WO2015190332A1 - 車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュール、車両のヘッドライト、および車両 - Google Patents
車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュール、車両のヘッドライト、および車両 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015190332A1 WO2015190332A1 PCT/JP2015/065735 JP2015065735W WO2015190332A1 WO 2015190332 A1 WO2015190332 A1 WO 2015190332A1 JP 2015065735 W JP2015065735 W JP 2015065735W WO 2015190332 A1 WO2015190332 A1 WO 2015190332A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- light
- lens
- emitting diode
- diffusion
- region
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B62—LAND VEHICLES FOR TRAVELLING OTHERWISE THAN ON RAILS
- B62J—CYCLE SADDLES OR SEATS; AUXILIARY DEVICES OR ACCESSORIES SPECIALLY ADAPTED TO CYCLES AND NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR, e.g. ARTICLE CARRIERS OR CYCLE PROTECTORS
- B62J6/00—Arrangement of optical signalling or lighting devices on cycles; Mounting or supporting thereof; Circuits therefor
- B62J6/02—Headlights
- B62J6/022—Headlights specially adapted for motorcycles or the like
- B62J6/026—Headlights specially adapted for motorcycles or the like characterised by the structure, e.g. casings
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21S—NON-PORTABLE LIGHTING DEVICES; SYSTEMS THEREOF; VEHICLE LIGHTING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR VEHICLE EXTERIORS
- F21S41/00—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps
- F21S41/10—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps characterised by the light source
- F21S41/14—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps characterised by the light source characterised by the type of light source
- F21S41/141—Light emitting diodes [LED]
- F21S41/143—Light emitting diodes [LED] the main emission direction of the LED being parallel to the optical axis of the illuminating device
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21S—NON-PORTABLE LIGHTING DEVICES; SYSTEMS THEREOF; VEHICLE LIGHTING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR VEHICLE EXTERIORS
- F21S41/00—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps
- F21S41/20—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps characterised by refractors, transparent cover plates, light guides or filters
- F21S41/25—Projection lenses
- F21S41/255—Lenses with a front view of circular or truncated circular outline
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21S—NON-PORTABLE LIGHTING DEVICES; SYSTEMS THEREOF; VEHICLE LIGHTING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR VEHICLE EXTERIORS
- F21S41/00—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps
- F21S41/20—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps characterised by refractors, transparent cover plates, light guides or filters
- F21S41/25—Projection lenses
- F21S41/275—Lens surfaces, e.g. coatings or surface structures
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21S—NON-PORTABLE LIGHTING DEVICES; SYSTEMS THEREOF; VEHICLE LIGHTING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR VEHICLE EXTERIORS
- F21S41/00—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps
- F21S41/20—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps characterised by refractors, transparent cover plates, light guides or filters
- F21S41/28—Cover glass
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F21—LIGHTING
- F21S—NON-PORTABLE LIGHTING DEVICES; SYSTEMS THEREOF; VEHICLE LIGHTING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR VEHICLE EXTERIORS
- F21S41/00—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps
- F21S41/20—Illuminating devices specially adapted for vehicle exteriors, e.g. headlamps characterised by refractors, transparent cover plates, light guides or filters
- F21S41/285—Refractors, transparent cover plates, light guides or filters not provided in groups F21S41/24 - F21S41/2805
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a vehicle headlight light module, a vehicle headlight, and a vehicle.
- a direct light module including a light emitting diode (hereinafter referred to as an LED) is known as a light module for a vehicle headlight.
- a light module using an LED as a light source has a characteristic of low power consumption.
- the direct light module includes an LED and a lens that is disposed in front of the LED and that refracts light from the LED. Light from the LED enters the lens without being reflected by a reflector or the like. The light incident on the lens is refracted when passing through the lens and is projected forward from the lens.
- Patent Document 1 describes a direct-type light module including an LED and a convex lens arranged in front of the LED.
- This direct-light type light module is used together with a projector-type or parabolic-type light module.
- a basic light distribution pattern formed by a projector-type or parabolic light module By combining a basic light distribution pattern formed by a projector-type or parabolic light module and a light distribution pattern formed by a direct-type light module, a low-beam light distribution pattern is formed.
- the direct light module including the LED it is possible to collect the light flux in the vicinity of the cut-off line. Therefore, it is easy to ensure the visibility in the distance.
- the direct-light type light module disclosed in Patent Document 1 needs to be used together with a projector-type or parabolic-type light module in order to form a light distribution pattern necessary for the low beam. Therefore, in the technique disclosed in Patent Document 1, it is necessary to install the same number of projector-type or parabolic-type light modules as the direct-light type light modules. Larger headlights were inevitable. A large-sized headlight may be difficult to be mounted on a vehicle depending on the size or type of the vehicle. Further, depending on the design of the vehicle, it may not be preferable to mount a large headlight. Thus, depending on the vehicle, it may be difficult to mount a large headlight on the vehicle.
- the object of the present invention is as follows. Regardless of whether the direct-light type light module is used together with the projector-type or multi-reflector type light module, it is preferable that the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be appropriately formed. According to such a direct-light type light module, the enlargement of the headlight can be suppressed by omitting the project type or multi-reflector type light module. Moreover, according to such a direct-light type light module, the degree of freedom in designing the light distribution pattern can be increased by being used together with the projector-type or multi-reflector type light module. Thereby, for example, a wider light distribution pattern can be formed. In addition, it is possible to form a light distribution pattern more suitable for the vehicle.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a light module that is a direct light module using an LED as a light source and can form a light distribution pattern required for a headlight.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a headlight including a direct light module using an LED as a light source, which can form a preferable light distribution pattern.
- a vehicle headlight light module includes a light emitting diode and a lens provided in front of the light emitting diode and transmitting light from the light emitting diode.
- the lens includes a first refracting portion and a first diffusing portion.
- the first refracting unit is positioned above the light emitting diode when the lens is viewed from the front, and is configured to refract light from the light emitting diode and guide it forward.
- the first diffusing portion has a diffuse transmittance higher than that of the first refracting portion, and is positioned below the light emitting diode when the lens is viewed from the front, and the light from the light emitting diode. Is diffused and guided forward.
- the light transmitted through the first refractive part of the lens is projected forward while maintaining the high directivity.
- the highly directional light from the light emitting diode the light transmitted through the first diffusion portion of the lens is diffused and projected forward.
- the first refracting portion is located above the light emitting diode.
- the first diffusion part is located below the light emitting diode. Therefore, highly directional light transmitted through the first refracting portion illuminates a distant road surface.
- the light that has passed through the first diffusing portion and diffused in a wide range illuminates a nearby road surface.
- the light module a near road surface can be irradiated over a wide range, illuminating a distant road surface brightly.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be formed. Therefore, according to the light module, by omitting the project-type or multi-reflector-type light module, it is possible to form a light distribution pattern required for the headlight while suppressing an increase in the size of the headlight. Further, according to the light module, it is possible to increase the degree of freedom in designing the light distribution pattern by using the light module together with the projector-type or multi-reflector type light module.
- the first diffusing portion is located below the first refracting portion on a vertical line passing through the light emitting diode when the lens is viewed from the front.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be formed more appropriately.
- the lens includes a second refraction part and a second diffusion part.
- the second refracting portion is positioned at a position different from the first refracting portion in the vertical direction when viewed from the front of the lens, and is configured to refract light from the light emitting diode and guide it forward.
- the second diffusing portion has a diffuse permeability higher than that of the second refracting portion, and the second refracting on a horizontal line passing through the second refracting portion when the lens is viewed from the front. It is located outward in the left-right direction with respect to the part, and is configured to diffuse light from the light emitting diode and guide it forward.
- a vehicle headlight to brightly illuminate the center of the vehicle in the left-right direction and to illuminate the outside of the vehicle in the left-right direction over a wide area.
- the outside in the left-right direction of the vehicle may be darker than the center in the left-right direction of the vehicle.
- the highly directional light transmitted through the second refracting portion illuminates the center in the left-right direction of the vehicle, and the light diffused over a wide range through the second diffusing portion is transmitted in the left-right direction of the vehicle. Can illuminate the outside. Therefore, the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be more appropriately formed.
- the lens has a third diffusing portion.
- the third diffusing portion has a diffuse permeability higher than that of the first refracting portion, and the first refracting on a horizontal line passing through the first refracting portion when the lens is viewed from the front. It is located outside the vehicle in the left-right direction of the vehicle, and is configured to diffuse the light from the light emitting diode and guide it forward.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be more appropriately formed.
- the lens has a refraction region and a diffusion region.
- the refraction region includes at least the first refraction part, and is configured to refract light from the light emitting diode and guide it forward.
- the diffusion region includes at least the first diffusion part, and is configured to diffuse light from the light emitting diode and guide it forward.
- the diffusion region is formed in a substantially U shape when the lens is viewed from the front.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be more appropriately formed.
- the diffusion region has a fourth diffusion part.
- the fourth diffusing unit is located on the left or right side of the light emitting diode and above the light emitting diode when the lens is viewed from the front.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be more appropriately formed.
- the diffusion region has a first region and a second region.
- the first region is located in a vertical section passing through the light emitting diode when the lens is viewed from the front.
- the second region is located outward in the left-right direction with respect to the first region.
- the vertical length of the second region is longer than the vertical length of the first region.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight can be more appropriately formed.
- the lens has a front surface convex toward the front and a back surface facing the light emitting diode.
- the first diffusing portion is formed by applying a texture to a part of the front surface or a part of the back surface of the lens.
- the first diffusion portion can be formed inexpensively and easily.
- the lens has a front surface convex toward the front and a back surface facing the light emitting diode.
- the first diffusion portion is formed by attaching a diffusion plate that diffuses transmitted light to a part of the front surface or a part of the back surface of the lens.
- the first diffusion portion can be formed inexpensively and easily.
- a vehicle headlight according to the present invention includes any one of the light modules described above.
- a preferable light distribution pattern can be formed.
- the headlight of another vehicle includes a light emitting diode, a lens, an outer cover, and a diffuser.
- the lens is disposed in front of the light emitting diode and refracts and transmits light from the light emitting diode.
- the outer cover is disposed in front of the lens and transmits light transmitted through the lens.
- the diffuser is configured to diffuse a part of the light transmitted through the lens under the other part of the light transmitted through the lens and guide it to the front of the outer cover.
- light having high directivity from the light emitting diode is refracted when passing through the lens, and is projected from the lens while maintaining high directivity.
- Part of the light transmitted through the lens is diffused by the diffuser below the other part of the light transmitted through the lens, and is guided to the front of the outer cover as diffused light.
- Another part of the light transmitted through the lens is projected to the front of the outer cover without being diffused by the diffuser. Therefore, light that is not diffused by the diffuser illuminates a distant road surface, and light diffused by the diffuser illuminates a nearby road surface.
- the headlight it is possible to irradiate the road surface in the vicinity over a wide range while illuminating the road surface far away using the direct light module using the LED as the light source. According to the headlight, a preferable light distribution pattern can be formed.
- the diffuser is disposed between the lens and the outer cover, and is configured to diffuse transmitted light.
- a part of light having high directivity from the light emitting diode can be diffused and projected to the front of the outer cover.
- the diffuser is attached to the outer cover and configured to diffuse transmitted light.
- a part of light having high directivity from the light emitting diode can be diffused and projected to the front of the outer cover.
- the diffuser is formed by applying a texture to a part of the outer cover.
- a vehicle according to the present invention includes the headlight.
- a direct light module that uses an LED as a light source and can form a light distribution pattern required for a headlight.
- a headlight provided with the direct-type light module which uses LED as a light source, Comprising: The headlight which can form a preferable light distribution pattern can be provided.
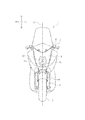
- FIG. 1 is a front view of the motorcycle according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a vertical sectional view of the headlight according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 3 is a vertical sectional view of the main part of the light module according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a front view of the lens of the light module according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 5A is a diagram schematically showing a light distribution pattern by a light module in which a lens has only a refractive region.
- FIG. 5B is a diagram schematically illustrating a light distribution pattern by the light module according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a vertical sectional view of a headlight according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a vertical cross-sectional view of the main part of the light module according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 8 is a vertical cross-sectional view of a headlight according to a modification of the second embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a vertical cross-sectional view of a main part of a light module according to another modification of the second embodiment.
- FIG. 10 is a vertical sectional view of the headlight according to the third embodiment.
- a direct-type light module using an LED as a light source has a characteristic that it is easy to obtain sufficient brightness because the light distribution range is narrow but the light distribution is concentrated in a narrow range. Therefore, when a direct light module using an LED as a light source is used as a headlight of a vehicle, there is an advantage that it can easily illuminate a far road surface brightly.
- a direct light module using LEDs as a light source has a narrow light distribution range. For this reason, it has been considered that it is difficult to obtain light distribution on a nearby road surface required for a low beam.
- the inventor of the present invention paid attention to the fact that a sufficient illuminance can be obtained even when light is irradiated on the road surface close to the vehicle with a small luminous intensity because the distance between the headlight of the vehicle and the road surface close to the vehicle is short.
- the present inventor has obtained the following knowledge in consideration of the above-described characteristics of a direct light module using LEDs as a light source and the above-described properties required for a headlight of a vehicle.
- the irradiation range can be expanded while ensuring sufficient illuminance by diffusing the road surface close to the vehicle. Thereby, it is possible to illuminate a wide area while ensuring sufficient illuminance on a nearby road surface while utilizing the advantage of the LED that it is easy to illuminate a far road surface brightly.
- Such a direct-light type light module can form a light distribution pattern required for a headlight without being used together with a projector-type or multi-reflector type light module. Unlike the projector-type and multi-reflector type light modules, such a direct-light type light module does not require a reflector to be installed above or below the light source. Accordingly, the vertical dimension can be reduced.
- such a direct-light type light module can be used together with a projector-type or multi-reflector type light module, thereby increasing the degree of freedom in designing a light distribution pattern. Thereby, for example, a wider light distribution pattern can be formed. In addition, it is possible to form a light distribution pattern more suitable for the vehicle.
- FIG. 1 is a front view of a motorcycle 1 as an example of a “vehicle”.
- the “vehicle” is not limited to the motorcycle 1.
- the “vehicle” may be, for example, an ATV (All Terrain Vehicle), a ROV (Recreational Off-highway Vehicle), or an automobile.
- the “vehicle” may be a vehicle that turns in a lean posture.
- a vehicle that turns in a lean posture is configured to lean while turning inside a curve and turn.
- the vehicle turning in a lean position is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include straddle-type vehicles such as motorcycles and motorcycles.
- the motorcycle 1 of the embodiment is an example of a vehicle that turns in a lean posture.
- front, rear, left, right, upper, and lower mean front, rear, left, right, upper, and lower, respectively, as viewed from the rider riding the motorcycle 1.
- Symbols F, Re, L, R, U, and D in the drawings represent front, rear, left, right, upper, and lower as viewed from the rider.
- the motorcycle 1 includes a front wheel 2, a rear wheel (not shown), and a power unit (not shown) that drives the rear wheel.
- the front wheel 2 is supported by the front fork 3.
- a front fender 4 is provided above the front wheel 2.
- a front cowl 5 is disposed above the front fender 4.
- the front cowl 5 is disposed in front of a head pipe (not shown).
- a headlight 10 is attached to the front cowl 5.
- the member to which the headlight 10 is attached is not particularly limited.
- the headlight 10 may be attached to a bracket supported by the vehicle body frame.
- the headlight 10 is a headlamp that irradiates the front of the motorcycle 1.
- the headlight 10 includes a light module 11 and a light module 12.
- the light modules 11 and 12 are light modules using LEDs as light sources.
- the front, back, left, right, top, and bottom in the following description of the light modules 11 and 12 are defined with reference to an optical axis Ax (see FIGS. 2 and 3) of the LED 21 described later.
- the front-rear direction of the light modules 11 and 12 is defined to match the direction in which the optical axis Ax of the LED 21 extends.
- the left and right direction and the up and down direction of the light modules 11 and 12 are defined to be orthogonal to each other on a plane orthogonal to the front and rear direction of the light modules 11 and 12.
- the left and right direction and the up and down direction predetermined for the light modules 11 and 12 may be applied.
- the left and right direction and the up and down direction of the light modules 11 and 12 may be defined with reference to the left and right direction and the up and down direction of the motorcycle 1 when the light modules 11 and 12 are provided in the motorcycle 1.
- front-rear direction, the left-right direction, and the up-down direction of the light modules 11, 12 substantially match the front-rear direction, the left-right direction, and the up-down direction of the motorcycle 1, respectively. Accordingly, in the following description of the light modules 11 and 12, front, rear, left, right, upper, and lower are front, rear, left, right, and the like when the light modules 11 and 12 are mounted on the motorcycle 1, respectively. It means upper and lower respectively.
- front, rear, left, right, upper, and lower mean front, rear, left, right, upper, and lower viewed from the rider of the motorcycle 1, respectively.
- the left and right when the lens 30 is viewed from the front may be used.
- the left and right when the lens 30 is viewed from the front correspond to the right and left viewed from the rider of the motorcycle 1, respectively.
- the front and rear direction of the motorcycle 1 is the front and rear direction of the light modules 11 and 12. May be defined to match.
- the light module 11 is disposed below the light module 12.
- the arrangement of the light modules 11 and 12 is not particularly limited.
- the light module 11 is a low beam light module, and lights up when the low beam is irradiated.
- the light module 12 is a high beam light module, and is turned on when high beam irradiation is performed.
- An operation switch 7 for operating the headlight 10 is provided on the handle 6 of the motorcycle 1.
- the headlight 10 includes a housing 13 that supports the light modules 11 and 12, and an outer cover 14 that transmits light.
- the light modules 11 and 12 may be directly supported by the housing 13 or indirectly supported by other members.
- the housing 13 and the outer cover 14 are assembled.
- a headlight chamber 15 is formed by the housing 13 and the outer cover 14.
- the light modules 11 and 12 are disposed in the headlight chamber 15.
- FIG. 3 is a vertical sectional view of the main part of the light module 11.
- FIG. 3 is a vertical sectional view passing through the optical axis Ax of the LED 21.
- the light module 11 includes an LED 21 as a light source and a lens 30 that transmits light from the LED 21.
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view, hatching indicating a cross section of the lens 30 is omitted in FIG. 3.
- LED21 is arrange
- the lens 30 is disposed in front of the LED 21.
- the LED 21 is provided on the substrate 22.
- a heat sink 24 having a plurality of heat radiation fins 23 is fixed to the back side of the substrate 22.
- the cooling device for cooling the substrate 22 is not limited to the heat sink 24.
- the light module 11 includes a casing 25 that houses at least the LED 21 and the substrate 22. However, the casing 25 is not necessarily required and can be omitted.
- the lens 30 is a convex lens that is convex forward.
- the lens 30 has a front surface 31 that is convex toward the front, and a back surface 32 that faces the LED 21.
- the shape of the lens 30 is not particularly limited.
- the convex lens here refers to a lens having a convex surface regardless of the shape of the back surface. Therefore, the shape of the back surface of the convex lens is not particularly limited. Examples of the back surface of the convex lens include a flat surface, a surface having a concave shape toward the front, a surface having a convex shape toward the rear, or a surface made of a combination thereof.
- the surface of the convex lens is not particularly limited as long as it is convex forward.
- the lens 30 includes a refraction region 40 that refracts light from the LED 21 and guides it forward, and a diffusion region 50 that diffuses light from the LED 21 and guides it forward.
- the diffusion transmittance of the diffusion region 50 is higher than that of the refractive region 40. Diffuse transmission refers to the property of diffusing and transmitting light in many directions regardless of the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically. The higher the ratio of the amount of light that diffuses and transmits regardless of the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically, the higher the diffuse transmittance.
- the diffusion region 50 and the refraction region 40 satisfy the relationship of the following expression.
- the refractive region 40 has substantially regular transparency. Regular transmission refers to the property of transmitting light according to the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically. That is, the refraction region 40 is configured to refract and transmit light substantially in accordance with the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically. The refracting region 40 overlaps the LED 21 in the front-back direction entirely or partially.
- FIG. 4 is a view of the lens 30 as viewed from the front.
- the diffusion region 50 is formed in a substantially U shape when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the diffusion region 50 includes a portion extending in the left-right direction below the LED 21, a portion extending in the up-down direction rightward from the LED 21, and a portion extending in the up-down direction leftward from the LED 21. It is substantially U-shaped by being continuous.
- the diffusion region 50 is substantially U-shaped by surrounding the lower side, the left side, and the right side of the LED 21 with a space from the LED 21.
- the shape of the diffusion region 50 is not particularly limited.
- the diffusion region 50 is formed by applying a graining process to a part of the surface 31 of the lens 30.
- the diffusion region 50 may be formed by applying a graining process to a part of the back surface 32 of the lens 30.
- a part of the front surface 31 and a part of the rear surface 32 of the lens 30 may be subjected to a graining process.
- “Wrinkle processing” means physically giving fine unevenness. Due to the fine unevenness, the light from the LED 21 is refracted in multiple directions irrespective of the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically. Thereby, the light from the LED 21 diffuses when passing through the diffusion region 50.
- “diffusion” does not mean that light from the LED 21 is regularly spread in one direction by gradually changing the refractive index as it goes in one direction of the lens 30. “Diffusion” in the present embodiment is to randomly spread light from the LED 21 in multiple directions by changing the refractive index discontinuously.
- the diffusion region 50 is formed so as to project light L1 obliquely upward with respect to the horizontal line and light L2 obliquely downward with respect to the horizontal line.
- the diffusion region 50 may be formed so as to project light inclined in one direction and light inclined in the other direction with respect to a straight line parallel to the optical axis in a cross section passing through the optical axis of the lens 30.
- the refraction region 40 has a first refraction part 41 located above the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the diffusion region 50 includes a first diffusion part 51 positioned below the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the first diffusing unit 51 is located below the first refracting unit 41 on the vertical line V1 passing through the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the diffusion permeability of the first diffusion part 51 is higher than that of the first refraction part 41.
- the first refraction part 41 is configured to refract and transmit light substantially according to the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically.
- the refraction region 40 has a second refraction part 42.
- the second refraction part 42 is located at a position different from the first refraction part 41 in the vertical direction when viewed from the front of the lens 30.
- the second refraction part 42 and the LED 21 are arranged in the left-right direction.
- at least a part of the second refracting part 42 and at least a part of the LED 21 overlap in the left-right direction.
- the second refraction unit 42 is configured to refract light from the LED 21 and guide it forward.
- the diffusion region 50 has a second diffusion part 52.
- the second diffusing unit When the lens 30 is viewed from the front, the second diffusing unit is located on the horizontal line H ⁇ b> 1 passing through the second refracting unit 42 and on the outer side in the left-right direction of the lens 30 with respect to the second refracting unit 42.
- the left-right direction of the lens 30 matches the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1. That is, when the lens 30 is viewed from the front, the second diffusing unit 52 is positioned on the outer side in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 with respect to the second refracting unit 42 on the horizontal line H1 passing through the second refracting unit 42.
- the outward in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 refers to a direction away from the center line C (see FIG.
- the outward direction in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 means the left in the region to the left of the center line C of the motorcycle 1, and the right in the region to the right of the center line C. means.
- the diffusion permeability of the second diffusion part 52 is higher than the diffusion permeability of the second refraction part 42.
- the second refraction part 42 is configured to refract and transmit light substantially according to the law of refraction when viewed macroscopically.
- the diffusion region 50 has a third diffusion part 53.
- the third diffusing unit 53 is positioned on the horizontal line H ⁇ b> 2 passing through the first refracting unit 41 and on the outer side in the left-right direction of the lens 30 with respect to the first refracting unit 41.
- the third diffusing unit 53 is located on the horizontal line H ⁇ b> 2 passing through the first refracting unit 41 and outward in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 with respect to the first refracting unit 41.
- the diffusion permeability of the third diffusion part 53 is higher than that of the first refraction part 41.
- the diffusion region 50 has a fourth diffusion part 54.
- the fourth diffusing unit 54 is located to the left of the LED 21 and above the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the fourth diffusing unit 54 may be located on the right side of the LED 21 and above the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the fourth diffusion part 54 may be located at least one of the left and right directions of the LED 21 and above the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the diffusion permeability of the fourth diffusion part 54 is higher than the diffusion permeability of the first refraction part 41.
- the diffusion region 50 is a first region R1 located on a vertical line V1 passing through the LED 21, and a first region R1 located outside the first region R1 in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1. And two regions R2.
- the vertical length A2 of the second region R2 is longer than the vertical length A1 of the first region R1.
- the shape and dimensions of the diffusion region 50 are examples. The shape and dimensions of the diffusion region 50 can be set as appropriate. Further, the number of diffusion regions 50 is not necessarily limited to one. A plurality of diffusion regions may be formed in a dispersed manner.
- the first refracting portion 41, the second refracting portion 42, the first diffusing portion 51, the second diffusing portion 52, the third diffusing portion 53, and the fourth diffusing portion 54 are portions of the lens 30 through which light from the LED 21 is transmitted. Formed. However, the entire lens 30 is not necessarily used in the light module 11.
- a part of the lens 30 is a transmissive part through which the light from the LED 21 is transmitted, but another part of the lens 30 may be a non-transmissive part through which the light from the LED 21 is not transmitted.
- the non-transmissive portion in the vertical cross section passing through the optical axis Ax, is formed above the upper edge UE of the transmissive portion.
- the non-transmissive portion is formed below the lower edge LE of the transmissive portion.
- the non-transmission part may be formed in any way.
- the non-transmission part may be a refraction part that refracts light when light is transmitted, or may be a diffusion part that diffuses light when light is transmitted.
- the non-transparent portion may be subjected to graining.
- the lens 30 may include a transmissive portion and a non-transmissive portion.
- the first refraction part 41 and the first diffusion part 51 are formed in the transmission part.
- the second refracting part 42, the second diffusing part 52, the third diffusing part 53, and / or the fourth diffusing part 54 may be formed in the transmission part.
- the refractive region 40 is located at the upper edge UE of the transmission part in the vertical cross section passing through the optical axis Ax.
- the optical axis Ax passes through the refractive region 40.
- the transmission region 50 is located at the lower edge LE of the transmission part. As shown in FIG.
- the boundary BL between the refracting region 40 and the transmissive region 50 is positioned below the optical axis Ax in a vertical cross section passing through the optical axis Ax. Note that the boundary BL between the refractive region 40 and the transmissive region 50 does not necessarily need to be clearly specified.
- the diffuse permeability may gradually change between the refractive region 40 and the transmission region 50.
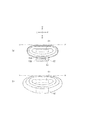
- FIG. 5B schematically shows a light distribution pattern that the light module 11 forms on the screen when a vertical screen is installed in front of the headlight 10.
- FIG. 5A is a diagram schematically showing a light distribution pattern formed on the screen when the lens 30 is not subjected to the graining process. That is, FIG. 5A is a diagram schematically showing a light distribution pattern when the lens 30 has only the refraction region 40.
- each line is a line connecting points having the same illuminance, and the inner line indicates that the illuminance is higher.
- the HH line in the figure is a horizontal line passing through HV (not shown) located in front of the headlight light source.
- the light emitted from the LED 21 has high directivity. Therefore, the range of light distribution is narrow. However, the light emitted from the LED 21 is concentrated and distributed in a narrow range. Therefore, according to LED21, it is easy to obtain sufficient brightness.
- the central region 61 of the light distribution pattern is very bright. A so-called hot zone is formed in the region 61. When there is no screen, the light in the region 61 can illuminate far away road surfaces.
- the light emitted from the LED 21 has high directivity. Therefore, there is a large difference in brightness between the bright area and the dark area. For example, in the region 62, the brightness difference is large between the region 62a above the line 63 and the region 62b below.
- the region 62b is hatched.
- sufficient brightness is obtained in the bright region 62a.
- the brightness is insufficient in the dark region 62b.
- the distance between the nearby road surface and the headlight 10 is short. Therefore, sufficient illuminance can be obtained even if light is irradiated onto a nearby road surface with a small luminous intensity.
- the lens 30 has the diffusion region 50.
- the diffusion region 50 Of the highly directional light from the LED 21, light that illuminates a nearby road surface is diffused by the diffusion region 50. As a result, the directivity of light illuminating a nearby road surface is weakened. Therefore, as shown in FIG.5 (b), according to the light module 11 which concerns on this embodiment, a wider range can be illuminated, ensuring sufficient illumination intensity to illuminate the near road surface. For example, as shown in FIG. 5B, the area 62 in which the bright area 62a and the dark area 62b are mixed in FIG. 5A, while ensuring the illuminance necessary to illuminate a nearby road surface, It can be illuminated relatively evenly.
- the light in the region 62 can irradiate a nearby road surface with sufficient illuminance over a wide area.
- the light module 11 according to the present embodiment can secure a bright region 61 that forms a hot zone. Furthermore, the light module 11 can expand an area having sufficient illuminance to illuminate a nearby road surface below, to the left, and to the right of the area 61.
- the lens 30 includes the first refracting portion 41 positioned above the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front as shown in FIG. And a first diffusion part 51 positioned below the LED 21.
- the light transmitted through the first refraction part 41 is refracted while maintaining high directivity and then projected forward.
- the highly directional light from the LED 21 the light that passes through the first diffusion part 51 is diffused and projected forward.
- the highly directional light that has passed through the first refraction part 41 illuminates a distant road surface.
- the light that has been transmitted through the first diffusion portion 51 and diffused in a wide range illuminates a nearby road surface.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10 can be formed without using the light module of the projector type or the multi-reflector type. There is no need to install a reflector above or below the LED 21.
- the light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10 can be formed only by the direct light module 11 having a small vertical dimension. Therefore, it is possible to form a light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10 while suppressing an increase in size of the headlight 10. Further, the light module 10 can be used together with a projector-type or multi-reflector type light module, so that the degree of freedom in designing the light distribution pattern can be increased.
- the first diffusion part 51 is located below the first refraction part 41 on the vertical line V1 passing through the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- a distant road surface can be illuminated by light having high directivity transmitted through the first refracting portion 41 located above the LED 21.
- the light diffused by the first diffusing section 51 located below the LED 21 can irradiate a nearby road surface over a wide range.
- the lens 30 has a second diffusing portion 52.
- the second diffusing unit 52 is located on the horizontal line H ⁇ b> 1 passing through the second refracting unit 42 and outward in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 with respect to the second refracting unit 42.
- the outer side of the motorcycle 1 in the left-right direction may be darker than the center of the motorcycle 1 in the left-right direction.
- the left and right direction of the motorcycle 1 is illuminated by the light diffused by the second diffusing unit 52 while brightly illuminating the front with the highly directional light transmitted through the second refracting unit 42.
- the road surface outside can be illuminated over a wide area.
- the diffusion region 50 has a third diffusion part 53.
- the third diffusing unit 53 is located on the horizontal line H ⁇ b> 2 passing through the first refracting unit 41 and outward in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 with respect to the first refracting unit 41.
- the light diffused by the third diffusing portion 53 can illuminate the outer road surface in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 over a wide range.
- the diffusion region 50 is formed in a substantially U shape when the lens 30 is viewed from the front. This makes it possible to illuminate a wide road and a nearby road surface and a laterally outward road surface of the motorcycle 1 while illuminating a distant road surface brightly.
- the diffusion region 50 has a fourth diffusion portion 54.
- the fourth diffusing unit 54 is located to the left or right of the LED 21 and above the LED 21 when the lens 30 is viewed from the front.
- the light diffused by the fourth diffusing unit 54 can illuminate the outer road surface of the motorcycle 1 in the left-right direction over a wider range.
- the diffusion region 50 is located on the vertical region V1 passing through the LED 21 and on the outer side in the left-right direction of the motorcycle 1 with respect to the first region R1.
- the vertical length A2 of the second region R2 is longer than the vertical length A1 of the first region R1.
- the lens 30 has a front surface 31 that is convex toward the front, and a back surface 32 that faces the LED 21.
- the first diffusing portion 51 is formed by applying a graining process to a part of the surface 31 of the lens 30.
- the first diffusion part 51 can be formed inexpensively and easily.
- the headlight 10 according to the second embodiment differs from the headlight 10 according to the first embodiment in the following points.
- the headlight 10 according to the second embodiment includes a light module 11 ⁇ / b> B instead of the light module 11.
- the headlight 10 according to the second embodiment includes a diffusion plate 55 that diffuses transmitted light between the light module 11 ⁇ / b> B and the outer cover 14.
- the diffusion plate 55 is an example of a diffuser that diffuses transmitted light.
- the diffuser is not limited to the diffusion plate 55.
- the light module 11B according to the second embodiment includes a lens that is not subjected to graining unlike the light module 11 according to the first embodiment.
- the lens 30 of the light module 11B does not include the diffusion region 50.
- the entire lens 30 is a refractive region 40.
- the lens 30 is different between the light module 11B and the light module 11, elements other than the lens 30 are the same.
- the light module 11B is a direct light module that uses the LED 21 as a light source.
- the light module 11B does not include a reflector separate from the lens 30 above or below the LED 21.
- headlight 10 according to the second embodiment are the same as those of the headlight 10 according to the first embodiment. Parts similar to those of the headlight 10 of the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted.
- the diffusion plate 55 is formed so as to diffuse a part L4 of the light transmitted through the lens 30 of the light module 11B and guide it forward.
- the diffusion plate 55 is formed to diffuse a part L4 of the light transmitted through the lens 30 of the light module 11B under the other part L3 of the light and guide it to the front of the outer cover 14.
- the shape of the diffusion plate 55 is not particularly limited.
- the diffusion plate 55 may have a shape similar to that of the diffusion region 50 (see FIG. 4) of the lens 30 of the first embodiment.
- the diffusion permeability of the diffusion plate 55 (diffuser) is higher than that of the lens 30 and the outer cover 14.
- the diffusing plate 55 may have a diffusing portion located below the LED 21 when the headlight 10 is viewed from the front, and has a diffusing portion located on the left or right side of the LED 21. May be.
- the diffusing portion has a diffuse permeability higher than that of the lens 30 and the outer cover 14.
- the diffusion plate 55 may be formed in a substantially U shape when the headlight 10 is viewed from the front.
- the diffusion plate 55 may include a transmission region that transmits light without diffusing and a diffusion region that diffuses transmitted light.
- the transmission region and the diffusion region may have the same shapes as the refractive region 40 and the diffusion region 50 of the lens 30 according to the first embodiment, respectively, when the headlight 10 is viewed from the front ( (See FIG. 4).
- the diffusion region has a diffusion permeability higher than that of the transmission region, the lens 30 and the outer cover 14.
- the diffusion plate 55 may be a lens.
- the diffusion plate 55 may include a refraction area that refracts light from the light module 11 and guides it forward, and a diffusion area that diffuses light from the light module 11 and guides it forward.
- the refraction area and the diffusion area may have the same shapes as the refraction area 40 and the diffusion area 50 of the lens 30 according to the first embodiment, respectively, when the headlight 10 is viewed from the front ( (See FIG. 4).
- the diffusion region has a diffusion permeability higher than that of the refraction region, the lens 30 and the outer cover 14.
- the headlight 10 can irradiate the road surface in the vicinity over a wide range while brightly illuminating the road surface far away. Therefore, the light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10 can be formed by the direct light module 11B using the LED 21 as a light source. Therefore, it is possible to form a light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10 while suppressing an increase in size of the headlight 10.
- the diffusion plate 55 is separated from the lens 30 and the outer cover 14.
- the diffusion plate 55 may be attached to the lens 30 or the outer cover 14.
- the diffusion plate 55 may be attached to the inner surface of the outer cover 14.
- the diffusion plate 55 may be a diffusion film that diffuses transmitted light. Although illustration is omitted, the diffusion plate 55 may be attached to the outer surface of the outer cover 14. As shown in FIG. 9, the diffusion plate 55 may be attached to the surface 31 of the lens 30. Although illustration is omitted, the diffusion plate 55 may be attached to the back surface 32 of the lens 30.
- the diffuser that diffuses the light from the LED 21 and guides it forward of the outer cover 14 is separate from the lens 30 and the outer cover 14, and between the lens 30 and the outer cover 14. Has been placed.
- the headlight 10 according to the third embodiment has a diffuser formed on the outer cover 14.
- the outer cover 14 is partially textured.
- the diffuser is formed by a region 14a of the outer cover 14 that has been subjected to a textured process.
- this region is referred to as a diffusion region 14a.
- the shape of the diffusion region 14a is not particularly limited. For example, when the headlight 10 is viewed from the front, it may have the same shape as the diffusion region 50 (see FIG. 4) of the lens 30 of the first embodiment. Good.
- the diffusion permeability of the diffusion region 14a is higher than the diffusion permeability of regions other than the diffusion region 14a in the diffuser.
- the light module 11B is the same as the light module 11B according to the second embodiment. That is, the light module 11 ⁇ / b> B is a direct light module using the LED 21 as a light source, and the lens 30 does not include the diffusion region 50. Accordingly, the diffuse permeability of the diffusion region 14 a is higher than the diffuse permeability of the lens 30.
- the light module 11B projects light with high directivity using the LED 21 as a light source.
- Part of the light L3 from the light module 11B passes through the region 14b other than the diffusion region 14a of the outer cover 14, and is projected forward as it is.
- This light L3 irradiates a distant road surface.
- the other part L4 of the light from the light module 11B diffuses when passing through the diffusion region 14a of the outer cover 14, and is projected forward as the diffused light L4a.
- This diffused light L4a irradiates a nearby road surface. Therefore, the headlight 10 according to the present embodiment can irradiate a nearby road surface over a wide range while brightly illuminating a distant road surface.
- the direct light module 11 ⁇ / b> B using the LED 21 as a light source can form a light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10. Therefore, it is possible to form a light distribution pattern required for the headlight 10 while suppressing an increase in size of the headlight 10.
- the embossing is formed on the inner surface of the outer cover 14.
- the embossing may be formed on the outer surface of the outer cover 14.
- both the inner surface and the outer surface of the outer cover 14 may be subjected to embossing.
- the diffusion region 14 a may be formed in the outer cover 14 by processing other than the texture processing.
- the headlight 10 includes the two light modules 11 and 12.
- the number of light modules in the headlight 10 is not limited to two.
- the headlight 10 may include three or more light modules.
- the headlight 10 may include one light module.
- the headlight 10 may include two or more light modules for low beams.
- the headlight 10 is provided on the left and right sides of the center line of the motorcycle 1 (for example, a vertical line passing through the center in the left-right direction of the front wheel 2 when viewed from the front). 11 may be provided.
- the light module 11B and the diffusion plate 55 according to the second embodiment or the third embodiment may be provided on the left side and the right side of the center line of the motorcycle 1.
- the vertical line V1 in FIG. 4 is the center line of the lens 30 in the left-right direction.
- the center line C (see FIG. 1) of the motorcycle 1 coincides with the center line V1 of the lens 30 of the light module 11.
- the center lines C and V1 do not necessarily need to coincide.
- the center line V1 of the lens 30 of each light module 11 does not coincide with the center line C of the motorcycle 1.
- the left light module 11 is arranged to the left of the center line C of the motorcycle 1.
- the right light module 11 is arranged on the right side of the center line C of the motorcycle 1.
- the third diffusing portion 53 of the lens 30 only needs to be formed on the left side of the center line V1 of the lens 30.
- the third diffusing portion 53 of the lens 30 only needs to be formed to the right of the center line V ⁇ b> 1 of the lens 30.
- the diffusion region 50 of the lens 30 of each light module 11 does not necessarily have to be substantially U-shaped.
- the diffusion region 50 of the lens 30 may be formed in a substantially L shape when viewed from the front.
- the diffusion region 50 of the lens 30 may be formed in a substantially J shape when viewed from the front.
- the lens 30 of the light module 11 includes the first refracting unit 41, the second refracting unit 42, the first diffusing unit 51, the second diffusing unit 52, the third diffusing unit 53, and the fourth diffusing unit 54.
- the lens 30 includes the first refracting portion 41 and the first diffusing portion 51.
- the second refracting part 42, the second diffusing part 52, the third diffusing part 53, and the fourth diffusing part 54 are not necessarily required.
- the diffusion region 50 is not limited to a substantially U shape, and may be a belt shape extending horizontally in the left-right direction when viewed from the front.
- the diffusion region 50 may not include the third diffusion part 53 but may include a first diffusion part 51, a second diffusion part 52, and a portion connecting the first diffusion part 51 and the second diffusion part 52. . As described above, the diffusion region 50 may be formed of a single region, or may include a plurality of regions separated from each other. The shape of the diffusion region 50 is not limited at all.
- the diffusion permeability of the first diffusion unit 51, the second diffusion unit 52, the third diffusion unit 53, and the fourth diffusion unit 54 may be the same or different from each other.
- the diffusion region 50 includes at least a first diffusion part 51.
- the diffusion region 50 may include at least one of the second diffusion part 52, the third diffusion part 53, and the fourth diffusion part 54.
- the diffusion part included in the diffusion region 50 is a part of the diffusion region 50 and does not necessarily have to be configured so as to be distinguished from the diffusion region 50. Moreover, it is not always necessary for each diffusion unit to be configured to be distinguished from each other.
- the diffuse permeability of the first refracting part 41 and the second refracting part 42 may be the same or different from each other.
- the diffusing part has a diffusive permeability higher than that of the refracting part.
- the refraction region 40 includes at least a first refraction part 41.
- the refraction region 40 may include a second refraction part 42.
- the refracting part included in the refracting region 40 is a part of the refracting region 40 and does not have to be configured to be distinguishable from the refracting region 40.
- Each refracting portion does not necessarily have to be configured so as to be distinguished from each other.
- the diffusion portions 51 to 54 and the diffusion region 50 may be provided on the front surface 31 of the lens 30 or may be provided on the back surface 32 of the lens 30.
- the positions of the diffusion portions 51 to 54 and the diffusion region 50 in the thickness direction of the lens 30 are not particularly limited.
- the diffusing part is configured to diffuse the light of the LED 21 and guide it forward so that the light transmitted through the diffusing part forms part of the light distribution pattern.
- the diffusion region 50 is configured to diffuse the light of the LED 21 and guide it forward so that the light transmitted through the diffusion region 50 forms part of the light distribution pattern.
- the light distribution pattern is a light distribution pattern on a road surface or a screen.
- the surface of the lens 30 may be composed only of the refraction region 40 and the diffusion region 50.
- the optical axis Ax of the LED 21 passes through the refraction region 40.
- the refractive region 40 overlaps the entire LED 21 in the front-rear direction.
- the diffusion region 50 does not overlap the LED 21 in the front-rear direction.
- all of the portions that overlap the LED 21 in the vertical direction above the LED 21 are the refraction region 40.
- the diffusion region 50 is not provided in a portion above the LED 21 and overlapping the LED 21 in the vertical direction.
- the diffusion region 50 has portions described in (A) to (C) below.
- C As shown in FIG. 4, when the lens 30 is viewed from the front, at least a part of the diffusion region 50 (for example, the third diffusion unit 53 and the fourth diffusion unit 54) is spaced apart from the LED 21 in the left-right direction.
- the lens 30 is vacant and positioned above the optical axis Ax of the LED 21 or the upper edge of the LED 21.
- the portions described in (A) to (C) are continuous.
- the diffusion region 50 is continuous along the outer edge of the lens 30 or the outer edge of the transmission portion of the lens 30 so as to include the portions described in (A) to (C) above.
- the motorcycle 1 When the motorcycle 1 goes straight, the light emitted from the light module 11 and reaching the road surface passes through the diffusion region 50.
- a portion close to the curve inside of the right portion or the left portion of the lens 30 approaches the road surface. Since at least a part of the diffusion region 50 is spaced above the LED 21 in the left-right direction and is located above the optical axis Ax of the LED 21 or the upper edge of the LED 21, the motorcycle 1 is turning in a lean position. Even if it exists, the light emitted from the light module 11 and reaching the road surface passes through the diffusion region 50.
- the light emitted from the light module 11 and reaching the road surface passes through the diffusion region 50.
- the change in reflected light from the road surface is small as seen from the rider.
- a portion of the right portion or the left portion of the lens 30 that is close to the outside of the curve is far from the road surface.
- At least a part of the diffusion region 50 is positioned above the optical axis Ax of the LED 21 or the upper edge of the LED 21 with a space in the left-right direction from the LED 21. Therefore, of the light that illuminates the outside of the curve upward when the motorcycle 1 is turning in a lean position, the amount of light that passes through the diffusion region 50 increases.
- the amount of light from the headlight is small and the change in the amount of light is small when viewed from an oncoming vehicle. Generation of glare (dazzling) can be reduced.
- Such a light distribution pattern is an example of a preferable light distribution pattern formed by the diffusion region 50.
- the light modules 11 and 12 may include one lens 30 and a plurality of LEDs 21.
- one lens 30 and the plurality of LEDs 21 may overlap in the front-rear direction.
- the refractive region 40 of one lens 30 and at least one of the plurality of LEDs 21 may overlap in the front-rear direction.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Non-Portable Lighting Devices Or Systems Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
本発明は、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールであって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを適切に形成することができるライトモジュールを提供することを目的とする。ライトモジュール(11)のレンズ(30)は、レンズ(30)を前方から見たときにLED(21)の上方に位置し、LED(21)からの光を屈折させて前方に導く第1屈折部と、レンズ(30)を前方から見たときにLED(21)より下方に位置し、LED(21)からの光を拡散させて前方に導く第1拡散部と、を有する。
Description
本発明は、車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュール、車両のヘッドライト、および車両に関する。
従来から、車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュールとして、発光ダイオード(Light Emitting Diode。以下、LEDという)を備えた直射型のライトモジュールが知られている。LEDを光源とするライトモジュールは、消費電力が少ないという特性を有する。直射型のライトモジュールは、LEDと、LEDの前方に配置され、LEDからの光を屈折させるレンズとを備える。LEDからの光は、リフレクタ等により反射されることなくレンズに入射する。レンズに入射した光は、レンズを通過する際に屈折し、レンズから前方へ向けて投射される。
特許文献1には、LEDと、LEDの前方に配置された凸レンズとを備えた直射型のライトモジュールが記載されている。この直射型のライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型またはパラボラ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられる。プロジェクタ型またはパラボラ型のライトモジュールにより形成される基本配光パターンと、直射型のライトモジュールにより形成される配光パターンとを合成することにより、ロービーム用の配光パターンが形成される。LEDを備えた直射型のライトモジュールによれば、カットオフラインの近傍に光束を集めることができる。そのため、遠方の視認性を確保しやすい。
しかし、特許文献1に開示された直射型のライトモジュールは、ロービームに必要な配光パターンを形成するために、プロジェクタ型またはパラボラ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられる必要がある。そのため、特許文献1に開示された技術では、車両に対して、直射型のライトモジュールと同数のプロジェクタ型またはパラボラ型のライトモジュールを設置する必要がある。ヘッドライトの大型化が避けられなかった。大型のヘッドライトは、車両の大きさ又は種類等によっては、車両へ搭載され難い場合があった。また、車両のデザイン等によっては、大型のヘッドライトの搭載が好ましくない場合があった。このように、車両によっては、大型のヘッドライトの車両への搭載が困難な場合があった。
上記の課題を踏まえ、本発明の目的は、次の通りである。
直射型のライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられるか否かに関わらず、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを適切に形成できることが好ましい。そのような直射型のライトモジュールによれば、プロジェクト型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールを省略することにより、ヘッドライトの大型化を抑制できる。また、そのような直射型のライトモジュールによれば、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられることにより、配光パターンの設計自由度を高めることができる。これにより、例えば、より広い配光パターンの形成が可能になる。また、車両により適した配光パターンの形成が可能になる。
直射型のライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられるか否かに関わらず、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを適切に形成できることが好ましい。そのような直射型のライトモジュールによれば、プロジェクト型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールを省略することにより、ヘッドライトの大型化を抑制できる。また、そのような直射型のライトモジュールによれば、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられることにより、配光パターンの設計自由度を高めることができる。これにより、例えば、より広い配光パターンの形成が可能になる。また、車両により適した配光パターンの形成が可能になる。
即ち、本発明の目的は、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールであって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを形成することができるライトモジュールを提供することである。本発明の他の目的は、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールを備えたヘッドライトであって、好ましい配光パターンを形成することのできるヘッドライトを提供することである。
本発明に係る車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュールは、発光ダイオードと、前記発光ダイオードの前方に設けられ、前記発光ダイオードからの光を透過させるレンズと、を備える。前記レンズは、第1屈折部と、第1拡散部とを有する。前記第1屈折部は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードの上方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成されている。前記第1拡散部は、前記第1屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードより下方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成されている。
上記ライトモジュールによれば、発光ダイオードからの指向性の高い光のうち、レンズの第1屈折部を透過する光は、高い指向性を保ったまま前方に投射される。発光ダイオードからの指向性の高い光のうち、レンズの第1拡散部を透過する光は、拡散してから前方に投射される。レンズを前方から見たときに、第1屈折部は発光ダイオードの上方に位置する。第1拡散部は発光ダイオードより下方に位置する。そのため、第1屈折部を透過した指向性の高い光は遠くの路面を照らす。第1拡散部を透過して広範囲に拡散した光は近くの路面を照らす。よって、上記ライトモジュールによれば、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら、近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。上記ライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられるか否かに関わらず、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。したがって、上記ライトモジュールによれば、プロジェクト型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールを省略することにより、ヘッドライトの大型化を抑制しつつ、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。また、上記ライトモジュールによれば、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられることにより、配光パターンの設計自由度を高めることができる。
本発明の好ましい一態様によれば、前記第1拡散部は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードを通る鉛直線上において、前記第1屈折部の下方に位置している。
上記態様によれば、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンをより適切に形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記レンズは、第2屈折部と、第2拡散部とを有する。前記第2屈折部は、前記レンズの前方から見たときに上下方向において前記第1屈折部と異なる位置に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成されている。前記第2拡散部は、前記第2屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、前記レンズを前方から見たときに、前記第2屈折部を通る水平線上において前記第2屈折部よりも左右方向の外方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成されている。
車両のヘッドライトでは、車両の左右方向の中央を明るく照らすとともに、車両の左右方向の外方を広範囲に照らしたいというニーズがある。この場合、車両の左右方向の外方は、車両の左右方向の中央よりも暗くてよい。上記態様によれば、第2屈折部を透過した指向性の高い光により、車両の左右方向の中央を照らしながら、第2拡散部を透過して広範囲に拡散した光により、車両の左右方向の外方を照らすことができる。よって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンをより適切に形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記レンズは、第3拡散部を有する。前記第3拡散部は、前記第1屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、前記レンズを前方から見たときに、前記第1屈折部を通る水平線上において前記第1屈折部よりも車両の左右方向の外方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成されている。
上記態様によれば、第1屈折部を透過した指向性の高い光により前方を照らしながら、第3拡散部を透過して広範囲に拡散した光により、車両の左右方向の外方を照らすことができる。よって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンをより適切に形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記レンズは、屈折領域と、拡散領域とを有している。前記屈折領域は、少なくとも前記第1屈折部を含み、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成されている。前記拡散領域は、少なくとも前記第1拡散部を含み、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成されている。前記拡散領域は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに略U字状に形成されている。
上記態様によれば、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら、近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。よって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンをより適切に形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記拡散領域は、第4拡散部を有している。前記第4拡散部は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードよりも左方または右方であってかつ前記発光ダイオードよりも上方に位置する。
上記態様によれば、車両の左右方向の外方の更に広い範囲を照射することができる。よって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンをより適切に形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記拡散領域は、第1領域と第2領域とを有する。前記第1領域は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに、前記発光ダイオードを通る鉛直断面内に位置する。前記第2領域は、前記第1領域よりも左右方向の外方に位置する。前記第2領域の上下方向の長さは、前記第1領域の上下方向の長さよりも長い。
上記態様によれば、車両の左右方向の外方において、より広い範囲を照射することができる。よって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンをより適切に形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記レンズは、前方に向かって凸状の表面と、前記発光ダイオードに対向する裏面とを有する。前記第1拡散部は、前記レンズの前記表面の一部または前記裏面の一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されている。
上記態様によれば、安価かつ簡易に第1拡散部を形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記レンズは、前方に向かって凸状の表面と、前記発光ダイオードに対向する裏面とを有する。前記第1拡散部は、前記レンズの前記表面の一部または前記裏面の一部に、透過する光を拡散させる拡散板を取り付けることにより形成されている。
上記態様によれば、安価かつ簡易に第1拡散部を形成することができる。
本発明に係る車両のヘッドライトは、前記のいずれか一つのライトモジュールを備えたものである。
上記ヘッドライトによれば、好ましい配光パターンを形成することができる。
本発明に係る他の車両のヘッドライトは、発光ダイオードと、レンズと、アウターカバーと、拡散体とを備える。前記レンズは、前記発光ダイオードの前方に配置され、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて透過させる。前記アウターカバーは、前記レンズの前方に配置され、前記レンズを透過した光を透過させる。前記拡散体は、前記レンズを透過した光の一部を、前記レンズを透過した光の他の一部の下方にて拡散させ、前記アウターカバーの前方に導くように構成されている。
上記ヘッドライトによれば、発光ダイオードからの指向性の高い光は、レンズを透過する際に屈折し、高い指向性を保ったままレンズから投射される。レンズを透過した光の一部は、レンズを透過した光の他の一部の下方において、拡散体により拡散し、拡散光としてアウターカバーの前方に導かれる。前記レンズを透過した光の他の一部は、拡散体によって拡散されずに、アウターカバーの前方へ投射される。そのため、拡散体により拡散されていない光は、遠くの路面を照らし、拡散体により拡散された光は近くの路面を照らす。よって、上記ヘッドライトによれば、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールを用いて、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。上記ヘッドライトによれば、好ましい配光パターンを形成することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記拡散体は、前記レンズと前記アウターカバーとの間に配置され、透過する光を拡散させるように構成されている。
上記態様によれば、レンズ自体に加工を施さなくても、発光ダイオードからの指向性の高い光の一部を、拡散させてアウターカバーの前方に投射することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記拡散体は、前記アウターカバーに取り付けられ、透過する光を拡散させるように構成されている。
上記態様によれば、レンズ自体に加工を施さなくても、発光ダイオードからの指向性の高い光の一部を、拡散させてアウターカバーの前方に投射することができる。
本発明の好ましい他の一態様によれば、前記拡散体は、前記アウターカバーの一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されている。
上記態様によれば、レンズ自体に加工を施さなくても、かつ、レンズとアウターカバーとの間に拡散板を配置しなくても、発光ダイオードからの指向性の高い光の一部を、拡散させてアウターカバーの前方に投射することができる。
本発明に係る車両は、前記ヘッドライトを備えたものである。
本発明によれば、前述の効果を奏する車両を得ることができる。
本発明によれば、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールであって、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを形成することができるライトモジュールを提供することができる。また、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールを備えたヘッドライトであって、好ましい配光パターンを形成することのできるヘッドライトを提供することができる。
本発明者は、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールを車両のヘッドライトに利用することについて鋭意検討した結果、以下の知見を得るに至った。LEDから出射される光は指向性が高い。そのため、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールは、配光の範囲が狭いが、狭い範囲に集中して配光するので十分な明るさを得やすいという特性を有する。そのため、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールを車両のヘッドライトに利用した場合、遠くの路面まで明るく照らしやすいという利点が得られる。一方、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールでは、配光の範囲が狭い。そのため、ロービームに求められる近くの路面での配光が得られにくいと考えられていた。
本発明者は、車両のヘッドライトと、車両に近い路面との距離が短いので、車両に近い路面に対して小さな光度で光を照射しても十分な照度が得られることに着目した。本発明者は、LEDを光源とする直射型のライトモジュールの上記特性と、車両のヘッドライトに求められる上記性質とを考慮し、以下の知見を得た。
ヘッドライトのLEDから投射される指向性の高い光のうち、車両に近い路面を拡散させることにより、十分な照度を確保しながら照射範囲を広げることができる。これにより、遠くの路面まで明るく照らしやすいというLEDの利点を活かしつつ、近くの路面に対して十分な照度を確保しながら広範囲を照らすことが可能となる。このような直射型のライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられなくても、ヘッドライトに求められる配光パターンを形成できる。このような直射型のライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型およびマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと異なり、光源の上方または下方にリフレクタを設置する必要がない。従って、上下方向の寸法を小さくすることができる。さらに、このような直射型のライトモジュールは、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられることにより、配光パターンの設計自由度を高めることができる。これにより、例えば、より広い配光パターンの形成が可能になる。また、車両により適した配光パターンの形成が可能になる。
以下に説明する本発明は、本発明者の上記知見に基づいてなされたものである。
(第1実施形態)
以下、本発明の実施の形態について説明する。図1は、「車両」の一例としての自動二輪車1の正面図である。「車両」は自動二輪車1に限定されない。「車両」は、例えば、ATV(All Terrain Vehicle)、ROV(Recreational Off-highway Vehicle)、または自動車であってもよい。「車両」は、リーン姿勢で旋回する車両であってもよい。リーン姿勢で旋回する車両は、カーブ走行時にカーブ内側にリーンして旋回するように構成されている。リーン姿勢で旋回する車両としては、特に限定されず、例えば、自動二輪車、自動三輪車等の鞍乗型車両が挙げられる。実施形態の自動二輪車1は、リーン姿勢で旋回する車両の一例である。以下の説明では、特に断らない限り、前、後、左、右、上、下とは、自動二輪車1に乗車したライダーから見た前、後、左、右、上、下をそれぞれ意味するものとする。図面中の符号F、Re、L、R、U、Dは、それぞれ上記ライダーから見た前、後、左、右、上、下を表す。
以下、本発明の実施の形態について説明する。図1は、「車両」の一例としての自動二輪車1の正面図である。「車両」は自動二輪車1に限定されない。「車両」は、例えば、ATV(All Terrain Vehicle)、ROV(Recreational Off-highway Vehicle)、または自動車であってもよい。「車両」は、リーン姿勢で旋回する車両であってもよい。リーン姿勢で旋回する車両は、カーブ走行時にカーブ内側にリーンして旋回するように構成されている。リーン姿勢で旋回する車両としては、特に限定されず、例えば、自動二輪車、自動三輪車等の鞍乗型車両が挙げられる。実施形態の自動二輪車1は、リーン姿勢で旋回する車両の一例である。以下の説明では、特に断らない限り、前、後、左、右、上、下とは、自動二輪車1に乗車したライダーから見た前、後、左、右、上、下をそれぞれ意味するものとする。図面中の符号F、Re、L、R、U、Dは、それぞれ上記ライダーから見た前、後、左、右、上、下を表す。
自動二輪車1は、前輪2と、後輪(図示せず)と、後輪を駆動するパワーユニット(図示せず)とを備える。前輪2は、フロントフォーク3に支持されている。前輪2の上方には、フロントフェンダ4が設けられている。フロントフェンダ4の上方には、フロントカウル5が配置されている。フロントカウル5は、図示しないヘッドパイプの前方に配置されている。
フロントカウル5には、ヘッドライト10が取り付けられている。ただし、ヘッドライト10が取り付けされる部材は特に限定されない。図示は省略するが、ヘッドライト10は、車体フレームに支持されるブラケットに取り付けられていてもよい。ヘッドライト10は、自動二輪車1の前方を照射する前照灯である。ヘッドライト10は、ライトモジュール11とライトモジュール12とを有している。ライトモジュール11および12は、LEDを光源とするライトモジュールである。以下のライトモジュール11および12に関する説明における前、後、左、右、上、下は、後述するLED21の光軸Ax(図2、3参照)を参照して定義される。即ち、ライトモジュール11、12の前後方向は、LED21の光軸Axが延びる方向と合致するように定義される。ライトモジュール11、12の左右方向及び上下方向は、ライトモジュール11、12の前後方向と直交する平面上において互いに直交するように定義される。この時、ライトモジュール11、12の左右方向及び上下方向としては、ライトモジュール11、12に予め定められた左右方向及び上下方向が適用されてもよい。また、ライトモジュール11、12の左右方向及び上下方向は、ライトモジュール11、12が自動二輪車1に設けられる時の自動二輪車1の左右方向及び上下方向を参照して定義されてもよい。なお、ライトモジュール11、12についての説明における「水平」は、ライトモジュール11、12の左右方向と平行な方向である。ライトモジュール11、12についての説明における「鉛直」は、ライトモジュール11、12の上下方向と平行な方向である。本実施形態では、ライトモジュール11、12の前後方向、左右方向及び上下方向は、それぞれ自動二輪車1の前後方向、左右方向及び上下方向と実質的に合致している。従って、以下のライトモジュール11および12に関する説明では、前、後、左、右、上、下は、ライトモジュール11および12が自動二輪車1に搭載された状態での前、後、左、右、上、下をそれぞれ意味するものとする。言い換えると、以下のライトモジュール11および12に関する説明では、前、後、左、右、上、下は、自動二輪車1のライダーから見た前、後、左、右、上、下をそれぞれ意味する。ただし、後述するレンズ30に関する説明では、レンズ30を前方から見た場合の左、右を用いる場合がある。レンズ30を前方から見た場合の左、右は、自動二輪車1のライダーから見た右、左にそれぞれ対応する。なお、自動二輪車1に設けられるライトモジュール11、12の光軸Axの方向と、自動二輪車1の前後方向とが合致しない場合に、自動二輪車1の前後方向が、ライトモジュール11、12の前後方向と合致するように定義されてもよい。
本実施形態では、ライトモジュール11はライトモジュール12の下方に配置されている。しかし、ライトモジュール11および12の配置は特に限定されない。ライトモジュール11は、ロービーム用のライトモジュールであり、ロービーム照射時に点灯する。ライトモジュール12は、ハイビーム用のライトモジュールであり、ハイビーム照射時に点灯する。自動二輪車1のハンドル6には、ヘッドライト10を操作するための操作スイッチ7が設けられている。
図2に示すように、ヘッドライト10は、ライトモジュール11および12を支持するハウジング13と、光を透過させるアウターカバー14とを有する。ライトモジュール11および12は、ハウジング13に直接支持されていてもよく、他の部材を介して間接的に支持されていてもよい。ハウジング13とアウターカバー14とは組み立てられている。ハウジング13およびアウターカバー14により、ヘッドライト室15が形成されている。ライトモジュール11および12は、ヘッドライト室15内に配置されている。
図3は、ライトモジュール11の主要部の鉛直断面図である。図3は、LED21の光軸Axを通る鉛直断面図である。図3に示すように、ライトモジュール11は、光源としてのLED21と、LED21からの光を透過させるレンズ30とを備えている。なお、図3は断面図であるが、図3では、レンズ30の断面を示すハッチングが省略されている。LED21は、光を前方に照射するように配置されている。レンズ30は、LED21の前方に配置されている。LED21は基板22上に設けられている。基板22の裏側には、複数の放熱フィン23を有するヒートシンク24が固定されている。ただし、基板22を冷却する冷却装置は、ヒートシンク24に限られない。ライトモジュール11は、少なくともLED21および基板22を収容するケーシング25を備えている。ただし、ケーシング25は必ずしも必要ではなく、省略することが可能である。
レンズ30は、前方に向けて凸状の凸レンズからなっている。レンズ30は、前方に向かって凸状の表面31と、LED21に対向する裏面32とを有する。ただし、レンズ30の形状は特に限定されない。また、ここでいう凸レンズは、裏面の形状に関わらず、表面が凸状であるレンズをいう。従って、凸レンズの裏面の形状は、特に限定されない。凸レンズの裏面としては、例えば、平坦面、前方に向けて凹状を有する面、後方に向けて凸状を有する面、又はこれらの組合せからなる面が挙げられる。また、凸レンズの表面は、前方に向けて凸状であれば、特に限定されない。レンズ30は、LED21からの光を屈折させて前方に導く屈折領域40と、LED21からの光を拡散させて前方に導く拡散領域50とを有する。拡散領域50の拡散透過性は、屈折領域40の拡散透過性よりも高い。拡散透過性は、巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に多くの方向に光を拡散して透過させる性質をいう。透過する全光量に対する、巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に拡散して透過する光量の割合が高いほど、拡散透過性が高い。一方、透過する全光量に対する、巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に拡散して透過する光量の割合が低いほど、拡散透過性が低い。この場合、透過する全光量のうち、巨視的に見て屈折の法則に従って透過する光量の割合が高い。
拡散透過性に関し、拡散領域50と屈折領域40とは、下式の関係を満たす。
[(巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に拡散して拡散領域50を透過する光量)/(拡散領域50を透過する全光量)]>[(巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に拡散して屈折領域40を透過する光量)/(屈折領域40を透過する全光量)]
本実施形態において、屈折領域40は、実質的に正透過性を有する。正透過性とは、巨視的に見て屈折の法則に従って光を透過させる性質をいう。即ち、屈折領域40は、巨視的に見て実質的に屈折の法則に従って光を屈折させて透過させるように構成されている。屈折領域40は、LED21と前後方向に全体的に又は部分的に重なり合う。
拡散透過性に関し、拡散領域50と屈折領域40とは、下式の関係を満たす。
[(巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に拡散して拡散領域50を透過する光量)/(拡散領域50を透過する全光量)]>[(巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に拡散して屈折領域40を透過する光量)/(屈折領域40を透過する全光量)]
本実施形態において、屈折領域40は、実質的に正透過性を有する。正透過性とは、巨視的に見て屈折の法則に従って光を透過させる性質をいう。即ち、屈折領域40は、巨視的に見て実質的に屈折の法則に従って光を屈折させて透過させるように構成されている。屈折領域40は、LED21と前後方向に全体的に又は部分的に重なり合う。
図4は、レンズ30を前方から見た図である。拡散領域50は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに略U字状に形成されている。レンズ30を前方から見たときに、拡散領域50は、LED21より下方において左右方向に延びる部分と、LED21より右方において上下方向に延びる部分と、LED21より左方において上下方向に延びる部分とが連続することにより略U字状を成している。レンズ30を前方から見たときに、拡散領域50は、LED21から間隔を空けてLED21の下方と左方と右方とを囲むことにより略U字状を成している。ただし、拡散領域50の形状は特に限定されない。本実施形態では、拡散領域50は、レンズ30の表面31の一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されている。なお、拡散領域50は、レンズ30の裏面32の一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されていてもよい。また、レンズ30の表面31の一部および裏面32の一部にシボ加工を施してもよい。「シボ加工」とは、物理的に細かい凹凸をつけることである。細かい凹凸により、LED21からの光は巨視的に見て屈折の法則と無関係に多方向に屈折される。これにより、LED21からの光は、拡散領域50を透過する際に拡散する。
本実施形態で言う「拡散」とは、LED21からの光を、レンズ30の一方向に行くにつれて屈折率を徐々に変化させることにより、一方向に規則的に広げることではない。本実施形態で言う「拡散」は、LED21からの光を、屈折率を非連続的に変化させることにより、多方向にランダムに広げることである。拡散領域50は、例えば図3に示すように、水平線に対して斜め上向きの光L1と、水平線に対して斜め下向きの光L2とを投射するように形成される。拡散領域50は、レンズ30の光軸を通る断面において、光軸と平行な直線に対し一方に傾いた光と他方に傾いた光とを投射するように形成されていてもよい。
図4に示すように、屈折領域40は、レンズ30を前方から見たときにLED21の上方に位置する第1屈折部41を有する。拡散領域50は、レンズ30を前方から見たときにLED21より下方に位置する第1拡散部51を有する。第1拡散部51は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、LED21を通る鉛直線V1上において、第1屈折部41の下方に位置している。第1拡散部51の拡散透過性は、第1屈折部41の拡散透過性よりも高い。第1屈折部41は、巨視的に見て実質的に屈折の法則に従って光を屈折させて透過させるように構成されている。
また、屈折領域40は第2屈折部42を有する。第2屈折部42は、レンズ30の前方から見たときに上下方向に第1屈折部41と異なる位置に位置する。レンズ30を前方から見たとき、図4に示すように、第2屈折部42とLED21とは左右方向に並んでいる。レンズ30を前方から見たとき、第2屈折部42の少なくとも一部と、LED21の少なくとも一部とが左右方向に重なる。第2屈折部42は、LED21からの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成されている。拡散領域50は、第2拡散部52を有する。第2拡散部は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、第2屈折部42を通る水平線H1上において、第2屈折部42よりもレンズ30の左右方向の外方に位置する。本実施形態において、レンズ30の左右方向は、自動二輪車1の左右方向と合致する。即ち、第2拡散部52は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、第2屈折部42を通る水平線H1上において、第2屈折部42よりも自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方に位置する。なお、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方とは、自動二輪車1の中心線C(図1参照)から遠ざかる方をいう。自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方は、自動二輪車1の中心線Cよりも左方の領域にあっては左方を意味し、中心線Cよりも右方の領域にあっては右方を意味する。第2拡散部52の拡散透過性は、第2屈折部42の拡散透過性よりも高い。第2屈折部42は、巨視的に見て実質的に屈折の法則に従って光を屈折させて透過させるように構成されている。
また、拡散領域50は、第3拡散部53を有する。第3拡散部53は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、第1屈折部41を通る水平線H2上において、第1屈折部41よりもレンズ30の左右方向の外方に位置する。第3拡散部53は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、第1屈折部41を通る水平線H2上において、第1屈折部41よりも自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方に位置する。第3拡散部53の拡散透過性は、第1屈折部41の拡散透過性よりも高い。
また、拡散領域50は、第4拡散部54を有する。第4拡散部54は、レンズ30を前方から見たときにLED21よりも左方であってかつLED21よりも上方に位置する。なお、第4拡散部54は、レンズ30を前方から見たときにLED21よりも右方であってかつLED21よりも上方に位置していてもよい。第4拡散部54は、レンズ30を前方から見たときにLED21の左右方向の少なくとも一方であって且つLED21よりも上方に位置していてもよい。第4拡散部54の拡散透過性は、第1屈折部41の拡散透過性よりも高い。
拡散領域50は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、LED21を通る鉛直線V1上に位置する第1領域R1と、第1領域R1よりも自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方に位置する第2領域R2とを有する。第2領域R2の上下方向の長さA2は、第1領域R1の上下方向の長さA1よりも長い。
なお、拡散領域50の上記形状および寸法は一例である。拡散領域50の形状および寸法は適宜設定することが可能である。また、拡散領域50は必ずしも1つに限られない。複数の拡散領域が分散して形成されていてもよい。第1屈折部41、第2屈折部42、第1拡散部51、第2拡散部52、第3拡散部53、および第4拡散部54は、レンズ30のうちLED21からの光が透過する部分に形成される。しかし、ライトモジュール11において、必ずしもレンズ30の全体が利用されるとは限らない。レンズ30の一部はLED21からの光が透過する透過部分であるが、レンズ30の他の部分はLED21からの光が透過しない非透過部分となる場合がある。図3に示すように、光軸Axを通る鉛直断面において、非透過部分は、透過部分の上縁UEより上方に形成されている。また、非透過部分は、透過部分の下縁LEより下方に形成されている。この場合、非透過部分は、どのように形成されていてもよい。非透過部分は、光が透過する場合には光を屈折させる屈折部であってもよく、光が透過する場合には光を拡散させる拡散部であってもよい。非透過部分にシボ加工が施されていてもよい。このように、レンズ30は、透過部分と非透過部分とを備えていてもよい。その場合、その透過部分に第1屈折部41および第1拡散部51が形成される。その透過部分に更に、第2屈折部42、第2拡散部52、第3拡散部53、および/または第4拡散部54が形成されていてもよい。ライトモジュール11では、図3に示すように、光軸Axを通る鉛直断面において、透過部分の上縁UEに、屈折領域40が位置している。光軸Axは、屈折領域40を通過している。透過部分の下縁LEに、透過領域50が位置している。図3に示すように、光軸Axを通る鉛直断面において、屈折領域40と透過領域50との境界BLは、光軸Axよりも下方に位置する。なお、屈折領域40と透過領域50との境界BLは、必ずしも明確に特定される必要はない。屈折領域40と透過領域50との間で、徐々に拡散透過性が変化していてもよい。
次に、ライトモジュール11が形成する配光パターンについて説明する。図5(b)は、ヘッドライト10の前方に垂直なスクリーンを設置した場合に、ライトモジュール11が上記スクリーン上に形成する配光パターンを模式的に示す図である。図5(a)は、レンズ30にシボ加工を施さない場合に、上記スクリーン上に形成される配光パターンを模式的に示す図である。すなわち、図5(a)は、レンズ30が屈折領域40のみを有する場合の配光パターンを模式的に示す図である。図5(a)および(b)において、各線は照度が等しい点を結んだ線であり、内側の線ほど照度が高いことを表す。なお、図中のH-H線は、ヘッドライト光源の前方に位置するH-V(図示せず)を通る水平線である。
図5(a)に示すように、LED21から出射される光は、高い指向性を有する。そのため、配光の範囲は狭い。しかし、LED21から出射される光は、狭い範囲に集中して配光する。従って、LED21によれば、十分な明るさを得やすい。特に、配光パターンの中央の領域61は非常に明るい。領域61には、いわゆるホットゾーンが形成される。領域61の光により、上記スクリーンがない場合、遠くの路面まで明るく照らすことができる。一方、LED21から出射される光は、高い指向性を有する。そのため、明るい領域と暗い領域との間で明るさの差が大きい。例えば、領域62のうち、線63の上方の領域62aと下方の領域62bとでは、明るさの差が大きい。なお、図5(a)において、領域62bにはハッチングが付されている。図5(a)に示す配光パターンでは、明るい領域62aでは十分な明るさが得られる。しかし、暗い領域62bでは明るさが不足する。領域62aと領域62bとでは明るさの差が大きい。そのため、上記スクリーンがない場合、ヘッドライト10の近くの路面では明るく照らされる部分と暗く照らされる部分とが存在する。これにより、それらの明るさの差が大きくなる。ところが、近くの路面とヘッドライト10との距離が近い。そのため、近くの路面に対して小さな光度で光を照射しても十分な照度が得られる。したがって、近くの路面を照らすこととなる領域62aの光では、光度を抑えることが可能である。一方、遠くの路面に比べて近くの路面に対しては、できるだけ広範囲を照らしたいというニーズが強い。領域62bを十分に照らしたいというニーズがある。
前述の通り、本実施形態に係るライトモジュール11では、レンズ30は拡散領域50を有している。LED21からの指向性の高い光のうち、近くの路面を照らす光は、拡散領域50によって拡散される。その結果、近くの路面を照らす光の指向性が弱められる。そのため、図5(b)に示すように、本実施形態に係るライトモジュール11によれば、近くの路面を照らすために十分な照度を確保しながら、より広い範囲を照らすことができる。例えば、図5(a)において明るい領域62aと暗い領域62bとが混在していた領域62を、図5(b)に示すように、近くの路面を照らすために必要な照度を確保しながら、比較的均等に照らすことができる。そのため、上記スクリーンがない場合、領域62の光により、近くの路面を十分な照度で広範囲に照射することができる。図5(b)に示すように、本実施形態に係るライトモジュール11は、ホットゾーンを形成する明るい領域61を確保できる。さらに、ライトモジュール11は、その領域61の下方、左方、および右方において、近くの路面を照らすのに十分な照度を有する領域を広げることができる。
以上のように、本実施形態に係るライトモジュール11によれば、レンズ30は、図4に示すようにレンズ30を前方から見たときに、LED21の上方に位置する第1屈折部41と、LED21より下方に位置する第1拡散部51とを有する。LED21からの指向性の高い光のうち、第1屈折部41を透過する光は、高い指向性を保ったまま屈折してから前方に投射される。LED21からの指向性の高い光のうち、第1拡散部51を透過する光は、拡散してから前方に投射される。第1屈折部41を透過した指向性の高い光は、遠くの路面を照らす。第1拡散部51を透過して広範囲に拡散された光は、近くの路面を照らす。よって、ライトモジュール11によれば、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら、近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。そのため、ライトモジュール11によれば、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いなくても、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。LED21の上方または下方にリフレクタが設置される必要がない。上下方向の寸法が小さい直射型のライトモジュール11のみにより、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。したがって、ヘッドライト10の大型化を抑制しつつ、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。また、ライトモジュール10は、プロジェクタ型またはマルチリフレクタ型のライトモジュールと共に用いられることにより、配光パターンの設計自由度を高めることができる。
また、第1拡散部51は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、LED21を通る鉛直線V1上において、第1屈折部41の下方に位置している。LED21の上方に位置する第1屈折部41を透過した指向性の高い光によって遠くの路面を照らすことができる。LED21より下方に位置する第1拡散部51によって拡散した光により、近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。
図4に示すように、レンズ30は、第2拡散部52を有する。第2拡散部52は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、第2屈折部42を通る水平線H1上において第2屈折部42よりも自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方に位置する。自動二輪車1のヘッドライト10では、自動二輪車1の左右方向の中央を明るく照らしたい一方、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方を広い範囲で照らしたいというニーズがある。この場合、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方は、自動二輪車1の左右方向の中央よりも暗くてもよい。本実施形態に係るライトモジュール11によれば、第2屈折部42を透過した指向性の高い光により前方を明るく照らしながら、第2拡散部52によって拡散された光により、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方の路面を広い範囲にわたって照らすことができる。
また、拡散領域50は、第3拡散部53を有する。第3拡散部53は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、第1屈折部41を通る水平線H2上において第1屈折部41よりも自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方に位置する。これにより、第3拡散部53によって拡散された光により、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方の路面を広い範囲にわたって照らすことができる。
図4に示すように、拡散領域50は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに略U字状に形成されている。このことにより、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら、近くの路面および自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方の路面を広い範囲にわたって照らすことができる。
また、拡散領域50は、第4拡散部54を有している。第4拡散部54は、レンズ30を前方から見たときにLED21よりも左方または右方であってかつLED21よりも上方に位置する。このことにより、第4拡散部54によって拡散される光によって、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方の路面を更に広い範囲にわたって照らすことができる。
また、拡散領域50は、レンズ30を前方から見たときに、LED21を通る鉛直線V1上に位置する第1領域R1と、第1領域R1よりも自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方に位置する第2領域R2とを有する。第2領域R2の上下方向の長さA2は、第1領域R1の上下方向の長さA1よりも長い。これにより、自動二輪車1の左右方向の外方の路面を広い範囲にわたって照らすことができる。
本実施形態ではレンズ30は、図3に示すように、前方に向かって凸状の表面31と、LED21に対向する裏面32とを有する。第1拡散部51は、レンズ30の表面31の一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されている。このことにより、安価かつ簡易に第1拡散部51を形成することができる。
(第2実施形態)
図6に示すように、第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10と、第1実施形態に係るヘッドライト10とでは、以下の点が異なる。第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、ライトモジュール11の代わりに、ライトモジュール11Bを備える。第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、ライトモジュール11Bとアウターカバー14との間に、透過する光を拡散させる拡散板55を備えている。拡散板55は、透過する光を拡散させる拡散体の一例である。ただし、拡散体は拡散板55に限定される訳ではない。
図6に示すように、第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10と、第1実施形態に係るヘッドライト10とでは、以下の点が異なる。第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、ライトモジュール11の代わりに、ライトモジュール11Bを備える。第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、ライトモジュール11Bとアウターカバー14との間に、透過する光を拡散させる拡散板55を備えている。拡散板55は、透過する光を拡散させる拡散体の一例である。ただし、拡散体は拡散板55に限定される訳ではない。
図7に示すように、第2実施形態に係るライトモジュール11Bは、第1実施形態に係るライトモジュール11と異なり、シボ加工が施されていないレンズを備える。ライトモジュール11Bのレンズ30は、拡散領域50を備えていない。レンズ30を前方から見たときレンズ30の全体が屈折領域40となっている。ライトモジュール11Bとライトモジュール11とでは、レンズ30が異なっているが、レンズ30以外の要素は同様である。ライトモジュール11Bは、第1実施形態に係るライトモジュール11と同様に、LED21を光源とする直射型のライトモジュールである。ライトモジュール11Bは、LED21の上方または下方に、レンズ30と別体のリフレクタを備えていない。
第2実施形態に係るヘッドライト10のその他の構成は、第1実施形態のヘッドライト10と同様である。第1実施形態のヘッドライト10と同様の部分には同様の符号を付し、その説明は省略する。
拡散板55は、ライトモジュール11Bのレンズ30を透過した光の一部L4を拡散させて前方に導くように形成されている。拡散板55は、ライトモジュール11Bのレンズ30を透過した光の一部L4を、前記光の他の一部L3の下方にて拡散させ、アウターカバー14の前方に導くように形成されている。拡散板55の形状は特に限定されない。拡散板55は、例えば、ヘッドライト10を前方から見たときに、第1実施形態のレンズ30の拡散領域50(図4参照)と同様の形状を有していてもよい。拡散板55(拡散体)の拡散透過性は、レンズ30及びアウターカバー14の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有する。例えば、拡散板55は、ヘッドライト10を前方から見たときにLED21より下方に位置する拡散部を有していてもよく、LED21よりも左方または右方に位置する拡散部を有していてもよい。この場合、拡散部が、レンズ30及びアウターカバー14の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有する。拡散板55は、ヘッドライト10を前方から見たときに略U字状に形成されていてもよい。
また、拡散板55は、光を拡散させずに透過させる透過領域と、透過する光を拡散させる拡散領域とを備えていてもよい。この場合、透過領域、拡散領域は、ヘッドライト10を前方から見たときに、それぞれ第1実施形態に係るレンズ30の屈折領域40、拡散領域50と同様の形状を有していてもよい(図4参照)。この場合、拡散領域は、透過領域、レンズ30及びアウターカバー14の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有する。
また、拡散板55はレンズであってもよい。拡散板55は、ライトモジュール11からの光を屈折させて前方に導く屈折領域と、ライトモジュール11からの光を拡散させて前方に導く拡散領域とを備えていてもよい。この場合、屈折領域及び拡散領域は、ヘッドライト10を前方から見たときに、それぞれ第1実施形態に係るレンズ30の屈折領域40及び拡散領域50と同様の形状を有していてもよい(図4参照)。この場合、拡散領域は、屈折領域、レンズ30及びアウターカバー14の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有する。
本実施形態によれば、ライトモジュール11Bからは、LED21を光源とする指向性の高い光が投射される。ライトモジュール11Bからの光の一部L3は、拡散板55を透過せずにそのまま前方に投射される。この光は、遠くの路面を照射する。一方、ライトモジュール11Bからの光の他の一部L4は、拡散板55を透過するときに拡散され、拡散光L4aとして前方に投射される。この拡散光L4aは、近くの路面を照射する。よって、本実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、第1実施形態に係るヘッドライト10と同様に、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら、近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。従って、LED21を光源とする直射型のライトモジュール11Bによって、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。したがって、ヘッドライト10の大型化を抑制しつつ、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。
本実施形態では、拡散板55は、レンズ30およびアウターカバー14から離間している。しかし、拡散板55は、レンズ30またはアウターカバー14に取り付けられていてもよい。例えば、図8に示すように、拡散板55はアウターカバー14の内面に貼り付けられていてもよい。拡散板55は、透過する光を拡散させる拡散フィルムであってもよい。図示は省略するが、拡散板55はアウターカバー14の外面に貼り付けられていてもよい。図9に示すように、拡散板55は、レンズ30の表面31に貼り付けられていてもよい。図示は省略するが、拡散板55は、レンズ30の裏面32に貼り付けられていてもよい。
(第3実施形態)
図6に示すヘッドライト10では、LED21からの光を拡散させてアウターカバー14の前方に導く拡散体が、レンズ30およびアウターカバー14と別体であり、レンズ30とアウターカバー14との間に配置されている。一方、図10に示すように、第3実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、拡散体がアウターカバー14に形成されたものである。
図6に示すヘッドライト10では、LED21からの光を拡散させてアウターカバー14の前方に導く拡散体が、レンズ30およびアウターカバー14と別体であり、レンズ30とアウターカバー14との間に配置されている。一方、図10に示すように、第3実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、拡散体がアウターカバー14に形成されたものである。
本実施形態では、アウターカバー14の一部にシボ加工が施されている。拡散体は、アウターカバー14のうちシボ加工が施された領域14aにより形成されている。以下、この領域を拡散領域14aと称する。拡散領域14aの形状は特に限定されず、例えば、ヘッドライト10を前方から見たときに、第1実施形態のレンズ30の拡散領域50(図4参照)と同様の形状を有していてもよい。拡散領域14aの拡散透過性は、拡散体における拡散領域14a以外の領域が有する拡散透過性よりも高い。
ライトモジュール11Bは、第2実施形態に係るライトモジュール11Bと同様である。すなわち、ライトモジュール11Bは、LED21を光源とする直射型のライトモジュールであって、レンズ30が拡散領域50を備えていないものである。従って、拡散領域14aの拡散透過性は、レンズ30の拡散透過性よりも高い。
ライトモジュール11Bからは、LED21を光源とする指向性の高い光が投射される。ライトモジュール11Bからの光の一部L3は、アウターカバー14の拡散領域14a以外の領域14bを透過し、そのまま前方に投射される。この光L3は、遠くの路面を照射する。一方、ライトモジュール11Bからの光の他の一部L4は、アウターカバー14の拡散領域14aを透過する際に拡散し、拡散光L4aとして前方に投射される。この拡散光L4aは、近くの路面を照射する。よって、本実施形態に係るヘッドライト10は、遠くの路面を明るく照らしながら、近くの路面を広い範囲にわたって照射することができる。従って、LED21を光源とする直射型のライトモジュール11Bは、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。したがって、ヘッドライト10の大型化を抑制しつつ、ヘッドライト10に求められる配光パターンを形成することができる。
本実施形態では、シボ加工が、アウターカバー14の内面に形成されている。しかし、シボ加工は、アウターカバー14の外面に形成されてもよい。また、アウターカバー14の内面および外面の両方にシボ加工が施されてもよい。シボ加工以外の加工により、アウターカバー14に拡散領域14aが形成されてもよい。
前記実施形態では、ヘッドライト10は、2つのライトモジュール11および12を備えている。しかし、ヘッドライト10におけるライトモジュールの個数は、2つに限られない。ヘッドライト10は、3つ以上のライトモジュールを備えていてもよい。ヘッドライト10は、1つのライトモジュールを備えていてもよい。また、ヘッドライト10は、ロービーム用のライトモジュールを2つ以上備えていてもよい。例えば、ヘッドライト10は、自動二輪車1の中心線(例えば、前方から見て、前輪2の左右方向の中央を通る鉛直線)の左方と右方とに、第1実施形態に係るライトモジュール11を備えていてもよい。自動二輪車1の中心線の左方と右方とに、第2実施形態または第3実施形態に係るライトモジュール11Bおよび拡散板55を備えていてもよい。
第1実施形態では、図4の鉛直線V1は、レンズ30の左右方向の中心線となる。第1実施形態では、自動二輪車1の中心線C(図1参照)と、ライトモジュール11のレンズ30の中心線V1とは一致する。しかし、上記両中心線C、V1は必ずしも一致する必要はない。例えば、自動二輪車1の中心線Cの左方および右方にそれぞれライトモジュール11を配置する場合、各ライトモジュール11のレンズ30の中心線V1は、自動二輪車1の中心線Cと一致しない。左のライトモジュール11は自動二輪車1の中心線Cよりも左方に配置される。右のライトモジュール11は自動二輪車1の中心線Cよりも右方に配置される。その場合、左のライトモジュール11において、レンズ30の第3拡散部53はレンズ30の中心線V1よりも左方に形成されていればよい。右のライトモジュール11において、レンズ30の第3拡散部53はレンズ30の中心線V1よりも右方に形成されていればよい。各ライトモジュール11のレンズ30の拡散領域50は、必ずしも略U字状でなくてもよい。例えば、前方から見て左のライトモジュール11において、レンズ30の拡散領域50は前方から見て略L字状に形成されていてもよい。前方から見て右のライトモジュール11において、レンズ30の拡散領域50は前方から見て略J字状に形成されていてもよい。
第1実施形態では、ライトモジュール11のレンズ30は、第1屈折部41、第2屈折部42、第1拡散部51、第2拡散部52、第3拡散部53、および第4拡散部54を備える。しかし、レンズ30は第1屈折部41および第1拡散部51を備えていれば足りる。第2屈折部42、第2拡散部52、第3拡散部53、および第4拡散部54は、必ずしも必要ではない。拡散領域50は、略U字状に限らず、前方から見て左右方向に横に延びる帯状であってもよい。拡散領域50は、第3拡散部53を備えず、第1拡散部51と、第2拡散部52と、第1拡散部51と第2拡散部52とをつなぐ部分とを備えていてもよい。前述の通り、拡散領域50は、1つの領域で形成されていてもよく、互いに分離した複数の領域を備えていてもよい。拡散領域50の形状は何ら限定されない。
第1拡散部51、第2拡散部52、第3拡散部53及び第4拡散部54の拡散透過性は、互いに同じであってもよく、異なっていてもよい。拡散領域50は、少なくとも第1拡散部51を含む。拡散領域50は、第2拡散部52、第3拡散部53及び第4拡散部54の少なくとも1つを含んでいてもよい。拡散領域50に含まれる拡散部は、拡散領域50の一部であり、必ずしも、拡散領域50と区別され得るように構成されている必要はない。また、各拡散部は、必ずしも、互いに区別され得るように構成されている必要はない。第1屈折部41及び第2屈折部42の拡散透過性は、互いに同じであってもよく、異なっていてもよい。いずれの拡散部といずれの屈折部との関係においても、拡散部の拡散透過性は、屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い。屈折領域40は、少なくとも第1屈折部41を含む。屈折領域40は、第2屈折部42を含んでいてもよい。屈折領域40に含まれる屈折部は、屈折領域40の一部であり、屈折領域40と区別され得るように構成されている必要はない。各屈折部は、必ずしも、互いに区別され得るように構成されている必要はない。また、拡散部51~54及び拡散領域50は、レンズ30の表面31に設けられていてもよく、レンズ30の裏面32に設けられていてもよい。レンズ30の厚さ方向(光軸Axの方向)における拡散部51~54及び拡散領域50の位置は、特に限定されない。また、各拡散部51~54に関し、拡散部は、拡散部を透過した光が配光パターンの一部を形成するようにLED21の光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成されている。即ち、拡散領域50は、拡散領域50を透過した光が配光パターンの一部を形成するようにLED21の光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成されている。配光パターンは、路面又はスクリーンでの配光パターンである。
レンズ30を前方から見た時、レンズ30の表面は、屈折領域40と、拡散領域50とのみからなっていてもよい。屈折領域40は、図4に示すように、LED21の光軸Axが通過する。レンズ30を前方から見た時、屈折領域40は、LED21の全体と前後方向に重なり合う。レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50は、LED21と前後方向に重ならない。レンズ30を前方から見た時、LED21より上方においてLED21と上下方向に重なる部分の全てが、屈折領域40である。レンズ30の前方から見た時、LED21より上方においてLED21と上下方向に重なる部分には、拡散領域50が設けられていない。
拡散領域50は、下記(A)~(C)に記載の部分を有している。
(A) レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50の少なくとも一部(例えば、第1拡散部51)は、LED21と上下方向に間隔を空けて、LED21よりも下方に位置し、LED21と上下方向に重なる。
(B) レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50の少なくとも一部は、LED21と左右方向に間隔を空けて、LED21と左右方向に並ぶ。
(C) 図4に示すように、レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50の少なくとも一部(例えば、第3拡散部53、第4拡散部54)は、LED21と左右方向に間隔を空けて、LED21の光軸Ax又はLED21の上縁よりも上方に位置する。
レンズ30を前方から見て、上記(A)~(C)に記載の部分は連続している。レンズ30を前方から見て、拡散領域50は、上記(A)~(C)に記載の部分を含むようにレンズ30の外縁、又はレンズ30の透過部分の外縁に沿って連続している。
拡散領域50は、下記(A)~(C)に記載の部分を有している。
(A) レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50の少なくとも一部(例えば、第1拡散部51)は、LED21と上下方向に間隔を空けて、LED21よりも下方に位置し、LED21と上下方向に重なる。
(B) レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50の少なくとも一部は、LED21と左右方向に間隔を空けて、LED21と左右方向に並ぶ。
(C) 図4に示すように、レンズ30を前方から見た時、拡散領域50の少なくとも一部(例えば、第3拡散部53、第4拡散部54)は、LED21と左右方向に間隔を空けて、LED21の光軸Ax又はLED21の上縁よりも上方に位置する。
レンズ30を前方から見て、上記(A)~(C)に記載の部分は連続している。レンズ30を前方から見て、拡散領域50は、上記(A)~(C)に記載の部分を含むようにレンズ30の外縁、又はレンズ30の透過部分の外縁に沿って連続している。
自動二輪車1が直進する時、ライトモジュール11から出射されて路面に達する光は、拡散領域50を通過する。自動二輪車1がリーン姿勢で旋回する時、レンズ30の右部分又は左部分のうち、カーブ内側に近い部分が、路面に近づく。拡散領域50の少なくとも一部が、LED21と左右方向に間隔を空けて、LED21の光軸Ax又はLED21の上縁よりも上方に位置するので、自動二輪車1がリーン姿勢で旋回している時であっても、ライトモジュール11から出射されて路面に達する光は、拡散領域50を通過する。自動二輪車1が直立走行時であるか又はリーン姿勢であるかに関わらず、ライトモジュール11から出射されて路面に達する光が、拡散領域50を通過する。ライダーから見て、路面からの反射光の変化が小さい。また、自動二輪車1がリーン姿勢で旋回する時、レンズ30の右部分又は左部分のうち、カーブ外側に近い部分が、路面から遠くなる。拡散領域50の少なくとも一部が、LED21と左右方向に間隔を空けて、LED21の光軸Ax又はLED21の上縁よりも上方に位置する。そのため、自動二輪車1がリーン姿勢で旋回している時にカーブ外側を上方へ向けて照らす光のうち、拡散領域50を通過する光の量が多くなる。対向車等から見て、ヘッドライトからの光量が少なく、且つ光量の変化が小さい。グレア(眩惑)の発生を低減できる。このような配光パターンは、拡散領域50により形成される、好ましい配光パターンの一例である。
ライトモジュール11、12は、1つのレンズ30と複数のLED21とを備えていてもよい。1つのレンズ30を前方から見た時、1つのレンズ30と複数のLED21とが前後方向に重なり合っていてもよい。1つのレンズ30の屈折領域40と複数のLED21の少なくとも1つとが前後方向に重なり合っていてもよい。
前記実施形態および変形例は、適宜に組み合わせることが可能である。
ここに用いられた用語及び表現は、説明のために用いられたものであって限定的に解釈するために用いられたものではない。ここに示されかつ述べられた特徴事項の如何なる均等物をも排除するものではなく、本発明のクレームされた範囲内における各種変形をも許容するものであると認識されなければならない。本発明は、多くの異なった形態で具現化され得るものである。この開示は本発明の原理の実施形態を提供するものと見なされるべきである。それらの実施形態は、本発明をここに記載しかつ/又は図示した好ましい実施形態に限定することを意図するものではないという了解のもとで、実施形態がここに記載されている。ここに記載した実施形態に限定されるものではない。本発明は、この開示に基づいて当業者によって認識され得る、均等な要素、修正、削除、組み合わせ、改良及び/又は変更を含むあらゆる実施形態をも包含する。クレームの限定事項はそのクレームで用いられた用語に基づいて広く解釈されるべきであり、本明細書あるいは本願のプロセキューション中に記載された実施形態に限定されるべきではない。
1 自動二輪車(車両)
10 ヘッドライト
11 ライトモジュール
13 ハウジング
14 アウターカバー
21 発光ダイオード
22 基板
24 ヒートシンク
30 レンズ
40 屈折領域
50 拡散領域
10 ヘッドライト
11 ライトモジュール
13 ハウジング
14 アウターカバー
21 発光ダイオード
22 基板
24 ヒートシンク
30 レンズ
40 屈折領域
50 拡散領域
Claims (15)
- 車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュールであって、
前記ライトモジュールは、
発光ダイオードと、
前記発光ダイオードの前方に設けられ、前記発光ダイオードからの光を透過させるレンズと
を備え、
前記レンズは、
前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードの上方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成された第1屈折部と、
前記第1屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードより下方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成された第1拡散部と、を有する。 - 請求項1に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記第1拡散部は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードを通る鉛直線上において、前記第1屈折部の下方に位置している。 - 請求項1または2に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記レンズは、
前記レンズの前方から見たときに上下方向において前記第1屈折部と異なる位置に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成された第2屈折部と、
前記第2屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記第2屈折部を通る水平線上において前記第2屈折部よりも左右方向の外方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成された第2拡散部と、
を有している。 - 請求項1~3のいずれか1に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記レンズは、
前記第1屈折部の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記第1屈折部を通る水平線上において前記第1屈折部よりも左右方向の外方に位置し、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成された第3拡散部を有している。 - 請求項1~4のいずれか1に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記レンズは、
少なくとも前記第1屈折部を含み、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて前方に導くように構成された屈折領域と、
前記屈折領域の拡散透過性よりも高い拡散透過性を有し、少なくとも前記第1拡散部を含み、前記発光ダイオードからの光を拡散させて前方に導くように構成された拡散領域と
を有し、
前記拡散領域は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに略U字状に形成されている。 - 請求項5に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記拡散領域は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに前記発光ダイオードよりも左方または右方であってかつ前記発光ダイオードよりも上方に位置する第4拡散部を有している。 - 請求項5または6に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記拡散領域は、前記レンズを前方から見たときに、前記発光ダイオードを通る鉛直線上に位置する第1領域と、前記第1領域よりも左右方向の外方に位置する第2領域とを有し、
前記第2領域の上下方向の長さは、前記第1領域の上下方向の長さよりも長い。 - 請求項1~7のいずれか1に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記レンズは、前方に向かって凸状の表面と、前記発光ダイオードに対向する裏面とを有し、
前記第1拡散部は、前記レンズの前記表面の一部または前記裏面の一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されている。 - 請求項1~7のいずれか1に記載のライトモジュールであって、
前記レンズは、前方に向かって凸状の表面と、前記発光ダイオードに対向する裏面とを有し、
前記第1拡散部は、前記レンズの前記表面の一部または前記裏面の一部に、透過する光を拡散させる拡散板を取り付けることにより形成されている。 - 車両のヘッドライトであって、
前記ヘッドライトは、請求項1~9のいずれか一つに記載の車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュールを備える。 - 車両のヘッドライトであって、
前記ヘッドライトは、
発光ダイオードと、
前記発光ダイオードの前方に配置され、前記発光ダイオードからの光を屈折させて透過させるレンズと、
前記レンズの前方に配置され、前記レンズを透過した光を透過させるアウターカバーと、
前記レンズを透過した光の一部を、前記レンズを透過した光の他の一部の下方にて拡散させ、前記アウターカバーの前方に導くように構成された拡散体と、
を備える。 - 請求項11に記載のヘッドライトであって、
前記拡散体は、前記レンズと前記アウターカバーとの間に配置され、透過する光を拡散させるように構成されている。 - 請求項11に記載のヘッドライトであって、
前記拡散体は、前記アウターカバーに取り付けられ、透過する光を拡散させるように構成されている。 - 請求項11に記載のヘッドライトであって、
前記拡散体は、前記アウターカバーの一部にシボ加工を施すことにより形成されている。 - 車両であって、
前記車両は、請求項10~14のいずれか一つに記載の車両のヘッドライトを備える。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016527749A JP6121629B2 (ja) | 2014-06-11 | 2015-06-01 | 車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュール、車両のヘッドライト、および車両 |
| TW104118823A TWI584977B (zh) | 2014-06-11 | 2015-06-10 | Vehicle headlight lamp module, vehicle headlights, and vehicles |
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014-120235 | 2014-06-11 | ||
| JP2014-120236 | 2014-06-11 | ||
| JP2014120236 | 2014-06-11 | ||
| JP2014120235 | 2014-06-11 | ||
| JP2015-009180 | 2015-01-21 | ||
| JP2015009180 | 2015-01-21 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015190332A1 true WO2015190332A1 (ja) | 2015-12-17 |
Family
ID=54833430
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/065735 Ceased WO2015190332A1 (ja) | 2014-06-11 | 2015-06-01 | 車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュール、車両のヘッドライト、および車両 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6121629B2 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI584977B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015190332A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3560805A1 (en) | 2018-04-25 | 2019-10-30 | Yamaha Hatsudoki Kabushiki Kaisha | Straddled vehicle |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI628977B (zh) * | 2017-09-22 | 2018-07-01 | 咸瑞科技股份有限公司 | Light source adjusting system capable of automatically adjusting brightness of light source and adjusting method thereof |
| CN113286967B (zh) * | 2018-12-25 | 2023-07-04 | 株式会社小糸制作所 | 光学单元 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH048303U (ja) * | 1990-05-11 | 1992-01-24 | ||
| JPH062504U (ja) * | 1992-06-12 | 1994-01-14 | スタンレー電気株式会社 | 車両用照明灯具 |
| JP2006082657A (ja) * | 2004-09-15 | 2006-03-30 | Koito Mfg Co Ltd | 二輪車用ヘッドランプ |
| US20100172146A1 (en) * | 2007-07-26 | 2010-07-08 | Jens Fischer | Method for producing a headlamp lens for a motor-vehicle headlamp |
| US20120069576A1 (en) * | 2010-09-17 | 2012-03-22 | Foxsemicon Integrated Technology, Inc. | Lens and light source module |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWM457665U (zh) * | 2012-10-26 | 2013-07-21 | Esuse Auto Parts Mfg Co Ltd | 車燈結構 |
| TWM477966U (zh) * | 2013-05-23 | 2014-05-11 | Jenn Feng New Energy Co Ltd | 車用輔助照明燈具 |
-
2015
- 2015-06-01 JP JP2016527749A patent/JP6121629B2/ja active Active
- 2015-06-01 WO PCT/JP2015/065735 patent/WO2015190332A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2015-06-10 TW TW104118823A patent/TWI584977B/zh active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH048303U (ja) * | 1990-05-11 | 1992-01-24 | ||
| JPH062504U (ja) * | 1992-06-12 | 1994-01-14 | スタンレー電気株式会社 | 車両用照明灯具 |
| JP2006082657A (ja) * | 2004-09-15 | 2006-03-30 | Koito Mfg Co Ltd | 二輪車用ヘッドランプ |
| US20100172146A1 (en) * | 2007-07-26 | 2010-07-08 | Jens Fischer | Method for producing a headlamp lens for a motor-vehicle headlamp |
| US20120069576A1 (en) * | 2010-09-17 | 2012-03-22 | Foxsemicon Integrated Technology, Inc. | Lens and light source module |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3560805A1 (en) | 2018-04-25 | 2019-10-30 | Yamaha Hatsudoki Kabushiki Kaisha | Straddled vehicle |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2015190332A1 (ja) | 2017-04-20 |
| JP6121629B2 (ja) | 2017-04-26 |
| TW201545921A (zh) | 2015-12-16 |
| TWI584977B (zh) | 2017-06-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4391870B2 (ja) | 車両用照明灯具 | |
| US8939623B2 (en) | Optical system unit and vehicular lamp | |
| JP5352263B2 (ja) | 車両用灯具 | |
| JP5752982B2 (ja) | 車両用照明灯具 | |
| CN112135998B (zh) | 车辆用灯具 | |
| JP6018651B2 (ja) | 車両のヘッドライトおよびそれを備えた車両 | |
| JP5714346B2 (ja) | 車両用前照灯 | |
| JP2006164858A (ja) | 車両用照明灯具 | |
| JP5897913B2 (ja) | 灯具ユニット | |
| JP2009301980A (ja) | 灯具ユニット | |
| JP2013016400A (ja) | 車両用前照灯 | |
| JP2013152813A (ja) | 車両用前照灯及び導光レンズ | |
| JP2012022988A (ja) | 車両用灯具 | |
| WO2020075536A1 (ja) | 車両用導光体および車両用灯具 | |
| CN108375048A (zh) | 车载灯具 | |
| JP6121629B2 (ja) | 車両のヘッドライト用ライトモジュール、車両のヘッドライト、および車両 | |
| JP6519353B2 (ja) | 車両用前照灯 | |
| JP5344957B2 (ja) | 車両用前照灯 | |
| JP2011025820A (ja) | 車両用灯具 | |
| JP7171413B2 (ja) | 車両用灯具 | |
| JP2010282790A (ja) | 車両用灯具 | |
| JP6435903B2 (ja) | 車両用前照灯 | |
| JP2014137902A (ja) | 車両用灯具 | |
| JP2015037037A (ja) | 車両用前照灯 | |
| JP2015002128A (ja) | 車両用灯具 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15806624 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016527749 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15806624 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |