WO2016002351A1 - 吸収性物品 - Google Patents
吸収性物品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016002351A1 WO2016002351A1 PCT/JP2015/063664 JP2015063664W WO2016002351A1 WO 2016002351 A1 WO2016002351 A1 WO 2016002351A1 JP 2015063664 W JP2015063664 W JP 2015063664W WO 2016002351 A1 WO2016002351 A1 WO 2016002351A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- cooling sensation
- absorbent article
- component
- contact layer
- layer
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/47—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins
- A61F13/472—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins specially adapted for female use
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers
- A61F13/515—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers characterised by the interconnection of the topsheet and the backsheet
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to absorbent articles.
- Patent Document 1 has a front surface layer, a back surface layer, and a main body absorption layer disposed between both layers, and has rear flaps on both sides of the longitudinal rear portion disposed near the wearer's back.
- a flap portion absorbent layer is disposed on the rear flap, and the upper surface of the flap portion absorbent layer is covered with an extending portion of a sheet material having a part on the upper surface of the main body absorbent layer.
- the sheet material is made of a water-repellent nonwoven fabric, and the portion located on the upper surface of the main body absorbent layer has water repellency, and the portion covering the flap portion absorbent layer is pressed together with the flap portion absorbent layer to form a concave shape.
- An absorbent article having an embossed portion formed in the above and bonded to the flap portion absorbent layer is described.
- Absorbent articles having hip flaps are less likely to leak menstrual blood.
- the hip flaps are used by the futon and the wearer.
- the wearer's buttocks that are sandwiched between the body and in contact with the hip flap part tend to feel stuffy. Therefore, this indication aims at providing the absorbent article which a wearer's buttocks, especially the part which contact
- the present disclosure includes a main body including a liquid permeable layer, a liquid impermeable layer, and an absorbent layer between the liquid permeable layer and the liquid impermeable layer, and a pair of hips extending from the main body.
- An absorbent article comprising a flap, wherein the pair of hip flaps includes a cooling sensation component application region to which a cooling sensation component is applied has been found.
- the absorbent article of the present disclosure is less susceptible to stuffiness at the wearer's buttocks, particularly the part that contacts the hip flap.
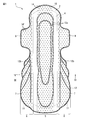
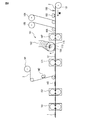
- FIG. 1 is a plan view of an absorbent article according to one of the embodiments of the present disclosure.
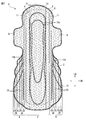
- FIG. 2 is a plan view of the absorbent article 1 shown in FIG. 1 with the top sheet 2 removed.
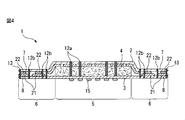
- 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III of FIG.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of an absorbent article according to another embodiment of the present disclosure corresponding to the III-III cross section of FIG.
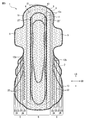
- FIG. 5 is a plan view corresponding to the plan view of FIG. 2 of an absorbent article according to another embodiment of the present disclosure.
- Drawing 6 is a figure for explaining an example of manufacture of an absorptive article according to one of the embodiments of this indication.
- Drawing 7 is a figure for explaining an example of manufacture of an absorptive article according to one of the embodiments of this indication.
- the “main part” is present in the center in the width direction of the absorbent article, and absorbs between the liquid-permeable layer, the liquid-impermeable layer, and the liquid-permeable layer and the liquid-impermeable layer.
- the part including the layer is meant.
- a hip flap is a part which exists in the width direction both ends of an absorbent article and is extended from a main-body part, Comprising: It is a part fixed to the inner side of clothes through an adhesion part. The hip flap is different in this respect from the side flap that is folded and fixed to the outside of the clothing through the adhesive portion. Further, the hip flap is generally present behind the absorbent article.
- the microcapsule means a capsule having a diameter of 1 to 1,000 ⁇ m and having a space containing a core material (cooling sensation component).
- the external shape is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include external shapes such as a spherical shape and an indefinite shape.
- the capsule may be a mononuclear type having one space for holding a core material or a multi-nucleus type having a plurality of spaces for holding a core material.
- Examples of the shape of the space include a space shape such as a spherical shape and an indefinite shape.
- the microcapsules include those having a spherical appearance and a multinuclear type space.
- water-disintegrating is a term relating to microcapsules, and to the extent that a cooling sensation component contained therein is released by contact with a body fluid, for example, a liquid (aqueous solution) such as sweat, menstrual blood, or urine. It means the property of collapsing. Specifically, when the microcapsule comes into contact with the liquid, the material of the microcapsule dissolves in water and collapses. When the microcapsule comes into contact with the liquid, the microcapsule swells in water and its strength decreases. Examples include a case where the capsule collapses due to destruction.
- “wearer” means a wearer of the absorbent article, for example, a baby in a disposable diaper, a care recipient, a woman in a sanitary napkin, and the like.
- “user” means a user of an absorbent article, and means a person who wears the absorbent article on the wearer, for example, a mother in a disposable diaper, a caregiver, etc. in addition to the above-mentioned wearer. .
- FIG. 1 is a front view of an absorbent article 1 according to one embodiment of the present disclosure, and more specifically, a front view of a sanitary napkin.
- FIG. 2 is a plan view of the absorbent article 1 shown in FIG. 1 with the top sheet 2 removed for illustration.
- 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III of FIG.
- the absorbent article 1 shown in FIGS. 1 to 3 includes a top sheet 2 as a liquid permeable layer, a back sheet 3 as a liquid impermeable layer, and an absorbent layer between the top sheet 2 and the back sheet 3.
- the main body 5 including the absorbent body 4 and a pair of hip flaps 6 extending from the main body 5 are provided.
- the pair of hip flaps 6 includes a skin contact layer 7 and a clothing contact layer 8.
- the top sheet 2 of the main body 5 and the skin contact layer 7 of the pair of hip flaps 6 are formed continuously (from a single material).
- the back sheet 3 of the main body 5 and the clothing contact layer 8 of the pair of hip flaps 6 are formed continuously (from a single material).
- the absorbent article 1 shown in FIGS. 1 to 3 includes a pair of side flaps 9 extending from the main body 5 at both ends in the width direction of the absorbent article and in front of the pair of hip flaps 6.
- the pair of side flaps 9 includes a skin contact layer 7 and a clothing contact layer 8, and the top sheet 2 of the main body 5 and the skin contact layer 7 of the pair of side flaps 9
- the back sheet 3 of the main body 5 and the clothing contact layer 8 of the pair of side flaps 9 are formed continuously (from a single material). ing.
- the side flap 9 is folded and fixed to the outer side of the clothing through the adhesive portion, the skin contact layer 7 does not contact the wearer's skin in the use state in the side flap 9. .
- the main body 5 further includes a central auxiliary sheet 10 between the top sheet 2 and the back sheet 3, and each hip flap 6 and each side flap 9 includes The side auxiliary sheet 11 is included between the skin contact layer 7 and the clothing contact layer 8.
- An absorbent article 1 shown in FIG. 1 to FIG. 3 is disposed in a main body 5, and is formed by embossing a top sheet 2, a central auxiliary sheet 10 and an absorbent body 4, and a pair of hips. It has the embossing part 12b formed by embossing the skin contact layer 7, the side part auxiliary
- the absorbent article 1 shown in FIGS. 1 to 3 has a round embossed part 13 formed by embossing the peripheral part of the absorbent article 1.
- the absorbent article 1 shown in FIGS. 1 to 3 includes an opening 14 formed in the main body 5 by opening the top sheet 2 and the central auxiliary sheet 10 and a pair of hip flaps. 6, the skin contact layer 7 and the side portion auxiliary sheet 11, which are formed by opening the skin contact layer 7 and the side portion auxiliary sheet 11.
- the absorbent article 1 includes a top sheet (not shown) and a layer adjacent to the top sheet (that is, the central auxiliary sheet 10, the side auxiliary sheet 11, the absorbent body 4, the back sheet 3, or the clothing). Between the contact layer 8), a plurality of adhesive application regions 21 to which an adhesive is applied are provided.
- each hip flap 6 includes a cooling sensation component application region 22 in which a cooling sensation composition is applied on the side auxiliary sheet 11 and the adhesive application region 21.
- the cooling sensation composition includes a cooling sensation component, a water-disintegrating microcapsule that encapsulates the cooling sensation component, a functional component, and a solvent that holds the cooling sensation component in the microcapsule.
- the opening 14 formed in the central auxiliary sheet 10 and the opening 14 ′ formed in the two side auxiliary sheets 11 are omitted for easy understanding.
- the cooling sensation composition will be described later.
- the adhesive application region 21 holds the adhesive region 23 that directly joins the skin contact layer 7 and the clothing contact layer 8 and the microcapsules contained in the cooling composition. And a microcapsule holding region 24.
- the adhesion region 23 is not in contact with the cooling sensation component application region 22, and more specifically, the adhesion region 23 does not contain the solvent that is a component of the cooling sensation composition, and the skin contact layer 7 and the clothing The contact layer 8 is bonded.
- an adhesive having adhesiveness holds the microcapsules contained in the cooling sensation composition.
- a microcapsule and a solvent it demonstrates in the location of a cooling sensation composition.
- FIG. 3 the cross-sectional view shown in FIG. 3 is enlarged particularly in the thickness direction of the absorbent article 1 to facilitate understanding of the present disclosure.
- the adhesion region 23 does not appear to adhere two adjacent layers. Two adjacent layers, that is, the skin contact layer 7 and the clothing contact layer 8 are joined.
- the adhesion part 15 for fixing the absorbent article 1 to a wearer's clothing is shown by FIG.
- each hip flap 6 includes a skin contact layer 7, a side auxiliary sheet 11, and a clothing contact layer 8.
- the hip flap includes an arbitrary layer, for example, a skin contact layer and a clothing contact layer.
- the cooling sensation component application region 22 includes a cooling sensation component, a water-disintegrating microcapsule containing the cooling sensation component, a functional component, and a cooling sensation component.
- the cooling sensation component application region is not limited to the above-mentioned cooling sensation composition. It can be formed by applying a cooling sensation component itself, a microcapsule containing the cooling sensation component or the like.
- the cooling sensation component (cooling sensation composition) is applied to an arbitrary surface of an arbitrary layer.
- the skin side surface or the clothing side surface of the skin contact layer, the clothing contact layer It is applied to the skin side surface, the skin side surface of the side auxiliary sheet, or the clothing side surface.
- cooling sensation component cooling sensation composition
- the cooling sensation component application region is, for example, between the skin contact layer and the clothing contact layer, between the skin contact layer and the side auxiliary sheet, or on the side portion. It can be formed between the auxiliary sheet and the clothing contact layer.
- the plurality of adhesive application areas 21 are formed by applying adhesive in the longitudinal direction LD of the absorbent article 1 while reciprocating in the width direction CD of the absorbent article 1.
- the adhesive application area is not particularly limited and is arranged in a manner known in the art.
- the adhesive application region can be arranged in a spiral shape, a Z shape, a linear shape, or a dot shape along the longitudinal direction or the width direction of the absorbent article.
- examples of the adhesive forming the adhesive application region include an adhesive known in the art, for example, a hot melt adhesive.
- the cooling sensation component application region 22 is arranged in a planar shape on the clothing contact layer 8 and the adhesive application region 21 of each hip flap 6.
- the arrangement of the sensitive component application region 22 is not limited to that shown in FIG.
- the cooling sensation component application region can be arranged along the longitudinal direction or the width direction of the absorbent article in a shape such as a planar shape, a linear shape, a spiral shape, a Z shape, a linear shape, or a dot shape.
- the cooling sensation component application region 22 is arranged with a certain distance from the main body 5.
- the cooling sensation component application region is arranged at a certain distance from the main body portion.
- the hips that come in contact with the hip flap have a relatively thick epidermis and a dull sensation, so it is preferable to place a larger amount of cooling sensation, while the crotch, particularly the excretory opening contact area, has a sharper sensation than the buttock. For this reason, it is not preferable that the crotch part comes into contact with the cold sensation component application region formulated and arranged for the hip flap.
- cooling sensation component examples include those known in the art as cooling sensation materials, such as those acting on a receptor activation channel (TRPM8) in skin nerves, such as menthol (for example, l-menthol) and derivatives thereof, methyl salicylate, camphor, essential oils derived from plants (for example, mint, eucalyptus), and the like.
- TRPM8 receptor activation channel 8
- menthol for example, l-menthol
- methyl salicylate for example, camphor
- essential oils derived from plants for example, mint, eucalyptus
- cooling sensation component examples include, for example, menthyl lactate, menthyl succinate, menthone glycerol acetal, 3-l-mentoxypropane-1,2-diol, p-menthane-3,8-diol, menthylethylaminooxalic acid, Menthanecarbonylglycine ethyl ester, N-ethyl-3-p-menthane carboxamide, N, 2,3-trimethyl-2-isopropylbutanamide, isopulegol, menthyl pyrrolidone carboxylic acid, menthyl acetate, cineol, borneol, thymol, etc. It is done.
- examples of the cooling sensation component include those that lower the ambient temperature by heat of vaporization, for example, alcohols such as methanol and ethanol.
- the cooling sensation component may be protected by a water-disintegrating protective material such as microcapsules in order to prevent volatilization before the absorbent article is used.
- the microcapsules contain a cooling sensation component, and disintegrate when touched by a liquid, thereby releasing the cooling sensation component to the outside.
- the released cooling sensation component evaporates due to the body temperature of the wearer, etc., and makes the wearer feel a sensation of cooling.
- the degree of water disintegration of the microcapsule varies depending on how the cooling sensation component is released after contact with the liquid.
- the water disintegration property is preferably high, and the water disintegration property is preferably low in order to gradually release the cooling sensation component.
- the microcapsules when the microcapsules are disintegrated by dissolving in water, the microcapsules are preferably 10 to 300 g, more preferably 20 to 200 g, with respect to 100 g of water at 25 ° C. More preferably, it has a water solubility in the range of 30 to 100 g.
- the above-mentioned water solubility is OECD guideline No. 1 except that the test temperature is 25 ° C. Measured according to the 105 flask method.
- Examples of the material of the microcapsule include saccharides such as monosaccharides (for example, glucose), disaccharides (for example, sucrose), polysaccharides (for example, dextrin, glucomannan, sodium alginate, water-soluble starch, etc.), Examples thereof include gelatin and water-soluble polymers (for example, polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinyl acetate, etc.).
- the microcapsule contains 50% by mass or more, and more preferably 70% by mass or more, of what passes through the sieve having an aperture of 75 ⁇ m and remains on the sieve having an aperture of 45 ⁇ m. This is from the viewpoint of dispersibility of the microcapsules in a solvent, coating properties, and the like.
- the microcapsules are commercially available, and examples thereof include INCAP (trademark) that is commercially available from Symrise.
- the microcapsules are also produced by dissolving the microcapsule material in water to form an aqueous solution, mixing the aqueous solution with a cooling sensation component and a surfactant, and drying under reduced pressure while spraying the aqueous solution. be able to.
- the cooling sensation component application region includes a cooling sensation component, a water-disintegrating microcapsule that contains the cooling sensation component, a functional component having volatility, and a cooling sensation component as a microcapsule. It may be formed by applying a cooling sensation composition containing a solvent to be held in an encapsulated state (hereinafter sometimes simply referred to as “cooling sensation composition”).
- cooling sensation composition a cooling sensation composition containing a solvent to be held in an encapsulated state
- the cooling sensation component application region can impart various functions to the wearer.
- each of the above functional components is not particularly limited as long as it provides a user with comfort as compared with the case where there is no such component.
- an aroma function for example, an aroma function, a cooling function, and a deodorizing function.
- An antibacterial function for example, an antibacterial function, a skin care function, and a function selected from the group consisting of any combination thereof.
- the functional component having a fragrance function is not particularly limited as long as it is used as a fragrance in this technical field.
- a highly volatile fragrance having a boiling point of about 250 ° C. or lower, a boiling point of about 250 to A mesovolatile fragrance at about 300 ° C. may be mentioned.
- the functional component which has an aroma function may be called an aroma component.
- fragrances examples include anisole, benzaldehyde, benzyl acetate, benzyl alcohol, benzyl formate, isobornyl acetate, citronellal, citronellol acetate, paracymene, decanal, dihydrolinalool, dihydromyrcenol, dimethylphenyl carbinol, Eucalyptol, l-carvone, geranial, geraniol, geranyl acetate, geranyl nitrile, nerol, neryl acetate, nonyl acetate, linalool, linalyl acetate, phenylethyl alcohol, ⁇ -pinene, ⁇ -pinene, ⁇ -pinene, ⁇ -ionone , ⁇ -ionone, ⁇ -terpineol, ⁇ -terpineol, terpinyl acetate, tent
- Examples of the medium volatile fragrance include, for example, amylcinnamaldehyde, methyl dihydrojasmonate, isoamyl salicylate, ⁇ -caryophyllene, cedrene, cedryl methyl ether, cinnamon alcohol, coumarin, dimethylbenzylcarbinyl acetate, ethyl vanillin, eugenol, iso Eugenol, ⁇ -methylionone, heliotropin, hexyl salicylate, cis-3-hexenyl salicylate, phenylhexanol, vanillin, pentalide and the like.
- the above fragrance component includes a fragrance having a green herbal-like fragrance.
- the above-mentioned fragrance having a green herbal-like fragrance can relieve mental unpleasant symptoms, especially among menstrual symptoms, safely and easily without giving physical stimulation to the body and not by oral administration. And give comfort to the user.
- green herbal-like fragrance is an incense tone including a green-like fragrance (green note) or a herbal-like fragrance (herbal note).
- Green-like aroma means a refreshing scent of grass and young leaves.
- Herbal-like fragrance is a natural and herb-like fragrance that uses herbs.
- fragrance having a green herbal-like odor examples include cis-3-hexenol, cis-3-hexenyl formate, cis-3-hexenyl acetate, cis-3-hexenyl propionate, cis-3-hexenyl butyrate, trans-2 -Hexenal, trans-2-hexenyl acetate, hexyl acetate, styryl acetate, 2-methyl-3- (3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl) -propanal (IFF company name, helional), 3 (4)-(5- Ethylbicyclo [2,2,1] heptyl-2) -cyclohexanol, allyl 2-pentyloxyglycolate (IFF company name, allyl amyl glycolate), 4-methyl-3-decen-5-ol (Givaudan company name, un Decaveltole), hexyl aldehyde, 2,4-dimethyl
- fragrance having a green herbal-like odor examples include l-menthol, 1,8-cineole, methyl salicylate, citronellal, camphor, borneol, isobornyl acetate, tarpinyl acetate, eugenol, anethole, 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol, and estragole. Can be mentioned.
- cooling sensation component As the functional component having the cooling sensation function (the functional component having the cooling sensation function may be referred to as “cooling sensation component”),
- deodorizing component examples include those known as deodorants in the art. .
- Examples of the skin care function include an anti-inflammatory function, an antipruritic function, a rash prevention function, and a moisturizing function, and examples of the functional component having the skin care function include menthol and methyl salicylate.
- the functional ingredient having the skin care function may be referred to as a skin care ingredient, and the functional ingredient having an anti-inflammatory function, an antipruritic function, an anti-rash function, and a moisturizing function, an anti-inflammatory ingredient, an anti-inflammatory ingredient, and an anti-rash ingredient, respectively. And may be referred to as moisturizing ingredients.
- the microcapsules are preferably insoluble in the solvent and preferably do not swell in a solvent that is a dispersion medium for the microcapsules. This is from the viewpoint of protection of the cooling sensation component contained.
- the above-mentioned microcapsules have a solvent solubility of preferably not more than 1.0 g, more preferably not more than 0.5 g, and still more preferably not more than 0.1 g with respect to 100 g of the solvent that is a dispersion medium of the microcapsules at 25 ° C. .
- the solvent solubility is as follows. At 25 ° C., a sample of 1.0 g (0.5 g, 0.1 g, etc.) is added to 100 g of solvent, allowed to stand for 24 hours, and gently stirred as necessary. It is evaluated by visually evaluating whether or not is dissolved.
- Each of the cooling sensation component and the functional component is volatile.
- the preferred vapor pressure varies depending on the function to be exhibited by the functional component, but the cooling component and the functional component are preferably 30 Pa or more, more preferably 50 Pa at 25 ° C. and 1 atm, for example.
- the vapor pressure is 70 Pa or more. If the vapor pressure is too low, it tends to be difficult to perform a desired function. If the vapor pressure is too high, the functional component volatilizes before the user uses the absorbent article. In some cases, the amount tends to decrease, and the wearer's skin is excessively functional.
- the solvent is one that retains the cooling sensation component in the microcapsule and retains the functional component, that is, dissolves the functional component but does not dissolve or swell the microcapsule. It is preferable.
- the solvent in which the microcapsules are dispersed may be referred to as a first solvent in order to distinguish it from the second solvent that can be included in the microcapsules together with the cooling sensation component.
- the solvent is preferably a lipophilic solvent.
- the solvent has an IOB described later of 0.00 or more and preferably 1.0 or less, more preferably 0.8 or less, and still more preferably 0.6 or less.
- IOB Inorganic Organic Balance
- IOB is an index indicating a balance between hydrophilicity and lipophilicity.
- Oda et al. IOB value calculated by inorganic value / organic value.
- the inorganic value and the organic value are represented by Fujita Minoru, “Prediction of organic compounds and conceptual diagram of organic compounds” in the field of chemistry Vol. 11, no. 10 (1957) p. 719-725).
- Table 1 summarizes the organic and inorganic values of the major groups by Mr. Fujita.
- the solvent preferably has a kinematic viscosity of 0.01 to 80 mm 2 / s at 40 ° C. from the viewpoint of the coating properties of the functional composition.
- the kinematic viscosity is measured according to JIS K 2283: 2000 “5. Kinematic Viscosity Test Method” using a Canon Fenceke reverse flow viscometer at a test temperature of 40 ° C.
- the above solvent preferably has a vapor pressure of 0.00 to 0.01 Pa, more preferably 0.000 to 0.001 Pa, and still more preferably 0.0000 to 0.0001 Pa at 1 atm and 25 ° C.
- the solvent is preferably 0.00 to 0.01 Pa, more preferably 0.000 to 0.001 Pa at 1 atm and 40 ° C.
- Examples of the solvent include lipophilic alcohol solvents, ester solvents, ether solvents, ketone solvents, and hydrocarbon solvents.
- An example of the hydrocarbon solvent is, for example, liquid paraffin, and an example of the ester solvent is isopropyl myristate.
- the solvent includes an IOB of 0.00 to 0.60, a kinematic viscosity of 0.01 to 80 mm 2 / s at 40 ° C., a water retention of 0.01 to 4.0% by mass, A component having a weight average molecular weight of less than 000 (hereinafter sometimes referred to as “body fluid lubricity imparting agent”) may be included.
- the body fluid lubricity-imparting agent is a component similar to the “blood modifying agent” described in International Publication No. 2012/133724, which is an application of the present applicant, and also International Publication No. 2013/129236 pamphlet. It is the same component as the “blood slipperiness imparting agent” described in 1.
- the said solvent contains a bodily fluid lubricity imparting agent, the bodily fluid etc. which reached
- body fluid lubricity imparting material examples include, for example, triglyceride, for example, Panacet 810s manufactured by NOF Corporation, Panacet 800, hydrocarbon, for example, Pearl Ream 6 manufactured by NOF Corporation.
- the functional composition present in the cooling sensation component application region has a desired function and a desired timing as follows.
- the functional component dissolved in the solvent (first solvent) is volatilized, and the function of the functional component is given to the user.
- the functional component is a fragrance component
- the user can feel the fragrance drifting around.
- the functional component when the functional component is a deodorizing component, when the user opens the absorbent article, the functional component exhibits a deodorizing function, and the user absorbs the liquid absorbed by the absorbent article to be replaced. It becomes difficult to feel the odor derived from it.
- the release amount of the functional component can be changed by the amount of the functional component, the vapor pressure of the functional component, and the like. For example, by increasing the amount of the functional component contained in the absorbent article or selecting a functional component having a high vapor pressure, the functional component can be released to the surroundings at a high concentration in a short time. On the other hand, for example, by selecting a functional component having a low vapor pressure, the functional component can be released to the surroundings for a long time.
- the absorbent article when packaged and sold as a package of individual absorbent articles, adjusting the form of the individual packaging and the packaging form, for example, absorbing with a non-woven fabric having air permeability
- the functional component can exhibit its function when the user opens the package by individually packaging the functional article and packaging the plurality of individually packaged absorbent articles with a polymer film.
- the wearer wears the absorbent article
- vaporization of the functional component is promoted by the body temperature of the wearer, and the function of the functional component is promoted.
- the functional component is a fragrance component, a cooling sensation component, a deodorizing component, an antibacterial component or a skin care component
- the fragrance function, the cooling sensation function, the deodorizing function, the antibacterial function or the skin care function are promoted, respectively.
- the absorbent article absorbs the liquid
- the absorbed liquid disintegrates the water-disintegrating microcapsules
- the cooling sensation component is released from the microcapsules, and the cooling sensation function is exhibited.
- the release amount of the cooling sensation component can be changed depending on the amount, the vapor pressure, the solubility of the microcapsule in water, the thickness of the microcapsule layer, the particle size of the microcapsule, and the like.
- the cooling sensation component can be released to the surroundings at a high concentration in a short time.
- cooling sensation component can be released gradually by increasing the thickness of the layer, increasing the particle size of the microcapsules, or the like.
- the microcapsule may further contain a solvent in addition to the cooling sensation component from the viewpoint of controlling the release of the cooling sensation component (this solvent may be referred to as a “second solvent”).
- this solvent may be referred to as a “second solvent”.
- the second solvent include those similar to the first solvent.
- the amount of the functional component varies depending on the function of the functional component and the like, but generally the cooling sensation composition contains the functional component, preferably 0.01 to 20% by mass. More preferably 0.05 to 15% by mass, and still more preferably 0.1 to 10% by mass.
- the cooling sensation composition preferably contains microcapsules containing a cooling sensation component in a ratio of 0.1 to 60% by mass, more preferably 5 to 40% by mass, and even more preferably 10 to 30% by mass. This is from the viewpoint of the coatability of the cooling sensation composition.
- the amount of the cooling sensation component in the cooling sensation composition varies depending on the function of the cooling sensation component and the like, but generally the cooling sensation composition contains the cooling sensation component, preferably 0.01 to 30 mass. %, More preferably 0.05 to 20% by weight, and still more preferably 1 to 15% by weight.
- the basis weight of the cooling sensation composition also varies depending on the concentration of the cooling sensation component and the functional component, but preferably 1 to 12 g / m 2 , and more preferably 2 to 10 g / m 2 .
- the basis weight is less than 1 g / m 2 , the cooling sensation component and the functional component may not easily function, and when the basis weight exceeds 12 g / m 2 , the solvent (first solvent). May hinder bonding with an adhesive.
- the adhesive application region is a layer adjacent to the absorbent article in the thickness direction, for example, a skin contact layer and a clothing contact layer, directly or indirectly. It is preferable to have an adhesive region to be joined. This is because the hip flap is less likely to sway during use.
- the adhesive region may be formed in a range where the adhesive application region does not overlap with the cooling sensation component application region in the thickness direction of the absorbent article.
- the adhesion region does not include a solvent constituting the cooling sensation composition. This is because the solvent tends to inhibit the adhesive from directly or indirectly joining the adjacent layers in the thickness direction of the absorbent article.
- that the adhesive region does not contain the solvent constituting the cooling sensation means that the adhesive constituting the adhesive region contains the solvent in an amount of 0 to 5% by mass.
- the adhesive application region preferably further includes a microcapsule holding region that holds the microcapsules. This is because the microcapsule holding region holds the microcapsule, and thus the position of the cooling sensation component is difficult to shift during use.
- the microcapsule holding region may be formed in a range where the adhesive application region overlaps the cooling sensation component application region in the thickness direction of the absorbent article.
- microcapsule holding region is preferably formed between the skin contact layer of each hip flap and a layer adjacent to the clothing contact layer side. This is because the liquid that has passed through the liquid-permeable layer can quickly reach the microcapsules, so that the cooling sensation component can be released with a small amount of liquid.
- the absorbent article has a cooling sensation component application region in between, as shown in FIGS. It is preferable to have an embossed portion formed by embossing at least the skin contact layer and the clothing contact layer.
- the adhesive tends to inhibit the skin contact layer and the clothing contact layer from being directly or indirectly joined by the solvent constituting the cooling sensation composition.
- the embossed portion holds the cooling sensation component while being encapsulated in the microcapsule.
- the microcapsules, and thus the cooling sensation component can be kept in a specific position.
- the embossed portion tends to lead the liquid to the embossed portion preferentially due to the high fiber density, the cooling sensation component can be released with a small amount of liquid.
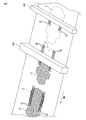
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of an absorbent article according to another embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view corresponding to the III-III cross section of FIG.
- the absorbent article 1 shown in FIG. 4 is the same as the embodiment shown in FIGS. 1 to 3 except that the central auxiliary sheet and the two side auxiliary sheets are not present.
- FIG. 5 is a plan view of the absorbent article 1 according to another embodiment of the present disclosure, and is a plan view corresponding to the plan view of FIG. 2.
- the main body 5 includes a cooling sensation component application region 22 ′ where a cooling sensation composition is applied.
- a main-body part contains a cooling sensation component application
- the main body part includes the cooling sensation component application region
- it is preferable that the total amount of cooling sensation component in each hip flap is larger than the total amount of cooling sensation component in the main body part. This is because the buttocks are less likely to feel cold than the crotch.
- the skin contact layer of the hip flap can be formed of the same material as the liquid permeable layer of the main body, and is formed of, for example, a nonwoven fabric.
- the skin contact layer may be formed continuously (from a single material) with the liquid permeable layer of the main body, or may be formed separately from the liquid permeable layer of the main body. .
- the clothing contact layer of the hip flap can be formed from the same material as the liquid-impermeable layer of the main body, for example, a film containing PE, PP, etc.
- the clothing contact layer may be formed continuously (from a single material) with the liquid-impermeable layer of the main body, or may be formed separately from the liquid-impermeable layer of the main body. Also good.
- the central auxiliary sheet and the side auxiliary sheet can be formed of the same material as the liquid-permeable layer of the main body.
- the central auxiliary sheet and the side auxiliary sheet are preferably formed from a fabric containing hydrophobic fibers and hydrophilic fibers, for example, a spunlace nonwoven fabric, a spunbond-meltblown-spunbond (SMS) nonwoven fabric. It is because it has a thin and supple property. Moreover, it is because a hydrophilic fiber tends to hold
- hydrophobic fibers examples include synthetic fibers such as polyethylene terephthalate fibers, and examples of the hydrophilic fibers include cellulosic fibers such as regenerated cellulosic fibers such as rayon.
- the central auxiliary sheet and the side auxiliary sheet can also be formed from an airlaid pulp sheet.
- the cooling sensation component can be applied in liquid or solid form.
- the cooling sensation component is applied in a solid state, for example, a cooling sensation component that is solid at room temperature as it is, when the cooling sensation component is supported on a porous material, or encapsulated in the microcapsule, the cooling sensation component is used.
- the sensitive component can be applied, for example, according to the method described in paragraphs [0052] and [0053] of JP2010-234027.
- the cooling sensation component When the cooling sensation component is in a liquid state, for example, when a cooling sensation component that is liquid at room temperature (25 ° C.) is applied as it is, the cooling sensation component that is solid at room temperature is heated to the melting point or higher and applied.
- the cooling sensation composition when the cooling sensation component is dissolved in a solvent and applied, or when applied as a cooling sensation composition, the cooling sensation composition is applied to a coating machine known in the art, for example, roll-type coating. Coating machine, curtain type coating machine, slit type coating machine, spray type coating machine, dip type coating machine, bead type coating machine, flexo type coating machine, gravure type coating machine, etc. sell.
- the liquid cooling sensation component is preferably applied by a contact-type coating machine in which the coating outlet is in contact with the surface to be applied. This is because the cooling sensation component can be arranged at a desired position without scattering the cooling sensation component, that is, the cooling sensation component application region can be arranged at a desired position.
- the contact type coating machine include a roll type coating machine, a slit type coating machine, a dip type coating machine, a bead type coating machine, a flexo type coating machine, and a gravure type coating machine.
- the said cooling sensation composition is formed by adding and mixing the microcapsule which includes a cooling sensation component and a functional component in the above-mentioned solvent, for example.
- the microcapsules enclosing the cooling sensation component are commercially available and can be formed as described above.
- a cooling sensation composition is applied from the cooling sensation composition applicator 102 to a surface (non-skin contact surface) on which the absorbent body of the belt-like top sheet 2 wound up from the top sheet roll 101 is stacked, and the top sheet 2
- a cooling sensation component application region 22 is formed on the substrate.
- an adhesive is applied from the adhesive applicator 103, and the adhesive application region 21 is formed on the top sheet 2 with the cooling sensation component application region 22 interposed therebetween.
- the band-shaped central auxiliary sheet 10 wound up from the central auxiliary sheet roll 104 is stacked on the adhesive application region 21, and is then unwound from the side auxiliary sheet roll 105. 11 are stacked to form a stack 106.
- the stack 106 is passed through the opening machine 107, and the openings 14 and 14 'are formed in the stack 106.
- the absorbent body 4 discharged from the absorbent body manufacturing apparatus 111 is stacked on the stacked body 106 in which the opening portions 14 and 14 ′ are formed, and the stacked body 121 is formed.
- the absorber manufacturing apparatus 111 is known in the art, and the absorber manufacturing apparatus 111 shown in FIG. 6 is formed on the outer peripheral surface of the material supply unit 112, the suction drum 113, and the suction drum 113. It has a concave mold 114 and a suction part 115.
- the embossed portion 12 a is formed on the stack 121 by embossing the stack 121 with a pair of embossing rolls 131.
- an adhesive is applied from the adhesive applicator 142 to the belt-like backsheet 3 unwound from the backsheet roll 141 and stacked on the stack 121 on which the embossed portion 12a is formed, thereby forming a stack 143.
- the embossed portion 12 b and the round embossed portion 13 are formed on the stack 143 with a pair of embossing rolls 151, and cut into the shape of the absorbent article with the cutter 161, thereby manufacturing the absorbent article 1.
- absorbent article of the present disclosure examples include sanitary napkins, panty liners, disposable diapers, urine absorption pads, and the like.
- Example 1 As a microcapsule containing a cooling sensation component, Symcap Inc. INCAP MENTHOL / IPM was prepared. INCAP MENTHOL / IPM contained menthol as a cooling sensation component, and the material of the microcapsule was material-modified starch. A solvent containing a fragrance component as a functional component was prepared. The solvent was IPM (isopropyl myristate). By mixing the microcapsules and the solvent at a mass ratio of 50:50, the cooling sensation composition No. 1 was prepared.
- the sanitary napkin No. 1 shown in FIGS. 1 and then sanitary napkin no. 1 was individually wrapped with a polyethylene film.
- the basis weight of the cooling composition was 4 g / m 2 .
- Sanitary napkin No. 1 was used by a plurality of volunteer subjects. After opening the individual package and during wearing, the sanitary napkin No. 1 was used. The fragrance of the fragrance drifts from 1 and the sanitary napkin No. 1 When I went to bed after wearing No. 1, I got a reply that I felt cold in the buttocks as I sweated.
Abstract
本開示は、着用者の臀部、特にヒップフラップと接する部分が蒸れを感じにくい吸収性物品を提供することを目的とする。本開示の吸収性物品は、以下の構成を有する。 液透過性層(2)と、液不透過性層(3)と、液透過性層(2)及び液不透過性層(3)の間の吸収層(4)とを含む本体部(5)と、本体部(5)から延びる一対のヒップフラップ(6)とを備える吸収性物品(1)であって、一対のヒップフラップ(6)が、冷感成分が塗布された冷感成分塗布領域(22)を含むことを特徴とする吸収性物品(1)。
Description
本開示は、吸収性物品に関する。
就寝中等に経血が吸収性物品の外部に漏れることを防止することを目的として、ヒップフラップを備える吸収性物品が市販されている。例えば、特許文献1には、表面層、裏面層及びこれら両層間に配置された本体吸収層を有し、着用者の背中寄りに配される長手方向後方部の両側部それぞれに後部フラップを有する吸収性物品であって、後部フラップには、フラップ部吸収層が配されており、フラップ部吸収層の上面が、本体吸収層の上面上に一部を有するシート材の延出部分によって覆われており、前記シート材は、撥水性不織布からなり、本体吸収層の上面上に位置する部分が撥水性を有すると共に、フラップ部吸収層を覆う部分に、該フラップ部吸収層と共に圧搾されて凹状に形成され該フラップ部吸収層と結合したエンボス部を有する吸収性物品が記載されている。
特許文献1に記載の吸収性物品のような、ヒップフラップを有する吸収性物品は、経血が漏れにくいが、例えば、就寝中に横向きに寝ている場合等、ヒップフラップが布団と着用者の体との間に挟まれ、ヒップフラップ部分と接する着用者の臀部が蒸れを感じやすい問題点がある。
従って、本開示は、着用者の臀部、特にヒップフラップと接する部分が蒸れを感じにくい吸収性物品を提供することを目的とする。
従って、本開示は、着用者の臀部、特にヒップフラップと接する部分が蒸れを感じにくい吸収性物品を提供することを目的とする。
本開示者らは、液透過性層と、液不透過性層と、上記液透過性層及び液不透過性層の間の吸収層とを含む本体部と、上記本体部から延びる一対のヒップフラップとを備える吸収性物品であって、一対のヒップフラップが、冷感成分が塗布された冷感成分塗布領域を含むことを特徴とする吸収性物品を見出した。
本開示の吸収性物品は、着用者の臀部、特にヒップフラップと接する部分が蒸れを感じにくい。
[定義]
本明細書における、いくつかの用語について、その定義を説明する。
[本体部]
本明細書において、「本体部」は、吸収性物品の幅方向中央に存在し、液透過性層と、液不透過性層と、上記液透過性層及び液不透過性層の間の吸収層とを含む部分を意味する。
本明細書における、いくつかの用語について、その定義を説明する。
[本体部]
本明細書において、「本体部」は、吸収性物品の幅方向中央に存在し、液透過性層と、液不透過性層と、上記液透過性層及び液不透過性層の間の吸収層とを含む部分を意味する。
[ヒップフラップ]
本明細書において、ヒップフラップは、吸収性物品の幅方向両端部に存在し且つ本体部から延びる部分であって、折り畳まれず、粘着部を介して着衣の内側に固定される部分である。ヒップフラップは、折り畳まれ、粘着部を介して着衣の外側に固定されるサイドフラップとはその点で異なる。また、ヒップフラップは、吸収性物品の後方に存在するのが一般的である。
本明細書において、ヒップフラップは、吸収性物品の幅方向両端部に存在し且つ本体部から延びる部分であって、折り畳まれず、粘着部を介して着衣の内側に固定される部分である。ヒップフラップは、折り畳まれ、粘着部を介して着衣の外側に固定されるサイドフラップとはその点で異なる。また、ヒップフラップは、吸収性物品の後方に存在するのが一般的である。
[マイクロカプセル]
本明細書において、マイクロカプセルは、直径1~1,000μmの大きさを有し、芯材(冷感成分)を内包する空間を有するカプセルを意味する。
上記カプセルは、芯材を内包し且つ芯材の放出を制御することができるものであれば、その外観形状は特に制限されず、例えば、球形、不定形等の外観形状が挙げられる。また、上記カプセルは、芯材を保持する空間を1つ有する単核型、又は芯材を保持する空間を複数有する多核型であることができる。上記空間の形状としては、球形、不定形等の空間形状が挙げられる。
上記マイクロカプセルの例としては、外観が球形であり且つ多核型の空間を有するものが挙げられる。
本明細書において、マイクロカプセルは、直径1~1,000μmの大きさを有し、芯材(冷感成分)を内包する空間を有するカプセルを意味する。
上記カプセルは、芯材を内包し且つ芯材の放出を制御することができるものであれば、その外観形状は特に制限されず、例えば、球形、不定形等の外観形状が挙げられる。また、上記カプセルは、芯材を保持する空間を1つ有する単核型、又は芯材を保持する空間を複数有する多核型であることができる。上記空間の形状としては、球形、不定形等の空間形状が挙げられる。
上記マイクロカプセルの例としては、外観が球形であり且つ多核型の空間を有するものが挙げられる。
[水崩壊性]
本明細書において、「水崩壊性」は、マイクロカプセルに関する用語であり、体液、例えば、汗、経血、尿等の液体(水溶液)と接することにより、内包する冷感成分を放出する程度に崩壊する性質を意味する。具体的には、マイクロカプセルが液体と接すると、マイクロカプセルの素材が水に溶解して崩壊する場合、マイクロカプセルが液体と接すると、マイクロカプセルが水に膨潤してその強度が低下し、マイクロカプセルが破壊されることにより崩壊する場合等が挙げられる。
本明細書において、「水崩壊性」は、マイクロカプセルに関する用語であり、体液、例えば、汗、経血、尿等の液体(水溶液)と接することにより、内包する冷感成分を放出する程度に崩壊する性質を意味する。具体的には、マイクロカプセルが液体と接すると、マイクロカプセルの素材が水に溶解して崩壊する場合、マイクロカプセルが液体と接すると、マイクロカプセルが水に膨潤してその強度が低下し、マイクロカプセルが破壊されることにより崩壊する場合等が挙げられる。
[着用者]
本明細書において、「着用者」は、吸収性物品の着用者を意味し、例えば、使い捨ておむつにおける赤ちゃん、要介護者等、生理用ナプキンにおける女性等を意味する。
[ユーザー]
本明細書において、「ユーザー」は、吸収性物品のユーザーを意味し、上述の着用者に加え、吸収性物品を着用者に着用させる者、例えば、使い捨ておむつにおける母親、介護者等を意味する。
本明細書において、「着用者」は、吸収性物品の着用者を意味し、例えば、使い捨ておむつにおける赤ちゃん、要介護者等、生理用ナプキンにおける女性等を意味する。
[ユーザー]
本明細書において、「ユーザー」は、吸収性物品のユーザーを意味し、上述の着用者に加え、吸収性物品を着用者に着用させる者、例えば、使い捨ておむつにおける母親、介護者等を意味する。
本開示の吸収性物品について、必要に応じて図面を用いて、以下、詳細に説明する。
図1は、本開示の実施形態の1つに従う吸収性物品1の正面図であり、より具体的には、生理用ナプキンの正面図である。図2は、説明のため、トップシート2が取り除かれた状態の、図1に示される吸収性物品1の平面図である。図3は、図1のIII-III断面における断面図である。
図1は、本開示の実施形態の1つに従う吸収性物品1の正面図であり、より具体的には、生理用ナプキンの正面図である。図2は、説明のため、トップシート2が取り除かれた状態の、図1に示される吸収性物品1の平面図である。図3は、図1のIII-III断面における断面図である。
図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1は、液透過性層としてのトップシート2と、液不透過性層としてのバックシート3と、トップシート2及びバックシート3の間の、吸収層としての吸収体4とを含む本体部5と、本体部5から延びる一対のヒップフラップ6とを備える。一対のヒップフラップ6は、肌当接層7及び着衣当接層8を含む。なお、図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1では、本体部5のトップシート2と、一対のヒップフラップ6の肌当接層7とが連続して(単一の素材から)形成されており、そして本体部5のバックシート3と、一対のヒップフラップ6の着衣当接層8とが連続して(単一の素材から)形成されている。
図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1は、吸収性物品の幅方向両端部且つ一対のヒップフラップ6の前方に、本体部5から延びる一対のサイドフラップ9を備える。一対のサイドフラップ9は、ヒップフラップ6と同様に、肌当接層7及び着衣当接層8を含み、本体部5のトップシート2と、一対のサイドフラップ9の肌当接層7とが連続して(単一の素材から)形成されており、そして本体部5のバックシート3と、一対のサイドフラップ9の着衣当接層8とが連続して(単一の素材から)形成されている。なお、サイドフラップ9は、折り畳まれ、粘着部を介して着衣の外側に固定されるため、サイドフラップ9において、肌当接層7は、使用状態において、着用者の肌に当接するものではない。
図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1において、本体部5は、トップシート2及びバックシート3の間に、中央部補助シート10をさらに含み、そして各ヒップフラップ6及び各サイドフラップ9は、肌当接層7及び着衣当接層8の間に、側部補助シート11を含む。
図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1は、本体部5に配置され、トップシート2、中央部補助シート10及び吸収体4をエンボスすることにより形成されたエンボス部12aと、一対のヒップフラップ6に配置され、肌当接層7、側部補助シート11及び着衣当接層8をエンボスすることにより形成されたエンボス部12bとを有する。
また、図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1は、吸収性物品1の周縁部をエンボスすることにより形成されたラウンドエンボス部13を有する。
また、図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1は、吸収性物品1の周縁部をエンボスすることにより形成されたラウンドエンボス部13を有する。
図1~図3に示される吸収性物品1は、本体部5に配置された、トップシート2及び中央部補助シート10を開孔することにより形成された開孔部14と、一対のヒップフラップ6に配置された、肌当接層7及び側部補助シート11を開孔することにより形成された開孔部14'とを有する。
図2において、吸収性物品1は、トップシート(図示せず)と、トップシートと隣接する層(すなわち、中央部補助シート10、側部補助シート11、吸収体4、バックシート3又は着衣当接層8)との間に、接着剤が塗布された、複数の接着剤塗布領域21を有する。また、図2において、各ヒップフラップ6は、側部補助シート11及び接着剤塗布領域21の上に、冷感組成物が塗布された冷感成分塗布領域22を有する。上記冷感組成物は、冷感成分と、当該冷感成分を内包する水崩壊性のマイクロカプセルと、機能性成分と、冷感成分をマイクロカプセルに内包させたまま保持する溶媒とを含む。
なお、図2は、理解しやすくするため、中央部補助シート10に形成された開孔部14と、2つの側部補助シート11に形成された開孔部14'とが省略されている。また、冷感組成物については、後述する。
また、図2の一対のヒップフラップ6では、接着剤塗布領域21が、肌当接層7及び着衣当接層8を直接接合する接着領域23と、冷感組成物に含まれるマイクロカプセルを保持するマイクロカプセル保持領域24とを有する。
接着領域23は、冷感成分塗布領域22と接しておらず、より具体的には、接着領域23が、冷感組成物の成分である溶媒を含まず、肌当接層7と、着衣当接層8とを接合している。
マイクロカプセル保持領域24では、粘着性を有する接着剤が、冷感組成物に含まれるマイクロカプセルを保持している。
なお、マイクロカプセル及び溶媒については、冷感組成物の箇所で説明する。
マイクロカプセル保持領域24では、粘着性を有する接着剤が、冷感組成物に含まれるマイクロカプセルを保持している。
なお、マイクロカプセル及び溶媒については、冷感組成物の箇所で説明する。
図3に示される断面図は、本開示を理解しやすくするため、特に吸収性物品1の厚さ方向に拡大されている点に留意されたい。例えば、図3では、冷感成分塗布領域22を一定の厚さで表示したため、接着領域23が、隣接する2つの層を接着していないように見えるが、実際には、接着領域23は、隣接する2つの層、すなわち、肌当接層7及び着衣当接層8を接合している。
なお、図3には、吸収性物品1を、着用者の着衣に固定するための粘着部15が示されている。
なお、図3には、吸収性物品1を、着用者の着衣に固定するための粘着部15が示されている。
図1~図3に示される実施形態では、各ヒップフラップ6が、肌当接層7、側部補助シート11及び着衣当接層8を含むが、本開示の吸収性物品では、当該実施形態に限定されず、ヒップフラップは、任意の層、例えば、肌当接層及び着衣当接層を含む。
図1~図3に示される実施形態では、冷感成分塗布領域22が、冷感成分と、冷感成分を内包する水崩壊性のマイクロカプセルと、機能性成分と、冷感成分をマイクロカプセルに内包させたまま保持する溶媒とを含む冷感組成物が塗布されることにより形成されたが、本開示の吸収性物品では、冷感成分塗布領域は、上記冷感組成物に限定されず、冷感成分そのもの、冷感成分を内包するマイクロカプセル等を塗布することにより形成されうる。
また、本開示の吸収性物品では、上記冷感成分(冷感組成物)は、任意の層の任意の面に塗布され、例えば、肌当接層の肌側面又は着衣側面、着衣当接層の肌側面、側部補助シートの肌側面又は着衣側面に塗布される。
上記冷感成分(冷感組成物)を着用者の肌に近い面に塗布することにより、すなわち、冷感成分塗布領域を、着用者の肌に近い場所に形成することにより、着用者が冷感を実感しやすくなる。また、冷感成分(冷感組成物)を着用者の肌から遠い面に塗布することにより、すなわち、冷感成分塗布領域を着用者の肌から遠い場所に形成することにより、着用者が冷感を長時間実感することができる。
上記冷感成分(冷感組成物)を着用者の肌に近い面に塗布することにより、すなわち、冷感成分塗布領域を、着用者の肌に近い場所に形成することにより、着用者が冷感を実感しやすくなる。また、冷感成分(冷感組成物)を着用者の肌から遠い面に塗布することにより、すなわち、冷感成分塗布領域を着用者の肌から遠い場所に形成することにより、着用者が冷感を長時間実感することができる。
また、本開示の吸収性物品では、上記冷感成分塗布領域は、例えば、肌当接層と、着衣当接層との間、肌当接層と、側部補助シートとの間、側部補助シートと、着衣当接層との間等に形成されうる。
図2では、複数の接着剤塗布領域21は、接着剤を、吸収性物品1の幅方向CDに往復しながら、吸収性物品1の長手方向LDに塗布することにより形成されているが、本開示の吸収性物品では、接着剤塗布領域は特に制限されず、当技術分野で公知の様式で配置される。例えば、接着剤塗布領域は、スパイラル状、Z状、線状、ドット状の形状で、吸収性物品の長手方向又は幅方向に沿って配置されることができる。
なお、本開示の吸収性物品では、上記接着剤塗布領域を形成する接着剤としては、当技術分野で公知の接着剤、例えば、ホットメルト接着剤が挙げられる。
なお、本開示の吸収性物品では、上記接着剤塗布領域を形成する接着剤としては、当技術分野で公知の接着剤、例えば、ホットメルト接着剤が挙げられる。
図2では、冷感成分塗布領域22は、各ヒップフラップ6の着衣当接層8及び接着剤塗布領域21の上に、面状に配置されているが、本開示の吸収性物品では、冷感成分塗布領域22の配置は、図2に示されるものに限定されない。例えば、冷感成分塗布領域は、面状、線状、スパイラル状、Z状、線状、ドット状等の形状で、吸収性物品の長手方向又は幅方向に沿って配置されることができる。
図2では、冷感成分塗布領域22が、本体部5と一定の間隔をあけて配置されている。本開示の吸収性物品では、冷感成分塗布領域が、本体部と一定の間隔をあけて配置されることが好ましい。ヒップフラップが当接する臀部は、表皮が比較的厚く、感覚が鈍いため、冷感成分を多めに配置することが好ましい一方で、股間部、特に排泄口当接域は、臀部よりも感覚が鋭いため、股間部がヒップフラップ用に処方及び配置された冷感成分塗布領域と接触することは好ましくないからである。
上記冷感成分としては、当技術分野で冷感材として知られているものが挙げられ、例えば、皮膚の神経にある受容体活性化チャネル(TRPM8)に作用するもの、例えば、メントール(例えば、l-メントール)及びその誘導体、サリチル酸メチル、カンファー、植物(例えば、ミント、ユーカリ)由来の精油等が挙げられる。
上記冷感成分としては、例えば、乳酸メンチル、コハク酸メンチル、メントングリセリンアセタール、3-l-メントキシプロパン-1,2-ジオール、p-メンタン-3,8-ジオール、メンチルエチルアミノシュウ酸、メンタンカルボニルグリシンエチルエステル、N-エチル-3-p-メンタンカルボキシアミド、N,2,3-トリメチル-2-イソプロピルブタンアミド、イソプレゴール、メンチルピロリドンカルボン酸、メンチルアセテート、シネオール、ボルネオール、チモール等が挙げられる。
また、上記冷感成分としては、気化熱により周囲の温度を下げるもの、例えば、アルコール、例えば、メタノール及びエタノールが挙げられる。
上記冷感成分としては、例えば、乳酸メンチル、コハク酸メンチル、メントングリセリンアセタール、3-l-メントキシプロパン-1,2-ジオール、p-メンタン-3,8-ジオール、メンチルエチルアミノシュウ酸、メンタンカルボニルグリシンエチルエステル、N-エチル-3-p-メンタンカルボキシアミド、N,2,3-トリメチル-2-イソプロピルブタンアミド、イソプレゴール、メンチルピロリドンカルボン酸、メンチルアセテート、シネオール、ボルネオール、チモール等が挙げられる。
また、上記冷感成分としては、気化熱により周囲の温度を下げるもの、例えば、アルコール、例えば、メタノール及びエタノールが挙げられる。
上記冷感成分は、吸収性物品が使用されるまでに揮発することを防止するため、水崩壊性の保護材、例えば、マイクロカプセルに保護されていてもよい。
上記マイクロカプセルは、冷感成分を内包し、液体に触れると崩壊し、冷感成分を外部に放出させる。放出された冷感成分は、着用者の体温等により気化し、着用者に冷感を実感させる。
上記マイクロカプセルは、冷感成分を内包し、液体に触れると崩壊し、冷感成分を外部に放出させる。放出された冷感成分は、着用者の体温等により気化し、着用者に冷感を実感させる。
上記マイクロカプセルの水崩壊性の度合いは、液体と接した後、冷感成分をどのように放出させるかによって異なり、例えば、液体と接した後に冷感成分を速やかに放出させるためには、上記水崩壊性が高いことが好ましく、そして冷感成分を徐放させるためには、上記水崩壊性が低いことが好ましい。
本開示の吸収性物品において、マイクロカプセルが水に溶解することにより崩壊する場合には、マイクロカプセルは、25℃において、水100gに対して、好ましくは10~300g、より好ましくは20~200g、そしてさらに好ましくは30~100gの範囲の水溶解度を有する。
上記水溶解度は、試験温度を25℃にした以外は、OECDガイドラインNo.105フラスコ法に従って測定される。
上記水溶解度は、試験温度を25℃にした以外は、OECDガイドラインNo.105フラスコ法に従って測定される。
上記マイクロカプセルの素材としては、例えば、糖類、例えば、単糖類(例えば、ブドウ糖)、二糖類(例えば、ショ糖)、多糖類(例えば、デキストリン、グルコマンナン、アルギン酸ナトリウム、水溶性でんぷん等)、ゼラチン、水溶性ポリマー(例えば、ポリビニルアルコール、ポリ酢酸ビニル等)等が挙げられる。
上記マイクロカプセルは、目開き75μmのふるいを通過し且つ目開き45μmのふるい上に残存するものを、好ましくは50質量%以上、そしてより好ましくは70質量%以上含む。マイクロカプセルの溶媒への分散性、塗工性等の観点からである。
上記マイクロカプセルは市販されており、例えば、Symrise社から市販される、INCAP(商標)等が挙げられる。
また、上記マイクロカプセルはまた、水にマイクロカプセルの素材を溶解させて水溶液を形成し、当該水溶液に冷感成分及び界面活性剤を混合し、上記水溶液をスプレーしながら減圧乾燥することにより製造することができる。
また、上記マイクロカプセルはまた、水にマイクロカプセルの素材を溶解させて水溶液を形成し、当該水溶液に冷感成分及び界面活性剤を混合し、上記水溶液をスプレーしながら減圧乾燥することにより製造することができる。
本開示の吸収性物品では、冷感成分塗布領域は、冷感成分と、冷感成分を内包する水崩壊性のマイクロカプセルと、揮発性を有する機能性成分と、冷感成分をマイクロカプセルに内包させたまま保持する溶媒とを含む冷感組成物(以下、単に「冷感組成物」と称する場合がある)を塗布することにより形成されてもよい。
冷感成分塗布領域が、冷感成分の他に機能性成分を含むことにより、着用者に種々の機能を付与することができる。
冷感成分塗布領域が、冷感成分の他に機能性成分を含むことにより、着用者に種々の機能を付与することができる。
上記機能性成分のそれぞれが有する機能は、ユーザーに、当該成分がない場合と比較して快適性を提供する機能であれば、特に制限されず、例えば、芳香機能、冷感機能、消臭機能、抗菌機能、スキンケア機能、並びにそれらの任意の組み合わせから成る群から選択される機能が挙げられる。
上記芳香機能を有する機能性成分としては、当技術分野で香料として用いられているものであれば、特に制限されず、例えば、沸点が約250℃以下の高揮発性香料、沸点が約250~約300℃の中揮発性香料が挙げられる。
なお、芳香機能を有する機能性成分を、芳香成分と称する場合がある。
なお、芳香機能を有する機能性成分を、芳香成分と称する場合がある。
上記高揮発性香料としては、例えば、アニソール、ベンズアルデヒド、酢酸ベンジル、ベンジルアルコール、ギ酸ベンジル、酢酸イソボルニル、シトロネラール、シトロネロール、酢酸シトロネリル、パラシメン、デカナール、ジヒドロリナロール、ジヒドロミルセノール、ジメチルフェニルカルビノール、ユーカリプトール、l-カルボン、ゲラニアール、ゲラニオール、酢酸ゲラニル、ゲラニルニトリル、ネロール、酢酸ネリル、酢酸ノニル、リナロール、酢酸リナリル、フェニルエチルアルコール、α-ピネン、β-ピネン、γ-ピネン、α-ヨノン、β-ヨノン、γ-ヨノン、α-テルピネオール、β-テルピネオール、酢酸テルピニル、テンタローム等が挙げられる。
上記中揮発性香料としては、例えば、アミルシンナムアルデヒド、ジヒドロジャスモン酸メチル、サリチル酸イソアミル、β-カリオフィレン、セドレン、セドリルメチルエーテル、桂皮アルコール、クマリン、ジメチルベンジルカルビニルアセテート、エチルバニリン、オイゲノール、イソオイゲノール、γ-メチルヨノン、ヘリオトロピン、サリチル酸ヘキシル、サリチル酸cis-3-ヘキセニル、フェニルヘキサノール、バニリン、ペンタライド等が挙げられる。
上記香料成分には、グリーンハーバル様香気を有する香料が含まれる。上記グリーンハーバル様香気を有する香料は、月経随伴性症状の中でも特に精神的な不快症状を、身体に物理的刺激を与えることなく、また、経口投与にもよらず、安全かつ簡便に緩和させることができ、そして、ユーザーに快適感も付与する。
上記グリーンハーバル様香気は、グリーン様香気(グリーンノート)又はハーバル様香気(ハーバルノート)を含む香調である。グリーン様香気とは、草や若葉のすがすがしい香調をいう。ハーバル様香気(ハーバルノート)とは、ハーブを用いた自然で、薬草的な香り立ちが特徴の香調をいう。
グリーンハーバル様香気を有する香料としては、例えば、cis-3-ヘキセノール、ギ酸cis-3-ヘキセニル、酢酸cis-3-ヘキセニル、プロピオン酸cis-3-ヘキセニル、酪酸cis-3-ヘキセニル、トランス-2-ヘキセナール、酢酸トランス-2-ヘキセニル、酢酸ヘキシル、酢酸スチラリル、2-メチル-3-(3,4-メチレンジオキシフェニル)-プロパナール(IFF社名、ヘリオナール)、3(4)-(5-エチルビシクロ[2,2,1]ヘプチル-2)-シクロヘキサノール、2-ペンチロキシグリコール酸アリル(IFF社名、アリルアミルグリコレート)、4-メチル-3-デセン-5-オール(Givaudan社名、ウンデカベルトール)、ヘキシルアルデヒド、2,4-ジメチル-3-シクロヘキセニルカルボキシアルデヒド(IFF社名、トリプラール)及びフェニルアセトアルデヒド等が挙げられる。
また、グリーンハーバル様香気を有する香料としては、l-メントール、1,8-シネオール、サリチル酸メチル、シトロネラール、カンファー、ボルネオール、酢酸イソボルニル、酢酸ターピニル、オイゲノール、アネトール、4-メトキシベンジルアルコール及びエストラゴールが挙げられる。
上記冷感機能を有する機能性成分(冷感機能を有する機能性成分を、「冷感成分」と称する場合がある)としては、
上記消臭機能を有する機能性成分(消臭機能を有する機能性成分を、「消臭成分」と称する場合がある)としては、当技術分野で消臭剤として知られているものが挙げられる。
上記消臭機能を有する機能性成分(消臭機能を有する機能性成分を、「消臭成分」と称する場合がある)としては、当技術分野で消臭剤として知られているものが挙げられる。
上記スキンケア機能としては、例えば、消炎機能、鎮痒機能、かぶれ防止機能、保湿機能等が挙げられ、そして上記スキンケア機能を有する機能性成分としては、例えば、メントール、サリチル酸メチル等が挙げられる。
なお、上記スキンケア機能を有する機能性成分を、スキンケア成分と称することがあり、消炎機能、鎮痒機能、かぶれ防止機能及び保湿機能を有する機能性成分を、それぞれ、消炎成分、鎮痒成分、かぶれ防止成分及び保湿成分と称する場合がある。
上記マイクロカプセルは、上記溶媒に不溶であることが好ましく、そして当該マイクロカプセルの分散媒である溶媒に膨潤しないことが好ましい。内包する冷感成分の保護の観点からである。
上記マイクロカプセルは、25℃において、マイクロカプセルの分散媒である溶媒100gに対して、好ましくは1.0g以下、より好ましくは0.5g以下、そしてさらに好ましくは0.1g以下の溶媒溶解度を有する。
上記マイクロカプセルは、25℃において、マイクロカプセルの分散媒である溶媒100gに対して、好ましくは1.0g以下、より好ましくは0.5g以下、そしてさらに好ましくは0.1g以下の溶媒溶解度を有する。
上記溶媒溶解度は、25℃において、100gの溶媒に、1.0g(0.5g,0.1g等)の試料を添加し、24時間静置し、必要に応じて軽く攪拌し、次いで、試料が溶解したか否か目視で評価することにより評価する。
冷感成分及び機能性成分のそれぞれは、揮発性を有する。上記揮発性は、機能性成分が発揮すべき機能によって、その好ましい蒸気圧は異なるが、冷感成分及び機能性成分は、例えば、25℃及び1気圧において、好ましくは30Pa以上、より好ましくは50Pa以上、そしてさらに好ましくは70Pa以上の蒸気圧を有する。上記蒸気圧が低すぎると、所望の機能を発揮しにくくなる傾向があり、そして上記蒸気圧が高すぎると、ユーザーが吸収性物品を使用するまでの間に、機能性成分が揮発し、その量が減少する傾向、着用者の皮膚に過度の機能を発揮する等の場合がある。
上記溶媒としては、冷感成分をマイクロカプセルに内包させたまま保持し且つ機能性成分を保持するものであること、すなわち、機能性成分を溶解させるが、マイクロカプセルを溶解又は膨潤させないものであることが好ましい。
なお、マイクロカプセルを分散させる溶媒は、冷感成分と共に、マイクロカプセルに内包されうる第2溶媒と区別するために、第1溶媒と称される場合がある。
なお、マイクロカプセルを分散させる溶媒は、冷感成分と共に、マイクロカプセルに内包されうる第2溶媒と区別するために、第1溶媒と称される場合がある。
水崩壊性のマイクロカプセルを崩壊させない観点からは、上記溶媒は、親油性溶媒であることが好ましい。
上記溶媒は、親油性の観点からは、後述のIOBが、0.00以上且つ好ましくは1.0以下、より好ましくは0.8以下、そしてさらに好ましくは0.6以下である。
上記溶媒は、親油性の観点からは、後述のIOBが、0.00以上且つ好ましくは1.0以下、より好ましくは0.8以下、そしてさらに好ましくは0.6以下である。
IOB(Inorganic Organic Balance)は、親水性及び親油性のバランスを示す指標であり、本明細書では、小田らによる次式:
IOB=無機性値/有機性値
により算出される値を意味する。
IOB=無機性値/有機性値
により算出される値を意味する。
上記無機性値と、有機性値とは、藤田穆「有機化合物の予測と有機概念図」化学の領域Vol.11,No.10(1957)p.719-725)に記載される有機概念図に基づく。
藤田氏による、主要な基の有機性値及び無機性値を、下記表1にまとめる。
藤田氏による、主要な基の有機性値及び無機性値を、下記表1にまとめる。
また、上記溶媒は、機能性組成物の塗工性の観点からは、40℃における0.01~80mm2/sの動粘度を有することが好ましい。
上記動粘度は、JIS K 2283:2000の「5.動粘度試験方法」に従って、キャノンフェンスケ逆流形粘度計を用いて、40℃の試験温度で測定する。
上記動粘度は、JIS K 2283:2000の「5.動粘度試験方法」に従って、キャノンフェンスケ逆流形粘度計を用いて、40℃の試験温度で測定する。
上記溶媒は、1気圧及び25℃において、好ましくは0.00~0.01Pa、より好ましくは0.000~0.001Pa、そしてさらに好ましくは0.0000~0.0001Paの蒸気圧を有する。本開示の吸収性物品が、人体に接して用いられることを考慮すると、上記溶媒は、1気圧及び40℃において、好ましくは0.00~0.01Pa、より好ましくは0.000~0.001Pa、そしてさらに好ましくは0.0000~0.0001Paの蒸気圧を有する。蒸気圧が高いと、保存中に気化し、溶媒及び機能性成分の量の減少、着用時の臭気等の問題が発生する場合があるからである。
上記溶媒としては、例えば、親油性のアルコール系溶媒、エステル系溶媒、エーテル系溶媒、ケトン系溶媒、炭化水素系溶媒が挙げられる。
上記炭化水素系溶媒の例としては、例えば、流動パラフィンが挙げられ、そして上記エステル系溶媒の例としては、ミリスチン酸イソプロピルが挙げられる。
上記炭化水素系溶媒の例としては、例えば、流動パラフィンが挙げられ、そして上記エステル系溶媒の例としては、ミリスチン酸イソプロピルが挙げられる。
また、上記溶媒は、0.00~0.60のIOBと、40℃における0.01~80mm2/sの動粘度と、0.01~4.0質量%の抱水率と、1,000未満の重量平均分子量とを有する成分(以下、「体液滑性付与剤」と称する場合がある)を含んでもよい。
上記体液滑性付与剤は、本件出願人の出願である、国際公開第2012/133724号パンフレットに記載の「血液改質剤」と同様の成分であり、そして同じく国際公開第2013/129236号パンフレットに記載の「血液滑性付与剤」と同一の成分である。
上記溶媒が体液滑性付与剤を含むことにより、長時間にわたり、液透過性層に到達した体液等を、吸収体の内部に迅速に滑落させることができる。
上記溶媒が体液滑性付与剤を含むことにより、長時間にわたり、液透過性層に到達した体液等を、吸収体の内部に迅速に滑落させることができる。
上記体液滑性付与材の例としては、例えば、トリグリセリド、例えば、日油株式会社製のパナセート810s,パナセート800、炭化水素、例えば、日油株式会社製のパールリーム6が挙げられる。
本開示の吸収性物品において、冷感成分塗布領域が冷感組成物を含む実施形態では、冷感成分塗布領域に存在する機能性組成物が、以下のように、所望の機能を所望のタイミングで発揮することができる。
ユーザーが吸収性物品を開封すると、上記溶媒(第1溶媒)に溶解した機能性成分が揮発し、ユーザーに機能性成分の機能が付与される。例えば、機能性成分が芳香成分である場合には、ユーザーが周囲に漂う芳香を感じることができる。
ユーザーが吸収性物品を開封すると、上記溶媒(第1溶媒)に溶解した機能性成分が揮発し、ユーザーに機能性成分の機能が付与される。例えば、機能性成分が芳香成分である場合には、ユーザーが周囲に漂う芳香を感じることができる。
また、上記機能性成分が消臭成分である場合には、ユーザーが吸収性物品を開封すると、機能性成分が消臭機能を発揮し、ユーザーが、交換すべき吸収性物品が吸収した液体に由来する臭気を感じにくくなる。
上記機能性成分の放出量は、機能性成分の量、機能性成分の蒸気圧等により変化させることができる。
例えば、吸収性物品に含まれる機能性成分の量を増やすこと、蒸気圧の高い機能性成分を選択すること等により、機能性成分を、短時間に高い濃度で周囲に放出することができる。
一方、例えば、蒸気圧の低い機能性成分を選択することにより、機能性成分を、長時間にわたり周囲に放出させることができる。
例えば、吸収性物品に含まれる機能性成分の量を増やすこと、蒸気圧の高い機能性成分を選択すること等により、機能性成分を、短時間に高い濃度で周囲に放出することができる。
一方、例えば、蒸気圧の低い機能性成分を選択することにより、機能性成分を、長時間にわたり周囲に放出させることができる。
なお、吸収性物品が、個包装の吸収性物品をまとめてパッケージ化して市販されている場合において、個包装の形態、並びにパッケージ化の形態を調整すること、例えば、通気性を有する不織布で吸収性物品を個包装化し、そして個包装化された複数の吸収性物品をポリマーフィルムによりパッケージ化することにより、ユーザーがパッケージを開封した際から、機能性成分はその機能を発揮することができる。
次いで、着用者が吸収性物品を着用すると、着用者の体温等によって、上記機能性成分の気化が促進され、機能性成分の機能が促進される。例えば、機能性成分が芳香成分、冷感成分、消臭成分、抗菌成分又はスキンケア成分である場合には、それぞれ、芳香機能、冷感機能、消臭機能、抗菌機能又はスキンケア機能が促進される。
次いで、吸収性物品が液体を吸収すると、吸収した液体が水崩壊性のマイクロカプセルを崩壊させ、マイクロカプセルから冷感成分が放出され、冷感機能を発揮する。
冷感成分の放出量は、その量、その蒸気圧、マイクロカプセルの水に対する溶解度、マイクロカプセルの層の厚さ、マイクロカプセルの粒径等により変化させることができる。
冷感成分の放出量は、その量、その蒸気圧、マイクロカプセルの水に対する溶解度、マイクロカプセルの層の厚さ、マイクロカプセルの粒径等により変化させることができる。
例えば、吸収性物品に含まれる冷感成分の量を増やすこと、蒸気圧の高い冷感成分を選択すること、マイクロカプセルの素材として水に対する溶解度の高いものを選択すること、マイクロカプセルの層の厚さを薄くすること、マイクロカプセルの粒径を小さくすること等により、冷感成分を、短時間に高濃度で周囲に放出することができる。
また、例えば、吸収性物品に含まれる冷感成分の量を減らすこと、蒸気圧の低い冷感成分を選択すること、マイクロカプセルの素材として水に対する溶解度の低いものを選択すること、マイクロカプセルの層の厚さを厚くすること、マイクロカプセルの粒径を大きくすること等により、冷感成分を、徐放させることができる。
なお、上記マイクロカプセルは、冷感成分の放出性を制御するため等の観点から、冷感成分の他に、溶媒をさらに含んでもよい(当該溶媒を、「第2溶媒」と称する場合がある)。
第2溶媒としては、第1溶媒と同様のものが挙げられる。
第2溶媒としては、第1溶媒と同様のものが挙げられる。
上記冷感組成物において、機能性成分の量は、機能性成分の機能等によって異なるが、一般的には、上記冷感組成物は、機能性成分を、好ましくは0.01~20質量%、より好ましくは0.05~15質量%、そしてさらに好ましくは0.1~10質量%の比率で含む。
上記冷感組成物は、冷感成分を含むマイクロカプセルを、好ましくは0.1~60質量%、より好ましくは5~40質量%、そしてさらに好ましくは10~30質量%の比率で含む。冷感組成物の塗工性の観点からである。
なお、冷感組成物中の冷感成分の量は、冷感成分の機能等によって異なるが、一般的には、上記冷感組成物は、冷感成分を、好ましくは0.01~30質量%、より好ましくは0.05~20質量%、そしてさらに好ましくは1~15質量%の比率で含む。
なお、冷感組成物中の冷感成分の量は、冷感成分の機能等によって異なるが、一般的には、上記冷感組成物は、冷感成分を、好ましくは0.01~30質量%、より好ましくは0.05~20質量%、そしてさらに好ましくは1~15質量%の比率で含む。
本開示の吸収性物品の冷感成分塗布領域が冷感組成物を含む実施形態では、冷感組成物の坪量は、冷感成分及び機能性成分の濃度等によっても変化するが、好ましくは1~12g/m2、そしてより好ましくは2~10g/m2である。上記坪量が1g/m2を下回ると、冷感成分及び機能性成分がその機能を発揮しにくくなる場合があり、そして上記坪量が12g/m2を上回ると、溶媒(第1溶媒)が接着剤による接合を阻害する場合がある。
本開示の吸収性物品では、各ヒップフラップにおいて、接着剤塗布領域が、吸収性物品の厚さ方向に隣接する層、例えば、肌当接層と、着衣当接層とを直接又は間接的に接合する接着領域を有することが好ましい。ヒップフラップが、使用時によれにくくなるからである。上記接着領域は、接着剤塗布領域が、冷感成分塗布領域と、吸収性物品の厚さ方向において重複しない範囲に形成されうる。
また、本開示の吸収性物品の冷感成分塗布領域が冷感組成物を含む実施形態では、上記接着領域が、冷感組成物を構成する溶媒を含まないことが好ましい。上記溶媒は、接着剤が、吸収性物品の厚さ方向に隣接する層を直接又は間接的に接合することを阻害する傾向があるからである。
なお、本明細書において、接着領域が冷感組成物を構成する溶媒を含まないとは、接着領域を構成する接着剤が、上記溶媒を0~5質量%の量で含むことを意味する。
なお、本明細書において、接着領域が冷感組成物を構成する溶媒を含まないとは、接着領域を構成する接着剤が、上記溶媒を0~5質量%の量で含むことを意味する。
また、本開示の吸収性物品の冷感成分塗布領域が冷感組成物を含む実施形態では、接着剤塗布領域が、マイクロカプセルを保持するマイクロカプセル保持領域をさらに有することが好ましい。マイクロカプセル保持領域が、マイクロカプセルを保持するため、使用時に、冷感成分の位置がずれにくくなるからである。上記マイクロカプセル保持領域は、接着剤塗布領域が、冷感成分塗布領域と、吸収性物品の厚さ方向に重複する範囲に形成されうる。
また、上記マイクロカプセル保持領域は、各ヒップフラップの肌当接層と、着衣当接層側に隣接する層との間に形成されることが好ましい。液透過性層を通過した液体をすばやくマイクロカプセルに到達させることができるため、少ない液体量で冷感成分を放出させることができるからである。
本開示の吸収性物品の冷感成分塗布領域が冷感組成物を含む実施形態では、吸収性物品が、図1~図3に示されるように、冷感成分塗布領域を間に挟んで、少なくとも肌当接層及び着衣当接層をエンボスすることにより形成されたエンボス部を有することが好ましい。冷感成分塗布領域では、冷感組成物を構成する溶媒により、接着剤が、肌当接層と、着衣当接層とを直接又は間接的に接合することを阻害する傾向がある。吸収性物品がエンボス部を有することにより、肌当接層と、着衣当接層との接合が強固になり、使用時に、ヒップフラップがよれにくくなる。
また、上記実施形態では、当該エンボス部が、冷感成分をマイクロカプセルに内包させたまま保持していることが好ましい。それにより、マイクロカプセル、ひいては冷感成分を特定の位置に保持し続けることができる。また、エンボス部は、繊維密度の高さから、液体を優先的にエンボス部に導く傾向があるので、少ない液体量で冷感成分を放出させることができる。
図4は、本開示の別の実施形態に従う吸収性物品の断面図である。図4は、図1のIII-III断面に相当する断面図である。図4に示される吸収性物品1は、中央部補助シートと、2つの側部補助シートとが存在しない以外は、図1~3に示される実施形態と同一である。
図5は、本開示の別の実施形態に従う吸収性物品1の平面図であり、図2の平面図に相当する平面図である。図5に示される吸収性物品1では、本体部5が、冷感組成物が塗布された冷感成分塗布領域22'を含む。
図5に示されるように、本体部が冷感成分塗布領域を含むことにより、着用者が蒸れをより感じにくくなる傾向がある。
なお、本体部が冷感成分塗布領域を含む実施形態では、各ヒップフラップにおける冷感成分の総量が、本体部の冷感成分の総量よりも多いことが好ましい。臀部は、股間部よりも冷感を実感しにくいためである。
図5に示されるように、本体部が冷感成分塗布領域を含むことにより、着用者が蒸れをより感じにくくなる傾向がある。
なお、本体部が冷感成分塗布領域を含む実施形態では、各ヒップフラップにおける冷感成分の総量が、本体部の冷感成分の総量よりも多いことが好ましい。臀部は、股間部よりも冷感を実感しにくいためである。
本開示の吸収性物品において、ヒップフラップの肌当接層は、本体部の液透過性層と同様の素材から形成されることができ、例えば、不織布から形成される。また、肌当接層は、本体部の液透過性層と連続して(単一の素材から)形成されていてもよく、又は本体部の液透過性層と別個に形成されていてもよい。
本開示の吸収性物品において、ヒップフラップの着衣当接層は、本体部の液不透過性層と同様の素材から形成されることができ、例えば、PE、PP等を含むフィルム、通気性を有する樹脂フィルム、スパンボンド又はスパンレース等の不織布に通気性を有する樹脂フィルムを接合したもの、SMS等の複層不織布等から形成される。また、着衣当接層は、本体部の液不透過性層と連続して(単一の素材から)形成されていてもよく、又は本体部の液不透過性層と別個に形成されていてもよい。
本開示の吸収性物品において、中央部補助シート及び側部補助シートは、本体部の液透過性層と同様の素材から形成されうる。
中央部補助シート及び側部補助シートは、疎水性繊維と、親水性繊維とを含む布帛、例えば、スパンレース不織布、スパンボンド-メルトブローン-スパンボンド(SMS)不織布から形成されることが好ましい。薄く且つしなやかな性質を有するからである。また、冷感成分保持領域が冷感組成物を含む場合には、冷感組成物の溶媒を親水性繊維が保持しやすいからである。
中央部補助シート及び側部補助シートは、疎水性繊維と、親水性繊維とを含む布帛、例えば、スパンレース不織布、スパンボンド-メルトブローン-スパンボンド(SMS)不織布から形成されることが好ましい。薄く且つしなやかな性質を有するからである。また、冷感成分保持領域が冷感組成物を含む場合には、冷感組成物の溶媒を親水性繊維が保持しやすいからである。
上記疎水性繊維としては、合成繊維、例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタラート繊維が挙げられ、そして上記親水性繊維としては、セルロース系繊維、例えば、再生セルロース系繊維、例えば、レーヨンが挙げられる。
中央部補助シート及び側部補助シートはまた、エアレイドパルプシートから形成されうる。
中央部補助シート及び側部補助シートはまた、エアレイドパルプシートから形成されうる。
[吸収性物品の製造]
上記冷感成分は、液状又は固形状で塗布されうる。
例えば、上記冷感成分が、固形状、例えば、室温で固体の冷感成分をそのまま塗布する場合、多孔質材料に担持されている場合、上記マイクロカプセルに内包されている場合等では、上記冷感成分は、例えば、特開2010-234027号の段落[0052]及び[0053]に記載される方法に従って塗布されうる。
上記冷感成分は、液状又は固形状で塗布されうる。
例えば、上記冷感成分が、固形状、例えば、室温で固体の冷感成分をそのまま塗布する場合、多孔質材料に担持されている場合、上記マイクロカプセルに内包されている場合等では、上記冷感成分は、例えば、特開2010-234027号の段落[0052]及び[0053]に記載される方法に従って塗布されうる。
上記冷感成分が、液状である場合、例えば、室温(25℃)で液体である冷感成分をそのまま塗布する場合、室温で固形状である冷感成分をその融点以上に加熱して塗布する場合、冷感成分を溶媒に溶解して塗布する場合、冷感組成物として塗布する場合等には、上記冷感組成物は、当技術分野で公知の塗工機、例えば、ロール型塗工機、カーテン型塗工機、スリット型塗工機、スプレー型塗工機、ディップ型塗工機、ビード型塗工機、フレキソ型塗工機、グラビア型塗工機等を用いて塗工されうる。
液状の冷感成分は、その塗出口が、塗布すべき面と接している接触型塗工機により塗布されることが好ましい。冷感成分を飛散させることなく、冷感成分を所望の位置に配置することができる、すなわち、冷感成分塗布領域を、所望の位置に配置することができるからである。
上記接触型塗工機としては、ロール型塗工機、スリット型塗工機、ディップ型塗工機、ビード型塗工機、フレキソ型塗工機、グラビア型塗工機が挙げられる。
上記接触型塗工機としては、ロール型塗工機、スリット型塗工機、ディップ型塗工機、ビード型塗工機、フレキソ型塗工機、グラビア型塗工機が挙げられる。
なお、上記冷感組成物は、例えば、上述の溶媒に、冷感成分を内包するマイクロカプセルと、機能性成分とを添加し、混合することにより形成される。冷感成分を内包するマイクロカプセルは、市販されているほか、上述のように形成することができる。
図1~図3に示される吸収性物品の製造例を、図6及び図7に示される塗工例を用いて説明する。
トップシートロール101から巻きだした、帯状のトップシート2の吸収体等が積み重ねられる面(非肌当接面)に、冷感組成物塗布機102から冷感組成物を塗布し、トップシート2の上に、冷感成分塗布領域22を形成する。次いで、接着剤塗布機103から接着剤を塗布し、トップシート2の上に、冷感成分塗布領域22を間に挟んで、接着剤塗布領域21を形成する。次いで、接着剤塗布領域21の上に、中央部補助シートロール104から巻きだした、帯状の中央部補助シート10を積み重ね、そして側部補助シートロール105から巻き出した、帯状の側部補助シート11を積み重ね、積み重ね物106を形成する。
トップシートロール101から巻きだした、帯状のトップシート2の吸収体等が積み重ねられる面(非肌当接面)に、冷感組成物塗布機102から冷感組成物を塗布し、トップシート2の上に、冷感成分塗布領域22を形成する。次いで、接着剤塗布機103から接着剤を塗布し、トップシート2の上に、冷感成分塗布領域22を間に挟んで、接着剤塗布領域21を形成する。次いで、接着剤塗布領域21の上に、中央部補助シートロール104から巻きだした、帯状の中央部補助シート10を積み重ね、そして側部補助シートロール105から巻き出した、帯状の側部補助シート11を積み重ね、積み重ね物106を形成する。
積み重ね物106を、開孔機107に通し、積み重ね物106に、開孔部14及び14'を形成する。次いで、開孔部14及び14'が形成された積み重ね物106の上に、吸収体製造装置111から排出された吸収体4を積み重ね、積み重ね物121を形成する。なお、吸収体製造装置111は、当技術分野で公知であり、図6に示される吸収体製造装置111は、材料供給部112と、サクションドラム113と、サクションドラム113の外周面に形成された凹型114と、サクション部115とを有する。
積み重ね物121を、一対のエンボスロール131でエンボスすることにより、積み重ね物121に、エンボス部12aを形成する。次いで、バックシートロール141から巻きだした、帯状のバックシート3に、接着剤塗布機142から接着剤を塗布し、エンボス部12aが形成された積み重ね物121に積み重ね、積み重ね物143を形成する。次いで、積み重ね物143を、一対のエンボスロール151にて、エンボス部12b及びラウンドエンボス部13を形成し、そしてカッター161で吸収性物品の形状にカットし、吸収性物品1を製造する。
本開示の吸収性物品の例としては、生理用ナプキン、パンティーライナー、使い捨ておむつ、尿取りパッド等が挙げられる。
以下、例を挙げて本開示を説明するが、本開示はこれらの例に限定されるものではない。
[実施例1]
冷感成分を内包するマイクロカプセルとして、Symrise社製のINCAP MENTHOL/IPMを準備した。INCAP MENTHOL/IPMは、冷感成分としてメントールを含有し、そしてマイクロカプセルの素材は、材質変性デンプンであった。
機能性成分としての香料成分を含有する溶媒を準備した。上記溶媒は、IPM(ミリスチン酸イソプロピル)であった。
上記マイクロカプセルと、溶媒とを、50:50の質量比で混合することにより、冷感組成物No.1を準備した。
[実施例1]
冷感成分を内包するマイクロカプセルとして、Symrise社製のINCAP MENTHOL/IPMを準備した。INCAP MENTHOL/IPMは、冷感成分としてメントールを含有し、そしてマイクロカプセルの素材は、材質変性デンプンであった。
機能性成分としての香料成分を含有する溶媒を準備した。上記溶媒は、IPM(ミリスチン酸イソプロピル)であった。
上記マイクロカプセルと、溶媒とを、50:50の質量比で混合することにより、冷感組成物No.1を準備した。
図6に示される製造工程を用いて、図1~図3に示される生理用ナプキンNo.1を製造し、次いで、生理用ナプキンNo.1を、ポリエチレンフィルムにより個包装した。
なお、冷感成分塗布領域において、冷感組成物の坪量は、4g/m2であった。
なお、冷感成分塗布領域において、冷感組成物の坪量は、4g/m2であった。
生理用ナプキンNo.1を、複数のボランティアの被験者に使用してもらったところ、個包装の開封後、並びに着用中において、生理用ナプキンNo.1から香料の香りが漂い、そして生理用ナプキンNo.1を着用後に就寝すると、汗をかくに伴い、臀部に冷感を覚えたとの回答を得た。
1 吸収性物品
2 トップシート
3 バックシート
4 吸収体
5 本体部
6 ヒップフラップ
7 肌当接層
8 着衣当接層
9 サイドフラップ
10 中央部補助シート
11 側部補助シート
12a,12b エンボス部
13 ラウンドエンボス部
14,14' 開孔部
15 粘着部
21 接着剤塗布領域
22 冷感成分塗布領域
23 接着領域
24 マイクロカプセル保持領域
101 トップシートロール
102 冷感組成物塗布機
103,142 接着剤塗布機
104 中央部補助シートロール
105 側部補助シートロール
106,121,143 積み重ね物
107 開孔機
111 吸収体製造装置
112 材料供給部
113 サクションドラム
114 凹型
115 サクション部
131,151 エンボスロール
141 バックシートロール
161 カッター
2 トップシート
3 バックシート
4 吸収体
5 本体部
6 ヒップフラップ
7 肌当接層
8 着衣当接層
9 サイドフラップ
10 中央部補助シート
11 側部補助シート
12a,12b エンボス部
13 ラウンドエンボス部
14,14' 開孔部
15 粘着部
21 接着剤塗布領域
22 冷感成分塗布領域
23 接着領域
24 マイクロカプセル保持領域
101 トップシートロール
102 冷感組成物塗布機
103,142 接着剤塗布機
104 中央部補助シートロール
105 側部補助シートロール
106,121,143 積み重ね物
107 開孔機
111 吸収体製造装置
112 材料供給部
113 サクションドラム
114 凹型
115 サクション部
131,151 エンボスロール
141 バックシートロール
161 カッター
Claims (12)
- 液透過性層と、液不透過性層と、前記液透過性層及び液不透過性層の間の吸収層とを含む本体部と、前記本体部から延びる一対のヒップフラップとを備える吸収性物品であって、
前記一対のヒップフラップが、冷感成分が塗布された冷感成分塗布領域を含む、
ことを特徴とする、前記吸収性物品。 - 前記一対のヒップフラップが肌当接層及び着衣当接層を含み、前記冷感成分塗布領域が、前記肌当接層の肌当接面の上、又は前記肌当接層及び着衣当接層の間に形成されている、請求項1に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記一対のヒップフラップが、前記肌当接層及び着衣当接層の間に、接着剤が塗布された接着剤塗布領域を有し、そして前記接着剤塗布領域が、前記肌当接層及び着衣当接層を直接又は間接的に接合する接着領域を有する、請求項2に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記接着剤塗布領域が、前記マイクロカプセルを保持するマイクロカプセル保持領域を有する、請求項3に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記冷感成分塗布領域が、前記冷感成分と、前記冷感成分を内包する水崩壊性のマイクロカプセルと、揮発性を有する機能性成分と、前記冷感成分を前記マイクロカプセルに内包させたまま保持する溶媒とを含む冷感組成物が塗布されることにより形成された、請求項1~4のいずれか一項に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記一対のヒップフラップが、前記肌当接層及び着衣当接層の間に側部補助シート層をさらに含み、そして前記冷感成分塗布領域が、前記肌当接層及び側部補助シート層の間に形成されている、請求項1~5のいずれか一項に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記側部補助シート層が、親水性繊維を含む布帛から形成される、請求項6に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記本体部が冷感成分を含み、各ヒップフラップにおける冷感成分の総量が、前記本体部の冷感成分の総量よりも多い、請求項1~7のいずれか一項に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記一対のヒップフラップにおいて、前記冷感成分塗布領域が、前記本体部と一定の間隔をあけて配置されている、請求項1~8のいずれか一項に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記一対のヒップフラップが、少なくとも前記肌当接層をエンボスすることにより形成されたエンボス部を有する、請求項1~9のいずれか一項に記載の吸収性物品。
- 上記溶媒が、0.00~0.60のIOBと、40℃における0.01~80mm2/sの動粘度と、1気圧及び25℃における0.00~0.01Paの蒸気圧を有する、請求項3に記載の吸収性物品。
- 前記機能性成分が、芳香機能、冷感機能、消臭機能、抗菌機能、スキンケア機能、並びにそれらの任意の組み合わせから成る群から選択される機能を有する、請求項3に記載の吸収性物品。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201580036093.6A CN106572924B (zh) | 2014-06-30 | 2015-05-12 | 吸收性物品 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014135208A JP6478495B2 (ja) | 2014-06-30 | 2014-06-30 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2014-135208 | 2014-06-30 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016002351A1 true WO2016002351A1 (ja) | 2016-01-07 |
Family
ID=55018906
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/063664 WO2016002351A1 (ja) | 2014-06-30 | 2015-05-12 | 吸収性物品 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6478495B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106572924B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016002351A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20150374875A1 (en) * | 2014-06-30 | 2015-12-31 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Absorbent article comprising a cooling system |
| DE102016110112B9 (de) | 2015-06-11 | 2021-04-01 | Denso Corporation | Kraftstoffeinspritzvorrichtung |
| JP3213494U (ja) * | 2017-09-01 | 2017-11-09 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 機能性物品 |
| CN110022809A (zh) * | 2017-11-08 | 2019-07-16 | 花王株式会社 | 吸收性物品 |
| JP7158923B2 (ja) * | 2018-07-02 | 2022-10-24 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品包装体 |
| JP7254045B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-31 | 2023-04-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品の個包装体 |
| JP7194718B2 (ja) * | 2020-10-20 | 2022-12-22 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2022087749A (ja) * | 2020-12-01 | 2022-06-13 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1085255A (ja) * | 1996-09-19 | 1998-04-07 | Ogawa Koryo Kk | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2004290600A (ja) * | 2003-03-28 | 2004-10-21 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2008006277A (ja) * | 2006-05-31 | 2008-01-17 | Daio Paper Corp | 使い捨て紙おむつ |
| WO2010114052A1 (ja) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2010114053A1 (ja) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2013129236A1 (ja) * | 2012-02-29 | 2013-09-06 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN2390584Y (zh) * | 1999-11-01 | 2000-08-09 | 陈朝根 | 超薄复合卫生巾 |
| JP3776014B2 (ja) * | 2001-08-22 | 2006-05-17 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品およびその製造方法 |
| JP3871611B2 (ja) * | 2002-05-30 | 2007-01-24 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN100482191C (zh) * | 2003-05-29 | 2009-04-29 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 卫生巾 |
| WO2005075068A1 (ja) * | 2004-02-05 | 2005-08-18 | Taiyo Kagaku Co., Ltd. | 多孔質シリカを含有する吸着能付与剤 |
| WO2008079898A1 (en) * | 2006-12-20 | 2008-07-03 | Pharmwest, Inc. | Methods and topical formulations comprising colloidal metal for treating or preventing skin conditions |
| EP2535061B1 (en) * | 2011-06-16 | 2014-07-16 | The Procter and Gamble Company | Cooling composition and absorbent article comprising the same |
| JP6116179B2 (ja) * | 2012-09-28 | 2017-04-19 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
-
2014
- 2014-06-30 JP JP2014135208A patent/JP6478495B2/ja active Active
-
2015
- 2015-05-12 WO PCT/JP2015/063664 patent/WO2016002351A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2015-05-12 CN CN201580036093.6A patent/CN106572924B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1085255A (ja) * | 1996-09-19 | 1998-04-07 | Ogawa Koryo Kk | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP2004290600A (ja) * | 2003-03-28 | 2004-10-21 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2008006277A (ja) * | 2006-05-31 | 2008-01-17 | Daio Paper Corp | 使い捨て紙おむつ |
| WO2010114052A1 (ja) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2010114053A1 (ja) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| WO2013129236A1 (ja) * | 2012-02-29 | 2013-09-06 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6478495B2 (ja) | 2019-03-06 |
| CN106572924B (zh) | 2020-02-28 |
| CN106572924A (zh) | 2017-04-19 |
| JP2016013153A (ja) | 2016-01-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6416516B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6478495B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6504756B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品の製造方法 | |
| CA2763180C (en) | Absorbent articles comprising an odour control system | |
| US20120226248A1 (en) | Absorbent article comprising cyclodextrin complex | |
| US9731042B2 (en) | Absorbent article comprising complexed or encapsulated reactive compounds | |
| JP4905961B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品の個装体 | |
| US20130158490A1 (en) | Absorbent article comprising a fragrance or odor control composition | |
| EP2916878B1 (en) | Triggerable compositions for two-stage, controlled release of active chemistry | |
| JP6684880B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| US9592168B2 (en) | Absorbent articles comprising an odour control system | |
| JP7194718B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| CN213250461U (zh) | 吸收性物品的独立包装体及收纳该独立包装体的包装体 | |
| JP7200071B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP7285136B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2018102616A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| WO2022071001A1 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| WO2020130982A2 (en) | A hygiene product having a controlled fragrance release mechanism | |
| JP2018102613A (ja) | 吸収性物品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15815524 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: IDP00201609104 Country of ref document: ID |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15815524 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |