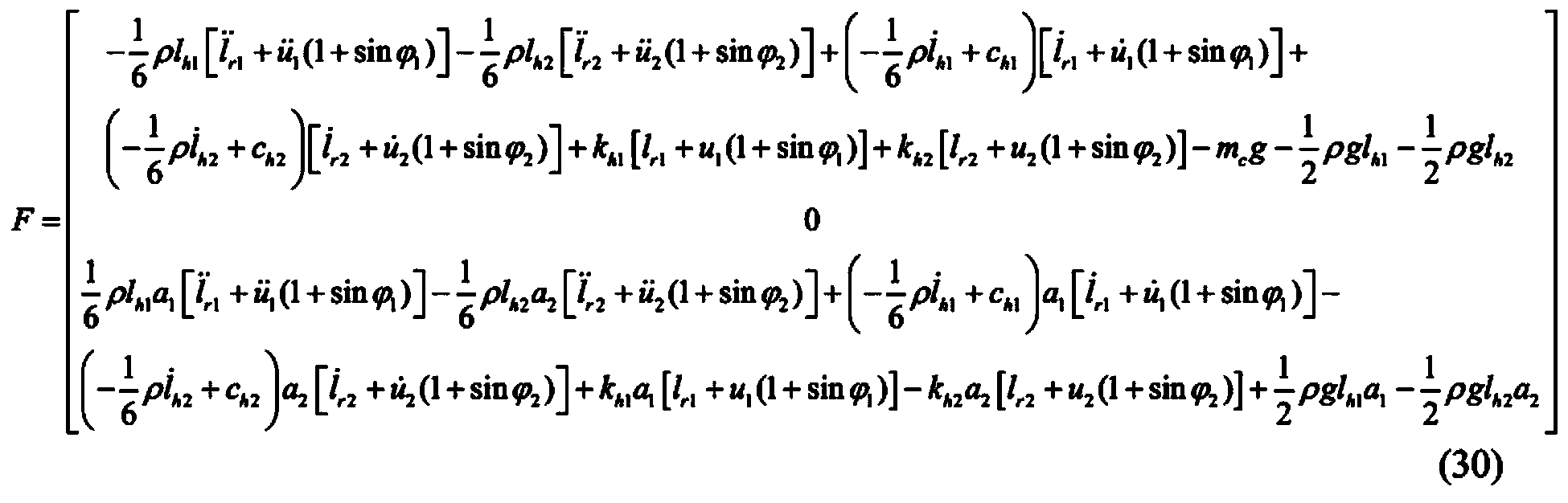WO2020206931A1 - 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 - Google Patents
一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020206931A1 WO2020206931A1 PCT/CN2019/105589 CN2019105589W WO2020206931A1 WO 2020206931 A1 WO2020206931 A1 WO 2020206931A1 CN 2019105589 W CN2019105589 W CN 2019105589W WO 2020206931 A1 WO2020206931 A1 WO 2020206931A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- double
- lifting
- subsystem
- vertical shaft
- ultra
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B7/00—Other common features of elevators
- B66B7/06—Arrangements of ropes or cables
- B66B7/10—Arrangements of ropes or cables for equalising rope or cable tension
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B1/00—Control systems of elevators in general
- B66B1/24—Control systems with regulation, i.e. with retroactive action, for influencing travelling speed, acceleration, or deceleration
- B66B1/28—Control systems with regulation, i.e. with retroactive action, for influencing travelling speed, acceleration, or deceleration electrical
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B19/00—Mining-hoist operation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66D—CAPSTANS; WINCHES; TACKLES, e.g. PULLEY BLOCKS; HOISTS
- B66D1/00—Rope, cable, or chain winding mechanisms; Capstans
- B66D1/28—Other constructional details
- B66D1/40—Control devices
- B66D1/48—Control devices automatic
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B1/00—Installations or systems with accumulators; Supply reservoir or sump assemblies
- F15B1/02—Installations or systems with accumulators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B15/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another; Gearing associated therewith
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B19/00—Testing; Calibrating; Fault detection or monitoring; Simulation or modelling of fluid-pressure systems or apparatus not otherwise provided for
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B19/00—Testing; Calibrating; Fault detection or monitoring; Simulation or modelling of fluid-pressure systems or apparatus not otherwise provided for
- F15B19/007—Simulation or modelling
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05B—CONTROL OR REGULATING SYSTEMS IN GENERAL; FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS OF SUCH SYSTEMS; MONITORING OR TESTING ARRANGEMENTS FOR SUCH SYSTEMS OR ELEMENTS
- G05B13/00—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion
- G05B13/02—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric
- G05B13/04—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric involving the use of models or simulators
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05B—CONTROL OR REGULATING SYSTEMS IN GENERAL; FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS OF SUCH SYSTEMS; MONITORING OR TESTING ARRANGEMENTS FOR SUCH SYSTEMS OR ELEMENTS
- G05B13/00—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion
- G05B13/02—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric
- G05B13/04—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric involving the use of models or simulators
- G05B13/042—Adaptive control systems, i.e. systems automatically adjusting themselves to have a performance which is optimum according to some preassigned criterion electric involving the use of models or simulators in which a parameter or coefficient is automatically adjusted to optimise the performance
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/10—Geometric CAD
- G06F30/17—Mechanical parametric or variational design
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/20—Design optimisation, verification or simulation
- G06F30/23—Design optimisation, verification or simulation using finite element methods [FEM] or finite difference methods [FDM]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2111/00—Details relating to CAD techniques
- G06F2111/10—Numerical modelling
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2113/00—Details relating to the application field
- G06F2113/06—Wind turbines or wind farms
Definitions
- the invention relates to a vertical shaft hoisting system, in particular to a double-rope winding type ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting system lifting container posture control method, belonging to the technical field of mine hoisting.
- the ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting system is a vertical shaft hoisting system with a mining depth greater than 1500m. Due to its deep mining depth, the commonly used rigid lifting container canway is prone to deformation and canway in the shaft when the lifting container is running at high speed and heavy load. Damage phenomena such as beam damage, beam nest looseness and operation instability, so they cannot be used for ultra-deep vertical shaft lifting; but when flexible tank channels are used for lifting, due to the difference in the diameter of the reel, the difference in the installation of the two steel ropes, and the elastic mold Inconsistent quantities and other factors, the military will cause the end of the two wire ropes of the lifting system to move out of sync, which will cause the lifting container to tilt, which will cause the tension of the two wire ropes to be inconsistent.
- the present invention provides a dual-rope winding type ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting system lifting container pose control method.
- the design process is simple, the control performance is good, and it can quickly respond to the leveling lifting system and tracking errors. small.
- a method for controlling the posture of a double-rope-wound ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting system of the present invention includes the following steps:
- Step 1 Establish a mathematical model of the double-rope-wound super-deep vertical shaft hoisting subsystem
- Step 2 Establish a closed-loop mathematical model of the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem
- Step 3 Flatness characteristics of the nonlinear system
- Step 4 Design the flatness controller of double rope winding ultra-deep mine hoisting subsystem
- Step 5 Design the position closed-loop flatness controller of the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem.
- step 1 the mathematical model of the double-rope winding ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting subsystem described in step 1 is as follows:
- the length of the two vertical steel ropes 5 in the process of lifting or lowering the lifting container is as follows:
- l h10 and l h20 are the initial lengths of the two vertical steel ropes
- T, U, D are the kinetic energy, potential energy and Rayleigh dissipation function of the lifting system respectively, and Q is the non-potential generalized force of the lifting subsystem without damping;
- m 1 and m 2 are the masses of the left and right floating sky wheels, r 1 and r 2 are the radii of the left and right floating sky wheels, and I 1 and I 2 are the moments of inertia of the left and right floating sky wheels;
- the kinetic energy formula of the lifting container is as follows:
- m c is the mass of the lifting container, and I c is the moment of inertia of the lifting container;
- k c1 and k h1 are the stiffness of the left string and the left vertical section of the wire rope respectively, and k c2 and k h2 are the stiffness of the right string and the right vertical section of the wire rope respectively;
- the potential energy of the lifting container system includes the potential energy of the lifting container and the potential energy of the flexible tank.
- the formula is as follows:
- c c1 and c c2 are the damping coefficients of the left string and the left vertical wire rope respectively, and c c2 and c h2 are the damping coefficients of the right string and the right vertical wire rope respectively;
- the Ruili energy dissipation formula for the lifting container system is as follows:
- Equation (31) can be further simplified as:
- formula (32) can be further simplified as:
- the selected state variable is Therefore, the dynamic model of the lifting subsystem can be transformed into a state space form
- h 1 B/A
- h 2 C/A
- h 3 R/A
- f F 0 /A
- step 2 the mathematical model of the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem described in step 2 is as follows:
- the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem includes the proportional servo valve and the double-rod hydraulic cylinder in the floating crown wheel system. Assume that for the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem, the displacement reference signal x p and the speed of the hydraulic cylinder Acceleration And jerk Are all bounded;
- Ap is the effective area of the piston of the hydraulic cylinder
- C tl is the total leakage coefficient of the hydraulic cylinder
- x p is the displacement of the piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder
- V t is the total volume of the oil inlet and return chambers of the hydraulic cylinder
- ⁇ e is the effective volume modulus of hydraulic cylinder oil
- p 1 is the pressure flowing into the hydraulic cylinder
- p 2 is the pressure flowing out of the hydraulic cylinder
- Q 1 is the flow into the hydraulic cylinder
- Q 2 is the flow out of the hydraulic cylinder.
- FL is the force of the double-rod hydraulic cylinder acting on the floating sky wheel
- m is the total mass of the floating sky wheel
- B p is the viscous damping coefficient of the hydraulic cylinder.
- the dynamic model of the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem can be transformed into the state space form:
- x is the system state variable
- u is the system control input with the same dimension as the system output y
- system state variable x and the system control input u can be expressed as the system output and its finite order differential equation form
- Equation (37) is called flatness, and the output of this system is the flatness output.
- the specific design of the posture leveling and flatness controller of the double-rope winding ultra-deep mine hoisting subsystem in step 4 is as follows:
- y 1d represents the expected output of the system, that is, the reference signal.
- the dynamic equation of the expected state variable x 1d of the system is as follows:
- the system open loop input u hd is as follows:
- a h is the Hurwitz matrix, and the error z 1 approaches 0 in an exponential manner. Since the approach rate cannot be based on the open-loop control input alone, the control input with state feedback is defined as
- step 5 design of the closed-loop flatness controller of the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem position in step 5 is as follows:
- the flatness equation of the control input u L is
- control input with state feedback is defined as
- the present invention omits the derivation process of system state variables, thus greatly simplifies the design process of the controller, so that the controller can shorten the response time, and the container can be lifted quickly. Reach the leveling state; and in the system application process, because the state variable derivation will amplify the sensor measurement noise and the unmodeled characteristics of the system, the design of the flatness controller can reduce the tracking error, make the control process more accurate and ensure its good Control performance.
- Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the lifting system of the present invention.
- Figure 2 is a dynamic model diagram of a double rod hydraulic cylinder
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram of the control system of the present invention.
- Fig. 4 is a comparison diagram of the tracking signal of the raised container angle of the flatness controller in the specific embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 5 is a partial enlarged view of the tracking signal of the raised container angle of the flatness controller in the specific embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 6 is a comparison diagram of tracking signals of the hydraulic cylinder 1 of the flatness controller in a specific embodiment of the present invention.
- Figure 7 is a tracking error diagram of the flatness controller hydraulic cylinder 1 in a specific embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 8 is a comparison diagram of tracking signals of the hydraulic cylinder 2 of the flatness controller in a specific embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 9 is a tracking error diagram of the hydraulic cylinder 2 of the flatness controller in a specific embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 10 is a comparison diagram of the tracking signal of the lifting container angle of the anti-step controller in a specific embodiment
- Fig. 11 is a partial enlarged view of the tracking signal of the lifting container angle of the anti-step controller in a specific embodiment
- FIG. 12 is a comparison diagram of tracking signals of the hydraulic cylinder 1 of the reverse step controller in a specific embodiment
- FIG. 13 is a tracking error diagram of the hydraulic cylinder 1 of the reverse step controller in a specific embodiment
- FIG. 14 is a comparison diagram of tracking signals of the hydraulic cylinder 2 of the reverse step controller in a specific embodiment
- Figure 15 is a tracking error diagram of the hydraulic cylinder 2 of the backstep controller in a specific embodiment
- Double drum In the picture: 1. Double drum; 2. String rope; 3. Floating crown wheel; 4. Double rod hydraulic cylinder; 5. Vertical steel wire rope; 6. Lifting container.
- the leveling steps of the flatness controller to lift the container are as follows:
- h 1 B/A
- h 2 C/A
- h 3 R/A
- f F 0 /A
- a 1 A p /m
- a 2 B p /m
- a 3 1/m
- a 4 4 ⁇ e A p /V t
- a 5 4 ⁇ e C tl /V t
- a 6 4 ⁇ e /V t ;
- the flatness controller improves the leveling performance of the container as shown in Figures 4 to 9;
- the back-step controller lifts the container's posture and leveling control design as follows:
- the position closed-loop control process of the electro-hydraulic servo subsystem of the backstep controller is as follows:
- the anti-step controller improves the leveling performance of the container as shown in Figure 10 to Figure 15;
- the lifting container can reach the leveling state within a certain period of time, but the flatness controller has made the lifting container reach the leveling state at 70ms, and the anti-step controller It takes 450ms to make the lifting container reach a stable state; from the perspective of the position tracking performance of the two hydraulic cylinders, the tracking error of the anti-step controller is larger than that of the flatness controller.
- the flatness controller has better control performance than the anti-stepping controller. Step controller.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- Control And Safety Of Cranes (AREA)
- Lift-Guide Devices, And Elevator Ropes And Cables (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims (10)
- 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法,其特征在于,包括以下步骤:步骤1:建立双绳缠绕式超深立井提升子系统数学模型;步骤2:建立电液伺服子系统位置闭环的数学模型;步骤3:非线性系统平整度特性;步骤4:设计双绳缠绕式超深矿井提升子系统平整度控制器;步骤5:设计电液伺服子系统位置闭环平整度控制器。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2020120878A RU2742676C1 (ru) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-09-12 | Способ управления пространственным расположением подъемного контейнера в подъемной системе двойного типа намотки канатов для работы в сверхглубокой вертикальной шахте |
| AU2019390995A AU2019390995B2 (en) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-09-12 | Hoisting container pose control method of double-rope winding type ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting system |
| US16/772,162 US11691846B2 (en) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-09-12 | Hoisting container pose control method of double-rope winding type ultra-deep vertical shaft hoisting system |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910284619.2A CN110145501B (zh) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-04-10 | 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 |
| CN201910284619.2 | 2019-04-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020206931A1 true WO2020206931A1 (zh) | 2020-10-15 |
Family
ID=67588960
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2019/105589 WO2020206931A1 (zh) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-09-12 | 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11691846B2 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN110145501B (zh) |
| AU (1) | AU2019390995B2 (zh) |
| RU (1) | RU2742676C1 (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2020206931A1 (zh) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117725696A (zh) * | 2023-12-18 | 2024-03-19 | 浙江大学 | 基于独立模态空间法的柔性臂无指令输入整形抑振方法 |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU2018448166B2 (en) * | 2018-10-31 | 2022-06-09 | China University Of Mining&Technology , Beijing | Mine vertical shaft lifting apparatus, mine vertical shaft lifting system and control method therefor |
| CN110145501B (zh) | 2019-04-10 | 2020-05-12 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 |
| CN112987575B (zh) * | 2021-03-05 | 2023-09-15 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种电液伺服系统位置闭环跟踪误差限定控制方法 |
| CN113536571B (zh) * | 2021-07-16 | 2022-12-23 | 重庆大学 | 矿井多绳缠绕式提升机动力学建模方法及系统、存储介质 |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011101938A (ja) * | 2009-11-12 | 2011-05-26 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | ロボットおよびその制御装置 |
| CN102602838A (zh) * | 2012-02-28 | 2012-07-25 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种立井施工吊盘的自动平衡调节系统及方法 |
| CN104035334A (zh) * | 2014-05-23 | 2014-09-10 | 中北大学 | 基于广义阻滞力的液压动态调平方法 |
| CN104444707A (zh) * | 2014-10-30 | 2015-03-25 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井提升机钢丝绳张力平衡系统及其方法 |
| CN104763694A (zh) * | 2015-03-18 | 2015-07-08 | 上海交通大学 | 一种掘进机液压推进系统分区压力设定值优化方法 |
| US20170305722A1 (en) * | 2015-12-04 | 2017-10-26 | China University Of Mining And Technology | A horizontally movable vertical shaft rope guide and regulating method thereof |
| CN109334380A (zh) * | 2018-11-16 | 2019-02-15 | 燕山大学 | 基于参数不确定性和外部扰动的非线性油气悬架主动控制方法 |
| CN110145501A (zh) * | 2019-04-10 | 2019-08-20 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1153088A1 (ru) * | 1983-12-23 | 1985-04-30 | Проектно-Технологический Трест Организации И Технологии Шахтного Строительства "Оргтехшахтострой" | Устройство дл транспортировки длинномеров в шахтах |
| RU2031830C1 (ru) * | 1992-07-21 | 1995-03-27 | Николай Гаврилович Огнев | Способ защиты шахтной подъемной установки от напуска тяговых канатов и устройство для его осуществления |
| RU2408516C1 (ru) * | 2009-10-08 | 2011-01-10 | Открытое акционерное общество Акционерная холдинговая компания "Всероссийский научно-исследовательский и проектно-конструкторский институт металлургического машиностроения имени академика Целикова" (ОАО АХК "ВНИИМЕТМАШ") | Комплекс для подземного сбора и хранения твердых бытовых отходов |
| CN102674125B (zh) * | 2011-03-16 | 2014-10-15 | 西门子(中国)有限公司 | 控制提升机的方法、装置、存储介质和提升机系统 |
| JP2014019519A (ja) * | 2012-07-17 | 2014-02-03 | Ohbayashi Corp | 高層建築物における竪穴区画構造 |
| CN203217866U (zh) * | 2013-04-13 | 2013-09-25 | 张凤嘉 | 单绳缠绕式立井提升系统教学模型 |
| CN103712682A (zh) * | 2013-11-30 | 2014-04-09 | 安徽恒源煤电股份有限公司 | 基于有限元分析法的主井提升机主轴振动监测方法 |
| CN103776577B (zh) * | 2014-01-03 | 2016-05-04 | 中国矿业大学 | 施工立井吊盘的稳绳张力检测装置和检测方法 |
| CN105565130B (zh) * | 2014-10-15 | 2018-07-31 | 中煤第三建设(集团)有限责任公司 | 一种煤矿立井混合提升系统 |
| CN104806226B (zh) * | 2015-04-30 | 2018-08-17 | 北京四利通控制技术股份有限公司 | 智能钻井专家系统 |
| CN105129583B (zh) * | 2015-07-03 | 2017-03-08 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种绳罐道罐笼能量收集装置及方法 |
| CN106154833B (zh) * | 2016-07-14 | 2019-09-27 | 南京理工大学 | 一种电液负载模拟装置输出反馈控制方法 |
| CN106121621A (zh) * | 2016-07-15 | 2016-11-16 | 西南石油大学 | 一种智能钻井专家系统 |
| CN106290035B (zh) * | 2016-07-18 | 2018-10-02 | 中国矿业大学 | 超深立井缠绕式提升钢丝绳摩擦腐蚀疲劳损伤监测装置及方法 |
| CN106904517B (zh) * | 2017-04-06 | 2020-02-07 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井提升机与提升方法 |
| CN107032245B (zh) * | 2017-05-02 | 2018-09-21 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井双绳提升系统的天轮自动调力装置及方法 |
| CN106946120B (zh) * | 2017-05-02 | 2019-02-19 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井提升容器端钢丝绳张力调节装置及方法 |
| CN108059056B (zh) * | 2017-12-19 | 2019-10-11 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井双滚筒驱动大载荷摩擦提升系统及方法 |
| CN108584616B (zh) * | 2018-07-11 | 2023-09-12 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井用牵引力均衡的提升装置及控制方法 |
| CN109292600A (zh) * | 2018-10-31 | 2019-02-01 | 中国矿业大学(北京) | 矿山立井提升装置、矿山立井提升系统及其控制方法 |
-
2019
- 2019-04-10 CN CN201910284619.2A patent/CN110145501B/zh active Active
- 2019-09-12 AU AU2019390995A patent/AU2019390995B2/en active Active
- 2019-09-12 RU RU2020120878A patent/RU2742676C1/ru active
- 2019-09-12 US US16/772,162 patent/US11691846B2/en active Active
- 2019-09-12 WO PCT/CN2019/105589 patent/WO2020206931A1/zh active Application Filing
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011101938A (ja) * | 2009-11-12 | 2011-05-26 | Yaskawa Electric Corp | ロボットおよびその制御装置 |
| CN102602838A (zh) * | 2012-02-28 | 2012-07-25 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种立井施工吊盘的自动平衡调节系统及方法 |
| CN104035334A (zh) * | 2014-05-23 | 2014-09-10 | 中北大学 | 基于广义阻滞力的液压动态调平方法 |
| CN104444707A (zh) * | 2014-10-30 | 2015-03-25 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种超深立井提升机钢丝绳张力平衡系统及其方法 |
| CN104763694A (zh) * | 2015-03-18 | 2015-07-08 | 上海交通大学 | 一种掘进机液压推进系统分区压力设定值优化方法 |
| US20170305722A1 (en) * | 2015-12-04 | 2017-10-26 | China University Of Mining And Technology | A horizontally movable vertical shaft rope guide and regulating method thereof |
| CN109334380A (zh) * | 2018-11-16 | 2019-02-15 | 燕山大学 | 基于参数不确定性和外部扰动的非线性油气悬架主动控制方法 |
| CN110145501A (zh) * | 2019-04-10 | 2019-08-20 | 中国矿业大学 | 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117725696A (zh) * | 2023-12-18 | 2024-03-19 | 浙江大学 | 基于独立模态空间法的柔性臂无指令输入整形抑振方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110145501B (zh) | 2020-05-12 |
| US20210070586A1 (en) | 2021-03-11 |
| AU2019390995B2 (en) | 2022-03-10 |
| RU2742676C1 (ru) | 2021-02-09 |
| US11691846B2 (en) | 2023-07-04 |
| CN110145501A (zh) | 2019-08-20 |
| AU2019390995A1 (en) | 2020-10-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2020206931A1 (zh) | 一种双绳缠绕式超深立井提升系统提升容器位姿控制方法 | |
| CN103046606B (zh) | 工程机械设备、可移动式配重系统及控制方法 | |
| CN103935848B (zh) | 一种超深矿井提升机多绳协同控制系统及方法 | |
| CN113465859A (zh) | 一种六自由度电液振动台的干扰力补偿方法 | |
| KR20170058925A (ko) | 로드의 운동을 제어하기 위한 시스템 | |
| US20230159136A1 (en) | Vessel attitude control arrangement | |
| CN109911771A (zh) | 变系数自抗扰控制器设计方法、及吊车自抗扰控制器 | |
| WO2020024653A1 (zh) | 一种支撑减振装置以及采用该支撑减振装置的车辆 | |
| CN110597051A (zh) | 基于RBF神经网络的Stewart稳定平台控制方法 | |
| KR20230054881A (ko) | 휠 지지력에 기반한 차량 액티브 서스펜션의 관성 조정 방법 및 제어 시스템 | |
| JP5362158B2 (ja) | ターンテーブル梯子装置 | |
| CN1259481A (zh) | 虚拟主动式电梯牵引装置 | |
| CN115468732A (zh) | 一种高速列车升力翼安装布置及协同控制方法 | |
| JP5253697B2 (ja) | ターンテーブル梯子装置 | |
| CN112811318B (zh) | 一种用于桥式起重机的消摆边界控制方法 | |
| Xu et al. | Review of Heave Compensation Systems: Design and Control Strategies | |
| Wang et al. | Design and simulation research of riser flexible hang-off system based on variable damping for drilling platform to avoid typhoon | |
| CN109270967B (zh) | 一种风机塔筒风致振动的半主动控制方法 | |
| Daher et al. | System synthesis and controller design of a novel pump controlled steer-by-wire system employing modern control techniques | |
| KR20120118696A (ko) | 자동화 건축을 위한 유압로봇의 동기제어 방법 | |
| CN106564579A (zh) | 液压收放减摇缓冲装置 | |
| CN215861052U (zh) | 一种吊放设备用主被动升沉补偿系统 | |
| CN101852229B (zh) | 一种用于液压伺服驱动系统动力学控制的实验台 | |
| CN210034034U (zh) | 飞机舵机并联双阀结构电液伺服阀加载系统 | |
| CN114572429A (zh) | 一种基于凸轮外形设计的普适火箭回收索系统 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2019390995 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20190912 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 19923748 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 19923748 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |