WO2017104441A1 - 内視鏡システム - Google Patents
内視鏡システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017104441A1 WO2017104441A1 PCT/JP2016/085869 JP2016085869W WO2017104441A1 WO 2017104441 A1 WO2017104441 A1 WO 2017104441A1 JP 2016085869 W JP2016085869 W JP 2016085869W WO 2017104441 A1 WO2017104441 A1 WO 2017104441A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- processor
- scope
- metal member
- wiring
- feedback
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00112—Connection or coupling means
- A61B1/00121—Connectors, fasteners and adapters, e.g. on the endoscope handle
- A61B1/00124—Connectors, fasteners and adapters, e.g. on the endoscope handle electrical, e.g. electrical plug-and-socket connection
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00064—Constructional details of the endoscope body
- A61B1/00071—Insertion part of the endoscope body
- A61B1/0008—Insertion part of the endoscope body characterised by distal tip features
- A61B1/00087—Tools
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00002—Operational features of endoscopes
- A61B1/00011—Operational features of endoscopes characterised by signal transmission
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00112—Connection or coupling means
- A61B1/00121—Connectors, fasteners and adapters, e.g. on the endoscope handle
- A61B1/00126—Connectors, fasteners and adapters, e.g. on the endoscope handle optical, e.g. for light supply cables
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/012—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor characterised by internal passages or accessories therefor
- A61B1/018—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor characterised by internal passages or accessories therefor for receiving instruments
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/04—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances
- A61B1/05—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances characterised by the image sensor, e.g. camera, being in the distal end portion
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/0661—Endoscope light sources
- A61B1/0669—Endoscope light sources at proximal end of an endoscope
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B18/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body
- A61B18/04—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body by heating
- A61B18/12—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body by heating by passing a current through the tissue to be heated, e.g. high-frequency current
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00131—Accessories for endoscopes
- A61B1/00135—Oversleeves mounted on the endoscope prior to insertion
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/005—Flexible endoscopes
- A61B1/01—Guiding arrangements therefore
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/0661—Endoscope light sources
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B18/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body
- A61B18/04—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body by heating
- A61B18/12—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body by heating by passing a current through the tissue to be heated, e.g. high-frequency current
- A61B18/14—Probes or electrodes therefor
- A61B18/1492—Probes or electrodes therefor having a flexible, catheter-like structure, e.g. for heart ablation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B23/00—Telescopes, e.g. binoculars; Periscopes; Instruments for viewing the inside of hollow bodies; Viewfinders; Optical aiming or sighting devices
- G02B23/24—Instruments or systems for viewing the inside of hollow bodies, e.g. fibrescopes
- G02B23/2476—Non-optical details, e.g. housings, mountings, supports
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an endoscope system.
- An endoscope system in which a scope is inserted into a lumen such as a human esophagus or intestine, and treatment is performed while observing the inside of the lumen.
- a treatment tool such as a forceps or a scalpel is passed through a scope and protruded from the distal end portion of the scope to treat the affected part in the lumen.
- a high-frequency treatment tool for performing excision of an affected part or hemostasis is known.
- Patent Document 1 discloses an endoscope system using a high-frequency knife.
- a high-frequency treatment instrument such as a high-frequency knife
- an induced current may flow in the metal member of the scope due to electromagnetic waves generated by the high-frequency treatment instrument.
- This induced current appears as noise in the captured image of the subject. Therefore, in the endoscope system described in Patent Document 1, a feedback terminal is provided in the scope in order to release the induced current.
- the feedback terminal By connecting the feedback terminal to the ground of the processor, for example, the current flowing in the metal member is released to the ground. Since the current flowing in the metal member has a high-frequency component, a capacitor for releasing the high-frequency current to the ground is usually arranged between the feedback terminal and the ground instead of the direct connection to the ground.
- a feedback terminal is provided on the outer surface of the scope. Therefore, when the used scope is washed or when the scope is transported, the insertion portion into the lumen of the scope may come into contact with the return terminal.
- the insertion part is covered with a protective tube to protect internal wiring and the like.
- a protective tube a soft material such as a thin resin is used so that the insertion portion is easily bent. Therefore, when the insertion portion comes into contact with the return terminal, the protective tube may be damaged.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide an endoscope system suitable for suppressing scope damage.
- An endoscope system includes a ground terminal provided on an exterior surface of a housing, and an external capacitor disposed on the exterior surface and disposed outside the housing.
- a processor having a feedback terminal connected to the ground terminal, a relay wiring connected to the feedback terminal and arranged in the housing, a connector part removable from the processor, and a channel into which the treatment instrument is inserted
- a scope having a feedback wiring for connecting a metal member in a position close to the channel to the connector portion.
- the metal member in the scope is grounded via the feedback wiring, the relay wiring, and the capacitor. Therefore, it is not necessary to provide a terminal for connecting a wiring for installing a metal member separately from the connector portion in the scope. Thereby, it can suppress that a scope contacts with a terminal and is damaged.
- the scope includes, for example, a flexible rod-shaped insertion portion that is inserted into a patient's lumen.
- the metal member is disposed in the insertion portion and has a long tube shape along the longitudinal direction of the insertion portion.
- the external capacitor is detachably connected to, for example, a ground terminal and a feedback terminal.
- the capacitor to be used can be easily exchanged according to the high-frequency treatment instrument to be used and the high-frequency power source.
- an endoscope system suitable for suppressing scope damage is provided.
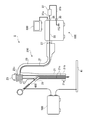
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of an endoscope system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of the endoscope system 1 of the present embodiment.
- the endoscope system 1 includes a processor 100, a scope 200, a monitor 300, a high-frequency treatment instrument 400, and a high-frequency power source 500.
- the scope 200 has an insertion portion 21 to be inserted into a patient's lumen, an operation portion 23 operated by an operator, a universal tube 25 extending from the operation portion 23, and a connector portion 27 detachably connected to the processor 100. is doing.
- a light guide that extends from the connector portion 27 to the distal end portion 21a of the insertion portion 21 and guides the irradiation light irradiated to the subject is disposed. In FIG. 1, the light guide is not shown.
- the processor 100 includes various electronic circuits for controlling the operation of the endoscope system 1, a light source unit that emits illumination light for illuminating a subject, and an operation panel that receives an operation by an operator.
- the electronic circuit, the light source unit, and the operation panel are not shown.
- the operation panel is used to change parameters relating to the operation of the endoscope system 1.
- Illumination light emitted from the light source unit enters the scope 200 via the connector unit 27.
- Illumination light incident on the scope 200 from the processor 100 is guided through the light guide, emitted from the distal end portion 21a of the insertion portion 21, and irradiated on the subject.
- the insertion portion 21 of the scope 200 has a long rod shape, and the distal end portion 21a is curved in response to an operation on the operation portion 23.
- the portions other than the distal end portion 21a of the insertion portion 21 are flexible.
- the insertion portion 21 has a surface covered with a protective tube 21b in order to protect internal wiring and structure and prevent liquid and dirt from entering the inside.
- the protective tube 21b is formed of a soft material such as a thin resin so that the flexibility of the insertion portion 21 is not impaired.
- the surgeon inserts the insertion portion 21 into the patient's lumen while bending the insertion portion 21.
- An imaging element (not shown) for imaging a subject in the lumen is provided at the distal end 21a of the insertion unit 21.
- An imaging signal of the subject imaged by the imaging element is input to the processor 100 via the connector unit 27.
- the processor 100 performs predetermined signal processing on the imaging signal of the subject input from the scope 200 to generate a video signal. By outputting this video signal to the monitor 300, a photographed image of the subject is displayed on the monitor 300.
- the scope 200 has a treatment instrument channel 29 through which various treatment instruments are inserted.
- the treatment instrument channel 29 is disposed in the insertion portion 21, one end is provided near the operation portion 23, and the other end is provided at the distal end portion 21 a of the insertion portion 21.
- the surgeon inserts the treatment instrument into the treatment instrument channel 29 from the operation unit 23 side and protrudes from the distal end 21 a of the insertion part 21.
- the surgeon can operate the treatment tool while viewing the captured image displayed on the monitor 300 to treat the affected part in the lumen.
- a high-frequency treatment instrument 400 is used as the treatment instrument inserted into the treatment instrument channel 29.
- the high-frequency treatment instrument 400 is connected to a high-frequency power source 500 that supplies a high-frequency current.
- the high-frequency treatment tool 400 is energized when a high-frequency current is supplied, and is used for performing treatment such as incision or coagulation of the affected part.
- the high-frequency treatment instrument 400 is roughly classified into a monopolar type such as a high-frequency knife and a bipolar type such as a high-frequency forceps.
- a high-frequency treatment instrument 400 shown in FIG. 1 is a monopolar type high-frequency treatment instrument 400.
- a patient counter electrode 41 is attached to the outer skin of the patient.
- the patient counter electrode 41 is connected to a high frequency power source 500.
- the high-frequency treatment tool 400 touches the body tissue in the lumen of the patient, the current supplied to the high-frequency treatment tool 400 flows to the patient counter electrode plate 41 through the patient's body. As the high-frequency current flows in this manner, Joule heat is generated and the affected area can be treated.
- the high-frequency forceps has two clamping parts that sandwich the affected part. Each of the two clamping portions is independently connected to the high frequency power source 500.
- the high-frequency current flows from one of the two clamping parts to the other through the affected part. Thereby, the treatment of the affected part pinched by the clamping part can be performed.
- the patient counter electrode 41 is not used.
- the high-frequency treatment instrument 400 When the monopolar type or the bipolar type is used as the high-frequency treatment instrument 400, it is common in that the high-frequency treatment instrument 400 generates Joule heat by a high-frequency current.
- electromagnetic noise may be generated from the high frequency treatment instrument 400.
- This electromagnetic noise can generate an induced current in the imaging element, the wiring connected thereto, the electronic circuit, the metal member 21c used for the insertion portion 21 of the scope 200, and the like that is close to the treatment instrument channel 29. There is sex.
- an induced current When an induced current is generated in the image sensor, wiring connected to the image sensor, and electronic circuit, noise may occur in a captured image of the subject.
- the insertion portion 21 is covered with a protective tube 21b that does not conduct electricity, and is configured so that the operator does not directly touch the metal member 21c.
- the metal member 21c is grounded via the processor 100 in order to more reliably prevent the surgeon from receiving an electric shock.
- the metal member 21 c is connected to the frame ground FG of the processor 100.
- the frame ground FG is, for example, a member formed of metal in the housing or chassis of the processor 100.
- the metal member 21 c has a long tube shape along the longitudinal direction of the insertion portion 21.
- the metal member 21c is disposed so as to cover the light guide and the treatment instrument channel 29, and protects them.
- a metal spiral tube is used for the metal member 21c.
- a metal spiral tube is a thin metal plate formed in a coil shape, and has flexibility. Therefore, even if the metal member 21c is disposed in the insertion portion 21, the insertion portion 21 can be flexible.
- the metal member 21 c is connected to a plate-like metal base material 23 c provided in the operation unit 23.
- the metal base material 23 c is used for supporting a bending operation knob (not shown) in the operation unit 23.
- the metal substrate 23c and the metal member 21c are electrically connected to each other and can be energized with each other.
- the metal substrate 23c and the connector part 27 are connected by a return wiring 31.
- the feedback wiring 31 is disposed from the operation unit 23 of the scope 200 to the universal cable 25, and is used to release the induced current generated in the metal member 21c to the frame ground FG.
- the feedback wiring 31 is connected to the relay wiring 33 in the processor 100 via the connector unit 27.
- the relay wiring 33 connects the feedback wiring 31 and the feedback terminal 35 provided on the exterior surface of the processor 100.
- a capacitor box 37 having a capacitor inside is disposed outside the processor 100.
- Two wirings 37 a and 37 b extend from the capacitor box 37, and the two wirings 37 a and 37 b are respectively connected to both ends of the capacitor in the capacitor box 37.
- the two wirings 37 a and 37 b extending from the capacitor box 37 are detachably connected to a feedback terminal 35 and a ground terminal 39 provided on the exterior surface of the processor 100, respectively.
- the ground terminal 39 is connected to the frame ground FG of the processor 100.
- the metal member 21 c of the insertion portion 21 is connected to the frame ground FG via the metal base 23 c of the operation portion 23, the return wiring 31, the relay wiring 33, and the capacitor box 37.
- the capacitor in the capacitor box 37 usually has a characteristic of passing an AC component of current. Therefore, by grounding the metal member 21c via the capacitor box 37 (AC coupling of the metal member 21c to the frame ground FG), high-frequency induced current generated in the metal member 21c is efficiently supplied to the frame ground FG. I can escape.
- the optimum capacity of the capacitor for allowing the induced current to escape to the frame ground FG and the electric circuit configuration of the capacitor box 37 differ depending on the frequency of the induced current. Therefore, by exchanging the capacitor box 37 connected to the processor 100 according to the high-frequency treatment instrument 400 or the high-frequency power source 500 to be used, the induced current can be more reliably released to the frame ground FG.
- the capacitor box 37 can be attached to and detached from the processor 100 (the feedback terminal 35 and the ground terminal 39), so that the capacitor box 37 can be easily replaced.
- the return wiring 31 is arranged in the scope 200 and is connected to the processor 100 via the connector unit 27. Therefore, unlike the prior art, the scope 200 of this embodiment does not need to be provided with a feedback terminal separately from the connector portion 27. Thereby, the protrusion by a feedback terminal can be reduced from the exterior of the scope 200.
- the insertion portion 21 can be prevented from coming into contact with the protrusions.
- the insertion part 21 is covered with a protective tube 21b made of a soft material. Therefore, by suppressing the contact between the insertion portion 21 and the protrusion, it is possible to suppress the soft protective tube 21b from being damaged due to the contact with the protrusion.
- the scope is provided with a connector portion and a feedback terminal separately. Therefore, in order to make the scope usable, it is necessary to separately perform the connection operation of the connector unit to the processor and the connection operation of the wiring to the feedback terminal.
- the connection portion of the feedback wiring 31 with the processor 100 (relay wiring 33) is arranged in the connector portion 27. Therefore, the feedback wiring 31 is connected to the relay wiring 33 by performing the connection operation of the connector unit 27 to the processor 100. Therefore, in this embodiment, the operation for enabling the scope 200 is easy, and it is possible to prevent the feedback wiring 31 from being forgotten to be grounded.
- the feedback wiring 31 is arranged from the connector portion 27 of the scope 200 to the operation portion 23, but the present invention is not limited to this configuration.
- the return wiring 31 may be connected to the metal member 21 c of the insertion portion 21.
- the metal member used in the insertion portion 21 is not limited to the coiled metal member 21c.
- the insertion part 21 may be disposed so as to cover the metal member 21c, for example, and may have a metal mesh formed in a tube shape.
- the metal mesh is used to shield electromagnetic noise radiated from the inside of the insertion portion 21 to the outside and electromagnetic noise entering the inside from the outside of the insertion portion 21.
- the metal mesh or both the metal mesh and the metal member 21c are connected to the metal base material 23c.
- the capacitor box 37 is connected to the processor 100 when the high frequency treatment instrument 400 is used as a treatment instrument. Therefore, the capacitor box 37 may be removed from the processor 100 when using a treatment instrument that does not need to supply a high-frequency current.
- Embodiments of the present invention are not limited to those described above, and various modifications are possible within the scope of the technical idea of the present invention.
- the embodiment of the present invention also includes contents appropriately combined with embodiments or the like clearly shown in the specification or obvious embodiments.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Otolaryngology (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
- Instruments For Viewing The Inside Of Hollow Bodies (AREA)
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201690001316.5U CN208837874U (zh) | 2015-12-16 | 2016-12-02 | 内窥镜系统 |
| US15/767,007 US20180289244A1 (en) | 2015-12-16 | 2016-12-02 | Endoscope system |
| DE112016004196.9T DE112016004196B4 (de) | 2015-12-16 | 2016-12-02 | Endoskopsystem |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015-244836 | 2015-12-16 | ||
| JP2015244836A JP6356656B2 (ja) | 2015-12-16 | 2015-12-16 | 内視鏡システム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017104441A1 true WO2017104441A1 (ja) | 2017-06-22 |
Family
ID=59056378
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/085869 Ceased WO2017104441A1 (ja) | 2015-12-16 | 2016-12-02 | 内視鏡システム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20180289244A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6356656B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN208837874U (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112016004196B4 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017104441A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11605941B2 (en) * | 2020-08-28 | 2023-03-14 | Michael Corsi | Method and system for monitoring and regulating induced ground line power |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004130126A (ja) * | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-30 | Pentax Corp | 電子内視鏡装置 |
| JP2014054318A (ja) * | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-27 | Fujifilm Corp | 内視鏡システム、内視鏡、光源装置、及びプロセッサ |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007202654A (ja) | 2006-01-31 | 2007-08-16 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp | 医療装置 |
-
2015
- 2015-12-16 JP JP2015244836A patent/JP6356656B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-12-02 US US15/767,007 patent/US20180289244A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2016-12-02 WO PCT/JP2016/085869 patent/WO2017104441A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2016-12-02 DE DE112016004196.9T patent/DE112016004196B4/de active Active
- 2016-12-02 CN CN201690001316.5U patent/CN208837874U/zh active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004130126A (ja) * | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-30 | Pentax Corp | 電子内視鏡装置 |
| JP2014054318A (ja) * | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-27 | Fujifilm Corp | 内視鏡システム、内視鏡、光源装置、及びプロセッサ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN208837874U (zh) | 2019-05-10 |
| DE112016004196B4 (de) | 2019-07-11 |
| DE112016004196T5 (de) | 2018-06-07 |
| JP2017108874A (ja) | 2017-06-22 |
| JP6356656B2 (ja) | 2018-07-11 |
| US20180289244A1 (en) | 2018-10-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4607621A (en) | Endoscopic apparatus | |
| CN109414250B (zh) | 超声波内窥镜 | |
| US8187175B2 (en) | Endoscope, endoscope apparatus, and method of connecting external equipment to endoscope | |
| EP3125740B1 (en) | Medical system and related methods for diagnosis and treatment | |
| US10070778B2 (en) | Endoscope system, endoscope, and endoscope connector | |
| WO2018221672A1 (ja) | 単回使用内視鏡装置 | |
| JP6594660B2 (ja) | 医療用カメラヘッド及び医療用カメラ装置 | |
| JP2014054318A (ja) | 内視鏡システム、内視鏡、光源装置、及びプロセッサ | |
| CN107530056B (zh) | 内窥镜用连接器 | |
| JP6356656B2 (ja) | 内視鏡システム | |
| CN109414253B (zh) | 超声波内窥镜 | |
| JP6602580B2 (ja) | 内視鏡システム | |
| JPWO2014174989A1 (ja) | 内視鏡用アダプタ及び内視鏡 | |
| KR101652417B1 (ko) | 복강경 장치 | |
| JP2007289674A (ja) | 肺癌治療カテーテル | |
| JP5458227B1 (ja) | 内視鏡の光源用電源装置とこの内視鏡の光源用電源装置を有する内視鏡システム。 | |
| JP2000245734A (ja) | 超音波内視鏡診断装置 | |
| CN112822969A (zh) | 用于一次性输尿管镜的按钮适配器 | |
| WO2014010283A1 (ja) | 超音波内視鏡 | |
| JP3210498U (ja) | 内視鏡装置のプロセッサ | |
| JPH04150826A (ja) | 内視鏡装置 | |
| JP2001061855A (ja) | 内視鏡用焼灼装置 | |
| JP7233933B2 (ja) | 電子内視鏡及び電子内視鏡システム | |
| JP3250790B2 (ja) | 内視鏡 | |
| JPS6397139A (ja) | 固体撮像素子を内装した内視鏡 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16875424 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15767007 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112016004196 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16875424 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |