WO2015075970A1 - タービンロータ組立体およびタービンロータ組立体における翼止板並びに翼止板の組付け方法 - Google Patents
タービンロータ組立体およびタービンロータ組立体における翼止板並びに翼止板の組付け方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015075970A1 WO2015075970A1 PCT/JP2014/069897 JP2014069897W WO2015075970A1 WO 2015075970 A1 WO2015075970 A1 WO 2015075970A1 JP 2014069897 W JP2014069897 W JP 2014069897W WO 2015075970 A1 WO2015075970 A1 WO 2015075970A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- blade
- stop plate
- axial
- rotor disk
- axial groove
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/30—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers
- F01D5/32—Locking, e.g. by final locking blades or keys
- F01D5/323—Locking of axial insertion type blades by means of a key or the like parallel to the axis of the rotor
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/30—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/30—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers
- F01D5/3007—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers of axial insertion type
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/30—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers
- F01D5/3007—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers of axial insertion type
- F01D5/3015—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers of axial insertion type with side plates
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2260/00—Function
- F05D2260/96—Preventing, counteracting or reducing vibration or noise
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a turbine rotor assembly, a blade stopper plate in the turbine rotor assembly, and a method for assembling the blade stopper plate.
- a moving blade group attached to an axial groove formed in the rotor disk via a blade root in the circumferential direction of the rotor disk is caused by centrifugal force or vibration based on the rotation of the rotor disk. External force is applied through the blade root. For this reason, the rotor blade group may move on the axial groove formed in the rotor disk via the blade root, and as a countermeasure therefor, a fixed body (hereinafter referred to as the blade blade) is disposed between the blade root and the axial groove. (Stop plate) is disposed (for example, Patent Document 1).
- the blade stop plate here has a base portion fitted in the axial groove and an end region protruding beyond the axial groove, and the end regions located on the downstream side and the upstream side are the blade roots. And the axial groove are bent so as to grip from behind. Further, in the end regions located on the downstream side and the upstream side, the end surfaces of the blade carriers disposed on both outer sides are opposed to each other, and a stopper is provided to avoid widening the end region. ing. That is, in Patent Document 1, the fixing element formed integrally with the blade carrier is disposed adjacent to the first end region of the blade stopper plate in the axial direction, and the blade stopper plate. For this purpose, an axial stopper is constructed.
- the first end region of the blade stop plate is located in the circumferential groove between the stopper and the blade carrier.
- the stopper prevents the blade stop plate from being axially displaced from its position or widening the end region, so that the blade root and the blade root make it possible to The position is supposed to be kept.
- Patent Document 2 in order to hold the moving blade without a gap and to be able to repeatedly use the components during disassembly and assembly, the axial hole extends across the bottom of the moving blade and the disk.
- a blade stop pin having a head with a diameter larger than the axial hole diameter and having a screw hole threaded at the tip is inserted into the axial hole, and has a head larger than the hole diameter. The screw is screwed into the screw hole of the blade stop pin.
- Patent Document 1 in order to avoid that the end surface of the blade carrier disposed on both outer sides is opposed to the end region of the blade stop plate and the end region is widened, a stopper is provided. Since the structure is arranged, it cannot be denied that the structure becomes complicated. Further, in Patent Document 2, since the structure is such that the moving blade is held without a gap and the parts can be used repeatedly during disassembly and assembly, it takes a lot of trouble to disassemble and assemble the moving blade. There is a problem that takes.
- Patent Document 2 in order to prevent the movement of the rotor blade in the radial direction of the disk, a blade stopper pin is inserted into an axial hole formed in the axial direction of the disk so that the blade stopper pin does not fall off. From the opposite side of the insertion direction of the wing stop pin, it is fastened with screws. For this reason, the external force applied to the rotor blades repeatedly in the disk axial direction is received by the screw head, which is screwed from the opposite side of the blade stop pin insertion direction. There is a risk that the exhaustion of the air will be accelerated, and there is a concern that the wing stop effect will be reduced, and it will be necessary to perform frequent inspections.
- An object of at least one embodiment of the present invention is to provide a turbine rotor assembly, a blade stopper plate in the turbine rotor assembly, and a method of assembling the blade stopper plate so that the moving blade can be held in its position with a simpler structure. Is to provide.
- a turbine rotor assembly includes a rotor disk, a plurality of axial grooves formed on the outer periphery of the rotor disk, and arranged along the circumferential direction of the rotor disk via a blade stop plate.
- a turbine rotor assembly that is planted in the axial groove, and a blade stop plate includes a base that fits in the axial groove, and both ends of the base, The end protruding in the axial direction from the axial groove is provided with a bent portion that is bent in the radial direction of the rotor disk and abuts against the axial end surface of the rotor disk, and at least one of the bent portions at both ends includes the rotor It is characterized in that it has inner and outer bent portions that project toward the end face in the axial direction toward the outer side and the inner side in the radial direction of the disk.
- the inner and outer bent portions are arranged at least on the downstream side of the working fluid passing through the blade group.
- the moving blade group is shifted from its position in the axial direction or the end of the blade stop plate. It is avoided that the partial area is expanded.
- the radially outer bent portion of the inner and outer bent portions is formed in a substantially square shape when viewed in the rotational axis direction, and the radially inner bent portion protrudes inward from the outer bent portion. A portion is formed.
- the outer bent portion and the inner bent portion of the inner and outer bent portions are in contact with the axial end surface of the rotor disk, which can counter the displacement force applied to the moving blades in a wider area. Can support the rotor blades.
- the blade stop plate in the turbine rotor assembly is arranged along the rotor disk, a plurality of axial grooves formed on the outer periphery of the rotor disk, and the circumferential direction of the rotor disk.
- the turbine rotor assembly comprising: a blade group planted in the axial groove through a blade stop plate; and a turbine rotor assembly for fixing the blade group to a rotor disk via a blade root.
- a wing stop plate having a length corresponding to the axial groove and configured to fit in the axial groove, and provided at both ends of the base, the boundary between the base A pair of end portions configured to be in contact with an axial end surface of the rotor disk by being bent at a position, and at least one end portion of the pair of end portions includes the end portion and the base portion.
- At least one of the end portions protruding from the axial groove of the blade stop plate is provided with a protruding portion from the boundary position between the end portion and the base portion to the inside of the base portion. It can be sufficiently maintained against the external force in the axial direction of the rotor blade.
- one end portion of the blade stop plate is connected to the outer side in the radial direction.
- a first step of forming an inner / outer bent portion that protrudes outward and inward by bending inward, a second step of fitting the base portion of the blade stop plate into the axial groove from above, and the blade root of the rotor blade as a shaft A third step of inserting into the directional groove from the other end side, and a fourth step of bending the other end portion and fixing the moving blade to the axial groove through the blade stop plate, It is characterized by that.
- the rotor blade can be easily assembled and fixed in the axial groove, and the turbine rotor assembly can be easily manufactured.
- the bent portion that is bent in the radial direction of the rotor disk and contacts the axial end surface of the rotor disk Since one of the bent portions has inner and outer bent portions that project both radially outward and inwardly, the force generated by the blade group is shifted from its position in the axial direction or the blade stop plate It is avoided that the end region is widened, so that the blade root and the blade are kept in their exact position by this blade root.
- a blade stop plate that can sufficiently maintain the moving blade against an external force in the axial direction of the moving blade is obtained.
- the rotor blade can be easily assembled and fixed in the axial groove, and the turbine rotor assembly can be easily manufactured.
- FIG. 1 is a partially external perspective view showing a first embodiment of a turbine rotor assembly according to the present invention. It is the top view which showed an example of the blade stop plate concerning this embodiment used for the turbine rotor assembly shown in FIG. It is a schematic perspective view for demonstrating the assembly procedure of the turbine rotor assembly concerning one Embodiment of this invention.
- FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram showing a procedure for assembling a moving blade after assembling a blade stop plate to the rotor disk shown in FIG. 3. It is a schematic diagram which shows the state which assembled
- FIG. 1 shows a turbine rotor assembly 1 according to the first embodiment.
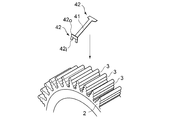
- the turbine rotor assembly 1 is mounted on, for example, an axial turbine, and includes a rotor disk 2, a plurality of axial grooves 3 (see FIG. 3) formed on the outer periphery of the rotor disk 2, and the circumference of the rotor disk 2. And a moving blade group 5n arranged in the axial groove 3 via the blade stop plate 4 and arranged along the direction.
- the rotor disk 2 rotates around the axis of the axial turbine with a rotating disk of a predetermined diameter.
- axial grooves 3 formed so as to form a predetermined angle in the axial direction are provided over the entire periphery at predetermined intervals.
- the axial groove 3 is a groove having a stepped wall that is dug in a multi-stage shape in a V shape when viewed from the axial end surface of the rotor disk 2, from the bottom toward the outer periphery of the rotor disk 2. Is expanding.
- the axial groove 3 is provided so as to penetrate the rotor disk 2 and may be provided parallel to the axial direction of the rotor disk 2 or provided at a predetermined angle with respect to the axial direction of the rotor disk 2. May be.
- the moving blade group 5n is arranged in an axial groove 3 in which the individual moving blades 5 are provided over the entire circumference of the rotor disk 2 at regular intervals.
- the moving blade 5 is substantially composed of a blade root 51, a blade base 52, and a blade 53 formed so as to be able to fit in the axial groove 3.
- the blade root 51 is formed in a stepped shape and a tapered shape so as to fit into the axial groove 3.
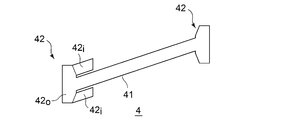
- the blade stop plate 4 is a thin plate body, and a base 41 that fits into a groove on the bottom side of the axial groove 3, and axial grooves at both ends of the base 41. 3 and a pair of end portions provided so as to protrude in the axial direction.
- the pair of end portions of the blade stop plate 4 form bent portions 42 and 42 which are bent in the radial direction of the rotor disk 2, that is, radially outward to come into contact with the axial end surface of the rotor disk 2.
- the bent parts 42, 42 have a width dimension that crosses the axis of the base 41 larger than the width of the base 41.
- At least one of the bent portions 42, 42 is an inner / outer bent portion (outer bent portion 42 o and inner bent portion 42 i) protruding from the base portion 41 toward the outer side and the inner side in the radial direction of the rotor disk 2. ).
- the outer bent portion 42o protrudes from the base 41 toward the radially outer side of the rotor disk 2 when the blade stop plate 4 is bent at a bend line at the boundary position between the bent portion 42 and the base 41.
- the inner bent portion 42 i protrudes from the base 41 toward the radially inner side of the rotor disk 2 when the blade stop plate 4 is bent at a bend line at the boundary position between the bent portion 42 and the base 41. It is like that.
- the blade stopper plate 4 has a pair of inwardly bent portions 42i.
- the base 41 has a length corresponding to the groove length of the axial groove 3 formed in the rotor disk 2. That is, the base 41 has substantially the same dimension as the axial dimension of the axial groove 3. Further, the base portion 41 and the bent portions 42 and 42 at both ends are deflected to the same angle as the forming angle of the axial groove 3 with respect to the axial direction.
- the blade stop plates 4 are attached to the axial grooves 3 arranged on the outer periphery of the rotor disk 2.
- the blade stop plate 4 is bent at a bend line at the boundary between the bent portion 42 and the base portion 41 in order to attach the blade stop plate 4 to each axial groove 3 as a first step.
- the bent portion 42 including the outer bent portion 42o and the inner bent portion 42i is bent outward in the radial direction.
- the outer bent portion 42o protrudes outward in the radial direction
- the inner bent portion 42i protrudes inward in the radial direction.
- the base 41 of the blade stop plate 4 is inserted into the axial groove 3 from above, and the base 41 is fitted into the axial groove 3.
- the base 41 and the axial groove 3 have substantially the same length, and the axial groove 3 is configured by a groove having a stepped wall that is dug in a V shape.
- the base 41 can be fitted into the axial groove 3 at a position where the width dimension of the base 41 and the groove width of the axial groove 3 are substantially the same.
- the outer bent portion 42o of the bent portion 42 and the pair of inner bent portions 42i are in contact with the axial end surface of the rotor disk 2, and the outer bent portion
- the end face in the axial direction can be supported by a wider area where only 42o abuts, and the moving blade 5 can be supported favorably against the displacement force applied to the moving blade 5.
- the other bent portion 42 of the blade stop plate 4 is not bent.
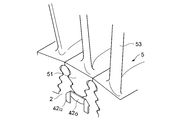
- the blade root 51 of the rotor blade 5 is inserted into the axial groove 3 from the end of the blade stop plate 4 that is not bent.
- the blade root 51 can be fitted into the axial groove 3 formed in a stepped shape while avoiding interference between the blade stop plate 4 and the blade root 51 of the rotor blade 5 (see FIG. 5).
- the bent portion 42 of the blade stop plate 4 that is not bent is finally bent radially outward so that the blade root 51 of the blade 5 and the axial groove 3 are fitted.
- the portion is sandwiched between the bent portions 42 and 42 of the blade stop plate 4 and can sufficiently withstand the external force applied at least in the axial direction of the rotor disk 2 (see FIG. 6).
- the moving blade 5 against the external force applied to the blade portion 53 of the moving blade 5 when the working fluid passes through the turbine moving blade group 5n from the upstream side to the downstream side, the moving blade 5 is arranged on the outer side on the downstream side.
- the displacement force applied to the rotor blade 5 is larger than when only the outer bent portion 42o is in contact.
- the rotor blades 5 can be supported suitably.
- the present invention can also be implemented by the second embodiment.
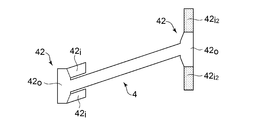
- the blade retaining plate 4 has a radius of only one bent portion 42 as in the first embodiment out of the end portions protruding in the axial direction from the axial groove 3.
- the outer bent portion 42o protrudes outward in the direction and the inner bent portion 42i protrudes inward in the radial direction.
- the other bent portion, that is, the bent portion 42 set on the upstream side of the rotor disk 2 in the axial direction is a second inner bent portion that is a protruding portion protruding in the longitudinal direction of the outer bent portion 42o. Part 42i2.
- the second inner bent portion 42i2 is bent radially inward after finishing the same steps (first step to fourth step) as in the first embodiment (see FIG. 8). That is, before mounting on the axial groove 3, the blade stop plate 4 is bent at the bending line at the boundary between the one bent portion 42 and the base portion 41 (first step), and the blade stop plate 4 in this state is connected to the axial groove 3.
- the blade root 51 of the rotor blade 5 is inserted into the axial groove 3 from the end portion of the blade stop plate 4 that is not bent (second step).
- the other bent portion 42 of the blade stop plate 4 that is not bent is bent radially outward (fourth step).
- the second bent portion 42i2 of the other bent portion 42 is bent inward in the radial direction.
- the second inwardly bent portion 42i2 comes into contact with the axial end surface of the rotor disk 2 as a protruding portion that protrudes radially inward, and the blade root 51 of the rotor blade 5 and the axial groove 3 are in contact with each other.
- the fitting portion is sandwiched between the bent portions 42, 42 of the blade stop plate 4, and the effect of preventing the shift is further enhanced at least against the external force applied in the axial direction of the rotor disk 2 ( (See FIG. 9).
- the first and second embodiments are shown, and the structure and the assembling process are shown and described.
- at least the axial direction of the rotor disk 2 is achieved by using the blade stop plate 4 to project the bent portions 42, 42 protruding in the axial direction from the axial groove 3 inward in the radial direction. It will be able to withstand the external force applied.
- the present invention can be applied not only to a turbine rotor assembly of an axial flow turbine but also to fixing blades of any rotating machine.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Turbine Rotor Nozzle Sealing (AREA)
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
Abstract
Description
すなわち、特許文献1では、翼担体と一体的に形成されている固定要素は、翼止板の第1の端部領域に軸方向に隣接するように配設されており、かつこの翼止板のために軸方向のストッパを構成する。また、翼止板の第1の端部領域は、ストッパと翼担体との間の周方向溝内に位置することになる。ストッパによって、翼止板が生じる力によって軸方向にその位置からずらされるか、端部領域が広げられてしまうことが回避され、これにより、翼根及びこの翼根により動翼は、その正確な位置を保たれるとしている。
また、特許文献2では、動翼を隙間のない状態で保持し、且つ、分解、組立の際に部品を繰り返して使用できるようにする構造であるから、動翼の分解、組み立てに大変な手間がかかる問題がある。しかも、特許文献2では、ディスクの径方向に対する動翼の動きを防止するために、ディスクの軸方向に穿設した軸方向穴に翼止めピンを挿入し、かかる翼止めピンが脱落しないように翼止めピンの挿入方向の反対側から、ねじで締めて固定している。そのため、繰り返し動翼に対してディスク軸方向にかかる外力を、翼止めピンの挿入方向の反対側からねじ止めした、ねじの頭で受ける構造であるから、ねじの頭に負荷が集中し、ねじの消耗が早まるおそれがあり、翼止め効果の低下が懸念され、頻繁に点検を行う必要性が出てくる。
本発明の少なくとも一実施形態の目的は、より簡単な構造で、動翼をその位置に保持できるようにした、タービンロータ組立体およびタービンロータ組立体における翼止板並びに翼止板の組付け方法を提供することである。
また、幾つかの実施形態によれば、動翼の軸方向への外力に対して動翼を十分に維持することができる翼止板が得られる。
また、幾つかの実施形態によれば、簡単に動翼を軸方向溝に組付け固定することができ、タービンロータ組立体を容易に製造することができる。
図1に、第1実施形態に係るタービンロータ組立体1を示す。タービンロータ組立体1は、例えば軸流タービンに搭載されるもので、ロータディスク2と、ロータディスク2の外周に形成される複数の軸方向溝3(図3参照)と、ロータディスク2の周方向に沿って配列されて、翼止板4を介して軸方向溝3内に植設された動翼群5nと、を具備する。
そしてかかる折り曲げ部42、42のうち少なくとも一方の折り曲げ部42は、ロータディスク2の半径方向の外側と内側とに指向して基部41から突出する内外折り曲げ部(外折り曲げ部42o及び内折り曲げ部42i)を有する。外折り曲げ部42oは、折り曲げ部42と基部41との境界位置にある折り曲げ線にて翼止板4を折り曲げた際にロータディスク2の半径方向外側に指向して基部41から突出するようになっている。一方、内折り曲げ部42iは、折り曲げ部42と基部41との境界位置にある折り曲げ線にて翼止板4を折り曲げた際に、ロータディスク2の半径方向内側に指向して基部41から突出するようになっている。なお、図2に示す例示的な実施形態では、翼止板4は、一対の内折り曲げ部42iを有する。
図3に示すように、先ず、ロータディスク2に動翼5を組み付けるのに先立って、ロータディスク2の外周に列設された軸方向溝3に翼止板4を装着する。
翼止板4は、第1工程として各軸方向溝3に対して装着するために、折り曲げ部42と基部41との境の折り曲げ線にて翼止板4を折り曲げられる。この際、基部41の折り曲げ部42、42のうち、外折り曲げ部42oと内折り曲げ部42iとを備えた折り曲げ部42を半径方向の外側に折り曲げるようにする。このことにより、外折り曲げ部42oは、半径方向の外側に突出し、内折り曲げ部42iは半径方向の内側に突出する。
また、軸方向溝3に基部41を嵌合すると、折り曲げ部42の外側折り曲げ部42oと、一対の内側折り曲げ部42iとが、ロータディスク2の軸方向端面に当接した状態となり、外側折り曲げ部42oのみが当接するより広い面積で軸方向端面を支えることができ、動翼5にかかるずれ力に対抗して、好適に動翼5を支えることができる。なお、このとき、翼止板4におけるもう一方の折り曲げ部42は、折り曲げられていない状態にある。
特に、作動流体がタービン動翼群5nを上流側から下流側へ通過する際に動翼5の翼部53にかかる外力に対しては、下流側において、動翼5は、下流側での外側折り曲げ部42oと、内側折り曲げ部42iとが、ロータディスク2の軸方向端面に当接した状態であるので、外側折り曲げ部42oのみが当接する場合より広い面積で、動翼5にかかるずれ力に対抗することができ、好適に動翼5を支えることができる。
本発明は、第2実施形態によっても実施することができる。
第2実施形態では、図7に示すように、翼止板4は、軸方向溝3から軸方向に突出した端部のうち、第1実施形態のように一方の折り曲げ部42だけが、半径方向の外側に突出する外折り曲げ部42oと、半径方向の内側に突出する内折り曲げ部42iとを有する。また、他方の折り曲げ部、すなわち、ロータディスク2軸方向上流側にセットされる折り曲げ部42は、外折り曲げ部42oに、外折り曲げ部42oの長手方向に突出される突出部である第2内折り曲げ部42i2を有している。
すなわち、軸方向溝3に対する装着前に一方の折り曲げ部42と基部41との境の折り曲げ線にて翼止板4を折り曲げ(第1工程)、この状態の翼止板4を軸方向溝3の上方から挿入し(第2工程)、翼止板4の折り曲げられていない方の端部側から動翼5の翼根51を軸方向溝3に挿入して嵌合し(第3工程)、翼止板4の折り曲げられていない他方の折り曲げ部42を径方向外側に折り曲げる(第4工程)。そして、最終的に、他方の折り曲げ部42の第2折り曲げ部42i2を径方向内側に折り曲げる。
こうして、第2内折り曲げ部42i2は径方向内側に指向して突出する突出部として、ロータディスク2の軸方向端面に当接した状態となり、動翼5の翼根51と軸方向溝3との嵌合部位が翼止板4の双方の折り曲げ部42、42によって挟持された状態となって、少なくともロータディスク2の軸方向にかかる外力に対して、さらにずれ止めの効果を高めるものとなる(図9参照)。
2 ロータディスク
3 軸方向溝
4 翼止板
41 基部
42 折り曲げ部
42o 外折り曲げ部
42i 内折り曲げ部
42i2 第2内折り曲げ部
5 動翼
5n 動翼群
51 翼根
52 翼部台部
53 翼部
Claims (5)
- ロータディスクと、該ロータディスクの外周に形成される複数の軸方向溝と、前記ロータディスクの周方向に沿って配列され、翼止板を介して前記軸方向溝内に植設された動翼群と、を具備するタービンロータ組立体であって、
前記翼止板は、
前記軸方向溝内に嵌合する基部と、
該基部の両端において前記軸方向溝から軸方向に突出するように設けられ、前記ロータディスクの径方向に折り曲げられて前記ロータディスクの軸方向端面に当接する折り曲げ部と、を備え、
前記両端の少なくとも一方の前記折り曲げ部は、前記ロータディスクの半径方向の外側と内側とに指向して前記軸方向端面に突出される内外折り曲げ部を備えている、ことを特徴とするタービンロータ組立体。 - 前記内外折り曲げ部は、少なくとも、動翼群を通過する作動流体の下流側に配置されている、ことを特徴とする請求項1記載のタービンロータ組立体。
- 前記内外折り曲げ部の径方向外側折り曲げ部は回転軸方向視において略方形状に形成され、径方向内側折り曲げ部は、前記外側折り曲げ部から内側に向けて突出する突出部が形成されている、ことを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載のタービンロータ組立体。
- ロータディスクと、該ロータディスクの外周に形成される複数の軸方向溝と、前記ロータディスクの周方向に沿って配列され、翼止板を介して前記軸方向溝内に植設された動翼群と、を具備するタービンロータ組立体において、前記動翼群を翼根を介して前記ロータディスクに固定するタービンロータ組立体における翼止板であって、
前記軸方向溝の溝長に対応した長さを有し、前記軸方向溝内に嵌合するように構成された基部と、
該基部の両端に設けられ、前記基部との間の境界位置において折り曲げられることで前記ロータディスクの軸方向端面に当接するように構成された一対の端部と、を備え、
前記一対の端部のうち少なくとも一方の端部は、該端部と前記基部との前記境界位置から前記基部内側への突出部を備えた、
ことを特徴とするタービンロータ組立体における翼止板。 - 請求項1に記載のタービンロータ組立体を組み立てるに当たり、
前記翼止板の一方の端部を、半径方向の外側に折り曲げることで外側と内側とに突出する前記内外折り曲げ部を形成する第1工程と、
前記翼止板における前記基部を前記軸方向溝内に、上方から嵌め込む第2工程と、
動翼の翼根を前記軸方向溝に他方の端部側から挿入する第3工程と、
該他方の端部を折り曲げて、前記翼止板を介して動翼を前記軸方向溝に固定する第4工程と、
を具備する、ことを特徴とする、タービンロータ組立体における翼止板の組付け方法。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14864540.1A EP3023590A4 (en) | 2013-11-20 | 2014-07-29 | TURBINE ROTOR ASSEMBLY, TURBO ROTOR PLATE FOR TURBINE ROTOR ASSEMBLY AND METHOD FOR MOUNTING A PLATE OF PLATE |
| CN201480046021.5A CN105473824A (zh) | 2013-11-20 | 2014-07-29 | 涡轮机转子组装体和涡轮机转子组装体的叶片止动板以及叶片止动板的组装方法 |
| KR1020167003952A KR20160030314A (ko) | 2013-11-20 | 2014-07-29 | 터빈 로터 조립체 및 터빈 로터 조립체에 있어서의 블레이드 정지판 그리고 블레이드 정지판의 설치 방법 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013-239794 | 2013-11-20 | ||
| JP2013239794A JP5999845B2 (ja) | 2013-11-20 | 2013-11-20 | タービンロータ組立体およびタービンロータ組立体における翼止板並びに翼止板の組付け方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015075970A1 true WO2015075970A1 (ja) | 2015-05-28 |
Family
ID=53179249
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/069897 WO2015075970A1 (ja) | 2013-11-20 | 2014-07-29 | タービンロータ組立体およびタービンロータ組立体における翼止板並びに翼止板の組付け方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3023590A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5999845B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20160030314A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN105473824A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015075970A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114076000A (zh) * | 2020-08-17 | 2022-02-22 | 中国航发商用航空发动机有限责任公司 | 叶片轴向限位装置、叶盘结构以及燃气轮机 |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6499777B2 (ja) * | 2016-01-13 | 2019-04-10 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | 翼引き抜き装置及び方法 |
| FR3057908B1 (fr) * | 2016-10-21 | 2019-11-22 | Safran Aircraft Engines | Ensemble rotatif d'une turbomachine muni d'un systeme de maintien axial d'une aube |
| WO2020202364A1 (ja) | 2019-03-29 | 2020-10-08 | 平田機工株式会社 | 測定装置 |
| EP3922402A4 (en) | 2019-03-29 | 2022-02-09 | Hirata Corporation | MANUFACTURING SYSTEM |
| JP7104240B2 (ja) | 2019-03-29 | 2022-07-20 | 平田機工株式会社 | 装着装置 |
| CN110259521A (zh) * | 2019-07-31 | 2019-09-20 | 中国科学院工程热物理研究所 | 一种用于叶轮机械的叶片保持器 |
| JP7416674B2 (ja) * | 2020-08-25 | 2024-01-17 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | タービンの組立方法、タービンの組立支援プログラム、及びタービンの組立支援装置 |
| CN112096653B (zh) * | 2020-11-18 | 2021-01-19 | 中国航发上海商用航空发动机制造有限责任公司 | 叶片缘板、叶片环、叶轮盘以及燃气涡轮发动机 |
| CN113478180B (zh) * | 2021-07-15 | 2022-11-25 | 重庆江增船舶重工有限公司 | 一种增压器锁紧片的加工方法及其翻边工具 |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2801074A (en) * | 1952-10-01 | 1957-07-30 | United Aircraft Corp | Blade retaining means |
| JPH0414702U (ja) * | 1990-05-24 | 1992-02-06 | ||
| JPH0514501U (ja) | 1991-08-01 | 1993-02-26 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 流体機械の動翼 |
| JPH0618601U (ja) * | 1992-08-10 | 1994-03-11 | 石川島播磨重工業株式会社 | タービン動翼のダンパー |
| JPH10317907A (ja) * | 1997-05-22 | 1998-12-02 | Hitachi Ltd | 圧縮機翼固定構造 |
| JP2001115801A (ja) * | 1999-08-31 | 2001-04-24 | General Electric Co <Ge> | タービン用の非一体型釣合カバープレートおよびそのセンタリング溝 |
| JP2009024698A (ja) * | 2007-07-19 | 2009-02-05 | General Electric Co <Ge> | 押付けプレートシール |
| JP4315801B2 (ja) | 2001-07-03 | 2009-08-19 | アーベーベー・ターボ・ジステムス・アクチエンゲゼルシヤフト | 軸流ターボ機械の動翼のための固定システム |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3045329A (en) * | 1959-07-30 | 1962-07-24 | Gen Electric | Method for assembling tongue-and-groove members with locking keys |
| DE19757188A1 (de) * | 1997-12-22 | 1999-06-24 | Asea Brown Boveri | Einrichtung zur Befestigung der Laufschaufeln einstufiger Axialturbinen |
| FR2921409B1 (fr) * | 2007-09-25 | 2009-12-18 | Snecma | Clinquant pour aube de turbomachine. |
-
2013
- 2013-11-20 JP JP2013239794A patent/JP5999845B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-07-29 CN CN201480046021.5A patent/CN105473824A/zh active Pending
- 2014-07-29 KR KR1020167003952A patent/KR20160030314A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2014-07-29 WO PCT/JP2014/069897 patent/WO2015075970A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2014-07-29 EP EP14864540.1A patent/EP3023590A4/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2801074A (en) * | 1952-10-01 | 1957-07-30 | United Aircraft Corp | Blade retaining means |
| JPH0414702U (ja) * | 1990-05-24 | 1992-02-06 | ||
| JPH0514501U (ja) | 1991-08-01 | 1993-02-26 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 流体機械の動翼 |
| JPH0618601U (ja) * | 1992-08-10 | 1994-03-11 | 石川島播磨重工業株式会社 | タービン動翼のダンパー |
| JPH10317907A (ja) * | 1997-05-22 | 1998-12-02 | Hitachi Ltd | 圧縮機翼固定構造 |
| JP2001115801A (ja) * | 1999-08-31 | 2001-04-24 | General Electric Co <Ge> | タービン用の非一体型釣合カバープレートおよびそのセンタリング溝 |
| JP4315801B2 (ja) | 2001-07-03 | 2009-08-19 | アーベーベー・ターボ・ジステムス・アクチエンゲゼルシヤフト | 軸流ターボ機械の動翼のための固定システム |
| JP2009024698A (ja) * | 2007-07-19 | 2009-02-05 | General Electric Co <Ge> | 押付けプレートシール |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP3023590A4 * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114076000A (zh) * | 2020-08-17 | 2022-02-22 | 中国航发商用航空发动机有限责任公司 | 叶片轴向限位装置、叶盘结构以及燃气轮机 |
| CN114076000B (zh) * | 2020-08-17 | 2024-05-07 | 中国航发商用航空发动机有限责任公司 | 叶片轴向限位装置、叶盘结构以及燃气轮机 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3023590A1 (en) | 2016-05-25 |
| EP3023590A4 (en) | 2016-09-07 |
| KR20160030314A (ko) | 2016-03-16 |
| JP5999845B2 (ja) | 2016-09-28 |
| JP2015098848A (ja) | 2015-05-28 |
| CN105473824A (zh) | 2016-04-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2015075970A1 (ja) | タービンロータ組立体およびタービンロータ組立体における翼止板並びに翼止板の組付け方法 | |
| KR101706379B1 (ko) | 이탈 방지 에어 포일 저널 베어링 | |
| JP4646159B2 (ja) | ロータにおける動翼の軸方向固定装置とその利用方法 | |
| JP5628190B2 (ja) | リングセグメントの位置決め部材 | |
| JP6527959B2 (ja) | タービンブレードのための固定デバイスを有するブレード締結機構 | |
| JP2006002762A (ja) | 送風機 | |
| JP2011102585A (ja) | 円周方向差込み型翼形部取付けシステム用の固定保持用スペーサ組立体 | |
| JP2015098848A5 (ja) | ||
| RU2016147075A (ru) | Способ сборки ступени статора газотурбинного двигателя | |
| US9951648B2 (en) | Guide blade ring for an axial turbomachine and method for designing the guide blade ring | |
| JP2016205402A (ja) | 翼止板 | |
| KR20160058929A (ko) | 너트 및 회전 기계 | |
| JP5449976B2 (ja) | 軸シール装置およびタービン装置並びに軸シール装置間隙調整方法 | |
| JP5149831B2 (ja) | タービン動翼の固定構造及びタービン | |
| JP5032597B2 (ja) | シール | |
| JP6476384B2 (ja) | レゾルバ | |
| WO2016132966A1 (ja) | タービン用シール装置及びタービン、並びにシール装置用の薄板 | |
| US9151163B2 (en) | Turbomachine rotor disk | |
| US20140308134A1 (en) | Turbomachine vane cooperating with a vane retention disk | |
| GB2566635A (en) | Assembly for attaching a nozzle to a structural element of a turbine engine | |
| JP6257991B2 (ja) | 動翼及び回転機械 | |
| JP2018003643A (ja) | バランスウェイトを備えたタービンロータ、及びバランスウェイト | |
| AU2018264866B2 (en) | Pin to reduce relative rotational movement of disk and spacer of turbine engine | |
| US20150003979A1 (en) | Steam turbine nozzle vane arrangement and method of manufacturing | |
| JP6276209B2 (ja) | タービン用シール装置及びタービン、並びにシール装置用の薄板 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201480046021.5 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14864540 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20167003952 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014864540 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014864540 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |