媒の流入口とされると共に、他方の貫通孔102が冷媒流路95からの流出口とされている。
そして、一方の貫通孔102(流入口)に接続されるチューブ104が外部から冷媒流路95へ冷媒を供給する冷媒供給路とされる。同様に、他方の貫通孔102(流出口)に接続されるチューブ104が冷媒流路95から外部へ冷媒を排出する冷媒排出路とされる。また、第一パーツ76において第二パーツ78への組付面79aに開口して、冷媒流路95の一部を構成する第一流通路形成部が円弧状凹部85により構成されている。同様に、第二パーツ78において第一パーツ76への組付面79bに開口して、冷媒流路95の一部を構成する第二流通路形成部が円弧状凹部92により構成されている。
なお、上記の如き冷却部品(第一パーツ76および第二パーツ78)は、例えば硬質の合成樹脂により好適に形成され得る。また、これら第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78のうち、通電部材であるバスバー32,34に接触する方(実施形態1では第一パーツ76)が熱伝導性が高い材料であることが好ましい。
<回路構成体10の組み付け工程>
続いて、回路構成体10の組み付け工程の一例について説明する。回路構成体10の組み付け工程は、以下の記載に限定されない。
続いて、回路構成体10の組み付け工程の一例について説明する。回路構成体10の組み付け工程は、以下の記載に限定されない。
まず、ベース部材28を構成するロアケース24とアッパケース26を準備する。次に、ロアケース24又はアッパケース26に対してリレー16とプリチャージ回路22を接続するバスバーやプリチャージ回路22内を接続するバスバーを収容配置する。続いて、ロアケース24に対してアッパケース26を上方から重ね合わせて、ロア側係合部36とアッパ側係合部46とを係合させる。これにより、ロアケース24とアッパケース26が組み付けられて、ベース部材28が形成される。
そして、アッパケース26の収容凹部48に対してリレー16を配置して、固定ボルト64によりベース部材28に対してリレー16を固定する。続いて、2つのリレー16に対してそれぞれバスバー32,34を配置する。なお、以下の説明では、左方のリレー16について説明する。
すなわち、バスバー32,34の第一接続部32a,34aがリレー16の接続部30a,30bに対して前方側から重ね合わされる。また、バスバー32,34の第二接続部32b,34bが収容凹部48の底面に対して前方側に位置する載置面50に上方から重ね合わされる。
次に、予め組み立てておいた冷却部品70(第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b)をリレー16の前端面に対してバスバー32,34の第一接続部32a,34aを介して重ね合わせる。そして、リレー16の接続部30a,30bと第一接続部32a,34aのボルト挿通孔66,66と第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bの内孔74(第一および第二の内孔74a,74b)とをそれぞれ位置合わせする。これら接続部30a,30b、ボルト挿通孔66,66、内孔74a,74bに締結部品としての固定ボルト108,108を挿通して締結する。これにより、リレー16の接続部30a,30bに対して第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bがバスバー32,34を介してボルト固定される。換言すれば、リレー16に対してバスバー32,34を固定する固定ボルト108,108を利用して、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bが共締めされている。即ち、冷却部品70において締結部品である固定ボルト108が挿通される締結部品挿通孔が、環状筒本体72の内孔74により構成されている。
これにより、バスバー32,34に対して第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bにおける第一および第二の底壁部80a,80bが直接的に当接することで、第一および第二の底壁部80a,80bが熱的に接触している。特に、第一および第二の底壁部80a,80bには、上下方向両側に突出する突出部分84,84が設けられており、バスバー32,34との接触面積が大きく確保されている。この結果、バスバー32,34から第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bへの電熱効率の向上が図られている。尤も、バスバー32,34と第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bとは熱的に接触していればよく、直接的に当接している必要はない。即ち、バスバーと冷却部品との間に伝熱性を有する部材が設けられてもよく、バスバーと冷却部品とは伝熱性を有する部材を介して間接的に当接していてもよい。
なお、固定ボルト108の締付けに際して、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bにおける突出部82,88や上下方向の突出部分84が、リレー16の接続部30a,30b間に設けられた仕切板部62に当接可能とされている。これにより、固定ボルト108,108と共に第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bが回転することが防止され得る。したがって、実施形態1では、冷却部品70において他部材への当接により冷却部品70の回転を阻止する回転阻止突部が、突出部82と突出部88と突出部分84との少なくとも一つにより構成されている。
上記の如き工程をもって回路構成体10が組み付けられている。なお、バスバー32,34の第二接続部32b,34bに対して電線末端の端子部が重ね合わされてボルト固定されることで、バスバー32,34を介してリレー16に電力が供給され得る。
以上の如き構造とされた実施形態1の回路構成体10では、リレー16に電力が供給されることでリレー16内部の接点部が発熱して、この熱は、リレー16に接続されるバスバー32,34に及ぼされる。ここにおいて、バスバー32,34には冷却部品70(第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b)が熱的に接触しており、当該冷却部品70の内部に冷媒が流通される冷媒流路95が構成されている。これにより、冷媒流路95内を冷媒が流通することで、バスバー32,34が効率的に冷却されて、リレー16の発熱が解消される。この結果、別途放熱用の経路等を設けることがなく、発熱部品の放熱が材料費や加工費の上昇を伴うことなく達成され得る。
また、実施形態1の回路構成体10では、バスバー32,34と共に第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bがボルト固定によりリレー16に共締めされている。それ故、発熱部品と通電部材との固定手段と、通電部材と冷却部品との固定手段を別個に設けることがなく、回路構成体10の構造が簡略化され得る。特に、放熱部位が、リレー16に直接的に固定される固定ボルト108,108とされることで、リレー16からの放熱が一層効率よく達成され得る。
さらに、実施形態1の回路構成体10では、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bにおける冷媒の流入口(貫通孔102)や流出口(貫通孔102)に対してチューブ104が接続されており、冷媒供給路および冷媒排出路を構成している。これにより、冷媒流路95への外部の冷媒源からの冷媒の供給や冷媒流路95からの外部の冷媒源への冷媒の排出がより確実に達成され得る。
特に、実施形態1の回路構成体10では、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bが締結部品挿通孔として利用可能な内孔74を有する環状筒本体72を有し、環状筒本体72が相互に別体とされた第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とを組み付けることで構成されている。そして、第一パーツ76の内部に設けられた第一流通路形成部(円弧状凹部85)と第二パーツ78の内部に設けられた第二流通路形成部(円弧状凹部92)とを含んで冷媒流路95が形成されている。これにより、締結部材により締結可能で内部に冷媒流路95を有する第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bを簡単な構造の成形型で形成することが可能となる。また、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78との組付面79a,79b間にシール部材としてのOリング96(外周側Oリング96aおよび内周側Oリング96b)が設けられていることから、組付面79a,79b間からの冷媒の漏れも防止され得る。加えて、環状筒本体72の内孔74を締結部品である固定ボルト108が挿通される締結部品挿通孔として利用していることから、締結部品により締結が可能となる冷却部品70をコンパクトに提供することができる。
さらに、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78においては、バスバー32,34に接触する第一パーツ76の方が熱伝導性が高い材料で形成されることが好適である。これにより、リレー16の発熱がバスバー32,34を介してより効率よく冷却部品70を構成する第一パーツ76に及ぼされて、冷却部品70による冷却がより確実に達成され得る。
更にまた、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bは、上下方向両側に突出する突出部82,88および突出部分84を備えており、左右方向寸法に比して上下方向寸法が大きくされている。これにより、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bに対して固定ボルト108,108を挿通して締結する際に、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bの上下方向両側部分が仕切板部62に当接することで、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bが、固定ボルト108,108と共に過度に回転することが防止され得る。
<実施形態2>
次に、本開示の実施形態2について、図7を参照しつつ説明する。図7に示される回路構成体120は、全体として、実施形態1の回路構成体10と同様の構造ではあるが、冷却部品70(第一の冷却部品70aおよび第二の冷却部品70b)を取り付ける位置が異なっている。以下の説明では、実施形態1の回路構成体10との相違点について説明して、同様の構造とされる部分の説明を省略する。また、以下の説明において、実施形態1と実質的に同一の部材又は部位には、図中に、実施形態1と同一の符号を付すことにより詳細な説明を省略する。
次に、本開示の実施形態2について、図7を参照しつつ説明する。図7に示される回路構成体120は、全体として、実施形態1の回路構成体10と同様の構造ではあるが、冷却部品70(第一の冷却部品70aおよび第二の冷却部品70b)を取り付ける位置が異なっている。以下の説明では、実施形態1の回路構成体10との相違点について説明して、同様の構造とされる部分の説明を省略する。また、以下の説明において、実施形態1と実質的に同一の部材又は部位には、図中に、実施形態1と同一の符号を付すことにより詳細な説明を省略する。
実施形態2では、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bが、バスバー32,34の第二接続部32b,34bに取り付けられている。即ち、ベース部材28の載置面50に設けられた貫通孔54と、第二接続部32b,34bに設けられたボルト挿通孔68と、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bにおける第一および第二の内孔74a,74bとがそれぞれ位置合わせされている。なお、第二接続部32b,34bと第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bとの間には、図示しない電線端末に設けられた端子部がボルト挿通孔と位置合わせされた状態で介在される。そして、これら貫通孔54とボルト挿通孔68と第一および第二の内孔74a,74bに固定ボルト108,108が挿通されて締結されている。
なお、バスバー32,34の第一接続部32a,34aには、図示しない電線末端の端子部が重ね合わされて、第一接続部32a,34aのボルト挿通孔66,66およびリレー16の接続部30a,30bと位置合わせされている。そして、これらにボルト122,122が挿通されて締結されている。
以上の如き構造とされた実施形態2における回路構成体120においても、リレー16の発熱が、バスバー32,34に伝達されると共に、当該バスバー32,34に対して熱的に接触する冷却部品70により放熱され得る。特に、実施形態2では、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bがバスバー32,34と共にベース部材28に対して共締めされており、実施形態1と同様に効率的な組付けが実現され得る。
なお、実施形態2では、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70b間に、ベース部材28に設けられた仕切壁部52が位置している。これにより、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bが回転した際に、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bにおいて前後方向両側に突出する突出部82,88および突出部分84が仕切壁部52に当接して、それ以上の回転が阻止されるようになっている。したがって、実施形態2においても、第一および第二の冷却部品70a,70bの回転を阻止する回転阻止突部が、突出部82と突出部88と突出部分84の少なくとも一つによって構成され得る。
<実施形態3>
次に、本開示の実施形態3について、図8を参照しつつ説明する。図8に示される回路構成体130は、全体として、実施形態1の回路構成体10と同様の構造ではあるが、実施形態1の回路構成体10とは、冷却部品132の構造が異なっている。以下の説明では、実施形態1の回路構成体10との相違点について説明して、同様な構造とされた部分の説明を省略する。
次に、本開示の実施形態3について、図8を参照しつつ説明する。図8に示される回路構成体130は、全体として、実施形態1の回路構成体10と同様の構造ではあるが、実施形態1の回路構成体10とは、冷却部品132の構造が異なっている。以下の説明では、実施形態1の回路構成体10との相違点について説明して、同様な構造とされた部分の説明を省略する。
すなわち、実施形態3の回路構成体130では、リレー16の接続部30a,30bに接続されるバスバー32,34の一方(バスバー32)に冷却部品132が熱的に接触している。このような構造とされた回路構成体130においてもリレー16の発熱に対する冷却効果は発揮され得る。実施形態3の冷却部品132も、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とから構成されて、第二パーツ78に2つの貫通孔102,102が設けられて、当該貫通孔102,102に対して冷媒供給路および冷媒排出路を構成するチューブ104,104が接続され得る。したがって、実施形態3の冷却部品132は、左右方向で隣り合う第一パーツ(76,76)を連結するチューブ(98)が設けられていない態様となっている。
なお、実施形態3の回路構成体130では、2つのリレー16が設けられており、それぞれに冷却部品132が設けられているが、冷却部品132は何れか一方のリレー16に設けられるだけでもよい。また、リレー16に接続される他方のバスバー34には、冷却部品は設けられなくてもよいし、従来公知の冷却部品を採用してもよい。
<実施形態4>
次に、本開示の実施形態4について、図9を参照しつつ説明する。図9に示される回路構成体140は、全体として、実施形態3の回路構成体130と同様の構造ではあるが、実施形態2の回路構成体120と同様に、冷却部品132が、バスバー32の第二接続部32bに対して熱的に接触している。
次に、本開示の実施形態4について、図9を参照しつつ説明する。図9に示される回路構成体140は、全体として、実施形態3の回路構成体130と同様の構造ではあるが、実施形態2の回路構成体120と同様に、冷却部品132が、バスバー32の第二接続部32bに対して熱的に接触している。
以上の如き構造とされた回路構成体140においても実施形態1と同様の効果が発揮され得る。
なお、図8に示される如きバスバーの第一接続部に冷却部品を熱的に接触させる態様と図9に示される如きバスバーの第二接続部に冷却部品を熱的に接触させる態様とは組み合わせて採用することが可能である。即ち、一方のバスバー32の第一接続部32aに冷却部品132を熱的に接触させると共に、他方のバスバー34の第二接続部34bに冷却部品132を熱的に接触させてもよい。その際、これら冷却部品132,132は、チューブ98により相互に連結されて1つの冷媒流路を構成してもよいし、相互に独立して、それぞれ別個の冷媒流路を構成してもよい。
<他の実施形態>
本明細書に記載された技術は上記記述および図面によって説明した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、例えば次のような実施形態も本明細書に記載された技術の技術的範囲に含まれる。
本明細書に記載された技術は上記記述および図面によって説明した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、例えば次のような実施形態も本明細書に記載された技術の技術的範囲に含まれる。
(1)前記実施形態1や実施形態2では、左右で隣り合う冷却部品として、同様の構造とされた冷却部品を採用していたが、相互に形状や大きさ等を異ならせてもよい。
(2)前記実施形態1や実施形態2では、隣り合う冷却部品70a,70bにおける第一パーツ76,76同士がチューブ98によって接続されると共に、第二パーツ78,78がそれぞれチューブ104を介して外部に接続されていた。このような態様に限定されず、第二パーツ同士がチューブによって接続されると共に、第一パーツがチューブを介して外部に接続されてもよいし、第一パーツと第二パーツとがチューブにより接続されてもよい。
(3)前記各実施形態では、第一パーツ76における円弧状凹部85と第二パーツ78における円弧状凹部92は、略等しい周方向長さを有して、且つ相互に対応する位置に設けられていた。このような態様に限定されず、例えば相互に周方向長さを異ならせたり、形成する位置を相互に周方向で異ならせてもよく、第一パーツと第二パーツの組付時に両パーツに設けられる周方向凹部が相互に連通するようになっていればよい。尤も、周方向凹部は第一パーツと第二パーツの両方に設けられる必要はなく、一方のパーツに設けられた周方向凹部の開口部を他方のパーツで覆蓋するようになっていてもよい。
(4)前記各実施形態では、冷却部品70,132が全体として円筒形状の本体部を有していたが、例えば角筒形状の本体部を有していてもよい。このような場合には、本体部の角部により冷却部品の回転を阻止する回転阻止突部が構成され得る。
(5)前記各実施形態では、第一パーツ76と第二パーツ78とが固定ボルト94により固定されていたが、両パーツの固定方法は限定されるものではなく、例えば接着や溶着、凹凸による係止等であってもよい。
10,10a,10b 回路構成体
12 電源
14 負荷
16 リレー(発熱部品)
18 プリチャージ抵抗
20 プリチャージリレー
22 プリチャージ回路
24 ロアケース
26 アッパケース
28 ベース部材
30a,30b 接続部
32,34 バスバー
32a,34a 第一接続部
32b,34b 第二接続部
36 ロア側係合部
38 リレー固定部
40 ボルト挿通部
42 上壁
44 周壁
46 アッパ側係合部
48 収容凹部
50 載置面
52 仕切壁部
54 貫通孔
56 プリチャージ抵抗装着部
58 プリチャージリレー装着部
60 リレー本体
62 仕切板部
63 脚部
64 固定ボルト
66,68 ボルト挿通孔
70 冷却部品
70a 第一の冷却部品
70b 第二の冷却部品
72 環状筒本体
72a 第一の環状筒本体
72b 第二の環状筒本体
74 内孔(締結部品挿通孔)
74a 第一の内孔
74b 第二の内孔
76 第一パーツ
78 第二パーツ
79a (第一パーツにおける第二パーツへの)組付面
79b (第二パーツにおける第一パーツへの)組付面
80a 第一の底壁部
80b 第二の底壁部
82 突出部(回転阻止突部)
83 ボルト穴
84 突出部分(回転阻止突部)
85 円弧状凹部(第一流通路形成部)
86a 第一の内側筒部
86b 第二の内側筒部
88 突出部(回転阻止突部)
90 ボルト孔
92 円弧状凹部(第二流通路形成部)
94 固定ボルト
95 冷媒流路
96 Oリング(シール部材)
96a 外周側Oリング
96b 内周側Oリング
98 チューブ
100 貫通孔
102 貫通孔(流入口、流出口)
104 チューブ(冷媒供給路、冷媒排出路)
108 固定ボルト
120 回路構成体
122 ボルト
130 回路構成体
132 冷却部品
140 回路構成体
12 電源
14 負荷
16 リレー(発熱部品)
18 プリチャージ抵抗
20 プリチャージリレー
22 プリチャージ回路
24 ロアケース
26 アッパケース
28 ベース部材
30a,30b 接続部
32,34 バスバー
32a,34a 第一接続部
32b,34b 第二接続部
36 ロア側係合部
38 リレー固定部
40 ボルト挿通部
42 上壁
44 周壁
46 アッパ側係合部
48 収容凹部
50 載置面
52 仕切壁部
54 貫通孔
56 プリチャージ抵抗装着部
58 プリチャージリレー装着部
60 リレー本体
62 仕切板部
63 脚部
64 固定ボルト
66,68 ボルト挿通孔
70 冷却部品
70a 第一の冷却部品
70b 第二の冷却部品
72 環状筒本体
72a 第一の環状筒本体
72b 第二の環状筒本体
74 内孔(締結部品挿通孔)
74a 第一の内孔
74b 第二の内孔
76 第一パーツ
78 第二パーツ
79a (第一パーツにおける第二パーツへの)組付面
79b (第二パーツにおける第一パーツへの)組付面
80a 第一の底壁部
80b 第二の底壁部
82 突出部(回転阻止突部)
83 ボルト穴
84 突出部分(回転阻止突部)
85 円弧状凹部(第一流通路形成部)
86a 第一の内側筒部
86b 第二の内側筒部
88 突出部(回転阻止突部)
90 ボルト孔
92 円弧状凹部(第二流通路形成部)
94 固定ボルト
95 冷媒流路
96 Oリング(シール部材)
96a 外周側Oリング
96b 内周側Oリング
98 チューブ
100 貫通孔
102 貫通孔(流入口、流出口)
104 チューブ(冷媒供給路、冷媒排出路)
108 固定ボルト
120 回路構成体
122 ボルト
130 回路構成体
132 冷却部品
140 回路構成体
Claims (6)
- 通電により発熱する発熱部品と、
前記発熱部品の接続部に接続される通電部材と、
内部に冷媒が流通されて前記通電部材に熱的に接触される冷却部品を含む回路構成体。 - 前記発熱部品の前記接続部に対して、前記冷却部品が前記通電部材を介して締結されている請求項1に記載の回路構成体。
- 前記冷却部品が、前記冷媒の流入口と流出口を備えた冷媒流路を有しており、前記流入口と前記流出口に外部の冷媒供給路と冷媒排出路が接続可能とされている請求項1または請求項2に記載の回路構成体。
- 前記冷却部品が、環状筒本体を有し、該環状筒本体の内孔が締結部品挿通孔とされており、
前記環状筒本体が、軸方向で相互に組み付けられる環状の第一パーツと環状の第二パーツを含み、前記第一パーツが前記第二パーツへの組付面に開口する凹状の第一流通路形成部を有し、前記第二パーツが前記第一パーツへの組付面に開口する凹状の第二流通路形成部を有し、
前記第一パーツと前記第二パーツが、シール部材を介して各前記組付面を密接させた状態で、相互に組み付けられて固定されることにより、前記環状筒本体の内部に前記第一流通路形成部と前記第二流通路形成部により区画された前記冷媒流路が構成されている請求項3に記載の回路構成体。 - 前記第一パーツと前記第二パーツのうち、前記通電部材に接触する一方のパーツが他方のパーツよりも熱伝導性が高い材料で形成されている請求項4に記載の回路構成体。
- 前記冷却部品が、前記通電部材に対してボルトを用いて接触状態に固定されており、前記冷却部品が他部材に当接して前記冷却部品の回転を阻止する回転阻止突部を有している請求項1から請求項5のいずれか1項に記載の回路構成体。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202080082065.9A CN114762204B (zh) | 2019-12-04 | 2020-11-26 | 电路结构体 |
| US17/779,074 US20220400580A1 (en) | 2019-12-04 | 2020-11-26 | Circuit assembly |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019219846A JP7352830B2 (ja) | 2019-12-04 | 2019-12-04 | 回路構成体 |
| JP2019-219846 | 2019-12-04 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021111984A1 true WO2021111984A1 (ja) | 2021-06-10 |
Family
ID=76220458
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/044063 WO2021111984A1 (ja) | 2019-12-04 | 2020-11-26 | 回路構成体 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20220400580A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7352830B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN114762204B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2021111984A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20240206136A1 (en) * | 2022-12-16 | 2024-06-20 | Bae Systems Controls Inc. | Cooling systems and methods for cooling contactors |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000058746A (ja) * | 1998-08-10 | 2000-02-25 | Toyota Motor Corp | モジュール内冷却装置 |
| JP2015084609A (ja) * | 2013-10-25 | 2015-04-30 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 接続導体の冷却装置及びそれを用いた電力変換装置 |
| WO2018021084A1 (ja) * | 2016-07-27 | 2018-02-01 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 冷却機能付き導電部材 |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63157449A (ja) * | 1986-12-22 | 1988-06-30 | Nec Corp | 集積回路の冷却構造 |
| US4965658A (en) * | 1988-12-29 | 1990-10-23 | York International Corporation | System for mounting and cooling power semiconductor devices |
| US5159529A (en) * | 1991-05-15 | 1992-10-27 | International Business Machines Corporation | Composite liquid cooled plate for electronic equipment |
| US5168425A (en) * | 1991-10-16 | 1992-12-01 | General Electric Company | Mounting arrangements for high voltage/high power semiconductors |
| US20020117291A1 (en) * | 2000-05-25 | 2002-08-29 | Kioan Cheon | Computer having cooling apparatus and heat exchanging device of the cooling apparatus |
| US7331378B2 (en) * | 2006-01-17 | 2008-02-19 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Microchannel heat sink |
| US9453691B2 (en) * | 2007-08-09 | 2016-09-27 | Coolit Systems, Inc. | Fluid heat exchange systems |
| KR101653453B1 (ko) * | 2014-11-03 | 2016-09-09 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | 전력반도체 양면 냉각방식 냉각장치 |
| JP6521171B2 (ja) * | 2016-03-10 | 2019-05-29 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 回路構成体 |
| JP6693480B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-22 | 2020-05-13 | 株式会社デンソー | 端子冷却装置 |
| KR102411445B1 (ko) * | 2017-07-20 | 2022-06-22 | 주식회사 아모그린텍 | 파워 릴레이 어셈블리 |
| JP7139603B2 (ja) * | 2017-12-28 | 2022-09-21 | 株式会社デンソー | 電力変換装置 |
| WO2019189450A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-03 | 日本電産株式会社 | 電力変換装置 |
| US10900412B2 (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2021-01-26 | Borg Warner Inc. | Electronics assembly having a heat sink and an electrical insulator directly bonded to the heat sink |
| US10920782B2 (en) * | 2019-01-30 | 2021-02-16 | Asia Vital Components (China) Co., Ltd. | Low-profile, high-power pump for electronics fluid cooling system |
| JP6750809B1 (ja) * | 2019-04-22 | 2020-09-02 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 冷却器 |
-
2019
- 2019-12-04 JP JP2019219846A patent/JP7352830B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-11-26 WO PCT/JP2020/044063 patent/WO2021111984A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2020-11-26 CN CN202080082065.9A patent/CN114762204B/zh active Active
- 2020-11-26 US US17/779,074 patent/US20220400580A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000058746A (ja) * | 1998-08-10 | 2000-02-25 | Toyota Motor Corp | モジュール内冷却装置 |
| JP2015084609A (ja) * | 2013-10-25 | 2015-04-30 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 接続導体の冷却装置及びそれを用いた電力変換装置 |
| WO2018021084A1 (ja) * | 2016-07-27 | 2018-02-01 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 冷却機能付き導電部材 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20220400580A1 (en) | 2022-12-15 |
| JP2021089984A (ja) | 2021-06-10 |
| CN114762204A (zh) | 2022-07-15 |
| JP7352830B2 (ja) | 2023-09-29 |
| CN114762204B (zh) | 2024-05-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2021090761A1 (ja) | 回路構成体 | |
| KR102530660B1 (ko) | 컨버터 | |
| KR101338432B1 (ko) | 자동차용 인버터 | |
| WO2014162939A1 (ja) | 温調装置 | |
| US20160276895A1 (en) | Mechanically and electrically integrated driving apparatus and manufacturing method therefor | |
| JP2021019499A (ja) | 車両用の液冷式充電システム | |
| JP7073299B2 (ja) | 車両用冷却システム | |
| JP2007008403A (ja) | 車両用電装ユニットの冷却装置 | |
| WO2021111984A1 (ja) | 回路構成体 | |
| JP5999631B2 (ja) | 加熱装置 | |
| KR20150105045A (ko) | 가열 및 냉각기능을 갖는 히트파이프 어셈블리, 상기 히트파이프 어셈블리를 이용한 친환경 자동차용 배터리 모듈, 상기 히트파이프 어셈블리의 제조방법, 상기 배터리 모듈의 제조방법, 상기 배터리 모듈의 운용방법 | |
| WO2021153373A1 (ja) | 回路構成体 | |
| JP6459904B2 (ja) | 電力変換装置 | |
| KR100462719B1 (ko) | 자동차용 히터코어의 보조발열장치 | |
| WO2024004727A1 (ja) | 回路構成体 | |
| WO2021153206A1 (ja) | 回路構成体 | |
| WO2014162780A1 (ja) | 冷却構造体 | |
| JP6722081B2 (ja) | パワーコントロールユニットの固定冷却装置 | |
| JP2012131331A (ja) | 車両用加熱装置 | |
| KR200349121Y1 (ko) | 냉각수 가열 방식의 히터장치 | |
| KR20160089113A (ko) | 자동차용 인덕션 히터 | |
| WO2024106330A1 (ja) | 冷却システム | |
| JP6686215B2 (ja) | 流体加熱装置 | |
| JP2024046107A (ja) | 電池ケース | |
| KR20230046394A (ko) | 차량용 배터리 방열유닛 및 이를 포함한 차량용 배터리 케이스 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20897249 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20897249 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |