WO2017130620A1 - Photoresist component concentration measurement device and concentration measurement method - Google Patents
Photoresist component concentration measurement device and concentration measurement method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017130620A1 WO2017130620A1 PCT/JP2016/088687 JP2016088687W WO2017130620A1 WO 2017130620 A1 WO2017130620 A1 WO 2017130620A1 JP 2016088687 W JP2016088687 W JP 2016088687W WO 2017130620 A1 WO2017130620 A1 WO 2017130620A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- photoresist
- stripping solution
- concentration
- photoresist stripping
- measuring
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N23/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00
- G01N23/22—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00 by measuring secondary emission from the material
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N23/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00
- G01N23/22—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00 by measuring secondary emission from the material
- G01N23/223—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00 by measuring secondary emission from the material by irradiating the sample with X-rays or gamma-rays and by measuring X-ray fluorescence
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G03—PHOTOGRAPHY; CINEMATOGRAPHY; ANALOGOUS TECHNIQUES USING WAVES OTHER THAN OPTICAL WAVES; ELECTROGRAPHY; HOLOGRAPHY
- G03F—PHOTOMECHANICAL PRODUCTION OF TEXTURED OR PATTERNED SURFACES, e.g. FOR PRINTING, FOR PROCESSING OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; MATERIALS THEREFOR; ORIGINALS THEREFOR; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR
- G03F7/00—Photomechanical, e.g. photolithographic, production of textured or patterned surfaces, e.g. printing surfaces; Materials therefor, e.g. comprising photoresists; Apparatus specially adapted therefor
- G03F7/26—Processing photosensitive materials; Apparatus therefor
- G03F7/42—Stripping or agents therefor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/027—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus and a concentration measuring method for measuring a photoresist concentration in a photoresist stripping solution used for photolithography.
- miniaturization and multilayering of wiring circuits are progressing along with high integration of semiconductor elements and reduction in chip size. Further, not only such minute parts but also an FPD (Flat Panel Display) such as a liquid crystal display requires a minute wiring circuit to form a pixel. In order to manufacture such a minute wiring circuit, a photolithography technique is essential.
- a material film for forming a wiring circuit is formed, and a photoresist is applied on the film. Then, after the photoresist is exposed to a pattern corresponding to the wiring and removed, the material film is etched. Finally, the photoresist is removed. In a positive photoresist, a photoresist stripping solution is used to remove the exposed photoresist.
- the photoresist stripping solution is used repeatedly to some extent, the photoresist concentration gradually increases.
- the repeated use of a photoresist stripper is an economic problem.
- the photoresist concentration increases to some extent, it is a problem in product quality that the use is stopped.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a method of obtaining the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution from the absorbance. This method utilizes the phenomenon that the absorbance increases as the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution increases. That is, the absorbance of the photoresist stripping solution whose photoresist concentration is known is obtained in advance, and the photoresist concentration is determined using this as the calibration curve.
- the concentration measurement by absorbance has a problem that the absorbance of the photoresist stripping solution changes with time even if the photoresist concentration is constant. This is probably because the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is gradually decomposed into low molecules, and the peak of the absorption spectrum is shifted to the low wavelength side.
- Patent Document 1 is a method using absorbance.
- the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is gradually decomposed into low molecules, and the peak of the absorption spectrum is shifted to the low wavelength side.
- photoresist strip molecules having various absorption spectra are mixed in the photoresist stripping solution.
- the calibration curve obtained in advance cannot be used with time, lacks accuracy, and it is impossible to accurately grasp the concentration of the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution. Had. In addition, there is a problem that the color changes when the photoresist component of the photoresist stripping solution is decomposed, causing an error in density measurement.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus and a photoresist component concentration measuring method capable of measuring accurately and accurately.
- the present invention specifies an element that is contained in the photoresist and is not contained in the photoresist stripping stock solution, and the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution. In this way, the intended purpose is achieved.
- the specific element is sulfur, and more specifically, the amount of sulfur is measured by fluorescent X-rays. More specifically, the concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution is calculated from the measured amount of fluorescent X-rays.
- a component that is contained in the photoresist but not in the photoresist stripping solution but does not decompose or change in the photoresist stripping solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified component in the photoresist stripping solution is measured. is there.
- the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution that is, the concentration of the dissolved resist in the photoresist stripping solution can be measured accurately and accurately.
- sulfur is contained in the photosensitive material component of the photoresist, and sulfur is contained when the photoresist stripping solution does not contain sulfur.
- Specified specific components may be photoresist, contained in the photoresist stripping stock solution and not decomposed in the photoresist stripping solution, and may be elements, chemical substances, or chemical components.
- an element that is included in the photoresist and is not included in the photoresist stripping solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution is measured.
- a photoresist component concentration measuring device that can accurately and accurately measure the photoresist concentration dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, the dissolved photoresist concentration, and A method for measuring the concentration of a photoresist component can be provided.
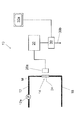
- FIG. 1 shows the configuration of a photoresist stripping apparatus 50 incorporating the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to the present embodiment.
- the photoresist stripping device 50 includes a photoresist stripping solution tank 52, a conveyor 54 that conveys the workpiece 60, a shower 56 that sprays the photoresist stripping solution M on the workpiece 60, and the photoresist component concentration measuring device 10.
- the photoresist stripping apparatus 50 operates as follows. The workpiece 60 is placed on the conveyor 54 and transferred. Then, the photoresist stripping solution M is sprayed on the photoresist stripping solution tank 52, and the photoresist is stripped. The photoresist stripping solution M is recycled.
- the specified specific component may be an element, a chemical substance, or a chemical component as long as it is not contained in the photoresist stripping solution and is not decomposed or changed in the photoresist stripping solution.
- the photoresist stripping stock solution refers to an unused photoresist stripping solution after preparation.
- the photoresist when the photoresist contains NQD (naphthoquinone diazide sulfonate ester) as a photosensitizer and a novolak resin as a polymer resin, the photoresist contains sulfur, that is, a sulfur element.
- NQD naphthoquinone diazide sulfonate ester
- the photoresist stripping stock solution has a composition of MEA (monoethanolamine), BDG (diethylene glycol monobutyl ether) and water
- the photoresist stripping stock solution does not contain sulfur, that is, elemental sulfur.
- the sulfur element itself will change even if the sulfur-containing component changes due to decomposition in the photoresist stripping solution. There is nothing to do.
- the concentration of the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution that is the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, The dissolved photoresist concentration can be calculated, and the photoresist concentration dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution can be measured accurately and accurately.
- the photoresist stripping solution M to be circulated is stored in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 and sent to the shower 56 via the shower pipe 56b by the pump 56a.
- the shower pipe 56b is preferably provided with a filter 56c. This is because clogging can be prevented by the solid content of the photoresist.
- the process returns to the photoresist stripping solution tank 52.
- the photoresist stripping solution M is used cyclically.
- the photoresist in the photoresist stripper M is dissolved in the photoresist stripper M after being stripped.
- the concentration of the dissolved photoresist in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 increases with time. Accordingly, the photoresist stripping solution M in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 is partially or entirely replaced with a new solution which is a photoresist stripping solution stock solution when the dissolved dissolved photoresist reaches a certain concentration.
- the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 takes out the photoresist stripping solution M from the photoresist stripping solution tank 52, measures the amount of sulfur as a specific element in the dissolved photoresist, and strips the photoresist again. It returns to the liquid tank 52.
- reference numeral 12 i denotes an inlet for the photoresist stripping solution M
- reference numeral 18 o denotes an outlet for returning the photoresist stripping solution M obtained by measuring the amount of sulfur in the dissolved photoresist to the photoresist stripping solution tank 52.
- the photoresist stripping solution M whose amount of sulfur is measured may be discharged out of the system without returning to the photoresist stripping solution tank 52.
- FIG. 2 shows the configuration of the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10.
- the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 includes a drawing pipe 12 communicating with the photoresist stripping solution tank 52, the drawing pipe 12, and a measuring unit 14 for measuring the photoresist stripping liquid M passing through the drawing pipe 12.
- a return pipe 18 is provided for returning the photoresist stripper M to the photoresist stripper tank 52.
- the fluorescent X-ray measuring device 20 as a measuring means for measuring the amount of sulfur as the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution M in the measuring unit 14, and the sulfur of the fluorescent X-ray measuring device 20
- a controller 30 is provided as calculation means for calculating the photoresist component concentration in the photoresist stripping solution M from the quantity measurement value.
- the extraction pipe 12 takes out a part of the photoresist stripping solution M from the photoresist stripping solution tank 52. Further, the drawing pipe 12 is provided with a pump 12a for transferring the photoresist stripping solution M. The pump 12a adjusts the pressure in the extraction pipe 12 at such a pressure that the photoresist stripping solution M can be handled without any trouble by the measurement unit 14 provided on the downstream side.
- the measuring unit 14 as a measuring means is provided continuously in the extraction pipe 12 so that the fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus 20 measures the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M, that is, the amount of sulfur. In FIG. 2, it is a portion that is continuously provided on the extraction pipe 12. In order to irradiate the photoresist stripping solution M with X-rays from the fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20, the measurement unit 14 uses a material that transmits X-rays.
- the form of the measuring unit 14 as a measuring means is not particularly limited.
- a resin pipe that transmits X-rays as viewed from fluorescent X-rays communicates with the extraction pipe 12 as the measurement unit 14, or a measurement container that temporarily stores the photoresist stripping solution M from the extraction pipe 12 continues to the extraction pipe 12. It is possible to consider a form in which it is provided.
- the measurement unit 14 is configured by a pipe (hereinafter referred to as “transmission pipe”) 24 that transmits X-rays communicated with the extraction pipe 12.
- transmission pipe a pipe that transmits X-rays communicated with the extraction pipe 12.
- the transmission pipe 24 is made of a material that is hardly deteriorated by the photoresist stripping solution and transmits X-ray fluorescence. Examples include fluororesin, polyester, polypropylene, and the like, which are made of a material that transmits fluorescent X-rays when sulfur is measured by fluorescent X-rays.
- not all the transmission pipes 24 may be formed of a material that transmits X-rays. That is, only the portion where X-rays are emitted and fluorescent X-rays are generated may be the transmission pipe 24, and the other portion may be a metal pipe such as stainless steel. Moreover, it is good also as piping material which X-ray permeate
- FIG. 1 A block diagram illustrating an exemplary computing system.
- the photoresist stripping solution M obtained from the extraction pipe 12 may be received once in a measurement container, and the amount of sulfur may be measured with the photoresist stripping solution in the measurement container.
- the return pipe 18 communicates with the permeation pipe 24. Therefore, the photoresist stripping solution M sucked up from the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 by the pump 12 a passes through the extraction pipe 12, passes through the permeation pipe 24, and passes through the return pipe 18 to enter the photoresist stripping liquid tank 52. Return to.
- the fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus 20 as a measuring means measures sulfur (S) as a specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution M.
- the positive photoresist is composed of a photosensitive agent NQD (naphthoquinone diazide sulfonate ester) and a novolac resin.
- the exposed NQD becomes indenecarboxylic acid in the presence of alcohol and dissolves in an alkaline solution. Then, the bonds between the novolak resins are broken, and the exposed photoresist is peeled off and dissolved with an alkaline solution.
- the photoresist stripping solution M is composed of a new solution which is a stock solution of the photoresist stripping solution M, a dissolved novolak resin, and a dissolved NQD including a dissolved and changed structure.
- the dissolved novolak resin and the dissolved NQD including those that have been dissolved and changed structure are called photoresist components.
- the photoresist component is a dissolved dissolved photoresist.
- photoresist components that is, dissolved photoresists, are not all in a single form, but also include large lumps or those dissolved and decomposed to the basic structure of novolak resin.
- the amount of sulfur present in NQD does not change. Therefore, by measuring the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M, the concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution M, that is, the dissolved dissolved photoresist concentration can be stably measured.
- the amount of sulfur that is, the amount of sulfur may be a value obtained by measuring the intensity of fluorescent X-rays of sulfur. That is, the sulfur amount may be the characteristic X-ray intensity (kcps) of sulfur.
- the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus of the present invention uses sulfur in the photoresist component as an index of the concentration of the photoresist component, that is, the dissolved dissolved photoresist concentration. Therefore, if the component in the photoresist stripping solution contains a sulfate group, the concentration of the photoresist component cannot be accurately measured.
- the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 can be used when the photoresist stripping solution is composed only of a material that does not contain a sulfur element.
- the element contained in the photoresist and not contained in the photoresist stripping solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution is measured.
- FIG. 2 shows the detection unit 20a of the fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20 in which an X-ray irradiation unit and a light receiving unit are combined.
- the irradiation unit and the light receiving unit may have different configurations.
- a controller 30 may be provided.
- the controller 30 calculates the photoresist component concentration in the photoresist stripping solution M from the flow rate of the photoresist stripping solution M in the permeation pipe 24 and the amount of sulfur measured by the fluorescent X-ray measuring device 20, and displays it on the display 30a. To display.
- the photoresist component concentration may be calculated as follows. First, a calibration solution having a determined photoresist component concentration is caused to flow through the permeation pipe 24 at a predetermined flow rate. Then, it is measured by the fluorescent X-ray measurement device 20.
- This measurement provides a calibration curve for the photoresist component concentration with respect to the measured sulfur content. Based on this calibration curve, the concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution M may be calculated.
- the controller 30 may have a transmission line 30b for transmitting a signal to another device when the photoresist component concentration reaches a certain value. This is to replace all or part of the photoresist stripping solution M in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 when the photoresist component concentration of the photoresist stripping solution M reaches a certain value.
- the operation of the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 having the above configuration will be described.
- the photoresist stripping solution M is transferred to the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 through the drawing pipe 12 (see FIG. 1).
- the internal pressure in the extraction pipe 12 is adjusted by the pump 12a, and the photoresist stripping solution M is sent to the permeation pipe 24.
- the photoresist remover M that has passed through the permeation pipe 24 is returned to the photoresist remover tank 52 through the return pipe 18.
- the fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20 measures the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M flowing in the transmission pipe 24 according to an instruction from the controller 30. Then, the measured value is notified to the controller 30.
- Controller 30 calculates the sulfur concentration in photoresist stripping solution M using a calibration curve prepared in advance. Therefore, the controller 30 that performs such an operation may be referred to as calculation means. The calculated sulfur concentration is displayed on the display 30a. Moreover, it transmits as a signal to another apparatus (30b).
- the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 does not contain the photoresist stripping solution stock solution but contains the dissolved photoresist.
- the photoresist stripping solution M is based on sulfur atoms in the photoresist. Since the concentration of the photoresist component therein is measured, accurate concentration measurement can be performed even if the dissolved resist component in the photoresist stripping solution M is decomposed, changes over time, or changes in color.
- the photoresist stripping solution was composed of 19% MEA (monoethanolamine), 60% BDG (diethylene glycol monobutyl ether), and 21% water. None of the materials contains elemental sulfur.
- a positive photoresist using a novolak resin was exposed to light and then dried and powdered. Sulfur was used as a specific element.
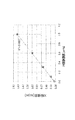
- the horizontal axis represents the concentration of the photoresist component which is the concentration of the dissolved photoresist (shown as “PR addition concentration [wt%]”), and the vertical axis represents the fluorescent X-ray intensity (“X-ray intensity”). (Kcps) ”).
- the X-ray intensity derived from the photoresist addition concentration and sulfur (S) with respect to the stripping solution has a wide range from a low concentration of 0.1 wt% or less to a high concentration of 1.0 wt%. There was a positive high correlation. Further, when the same sample was left for one week and remeasured, no change was observed.
- This graph is a result of measuring the concentration of the photoresist component, that is, the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution whose concentration of dissolved dissolved photoresist is known in advance by fluorescent X-ray. This can be used as a calibration curve as a calculation means.
- the concentration of the photoresist component that is, the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution whose concentration of dissolved dissolved photoresist is not known is measured by fluorescence X
- the concentration of the photoresist component can be obtained in reverse from the X-ray intensity.
- the calibration curve may not be a graph as shown in FIG. 3, but may be a table made up of numerical data.
- the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus can be suitably used for a photoresist stripping process when performing fine processing using photolithography.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Photosensitive Polymer And Photoresist Processing (AREA)
- Exposure Of Semiconductors, Excluding Electron Or Ion Beam Exposure (AREA)
- Analysing Materials By The Use Of Radiation (AREA)
Abstract
A photoresist stripping solution used for recycling denatures over time as dissolved photoresist increases, and thus concentration measurement by absorbance suffered from the problem of a calibration curve shifting. This photoresist component concentration measurement device is characterized by being provided with a measuring means that specifies an element that is contained in a photoresist but is not contained in the photoresist stripping solution, and measures the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution.
Description
本発明は、フォトリソグラフィに用いられるフォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト濃度を測定するフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置および濃度測定方法に関する。
The present invention relates to a photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus and a concentration measuring method for measuring a photoresist concentration in a photoresist stripping solution used for photolithography.
ICやLSI等では、半導体素子の高集積化とチップサイズの縮小化に伴い、配線回路の微細化及び多層化が進んでいる。また、このような微小部品だけでなく、液晶ディスプレイ等のFPD(Flat Panel Display)でも画素の形成には、微小な配線回路を必要とする。このような微小配線回路を作製するためには、フォトリソグラフィの技術が必須である。
In ICs, LSIs, etc., miniaturization and multilayering of wiring circuits are progressing along with high integration of semiconductor elements and reduction in chip size. Further, not only such minute parts but also an FPD (Flat Panel Display) such as a liquid crystal display requires a minute wiring circuit to form a pixel. In order to manufacture such a minute wiring circuit, a photolithography technique is essential.
フォトリソグラフィでは、配線回路にするための材料膜を形成し、その膜上にフォトレジストを塗布する。そして、フォトレジストを配線に応じたパターンに感光させ、除去した後、材料膜をエッチングする。最後にフォトレジストを除去する。ポジ型フォトレジストでは、感光したフォトレジストを除去するために、フォトレジスト剥離液が用いられる。
In photolithography, a material film for forming a wiring circuit is formed, and a photoresist is applied on the film. Then, after the photoresist is exposed to a pattern corresponding to the wiring and removed, the material film is etched. Finally, the photoresist is removed. In a positive photoresist, a photoresist stripping solution is used to remove the exposed photoresist.
フォトレジスト剥離液は、ある程度繰り返し使用されるため、徐々にフォトレジスト濃度が高まる。フォトレジスト剥離液を繰り返し使用するのは、経済的な問題である。また、ある程度フォトレジスト濃度が高まると、使用をやめるのは、製品の品質上の問題である。
Since the photoresist stripping solution is used repeatedly to some extent, the photoresist concentration gradually increases. The repeated use of a photoresist stripper is an economic problem. In addition, when the photoresist concentration increases to some extent, it is a problem in product quality that the use is stopped.
つまり、フォトレジスト剥離液は、使用されている最中に、フォトレジスト濃度をモニタし、所定の濃度以上になったら、全部若しくは一部を交換することが必要となる。
That is, it is necessary to monitor the photoresist concentration while it is being used, and to replace all or part of the photoresist stripping solution when it reaches a predetermined concentration or more.
フォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト濃度の測定には、いくつかの方法が考えられる。大量生産を行う工場においては、短時間で、ある程度の精度で、フォトレジスト濃度を決定できる方法が必要とされる。
Several methods are conceivable for measuring the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution. In a factory that performs mass production, a method that can determine the photoresist concentration with a certain degree of accuracy in a short time is required.
特許文献1には、フォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト濃度を吸光度から求める方法が開示されている。この方法では、フォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト濃度の上昇に応じて、吸光度が高くなるという現象を利用する。つまり、予めフォトレジスト濃度の分かったフォトレジスト剥離液の吸光度を求めておき、それを検量線として、フォトレジスト濃度を決定する。
Patent Document 1 discloses a method of obtaining the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution from the absorbance. This method utilizes the phenomenon that the absorbance increases as the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution increases. That is, the absorbance of the photoresist stripping solution whose photoresist concentration is known is obtained in advance, and the photoresist concentration is determined using this as the calibration curve.
しかし、吸光度による濃度測定では、フォトレジスト濃度は一定であっても、フォトレジスト剥離液の吸光度は時間と共に変化するという課題がある。これはフォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジストが徐々に低分子に分解され、吸光スペクトルのピークが低波長側にシフトするためと考えられる。
However, the concentration measurement by absorbance has a problem that the absorbance of the photoresist stripping solution changes with time even if the photoresist concentration is constant. This is probably because the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is gradually decomposed into low molecules, and the peak of the absorption spectrum is shifted to the low wavelength side.
また、吸光度による濃度測定では、被測定物の温度管理が重要になる。
Also, in concentration measurement by absorbance, temperature management of the object to be measured is important.
実際の製造プロセスでは、数週間に渡って、フォトレジスト剥離液を継ぎ足しながら生産を継続する。つまり、さまざまな吸光スペクトルを持つ、溶解したフォトレジストの分解成分がフォトレジスト剥離液中には混在することとなる。すると、特許文献1の方法では、正確なフォトレジスト濃度を測定するのは困難であると言える。
In the actual manufacturing process, production is continued for several weeks while adding photoresist stripping solution. That is, dissolved photoresist decomposition components having various absorption spectra are mixed in the photoresist stripping solution. Then, it can be said that it is difficult to measure an accurate photoresist concentration by the method of Patent Document 1.
特許文献1は、吸光度を用いる方法である。フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジストは徐々に低分子に分解され、吸光スペクトルのピークが低波長側にシフトする。その結果、フォトレジスト剥離液中には、さまざまな吸光スペクトルを持つ、フォトレジスト成分の分子が混在することとなる。
Patent Document 1 is a method using absorbance. The photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is gradually decomposed into low molecules, and the peak of the absorption spectrum is shifted to the low wavelength side. As a result, photoresist strip molecules having various absorption spectra are mixed in the photoresist stripping solution.
その結果、吸光度を用いる方法では予め求めておいた検量線が、時間と共に利用できなくなり、正確さに欠け、フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジスト濃度を正確に把握することができないという課題を有していた。また、フォトレジスト剥離液のフォトレジスト成分が分解することによって色味が変化して、濃度測定に誤差を生じさせるという課題を有していた。
As a result, in the method using absorbance, the calibration curve obtained in advance cannot be used with time, lacks accuracy, and it is impossible to accurately grasp the concentration of the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution. Had. In addition, there is a problem that the color changes when the photoresist component of the photoresist stripping solution is decomposed, causing an error in density measurement.
本発明は、このような従来の課題を解決するものであり、フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジストが徐々に低分子に分解されても、フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジスト濃度を正確に、精度良く測定することができるフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置、およびフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法を提供することを目的とする。
The present invention solves such a conventional problem, and even if the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is gradually decomposed into low molecules, the concentration of the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is reduced. An object of the present invention is to provide a photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus and a photoresist component concentration measuring method capable of measuring accurately and accurately.
そして、この目的を達成するために、本発明は、フォトレジストに含まれていて、かつフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれない元素を特定し、その特定された特定元素のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定する構成にしたものであり、これにより所期の目的を達成するものである。
In order to achieve this object, the present invention specifies an element that is contained in the photoresist and is not contained in the photoresist stripping stock solution, and the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution. In this way, the intended purpose is achieved.
具体的には、特定元素を硫黄とするものであり、また、より具体的には、硫黄の量を蛍光X線で測定するものである。また、より具体的には、蛍光X線の測定量からフォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト成分濃度を算出するものである。
Specifically, the specific element is sulfur, and more specifically, the amount of sulfur is measured by fluorescent X-rays. More specifically, the concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution is calculated from the measured amount of fluorescent X-rays.
フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれずフォトレジスト剥離液中で分解、あるいは変化しない成分を特定し、その特定された成分のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定する構成にしたものである。
A component that is contained in the photoresist but not in the photoresist stripping solution but does not decompose or change in the photoresist stripping solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified component in the photoresist stripping solution is measured. is there.
その構成により、フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジスト、すなわちフォトレジスト剥離液中の溶解レジスト濃度を正確に、精度良く測定することができるものである。
With this configuration, the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, the concentration of the dissolved resist in the photoresist stripping solution can be measured accurately and accurately.
特定された特定成分としては、例えば、フォトレジストの感光材成分に硫黄を含有し、フォトレジスト剥離原液に硫黄を含有しない場合には、硫黄がある。
As the specified specific component, for example, sulfur is contained in the photosensitive material component of the photoresist, and sulfur is contained when the photoresist stripping solution does not contain sulfur.
特定された特定成分としては、フォトレジストが含有しフォトレジスト剥離原液には含まれず、フォトレジスト剥離液中で分解されなければ良く、元素でも、或いは化学物質、あるいは化学成分でも良い。
Specified specific components may be photoresist, contained in the photoresist stripping stock solution and not decomposed in the photoresist stripping solution, and may be elements, chemical substances, or chemical components.
本発明によれば、フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれない元素を特定し、その特定された特定元素のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定する構成にしたものである。
According to the present invention, an element that is included in the photoresist and is not included in the photoresist stripping solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution is measured.
これにより、フォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト濃度であるフォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジスト濃度、すなわち溶解フォトレジスト濃度を正確に、精度良く測定することができるフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置、およびフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法を提供することができる。
Thus, a photoresist component concentration measuring device that can accurately and accurately measure the photoresist concentration dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, the dissolved photoresist concentration, and A method for measuring the concentration of a photoresist component can be provided.
また、フォトレジスト剥離液のフォトレジスト成分が分解することによって色味が変化しても、濃度測定に誤差を生じさせない。
Also, even if the color changes due to decomposition of the photoresist component of the photoresist stripping solution, no error is caused in the concentration measurement.
以下に本発明に係るフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置について図面を用いて説明を行う。なお、以下の説明は本発明の一実施形態を例示するものであり、本発明は以下の説明に限定されることはない。本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない限りにおいて自由に改変することができる。
Hereinafter, a photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In addition, the following description illustrates one embodiment of the present invention, and the present invention is not limited to the following description. Modifications can be freely made without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
図1には、本実施の形態に係るフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置を組み込んだ、フォトレジスト剥離装置50の構成を示す。フォトレジスト剥離装置50は、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52と、被処理物60を搬送するコンベア54と、被処理物60にフォトレジスト剥離液Mを散布するシャワー56と、フォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10を有する。
FIG. 1 shows the configuration of a photoresist stripping apparatus 50 incorporating the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to the present embodiment. The photoresist stripping device 50 includes a photoresist stripping solution tank 52, a conveyor 54 that conveys the workpiece 60, a shower 56 that sprays the photoresist stripping solution M on the workpiece 60, and the photoresist component concentration measuring device 10. Have
フォトレジスト剥離装置50は、以下のように動作する。被処理物60は、コンベア54上に載置され、移送される。そして、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52上でフォトレジスト剥離液Mが散布され、フォトレジストが剥離される。フォトレジスト剥離液Mは循環使用される。
The photoresist stripping apparatus 50 operates as follows. The workpiece 60 is placed on the conveyor 54 and transferred. Then, the photoresist stripping solution M is sprayed on the photoresist stripping solution tank 52, and the photoresist is stripped. The photoresist stripping solution M is recycled.
フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれずフォトレジスト剥離液中で分解、あるいは変化しない成分を特定する。その特定された特定成分としては、フォトレジストが含有しフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれず、フォトレジスト剥離液中で分解、あるいは変化されなければ良く、元素でも、或いは化学物質、あるいは化学成分でも良い。なお、ここでフォトレジスト剥離原液とは、調製後の未使用のフォトレジスト剥離液をいう。
Identifies components that are contained in the photoresist but not in the photoresist stripping solution and do not decompose or change in the photoresist stripping solution. The specified specific component may be an element, a chemical substance, or a chemical component as long as it is not contained in the photoresist stripping solution and is not decomposed or changed in the photoresist stripping solution. Here, the photoresist stripping stock solution refers to an unused photoresist stripping solution after preparation.
例えば、フォトレジストが感光剤のNQD(ナフトキノンジアジドスルフォン酸エステル)と高分子樹脂のノボラック樹脂を含む場合は、フォトレジストは硫黄、すなわち硫黄元素を含むことになる。
For example, when the photoresist contains NQD (naphthoquinone diazide sulfonate ester) as a photosensitizer and a novolak resin as a polymer resin, the photoresist contains sulfur, that is, a sulfur element.
例えば、フォトレジスト剥離原液をMEA(モノエタノールアミン)とBDG(ジエチレングリコールモノブチルエーテル)と水の組成とした場合は、フォトレジスト剥離原液は硫黄、すなわち硫黄元素を含まないことになる。
For example, when the photoresist stripping stock solution has a composition of MEA (monoethanolamine), BDG (diethylene glycol monobutyl ether) and water, the photoresist stripping stock solution does not contain sulfur, that is, elemental sulfur.
フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれない成分、或いは元素を硫黄元素と特定すれば、硫黄を含有する成分がフォトレジスト剥離液中で分解等により変化しても硫黄元素そのものは変化することがない。
If the component contained in the photoresist and not in the photoresist stripping solution or the element is identified as sulfur element, the sulfur element itself will change even if the sulfur-containing component changes due to decomposition in the photoresist stripping solution. There is nothing to do.
したがって、その特定された特定元素である硫黄元素のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定することにより、フォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト濃度であるフォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジスト濃度、すなわち溶解フォトレジスト濃度を算出でき、フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解したフォトレジスト濃度を正確に、精度良く測定することができることとなる。
Therefore, by measuring the concentration of the specified elemental sulfur element in the photoresist stripping solution, the concentration of the photoresist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution that is the photoresist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution, that is, The dissolved photoresist concentration can be calculated, and the photoresist concentration dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution can be measured accurately and accurately.
循環使用されるフォトレジスト剥離液Mは、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52に貯留されており、ポンプ56aによってシャワー配管56bを介して、シャワー56に送られる。なお、シャワー配管56bには、フィルタ56cが備えられていると望ましい。フォトレジストの固形分等により目詰りを防止できるからである。
The photoresist stripping solution M to be circulated is stored in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 and sent to the shower 56 via the shower pipe 56b by the pump 56a. The shower pipe 56b is preferably provided with a filter 56c. This is because clogging can be prevented by the solid content of the photoresist.
そして、被処理物60のフォトレジストを剥離した後、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52に戻る。このようにフォトレジスト剥離液Mは循環的に利用される。フォトレジスト剥離液M中のフォトレジストは、剥離された後フォトレジスト剥離液Mに溶解する。
Then, after removing the photoresist of the workpiece 60, the process returns to the photoresist stripping solution tank 52. In this way, the photoresist stripping solution M is used cyclically. The photoresist in the photoresist stripper M is dissolved in the photoresist stripper M after being stripped.
これによって、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52内の溶解されたフォトレジストの濃度は、経時的に増加する。したがって、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52中のフォトレジスト剥離液Mは、溶解された溶解フォトレジストが一定濃度になったら、一部若しくは全部をフォトレジスト剥離液原液である新液と入れ替える。
Thereby, the concentration of the dissolved photoresist in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 increases with time. Accordingly, the photoresist stripping solution M in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 is partially or entirely replaced with a new solution which is a photoresist stripping solution stock solution when the dissolved dissolved photoresist reaches a certain concentration.
本発明に係るフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10は、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52からフォトレジスト剥離液Mを取り出し、溶解されたフォトレジスト中の特定元素としての硫黄の量を測定し、再びフォトレジスト剥離液槽52に戻す。
The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 according to the present invention takes out the photoresist stripping solution M from the photoresist stripping solution tank 52, measures the amount of sulfur as a specific element in the dissolved photoresist, and strips the photoresist again. It returns to the liquid tank 52.
なお、符号12iはフォトレジスト剥離液Mの吸入口であり、符号18oは溶解されたフォトレジスト中の硫黄量を測定したフォトレジスト剥離液Mをフォトレジスト剥離液槽52に戻す排出口である。
Note that reference numeral 12 i denotes an inlet for the photoresist stripping solution M, and reference numeral 18 o denotes an outlet for returning the photoresist stripping solution M obtained by measuring the amount of sulfur in the dissolved photoresist to the photoresist stripping solution tank 52.
なお、図示していないが、硫黄の量を測定したフォトレジスト剥離液Mをフォトレジスト剥離液槽52に戻さずに系外に排出しても良い。
Although not shown, the photoresist stripping solution M whose amount of sulfur is measured may be discharged out of the system without returning to the photoresist stripping solution tank 52.
図2には、フォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10の構成を示す。フォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10は、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52内に連通した引出配管12と、前記引出配管12と、前記引出配管12内を通過するフォトレジスト剥離液Mを測定する測定部14と、フォトレジスト剥離液Mを前記フォトレジスト剥離液槽52にもどす戻し配管18を有する。
FIG. 2 shows the configuration of the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10. The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 includes a drawing pipe 12 communicating with the photoresist stripping solution tank 52, the drawing pipe 12, and a measuring unit 14 for measuring the photoresist stripping liquid M passing through the drawing pipe 12. A return pipe 18 is provided for returning the photoresist stripper M to the photoresist stripper tank 52.
更に、前記測定部14内の前記フォトレジスト剥離液M中の特定された特定元素としての硫黄の量を測定する測定手段としての蛍光X線測定装置20と、前記蛍光X線測定装置20の硫黄量測定値から前記フォトレジスト剥離液M中のフォトレジスト成分濃度に算出する算出手段としての制御器30を有する。
Furthermore, the fluorescent X-ray measuring device 20 as a measuring means for measuring the amount of sulfur as the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution M in the measuring unit 14, and the sulfur of the fluorescent X-ray measuring device 20 A controller 30 is provided as calculation means for calculating the photoresist component concentration in the photoresist stripping solution M from the quantity measurement value.
引出配管12は、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52からフォトレジスト剥離液Mの一部を取り出す。また、引出配管12には、フォトレジスト剥離液Mを移送するためのポンプ12aが設けられている。ポンプ12aは、下流側に設けられる測定部14でフォトレジスト剥離液Mが支障なく取り扱えるような圧力で引出配管12中の圧力を調節する。
The extraction pipe 12 takes out a part of the photoresist stripping solution M from the photoresist stripping solution tank 52. Further, the drawing pipe 12 is provided with a pump 12a for transferring the photoresist stripping solution M. The pump 12a adjusts the pressure in the extraction pipe 12 at such a pressure that the photoresist stripping solution M can be handled without any trouble by the measurement unit 14 provided on the downstream side.
測定手段としての測定部14は、蛍光X線測定装置20がフォトレジスト剥離液M中の硫黄の量、すなわち硫黄量を測定するために、引出配管12に連続して設けられたものである。図2では、引出配管12に連続して設けられた部分である。蛍光X線測定装置20からのX線をフォトレジスト剥離液Mに照射するため、測定部14は、X線を透過する材料を用いている。
The measuring unit 14 as a measuring means is provided continuously in the extraction pipe 12 so that the fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus 20 measures the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M, that is, the amount of sulfur. In FIG. 2, it is a portion that is continuously provided on the extraction pipe 12. In order to irradiate the photoresist stripping solution M with X-rays from the fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20, the measurement unit 14 uses a material that transmits X-rays.
測定手段としての測定部14の形態は特に限定されるものではない。例えば、蛍光X線から見てX線を透過する樹脂のパイプを測定部14として引出配管12に連通したり、引出配管12から一度フォトレジスト剥離液Mを貯留する測定容器を引出配管12に連続して設けるといった形態が考えられる。
The form of the measuring unit 14 as a measuring means is not particularly limited. For example, a resin pipe that transmits X-rays as viewed from fluorescent X-rays communicates with the extraction pipe 12 as the measurement unit 14, or a measurement container that temporarily stores the photoresist stripping solution M from the extraction pipe 12 continues to the extraction pipe 12. It is possible to consider a form in which it is provided.
本実施の形態では、引出配管12に連通したX線を透過する配管(以後「透過配管」と呼ぶ。)24で測定部14を構成した場合について説明する。
In the present embodiment, a case will be described in which the measurement unit 14 is configured by a pipe (hereinafter referred to as “transmission pipe”) 24 that transmits X-rays communicated with the extraction pipe 12.
この構成では、透過配管24中を流れるフォトレジスト剥離液M中の硫黄量を測定する。透過配管24は、フォトレジスト剥離液で劣化しにくく、且つ、蛍光X線を透過する材料が用いられる。一例としてフッ素樹脂、ポリエステル、ポリプロピレン等が挙げられ、蛍光X線で硫黄を測定する際に蛍光X線が透過する材質で構成されている。
In this configuration, the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripper M flowing in the permeation pipe 24 is measured. The transmission pipe 24 is made of a material that is hardly deteriorated by the photoresist stripping solution and transmits X-ray fluorescence. Examples include fluororesin, polyester, polypropylene, and the like, which are made of a material that transmits fluorescent X-rays when sulfur is measured by fluorescent X-rays.
また、透過配管24全てがX線の透過する材料で形成されていなくてもよい。つまり、X線が照射され、蛍光X線は発生する部分だけ透過配管24とし、他の部分はステンレス鋼などの金属配管であってもよい。また、引出配管12の一部だけをX線が透過する配管材料としてもよい。
Further, not all the transmission pipes 24 may be formed of a material that transmits X-rays. That is, only the portion where X-rays are emitted and fluorescent X-rays are generated may be the transmission pipe 24, and the other portion may be a metal pipe such as stainless steel. Moreover, it is good also as piping material which X-ray permeate | transmits only part of the extraction piping 12. FIG.
なお、引出配管12から得たフォトレジスト剥離液Mを一度測定容器で受けて、測定容器内のフォトレジスト剥離液で硫黄量を測定してもよい。
Note that the photoresist stripping solution M obtained from the extraction pipe 12 may be received once in a measurement container, and the amount of sulfur may be measured with the photoresist stripping solution in the measurement container.
透過配管24には戻し配管18が連通される。したがって、ポンプ12aによって、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52から吸い上げられたフォトレジスト剥離液Mは、引出配管12を通過し、透過配管24内を通り、戻し配管18中を介してフォトレジスト剥離液槽52に戻る。
The return pipe 18 communicates with the permeation pipe 24. Therefore, the photoresist stripping solution M sucked up from the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 by the pump 12 a passes through the extraction pipe 12, passes through the permeation pipe 24, and passes through the return pipe 18 to enter the photoresist stripping liquid tank 52. Return to.
測定手段としての蛍光X線測定装置20は、フォトレジスト剥離液M中の特定された特定元素としての硫黄(S)を測定する。ポジ型フォトレジストは、感光剤のNQD(ナフトキノンジアジドスルフォン酸エステル)とノボラック樹脂で構成されている。
The fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus 20 as a measuring means measures sulfur (S) as a specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution M. The positive photoresist is composed of a photosensitive agent NQD (naphthoquinone diazide sulfonate ester) and a novolac resin.
感光されたNQDは、アルコール存在下ではインデンカルボン酸となり、アルカリ溶液に溶解する。するとノボラック樹脂同士の結合が切れ、感光されたフォトレジストはアルカリ溶液で剥離、溶解される。
The exposed NQD becomes indenecarboxylic acid in the presence of alcohol and dissolves in an alkaline solution. Then, the bonds between the novolak resins are broken, and the exposed photoresist is peeled off and dissolved with an alkaline solution.
フォトレジスト剥離液Mは、フォトレジスト剥離液Mの原液である新液と、溶解したノボラック樹脂と、溶解し構造を変えたものも含む溶解したNQDで構成されている。溶解したノボラック樹脂と、溶解し構造を変えたものも含む溶解したNQDをフォトレジスト成分と呼ぶ。フォトレジスト成分は溶解した溶解フォトレジストである。
The photoresist stripping solution M is composed of a new solution which is a stock solution of the photoresist stripping solution M, a dissolved novolak resin, and a dissolved NQD including a dissolved and changed structure. The dissolved novolak resin and the dissolved NQD including those that have been dissolved and changed structure are called photoresist components. The photoresist component is a dissolved dissolved photoresist.
これらのフォトレジスト成分、すなわち溶解フォトレジストは、全てが単一の形態ではなく、大きな塊であったり、溶解してノボラック樹脂の基本構造まで分解したものも含まれている。
These photoresist components, that is, dissolved photoresists, are not all in a single form, but also include large lumps or those dissolved and decomposed to the basic structure of novolak resin.
そして、フォトレジスト剥離液Mは循環するほど、新たなフォトレジスト成分が追加される。また、時間が経過するほど溶解した溶解フォトレジストであるフォトレジスト成分が分解して変化する。
Further, as the photoresist stripping solution M circulates, new photoresist components are added. Further, as the time elapses, the dissolved photoresist component that is dissolved dissolves and changes.
しかし、NQDに存在する硫黄の量は変化しない。したがって、フォトレジスト剥離液M中の硫黄の量を測定することで、フォトレジスト剥離液M中のフォトレジスト成分の濃度、すなわち、溶解した溶解フォトレジスト濃度を安定的に測定することができる。
However, the amount of sulfur present in NQD does not change. Therefore, by measuring the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M, the concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution M, that is, the dissolved dissolved photoresist concentration can be stably measured.
なお、ここで硫黄の量、すなわち硫黄量とは、硫黄の蛍光X線の強度を計測したものであってよい。つまり、硫黄量とは、硫黄の特性X線の強度(kcps)であってもよい。
Here, the amount of sulfur, that is, the amount of sulfur may be a value obtained by measuring the intensity of fluorescent X-rays of sulfur. That is, the sulfur amount may be the characteristic X-ray intensity (kcps) of sulfur.
以上のように、本発明のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置は、フォトレジスト成分の中の硫黄をフォトレジスト成分の濃度、すなわち、溶解した溶解フォトレジスト濃度の指標として利用する。したがって、フォトレジスト剥離液中の成分に硫酸基が含まれていると、フォトレジスト成分の濃度を正確に計測することができない。
As described above, the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus of the present invention uses sulfur in the photoresist component as an index of the concentration of the photoresist component, that is, the dissolved dissolved photoresist concentration. Therefore, if the component in the photoresist stripping solution contains a sulfate group, the concentration of the photoresist component cannot be accurately measured.
すでに説明したように、フォトレジスト剥離液は、使用済みのフォトレジスト剥離液の一部を廃棄、あるいは排出し、残りにフォトレジスト剥離原液である新液又は再生液を継ぎ足しされて使用される場合が多い。
As already explained, when the photoresist stripping solution is used after discarding or discharging a part of the used photoresist stripping solution and adding the new solution or regenerating solution as the photoresist stripping stock solution to the rest There are many.
フォトレジスト剥離原液に硫黄を含む場合は、現時点の硫黄量は、フォトレジスト成分に由来するものか、フォトレジスト剥離液自体に由来するものであるのか区別が付かなくなる。
When sulfur is contained in the photoresist stripping solution, it is impossible to distinguish whether the current sulfur amount is derived from the photoresist component or the photoresist stripping solution itself.
したがって、本発明に係るフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10は、フォトレジスト剥離液が硫黄元素を有しない材料だけで構成される場合に用いることができる。
Therefore, the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 according to the present invention can be used when the photoresist stripping solution is composed only of a material that does not contain a sulfur element.
フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液は含有しない元素を特定し、その特定された特定元素のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定するものである。
The element contained in the photoresist and not contained in the photoresist stripping solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution is measured.
これにより、元素そのものはフォトレジスト剥離液中で分解、あるいは変化しないので、フォトレジスト剥離液中に溶解した溶解レジストが分解しても、正確にフォトレジスト剥離液中の溶解した溶解レジスト濃度を求めることができるものである。
As a result, since the element itself is not decomposed or changed in the photoresist stripping solution, even if the dissolved resist dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution is decomposed, the dissolved resist concentration in the photoresist stripping solution is accurately obtained. It is something that can be done.
蛍光X線測定装置20の検出部20aは、図2では、X線照射部と受光部が1つになった物を示している。しかし、照射部と受光部は別々の構成であってもよい。
FIG. 2 shows the detection unit 20a of the fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20 in which an X-ray irradiation unit and a light receiving unit are combined. However, the irradiation unit and the light receiving unit may have different configurations.
蛍光X線測定装置20が測定したフォトレジスト剥離液M中の硫黄量を、濃度に換算するために、制御器30が備えられていてもよい。制御器30は、透過配管24中のフォトレジスト剥離液Mの流量と、蛍光X線測定装置20による硫黄測定量からフォトレジスト剥離液M中のフォトレジスト成分濃度を算出し、それを表示器30aに表示する。
In order to convert the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M measured by the fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20 into a concentration, a controller 30 may be provided. The controller 30 calculates the photoresist component concentration in the photoresist stripping solution M from the flow rate of the photoresist stripping solution M in the permeation pipe 24 and the amount of sulfur measured by the fluorescent X-ray measuring device 20, and displays it on the display 30a. To display.
また、次のようにしてフォトレジスト成分濃度を算出してもよい。まず、フォトレジスト成分濃度が決まった校正液を透過配管24中に所定の流量で流す。そして、それを蛍光X線測定装置20で計測する。
Also, the photoresist component concentration may be calculated as follows. First, a calibration solution having a determined photoresist component concentration is caused to flow through the permeation pipe 24 at a predetermined flow rate. Then, it is measured by the fluorescent X-ray measurement device 20.
この計測によって、測定された硫黄量に対するフォトレジスト成分濃度の検量線が求まる。この検量線に基づいてフォトレジスト剥離液M中のフォトレジスト成分濃度を算出してもよい。
This measurement provides a calibration curve for the photoresist component concentration with respect to the measured sulfur content. Based on this calibration curve, the concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution M may be calculated.
制御器30はフォトレジスト成分濃度が一定値に達したら、他の機器へ信号を送信する送信線30bを有していてもよい。フォトレジスト剥離液Mのフォトレジスト成分濃度が一定値に達したら、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52中のフォトレジスト剥離液Mの全部若しくは一部を入れ替えるためである。
The controller 30 may have a transmission line 30b for transmitting a signal to another device when the photoresist component concentration reaches a certain value. This is to replace all or part of the photoresist stripping solution M in the photoresist stripping solution tank 52 when the photoresist component concentration of the photoresist stripping solution M reaches a certain value.
以上の構成を有するフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10の動作について動作を説明する。フォトレジスト剥離液Mは引出配管12を通ってフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10に移送される(図1参照)。
The operation of the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 having the above configuration will be described. The photoresist stripping solution M is transferred to the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 through the drawing pipe 12 (see FIG. 1).
ポンプ12aで引出配管12内の内圧を調整し、フォトレジスト剥離液Mは、透過配管24に送られる。透過配管24を通過したフォトレジスト剥離液Mは、戻し配管18を通って、フォトレジスト剥離液槽52にもどされる。
The internal pressure in the extraction pipe 12 is adjusted by the pump 12a, and the photoresist stripping solution M is sent to the permeation pipe 24. The photoresist remover M that has passed through the permeation pipe 24 is returned to the photoresist remover tank 52 through the return pipe 18.
蛍光X線測定装置20は、制御器30の指示で透過配管24中に流れるフォトレジスト剥離液M中の硫黄の量を測定する。そして測定値は制御器30に通知される。
The fluorescent X-ray measurement apparatus 20 measures the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution M flowing in the transmission pipe 24 according to an instruction from the controller 30. Then, the measured value is notified to the controller 30.
制御器30は、予め用意されていた検量線を用いて、フォトレジスト剥離液M中の硫黄濃度を算出する。したがって、このような動作をする制御器30は算出手段といってよい。算出された硫黄濃度は、表示器30aに表示される。また、他の機器への信号として送信される(30b)。
Controller 30 calculates the sulfur concentration in photoresist stripping solution M using a calibration curve prepared in advance. Therefore, the controller 30 that performs such an operation may be referred to as calculation means. The calculated sulfur concentration is displayed on the display 30a. Moreover, it transmits as a signal to another apparatus (30b).
以上のように、本発明に係るフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置10は、フォトレジスト剥離液原液が含有せず溶解フォトレジストが含有する、例えば、フォトレジスト中の硫黄原子に基づいてフォトレジスト剥離液M中のフォトレジスト成分濃度を測定するので、フォトレジスト剥離液M中の溶解レジスト成分が分解し、経時変化し、あるいはおよび色味が変化しても正確な濃度測定を行うことが出来る。
As described above, the photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus 10 according to the present invention does not contain the photoresist stripping solution stock solution but contains the dissolved photoresist. For example, the photoresist stripping solution M is based on sulfur atoms in the photoresist. Since the concentration of the photoresist component therein is measured, accurate concentration measurement can be performed even if the dissolved resist component in the photoresist stripping solution M is decomposed, changes over time, or changes in color.
以下にフォトレジスト成分を蛍光X線測定装置で測定した実験結果を示す。分析装置としては、株式会社リガク製の走査型蛍光X線分析装置(ZSX PrimusII)を用いた。
The experimental results obtained by measuring the photoresist component with a fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus are shown below. As the analyzer, a scanning X-ray fluorescence analyzer (ZSX Primus II) manufactured by Rigaku Corporation was used.
フォトレジスト剥離液は、MEA(モノエタノールアミン)19%、BDG(ジエチレングリコールモノブチルエーテル)60%、水21%の組成のものを用いた。何れの材料も硫黄元素を含んでいない。
The photoresist stripping solution was composed of 19% MEA (monoethanolamine), 60% BDG (diethylene glycol monobutyl ether), and 21% water. None of the materials contains elemental sulfur.
サンプルのフォトレジスト成分としては、ノボラック樹脂を用いたポジ型フォトレジストを感光後、乾燥・粉末にしたものを用いた。硫黄を特定元素とした。
As the photoresist component of the sample, a positive photoresist using a novolak resin was exposed to light and then dried and powdered. Sulfur was used as a specific element.
<実験方法>
フォトレジスト剥離液に対し、サンプルのフォトレジスト成分(粉末)を溶解し、0.1、0.3、0.6、1.0wt%の擬似フォトレジスト剥離液を作成した。そして、上記分析装置でそれぞれの擬似フォトレジスト剥離液の、硫黄のみのX線(Kα線)強度を測定した。結果を図3に示す。 <Experiment method>
The photoresist component (powder) of the sample was dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution to prepare 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, and 1.0 wt% pseudo photoresist stripping solution. Then, the X-ray (Kα-ray) intensity of only sulfur of each pseudo photoresist stripping solution was measured with the above analyzer. The results are shown in FIG.
フォトレジスト剥離液に対し、サンプルのフォトレジスト成分(粉末)を溶解し、0.1、0.3、0.6、1.0wt%の擬似フォトレジスト剥離液を作成した。そして、上記分析装置でそれぞれの擬似フォトレジスト剥離液の、硫黄のみのX線(Kα線)強度を測定した。結果を図3に示す。 <Experiment method>
The photoresist component (powder) of the sample was dissolved in the photoresist stripping solution to prepare 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, and 1.0 wt% pseudo photoresist stripping solution. Then, the X-ray (Kα-ray) intensity of only sulfur of each pseudo photoresist stripping solution was measured with the above analyzer. The results are shown in FIG.
図3において、横軸は溶解フォトレジストの濃度であるフォトレジスト成分の濃度(「PR添加濃度[wt%]」と示した。)であり、縦軸は蛍光X線の強度(「X線強度(kcps)」と示した。)である。
In FIG. 3, the horizontal axis represents the concentration of the photoresist component which is the concentration of the dissolved photoresist (shown as “PR addition concentration [wt%]”), and the vertical axis represents the fluorescent X-ray intensity (“X-ray intensity”). (Kcps) ”).
図3を参照して、剥離液に対するフォトレジスト添加濃度と硫黄(S)に由来するX線強度には、0.1wt%以下の低濃度から、1.0wt%の高濃度まで、広いレンジで正の高い相関があった。また、同じサンプルを1週間放置して、再測定したところ、変化は見られなかった。
Referring to FIG. 3, the X-ray intensity derived from the photoresist addition concentration and sulfur (S) with respect to the stripping solution has a wide range from a low concentration of 0.1 wt% or less to a high concentration of 1.0 wt%. There was a positive high correlation. Further, when the same sample was left for one week and remeasured, no change was observed.
このグラフは、予めフォトレジスト成分の濃度、すなわち溶解した溶解フォトレジストの濃度がわかったフォトレジスト剥離液の硫黄の量を蛍光X線で測定した結果である。これは算出手段としての検量線として利用することができる。
This graph is a result of measuring the concentration of the photoresist component, that is, the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution whose concentration of dissolved dissolved photoresist is known in advance by fluorescent X-ray. This can be used as a calibration curve as a calculation means.
フォトレジスト成分の濃度、すなわち溶解した溶解フォトレジストの濃度がわからないフォトレジスト剥離液の硫黄の量を蛍光Xで測定した場合、X線強度からフォトレジスト成分の濃度を逆に求めることができる。
When the concentration of the photoresist component, that is, the amount of sulfur in the photoresist stripping solution whose concentration of dissolved dissolved photoresist is not known is measured by fluorescence X, the concentration of the photoresist component can be obtained in reverse from the X-ray intensity.
これは濃度を算出するといってもよい。なお、検量線は、図3のようなグラフでなくても、数値データからなるテーブルであってもよい。
This may be said to calculate the concentration. Note that the calibration curve may not be a graph as shown in FIG. 3, but may be a table made up of numerical data.
本発明に係るフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置は、フォトリソグラフィを用いた微細加工を行う際のフォトレジスト剥離工程に好適に利用することができる。
The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to the present invention can be suitably used for a photoresist stripping process when performing fine processing using photolithography.
10 フォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置
12 引出配管
12a ポンプ
12i 吸入口
14 測定部
18 戻し配管
18o 排出口
20 蛍光X線測定装置
20a 検出部
24 透過配管
30 制御器
30a 表示器
30b 送信線
50 フォトレジスト剥離装置
52 フォトレジスト剥離液槽
54 コンベア
56 シャワー
60 被処理物
56a ポンプ
56b シャワー配管
56c フィルタ
M フォトレジスト剥離液 DESCRIPTION OFSYMBOLS 10 Photoresist component density | concentration measuring apparatus 12 Extraction piping 12a Pump 12i Inlet 14 Measuring part 18 Returning pipe 18o Outlet 20 Fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus 20a Detection part 24 Transmission piping 30 Controller 30a Display 30b Transmission line 50 Photoresist peeling apparatus 52 Photoresist stripping solution tank 54 Conveyor 56 Shower 60 Processed object 56a Pump 56b Shower piping 56c Filter M Photoresist stripping solution
12 引出配管
12a ポンプ
12i 吸入口
14 測定部
18 戻し配管
18o 排出口
20 蛍光X線測定装置
20a 検出部
24 透過配管
30 制御器
30a 表示器
30b 送信線
50 フォトレジスト剥離装置
52 フォトレジスト剥離液槽
54 コンベア
56 シャワー
60 被処理物
56a ポンプ
56b シャワー配管
56c フィルタ
M フォトレジスト剥離液 DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (13)
- フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれない元素を特定し、その特定された特定元素のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定する測定手段を備えることを特徴とするフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 Photoresist component concentration measurement characterized by comprising a measurement means for identifying an element contained in a photoresist but not in a photoresist stripping stock solution and measuring the concentration of the identified specific element in the photoresist stripping solution apparatus.
- 特定元素を硫黄とする請求項1記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 2. The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the specific element is sulfur.
- 測定手段は硫黄の量を蛍光X線測定装置で測定する請求項2記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 3. The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to claim 2, wherein the measuring means measures the amount of sulfur with a fluorescent X-ray measuring apparatus.
- 蛍光X線測定装置の測定量からフォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト成分濃度を算出する算出手段を備えることを特徴とする請求項3記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 4. The photoresist component concentration measuring device according to claim 3, further comprising a calculating means for calculating a photoresist component concentration in the photoresist stripping solution from a measured amount of the fluorescent X-ray measuring device.
- フォトレジスト剥離液槽内に連通した引出配管と、前記引出配管に設けられる測定手段で測定することを特徴とする請求項4記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 5. The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to claim 4, wherein the measurement is performed by a drawing pipe communicating with the inside of the photoresist stripping solution tank and a measuring means provided in the drawing pipe.
- 引出配管に連通されたX線透過配管を備えることを特徴とする請求項5記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 6. The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to claim 5, further comprising an X-ray transmission pipe communicated with the extraction pipe.
- 引出配管から吐出される前記フォトレジスト剥離液を受ける測定容器を備えることを特徴とする請求項5記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定装置。 6. The photoresist component concentration measuring apparatus according to claim 5, further comprising a measuring container for receiving the photoresist stripping solution discharged from the drawing pipe.
- フォトレジストに含まれてフォトレジスト剥離原液に含まれない元素を特定し、その特定された特定元素のフォトレジスト剥離液中の濃度を測定することを特徴とするフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法。 A method for measuring a concentration of a photoresist component, characterized in that an element contained in a photoresist but not in a photoresist stripping stock solution is specified, and the concentration of the specified element in the photoresist stripping solution is measured.
- 特定元素を硫黄とする請求項8記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法。 The method for measuring a concentration of a photoresist component according to claim 8, wherein the specific element is sulfur.
- 硫黄の量を蛍光X線で測定する請求項9記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法。 The method for measuring a concentration of a photoresist component according to claim 9, wherein the amount of sulfur is measured by fluorescent X-rays.
- 硫黄の量から前記フォトレジスト剥離液中のフォトレジスト成分の濃度を算出する算出工程を含むことを特徴とする請求項10記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法。 The method for measuring a concentration of a photoresist component according to claim 10, further comprising a calculation step of calculating a concentration of the photoresist component in the photoresist stripping solution from an amount of sulfur.
- フォトレジスト剥離液槽内からフォトレジスト剥離液を取り出しその取り出された流動する前記フォトレジスト剥離液の硫黄の量を測定することを特徴とする請求項11記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法。 12. The method for measuring a concentration of a photoresist component according to claim 11, wherein the photoresist stripping solution is taken out of the photoresist stripping solution tank, and the amount of sulfur in the removed photoresist stripping solution is measured.
- フォトレジスト剥離液槽内からフォトレジスト剥離液を取り出しその取り出されたフォトレジスト剥離液を一度測定容器に貯留した後に硫黄の量を測定することを特徴とする請求項11記載のフォトレジスト成分濃度測定方法。 12. The photoresist component concentration measurement according to claim 11, wherein the amount of sulfur is measured after taking out the photoresist stripping solution from the photoresist stripping solution tank and storing the removed photoresist stripping solution in a measuring container once. Method.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201680079908.3A CN108604534B (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2016-12-26 | Apparatus and method for measuring concentration of photoresist component |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016-012558 | 2016-01-26 | ||
| JP2016012558A JP6643710B2 (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2016-01-26 | Photoresist component concentration measuring device and concentration measuring method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017130620A1 true WO2017130620A1 (en) | 2017-08-03 |
Family
ID=59398246
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/088687 WO2017130620A1 (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2016-12-26 | Photoresist component concentration measurement device and concentration measurement method |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6643710B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN108604534B (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI697743B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2017130620A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11715656B2 (en) * | 2019-12-26 | 2023-08-01 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Chemical liquid supplying system and method of supplying chemical liquid |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000058411A (en) * | 1998-08-04 | 2000-02-25 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Semiconductor manufacturing apparatus |
| JP2005191030A (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-14 | Sharp Corp | Apparatus and method of removing resist |
| JP2005535780A (en) * | 2002-08-09 | 2005-11-24 | イー・アイ・デュポン・ドウ・ヌムール・アンド・カンパニー | Photoresist, fluoropolymer and method for 157 nm microlithographic printing |
| JP2014096462A (en) * | 2012-11-08 | 2014-05-22 | Panasonic Corp | Device for measuring photoresist concentration and measuring method |
| JP2015162659A (en) * | 2014-02-28 | 2015-09-07 | 芝浦メカトロニクス株式会社 | Processing device and processing method |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3093975B2 (en) * | 1996-07-02 | 2000-10-03 | 株式会社平間理化研究所 | Resist stripper management system |
| JP2007316360A (en) * | 2006-05-26 | 2007-12-06 | Nishimura Yasuji | Management method and management device for water-based photoresist stripping liquid |
| JP4923882B2 (en) * | 2006-09-07 | 2012-04-25 | 三菱化学エンジニアリング株式会社 | Photoresist supply apparatus and photoresist supply method |
| JP5019393B2 (en) * | 2008-04-14 | 2012-09-05 | 東亞合成株式会社 | Method and apparatus for removing resist film on conductive polymer film |
-
2016
- 2016-01-26 JP JP2016012558A patent/JP6643710B2/en active Active
- 2016-12-26 WO PCT/JP2016/088687 patent/WO2017130620A1/en active Application Filing
- 2016-12-26 CN CN201680079908.3A patent/CN108604534B/en active Active
- 2016-12-30 TW TW105144149A patent/TWI697743B/en active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000058411A (en) * | 1998-08-04 | 2000-02-25 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Semiconductor manufacturing apparatus |
| JP2005535780A (en) * | 2002-08-09 | 2005-11-24 | イー・アイ・デュポン・ドウ・ヌムール・アンド・カンパニー | Photoresist, fluoropolymer and method for 157 nm microlithographic printing |
| JP2005191030A (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-14 | Sharp Corp | Apparatus and method of removing resist |
| JP2014096462A (en) * | 2012-11-08 | 2014-05-22 | Panasonic Corp | Device for measuring photoresist concentration and measuring method |
| JP2015162659A (en) * | 2014-02-28 | 2015-09-07 | 芝浦メカトロニクス株式会社 | Processing device and processing method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017135204A (en) | 2017-08-03 |
| TWI697743B (en) | 2020-07-01 |
| CN108604534A (en) | 2018-09-28 |
| JP6643710B2 (en) | 2020-02-12 |
| CN108604534B (en) | 2022-06-21 |
| TW201736987A (en) | 2017-10-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3093975B2 (en) | Resist stripper management system | |
| JP3869730B2 (en) | Process liquid preparation and supply method and apparatus | |
| KR102455657B1 (en) | Detergent composition for resin mask peeling | |
| SG194145A1 (en) | Photoresist stripping solution, stripping solution recycling system and operating method, and method for recycling stripping solution | |
| TW201704902A (en) | Component concentration measuring method and apparatus for developing solution, and developing solution managing method and apparatus provides a highly precise component concentration estimation method and apparatus | |
| KR20210063248A (en) | Quaternary alkyl ammonium hypochlorite solution, method of producing the same, and method for processing semiconductor wafers | |
| WO2017130620A1 (en) | Photoresist component concentration measurement device and concentration measurement method | |
| TWI312105B (en) | ||
| WO2015008443A1 (en) | Cleaning liquid, cleaning apparatus and cleaning method for resist remover liquid filtration filter | |
| JP3126690B2 (en) | Resist stripper management system | |
| WO2020022491A1 (en) | Cleaning method | |
| JPH10207082A (en) | Method for analyzing and managing alkaline developer for photoresist or waste developer thereof or processing liquid therefor and apparatus therefor | |
| JP2012242697A (en) | Stripping liquid recycling system and operation method, and method for recycling stripping liquid | |
| KR20030001335A (en) | Apparatus and method for controlling resist stripping nonaqueous solution | |
| JP2007316360A (en) | Management method and management device for water-based photoresist stripping liquid | |
| KR20080020140A (en) | Etching solution control system and etching apparatus and etching solution control method thereof | |
| JP2016136139A (en) | Measuring method and measuring device of oxidizing agent concentration, and electronic material cleaning device | |
| RU2439641C1 (en) | Method of treating liquid | |
| JP2005191030A (en) | Apparatus and method of removing resist | |
| CN104330959A (en) | Preparation method of photoresist stripping liquid | |
| TW201800751A (en) | Method and device for measuring oxidant concentration, and electronic material cleaning device | |
| JP2017050351A (en) | Carbonic acid concentration management method in resist exfoliation liquid and carbonic acid concentration managing device | |
| JP2003122029A (en) | Method for controlling resist removing liquid | |
| JP6551787B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for managing carbonic acid concentration in resist stripping solution | |
| KR100921403B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling etchant composition using spectroscope |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16888204 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16888204 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |