WO2015146753A1 - 走行装置 - Google Patents
走行装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015146753A1 WO2015146753A1 PCT/JP2015/058126 JP2015058126W WO2015146753A1 WO 2015146753 A1 WO2015146753 A1 WO 2015146753A1 JP 2015058126 W JP2015058126 W JP 2015058126W WO 2015146753 A1 WO2015146753 A1 WO 2015146753A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- rolling wheel
- width direction
- projection
- drive
- guide
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B62—LAND VEHICLES FOR TRAVELLING OTHERWISE THAN ON RAILS
- B62D—MOTOR VEHICLES; TRAILERS
- B62D55/00—Endless track vehicles
- B62D55/08—Endless track units; Parts thereof
- B62D55/18—Tracks
- B62D55/24—Tracks of continuously flexible type, e.g. rubber belts
- B62D55/244—Moulded in one piece, with either smooth surfaces or surfaces having projections, e.g. incorporating reinforcing elements
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B62—LAND VEHICLES FOR TRAVELLING OTHERWISE THAN ON RAILS
- B62D—MOTOR VEHICLES; TRAILERS
- B62D55/00—Endless track vehicles
- B62D55/08—Endless track units; Parts thereof
- B62D55/12—Arrangement, location, or adaptation of driving sprockets
- B62D55/125—Final drives
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B62—LAND VEHICLES FOR TRAVELLING OTHERWISE THAN ON RAILS
- B62D—MOTOR VEHICLES; TRAILERS
- B62D55/00—Endless track vehicles
- B62D55/08—Endless track units; Parts thereof
- B62D55/14—Arrangement, location, or adaptation of rollers
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a traveling device including a sprocket that is rotatably supported, a rubber crawler that is rotatable around the sprocket, and a plurality of rolling wheels that roll on the inner circumferential surface of the rubber crawler. Concerned.
- Such a traveling device is provided, for example, as a pair on both sides in the width direction of the vehicle, and the vehicle travels by driving the pair of traveling devices, and the vehicle is divided by providing a difference in the number of rotations of the pair of traveling devices. It can be turned.
- the rubber crawler of the traveling device provided in such a vehicle is generally used in a vehicle for high-speed traveling because it is lightweight and has low traveling resistance and vibration as compared with a metal crawler.
- This rubber crawler is provided, for example, with a gap on the inner peripheral surface of the center portion in the width direction of an endless rubber elastic body to prevent separation of the rolling wheels, and both side portions in the width direction of the rubber elastic body.
- the rubber crawler is less rigid than a metal crawler because there is no metallic reinforcing core inside.
- the steel cord row reinforces the tensile force acting in the circumferential direction of the rubber elastic body, and the bias cord row reinforces the force (for example, twist) acting in the lateral direction of the rubber elastic body.
- a plurality of rolling wheels are rollably provided on the inner peripheral surface of such a rubber crawler. Loads such as an impact received from the ground are absorbed by the rolling wheels to reduce vibration.
- the roller has a disk-shaped first roller main body portion and a second roller main body integrated integrally opposed to each other so as to straddle the guide projections in the width direction of the rubber crawler.
- the first rolling wheel main body portion is disposed between one of the pair of drive protrusions and the guide protrusion
- the second rolling wheel main body portion is disposed between the other of the pair of drive protrusions and the guide protrusion
- the ring rolls on the inner circumferential surface of the rubber elastic body while sandwiching the guide projection between the first rolling wheel main body portion and the second rolling wheel main body portion.
- the rubber crawler rotates while circulating between a sprocket serving as a driving wheel and a driven wheel, and as the rubber crawler rotates, the rolling wheels roll on the inner circumferential surface of the rubber crawler.
- the guide projection sandwiched between the first rolling wheel main body portion and the second rolling wheel main body portion of the rolling wheel There is a risk that the rubber crawler may be damaged from the load in the width direction of the rubber crawler from the wheel. Therefore, there is a risk that the rolling wheels will be released from the rubber crawler.
- At least some embodiments of the present invention aim to provide a traveling device without fear that the guide projections of the rubber crawler are damaged and the rolling wheels are disengaged when the vehicle turns. Do.
- a traveling device A rolling wheel disposed on a widthwise central portion of an inner circumferential surface of an endless rubber crawler and straddling a guide projection and rolling on the inner circumferential surface of the rubber crawler is a side surface of the guide projection and A traveling device in surface contact with side surfaces of driving protrusions provided on both sides in the width direction of the inner circumferential surface of the rubber crawler, Side surfaces which can be surface-contacted with the side surfaces of the guide protrusion and the drive protrusion are formed at the width direction end of the rolling wheel, The side surfaces of the rolling wheel are disposed opposite to the side surfaces of the guide projection and the driving projection so that the side surfaces of the guiding projection and the side surfaces of the driving projection are brought into surface contact by swinging of the rolling wheel in the crawler width direction. Configured to be.
- the side surface of the rolling wheel comes into surface contact with the side surface of the driving protrusion along with the side surface of the guide protrusion due to the swinging of the rolling wheel in the crawler width direction.
- the guide projections and the drive projections are disposed to face each side, when a load in the rubber crawler width direction is applied to the guide projections from the rolling wheels when the rolling wheels swing, this load is Can be received by two projections. Therefore, since the load can be dispersed to the guide projection and the drive projection, it is possible to realize a traveling device capable of preventing the possibility of the wheel being detached from being damaged by damage of the guide projection.
- the rolling wheel includes a pair of rolling wheel main portions disposed opposite to each other in the width direction of the guide protrusion, Side surfaces are formed at peripheral portions on both sides in the width direction of the pair of roller main body portions, By swinging of the rolling wheel, one of the side surfaces of the pair of rolling wheel main body portions comes into surface contact with the side surface of the guide projection, and the other side surface comes into surface contact with the side surface of the driving projection.
- a gap between any one side surface of the pair of rolling wheel main portions and a side surface of the guide protrusion is a gap between any other side surface of the pair of rolling wheel main portions and a side surface of the drive protrusion. It is configured to have the same size as
- the gap between any one side surface of the pair of rolling wheel main portions and the side surface of the guide protrusion is between the other side surface of the pair of rolling wheel main portions and the side surface of the driving protrusion. Since it has the same size as the gap, the pair of rolling wheel main body portions simultaneously contact the drive protrusion and the guide protrusion, so that the deformation amounts of the drive protrusion and the guide protrusion can be made equal. In addition, it is possible to equalize the amount of wear of the contact portions of the pair of roller main body portions in contact with the drive protrusion and the guide protrusion.
- the guide protrusion and the drive protrusion disposed adjacent to each other in the width direction of the rubber crawler are formed such that the rigidity in the width direction to a load directed in the width direction is lower than that of any one of the other.
- the gap between the side surface of the guide protrusion and the drive protrusion having the lower width direction rigidity and the side surface of the rolling wheel is the side surface of the guide protrusion and the drive protrusion having the higher width direction rigidity and the side surface It is configured to be smaller than the gap between the roller and the side surface.
- the gap between the side surface of the guide protrusion and the drive protrusion having the lower rigidity in the width direction and the side surface of the rotating wheel is the same as the side surface of the guide protrusion and the drive protrusion having the higher rigidity in the width direction. Since it is smaller than the gap with the side of the ring, when the rolling wheel is swinging, if a load from the rolling wheel to the widthwise direction acts on the guide projection, the rolling wheel first strikes the low width direction rigid projection It is elastically deformed and then hits a protrusion with high width direction rigidity. Thus, the load can be received by the two guide protrusions and the drive protrusions. Therefore, the load can be dispersed to the guide protrusions and the drive protrusions, and the possibility of damage to the guide protrusions can be suppressed.
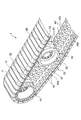
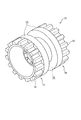
- FIG. 6 is a partial perspective view of the traveling device on the side on which the sprockets of the traveling device are disposed. It is a perspective view of a sprocket. It is a perspective view of a rolling wheel.
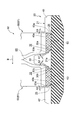
- FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of a portion corresponding to the II arrow view of FIG. 1 when the clearances between the rotating wheel and the rubber crawler are equal.
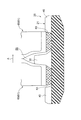
- FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of the rolling wheel and the rubber crawler when the rubber crawler receives a lateral load from the rolling wheel.
- FIG. 12 is a cross-sectional view of a portion corresponding to the II arrow view of FIG. 1 when the clearance between the rotating wheel and the rubber crawler is different in another embodiment. In other embodiment, it is sectional drawing of a rolling wheel and a rubber crawler when a rubber crawler is receiving the side load from a rolling wheel.
- FIGS. 1 to 8 a traveling device provided in a vehicle will be described as an example.
- the material of the component described in this embodiment, the shape, the relative arrangement, etc. are not the meaning which limits the scope of the present invention to this, but are only a mere illustration example.
- the traveling device 1 is, as shown in FIG. 1 (side view), a driving wheel 10 rotatably supported at one end in the front-rear direction of a side portion of the vehicle body (not shown).
- a driven wheel 17 rotatably supported at an end, a rubber crawler 20 wound around the driving wheel 10 and the driven wheel 17, and a plurality of rolls rolling on the lower inner peripheral surface of the rubber crawler 20 And a wheel 60.
- the drive wheel 10 is rotatable in response to a drive force from an engine or the like provided in the vehicle.
- the drive wheel 10 is provided with a pair of sprockets 11 disposed opposite to each other with a predetermined interval in the width direction, and the pair of sprockets 11 are attached to the tip of a drive shaft extending from the vehicle to form the drive wheel 10 ing.
- the teeth 12 mesh with the drive projections 40 of the rubber crawler 20 to transmit rotational force to the rubber crawler 20.
- a guide roller 13 disposed concentrically with the sprocket 11 to prevent the rubber crawler 20 from coming off the wheel. Between the guide rollers 13 of the pair of sprockets 11, there is provided a gap 15 through which the guide projection 30 provided at the center of the rubber crawler 20 in the width direction can pass. For this reason, the drive wheel 10 can transmit the rotational force of the drive wheel 10 to the rubber crawler 20 without being disengaged from the rubber crawler 20 by the pair of guide rollers 13.
- the rolling wheel 60 includes a pair of rolling wheel main body portions 61 which are disposed opposite to each other with a constant interval in the width direction, and the pair of rolling wheel main body portions 61 Is rotatably attached to the tip of a support shaft (not shown) extending from the vehicle body of the vehicle.
- the support shaft is supported movably in the vertical direction with respect to the vehicle body of the vehicle.
- An annular body 63 made of rubber is mounted on the outer peripheral surface of the wheel body 61. The annular body 63 can absorb an impact received from the road surface.
- a gap 65 through which the guide projection 30 of the rubber crawler 20 can pass is provided between the pair of roller main body portions 61.
- first rolling wheel main portion 68 the rolling wheel main portion 61 disposed outside the vehicle is referred to as “first rolling wheel main portion 68"
- second rolling wheel main portion 69 the rolling wheel main portion 61 disposed inside the vehicle is It describes as “the 2nd rolling-wheel main-body part 69.”
- a first outer sliding contact surface 63 a annularly formed along the peripheral edge portion is formed at the outer peripheral edge portion in the width direction of the annular body 63 of the first rolling wheel main body portion 68.
- the first outer sliding contact surface 63 a is formed as a flat inclined surface which is inclined inward of the first rolling wheel main body 68 as it proceeds radially outward of the first rolling wheel main body 68.
- the first outer sliding contact surface 63 a is inclined at an angle of about 80 degrees with respect to the inner peripheral surface 21 a of the rubber elastic body 21.
- the first outer sliding contact surface 63 a is disposed to face the inner surface of the drive projection 40. Details of the inner surface of the drive projection 40 will be described later.
- a first inner sliding contact surface 63b annularly formed along the peripheral edge portion is formed at the inner peripheral edge portion in the width direction of the annular body 63 of the first rolling wheel main body portion 68.
- the first inner sliding contact surface 63 b is formed as a flat inclined surface which inclines inward of the first rolling wheel main body 68 as it proceeds radially outward of the first rolling wheel main body 68.
- the first inner sliding contact surface 63 b is inclined at an angle of about 50 degrees with respect to the inner peripheral surface 21 a of the rubber elastic body 21.
- the first inner sliding contact surface 63 b is disposed to face the outer surface of the guide protrusion 30. Details of the outer surface of the guide protrusion 30 will be described later.
- a second outer sliding contact surface 63c annularly formed along the peripheral edge portion is formed at the outer peripheral edge portion in the width direction of the annular body 63 of the second roller main body portion 69.
- the second outer sliding contact surface 63 c is formed as a flat inclined surface which is inclined inward of the second rolling wheel main body 69 as it proceeds radially outward of the second rolling wheel main body 69.
- the second outer sliding contact surface 63c is inclined at an angle of about 50 degrees with respect to the inner peripheral surface 21a of the rubber elastic body 21.
- the second outer sliding contact surface 63 c is disposed to face the inner surface of the guide projection 30. Details of the inner surface of the guide protrusion 30 will be described later.
- a second inner sliding contact surface 63 d annularly formed along the peripheral edge portion is formed at the outer peripheral edge portion in the width direction of the annular body 63 of the second roller main body portion 69.
- the second inner sliding contact surface 63 d is formed as a flat inclined surface which inclines inward of the second rolling wheel main body portion 69 as it proceeds radially outward of the second rolling wheel main body portion 69.
- the second inner sliding contact surface 63 d is inclined at an angle of about 80 degrees with respect to the inner peripheral surface 21 a of the rubber elastic body 21.
- the second inner sliding contact surface 63 d is disposed to face the inner surface of the drive projection 40. Details of the inner surface of the drive projection 40 will be described later.
- the rubber crawler 20 as shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 5, is provided with a constant interval in the circumferential direction at the central portion in the width direction of the endless rubber elastic body 21 and the inner peripheral surface 21a of the rubber elastic body 21. Are provided with a constant pitch in the circumferential direction on both widthwise outer side portions of the inner peripheral surface 21a of the rubber elastic body 21 so as to mesh with the sprocket 11 And a driving protrusion 40.
- the rubber elastic body 21 is made of rubber, is endless, and is formed in a band shape.
- a plurality of lugs 22 are provided on the outer peripheral surface 21 b of the rubber elastic body 21 so as to protrude radially outward and have an interval in the circumferential direction of the rubber elastic body 21.
- the guide projection 30 provided on the inner circumferential surface 21 a of the rubber elastic body 21 is formed in a substantially rectangular parallelepiped shape extending in a direction substantially orthogonal to the inner circumferential surface 21 a.
- the guide protrusion 30 is formed to be gradually tapered as it deviates from the inner circumferential surface 21 a of the rubber elastic body 21 in a side view. For this reason, when the rubber crawler 20 rotates while being bent to the sprocket 11, the guide projections 30 adjacent in the circumferential direction of the rubber crawler 20 are prevented from coming in contact with each other.
- a guide protrusion outer side surface 30a is formed on the outer side in the width direction of the root side of the guide protrusion 30 so as to face the first inner sliding contact surface 63b of the first rolling wheel main body 68 of the rolling wheel 60.
- the guide projection outer side surface 30a is formed to extend substantially in parallel with the first inner sliding contact surface 63b.
- a predetermined gap 32 is formed between the guide protrusion outer side surface 30a and the first inner sliding contact surface 63b. Details of the size A1 of the gap 32 will be described later.
- a guide projection inner side surface 30b is formed opposite to the second outer sliding contact surface 63c of the second rolling wheel main body 69 of the rolling wheel 60.
- the guide projection inner side surface 30b is formed to extend substantially in parallel with the second outer sliding contact surface 63c.
- a predetermined gap 33 is formed between the guide projection inner side surface 30b and the second outer sliding contact surface 63c. Details of the size A2 of the gap 33 will be described later.
- the guide projection 30 has such a size that it can pass in the gap 15 between the pair of sprockets 11 and in the gap 65 between the pair of rolling wheel bodies 61 of the rolling wheels 60, and the rolling wheel 60 is removed from the rubber crawler 20. It has a height that can be restricted from turning.
- the drive protrusions 40 and 40 'provided on both sides in the width direction of the inner peripheral surface 21a of the rubber elastic body 21 are formed to be gradually tapered as they move away from the inner peripheral surface 21a of the rubber elastic body 21 in side view It is formed in a horizontally long rectangular shape in plan view.
- the drive protrusion inner side outer surface 40a extending in the vertical direction is formed.
- the drive projection inner side surface outside 40 a is formed in a planar shape, and is disposed to face the first outer sliding contact surface 63 a of the first rolling wheel main body 68.
- the drive projection inner side surface outside 40a is inclined so as to be inclined outward in the width direction as it moves upward, is formed in a planar shape, and is disposed to face the first outer sliding contact surface 63a of the first rolling wheel main body 68.
- the drive projection inner side surface outside 40a extends substantially parallel to the first outer sliding contact surface 63a, and a gap 64 is formed between the drive projection inner side outer surface 40a and the first outer sliding contact surface 63a. Details of the size A3 of the gap 33 will be described later.
- an inner side surface 40 b of the drive protrusion inner side extending in the vertical direction is formed at the width direction inner end of the drive protrusion 40 ′ provided on the inner side in the width direction of the rubber elastic body 21.
- the inner side 40b of the drive projection inner surface is formed in a planar shape, and is disposed to face the second inner sliding contact surface 63d of the second rolling wheel main body 69.
- the inner side 40b of the drive projection is inclined so as to be inclined outward in the width direction as it moves upward, is formed in a planar shape, and is disposed to face the second inner sliding contact surface 63d of the second rolling wheel main body 69.
- the inner side 40b of the drive projection inner side extends substantially parallel to the second inner sliding contact surface 63d, and a gap 35 is formed between the inner side 40b of the drive projection inner surface and the second inner slide contact surface 63d. Details of the size A4 of the gap 35 will be described later.
- the drive projections 40 and 40 ' are provided on the inner circumferential surface 21a with the same pitch as the teeth 12 of the sprocket 11. Therefore, the drive protrusions 40 and 40 'mesh well with the teeth 12 of the sprocket 11, and the driving force of the sprocket 11 is transmitted to the rubber elastic body 21 through the drive protrusions 40 and 40'.
- the pair of drive projections 40 and 40 'provided on both sides in the width direction of the inner peripheral surface 21a of the rubber elastic body 21 together with the guide projections 30 provided on the central part in the width direction of the inner peripheral surface 21a Are arranged in a straight line in the direction orthogonal to the circumferential direction.
- the size A1 of the gap 32 between the guide projection outer surface 30a and the first inner sliding contact surface 63b is the size A4 of the gap 35 between the drive projection inner side surface 40b and the second inner sliding contact surface 63d. equal.
- the size A2 of the gap 33 between the guide projection inner side surface 30b and the second outer sliding contact surface 63c is the size of the gap 64 between the drive projection inner side outer surface 40a and the first outer sliding contact surface 63a. It is formed to be equal to A3.
- the traveling device 1 when the drive wheel 10 rotates, the rubber crawler 20 rotates between the drive wheel 10 and the driven wheel 17 as the drive wheel 10 rotates.
- the rolling wheels 60 roll on the inner circumferential surface 21 a of the rubber elastic body 21 of the rubber crawler 20.
- the traveling devices 1 provided on the left and right of the vehicle operate so as to turn the vehicle at the time of rotation of the rubber crawler 20, for example, as shown in FIG. A load is directed to one side of the rubber crawler 20 in the width direction of the rubber crawler from the rolling wheel 60 while swinging to the one side (the direction of arrow A).
- the first outer sliding contact surface 63a of the first rolling wheel main body 68 contacts the drive projection inner side outer surface 40a of the drive projection 40
- the second outer sliding contact of the second rolling wheel main body 69 The surface 63 c contacts the inner surface 30 b of the guide projection 30. Moreover, these contacts are performed substantially simultaneously.
- the size A2 of the gap 33 between the guide projection inner side surface 30b and the second outer sliding contact surface 63c is the size of the gap 64 between the drive projection inner side outer surface 40a and the first outer sliding contact surface 63a. Since it is equal to A3, the first rolling wheel main body 68 and the second rolling wheel main body 69 of the rolling wheel 60 simultaneously hit the drive projection 40 and the guide projection 30, and the deformation amounts of the drive projection 40 and the guide projection 30 are made equal. be able to. Further, the wear amount of the contact portion (annular body 63) of the first rolling wheel main body portion 68 and the second rolling wheel main body portion 69 of the rolling wheel 60 in contact with the drive projection 40 and the guide projection 30 can be made equal.
- the size A1 of the gap 32 between the guide projection outer surface 30a and the first inner sliding contact surface 63b is the size A4 of the gap 35 between the drive projection inner side surface 40b and the second inner sliding contact surface 63d. Since they are equal, the first rolling wheel main body 68 and the second rolling wheel main body 69 of the rolling wheel 60 simultaneously contact the drive projection 40 'and the guide projection 30, and equalize the deformation amounts of the drive projection 40' and the guide projection 30. be able to. Further, the wear amount of the contact portion (annular body 63) of the first rolling wheel main body portion 68 and the second rolling wheel main body portion 69 of the rolling wheel 60 in contact with the drive projection 40 'and the guide projection 30 can be made equal. .
- the size A3 of the gap 34 between the drive projection inner side outer surface 40a and the first outer sliding contact surface 63a is equal to that of the guide projection inner side 30b and the second outer sliding contact surface 63c.
- the widthwise rigidity of the drive projection 40 may be smaller than the widthwise rigidity of the guide projection 30.
- the adjustment of the rigidity in the width direction may be performed by adjusting the installation position of the core metal 71, 72 embedded in the rubber elastic body in the rubber elastic body, with the rubber hardness of the rubber elastic body 21 unchanged. it can.
- the first wheel main body 68 of the wheel 60 is first lowered It strikes the drive projection 40 which is rigid in the width direction and elastically deforms the drive projection 40. And after that, the 2nd rolling wheel main-body part 69 of the rolling wheel 60 hits the high elastic guide protrusion 30. As shown in FIG. Therefore, the load can be received by the two guide protrusions 30 and the drive protrusions 40. Therefore, the load can be dispersed to the guide projection 30 and the drive projection 40, and the possibility of damage to the guide projection 30 can be suppressed.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Harvester Elements (AREA)
Abstract
走行装置は、無端状のゴムクローラの内周面の幅方向中央部に設けられたガイド突起を跨いだ状態で配置されて前記ゴムクローラの内周面上を転動する転輪が、前記ガイド突起の側面と、前記ゴムクローラの前記内周面の幅方向両側に設けられた駆動突起の側面に面接触する走行装置であって、前記転輪の幅方向端部には、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に面接触可能な側面が形成され、前記転輪の前記側面は、前記転輪のクローラ幅方向の揺動により前記ガイド突起の側面とともに前記駆動突起の側面に面接触するように、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に対向配置されている。
Description
本開示は、回転駆動可能に支持されたスプロケットと、該スプロケットに掛け回されて回転可能なゴムクローラと、該ゴムクローラの内周面上を転動する複数の転輪とを備える走行装置に係る。
このような走行装置は、例えば、車両の幅方向両側に一対設けられ、一対の走行装置を駆動させることで車両が走行し、一対の走行装置の回転数に差を設けること等によって、車両を旋回させることができる。このような車両に設けられる走行装置のゴムクローラは、金属製クローラと比較して、軽量であり、走行抵抗や振動が小さいことから、一般的に高速走行用の車両に使用される。
このゴムクローラは、例えば、無端状のゴム弾性体の幅方向中央部の内周面に間隔を有して設けられ転輪の離脱を防止するガイド突起と、ゴム弾性体の幅方向両側部の内周面に一定の間隔を有して設けられスプロケットに歯合する一対の駆動突起と、を有して構成されたものがある。このゴムクローラは、内部に金属性の補強芯材が存在しないので、金属製クローラと比較して、剛性は弱い。
そこで、ゴムクローラの内部に、ゴム弾性体の周方向に延在された複数列のスチールコード列や、スチールコード列の少なくとも下方のゴム弾性体内に配置されてゴム弾性体の周方向に対して所定角度を有して斜めに延びる複数列のバイアスコード列が設けられたものが提案されている(特許文献1参照)。このスチールコード列によってゴム弾性体の周方向に作用する引っ張り力が補強され、バイアスコード列によってゴム弾性体の横方向に作用する力(例えば、ねじり)が補強される。
このようなゴムクローラの内周面上には複数の転輪が転動可能に設けられている。この転輪によって、地面から受ける衝撃等の負荷が吸収されて振動を軽減するように構成されている。転輪は、ゴムクローラの幅方向にガイド突起を跨ぐようにして対向配置されて一体化された円盤状の第1転輪本体部及び第2転輪本体部を備える。第1転輪本体部は、一対の駆動突起の一方とガイド突起との間に配置され、第2転輪本体部は、一対の駆動突起の他方とガイド突起との間に配置されて、転輪は、ガイド突起を第1転輪本体部及び第2転輪本体部間に挟むようにしながらゴム弾性体の内周面上を転動する。
このゴムクローラは、走行時には、駆動輪となるスプロケットと従動輪との間を循環しながら回動し、ゴムクローラの回動に伴って転輪がゴムクローラの内周面上を転動する。しかしながら、車両の旋回時には、転輪はゴムクローラの幅方向一方側に移動しようとするため、転輪の第1転輪本体部及び第2転輪本体部間に挟まれたガイド突起は、転輪からゴムクローラ幅方向の荷重を受けて損傷する虞が生じる。従って、転輪がゴムクローラから脱輪する虞が生じる。
上述の事情に鑑みて、本発明の少なくとも幾つかの実施形態は、車両の旋回時に、ゴムクローラのガイド突起が損傷して転輪が脱輪する虞のない走行装置を提供することを目的とする。
本発明の幾つかの実施形態に係わる走行装置は、
無端状のゴムクローラの内周面の幅方向中央部に設けられたガイド突起を跨いだ状態で配置されて前記ゴムクローラの内周面上を転動する転輪が、前記ガイド突起の側面と、前記ゴムクローラの前記内周面の幅方向両側に設けられた駆動突起の側面に面接触する走行装置であって、
前記転輪の幅方向端部には、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に面接触可能な側面が形成され、
前記転輪の前記側面は、前記転輪のクローラ幅方向の揺動により前記ガイド突起の側面とともに前記駆動突起の側面に面接触するように、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に対向配置されているように構成される。
無端状のゴムクローラの内周面の幅方向中央部に設けられたガイド突起を跨いだ状態で配置されて前記ゴムクローラの内周面上を転動する転輪が、前記ガイド突起の側面と、前記ゴムクローラの前記内周面の幅方向両側に設けられた駆動突起の側面に面接触する走行装置であって、
前記転輪の幅方向端部には、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に面接触可能な側面が形成され、
前記転輪の前記側面は、前記転輪のクローラ幅方向の揺動により前記ガイド突起の側面とともに前記駆動突起の側面に面接触するように、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に対向配置されているように構成される。
上記走行装置によれば、転輪のクローラ幅方向への揺動時に、転輪の側面は、転輪のクローラ幅方向の揺動によりガイド突起の側面とともに駆動突起の側面に面接触するように、ガイド突起及び駆動突起の各側面に対向配置されているので、転輪の揺動時に、転輪からガイド突起にゴムクローラ幅方向の荷重が作用すると、この荷重をガイド突起及び駆動突起の2つの突起で受けることができる。このため、荷重をガイド突起及び駆動突起に分散することができるので、ガイド突起が損傷して転輪が脱輪する虞を防止可能な走行装置を実現できる。
また、幾つかの実施形態では、
前記転輪は、前記ガイド突起の幅方向両側に対向配置された一対の転輪本体部を含み、
前記一対の転輪本体部の各幅方向両側の周縁部に側面が形成され、
前記転輪の揺動により、前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面が前記ガイド突起の側面に面接触するとともに、いずれか他方の側面が前記駆動突起の側面に面接触するように構成される。
前記転輪は、前記ガイド突起の幅方向両側に対向配置された一対の転輪本体部を含み、
前記一対の転輪本体部の各幅方向両側の周縁部に側面が形成され、
前記転輪の揺動により、前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面が前記ガイド突起の側面に面接触するとともに、いずれか他方の側面が前記駆動突起の側面に面接触するように構成される。
この場合には、転輪の揺動時に、一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面がガイド突起の側面に面接触するとともに、いずれか他方の側面が駆動突起の側面に面接触するので、転輪の揺動に伴って、転輪からガイド突起にガイド突起幅方向に向く荷重が作用すると、この荷重はガイド突起及び駆動突起の2つの突起で受けることができる。このため、荷重をガイド突起及び駆動突起に分散することができるので、ガイド突起が損傷する虞を抑制することができる。
また、幾つかの実施形態では、
前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面と前記ガイド突起の側面との間の隙間は、前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか他方の側面と前記駆動突起の側面との間の隙間と同じ大きさを有しているように構成される。
前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面と前記ガイド突起の側面との間の隙間は、前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか他方の側面と前記駆動突起の側面との間の隙間と同じ大きさを有しているように構成される。
この場合には、一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面とガイド突起の側面との間の隙間は、一対の転輪本体部のいずれか他方の側面と駆動突起の側面との間の隙間と同じ大きさであるので、一対の転輪本体部は駆動突起とガイド突起に同時に当たるので、駆動突起及びガイド突起の変形量を同等にすることができる。また、駆動突起及びガイド突起に接触する一対の転輪本体部の接触部分の摩耗量を同等にすることができる。
また、幾つかの実施形態では、
前記ゴムクローラの幅方向に隣接して配設された前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起は、いずれか一方がいずれか他方よりも幅方向に向く荷重に対する幅方向剛性が低くなるように形成され、
前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起のうち幅方向剛性が低い方の側面と前記転輪の側面との間の隙間は、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起のうちの幅方向剛性が高い方の側面と前記転輪の側面との間の隙間よりも小さいように構成される。
前記ゴムクローラの幅方向に隣接して配設された前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起は、いずれか一方がいずれか他方よりも幅方向に向く荷重に対する幅方向剛性が低くなるように形成され、
前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起のうち幅方向剛性が低い方の側面と前記転輪の側面との間の隙間は、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起のうちの幅方向剛性が高い方の側面と前記転輪の側面との間の隙間よりも小さいように構成される。
この場合には、ガイド突起及び駆動突起のうち幅方向剛性が低い方の側面と転輪の側面との間の隙間は、ガイド突起及び駆動突起のうちの幅方向剛性が高い方の側面と転輪の側面との間の隙間よりも小さいので、転輪の揺動時に、転輪からガイド突起に幅方向に向く荷重が作用すると、転輪は、先ず、低い幅方向剛性の突起に当たって突起を弾性変形させ、その後に、高い幅方向剛性の突起に当たる。このため、荷重を2つのガイド突起及び駆動突起で受けることができる。このため、荷重をガイド突起及び駆動突起に分散することができ、ガイド突起が損傷する虞を抑制することができる。
本発明の少なくとも幾つかの実施形態によれば、車両の旋回時に、ゴムクローラのガイド突起がもげて転輪が脱輪する虞のない走行装置を提供することができる。
以下、添付図面に従って本発明のゴムクローラの実施形態について、図1~図8を参照しながら説明する。本実施形態では、車両に設けられた走行装置を例にして説明する。なお、この実施形態に記載されている構成部品の材質、形状、その相対的配置等は、本発明の範囲をこれに限定する趣旨ではなく、単なる説明例にすぎない。
走行装置1は、図1(側面図)に示すように、図示しない車両の車体の側部の前後方向一端部に回転駆動可能に支持された駆動輪10と、車体の側部の前後方向他端部に回転自在に支持された従動輪17と、駆動輪10及び従動輪17間に掛け回されたゴムクローラ20と、ゴムクローラ20の下側の内周面上を転動する複数の転輪60とを有してなる。
駆動輪10は、図2(斜視図)及び図3(斜視図)に示すように、車両に設けられたエンジン等からの駆動力を受けて回転可能である。駆動輪10は、幅方向に一定の間隔を有して対向配置され一対のスプロケット11を備え、これら一対のスプロケット11が車両から延びる駆動軸の先端部に取り付けられて、駆動輪10を形成している。スプロケット11の外周縁には、周方向に一定の間隔を有して設けられた複数の歯部12が形成されている。この歯部12がゴムクローラ20の駆動突起40と歯合してゴムクローラ20に回転力を伝達する。スプロケット11の内側には、スプロケット11と同心軸上に配置されてゴムクローラ20から脱輪するのを防止するためのガイドローラ13が設けられている。一対のスプロケット11のガイドローラ13間には、ゴムクローラ20の幅方向中央部に設けられたガイド突起30が通過可能な隙間15が設けられている。このため、駆動輪10は、一対のガイドローラ13によってゴムクローラ20から脱輪することなく、駆動輪10の回転力をゴムクローラ20に伝達可能である。
転輪60は、図4(斜視図)に示すように、幅方向に一定の間隔を有して対向配置された一対の転輪本体部61を備え、これら一対の転輪本体部61が車両の車体から延びる支持軸(図示せず)の先端部に回転自在に取り付けられている。この支持軸は車両の車体に対して上下方向に移動自在に支持されている。転輪本体部61の外周面には、ゴム製の環状体63が装着されている。この環状体63によって路面から受ける衝撃を吸収可能である。一対の転輪本体部61間には、一対のスプロケット11と同様に、ゴムクローラ20のガイド突起30が通過可能な隙間65が設けられている。なお、一対の転輪本体部61のうち、車両外側に配設された転輪本体部61を「第1転輪本体部68」と記し、車両内側に配設された転輪本体部61を「第2転輪本体部69」と記す。
第1転輪本体部68の環状体63の幅方向外側の周縁部には、周縁部に沿って環状に形成された第1外側摺接面63aが形成されている。この第1外側摺接面63aは、第1転輪本体部68の径方向外側へ進むに従って第1転輪本体部68の内側へ傾く平面状の傾斜面として形成されている。図面では、第1外側摺接面63aは、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aに対して約80度の角度を有して傾斜している。この第1外側摺接面63aは、駆動突起40の内側の面に対向配置される。駆動突起40の内側の面の詳細については後述する。
また、第1転輪本体部68の環状体63の幅方向内側の周縁部には、周縁部に沿って環状に形成された第1内側摺接面63bが形成されている。この第1内側摺接面63bは、第1転輪本体部68の径方向外側へ進むに従って第1転輪本体部68の内側へ傾く平面状の傾斜面として形成されている。図面では、第1内側摺接面63bは、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aに対して約50度の角度を有して傾斜している。この第1内側摺接面63bは、ガイド突起30の外側の面に対向配置される。ガイド突起30の外側の面の詳細については後述する。
一方、第2転輪本体部69の環状体63の幅方向外側の周縁部には、周縁部に沿って環状に形成された第2外側摺接面63cが形成されている。この第2外側摺接面63cは、第2転輪本体部69の径方向外側へ進むに従って第2転輪本体部69の内側へ傾く平面状の傾斜面として形成されている。図面では、第2外側摺接面63cは、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aに対して約50度の角度を有して傾斜している。この第2外側摺接面63cは、ガイド突起30の内側の面に対向配置される。ガイド突起30の内側の面の詳細については後述する。
また、第2転輪本体部69の環状体63の幅方向外側の周縁部には、周縁部に沿って環状に形成された第2内側摺接面63dが形成されている。この第2内側摺接面63dは、第2転輪本体部69の径方向外側へ進むに従って第2転輪本体部69の内側へ傾く平面状の傾斜面として形成されている。図面では、第2内側摺接面63dは、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aに対して約80度の角度を有して傾斜している。この第2内側摺接面63dは、駆動突起40の内側の面に対向配置される。駆動突起40の内側の面の詳細については後述する。
次に、ゴムクローラ20について、図2、図5を参照しながら説明する。ゴムクローラ20は、図2及び図5に示すように、無端状のゴム弾性体21と、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aの幅方向中央部に周方向に一定の間隔を有して設けられて転輪60の脱輪を防止するガイド突起30と、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aの幅方向両外側部に周方向に一定のピッチを有して設けられてスプロケット11と歯合される駆動突起40と、を備えてなる。
ゴム弾性体21は、ゴム製であり、無端状であって帯状に形成されている。ゴム弾性体21の外周面21bには、径方向外側へ突出してゴム弾性体21の周方向に間隔を有して設けられたラグ22が複数形成されている。
一方、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aに設けられたガイド突起30は、内周面21aに対して略直交する方向に延びる略直方体状に形成されている。ガイド突起30は、側面視において、ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aから離反するに従って漸次先細になるように形成されている。このため、ゴムクローラ20がスプロケット11に屈曲しながら回転する際に、ゴムクローラ20の周方向に隣接するガイド突起30同士が接触するのを防止している。
ガイド突起30の根元側の幅方向外側には、転輪60の第1転輪本体部68の第1内側摺接面63bに対向配置されるガイド突起外側面30aが形成されている。このガイド突起外
側面30aは、第1内側摺接面63bと略並行に延びるように形成されている。ガイド突起外側面30aと第1内側摺接面63bとの間には、所定の隙間32が形成されている。この隙間32の大きさA1の詳細については後述する。
側面30aは、第1内側摺接面63bと略並行に延びるように形成されている。ガイド突起外側面30aと第1内側摺接面63bとの間には、所定の隙間32が形成されている。この隙間32の大きさA1の詳細については後述する。
また、ガイド突起30の根元側の幅方向内側には、転輪60の第2転輪本体部69の第2外側摺接面63cに対向配置されるガイド突起内側面30bが形成されている。このガイド突起内側面30bは、第2外側摺接面63cと略並行に延びるように形成されている。ガイド突起内側面30bと第2外側摺接面63cとの間には、所定の隙間33が形成されている。この隙間33の大きさA2の詳細については後述する。
ガイド突起30は、一対のスプロケット11間の隙間15内及び、転輪60の一対の転輪本体61間の隙間65内を通過可能な大きさを有するとともに、転輪60がゴムクローラ20から脱輪するのを規制可能な高さを有している。
ゴム弾性体21の内周面21aの幅方向両側に設けられた駆動突起40、40'は、側面視においてゴム弾性体21の内周面21aから離反するに従って漸次先細になるように形成され、平面視において横長の矩形状に形成されている。ゴム弾性体21の幅方向外側に設けられた駆動突起40の幅方向内側端には、上下方向に延びる駆動突起内側面外40aが形成されている。この駆動突起内側面外40aは、平面状に形成されて、第1転輪本体部68の第1外側摺接面63aに対向するように配設されている。駆動突起内側面外40aは、上方へ進むに従って幅方向外側へ傾斜するように傾き、平面状に形成されて、第1転輪本体部68の第1外側摺接面63aに対向配置される。駆動突起内側面外40aは、第1外側摺接面63aと略並行に延び、駆動突起内側面外40aと第1外側摺接面63aとの間には隙間64が形成されている。この隙間33の大きさA3の詳細については後述する。
また、ゴム弾性体21の幅方向うち側に設けられた駆動突起40'の幅方向内側端には、上下方向に延びる駆動突起内側面内40bが形成されている。この駆動突起内側面内40bは、平面状に形成されて、第2転輪本体部69の第2内側摺接面63dに対向するように配設されている。駆動突起内側面内40bは、上方へ進むに従って幅方向外側へ傾斜するように傾き、平面状に形成されて、第2転輪本体部69の第2内側摺接面63dに対向配置される。駆動突起内側面内40bは、第2内側摺接面63dと略並行に延び、駆動突起内側面内40bと第2内側摺接面63dとの間には隙間35が形成されている。この隙間35の大きさA4の詳細については後述する。
これらの駆動突起40、40'はスプロケット11の歯部12と同一ピッチを有して内周面21aに設けられている。このため、駆動突起40、40'はスプロケット11の歯部12と良好に歯合して、スプロケット11の駆動力が駆動突起40、40'を介してゴム弾性体21に伝達される。
このゴム弾性体21の内周面21aの幅方向両側に設けられた一対の駆動突起40、40'は、内周面21aの幅方向中央部に設けられたガイド突起30とともに、ゴム弾性体21の周方向に対して直交する方向に直線状に配置されている。
ガイド突起外側面30aと第1内側摺接面63bとの間の隙間32の大きさA1は、駆動突起内側面内40bと第2内側摺接面63dとの間の隙間35の大きさA4と等しい。また、ガイド突起内側面30bと第2外側摺接面63cとの間の隙間33の大きさA2は、駆動突起内側面外40aと第1外側摺接面63aとの間に隙間64の大きさA3と等しいように形成されている。
次に、走行装置1の作動について、図1、図2、図6を参照しながら説明する。図1及び図2に示すように、駆動輪10が回転すると、駆動輪10の回転に伴ってゴムクローラ20が駆動輪10と従動輪17との間を回転する。ゴムクローラ20の回転時には、転輪60はゴムクローラ20のゴム弾性体21の内周面21a上を転動する。
ここで、ゴムクローラ20の回転時に、車両を旋回させるように、車両の左右に設けられた走行装置1が作動すると、図6に示すように、例えば、転輪60がゴムクローラ20の幅方向一方側(矢印A方向)に揺動して、転輪60からゴムクローラ20のガイド突起30にゴムクローラ幅方向一方側へ向く荷重が作用する。この荷重の作用時には、第1転輪本体部68の第1外側摺接面63aが駆動突起40の駆動突起内側面外40aに接触するとともに、第2転輪本体部69の第2外側摺接面63cがガイド突起30のガイド突起内側面30bに接触する。また、これらの接触は略同時に行われる。
このため、転輪60からの荷重は、ガイド突起30及び駆動突起40の2つの突起で受けられる。従って、荷重をガイド突起30及び駆動突起40に分散することができるので、ガイド突起30が損傷する虞を抑制することができる。また、ガイド突起内側面30bと第2外側摺接面63cとの間の隙間33の大きさA2は、駆動突起内側面外40aと第1外側摺接面63aとの間に隙間64の大きさA3と等しいので、転輪60の第1転輪本体部68及び第2転輪本体部69が駆動突起40とガイド突起30に同時に当たり、駆動突起40及びガイド突起30の変形量を同等にすることができる。また、駆動突起40及びガイド突起30に接触する転輪60の第1転輪本体部68及び第2転輪本体部69の接触部分(環状体63)の摩耗量を同等にすることができる。
一方、車両の旋回時に、図5に示すように、転輪60がゴムクローラ20の幅方向他方側(矢印B方向)に揺動すると、転輪60からゴムクローラ20のガイド突起30にゴムクローラ幅方向他方側に向く荷重が作用する。この荷重の作用時には、第1転輪本体部68の第1内側摺接面63bがガイド突起30のガイド突起外側面30aに接触するとともに、第2転輪本体部69の第2内側摺接面63dが駆動突起40'の駆動突起内側面内40bに接触する。また、これらの接触は略同時に行われる。
このため、転輪60からの荷重は、ガイド突起30及び駆動突起40の2つの突起で受けられる。従って、荷重をガイド突起30及び駆動突起40に分散することができるので、ガイド突起30がもげる虞を抑制することができる。ガイド突起外側面30aと第1内側摺接面63bとの間の隙間32の大きさA1は、駆動突起内側面内40bと第2内側摺接面63dとの間の隙間35の大きさA4と等しいので、転輪60の第1転輪本体部68及び第2転輪本体部69が駆動突起40'とガイド突起30に同時に当たり、駆動突起40'及びガイド突起30の変形量を同等にすることができる。また、駆動突起40'及びガイド突起30に接触する転輪60の第1転輪本体部68及び第2転輪本体部69の接触部分(環状体63)の摩耗量を同等にすることができる。
また、図7に示すように、駆動突起内側面外40aと第1外側摺接面63aとの間に隙間34の大きさA3は、ガイド突起内側面30bと第2外側摺接面63cとの間の隙間33の大きさA2よりも小さい場合、駆動突起40の幅方向剛性をガイド突起30の幅方向剛性よりも小さくするようにしてもよい。この場合、幅方向剛性の調整は、ゴム弾性体21のゴム硬度はそのままで、例えば、ゴム弾性体に埋設される芯金71、72のゴム弾性体内の設置位置を調整することで行うことができる。
このようにすると、図8に示すように、車両の旋回時に、転輪60がゴムクローラ20の幅方向一方側へ揺動すると、転輪60の第1転輪本体部68が、先ず、低い幅方向剛性の駆動突起40に当たって駆動突起40を弾性変形させる。そして、その後に、転輪60の第2転輪本体部69が高い弾性のガイド突起30に当たる。このため、荷重を2つのガイド突起30及び駆動突起40で受けることができる。このため、荷重をガイド突起30及び駆動突起40に分散することができ、ガイド突起30が損傷する虞を抑制することができる。
以上、本発明の実施形態について説明したが、本発明は上記の形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の目的を逸脱しない範囲での種々の変更が可能である。例えば、上述した各種実施形態を適宜組み合わせてもよい。
1 走行装置
10 駆動輪
11 スプロケット
12 歯部
13 ガイドローラ
15、32、33、34、35、65 隙間
20 ゴムクローラ
21 ゴム弾性体
21a 内周面
21b 外周面
22 ラグ
30 ガイド突起
30a ガイド突起外側面(側面)
30b ガイド突起内側面(側面)
40、40' 駆動突起
40a 駆動突起内側面外(側面)
40b 駆動突起内側面内(側面)
45 スチールコード列
46 スチールコード
47 バイアスコード列
48 バイアスコード
60 転輪
61 転輪本体部
63 環状体
63a 第1外側摺接面(側面)
63b 第1内側摺接面(側面)
63c 第2外側摺接面(側面)
63d 第2内側摺接面(側面)
68 第1転輪本体部(転輪本体部)
69 第2転輪本体部(転輪本体部)
71、72 芯金
10 駆動輪
11 スプロケット
12 歯部
13 ガイドローラ
15、32、33、34、35、65 隙間
20 ゴムクローラ
21 ゴム弾性体
21a 内周面
21b 外周面
22 ラグ
30 ガイド突起
30a ガイド突起外側面(側面)
30b ガイド突起内側面(側面)
40、40' 駆動突起
40a 駆動突起内側面外(側面)
40b 駆動突起内側面内(側面)
45 スチールコード列
46 スチールコード
47 バイアスコード列
48 バイアスコード
60 転輪
61 転輪本体部
63 環状体
63a 第1外側摺接面(側面)
63b 第1内側摺接面(側面)
63c 第2外側摺接面(側面)
63d 第2内側摺接面(側面)
68 第1転輪本体部(転輪本体部)
69 第2転輪本体部(転輪本体部)
71、72 芯金
Claims (4)
- 無端状のゴムクローラの内周面の幅方向中央部に設けられたガイド突起を跨いだ状態で配置されて前記ゴムクローラの内周面上を転動する転輪が、前記ガイド突起の側面と、前記ゴムクローラの前記内周面の幅方向両側に設けられた駆動突起の側面に面接触する走行装置であって、
前記転輪幅方向端部には、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に面接触可能な側面が形成され、
前記転輪の前記側面は、前記転輪のクローラ幅方向の揺動により前記ガイド突起の側面とともに前記駆動突起の側面に面接触するように、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起の各側面に対向配置されている
ことを特徴とする走行装置。 - 前記転輪は、前記ガイド突起の幅方向両側に対向配置された一対の転輪本体部を含み、
前記一対の転輪本体部の各幅方向両側の周縁部に側面が形成され、
前記転輪の揺動により、前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面が前記ガイド突起の側面に面接触するとともに、いずれか他方の側面が前記駆動突起の側面に面接触する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の走行装置。 - 前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか一方の側面と前記ガイド突起の側面との間の隙間は、前記一対の転輪本体部のいずれか他方の側面と前記駆動突起の側面との間の隙間と同じ大きさを有している
ことを特徴とする請求項2に記載の走行装置。 - 前記ゴムクローラの幅方向に隣接して配設された前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起は、いずれか一方がいずれか他方よりも幅方向に向く荷重に対する幅方向剛性が低くなるように形成され、
前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起のうち幅方向剛性が低い方の側面と前記転輪の側面との間の隙間は、前記ガイド突起及び前記駆動突起のうちの幅方向剛性が高い方の側面と前記転輪の側面との間の隙間よりも小さい
ことを特徴とする請求項2に記載の走行装置。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/128,498 US10668964B2 (en) | 2014-03-24 | 2015-03-18 | Running device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014-059842 | 2014-03-24 | ||
| JP2014059842A JP6305145B2 (ja) | 2014-03-24 | 2014-03-24 | 走行装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015146753A1 true WO2015146753A1 (ja) | 2015-10-01 |
Family
ID=54195274
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/058126 WO2015146753A1 (ja) | 2014-03-24 | 2015-03-18 | 走行装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10668964B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6305145B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015146753A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112389556B (zh) * | 2020-11-28 | 2023-05-05 | 哈尔滨北方防务装备股份有限公司 | 双节履带车滚齿啮合驱动结构 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05162667A (ja) * | 1991-12-16 | 1993-06-29 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ用芯金及びゴムクロ−ラ走行装置 |
| JPH0632262A (ja) * | 1992-07-10 | 1994-02-08 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ |
| JPH08119161A (ja) * | 1994-10-24 | 1996-05-14 | Ohtsu Tire & Rubber Co Ltd :The | 弾性クローラの脱輪防止構造 |
| JP2005225367A (ja) * | 2004-02-13 | 2005-08-25 | Sumitomo Rubber Ind Ltd | ゴムクローラ |
| JP2005271658A (ja) * | 2004-03-23 | 2005-10-06 | Sumitomo Rubber Ind Ltd | 弾性クローラ |
| JP2007145096A (ja) * | 2005-11-24 | 2007-06-14 | Bridgestone Corp | 芯金レスゴムクロ−ラ |
| JP2007216837A (ja) * | 2006-02-16 | 2007-08-30 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63258276A (ja) * | 1987-04-16 | 1988-10-25 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ |
| US5295741A (en) * | 1991-01-30 | 1994-03-22 | Bridgestone Corporation | Core bar for rubber track and rubber track traveling device |
| US6983812B2 (en) * | 2003-09-17 | 2006-01-10 | Tucker Sno-Cat Corporation | Tracked vehicle with improved track drive unit |
| JP2007191089A (ja) | 2006-01-20 | 2007-08-02 | Bridgestone Corp | 芯金レスゴムクロ−ラ |
-
2014
- 2014-03-24 JP JP2014059842A patent/JP6305145B2/ja active Active
-
2015
- 2015-03-18 WO PCT/JP2015/058126 patent/WO2015146753A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2015-03-18 US US15/128,498 patent/US10668964B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05162667A (ja) * | 1991-12-16 | 1993-06-29 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ用芯金及びゴムクロ−ラ走行装置 |
| JPH0632262A (ja) * | 1992-07-10 | 1994-02-08 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ |
| JPH08119161A (ja) * | 1994-10-24 | 1996-05-14 | Ohtsu Tire & Rubber Co Ltd :The | 弾性クローラの脱輪防止構造 |
| JP2005225367A (ja) * | 2004-02-13 | 2005-08-25 | Sumitomo Rubber Ind Ltd | ゴムクローラ |
| JP2005271658A (ja) * | 2004-03-23 | 2005-10-06 | Sumitomo Rubber Ind Ltd | 弾性クローラ |
| JP2007145096A (ja) * | 2005-11-24 | 2007-06-14 | Bridgestone Corp | 芯金レスゴムクロ−ラ |
| JP2007216837A (ja) * | 2006-02-16 | 2007-08-30 | Bridgestone Corp | ゴムクロ−ラ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015182547A (ja) | 2015-10-22 |
| JP6305145B2 (ja) | 2018-04-04 |
| US20170106923A1 (en) | 2017-04-20 |
| US10668964B2 (en) | 2020-06-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TW201404659A (zh) | 用於腳踏車變速齒輪的後脫軌裝置的導鏈滾輪和具有此種導鏈滾輪的後脫軌裝置 | |
| JP2008502524A (ja) | クローラ走行体のクローラチェーンのためのトラックローラアセンブリ | |
| WO2015159896A1 (ja) | クローラ | |
| JP6479318B2 (ja) | ゴムクローラ | |
| CN102686475A (zh) | 链轮和具有该链轮的橡胶履带组装体 | |
| WO2015146753A1 (ja) | 走行装置 | |
| US20050104449A1 (en) | Mid-roller wheels for endless drive track system | |
| JP5001997B2 (ja) | 汚泥掻き寄せ装置 | |
| US10308297B2 (en) | Elastic crawler drive mechanism | |
| JP6799926B2 (ja) | 軸受装置およびローラ装置 | |
| JP5415894B2 (ja) | 弾性履帯車両 | |
| JP5213377B2 (ja) | ゴムクローラ | |
| JP2015182547A5 (ja) | ||
| KR20180102003A (ko) | 탄성 크롤러 | |
| JP5939762B2 (ja) | 弾性クローラ | |
| KR102540507B1 (ko) | 마사지모듈 이송용 이중롤러 가이드장치 | |
| JP6479319B2 (ja) | ゴムクローラ | |
| JP6712086B2 (ja) | クローラ装置 | |
| US9446806B2 (en) | Rubber crawler | |
| JP2017218014A (ja) | 全方向車輪および全方向移動体 | |
| JP6616641B2 (ja) | 弾性クローラおよび弾性クローラ装置 | |
| JP6505042B2 (ja) | クローラ | |
| WO2017017958A1 (ja) | 弾性クローラ | |
| JP2006248248A (ja) | クローラベルト用プーリ | |
| JP6926867B2 (ja) | 弾性クローラ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15770032 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15128498 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15770032 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |