WO2017159342A1 - Dispositif de rayonnement ultraviolet - Google Patents
Dispositif de rayonnement ultraviolet Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017159342A1 WO2017159342A1 PCT/JP2017/007694 JP2017007694W WO2017159342A1 WO 2017159342 A1 WO2017159342 A1 WO 2017159342A1 JP 2017007694 W JP2017007694 W JP 2017007694W WO 2017159342 A1 WO2017159342 A1 WO 2017159342A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- ozone
- ultraviolet
- generation layer
- radiation device
- ozone generation
- Prior art date
Links
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 107
- CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ozone Chemical compound [O-][O+]=O CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 207
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 52
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 abstract description 23
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 29
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 24
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000005469 synchrotron radiation Effects 0.000 description 10
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000001954 sterilising effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000004659 sterilization and disinfection Methods 0.000 description 6
- JWNBYUSSORDWOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Kr]Cl Chemical compound [Kr]Cl JWNBYUSSORDWOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 5
- OPBJIDJILCEYRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Kr]Br Chemical compound [Kr]Br OPBJIDJILCEYRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ISQINHMJILFLAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N argon hydrofluoride Chemical compound F.[Ar] ISQINHMJILFLAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- VZPPHXVFMVZRTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Kr]F Chemical compound [Kr]F VZPPHXVFMVZRTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GKUXZDSXCFGSFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Xe]I Chemical compound [Xe]I GKUXZDSXCFGSFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004332 deodorization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000005350 fused silica glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005949 ozonolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine atom Chemical compound [F] YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000006750 UV protection Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052743 krypton Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DNNSSWSSYDEUBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N krypton atom Chemical compound [Kr] DNNSSWSSYDEUBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005979 thermal decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L2/00—Methods or apparatus for disinfecting or sterilising materials or objects other than foodstuffs or contact lenses; Accessories therefor
- A61L2/02—Methods or apparatus for disinfecting or sterilising materials or objects other than foodstuffs or contact lenses; Accessories therefor using physical phenomena
- A61L2/08—Radiation
- A61L2/10—Ultraviolet radiation
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J19/00—Chemical, physical or physico-chemical processes in general; Their relevant apparatus
- B01J19/08—Processes employing the direct application of electric or wave energy, or particle radiation; Apparatus therefor
- B01J19/12—Processes employing the direct application of electric or wave energy, or particle radiation; Apparatus therefor employing electromagnetic waves
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01J—ELECTRIC DISCHARGE TUBES OR DISCHARGE LAMPS
- H01J61/00—Gas-discharge or vapour-discharge lamps
- H01J61/02—Details
- H01J61/30—Vessels; Containers
- H01J61/34—Double-wall vessels or containers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01J—ELECTRIC DISCHARGE TUBES OR DISCHARGE LAMPS
- H01J65/00—Lamps without any electrode inside the vessel; Lamps with at least one main electrode outside the vessel
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an ultraviolet radiation device, and more particularly to an ultraviolet radiation device suitably used for sterilization treatment and deodorization treatment of skin and the like.
- ultraviolet rays are suitably used for sterilization treatment of skin and the like, deodorization treatment, and organic contaminant removal treatment.
- an ultraviolet light source an excimer lamp is widely known (for example, see Patent Document 1).
- an excimer lamp As an excimer lamp, as shown in FIG. 6, it is smaller than the inner diameter of a cylindrical outer tube 22 and the outer tube 22 arranged along the tube axis in the outer tube 22.
- An arc tube 21 having a double tube structure made of synthetic quartz glass having a cylindrical inner tube 23 having an outer diameter is provided.
- both end portions of the outer tube 22 and the inner tube 23 are joined by the sealing wall members 24 ⁇ / b> A and 24 ⁇ / b> B, and an annular inner space S ⁇ b> 1 is formed between the outer tube 22 and the inner tube 23.
- the internal space S1 is filled with a discharge gas.
- the arc tube 21 is provided with a net-like outer electrode 25 on the outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22, and a film-like inner electrode 26 is provided on the inner peripheral surface of the inner tube 23. 26 are each connected to a high frequency power source 19. In this excimer lamp 20, when a high frequency high voltage is applied between the outer electrode 25 and the inner electrode 26 by the high frequency power source 19, excimer discharge is generated in the internal space S1, and excimer light is emitted.
- ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of around 200 nm specifically, ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of approximately 200 to 250 nm are used.
- the excimer lamp can adjust the wavelength characteristics (wavelength range) of the light emitted depending on the type of discharge gas. Therefore, by using an appropriate gas as the discharge gas, the excimer lamp has a wavelength around 200 nm. Radiation light (ultraviolet light) having a center wavelength can be obtained.
- a discharge gas for obtaining synchrotron radiation having a central wavelength in the vicinity of a wavelength of 200 nm
- argon fluoride (ArF) gas for example, argon fluoride (ArF) gas (radiation obtained) (Central wavelength of light 193 nm), krypton bromide (KrBr) gas (central wavelength of the obtained synchrotron radiation 207 nm), krypton chloride (KrCl) gas (central wavelength of the synchrotron radiation obtained 222 nm), krypton fluoride (KrF) gas
- the obtained synchrotron radiation has a central wavelength of 248 nm), xenon iodide (XeI) gas (the central wavelength of the synchrotron radiation obtained is 253 nm), and chlorine (Cl 2 ) gas (the central wavelength of the synchrotron radiation obtained is 259 nm).
- the emitted light of the excimer lamp can be regarded as monochromatic light in practice, and its spectrum (radiation spectrum) is a line spectrum, but has a certain spectral line width. Therefore, the emitted light of the excimer lamp includes light having a longer wavelength than the center wavelength and light having a shorter wavelength than the center wavelength, as well as light having the center wavelength. Therefore, in an excimer lamp in which a specific discharge gas is sealed (hereinafter also referred to as “specific excimer lamp”), when the emitted light contains ultraviolet light having a wavelength of less than 190 nm, ozone (O 3 ) appear.
- ozone-generating ultraviolet rays ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of less than 190 nm are absorbed by oxygen and generate ozone (hereinafter also referred to as “ozone-generating ultraviolet rays”).
- ozone is efficiently generated by emitting ozone-generating ultraviolet rays in an oxygen-existing atmosphere. Therefore, when the specific excimer lamp is turned on in the air atmosphere, ozone is generated by absorbing the ozone-generating ultraviolet rays into the oxygen in the air.
- high-concentration ozone adversely affects the human body, when using a specific excimer lamp particularly in a living space, for example, when using an excimer lamp for sterilization of the skin, for example. Needs to suppress the generation of ozone.
- the inventors of the present invention have studied using a glass tube or a coating agent used as a vacuum ultraviolet ray-cutting member as a constituent material of an arc tube of a specific excimer lamp. Specifically, the use of a glass tube doped with titanium oxide (TiO 2 ), which is generally used as a vacuum ultraviolet ray-cutting member, was examined as a constituent material of the arc tube of the specific excimer lamp. However, since titanium oxide has a characteristic of absorbing not only ozone-generated ultraviolet rays but also ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of 200 nm, ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of 200 nm generated in the inner space of the arc tube are caused by the arc tube (titanium oxide).
- the present invention has been found as a result of the inventors of the present invention conducting research on ultraviolet radiation means that can be suitably used in an air atmosphere, and the object thereof is to be used in an air atmosphere. Even in such a case, it is an object to provide an ultraviolet radiation device capable of suppressing the generation of ozone in the ambient atmosphere outside the device and emitting ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of around 200 nm with high emission intensity.
- the ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention includes an ultraviolet light source that emits light including ultraviolet light having a wavelength that is absorbed by oxygen and generates ozone, and ultraviolet light that is disposed apart from the ultraviolet light source. It has an ozone generation layer forming member for forming an ozone generation layer with a gas that absorbs and generates ozone, The light from the ultraviolet light source is emitted through the ozone generation layer forming member.
- the ozone generation layer forming member constitutes a mantle tube, and the mantle tube is disposed so as to surround the ultraviolet light source.
- the ultraviolet light source is preferably an excimer lamp.
- the ultraviolet light source is preferably an LED element.
- the ozone generation layer is preferably an air layer, and the thickness of the air layer is preferably 20 mm or less.
- the ozone generation layer made of a gas that absorbs ultraviolet rays and generates ozone emits light including ultraviolet rays having a wavelength that is absorbed by oxygen and generates ozone (ozone-generating ultraviolet rays).
- the ozone generating layer forming member, and light from the ultraviolet light source is emitted through the ozone generating layer forming member. Therefore, the ozone generation ultraviolet rays contained in the light from the ultraviolet light source are selectively absorbed in the ozone generation layer.
- the emission intensity of ozone-generated ultraviolet light can be reduced without greatly reducing the emission intensity of ultraviolet light other than ozone-generated ultraviolet light.
- the ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention even when used in an air atmosphere, generation of ozone in the ambient atmosphere outside the device can be suppressed, and ultraviolet light having a wavelength of around 200 nm can be emitted with high emission intensity. Can be emitted.
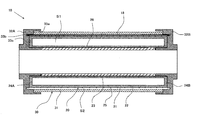
- FIG. 1 is an explanatory sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the first ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention.
- the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 includes an ultraviolet light source composed of a straight tubular excimer lamp 20 and a long cylindrical mantle member 30 disposed so as to surround the excimer lamp 20.
- the outer cover member 30 is disposed so as to extend along the lamp central axis of the excimer lamp 20.
- the outer cover member 30 extends along with the excimer lamp 20 along the lamp central axis of the excimer lamp 20.
- the reflection member 18 is disposed.
- the reflecting member 18 has a full length longer than the full length of the excimer lamp 20 and is a rectangular curved plate-shaped aluminum recess curved in a semicircular shape along the circumferential direction of the excimer lamp 20. It consists of a plane mirror.
- the reflecting member 18 is disposed so that the reflecting surface (inner peripheral surface) of the reflecting member 18 faces the excimer lamp 20.
- the reflecting member 18 is an inner peripheral surface of the outer member 30 (specifically, an inner peripheral surface of the outer tube 31) or an outer peripheral surface of the excimer lamp 20 (specifically, an outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22). ) May be formed of an aluminum vapor deposition film provided on the substrate.
- the excimer lamp 20 includes an arc tube 21 made of a dielectric material that transmits ultraviolet rays, such as synthetic quartz glass and fused silica glass.
- the arc tube 21 has a cylindrical outer tube 22 and a cylindrical inner tube 23 having an outer diameter smaller than the inner diameter of the outer tube 22 disposed along the tube axis in the outer tube 22. It has a double tube structure.
- the outer tube 22 and the inner tube 23 are arranged so that the tube axis of the outer tube 22 and the tube axis of the inner tube 23 coincide with each other.
- the tube axis 23 of the tube is the lamp central axis.
- both end portions of the outer tube 22 and the inner tube 23 are joined by sealing wall members 24 ⁇ / b> A and 24 ⁇ / b> B, and an annular inner space S ⁇ b> 1 is formed between the outer tube 22 and the inner tube 23. Is formed.
- the internal space S1 is filled with a discharge gas.
- the arc tube 21 is provided with a net-like outer electrode 25 made of, for example, stainless steel in close contact with the outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22, and the inner peripheral surface of the inner tube 23 has the inner peripheral surface thereof. Close to the surface, a film-like inner electrode 26 made of, for example, aluminum is provided.
- a pair of electrodes composed of the outer electrode 25 and the inner electrode 26 are arranged so as to face each other, and at the boundary between the outer electrode 25 and the inner electrode 26 and the inner space S1, each arc tube 21 tube walls (dielectric material) are interposed.
- a discharge region is formed in a region where the pair of electrodes face each other with the tube wall (dielectric material) of the arc tube 21 and the internal space S1 therebetween.
- the outer electrode 25 and the inner electrode 26 are each connected to a high-frequency power source (not shown) via lead wires (not shown).
- the outer electrode 25 is a ground electrode (low voltage side electrode)
- the inner electrode 26 is a high voltage supply electrode.
- a lamp having a central wavelength in the wavelength range of 190 to 250 nm is preferably used.
- the excimer lamp used as the excimer lamp 20 and having a center wavelength in the wavelength range of 190 to 250 nm light including ozone-generated ultraviolet rays is emitted.
- an ultraviolet excimer fluorescent lamp having a configuration in which an ultraviolet light emitting phosphor having a peak wavelength in a wavelength range of 200 to 250 nm is applied to the inner peripheral surface of the arc tube 21 can be used.
- the fluorescence from the ultraviolet light emitting phosphor has a certain spectral line width, similar to the emitted light of the excimer lamp, and therefore, the peak wavelength light, the light on the longer wavelength side than the peak wavelength, and the center. It also includes light on the shorter wavelength side than the wavelength. Therefore, an ultraviolet excimer fluorescent lamp in which an ultraviolet light emitting phosphor having a peak wavelength in a wavelength range of 200 to 250 nm is applied emits light containing ozone-generated ultraviolet light. That is, when an ultraviolet excimer fluorescent lamp is lit in an air atmosphere, ozone (O 3 ) is generated by the absorption of ozone-generated ultraviolet light contained in the emitted light of the ultraviolet excimer fluorescent lamp by oxygen. Become.
- the discharge gas used in the excimer lamp 20 include, for example, argon fluoride (ArF) gas (center wavelength of the obtained radiation light 193 nm), krypton bromide (KrBr) gas (center wavelength of the obtained radiation light) 207 nm), krypton chloride (KrCl) gas (center wavelength of the obtained synchrotron radiation 222 nm), krypton fluoride (KrF) gas (center wavelength of the synchrotron radiation obtained 248 nm), xenon iodide (XeI) gas (the synchrotron radiation obtained) And a chlorine (Cl 2 ) gas (a central wavelength of the obtained synchrotron radiation of 259 nm).
- ArF argon fluoride
- KrBr krypton bromide
- KrCl krypton chloride
- KrF krypton fluoride
- XeI xenon iodide
- XeI xenon
- argon fluoride gas, krypton bromide gas, and krypton chloride gas are preferable, krypton bromide gas and krypton chloride gas are more preferable, and krypton chloride gas is particularly preferable.
- the outer member 30 includes a cylindrical ozone generation layer forming member (outer tube) 31 that transmits radiated light (ultraviolet rays) from the excimer lamp 20, and base members 32 ⁇ / b> A and 32 ⁇ / b> B disposed at both ends of the outer tube 31. It is equipped with.
- the outer tube 31 has an inner diameter larger than the outer diameter of the excimer lamp 20 (specifically, the outer diameter of the outer tube 22 provided with the outer electrode 25), and the length of the discharge region, that is, the excimer lamp. 20 has an overall length that is longer than the length of the region in which the inner electrode 26 is disposed in the lamp central axis direction (left-right direction in FIG. 1).
- the base members 32A and 32B support and fix the outer tube 31 and support and fix the excimer lamp 20 and the reflection member 18.
- each of the base members 32A and 32B has an inner diameter slightly smaller than the inner diameter of the inner tube 23 of the excimer lamp 20, and an outer diameter slightly larger than the outer diameter of the outer tube 31. It is an annular tube-shaped thing having. Since the base members 32A and 32B are in the shape of an annular tube, the excimer lamp 20 can be cooled by the air constituting the external environment atmosphere of the apparatus.
- an annular outer tube support groove 33a and an annular tube provided on the inner side of the outer tube support groove 33a are provided on the inner surfaces of the base members 32A and 32B (the surface facing the excimer lamp 20).
- the reflecting member supporting groove 33b and an annular lamp supporting groove 33c provided on the inner side of the reflecting member supporting groove 33b are formed concentrically.
- the entire inner peripheral surface of the inner tube 21 is covered with the inner electrode 26 and the base members 32A and 32B. For this reason, no light (ultraviolet rays) is emitted through the inner tube 23, and therefore no ozone is generated due to the light being irradiated from the inner tube 23 to the outside of the apparatus.
- the outer member 30 is arranged so that the outer tube 31 surrounds the excimer lamp 20 in a state of being separated from the excimer lamp 20.
- the excimer lamp 20 is disposed apart from the outer tube 31 inside the outer member 30.
- the outer tube 31 is supported by the base members 32 ⁇ / b> A and 32 ⁇ / b> B so that the tube axis of the outer tube 31 coincides with the lamp central axis of the excimer lamp 20. That is, the outer tube 31 is separated from the outer peripheral surface of the excimer lamp 20 (specifically, the outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22 provided with the outer electrode 25) over the entire inner peripheral surface of the outer tube 31. It is said that.
- ozone generation layer formation space S2 In the space between the excimer lamp 20 and the outer tube 31 (hereinafter also referred to as “ozone generation layer formation space”) S2, a gas that absorbs ultraviolet rays and generates ozone (hereinafter referred to as “ozone generation gas”).
- the ozone generation layer is formed by the ozone generation gas.
- the ozone-generating gas include oxygen-containing gas, specifically air (air constituting the apparatus external environment atmosphere).
- an annular ozone generation layer forming space S2 is formed between the excimer lamp 20 and the outer tube 31, and the reflecting member 18 is formed in the annular ozone generation layer forming space S2. Is located.
- the reflecting member 18 has the reflecting surface (inner peripheral surface) of the reflecting member 18 facing the excimer lamp 20 with a very small gap inside the outer cover member 30, and the rear surface (outer peripheral surface) of the reflecting member 18. ) Is arranged to face the outer tube 31 with a very small gap. And the ultraviolet radiation area
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space where ozone generated in the ozone generation layer does not leak.
- the thickness of the ozone generation layer that is, the separation distance between the excimer lamp 20 and the outer tube 31 depends on the type of the ozone generating gas (specifically, the type of discharge gas, etc.) and the excimer lamp 20. It is determined appropriately in consideration of lighting conditions and the like. Specifically, when the ozone generating gas is air, that is, when the ozone generating layer is an air layer, the thickness of the ozone generating layer is preferably 0.1 to 20 mm, and more preferably 1 to 2 mm.
- the ozone generation layer absorbs less ozone, and the amount of ozone generated in the ozone generation layer, that is, the amount of ozone generation UV absorbed in the ozone generation layer. Becomes smaller. Therefore, there is a possibility that the generation of ozone in the environment outside the apparatus cannot be sufficiently suppressed.
- the thickness of the ozone generation layer is excessive, the heat retaining effect by the ozone generation layer is increased. Therefore, the excimer lamp 20 may be shortened in service life due to excessive heating of the excimer lamp 20 due to heat generated when the excimer lamp 20 is turned on.
- the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 by applying a high frequency high voltage to the pair of electrodes of the excimer lamp 20 by a high frequency power source, excimer discharge is generated in the internal space S1, and the type of discharge gas or ultraviolet light is generated.
- Excimer light corresponding to the type of the light-emitting phosphor is emitted from the outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22 as radiated light, either directly or after being reflected by the inner electrode 26.
- the emitted light from the excimer lamp 20 is emitted from the ultraviolet emission region of the outer tube 31 after a part thereof is reflected directly and the other part is reflected by the reflecting member 18.
- an ozone generation layer is formed in the ozone generation layer formation space S ⁇ b> 2 between the excimer lamp 20 and the outer tube 31. For this reason, ozone-generating ultraviolet rays contained in the emitted light of the excimer lamp 20 are selectively absorbed in the ozone-generating layer. As a result, it is possible to reduce the emission intensity of the ozone-generated ultraviolet light without reducing the emission intensity of ultraviolet light other than the ozone-generated ultraviolet light in the emitted light of the first ultraviolet radiation device 10.
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 in which the ozone generation layer is formed is a substantially airtight closed space, ozone generated by the ozone generation layer absorbing ozone generation ultraviolet rays in the ozone generation layer. , It will not leak outside the device.
- a discharge may occur between the outer electrode 25 and the outer tube 22, and when this discharge occurs, ozone is generated due to the discharge. Although it occurs, the ozone does not leak outside the device.
- the ozone generation layer is heated by heat from the excimer lamp 20 and the temperature is raised, the ozone generated in the ozone generation layer is heated and thus quickly decomposed (thermally decomposed) to generate oxygen. Generated. Therefore, even if the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space, the ozone generation ultraviolet absorption capacity of the ozone generation layer does not deteriorate with time.
- the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 even when used in an air atmosphere, the generation of ozone in the external environment atmosphere of the device can be suppressed, and in the excimer lamp 20, a discharge gas or By selecting and using an ultraviolet light-emitting phosphor, ultraviolet light having a desired wavelength range around 200 nm can be emitted with high emission intensity. Moreover, even if the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 generates ozone inside the device, the ozone does not leak out of the device.
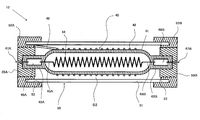
- FIG. 2 is an explanatory sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the second ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention.
- the second ultraviolet radiation device 11 is the same as the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 according to FIG. 1 except that the configuration of the outer cover member 35 is different and the reflective member is not provided inside the outer cover member 35. It has the structure of. Further, in the second ultraviolet radiation device 11, the excimer lamp 20 has the same configuration as the excimer lamp 20 in the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 according to FIG.
- the outer member 35 is also referred to as an ozone generation layer forming member (hereinafter referred to as “window forming curved plate member”) through which the outer tube 36 transmits the radiated light (ultraviolet rays) from the excimer lamp 20. ) 37 and the outer cover member 30 in the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 according to FIG. 1 except that it is constituted by a reflection block member 38 having a reflection surface that reflects the radiation light (ultraviolet rays) from the excimer lamp 20. And basically the same configuration.
- the outer cover member 35 has a rectangular curved plate-like window-forming curved plate member 37 that is curved in a semicircular shape along the circumferential direction of the excimer lamp 20 and the entire length of the window-forming curved plate member 37.
- An outer tube 36 having a full length and a substantially V-shaped reflection block member 38 bent along the circumferential direction of the excimer lamp 20 is provided.
- the fitting edge portion 37 a of the window forming curved plate member 37 is fitted into the fitting groove 38 a formed on the connection surface of the reflection block member 38.
- the outer tube 36 has an inner diameter larger than the outer diameter of the excimer lamp 20 (specifically, the outer diameter of the outer tube 22 provided with the outer electrode 25), and the length of the discharge region, that is, The excimer lamp 20 has an overall length longer than the length of the region where the inner electrode 26 is disposed in the lamp central axis direction (direction perpendicular to the paper surface in FIG. 2).
- Base members (not shown) are disposed at both ends of the outer tube 36. The base member supports and fixes the outer tube 36 and also supports and fixes the excimer lamp 20.
- the outer member 35 is arranged so that the outer tube 36 surrounds the excimer lamp 20 in a state of being separated from the excimer lamp 20, and an ozone generation layer forming space S ⁇ b> 2 between the outer tube 36 and the excimer lamp 20.
- An ozone generation layer is formed on the surface.
- the outer tube 36 is supported by the base member so that the tube axis of the outer tube 36 coincides with the lamp central axis of the excimer lamp 20. That is, the outer tube 36 is separated from the outer peripheral surface of the excimer lamp 20 (specifically, the outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22 provided with the outer electrode 25) over the entire inner peripheral surface of the outer tube 36. It is said that.
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space where ozone generated in the ozone generation layer does not leak.
- excimer discharge is generated in the internal space S1, and the type of discharge gas or ultraviolet light is generated.
- Excimer light corresponding to the type of the light-emitting phosphor is emitted from the outer peripheral surface of the outer tube 22 as radiated light, either directly or after being reflected by the inner electrode 26.
- the emitted light from the excimer lamp 20 is emitted from the window forming curved plate member 37 after a part thereof is reflected directly and the other part is reflected by the reflection block member 38.
- an ozone generation layer is formed in the ozone generation layer formation space S ⁇ b> 2 between the excimer lamp 20 and the outer tube 36. For this reason, ozone-generating ultraviolet rays contained in the emitted light of the excimer lamp 20 are selectively absorbed in the ozone-generating layer. As a result, the emission intensity of the ozone-generated ultraviolet light can be reduced in the outgoing light of the second ultraviolet radiation device 11 without reducing the emission intensity of ultraviolet light other than the ozone-generated ultraviolet light.
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 in which the ozone generation layer is formed is a substantially airtight closed space, ozone generated by the ozone generation layer absorbing ozone generation ultraviolet rays in the ozone generation layer. , It will not leak outside the device.
- a discharge may occur between the outer electrode 25 and the outer tube 22, and when this discharge occurs, ozone is generated due to the discharge. Although it occurs, the ozone does not leak outside the device.
- the ozone generation layer is heated by heat from the excimer lamp 20 and the temperature is raised, the ozone generated in the ozone generation layer is heated and thus quickly decomposed (thermally decomposed) to generate oxygen. Generated. Therefore, even if the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space, the ozone generation ultraviolet absorption capacity of the ozone generation layer does not deteriorate with time.
- the second ultraviolet radiation device 11 even when used in an air atmosphere, generation of ozone in the external environment atmosphere of the device can be suppressed, and in the excimer lamp 20, a discharge gas or By selecting and using an ultraviolet light-emitting phosphor, ultraviolet light having a desired wavelength range around 200 nm can be emitted with high emission intensity. Moreover, even if the second ultraviolet radiation device 11 generates ozone inside the device, the ozone does not leak out of the device.
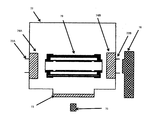
- FIG. 3 is an explanatory sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the third ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention.
- the third ultraviolet radiation device 12 is the same as that of the first ultraviolet ray according to FIG. 1 except that the configuration of the excimer lamp 40 constituting the ultraviolet light source is different and that no reflective member is provided in the outer cover member 50. It has the same configuration as the radiation device 10.
- the outer member 50 has basically the same configuration as the outer member 30 in the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 according to FIG. 1, and specifically, an excimer lamp.
- a cylindrical sheath tube (ozone generating layer forming member) 31 that transmits radiation light (ultraviolet rays) from 40 and base members 52A and 52B disposed at both ends of the sheath tube 31 are provided.
- the excimer lamp 40 is provided with an arc tube 41 having a single tube structure. More specifically, the excimer lamp 40 is made of a dielectric material that transmits ultraviolet rays, such as synthetic quartz glass and fused silica glass, and has flat sealing portions 42A and 42B formed at both ends by a pinch seal method. A long cylindrical arc tube 41 is formed. The arc tube 41 is filled with a discharge gas, and a coiled internal electrode 44 is disposed so as to extend along the tube axis of the arc tube 41.
- the internal electrode 44 is electrically connected to the metal foils 46A and 46B embedded in the sealing portions 42A and 42B through the internal leads 45A and 45B, and the sealing portions 42A are connected to the metal foils 46A and 46B. , 42B, one end portions of the internal electrode external leads 47A, 47B projecting outward from the outer end face are electrically connected.
- a net-like external electrode 48 is provided on the outer peripheral surface of the arc tube 41, and one end of an external electrode external lead 49 extending along the sealing portion 42A is electrically connected to the external electrode 48. ing.
- a discharge region is formed in a region where the internal electrode 44 and the external electrode 48 face each other through the internal space of the arc tube 41 and the tube wall (dielectric material) of the arc tube 41.
- ceramic lamp base members 55A and 55B are mounted on the sealing portions 42A and 42B of the excimer lamp 40, respectively.
- the lamp base members 55A and 55B have a columnar appearance.
- the external lead for external electrodes 49 and the external leads for internal electrodes 47A and 47B are each connected to a high-frequency power source (not shown) via a feeder line (not shown).
- the external electrode 48 is a ground electrode (low voltage side electrode)
- the internal electrode 44 is a high voltage supply electrode.
- the excimer lamp 40 a lamp having a central wavelength in the wavelength range of 190 to 250 nm is used, like the excimer lamp 20 according to the first ultraviolet radiation device 10.
- the excimer lamp used as the excimer lamp 40 and having a center wavelength in the wavelength range of 190 to 250 nm light including ozone-generated ultraviolet rays is emitted.
- the outer member 50 is arranged so that the outer tube 31 surrounds the excimer lamp 40 in a state of being separated from the excimer lamp 40, and an ozone generation layer forming space between the outer tube 31 and the excimer lamp 40.
- an ozone generation layer is formed.
- the base members 52A and 52B each have an inner diameter equivalent to the outer diameter of the lamp base members 55A and 55B, and have an annular cylindrical shape having an outer diameter slightly larger than the outer tube 31. belongs to.
- An annular outer tube support groove 53 is formed on the inner surfaces of the base members 52A and 52B (the surface facing the excimer lamp 40).
- the excimer lamp 40 is supported by the base members 52A and 52B in a state where the lamp base members 55A and 55B are mounted on the sealing portions 42A and 42B.
- the outer tube 31 is supported by the base members 52 ⁇ / b> A and 52 ⁇ / b> B so that the tube axis of the outer tube 31 coincides with the tube axis of the arc tube 41. That is, the outer tube 31 is separated from the outer peripheral surface of the excimer lamp 40 (specifically, the outer peripheral surface of the arc tube 41 provided with the external electrode 48) over the entire inner peripheral surface of the outer tube 31. It is said that.
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space where ozone generated in the ozone generation layer does not leak.
- excimer discharge is generated inside the arc tube 41 by applying a high-frequency high voltage to the internal electrode 44 and the external electrode 48 of the excimer lamp 40 by a high-frequency power source.
- Excimer light corresponding to the type of working gas or the type of ultraviolet light emitting phosphor is emitted from the outer peripheral surface of the arc tube 41 as emitted light.
- the emitted light from the excimer lamp 40 is directly emitted from the outer tube 31.
- an ozone generation layer is formed in the ozone generation layer formation space S ⁇ b> 2 between the excimer lamp 40 and the outer tube 31. For this reason, the ozone-generating ultraviolet rays contained in the radiated light of the excimer lamp 40 are selectively absorbed in the ozone-generating layer. As a result, it is possible to reduce the emission intensity of the ozone-generated ultraviolet light without reducing the emission intensity of ultraviolet light other than the ozone-generated ultraviolet light in the emitted light of the third ultraviolet radiation device 12.
- the ozone generation layer forming space S2 in which the ozone generation layer is formed is a substantially airtight closed space, ozone generated by ozone generation ultraviolet rays being absorbed in the ozone generation gas in the ozone generation layer. However, it does not leak outside the device.
- a discharge may occur between the external electrode 48 and the arc tube 41. When this discharge occurs, ozone is generated due to the discharge. Although it occurs, the ozone does not leak outside the device.
- the ozone generation layer is heated by the heat from the excimer lamp 40 and the temperature is raised, the ozone generated in the ozone generation layer is heated and thus quickly decomposed (thermally decomposed) to generate oxygen. Generated. Therefore, even if the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space, the ozone generation ultraviolet absorption capacity of the ozone generation layer does not deteriorate with time.
- the third ultraviolet radiation device 12 it is possible to suppress the generation of ozone in the ambient atmosphere outside the device, even when used in an air atmosphere, and in the excimer lamp 40, the discharge gas or By selecting and using an ultraviolet light-emitting phosphor, ultraviolet light having a desired wavelength range around 200 nm can be emitted with high emission intensity. Moreover, even if the third ultraviolet radiation device 12 generates ozone inside the device, the ozone does not leak out of the device.
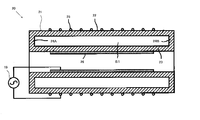
- FIG. 4 is an explanatory sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the fourth ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention.
- the fourth ultraviolet radiation device 13 is shown in FIG. 1 except that the ultraviolet light source is composed of the LED element 62, the configuration of the outer cover member 65 is different, and no reflective member is provided inside the outer cover member 65.
- the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 has the same configuration.
- the fourth ultraviolet radiation device 13 includes a plurality (9 in the illustrated example) of ultraviolet light sources composed of LED elements 62.
- the plurality of LED elements 62 are constant in the longitudinal direction (left and right direction in FIG. 4) of the LED substrate 61 on the surface (lower surface in FIG. 4) of the long rectangular flat LED substrate 61. They are arranged side by side (for example, at equal intervals).
- the light source unit 60 is constituted by the plurality of LED elements 62 and the LED substrate 61.
- the LED element 62 an appropriate one is used according to the use application of the fourth ultraviolet radiation device 13, specifically according to the wavelength range of ultraviolet rays required in the fourth ultraviolet radiation device 13. It is done. For example, those having a center wavelength in the wavelength range of 190 to 250 nm are used. In the LED element having the center wavelength in the wavelength range of 190 to 250 nm used as the LED element 62, light including ozone-generated ultraviolet rays is emitted.
- all of the plurality of LED elements 62 may be of the same type, or part or all of them may be of different types.
- the outer cover member 65 includes an LED substrate 61, an ozone generation layer forming member (hereinafter also referred to as a “window forming flat plate member”) 66 that transmits ultraviolet rays from the plurality of LED elements 62, and the LED substrate 61.
- the structure is basically the same as that of the mantle member 30 in the first ultraviolet radiation device 10 according to FIG. 1 except that the frame member 67 is disposed along the frame member 67.
- a rectangular tubular mantle tube is constituted by the LED substrate 61, the window forming flat plate member 66, and the side surface portion (not shown) of the frame member 67 extending in the longitudinal direction of the LED substrate 61.
- the outer cover member 65 is disposed along the periphery of the LED substrate 61 so as to surround the LED substrate 61 and the surface of the LED substrate 61 (the surface on which the plurality of LED elements 62 are disposed).
- a rectangular frame member 67 is made of a material having ultraviolet resistance and ozone resistance such as fluorine-based resin, ceramics, and metal, and is configured by four flat plate-like parts perpendicular to the LED substrate 61.
- a fitting groove 68 having a rectangular cross section is formed over the entire circumference of the inner peripheral surface on the front end side (the lower end side in FIG. 4) of the inner peripheral surface of the frame member 67.
- the window forming flat plate member 66 is supported in a state parallel to the LED substrate 61 by a frame member 67.
- the outer cover member 65 is disposed so as to surround the plurality of LED elements 62 in a state in which the window forming flat plate member 66 is separated from the plurality of LED elements 62, and the window forming flat plate member 66 and the light source unit 60 (the plurality of LED elements).
- An ozone generation layer is formed in the ozone generation layer formation space S2 between the element 62).
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space in which ozone generated in the ozone generation layer does not leak.
- ozone decomposition means including a device for thermally decomposing ozone generated in the ozone generation layer, that is, a device for heating the ozone generation layer may be arranged.
- the ozonolysis means include, for example, a heater.
- the plurality of LED elements 62 are turned on all at once, so that the radiation light (ultraviolet rays) from the plurality of LED elements 62 is directly or partially. The other part is reflected by the frame member 67 and then emitted from the window forming flat plate member 66.
- an ozone generation layer is formed in the ozone generation layer formation space S ⁇ b> 2 between the light source unit 60 (the plurality of LED elements 62) and the window forming flat plate member 66. Therefore, the ozone generating ultraviolet rays contained in the radiated light of the light source unit 60 are selectively absorbed in the ozone generating layer. As a result, the emission intensity of the ozone-generated ultraviolet light can be reduced without reducing the emission intensity of ultraviolet light other than the ozone-generated ultraviolet light in the outgoing light of the fourth ultraviolet radiation device 13.
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 in which the ozone generation layer is formed is a substantially airtight closed space, ozone generated by the ozone generation layer absorbing ozone generation ultraviolet rays in the ozone generation layer. , It will not leak outside the device.
- the ozone generation layer is brought into a high temperature state by heat from the light source unit 60 and heat from a heating means such as a heater provided as necessary, ozone generated in the ozone generation layer Is heated, so that it is quickly decomposed (thermally decomposed) to generate oxygen.
- the ozone generation layer formation space S2 is a substantially airtight closed space, the ozone generation ultraviolet absorption capacity of the ozone generation layer does not deteriorate with time. Therefore, according to the 4th ultraviolet radiation device 13, even if it is a case where it uses in an atmospheric condition, generation
- Such an ultraviolet radiation device of the present invention can be suitably used in a use application where ultraviolet rays having a wavelength range of 190 nm to 250 nm are required in a living space. Specifically, for example, it can be suitably used for skin sterilization treatment using ultraviolet rays having a wavelength of 230 nm or less.
- the ozone generation layer formation space between the ultraviolet light source and the ozone generation layer formation member need not be a closed space, but may be an open space. Even when the ozone generation layer formation space is an open space, the ozone generation layer is heated by heat from an ultraviolet light source, etc., so that the temperature is high, and the ozone generation gas constituting the ozone generation layer flows. Therefore, ozone generated in the ozone generation layer is quickly decomposed (thermally decomposed). Therefore, ozone generated in the ozone generation layer does not leak outside the apparatus.
- the ozone generation layer between the ultraviolet light source and the ozone generation layer forming member may be arranged in the formation space.
- Ozone decomposition means may be arranged in the formation space.
- the ozonolysis means an apparatus for thermally decomposing ozone generated in the ozone generation layer, specifically, for example, a heater or the like can be used.
- the first ultraviolet radiation device has a configuration in which the base member is not provided at both ends of the outer tube, and the outer tube and the arc tube of the excimer lamp are connected by glass processing or an adhesive. May be.
- Example 1 An ultraviolet radiation device having the configuration shown in FIG. 1 (hereinafter also referred to as “ultraviolet radiation device (1)”) was produced.
- the produced ultraviolet radiation device (1) has the following specifications.
- the measurement mechanism is provided with an ultraviolet irradiation window member 73 on the bottom surface, an air inlet 72A is formed on one of the side surfaces facing each other, and an exhaust port 72B is formed on the other side surface.
- a rectangular box-shaped casing 72 is provided. The intake port 72A and the exhaust port 72B are disposed to face each other.
- an intake fan 74A is disposed so as to close the intake port 72A
- an exhaust fan 74B is disposed so as to close the exhaust port 72B.
- a spectral irradiance meter 75 (“USR-45DA” (USHIO Inc.)) is disposed outside the casing 72 so as to face the ultraviolet irradiation window member 73, and is opposed to the exhaust port 72B.
- an ozone concentration meter 76 (“SM70” (manufactured by Aeroqual) is arranged.
- the object to be measured 79 that is, the ultraviolet radiation device (1) is disposed at a position between the intake fan 74 ⁇ / b> A and the exhaust fan 74 ⁇ / b> B inside the housing 72, and the ultraviolet radiation area of the outer tube is the ultraviolet radiation window member 73. Arranged to face each other.
- Excimer lamp (1) An excimer lamp similar to the excimer lamp (hereinafter also referred to as “excimer lamp (1)”) that constitutes the ultraviolet radiation device (1) according to the first embodiment is manufactured by the same method as in the first embodiment.
- the ultraviolet output (light emission intensity) of the ultraviolet radiation device (1) according to Example 1 is based on the cumulative light emission intensity of ultraviolet rays in the wavelength range of 200 to 230 nm in the excimer lamp (1) according to Comparative Example 1.
- the relative value of the integrated emission intensity in the wavelength range of 200 to 230 nm in the ultraviolet radiation device (1) is shown as 1.
- the ozone concentration of the ultraviolet radiation device (1) is set to 1 based on the ozone concentration in the external environment atmosphere at the time of operation of the excimer lamp (1). The relative value of the ozone concentration is shown.
- the ultraviolet radiation device (1) it is possible to suppress the generation of ozone in the ambient atmosphere outside the device, even when it is used in the atmospheric air, and the wavelength. It was confirmed that ultraviolet rays near 200 nm can be emitted with high emission intensity. More specifically, an ozone generating layer is provided between the outer tube and the excimer lamp (1) by arranging the outer tube (ozone generating layer forming member) so as to surround the excimer lamp (1). According to the ultraviolet radiation device (1) having the configuration, although the radiation intensity of ultraviolet rays in the wavelength range of 200 to 230 nm is reduced by only 5%, the ozone concentration in the atmosphere outside the device is reduced to 1/3 or less. Obviously you can.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Physical Or Chemical Processes And Apparatus (AREA)
- Apparatus For Disinfection Or Sterilisation (AREA)
- Radiation-Therapy Devices (AREA)
- Vessels And Coating Films For Discharge Lamps (AREA)
Abstract
La présente invention vise à fournir un dispositif de rayonnement ultraviolet qui est capable d'émettre de la lumière ultraviolette ayant une longueur d'onde d'environ 200 nm avec une haute intensité lumineuse, et qui est également capable de supprimer la génération d'ozone dans l'environnement à l'extérieur du dispositif meme si le dispositif est utilisé dans l'atmosphère. À cet effet, la présente invention concerne un dispositif de rayonnement ultraviolet équipé: d'une source de lumière ultraviolette qui émet de la lumière comprenant la lumière ultraviolette ayant une longueur d'onde qui est absorbée par l'oxygène et génère de l'ozone; d'un élément de formation de couche de génération d'ozone qui est prévu à une certaine distance de la source de lumière ultraviolette et forme une couche de génération d'ozone entre ledit élément et la source de lumière ultraviolette, ladite couche de génération d'ozone étant constituée d'un gaz qui génère de l'ozone par l'absorption de lumière ultraviolette. Le dispositif de rayonnement ultraviolet est caractérisé en ce que la lumière provenant de la source de lumière ultraviolette est émise à travers l'élément de formation de couche de génération d'ozone.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016050936A JP6561881B2 (ja) | 2016-03-15 | 2016-03-15 | 紫外線放射装置 |
| JP2016-050936 | 2016-03-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017159342A1 true WO2017159342A1 (fr) | 2017-09-21 |
Family
ID=59851450
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/007694 WO2017159342A1 (fr) | 2016-03-15 | 2017-02-28 | Dispositif de rayonnement ultraviolet |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6561881B2 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2017159342A1 (fr) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11295946B2 (en) * | 2020-07-14 | 2022-04-05 | Unilam Co., Ltd. | Triple tube type excimer lamp |
| EP4230166A1 (fr) * | 2022-02-17 | 2023-08-23 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Dispositif de traitement à lumière |
| JP7549294B2 (ja) | 2021-02-03 | 2024-09-11 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | エキシマランプ |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2559216B (en) * | 2017-07-17 | 2019-02-06 | Acxel Tech Ltd | An electrowetting on dielectric droplet manipulation device |
| JP6493703B1 (ja) | 2017-09-28 | 2019-04-03 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | 殺菌方法、殺菌装置 |
| CA3100907A1 (fr) * | 2018-06-08 | 2019-12-12 | Stephen R. Wood | Dispositif dote d'une surface auto-desinfectante |
| JP7182078B2 (ja) * | 2019-03-29 | 2022-12-02 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | 殺菌状態検出方法、殺菌方法、殺菌状態検出装置、殺菌装置 |
| US11020502B1 (en) | 2020-05-01 | 2021-06-01 | Uv Innovators, Llc | Ultraviolet (UV) light emission device, and related methods of use, particularly suited for decontamination |
| KR102346972B1 (ko) * | 2020-10-08 | 2022-01-05 | 조병우 | 방역 살균을 위한 램프 팩키지 |
| KR102427239B1 (ko) * | 2020-10-22 | 2022-08-22 | (주)아덴하이진 | 인체무해 uv광원을 이용한 살균장치 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS52151269A (en) * | 1976-06-04 | 1977-12-15 | Perkin Elmer Corp | Ozone absorption control device |
| JPS6271533A (ja) * | 1985-09-26 | 1987-04-02 | Toshiba Corp | 紫外線照射装置 |
| JP2006092800A (ja) * | 2004-09-21 | 2006-04-06 | Harison Toshiba Lighting Corp | 紫外線ランプ、空気清浄機 |
-
2016
- 2016-03-15 JP JP2016050936A patent/JP6561881B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-02-28 WO PCT/JP2017/007694 patent/WO2017159342A1/fr active Application Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS52151269A (en) * | 1976-06-04 | 1977-12-15 | Perkin Elmer Corp | Ozone absorption control device |
| JPS6271533A (ja) * | 1985-09-26 | 1987-04-02 | Toshiba Corp | 紫外線照射装置 |
| JP2006092800A (ja) * | 2004-09-21 | 2006-04-06 | Harison Toshiba Lighting Corp | 紫外線ランプ、空気清浄機 |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11295946B2 (en) * | 2020-07-14 | 2022-04-05 | Unilam Co., Ltd. | Triple tube type excimer lamp |
| JP7549294B2 (ja) | 2021-02-03 | 2024-09-11 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | エキシマランプ |
| EP4230166A1 (fr) * | 2022-02-17 | 2023-08-23 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Dispositif de traitement à lumière |
| WO2023156325A1 (fr) * | 2022-02-17 | 2023-08-24 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Dispositif de traitement par la lumière |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017168252A (ja) | 2017-09-21 |
| JP6561881B2 (ja) | 2019-08-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6561881B2 (ja) | 紫外線放射装置 | |
| CN110167605B (zh) | 紫外线杀菌装置 | |
| JP6558376B2 (ja) | 紫外線放射装置 | |
| JP6604339B2 (ja) | 紫外線殺菌装置 | |
| JP6365096B2 (ja) | 紫外線照射式オゾン生成装置 | |
| WO2017033727A1 (fr) | Générateur d'ozone | |
| JP6564663B2 (ja) | エキシマランプ装置 | |
| WO2014148325A1 (fr) | Lampe à excimère fluorescent et appareil de traitement de fluide | |
| TW526287B (en) | Dielectric barrier discharge lamp and dry cleaning device using the same | |
| JP2006040867A (ja) | エキシマランプ装置 | |
| JP6947261B1 (ja) | 紫外線照射装置 | |
| JP6693331B2 (ja) | オゾン発生器 | |
| JP4736900B2 (ja) | ショートアーク型水銀ランプ | |
| JP2012240033A (ja) | 紫外線浄化処理装置 | |
| JP2011048968A (ja) | 低圧水銀ランプ及び、殺菌または消毒方法 | |
| JP2021051937A (ja) | バリア放電ランプおよび紫外線照射ユニット | |
| JP2005222905A (ja) | エキシマランプ | |
| JP3564988B2 (ja) | 光源装置 | |
| JP6972657B2 (ja) | 光処理装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP3178184B2 (ja) | 誘電体バリヤ放電ランプ | |
| JPH07330308A (ja) | 短波長紫外線ランプ | |
| RU225358U1 (ru) | Открытый бактерицидный обеззараживатель для санитарно-бытовых помещений железнодорожного транспорта | |
| WO2024166702A1 (fr) | Élément émetteur de lumière ultraviolette et dispositif de rayonnement de lumière ultraviolette | |
| TWI825353B (zh) | 紫外線照射裝置 | |
| RU2746384C1 (ru) | Бактерицидный облучатель |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17766345 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17766345 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |