WO2016009851A1 - 静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置 - Google Patents
静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016009851A1 WO2016009851A1 PCT/JP2015/069166 JP2015069166W WO2016009851A1 WO 2016009851 A1 WO2016009851 A1 WO 2016009851A1 JP 2015069166 W JP2015069166 W JP 2015069166W WO 2016009851 A1 WO2016009851 A1 WO 2016009851A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- touch panel
- display device
- light
- input device
- transparent
- Prior art date
Links
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 36
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 36
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 36
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 115
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 48
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 48
- 239000002070 nanowire Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 90
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 44
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000010419 fine particle Substances 0.000 claims description 26
- -1 copper halide Chemical class 0.000 claims description 15
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000011342 resin composition Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000002835 absorbance Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl Chemical group C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910002367 SrTiO Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910010413 TiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000009719 polyimide resin Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000004305 biphenyl Chemical group 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000010290 biphenyl Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl ether Chemical group C=1C=CC=CC=1OC1=CC=CC=C1 USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000011358 absorbing material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000031700 light absorption Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000000149 argon plasma sintering Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010946 fine silver Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 52
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 17
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000005345 chemically strengthened glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 229920003207 poly(ethylene-2,6-naphthalate) Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000011112 polyethylene naphthalate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000005388 borosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000002858 crystal cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N lead(0) Chemical compound [Pb] WABPQHHGFIMREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920006267 polyester film Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000005341 toughened glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910018182 Al—Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Carbonate Chemical compound [O-]C([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229910018054 Ni-Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910018481 Ni—Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004677 Nylon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002668 Pd-Cu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002390 adhesive tape Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L copper(II) chloride Chemical compound Cl[Cu]Cl ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002736 metal compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920001778 nylon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920001483 poly(ethyl methacrylate) polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000747 poly(lactic acid) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003229 poly(methyl methacrylate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006122 polyamide resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004431 polycarbonate resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005668 polycarbonate resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004645 polyester resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001225 polyester resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004626 polylactic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004926 polymethyl methacrylate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005672 polyolefin resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005990 polystyrene resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011343 solid material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007480 spreading Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/03—Arrangements for converting the position or the displacement of a member into a coded form
- G06F3/041—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means
- G06F3/044—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means by capacitive means
- G06F3/0443—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means by capacitive means using a single layer of sensing electrodes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B5/00—Optical elements other than lenses
- G02B5/20—Filters
- G02B5/22—Absorbing filters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B5/00—Optical elements other than lenses
- G02B5/20—Filters
- G02B5/28—Interference filters
- G02B5/281—Interference filters designed for the infrared light
- G02B5/282—Interference filters designed for the infrared light reflecting for infrared and transparent for visible light, e.g. heat reflectors, laser protection
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/13338—Input devices, e.g. touch panels
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1335—Structural association of cells with optical devices, e.g. polarisers or reflectors
- G02F1/133504—Diffusing, scattering, diffracting elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1335—Structural association of cells with optical devices, e.g. polarisers or reflectors
- G02F1/133509—Filters, e.g. light shielding masks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1335—Structural association of cells with optical devices, e.g. polarisers or reflectors
- G02F1/1336—Illuminating devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1343—Electrodes
- G02F1/13439—Electrodes characterised by their electrical, optical, physical properties; materials therefor; method of making
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/136—Liquid crystal cells structurally associated with a semi-conducting layer or substrate, e.g. cells forming part of an integrated circuit
- G02F1/1362—Active matrix addressed cells
- G02F1/136286—Wiring, e.g. gate line, drain line
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/03—Arrangements for converting the position or the displacement of a member into a coded form
- G06F3/041—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means
- G06F3/0416—Control or interface arrangements specially adapted for digitisers
- G06F3/04164—Connections between sensors and controllers, e.g. routing lines between electrodes and connection pads
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/03—Arrangements for converting the position or the displacement of a member into a coded form
- G06F3/041—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means
- G06F3/044—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means by capacitive means
- G06F3/0446—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means by capacitive means using a grid-like structure of electrodes in at least two directions, e.g. using row and column electrodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B1/00—Conductors or conductive bodies characterised by the conductive materials; Selection of materials as conductors
- H01B1/02—Conductors or conductive bodies characterised by the conductive materials; Selection of materials as conductors mainly consisting of metals or alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B5/00—Non-insulated conductors or conductive bodies characterised by their form
- H01B5/14—Non-insulated conductors or conductive bodies characterised by their form comprising conductive layers or films on insulating-supports
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/136—Liquid crystal cells structurally associated with a semi-conducting layer or substrate, e.g. cells forming part of an integrated circuit
- G02F1/1362—Active matrix addressed cells
- G02F1/136286—Wiring, e.g. gate line, drain line
- G02F1/136295—Materials; Compositions; Manufacture processes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F2203/00—Function characteristic
- G02F2203/05—Function characteristic wavelength dependent
- G02F2203/055—Function characteristic wavelength dependent wavelength filtering
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2203/00—Indexing scheme relating to G06F3/00 - G06F3/048
- G06F2203/041—Indexing scheme relating to G06F3/041 - G06F3/045
- G06F2203/04103—Manufacturing, i.e. details related to manufacturing processes specially suited for touch sensitive devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2203/00—Indexing scheme relating to G06F3/00 - G06F3/048
- G06F2203/041—Indexing scheme relating to G06F3/041 - G06F3/045
- G06F2203/04111—Cross over in capacitive digitiser, i.e. details of structures for connecting electrodes of the sensing pattern where the connections cross each other, e.g. bridge structures comprising an insulating layer, or vias through substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10K—ORGANIC ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES
- H10K59/00—Integrated devices, or assemblies of multiple devices, comprising at least one organic light-emitting element covered by group H10K50/00
- H10K59/40—OLEDs integrated with touch screens
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a display device including, as an input device, a capacitively coupled touch panel using a metal nanowire conductive film as a transparent electrode.
- An active matrix display device using thin film transistors has advantages such as thinness and light weight, and is generally used as a display device for televisions, computers, mobile phones, small portable devices, in-vehicle devices, and various other electronic devices. ing. Most of these display devices are liquid crystals comprising a combination of a liquid crystal cell in which a liquid crystal is sandwiched between a pair of transparent substrates, an optically anisotropic film bonded to both outer sides of the liquid crystal cell, and a backlight serving as a display light source.
- a display device or an organic electroluminescence display device that emits light by sandwiching an organic electroluminescence material between electrodes and changing the power applied to the electrodes to light emission.
- the touch panel is a device having a function of detecting a position by touching a screen corresponding to a display area of the display device with a finger or a pen and inputting a position coordinate or the like to the display device by combining with the display device.
- touch panels There are various types of touch panels in terms of their operating principles, but recently, capacitive touch panels are mainly used for small portable devices.
- a plurality of grid-patterned transparent electrodes composed of two layers in length and width to detect a touched position are formed on a touch panel screen on a touch panel substrate corresponding to a display device display area.
- Wiring for extracting a position detection signal from the transparent electrode is formed around the screen, and includes a wiring circuit for outputting the position detection signal to an external detection circuit.
- This method has an advantage that the position touched at high speed can be detected.
- the position is detected by detecting a change in capacitance between the fingertip and the position detection electrode. For example, when the XY position coordinates are detected individually, the X position coordinate detection electrode and the Y position coordinate detection electrode are insulated from each other.
- a metal oxide conductor such as ITO (indium tin oxide) is typically used for the transparent electrode in terms of conductivity and light transmission.
- ITO indium tin oxide
- a metal oxide film is usually formed by vacuum using a sputtering method, so that it requires formation cost.
- indium tin oxide is 200 ° C. to form a film having excellent conductivity and light transmittance. Since near high temperature conditions are required, there are problems such as high internal stress of the formed film and stress load on the formed substrate.
- a capacitively coupled touch panel using a conductive film containing metal nanowires instead of such a metal oxide film is also known.
- the metal nanowire is a conductive fiber material that has a diameter of a nanometer unit and has been developed for a transparent conductive film.
- the metal nanowires are electrically connected to each other to bring about conductive characteristics.
- metal nanowires are contained in a coating solution, and are applied onto a substrate using an ink jet method, a dispensing method, or a screen printing method, and dried to form a transparent conductive film. In these methods, the dry shrinkage of the film from the time of application to the formation of the dry film causes a problem in that the contact bonding state between the metal nanowires varies to cause individual differences for each film.
- Patent Document 1 using a support film provided with a photosensitive resin composition film containing metal nanowires in a transparent resin, a conductive film containing metal nanowires in the transparent resin by film transfer, exposure, and development.
- variation in the distribution of metal nanowire by forming the transparent electrode which consists of is disclosed.
- Display devices with capacitively coupled touch panel input devices are currently rapidly spreading worldwide as input / display devices for mobile terminal devices such as smartphones and tablet PCs, and the volume of product shipments is increasing.
- the performance of such portable terminal devices has been improving year by year, and as a result, internal electronic circuit components have increased power consumption as the speed and functionality have increased, and the amount of heat generated from circuit components and power batteries has increased. is doing.
- These are also assumed to be used outdoors as portable terminals. For this reason, as electronic devices, reliability such as high temperature, high humidity, outdoor environment sunlight, and the like has become more important issues than ever before.
- a touch panel when a conductive film containing metal nanowires is used as an electrode, the metal nanowires are brought into contact with each other to conduct electrical connection and develop conductive characteristics.
- the touch panel attached to the portable terminal device is exposed to high temperature, high humidity environment, and incidence of sunlight in the use environment as described above.
- the component of the metal nanowire is made of a metal or a metal compound that is not inactive except for Au and Pt, particularly when the metal nanowire is irradiated with light at high temperature and high humidity, It has been found that there is a problem that impairs the reliability of electrical characteristics as an electronic component.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a display device with a capacitive touch panel input device using a conductive film containing metal nanowires as an electrode, and particularly a display device with high reliability of electrical characteristics.
- a transparent electrode for detecting XY position coordinates on the surface of a substrate is provided on the transparent substrate, and a position touched with respect to the transparent electrode is detected by capacitive coupling.
- a display device having a capacitively coupled touch panel as an input device has a structure in which a touch panel substrate is bonded to the upper surface of the display device, and a visible wavelength of 430 nm or more on the upper surface side of the touch panel substrate or on the upper surface side and lower surface side of the touch panel.
- a light transmission layer that transmits light is provided.
- the display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device includes a structure in which a transparent resin of the conductive film is bonded to the surface of the transparent substrate,
- the surface layer of the metal nanowire was configured to contain 10 to 200 nm in thickness.
- the display device with the capacitive coupling type touch panel input device is configured such that the transparent resin of the conductive film is formed of a photosensitive resin composition.
- the present invention provides the display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device, wherein the light transmission layer includes light absorption and light composed of a semiconductor compound having a band gap at a light wavelength of less than 430 nm.
- the scattering reflector was configured to be contained in an optically transparent resin.
- the display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device is the light absorbing material, wherein the light transmission layer is made of a compound having an absorbance maximum at a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm.
- the light transmission layer is made of a compound having an absorbance maximum at a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm.
- a material comprising a molecular structure having an absorbance maximum at a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm is included.
- a display device with a capacitive coupling type touch panel input device that realizes detection of a change in capacitance using a conductive film of metal nanowires, which is highly reliable in environment especially in electrical characteristics. it can.
- FIG. 3A is an enlarged view and FIG. 2B is a cross-sectional view for explaining a connection portion between a transparent electrode and a lead wiring of the capacitive coupling touch panel according to the present invention. It is (a) enlarged view and (b) sectional drawing for demonstrating the cross
- FIG. 12 is a process diagram for explaining an example of the manufacturing method of the capacitive coupling touch panel shown in FIG. 8 following FIG. 11.
- the display device with a touch panel input device of the present invention is provided with a transparent electrode for detecting XY position coordinates on a transparent substrate, and the position touched with respect to the transparent electrode is statically detected. It has a structure in which a touch panel substrate with a capacitive coupling type touch panel that is detected by capacitive coupling as an input device is bonded to the upper surface of the display device, and has a wavelength on the upper surface side of the touch panel substrate or on the upper surface side and lower surface side of the touch panel. A light transmission layer that transmits visible light of 430 nm or more is provided.
- the transparent electrode is composed of a conductive film containing metal nanowires in a transparent resin, laminated on a part of the surface of the conductive film, and exposed from the surface layer of the transparent resin. And a connection electrode for connecting the lead-out wiring for connecting to the external circuit of the touch panel and the transparent electrode.
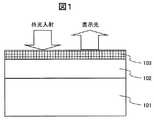
- the display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device of the first embodiment is shown in a sectional view of FIG.
- the display device with the capacitive coupling type touch panel input device of the present embodiment includes a capacitive coupling type touch panel 102 on the upper surface of the display device 101, and further transmits light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more on the upper surface of the touch panel.
- a light transmitting layer 103 having a specific wavelength band serving as a layer is provided.
- the display device 101 is a liquid crystal display device
- the liquid crystal display device 201 has the following structure.
- a display circuit which is a pixel assembly of thin film transistor circuits arranged in a matrix on a first transparent substrate 205 is provided, and a second transparent substrate 207 is provided on an opposing surface of the first transparent substrate 205, and the opposing substrate
- a liquid crystal layer 206 sandwiched between 205 and 207 is provided.
- the substrates 205 and 207 are provided two polarizing plates 204 and 208 that are in a combination of optical orthogonal states with respect to the polarized light, and the light emission in the visible light region from the backlight 203 is the polarizing plate 204 and the substrate 205.
- the light passes through the polarizing plate 208 as image display light.
- a capacitively coupled touch panel 202 (details of the configuration of the touch panel will be described later) is bonded to the upper surface of the liquid crystal display device 201 via an optically transparent adhesive layer 209.
- the touch panel 202 includes a touch panel transparent electrode circuit 211 for detecting touch position coordinates on the surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 210.
- a cover transparent substrate 213 that protects the surface is bonded to the upper surface of the touch panel 202 via an optically transparent adhesive layer 212.
- the cover transparent substrate surface is provided with a light transmission layer 214 in a specific wavelength range that serves as a light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more.
- the light transmitting layer 214 is present on the surface of the cover transparent substrate 213, but conversely, the light transmitting layer 214 may be provided in the lower layer and the cover transparent substrate 213 may be provided on the outermost surface.
- the liquid crystal display device 201 drives the liquid crystal as an optical shutter, and the liquid crystal driving method includes FFS (Fringe Field Switching), IPS (In-Place-Switching), VA (Vertical Alignment), and TN. (Twisted Nematic) are known and can be used.
- a glass substrate such as alkali glass such as soda glass or borosilicate glass, non-alkali glass, or chemically strengthened glass is suitable.
- polyester films such as polyethylene terephthalate having transparency and polyethylene naphthalate, polyimide films having high heat resistance and transparency are also known, and it is also possible to use such resin-based substrates having transparency. .
- the light transmission layer 214 that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more used in the present invention is made of a material film in which semiconductor compound fine particles having a band gap at a light wavelength of less than 430 nm are contained in an optically transparent resin. It is suitable for transmitting visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more by light absorption and light scattering reflection of semiconductor compound fine particles.
- semiconductor compound fine particles having a band gap at an optical wavelength of less than 430 nm those obtained by adding compound fine particles mainly composed of SiC fine particles and selected from ZnO, WO 3 , TiO 2 and SrTiO 3 are suitable.
- As the shape of the fine particles a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- polyolefin resin As the optically transparent resin containing semiconductor compound fine particles, polyolefin resin, polyester resin, polyamide resin, polyimide resin, polystyrene resin, polycarbonate resin, acrylic resin and the like are suitable. More specifically, polyethylene, polypropylene, cyclic polyolefin, polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene naphthalate, polybutylene terephthalate, polylactic acid, nylon, polycarbonate, polyester carbonate, polymethyl methacrylate, polyethyl methacrylate, and the like are suitable. In the case of a polyimide resin, a polyimide having a structure combining a diphenyl ether skeleton or a biphenyl skeleton as a molecular structure is desirable.
- the light transmitting layer 214 that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more used in the present invention includes a light absorbing material made of a compound having an absorbance maximum at a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm, or a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm A material composed of a molecular structure having an absorbance maximum is included.
- a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- the compound having an absorbance maximum at a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm copper halide fine particles, silver fine particles and the like are suitable.
- the shape of the fine particles a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- a material comprising a molecular structure having an absorbance maximum at a light wavelength of 380 nm or more and less than 430 nm a polyimide resin having a structure combining a diphenyl ether skeleton or a biphenyl skeleton as the molecular structure is suitable.
- the light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more has a light transmittance of 50% or more of the wavelength of 430 nm or more.
- optically transparent adhesive layer 209 a liquid adhesive material or an adhesive tape generally called an optically transparent adhesive (Optically Clear Adhesive) is suitable.
- optically transparent adhesive Optically Clear Adhesive
- cover transparent substrate 213 chemically strengthened glass is suitable.
- the cover transparent substrate 213 and the specific wavelength region light transmission layer 214 are separately provided.
- the chemically tempered glass to be the cover transparent substrate SiC, ZnO, WO 3 , TiO 2 , SrTiO 3 , halogen
- fine particles such as copper chloride and silver
- a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- the display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device of the second embodiment is shown in the cross-sectional view of FIG.
- the capacitive coupling type touch panel 302 is bonded to the upper surface of the liquid crystal display device 301 via an optically transparent adhesive layer 309.
- the touch panel 302 includes a touch panel transparent electrode circuit 310 for detecting touch position coordinates on the surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 311.
- a second specific wavelength region light transmission layer 312 serving as a light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more is provided on the upper surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 311.
- the touch panel transparent substrate 311 and the specific wavelength region light transmission layer 312 are separately provided.
- the transparent substrate SiC, ZnO, WO 3 , TiO 2 , SrTiO 3 , copper halide, silver, etc.
- fine particles or the like it is possible to integrate the function of the specific wavelength region light transmission layer into the transparent substrate.
- a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- a display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device is shown in a sectional view of FIG.
- the display device with the capacitive coupling touch panel input device includes a first specific wavelength region light transmission layer 402 serving as a light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more on the upper surface of the display device 401.
- a capacitive coupling type touch panel 403 is provided on the upper surface, and a second specific wavelength region light transmitting layer 404 serving as a light transmitting layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more is provided on the upper surface of the touch panel.
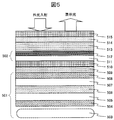
- FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of an embodiment in which the display device is a liquid crystal display device.
- the liquid crystal display device 501 has the following structure.
- a display circuit which is a pixel assembly of thin film transistor circuits arranged in a matrix on a first transparent substrate 505 is provided, and a second transparent substrate 507 is provided on the opposite surface of the first transparent substrate 505.
- a liquid crystal layer 506 sandwiched between 505 and 507 is provided.
- the substrates 505 and 507 there are two polarizing plates 504 and 508 that are in a combination of optical orthogonal states with respect to the polarized light, and the light emission from the backlight 503 in the visible light region is the polarizing plate 504 and the substrate 505. Then, the light passes through the polarizing plate 508 as image display light.
- the upper surface of the liquid crystal display device 501 includes a first specific wavelength range light transmission layer 510 serving as a light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more through an optically transparent adhesive layer 509, and the upper surface thereof.
- the touch panel 502 includes a touch panel transparent electrode circuit 512 for detecting touch position coordinates on the surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 511.
- a cover transparent substrate 514 that protects the surface is bonded to the upper surface of the touch panel 502 via an optically transparent adhesive layer 513.
- the cover transparent substrate surface is provided with a second specific wavelength region light transmission layer 515 serving as a light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more.
- the light transmission layer 515 is present on the surface of the cover transparent substrate 514, but conversely, the light transmission layer 515 may be provided in the lower layer and the cover transparent substrate 514 may be provided on the outermost surface.
- the cover transparent substrate 514 and the specific wavelength range light transmission layer 515 are separately provided.
- the chemically strengthened glass to be the cover transparent substrate SiC, ZnO, WO 3 , TiO 2 , SrTiO 3 are used.
- fine particles such as copper halide and silver, it is possible to integrate the function of the light transmitting layer in the specific wavelength region into the cover transparent substrate.
- the shape of the fine particles a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- the touch panel transparent substrate 511 and the specific wavelength band light transmission layer 510 are separately provided.
- the transparent substrate SiC, ZnO, WO 3 , TiO 2 , SrTiO 3 , copper halide, silver It is also possible to integrate the function of the specific wavelength region light transmission layer into the transparent substrate by including fine particles such as. As the shape of the fine particles, a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
- the touch panel transparent substrate 511 it is also possible to integrate the function of the light transmission layer in a specific wavelength region into the transparent substrate by using a polyimide resin having a structure in which a diphenyl ether skeleton or a biphenyl skeleton is combined as a molecular structure. .
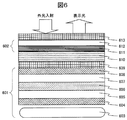
- a display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device is shown in a sectional view of FIG.
- a display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device has a first specific wavelength band light transmitting layer 609 serving as a light transmitting layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more directly on the upper surface of the liquid crystal display device 601.
- a capacitively coupled touch panel 602 is bonded through an optically transparent adhesive layer 610.
- the touch panel 602 includes a touch panel transparent electrode circuit 611 for detecting touch position coordinates on the surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 612.
- a second specific wavelength region light transmission layer 613 is provided on the upper surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 612 as a light transmission layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more.
- a display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device is shown in a sectional view of FIG.
- the display device with a capacitively coupled touch panel input device of this embodiment includes an organic electroluminescence display device 701.
- a display circuit layer 704 which is a pixel aggregate of thin film transistor circuits arranged in a matrix on a first substrate 703 of a display device 701 is provided, and an ultrathin film of an organic electroluminescent material is formed between electrode layers connected to the thin film transistor circuit on the upper layer.
- a circuit layer 705 in which the organic electroluminescent material emits light by applying current to the electrode is provided.
- a transparent substrate 707 bonded to the opposite surface of the substrate 703 with a transparent sealing layer 706 for light transmission is sealed from the outside environment.
- Light emitted from the organic electroluminescence light emitting circuit layer 705 is transmitted through the sealing layer 706 and the counter substrate 707 to become display light, whereby the organic electroluminescence display device 701 is realized.
- a capacitive coupling type touch panel 702 is bonded to the upper surface of the display device 701 through an optically transparent adhesive layer 708.
- the touch panel 702 includes a touch panel transparent electrode circuit 710 for detecting touch position coordinates on the surface of the touch panel transparent substrate 709.
- a cover transparent substrate 712 that protects the surface is bonded to the upper surface of the touch panel 702 via an optically transparent adhesive layer 711.
- the cover transparent substrate surface is provided with a light transmitting layer 713 having a specific wavelength range that serves as a light transmitting layer that transmits visible light having a wavelength of 430 nm or more.
- the light transmissive layer 713 is present on the surface of the cover transparent substrate 712. Conversely, the light transmissive layer 713 may be provided on the lower layer, and the cover transparent substrate 712 may be provided on the outermost surface.
- the cover transparent substrate 712 and the specific wavelength region light transmission layer 713 are separately provided.
- the chemically tempered glass serving as the cover transparent substrate SiC, ZnO, WO 3 , TiO 2 , SrTiO 3 are used.
- fine particles such as copper halide and silver, it is possible to integrate the function of the light transmitting layer in the specific wavelength region into the cover transparent substrate.
- a diameter range of 10 nm to 100 nm is suitable.
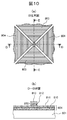
- the capacitive coupling type touch panel according to Examples 1 to 5 described above is shown in the substrate plan view of FIG.
- this touch panel there is a touch screen 802 that is an area for detecting touch position coordinates on one surface of a transparent substrate 801, and each transparent electrode 803 that detects an electrostatic capacitance change and outputs X and Y position coordinates in this area. , 804.
- Transparent electrodes 803 for detecting the X position coordinates are connected to the transparent electrodes 803 corresponding to the same X position coordinates, and the transparent electrodes 804 for detecting the Y position coordinates correspond to the same Y position coordinates.
- the transparent electrodes 804 are connected to each other.
- These transparent electrodes are provided with a lead wiring 805 for connecting to an element circuit for controlling an electrical signal as a touch panel, an electrode 806 for connecting the lead wiring and the transparent electrode, and a terminal portion 807 for connecting to a drive circuit element. Has been.
- glass substrates such as soda glass, alkali glass such as borosilicate glass, non-alkali glass, and chemically strengthened glass are suitable.
- polyester films such as polyethylene terephthalate having transparency and polyethylene naphthalate, polyimide films having high heat resistance and transparency are also known, and it is possible to use such resin-based substrates having transparency. .
- a metal electrode formed by sputtering or vapor deposition is suitable. Specific examples include alloys such as Ag—Pd—Cu, Al—Cu, Ni—Cu, Al, Cu, and Ni, laminated electrodes, and single electrodes. Further, it can be formed using an Ag conductive paste.
- FIG. 9 shows an enlarged view and a cross-sectional structure of the connection portion between the lead wiring 805 and the transparent electrode 804 that outputs the Y position coordinates.
- the electrode 806 that connects the lead wiring 805 and the transparent electrode 804 is formed in a structure that is laminated on the end of the transparent electrode 804 when the lead wiring 805 is formed. It is not required.
- the transparent electrodes 804 are connected to the lead-out wiring 805 by connecting the transparent electrodes corresponding to the same Y position coordinate.
- the cross-sectional structure of the connection portion between the lead wiring 805 and the transparent electrode 803 that outputs the X position coordinate is the same.
- FIG. 10 shows an enlarged B view and a DD cross-sectional structure at the intersection of the connection portions of the transparent electrodes 803 and 804 corresponding to these X and Y position coordinates.
- the intersection of the connecting portion of the transparent electrode 803 that outputs the X coordinate is insulated from the connecting portion of the transparent electrode 804 that outputs the Y position coordinate by the transparent resin layer 812 made of an insulating resin.
- the metal nanowires contained in the transparent electrodes 803 and 804 nanowires such as Ag, Cu, Co, C, and Pd can be used.
- Ag nanowire is the most suitable constituent material from the viewpoints of conductivity and light transmission as a conductive film.
- the metal nanowires in this touch panel have a cross-sectional diameter of 10 to 100 nm and a length of 1 to 100 ⁇ m. Further, this touch panel has a structure in which a transparent resin 810, 812 of a conductive film is bonded to the surface of the transparent substrate 801, and the surface layer (811, 813) of the conductive film contains metal nanowires in a thickness of 10 to 200 nm. . Further, metal nanowires may be unevenly distributed on the surface side of the transparent substrate 801 (with a thickness of 10 to 200 nm from the surface).
- the touch panel of Example 6 was manufactured under the following conditions in the steps shown in FIGS. First, as shown in FIG. 11 (1), a photosensitive resin composition film 821 in which metal nanowires are contained in a transparent resin (the photosensitive resin composition film described in “WO2010 / 021224” can be used.
- a support film 822 provided with a) is prepared. This is a member having a film structure in which a photosensitive resin composition film 821 is laminated on a support film 822 for supporting the photosensitive resin composition film 821.
- This photosensitive resin composition film 821 includes a metal nanowire-containing layer 823.
- a photosensitive resin composition film 821 including a metal nanowire-containing layer 823 laminated on a support film 822 is bonded to a transparent substrate 801 by film transfer.
- the photosensitive resin composition film 821 is exposed to a desired shape through a light shielding mask, and an unexposed portion in the exposure step is removed using an alkaline developer.
- a transparent electrode 804 that outputs a Y position coordinate formed of a conductive film 811 of metal nanowires contained in a transparent resin 810 formed in a desired shape on a transparent substrate 801 is formed.
- FIG. 11 (3) represents the DD cross section of FIG. 10
- FIG. 11 (4) represents the EE cross section of FIG.
- the desired shape is exposed through a light-shielding mask, and an unexposed portion in the exposure process is exposed using an alkaline developer.
- the transparent electrode 803 that outputs the X position coordinates composed of the conductive film 813 of the metal nanowire contained in the transparent resin 812 formed in a desired shape on the transparent substrate 801 is removed.
- a lead wire 805 for connecting to an external circuit and a connection electrode 806 for connecting the lead wire 805 and the transparent electrode 804 are formed on the surface of the transparent substrate 801.
- the lead wiring 805 and the connection electrode 806 are formed at the same time by screen printing using a conductive paste material containing flaky Ag.
- the relative positional relationship between the metal nanowires is film transfer. Since the conductive film is not changed even after the conductive film is formed by exposure or development, it is possible to create a capacitive coupling type touch panel having transparent electrodes 803 and 804 having high-quality XY position coordinates. A display device with a combined touch panel input device is realized.
- Cover transparent substrate 214 ... Specific wavelength range light transmission layer , DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 301 ... Liquid crystal display device 302 ... Capacitance coupling type touch panel, 303 ... Back light, 304 ... 1st polarizing plate, 305 ... 1st transparent substrate (thin-film transistor circuit board), 306 ... Liquid crystal layer, 307 ... 2nd 308 ... second polarizing plate, 309 ... optical transparency adhesive layer, 310 ... touch panel transparent electrode circuit, 311 ... touch panel transparent substrate, 312 ... specific wavelength band light transmission layer, 401 ... display device 402 ... first specific wavelength range light transmission layer, 403 ... capacitive coupling touch panel, 404 ...
- second specific wavelength range light transmission layer 501 ... Liquid crystal display device, 502 ... Capacitive coupling type touch panel, 503 ... Backlight, 504 ... First polarizing plate, 505 ... First transparent substrate (thin film transistor circuit substrate), 506 ... Liquid crystal layer, 507 ... Second 508 ... second polarizing plate, 509 ... optical transparency adhesive layer, 510 ... first specific wavelength region light transmission layer, 511 ... touch panel transparent substrate, 512 ... touch panel transparent electrode circuit, 513 ... optical Transparent adhesive layer, 514 ... cover transparent substrate, 515 ... second specific wavelength range light transmitting layer, 601 ... Liquid crystal display device, 602 ... Capacitive coupling type touch panel, 603 ...
- First polarizing plate 605 ... First transparent substrate (thin film transistor circuit substrate), 606 ... Liquid crystal layer, 607 ... Second 608 ... second polarizing plate, 609 ... first specific wavelength range light transmission layer, 610 ... optical transparency adhesive layer, 611 ... touch panel transparent electrode circuit, 612 ... touch panel transparent substrate, 613 ... second Specific wavelength region light transmission layer, 701 ... Organic electroluminescence display device, 702 ... Capacitive coupling type touch panel, 703 ... First substrate, 704 ... Thin film transistor circuit substrate layer, 705 ... Organic electroluminescence light emitting circuit layer, 706 ... Optical transparent sealing layer, 707 ... Opposite sealing transparent substrate, 708 ...
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Position Input By Displaying (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
Abstract
Description
これらの表示装置の多くは、1対の透明基板で液晶を挟持した液晶セルと、液晶セルの両外側に貼り合わせた光学異方性フィルムと、表示光源となるバックライトとの組み合わせからなる液晶表示装置、あるいは、有機エレクトロルミネッセンス材料を電極間に挟みこんで電極への印加電力を発光に変えて自発光する有機エレクトロルミネッセンス表示装置である。
タッチパネルは、その動作原理において様々な方式が存在するが、最近では、小型携帯機器用途において静電容量結合方式のタッチパネルが主体となっている。
本方式では高速にタッチされた位置を検出できる利点があり、指タッチを基本として、指先と位置検出電極との間での静電容量の変化を捉えて位置を検出する。例えばXY位置座標を個別に検出する場合に、X位置座標検出電極-Y位置座標検出電極間は絶縁された構造を有している。
以下、本発明の実施の形態について、図1乃至図12を用いて説明する。
本実施例の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置は、表示装置101の上面に静電容量結合方式タッチパネル102を備え、さらにタッチパネルの上面に、波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる特定波長域光透過層103を備えている。
表示装置が液晶表示装置の場合、液晶表示装置201は次のような構造を備えている。第1の透明基板205上にマトリクス状に配置される薄膜トランジスタ回路の画素集合体である表示回路を備え、第1の透明基板205の対向面に、第2の透明基板207があり、対向する基板205と207により挟持された液晶層206を備えている。基板205と207の外側には、偏光に対して光学的直交状態の組み合わせとなる2つの偏光板204,208を備えており、バックライト203からの可視光領域の発光が偏光板204ならびに基板205を通して、画像表示光として、偏光板208を透過する。
上記の実施例において、液晶表示装置201は、液晶を光学シャッターとして駆動させるが、液晶駆動方式には、FFS(Fringe Field Switching)、IPS(In-Place-Switching)、VA(Vertical Alignment)、TN(Twisted Nematic)が知られており、これらを用いることが可能である。
光波長430nm未満にバンドギャップを有する半導体化合物微粒子は、SiC微粒子を主体に、ZnO、WO3、TiO2、SrTiO3から選ばれた化合物微粒子を加えたものが適している。微粒子の形状としては、直径10nmから100nm範囲が適している。
光波長380nm以上430nm未満に吸光度極大を有する化合物としては、ハロゲン化銅微粒子、銀微粒子などが適している。微粒子の形状としては、直径10nmから100nm範囲が適している。
光波長380nm以上430nm未満に吸光度極大を有する分子構造体からなる材料としては、分子構造としてジフェニルエーテル骨格、あるいはビフェニル骨格を組み合わせた構造を有するポリイミド樹脂が適している。
本発明の静電容量結合方式タッチパネルを備えた表示装置では、波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層が、波長430nm以上の光透過率が50%以上である。
カバー透明基板213としては、化学強化ガラスが適している。
本実施例の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置は、液晶表示装置301の上面に、光学的に透明な接着層309を介して、静電容量結合方式タッチパネル302を貼り合わせている。タッチパネル302は、タッチパネル透明基板311面にタッチ位置座標を検出するためのタッチパネル透明電極回路310を備えている。
さらにタッチパネル透明基板311の上面に、波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる第2の特定波長域光透過層312を備えている。
また、タッチパネル透明基板311として、分子構造としてジフェニルエーテル骨格、あるいはビフェニル骨格を組み合わせた構造を有するポリイミド樹脂を用いることで、透明基板に特定波長域光透過層の機能を一体化することも可能である。
本実施例の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置は、表示装置401の上面に、波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる第1の特定波長域光透過層402を、その上面に静電容量結合方式タッチパネル403を、さらにタッチパネルの上面に波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる第2の特定波長域光透過層404を備えている。
タッチパネル502は、タッチパネル透明基板511表面にタッチ位置座標を検出するためのタッチパネル透明電極回路512を備えている。
本実施例では、タッチパネル502上面に光学的透明性接着層513を介して、表面を保護するカバー透明基板514を貼り合わせている。このカバー透明基板表面に波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる第2の特定波長域光透過層515を備えている。
また、本実施例では、タッチパネル透明基板511と特定波長域光透過層510を分けて設けているが、透明基板中に、SiC、ZnO、WO3、TiO2、SrTiO3、ハロゲン化銅、銀などの微粒子などを含有させることで、透明基板に特定波長域光透過層の機能を一体化することも可能である。微粒子の形状としては、直径10nmから100nm範囲が適している。
また、タッチパネル透明基板511として、分子構造としてジフェニルエーテル骨格、あるいはビフェニル骨格を組み合わせた構造を有するポリイミド樹脂を用いることで、透明基板に特定波長域光透過層の機能を一体化することも可能である。
本実施例の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置は、液晶表示装置601の上面に直接、波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる第1の特定波長域光透過層609を備え、光学的に透明な接着層610を介して、静電容量結合方式タッチパネル602を貼り合わせている。タッチパネル602は、タッチパネル透明基板612面にタッチ位置座標を検出するためのタッチパネル透明電極回路611を備えている。
さらにタッチパネル透明基板612の上面に、波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層となる第2の特定波長域光透過層613を備えている。
本実施例の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置は、有機エレクトロルミネッセンス表示装置701を備えている。表示装置701の第1の基板703にマトリクス状に配置される薄膜トランジスタ回路の画素集合体である表示回路層704を備え、その上層に薄膜トランジスタ回路とつながる電極層間に有機エレクトロルミネッセンス材料の極薄膜を形成して、電極へ電流印加により有機エレクトロルミネッセンス材料が発光する回路層705を備えている。基板703の対向面に、光透過のために透明な封止層706で接合されている透明基板707で外環境に対して封止されている。有機エレクトロルミネッセンス発光回路層705からの発光が、封止層706、対向基板707を透過して表示光となり、有機エレクトロルミネッセンス表示装置701を実現する。
本タッチパネルでは、透明基板801の片面上にタッチ位置座標を検出する領域であるタッチ画面802があり、この領域に静電容量変化を検出してX、Y位置座標を出力するそれぞれの透明電極803,804を備えている。X位置座標を検出するための透明電極803は、同一のX位置座標に対応する透明電極803同士が接続され、Y位置座標を検出するための透明電極804は、同一のY位置座標に対応する透明電極804同士が接続される。これら透明電極には、タッチパネルとしての電気信号を制御する素子回路と接続するための引出し配線805と、その引出し配線と透明電極を接続する電極806、ならびに駆動回路素子と接続する端子部807が配置されている。
この引出し配線805と透明電極804を接続する電極806は、引出し配線805を形成する際に、透明電極804の端部に積層する構造で形成されるものであり、特に引出し配線と個別の工程が必要とされるものではない。透明電極804は、同一のY位置座標に対応する透明電極同士が接続されて、引出し配線805と接続される。引出し配線805と、X位置座標を出力する透明電極803の接続部の断面構造も同様である。
Y位置座標を出力する透明電極804の接続部に対して、X座標を出力する透明電極803の接続部の交差部は、絶縁樹脂からなる透明樹脂層812により、絶縁された構造となっている。
上記の透明電極803,804に含有される金属ナノワイヤは、Ag、Cu、Co、C、Pdなどのナノワイヤを用いることができる。この中でも、導電膜としての導電性と光透過性の観点からAgナノワイヤが最も適する構成材料である。
このタッチパネルにおける金属ナノワイヤは、断面直径10~100nm、長さ1~100μm範囲にある。
また、このタッチパネルにおいて、透明基板801表面に対して導電膜の透明樹脂810,812が接合する構造を備え、導電膜の表面層(811,813)10~200nm厚に金属ナノワイヤを含有している。
また、金属ナノワイヤが透明基板801表面側に偏在(表面から10~200nm厚さに)してもよい。
まず、図11(1)に示すように、透明樹脂中に金属ナノワイヤが含有された感光性樹脂組成物フィルム821(「WO2010/021224」に記載される感光性樹脂組成物フィルムを使用することができる。)を備えた支持体フィルム822を用意する。これは、感光性樹脂組成物フィルム821を支持するための支持体フィルム822に、感光性樹脂組成物フィルム821が積層されたフィルム構造の部材である。この感光性樹脂組成物フィルム821には、金属ナノワイヤ含有層823を含む。
201…液晶表示装置、202…静電容量結合方式タッチパネル、203…バックライト、204…偏光板、205…第1の透明基板(薄膜トランジスタ回路基板)206…液晶層、207…第2の透明基板、208…偏光板、209…光学的透明性接着層、210…タッチパネル透明基板、211…タッチパネル透明電極回路、212…光学的透明性接着層、213…カバー透明基板、214…特定波長域光透過層、
301…液晶表示装置、302…静電容量結合方式タッチパネル、303…バックライト、304…第1の偏光板、305…第1の透明基板(薄膜トランジスタ回路基板)、306…液晶層、307…第2の透明基板、308…第2の偏光板、309…光学的透明性接着層、310…タッチパネル透明電極回路、311…タッチパネル透明基板、312…特定波長域光透過層、
401…表示装置、402…第1の特定波長域光透過層、403…静電容量結合方式タッチパネル、404…第2の特定波長域光透過層、
501…液晶表示装置、502…静電容量結合方式タッチパネル、503…バックライト、504…第1の偏光板、505…第1の透明基板(薄膜トランジスタ回路基板)、506…液晶層、507…第2の透明基板、508…第2の偏光板、509…光学的透明性接着層、510…第1の特定波長域光透過層、511…タッチパネル透明基板、512…タッチパネル透明電極回路、513…光学的透明性接着層、514…カバー透明基板、515…第2の特定波長域光透過層、
601…液晶表示装置、602…静電容量結合方式タッチパネル、603…バックライト、604…第1の偏光板、605…第1の透明基板(薄膜トランジスタ回路基板)、606…液晶層、607…第2の透明基板、608…第2の偏光板、609…第1の特定波長域光透過層、610…光学的透明性接着層、611…タッチパネル透明電極回路、612…タッチパネル透明基板、613…第2の特定波長域光透過層、
701…有機エレクトロルミネッセンス表示装置、702…静電容量結合方式タッチパネル、703…第1の基板、704…薄膜トランジスタ回路基板層、705…有機エレクトロルミネッセンス発光回路層、706…光学的透明性封止層、707…対向封止透明基板、708…光学的透明性接着層、709…タッチパネル透明基板、710…タッチパネル透明電極回路、711…光学的透明性接着層、712…カバー透明基板、713…特定波長域光透過層、
801…タッチパネル透明基板、802…タッチ画面、803…静電容量結合検出透明電極(X座標)、804…静電容量結合検出透明電極(Y座標)、805…タッチパネル回路接続引出し配線、806…透明電極と引出し配線の接続電極、807…タッチパネル駆動回路素子接続端子、810…透明電極の透明樹脂層、811…透明電極の金属ナノワイヤ含有層、812…透明電極の透明樹脂層、813…透明電極の金属ナノワイヤ含有層、821…透明樹脂中に金属ナノワイヤを含有する感光性樹脂組成物フィルム、822…支持体フィルム、823…金属ナノワイヤ含有層、824…転写貼り付け後の感光性樹脂組成物フィルム。
Claims (16)
- 透明基板上に基板表面のXY位置座標を検出する透明電極が設けられ、前記透明電極に対してタッチされた位置を静電容量結合により検出する静電容量結合方式タッチパネルを入力装置として備えた表示装置において、
前記表示装置上面にタッチパネル基板を貼り合わせた構造を備え、及び
タッチパネル基板の上面側、またはタッチパネルの上面側と下面側に波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層を備えることを特徴とする静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。 - 前記タッチパネルは、
前記透明電極が、透明樹脂中に金属ナノワイヤが含有された導電膜より構成され、
前記導電膜の一部表面に積層して、前記透明樹脂の表面層から露出された前記金属ナノワイヤと接合され、前記タッチパネルの位置座標を出力するために、外部回路へ引き出す配線の接続電極を有することを特徴とする請求項1記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。 - 前記タッチパネルは、
前記透明電極が透明樹脂中に金属ナノワイヤが含有された導電膜を有し、
前記金属ナノワイヤが断面直径10~100nm、長さ1~100μmの寸法であることを特徴とする請求項1、または請求項2に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。 - 前記透明基板表面に対して前記導電膜の透明樹脂が接合する構造を備え、
前記導電膜の表面層10~200nm厚さに前記金属ナノワイヤを含有することを特徴とする請求項2に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。 - 前記金属ナノワイヤがAu、Ptを除いた金属からなることを特徴とする請求項2に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記導電膜の透明樹脂は感光性樹脂組成物から形成されることを特徴とする請求項2に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記透明基板表面に対して前記導電膜の透明樹脂が接合する構造を備え、
前記導電膜の表面層10~200nm厚さに前記金属ナノワイヤを含有することを特徴とする請求項3に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。 - 前記金属ナノワイヤがAu、Ptを除いた金属からなることを特徴とする請求項3に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記表示装置は、対向配置される第1の透明基板および第2の透明基板により液晶層を挟持し、表示光源となるバックライトを備えていることを特徴とする請求項1記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記表示装置は、対向配置される第1基板および第2基板からなり、前記第1基板上に電極層間に有機エレクトロルミネッセンス層を形成した発光素子を備え、前記第2基板により密閉封止した有機エレクトロルミネッセンス表示装置であることを特徴とする請求項1記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記導電膜の透明樹脂は感光性樹脂組成物から形成されることを特徴とする請求項3に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記波長430nm以上の可視光を透過させる光透過層は、波長430nm以上の光透過率が50%以上となる光透過性を有していることを特徴とする請求項1記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記光透過層は、光波長430nm未満にバンドギャップを有する半導体化合物からなる光吸収、光散乱反射材を光学的に透明な樹脂中に含有させていることを特徴とする請求項1記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記光波長430nm未満にバンドギャップを有する半導体化合物微粒子は、SiC微粒子を主体に、ZnO、WO3、TiO2、SrTiO3から選ばれた化合物微粒子を加えたものであることを特徴とする請求項13に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記光透過層は、光波長380nm以上430nm未満に吸光度極大を有する化合物からなる光吸収材、あるいは光波長380nm以上430nm未満に吸光度極大を有する分子構造体からなる材料を含んでいることを特徴とする請求項1記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
- 前記光波長380nm以上430nm未満に吸光度極大を有する化合物は、ハロゲン化銅微粒子、または銀微粒子から選ばれ、あるいは前記光波長380nm以上430nm未満に吸光度極大を有する分子構造体からなる材料は、分子構造としてジフェニルエーテル骨格、またはビフェニル骨格を組み合わせた構造を有するポリイミド樹脂から選ばれることを特徴とする請求項15に記載の静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/325,781 US20170168337A1 (en) | 2014-07-15 | 2015-07-02 | Display Device with Capacitive Coupling Type Touch Panel Input Device |
| KR1020177001068A KR20170018922A (ko) | 2014-07-15 | 2015-07-02 | 정전 용량 결합 방식 터치 패널 입력 장치 부착 표시 장치 |
| CN201580038014.5A CN106537306A (zh) | 2014-07-15 | 2015-07-02 | 带静电电容耦合方式触摸屏输入装置的显示装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014144900A JP2016021170A (ja) | 2014-07-15 | 2014-07-15 | 静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置 |
| JP2014-144900 | 2014-07-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016009851A1 true WO2016009851A1 (ja) | 2016-01-21 |
Family
ID=55078349
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/069166 WO2016009851A1 (ja) | 2014-07-15 | 2015-07-02 | 静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20170168337A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2016021170A (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20170018922A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106537306A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI576751B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016009851A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109791458B (zh) * | 2016-10-06 | 2022-02-25 | 阿尔卑斯阿尔派株式会社 | 静电电容式传感器 |
| JP2019036399A (ja) * | 2017-08-10 | 2019-03-07 | 株式会社小糸製作所 | 車両用表示装置 |
| US20210165511A1 (en) | 2018-01-11 | 2021-06-03 | Mitsubishi Paper Mills Limited | Conductive material and treatment method |
| CN110322782B (zh) * | 2018-03-28 | 2021-12-07 | 英属开曼群岛商镎创科技股份有限公司 | 显示基板与显示面板 |
| TWI662521B (zh) * | 2018-03-28 | 2019-06-11 | 英屬開曼群島商錼創科技股份有限公司 | 顯示基板與顯示面板 |
| US11003226B1 (en) * | 2018-08-09 | 2021-05-11 | Rockwell Collins, Inc. | Touchscreen sensor electromagnetic interference protection apparatus |
| CN113900348A (zh) * | 2020-07-06 | 2022-01-07 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | 投影幕布及其制造方法、投影显示系统及显示方法 |
| KR102160300B1 (ko) * | 2020-07-29 | 2020-09-25 | 주식회사 예건 | 열차용 통합안테나장치 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003011284A (ja) * | 2001-07-04 | 2003-01-15 | Mitsui Chemicals Inc | 積層フィルムないしシート、およびその製造方法 |
| JP2004255635A (ja) * | 2003-02-25 | 2004-09-16 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 透明積層フィルム、反射防止フィルム及びそれを用いた偏光板、液晶表示装置 |
| JP2007178915A (ja) * | 2005-12-28 | 2007-07-12 | Fujifilm Corp | 金属微粒子分散物及び赤外線遮蔽フィルター |
| JP2012254621A (ja) * | 2011-05-19 | 2012-12-27 | Arakawa Chem Ind Co Ltd | ガスバリア性積層ポリイミドフィルム、機能性薄膜層積層ガスバリア性積層ポリイミドフィルム、ディスプレイ及び太陽電池 |
| JP2013200891A (ja) * | 2011-12-05 | 2013-10-03 | Hitachi Chemical Co Ltd | タッチパネル用電極の保護膜及びタッチパネル |
| JP2014010516A (ja) * | 2012-06-28 | 2014-01-20 | Hitachi Chemical Co Ltd | 静電容量結合方式タッチパネルおよびその製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5352725A (en) * | 1991-09-27 | 1994-10-04 | Kerr-Mcgee Chemical Corporation | Attenuation of polymer substrate degradation due to ultraviolet radiation |
| WO2004067609A1 (ja) * | 2003-01-31 | 2004-08-12 | Trial Corporation | 密度を制御した微小粒子 |
| CN101493532A (zh) * | 2008-01-24 | 2009-07-29 | Tcl集团股份有限公司 | 一种显示装置 |
| US20100108409A1 (en) * | 2008-11-06 | 2010-05-06 | Jun Tanaka | Capacitive coupling type touch panel |
| CN103430134B (zh) * | 2011-01-19 | 2017-03-29 | Lg伊诺特有限公司 | 触摸板及其制造方法 |
| KR101861737B1 (ko) * | 2011-11-17 | 2018-05-29 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 광학 유닛 및 이를 포함하는 표시 장치 |
| WO2013084284A1 (ja) * | 2011-12-05 | 2013-06-13 | 日立化成株式会社 | タッチパネル用電極の保護膜の形成方法、感光性樹脂組成物及び感光性エレメント |
| WO2013084883A1 (ja) * | 2011-12-05 | 2013-06-13 | 日立化成株式会社 | タッチパネル用電極の保護膜の形成方法、感光性樹脂組成物及び感光性エレメント、並びに、タッチパネルの製造方法 |
| WO2013084282A1 (ja) * | 2011-12-05 | 2013-06-13 | 日立化成株式会社 | 樹脂硬化膜パターンの形成方法、感光性樹脂組成物及び感光性エレメント |
| KR102644240B1 (ko) * | 2012-07-20 | 2024-03-07 | 가부시키가이샤 한도오따이 에네루기 켄큐쇼 | 표시 장치 |
| JP6144548B2 (ja) * | 2012-08-01 | 2017-06-07 | 日東電工株式会社 | 透明導電性積層フィルム、その製造方法及びタッチパネル |
| US9354755B2 (en) * | 2012-11-27 | 2016-05-31 | Guardian Industries Corp. | Projected capacitive touch panel with a silver-inclusive transparent conducting layer(s) |
| JP5987668B2 (ja) * | 2012-12-06 | 2016-09-07 | 日立化成株式会社 | 表示装置およびその製造方法 |
| TWM465615U (zh) * | 2013-05-31 | 2013-11-11 | Hitachi Chemical Co Ltd | 觸碰面板 |
| CN103646958A (zh) * | 2013-11-18 | 2014-03-19 | 上海和辉光电有限公司 | 一种显示面板及其制作方法 |
-
2014
- 2014-07-15 JP JP2014144900A patent/JP2016021170A/ja active Pending
-
2015
- 2015-06-09 TW TW104118653A patent/TWI576751B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2015-07-02 WO PCT/JP2015/069166 patent/WO2016009851A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2015-07-02 CN CN201580038014.5A patent/CN106537306A/zh not_active Withdrawn
- 2015-07-02 KR KR1020177001068A patent/KR20170018922A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2015-07-02 US US15/325,781 patent/US20170168337A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003011284A (ja) * | 2001-07-04 | 2003-01-15 | Mitsui Chemicals Inc | 積層フィルムないしシート、およびその製造方法 |
| JP2004255635A (ja) * | 2003-02-25 | 2004-09-16 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 透明積層フィルム、反射防止フィルム及びそれを用いた偏光板、液晶表示装置 |
| JP2007178915A (ja) * | 2005-12-28 | 2007-07-12 | Fujifilm Corp | 金属微粒子分散物及び赤外線遮蔽フィルター |
| JP2012254621A (ja) * | 2011-05-19 | 2012-12-27 | Arakawa Chem Ind Co Ltd | ガスバリア性積層ポリイミドフィルム、機能性薄膜層積層ガスバリア性積層ポリイミドフィルム、ディスプレイ及び太陽電池 |
| JP2013200891A (ja) * | 2011-12-05 | 2013-10-03 | Hitachi Chemical Co Ltd | タッチパネル用電極の保護膜及びタッチパネル |
| JP2014010516A (ja) * | 2012-06-28 | 2014-01-20 | Hitachi Chemical Co Ltd | 静電容量結合方式タッチパネルおよびその製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016021170A (ja) | 2016-02-04 |
| TW201602887A (zh) | 2016-01-16 |
| TWI576751B (zh) | 2017-04-01 |
| US20170168337A1 (en) | 2017-06-15 |
| KR20170018922A (ko) | 2017-02-20 |
| CN106537306A (zh) | 2017-03-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2016009851A1 (ja) | 静電容量結合方式タッチパネル入力装置付き表示装置 | |
| TWI477851B (zh) | 觸控顯示面板與觸控液晶顯示面板 | |
| CN103543486B (zh) | 具有透明电屏蔽层的触摸屏显示器 | |
| TWI502429B (zh) | 觸控式顯示裝置及其製作方法 | |
| US9696830B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing transparent circuit substrate for touch screen | |
| TWI408583B (zh) | 薄型化觸控裝置 | |
| US10289224B2 (en) | Pressure sensing display and manufacturing method thereof | |
| TWI536217B (zh) | 觸控顯示裝置 | |
| JP5732317B2 (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| JP2011070092A (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| JP6148913B2 (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| TWI452612B (zh) | 觸控面板及觸控顯示面板 | |
| JP5923417B2 (ja) | 表示装置及びカバー部材 | |
| JP2012220670A (ja) | タッチパネル電極付きカラーフィルタとその製造方法 | |
| TW202009673A (zh) | 觸控顯示裝置 | |
| JP2016021170A5 (ja) | ||
| TWI684118B (zh) | 具有壓力感測的顯示裝置 | |
| JP5987668B2 (ja) | 表示装置およびその製造方法 | |
| US20160132175A1 (en) | Optical film and touch controlled display apparatus using the same | |
| JP2017142382A (ja) | 電極付きカラーフィルタ基板および液晶ディスプレイ | |
| TWI718470B (zh) | 觸控偏光結構及其應用之觸控顯示裝置 | |
| KR102193795B1 (ko) | 보강부재가 도포된 터치 패널 | |
| KR102227163B1 (ko) | 표시 장치 | |
| JP2015011109A (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| JP2013025675A (ja) | センシング基板及び表示装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15822870 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15325781 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20177001068 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15822870 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |