WO2015037682A1 - ネットワーク接続システム及びその方法 - Google Patents
ネットワーク接続システム及びその方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015037682A1 WO2015037682A1 PCT/JP2014/074146 JP2014074146W WO2015037682A1 WO 2015037682 A1 WO2015037682 A1 WO 2015037682A1 JP 2014074146 W JP2014074146 W JP 2014074146W WO 2015037682 A1 WO2015037682 A1 WO 2015037682A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- application
- network connection
- information terminal
- portable information
- communication
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/24—Traffic characterised by specific attributes, e.g. priority or QoS
- H04L47/2408—Traffic characterised by specific attributes, e.g. priority or QoS for supporting different services, e.g. a differentiated services [DiffServ] type of service
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/20—Traffic policing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/24—Traffic characterised by specific attributes, e.g. priority or QoS
- H04L47/2475—Traffic characterised by specific attributes, e.g. priority or QoS for supporting traffic characterised by the type of applications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/60—Network streaming of media packets
- H04L65/75—Media network packet handling
- H04L65/765—Media network packet handling intermediate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L65/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services for supporting real-time applications in data packet communication
- H04L65/80—Responding to QoS
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a network connection system used in a mobile network, and more particularly to a network connection system for specifically controlling priority / band control of a connection communication band of a specific application installed in a terminal device on a mobile network and the same It is about the method.
- application software is configured to connect to a specific service server placed on the Internet and receive various information from the service server to present information requested by the user on the smartphone. .
- IP packets from application software are transferred on a best effort basis, and the IP packets cannot be preferentially controlled so as to be selected for each application. Therefore, for example, control of giving priority to communication of application software that handles voice information such as an IP phone cannot be performed over other application software, leading to dissatisfaction with smartphone users.
- IP address of a specific smartphone in the router it is possible to set the IP address of a specific smartphone in the router in advance and preferentially control the connection from that smartphone, but in that case, not only the IP phone but also the connection of all applications of that smartphone is prioritized. Will be.
- preferentially control only connections addressed to a specific service server for example, recent IP telephone services are provided in cooperation with a plurality of servers. It is difficult to grasp all the IP addresses and set them in the router in advance.
- the present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and provides a high-quality service with a very simple configuration even when a plurality of different applications are executed on a portable information terminal.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a network connection system that can be used.
- a bandwidth control router placed between a mobile network and the Internet
- a network connection system configured such that a plurality of application software installed in a mobile information terminal on a mobile network is connected to a service server on the Internet via the bandwidth control router,
- This system An application communication environment management server provided on the Internet, which detects the type of application trying to connect to the service server from a specific portable information terminal, and determines a connection policy (bandwidth control, priority communication) according to the type of application.
- the bandwidth control router is configured to transfer packets from the specified portable information terminal with priority control or a predetermined priority communication bandwidth according to a connection policy received from the application communication environment management server.
- a network connection system is provided.
- the application connection server displays the detection of the type of application that is going to connect to the service server from a specific portable information terminal as the frontmost display on the portable information terminal. This is done by receiving the type of application that is running.
- the application connection server includes, in a packet transmitted from the mobile information terminal, detection of the type of application that is going to connect to the service server from a specific mobile information terminal. This is based on the tag to be used.
- the tag is a process ID of the application generated by an OS of the portable information terminal or an identifier related to the process ID.
- the bandwidth control router sets different IP addresses or / and port numbers for each application included in the packet. Accordingly, according to an individual connection policy, the packet from the specified portable information terminal is transferred with priority control or a predetermined priority communication band.
- the bandwidth control router when a plurality of types of the applications are detected at the same time, the IP address or / and the port number for each application included in the packet Accordingly, the packet from the specified portable information terminal is transferred with priority control or a predetermined priority communication band according to the individual connection policy.
- the application connection environment management server refers to a table storing a type of application to be preferentially connected or bandwidth controlled and a connection policy of the application. A connection policy corresponding to the type of software is extracted from the table and transmitted to the bandwidth control router.
- the connection policy includes a setting of a communication priority or a communication band that is different for each specific application.
- the system of the present invention monitors the data communication amount of each portable communication terminal by the bandwidth control router, and downloads for each application according to the type of application active in the portable information terminal.
- a data communication amount recording unit for recording the data communication amount;
- a traffic volume upper limit determination unit that determines whether the data traffic volume for each application recorded by the data traffic volume recording unit has reached a predetermined upper limit value.
- the system preferably includes a communication limiting unit that limits packet transfer from the portable information terminal by the bandwidth limiting router in accordance with the determination by the communication amount upper limit determination unit.
- a line communication congestion level for each application is calculated, and a congestion level display interface for displaying the congestion level to a user who generates the congestion level is generated. It is preferable to have a congestion degree display portion. Further, it is preferable to have a communication amount display unit for generating a data communication amount display interface for displaying the data communication amount for each application recorded by the data communication amount recording unit to the user. Furthermore, it is preferable to charge the user based on the data communication amount for each application recorded by the data communication amount recording unit.
- connection policy includes a setting of a data compression degree that differs for each specific application.
- the system of the present invention includes a data conversion method setting in which the data compression degree of the connection policy differs for each specific application.
- the connection policy includes a setting of a time zone and a location where communication is possible for each specific application.
- the information specifying the mobile information terminal is an IP address of the information mobile terminal.
- the system of the present invention includes a user billing information acquisition unit that receives user billing information and associates it with a portable information terminal.
- the type of application received from the portable information terminal specifies the type of service provided by the application.
- the system of the present invention generates a setting interface for setting a connection condition for a user and sets the setting through the interface.
- the application software to be preferentially connected or the type of service provided by the application software includes at least application software or service for voice call.
- the system of the present invention is installed in the portable information communication terminal, and causes the portable information terminal to detect the type of application that is actively displayed on the display of the portable information terminal.
- the system of the present invention comprises means for detecting a process ID of an application installed on the portable information communication terminal and started on the portable information terminal.
- it includes an application management software program that includes a specific tag that is different for each process, and has a means for transmitting the information to the bandwidth control system together with information for specifying the portable state terminal.
- the system of the present invention is installed in the portable information communication terminal, Means for causing the portable information terminal to detect an IP address or / and a port number of an application started on the portable information terminal; for allowing the portable information terminal to uniquely identify the portable information terminal on a communication network; Means for acquiring the portable information terminal specifying information; and including the IP address and / or port number in a packet transmitted from the application in the portable information terminal, together with information for specifying the portable state terminal, the band control system And having an application management software program having means for transmitting the data.
- the system of the present invention is installed in the portable information communication terminal, and causes the portable information terminal to receive a communication state for each application from the bandwidth control system.
- An application management software program having means for displaying on a display is provided.
- a plurality of application software having a bandwidth control router placed between a mobile network and the Internet and installed in a portable information terminal on the mobile network is provided with the bandwidth
- the type of application to be connected to the server from the information terminal is detected, and the connection policy (control bandwidth, compression presence / absence, etc.) according to the type of application software and the band (information such as IP address) specifying the portable information terminal Process to send to control router
- the bandwidth control router preferentially controls the packet from the specified portable information terminal according to the connection policy (control bandwidth, compression presence / absence, etc.) received from the application connection environment management server. And a transferring method.
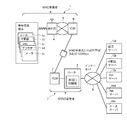
- FIG. 1 is an overall schematic configuration diagram showing a data communication environment through a mobile network.
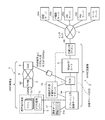
- FIG. 2 is an overall schematic configuration diagram showing a data communication environment according to an embodiment of the present invention.
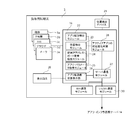
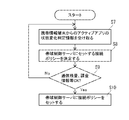
- FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing the application management software.
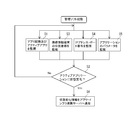
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing processing steps of the application management software.
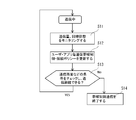
- FIG. 5 is a schematic configuration diagram showing the application / infrastructure cooperation server.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing processing steps of the application / infrastructure cooperation server.
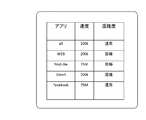
- FIG. 7 is also a conceptual diagram for explaining a band control connection policy.
- FIG. 8 is also a conceptual diagram for explaining a band control connection policy.
- FIG. 9 is also a conceptual diagram for explaining a band control connection policy.
- FIG. 10 is also a conceptual diagram for explaining a band control connection policy.
- FIG. 10 is also a conceptual diagram for explaining a band control connection policy.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing processing steps of the application / infrastructure cooperation server.
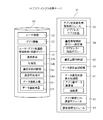
- FIG. 12 is also a diagram showing an example of a display screen of the portable information terminal.
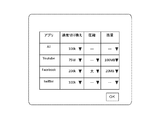
- FIG. 13 is also a view showing a display screen example of the portable information terminal.
- FIG. 14 is also a flowchart showing a charging process performed by the charging server.
- FIG. 15 is a schematic diagram illustrating a bandwidth control method according to another embodiment.
- a network connection system including a bandwidth control router is a virtual mobile network operator (Mobile Virtual Network).
- Mobile Virtual Network An example provided by an operator (hereinafter referred to as “MVNO operator”) will be described.
- An MVNO operator does not own a physical mobile line network called a mobile network, but borrows it from a mobile communication operator (Mobile Network Operator, hereinafter referred to as “MNO operator”).
- MNO operator Mobile Network Operator
- FIG. 1 Data communication environment as a premise of the present invention
- a mobile network of the MNO operator is indicated by 1 in the figure
- a network connection system of the MVNO operator is indicated by 2.
- the service gateway 6 (SGW) on the MVO operator side is connected to the MVNO operator side. It is routed to the network connection system 2 of the MVNO operator via the packet data network gateway 7 (PGG), and then connected to various servers 10a to 10e on the Internet by the router 8 provided in the network connection system 2. It has become. Between the service gateway 6 on the MVO carrier side and the packet gateway 7 on the MVNO carrier side, a communication band based on a contract between the MVO carrier and the MVNO carrier, for example, 100 Mbps is secured. Yes.
- the user's portable information terminal 3 is a so-called smartphone, and has a CPU, a RAM, and a ROM (not shown).
- the operating system software program (hereinafter referred to as “OS”) such as iOS (trade name) and Android (trade name) and various application software programs (hereinafter simply referred to as “applications”) 3a to 3e are installed in the ROM.
- OS operating system software program
- applications application software programs
- data used by these OS and applications 3a to 3e is stored.
- the applications 3a to 3e installed in the user's portable information terminal 3 include video software 3a, IP phone 3b, SNS 3c, browser 3d, mailer 3e, etc., but the user can freely add additional applications according to his / her preference. It can be installed.
- the applications 3a to 3e on the portable information terminal 3 are appropriately called and expanded and executed on the RAM by the CPU, so that the mobile network 5 of the MNO carrier and the network connection system 2 of the MVNO carrier are used.
- various processes are performed by connecting to various servers 10a to 10e on the Internet 9 and performing necessary data communication with these servers 10a to 10e as appropriate.
- the router 8 provided in the network connection system 2 appropriately sends the packets 3a to 3e to the destination servers 10a to 10e based on the destination IP address included in the header information of the packet from the portable information terminal 3. It is supposed to transfer.
- the router 8 has a bandwidth control function 12 for controlling the transfer order and transfer speed of packets passing based on the IP address of the portable information terminal 3.
- the bandwidth control function is also called a QoS function, and can be roughly classified into “priority control” and “bandwidth control”.
- the priority control method is a method of distinguishing application types based on transmission source IP addresses for packets flowing on the network, and assigning absolute priority for each application. This is a method of assigning an upper limit of a communication band that can be used for each application.
- high priority application packets are always output with priority, or a larger communication bandwidth can be used, and packets related to high priority services can be transferred stably. Is possible.
- the router 8 needs to specify only the IP packets of the moving image software and the IP phone from the received many packets. The identification of this IP packet is generally performed based on the IP address and transfer port number of the source and destination.
- the target packet can be reliably identified by specifying the IP address of the terminal device at the source. It is done.
- this method cannot be used in the case where a plurality of apps with different priorities are running on the same terminal, such as the portable information terminal 3 described above. That is, if it is attempted to identify a packet using only IP address information, priority control / bandwidth control is performed even for communications that do not need to be prioritized. Further, in an environment in which an IP address is automatically allocated to a portable information terminal by DHCP, it is impossible to determine which terminal is the original by looking at the IP address.
- the application type may be identified based on the IP addresses of the destination servers 10a to 10e. For example, when a packet from the portable information terminal 3 is always connected to a specific IP telephone server 10b, the service type to which the target packet belongs can be assured by specifying the IP address of the IP telephone server 10b. Can be distinguished. However, some recent applications connect to many different servers in one application, and it has been difficult and practically impossible to specify addresses of all these servers.
- the system 2 of the MVNO operator has the present invention in addition to the bandwidth control router 8 having basically the same configuration and function as shown in FIG.
- Application / infrastructure cooperation server 14 (“application connection environment management server” of the present invention) corresponding to the functions of the network, line status / use amount sensing server 15 for monitoring the line market status, and charging according to the bandwidth used. It has a billing server 17 to be managed, a compression conversion proxy server 19, and application management software 16 installed in the portable information terminal 3.
- the system 2 on the MVNO provider side including the bandwidth control router 8 is referred to as a “bandwidth control system”.
- the application management software 16 is installed in the portable information terminal 3.
- the application management software 16 stores information on the types of applications 3a to 3e activated on the portable information terminal 3 together with the IP address / port number for identifying the portable state terminal 3 in the application / infrastructure linking server. 14 is transmitted.
- the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14 is provided in the system 2 of the MVNO operator and is designed to cooperate with the application management software 16 installed in the portable information terminal 3.
- the type of the applications 3a to 3e active on the information terminal 3 is detected, and the connection policy corresponding to the type of the applications 3a to 3e is sent to the bandwidth control router 8 together with the IP address / port number for specifying the portable information terminal 3 Has the function to set.
- the bandwidth control router 8 transfers packets from the specified mobile information terminal 3 with priority control or a predetermined priority communication bandwidth in accordance with the connection policy received from the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14. As a result, communication is performed with priority control according to the types of the applications 3a to 3e or with a predetermined priority communication band.
- the line status / usage monitoring server 15 monitors packets passing through the packet gateway 7 (PGW) provided in the system 2 on the MVNO provider side, and associates them with the IP address / port number of the portable information terminal 3. The amount of data communication is output and notified to the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14.
- PGW packet gateway 7
- FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing the portable information terminal 3 of the user.
- an OS (not shown), a plurality of different applications 3a to 3e, and application management software 16 of the present invention are installed.
- the application management software 16 includes an application detection module 22 that detects that a specific application is activated and activated in cooperation with an OS (not shown) of the portable information terminal 3, and a GPS or the like mounted on the portable information terminal 3.
- a position detection module 23 that detects the geographical position of the portable information terminal 3 in cooperation with the position detection device 21, and a terminal IP address / port number that detects the IP address and port number of the portable information terminal 3 in cooperation with the OS.
- the communication state of the active application of the mobile information terminal 3, the communication state of each application received from the server 14, and the line congestion state are transmitted to the server communication module 27 that transmits the state change determined by the mobile application state change determination module 25.
- an application communication state display unit 28 that displays on the display screen 29 of the portable information terminal 3.
- the application management software 16 is implemented in the form of an API for the OS.
- Reference numerals S1 to S6 in the figure are for referring to the steps, and correspond to steps S1 to S6 in the following description.
- the application activation detection module 22 is activated, and any of the applications 3a to 3e installed in the portable information terminal 3 is activated and activated on the display screen 29 of the portable information terminal 3 Is monitored (step S1 shown in the figure).
- “active” means that the activated application is displayed on the foreground of the display screen 29 of the terminal 3 and acquires the user's focus.
- the application activation detection module 22 monitors whether the application is active at certain time intervals or whether another application is activated and activated. When a specific application is active, the application activation detection module 22 outputs an application name (a unique name of an application output by the OS) and sends it to the active application state change determination module 26.
- the active application state change determination module 26 determines that the “active application state change” has occurred when the application name received from the application activation detection module 22 changes, that is, when the active application changes ( Step S2).
- the position detection module 23 monitors the signal from the location signal detection device 21 (step S3), and sends the current position coordinates of the mobile information terminal 3 to the active application state change determination module 26.
- the active application state change determination module 26 determines that an “active application state change” has occurred when the position coordinate information received from the position detection module fluctuates more than a certain value or when a certain condition is met (step S2).
- the terminal IP address / port number detection module 24 monitors the current IP address of the portable information terminal 3 and the number of the communication port currently used in conjunction with the communication module 30 of the portable information terminal 3.
- the acquired information is sent to the state change determination module 26 of the active application.
- the active application state change determination module 26 determines that an “active application state change” has occurred when the IP address or port name received from the terminal IP address / port number detection module changes (step S2).
- the application / parameter acquisition module 25 is linked with a specific application, acquires parameters associated with the application (step S5), and sends the parameters to the active application state change determination module 26.
- a connection destination URL corresponds to a browser
- a connection destination telephone number corresponds to an IP phone.
- the active application state change determination module 26 determines that “active application state change” has occurred when the parameter fluctuates (step S2).
- step S6 When the state change determination module 26 of the active application determines whether it is a “state change of the active application” based on the information received from each of the modules 22 to 25 as described above, Only the determination result is sent to the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14 (step S6).
- FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram showing a configuration of the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14 that receives the state change state.
- the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14 has an OS, RAM, various input / output interfaces (not shown), and a data storage unit 30 and a program storage unit 31 shown in FIG.
- the data storage unit 30 stores user information 32, application information 33 for bandwidth control in this system, and a user / application bandwidth control connection policy 34 set based on the terminal state change determination information. Yes.
- the application state change information acquisition module 36 that receives change information of the communication state of the application on the terminal 3 from the portable information terminal 3, and the information acquired by the application state change information acquisition module 36 Based on the policy setting unit 38 that acquires the communication band control / connection policy 34 for each user / application and transmits it to the communication band control router 8, and acquires the communication volume of the terminal 3 from the line status / usage sensing server 15.
- a data communication amount recording unit 39 stored in the data storage unit 30 in association with the user / application, and a communication upper limit for determining the communication upper limit by applying the communication amount for each application to the communication bandwidth control connection policy for each user / application.
- the application management software communication module 42 communicates with the server communication module 27, whereby communication with the portable information terminal 3 is performed.
- the application state change information acquisition module 36 receives the state change information transmitted from the application management software 16 of the portable information terminal 3 through the application management software communication module 42.
- this state information includes the application name, domain name base, coordinate position, application parameters of the application that is active on the user's terminal 3, and the IP address / port number used of the portable terminal 3.
- the communication band control policy setting unit 38 sets a control band connection policy for each user / application based on the state change information.
- the user information 32 (FIG. 5) is information for associating the portable information terminal 3 with the attributes of the user. Examples of such user information include the IP address and port number received from the terminal 3 above. Can be stored, and information on whether the user has a specific contract regarding the communication band can be included. When the specific contract is charged, the charging server 17 performs charging processing for the user through the charging processing module 43 as will be described later.
- the communication band control policy setting unit 38 recognizes that the state change information received from the terminal 3 is linked to a specific user by the user information 32.
- the application information 33 (FIG. 5) stores identification information of a specific application to be bandwidth controlled in this system.
- the application information 33 stores identification information of a specific application to be bandwidth controlled in this system.
- only a part of applications installed in the portable information terminal 3 are identified and band control connection is made, and the application name of band control target is registered in the application information 33.
- information unique to the application information 33 is recognized in the application information 33 so as to recognize each software of a web browser, YouTube, Gmail, Facebook, Twitter, Yahoo (all are registered trademarks) and 050 (IP phone). Is stored.
- the communication band control policy setting unit 38 recognizes whether the application is a control target application based on the application information 33.
- the communication bandwidth control policy setting unit 38 specifies the connection policy for each user / application from the postscript bandwidth control connection policy 34 for each user / application by referring to the state change information, the user information 32, and the application information 33. Then, it is set in the bandwidth control router 8 (the compression degree is the compression conversion proxy 19 (hereinafter, description of the setting of the compression conversion proxy 19 is omitted as being included in the bandwidth control setting)).
- the specific connection policy 34 includes a communication band 34a, a data compression degree 34b, a communicable time zone 34c, a communicable place 34d, a data communication amount upper limit 34e, and a data communication remaining amount 34f.
- FIG. 7 to 10 are schematic diagrams for explaining the concept of the connection policy set in this embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a conceptual diagram showing an example of policy setting related to the user application and the line speed (communication bandwidth) (34a).
- the default connection speed (connection bandwidth) other than the specific application described above is set to 100 kbps, and the LTE speed is set for the specific application.
- connection bandwidth connection bandwidth
- the LTE speed is set for the specific application.
- mobile connection is not permitted, and only WiFi connection is possible.
- FIG. 8 is a conceptual diagram showing an example of policy setting related to the user application and the remaining download amount (34e, 34f) for each application.
- the default is unlimited, a specific application whose connection speed is set to the LTE speed is initially set to 100 MB.
- the user can set an option to increase the upper limit, and in this case, the billing server 17 can perform billing processing for the usage exceeding the initial setting. ing.
- the billing method is not limited to this, and various methods can be adopted.
- the main connection policy is to set the line speed (bandwidth control) and the remaining download amount as described above.
- various policies can be set. FIG. 9 comprehensively shows such examples.
- bandwidth control based on parameters specific to the application can be performed.
- a line speed is defined for each connection destination URL of the browser. This information is also stored in the data storage unit 30 as the connection policy 34.
- the server 14 receives the state change signal received from the application management software 16 by the application state change information acquisition module 36. (Step S7), identifies the user from the IP address and port number, applies the application name and user name to the user information 32, application information 33 and policy 34, and identifies the connection policy for the application (step S7). S8).
- connection policy shown above as a default is set
- the communication speed is 100 kbps
- the communication upper limit is set to unlimited regardless of the location and time.
- the connection policy specified by the YouTube in FIG. 9 is specified (step S8).
- the communication band control policy setting unit 38 checks other conditions, in this embodiment, the remaining communication amount (step S9). If the condition is cleared, the connection policy determined above is sent to the band control router 8. Transmit and set (step S10). This policy is set in the bandwidth control router 8 together with information for specifying the terminal 3, in this example, an IP address and a port number.
- the bandwidth control router 8 executes bandwidth control based on the connection policy corresponding to the IP address and port number of the transmission source included in the packet.
- the bandwidth control router 8 performs bandwidth control for all packets from the specific portable information terminal 3 at a time, and the bandwidth based on the application (in this case, the YouTube) that the user is actively using at that time. As a result, the speed band that matches the type of application is secured.
- the time lag from when the user switches the active application on the terminal 3 to when the bandwidth control is set becomes important.
- the time lag is 10 seconds or less. Yes, a new band will be set while the application is loaded, so the user will not experience the set delay. (Operation during bandwidth control communication)
- the operation of the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14 during the bandwidth control communication will be described with reference to FIG.
- the data communication amount recording unit 39 (shown in FIG. 5) of the server 14 monitors the communication state through the line status / use amount sensing server 15, and the unit time of the portable information terminal 3 of the specific user.
- Each traffic volume is recorded in association with the application that is communicating at that time (steps S11 and S12). As shown in the schematic diagram of FIG. 8, this recording is executed by appropriately updating the communication remaining amount (currently 50 MB in the example of the YouTube) of the communication band control connection policy 34 for each user / application.
- the communication upper limit determination unit 40 determines whether or not the remaining communication capacity of the user / application communication bandwidth control connection policy 34 has reached the upper limit (1G in the example of the YouTube) (step S13). If the current communication is continued and reached, the bandwidth control is returned to the default value and set in the control bandwidth server (step S14). As a result, the priority bandwidth control (75 Mbps in this example) of the application (in this example, youtube) is terminated, and the default (default) line speed is limited to 100 kbps.
- the data communication state display processing unit 41 shown in FIG. 5 has a function of presenting the data communication amount and the line congestion level for each application to the user's portable information terminal 3. Specifically, the data communication state display processing unit 41 transmits time series data for each application to be presented to the user in response to a request from the terminal 3 of the user. This data is displayed on the screen as shown in FIGS. 12 and 13 by the communication status display unit 28 for each application provided in the application management software of the terminal 3 of the user.
- FIG. 12 is an interface showing the degree of line congestion for each application. According to this figure, although the Web connection is congested, it can be seen that YouTube still has room. By looking at such an interface, the user can know which software can perform comfortable communication.
- FIG. 13 shows a user interface for setting a connection policy for each application. From this screen, the user can set the connection speed, data compression degree, and download remaining amount for each application. That is, each setting value can be selected and set in a pull-down manner, and the setting can be made by pressing the OK button on this screen.
- the set value is written and updated in the data storage unit 30 (34) by the communication band control policy setting unit 38 of the application / infrastructure cooperation server 14. (Billing process)
- the billing server 17 is configured to perform billing according to the user's data usage and bandwidth.
- the billing server 17 cooperates with the billing processing module 43 of the app / infrastructure linking server 14, and the bandwidth control / connection policy for each user / application in the data storage unit 30. 34 is searched, and the registered communication band and usage (remaining amount) are acquired (S15).
- the billing processing module 43 transmits the information to the billing server 17 together with information specifying the user.
- the charging server 17 holds a charging policy (indicated by 17a in FIG. 2), and specifies a charging policy for each user based on the user information acquired from the cooperation server 14 (step S16).
- a charging policy for example, a user YouTube or the like can be set to have a low data communication fee for moving images and a high data communication fee such as WEB. Thereby, it is possible to perform a billing process according to the connection bandwidth and the usage amount for each application for the user (step S17).
- the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made without changing the gist of the invention.
- connection band control of the terminal 3 is performed based on the type of application that is actively displayed on the forefront of the display screen 29 of the terminal 3 and gains the user's focus.
- bandwidth control may be performed based on the types of a plurality of applications 3a and 3b including applications that operate in the background.
- the OS for example, Android (registered trademark)
- the portable information terminal 3 When the OS (for example, Android (registered trademark)) of the portable information terminal 3 starts an application on the terminal 3, it also starts a process and outputs a unique process ID for each application.
- This process ID is detected by the IP address / port number detection module 25 of the application management software 50, and based on this, the per-process communication tag assignment module indicated by 50 in FIG. 15 assigns a different tag for each process number to the packet. To do.
- This tag may be the process ID itself of the above embodiment, the application name, or another identifier related to the process ID.
- a tag release module 51 provided in the system 2 of the MVNO operator, and is configured to delete the tag after bandwidth control.
- the application state change information acquisition module 36 receives the state change information transmitted from the application management software 16 of the portable information terminal 3 through the application management software communication module 42. receive.
- a tag assigned based on the process ID of each application started on the user's terminal 3 (in the above embodiment, the application name is output based on whether it is active). Domain name base, coordinate position, application parameters, process name, IP address / port number of the mobile terminal 3 are included.
- step S8 the communication band control policy setting unit 38 sets a control band connection policy for each user / application based on the state change information.
- the communication band control policy setting unit 38 sets a control band connection policy for each user / application based on the state change information.
- it is necessary to transmit the association between the tag and the application name to the application infrastructure cooperation server 14 in advance. Is executed by the state change determination module 26.
- the tunnel connection may be established by assigning a different port number or assigning a different IP address (virtual IP address) in addition to attaching a tag for each application.
- This function is executed by the function 50 of the tag addition module and the network stack. According to such a configuration, even when a plurality of applications are simultaneously communicating on the terminal 3, it is possible to individually control (band control, priority control) the communication band of each application packet. It should be noted that when the priority order is determined between applications, the connection policy determined on the management server side is used. In this case, the tunnel connection is executed by the tag cancellation module 51, and the IP address or / and port number for each application is deleted from each packet.
- connection policy 34 is not limited to that of the above embodiment, and other policies can be included.
- a specific image conversion method or moving image conversion method can be defined. For example, if the image is converted to black and white, it can be converted to high definition or set.
- the bandwidth control function is provided by a method of assigning a specific line speed value by bandwidth control.
- priority control relative rather than absolute value of the line speed
- This function may be provided by priority assignment).
- the connection policy is directly set in the bandwidth control router 8, but the present invention is not limited to this. It may be performed indirectly, such as through the PGW 7.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015536635A JP6055104B2 (ja) | 2013-09-11 | 2014-09-11 | ネットワーク接続システム及びその方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013-188736 | 2013-09-11 | ||
| JP2013188736 | 2013-09-11 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015037682A1 true WO2015037682A1 (ja) | 2015-03-19 |
Family
ID=52665782
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/074146 Ceased WO2015037682A1 (ja) | 2013-09-11 | 2014-09-11 | ネットワーク接続システム及びその方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (4) | JP6055104B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015037682A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017138403A1 (ja) * | 2016-02-09 | 2017-08-17 | 日本電気株式会社 | 制御装置、制御方法及びプログラムを記憶する記憶媒体 |
| JP2021013157A (ja) * | 2019-06-04 | 2021-02-04 | ザ・ボーイング・カンパニーThe Boeing Company | 認証連携されたサービス及びユーザグループに基づいてネットワークトラフィックを処理するためのシステム及び方法 |
| JP7318145B1 (ja) | 2023-01-27 | 2023-07-31 | Kddi株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020067403A1 (ja) | 2018-09-28 | 2020-04-02 | 日本電気株式会社 | 通信装置、通信方法及びプログラム |
| KR102698814B1 (ko) | 2020-02-05 | 2024-08-27 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 디스플레이 장치 및 그 통신 방법 |
| JP7144636B1 (ja) * | 2022-03-22 | 2022-09-29 | Kddi株式会社 | 通信システム、車載通信端末、中継装置、通信方法およびプログラム |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005204309A (ja) * | 2005-01-07 | 2005-07-28 | Hitachi Ltd | 衛星通信サービス方式,衛星通信端末 |
| WO2006095438A1 (ja) * | 2005-03-11 | 2006-09-14 | Fujitsu Limited | アクセス制御方法、アクセス制御システムおよびパケット通信装置 |
| JP2012138904A (ja) * | 2010-12-27 | 2012-07-19 | Pantech Co Ltd | データ使用量を測定する端末機及びその制御方法 |
| US20120260179A1 (en) * | 2011-04-08 | 2012-10-11 | Reshadi Mehrdad Mohammad H | Method and apparatus for optimized execution using resource utilization maps |
| JP2012215943A (ja) * | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-08 | Kddi Corp | サービス制御装置およびサービス制御プログラム |
| JP2013058994A (ja) * | 2011-09-09 | 2013-03-28 | Actis:Kk | 通信速度制御システム |
| JP2013131940A (ja) * | 2011-12-21 | 2013-07-04 | Fujitsu Ltd | 携帯端末装置、携帯端末装置の制御プログラム及び制御方法 |
| JP2013207504A (ja) * | 2012-03-28 | 2013-10-07 | Panasonic Corp | 無線通信装置 |
| JP2014146950A (ja) * | 2013-01-29 | 2014-08-14 | Freebit Co Ltd | ネットワーク通信システム |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3486125B2 (ja) * | 1999-01-14 | 2004-01-13 | 富士通株式会社 | ネットワーク機器制御システム及び装置 |
| JP4657433B2 (ja) * | 2000-10-02 | 2011-03-23 | 富士通株式会社 | 帯域制御サービス管理装置 |
| JP5157472B2 (ja) * | 2008-01-22 | 2013-03-06 | 富士通株式会社 | 帯域制御機能を有する負荷分散装置およびその設定方法 |
| EP2624503B1 (en) * | 2008-10-31 | 2018-04-18 | Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson (publ) | Policy and charging control user terminal |
| JP2010206376A (ja) * | 2009-03-02 | 2010-09-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | 帯域制御システム |
| US8499087B2 (en) * | 2009-11-30 | 2013-07-30 | At&T Mobility Ii Llc | Service-based routing for mobile core network |
| JP4935911B2 (ja) * | 2010-01-28 | 2012-05-23 | 沖電気工業株式会社 | 通信制御装置 |
| WO2013063142A2 (en) * | 2011-10-24 | 2013-05-02 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Technique for prioritizing traffic at a router |
-
2014
- 2014-09-11 WO PCT/JP2014/074146 patent/WO2015037682A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2014-09-11 JP JP2015536635A patent/JP6055104B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-12-01 JP JP2016234051A patent/JP6272980B2/ja active Active
-
2018
- 2018-01-04 JP JP2018000138A patent/JP6585740B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-09-05 JP JP2019162098A patent/JP7026085B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005204309A (ja) * | 2005-01-07 | 2005-07-28 | Hitachi Ltd | 衛星通信サービス方式,衛星通信端末 |
| WO2006095438A1 (ja) * | 2005-03-11 | 2006-09-14 | Fujitsu Limited | アクセス制御方法、アクセス制御システムおよびパケット通信装置 |
| JP2012138904A (ja) * | 2010-12-27 | 2012-07-19 | Pantech Co Ltd | データ使用量を測定する端末機及びその制御方法 |
| JP2012215943A (ja) * | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-08 | Kddi Corp | サービス制御装置およびサービス制御プログラム |
| US20120260179A1 (en) * | 2011-04-08 | 2012-10-11 | Reshadi Mehrdad Mohammad H | Method and apparatus for optimized execution using resource utilization maps |
| JP2013058994A (ja) * | 2011-09-09 | 2013-03-28 | Actis:Kk | 通信速度制御システム |
| JP2013131940A (ja) * | 2011-12-21 | 2013-07-04 | Fujitsu Ltd | 携帯端末装置、携帯端末装置の制御プログラム及び制御方法 |
| JP2013207504A (ja) * | 2012-03-28 | 2013-10-07 | Panasonic Corp | 無線通信装置 |
| JP2014146950A (ja) * | 2013-01-29 | 2014-08-14 | Freebit Co Ltd | ネットワーク通信システム |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| "Honban! Enterprise Smartphone Jirei Kenkyu (2) Suntory User Kigyo ga Shudoken o Nigiru Dokuji Apuri de Android o Secure ni", NIKKEI COMMUNICATIONS, no. 570, 1 July 2011 (2011-07-01), pages 20 - 21 * |
| "Toshitaikoka no Takai WAN Application Haishin Kiki no Sentakuho", NIKKEI COMMUNICATIONS, no. 502, 15 January 2008 (2008-01-15), pages 14 - 15 * |
| HIDEO KOBAYASHI: "UTM (Togo Kyoi Kanri) Appliance Tanmatsu·Apuri Riyo Keitai ni Ojite Shinka", TELECOMMUNICATION, vol. 30, no. 1, 25 December 2012 (2012-12-25), pages 46 - 50 * |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017138403A1 (ja) * | 2016-02-09 | 2017-08-17 | 日本電気株式会社 | 制御装置、制御方法及びプログラムを記憶する記憶媒体 |
| JP2021013157A (ja) * | 2019-06-04 | 2021-02-04 | ザ・ボーイング・カンパニーThe Boeing Company | 認証連携されたサービス及びユーザグループに基づいてネットワークトラフィックを処理するためのシステム及び方法 |
| JP7582796B2 (ja) | 2019-06-04 | 2024-11-13 | ザ・ボーイング・カンパニー | 認証連携されたサービス及びユーザグループに基づいてネットワークトラフィックを処理するためのシステム及び方法 |
| JP7318145B1 (ja) | 2023-01-27 | 2023-07-31 | Kddi株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム |
| JP2024106452A (ja) * | 2023-01-27 | 2024-08-08 | Kddi株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6585740B2 (ja) | 2019-10-02 |
| JP7026085B2 (ja) | 2022-02-25 |
| JPWO2015037682A1 (ja) | 2017-03-02 |
| JP6055104B2 (ja) | 2016-12-27 |
| JP2017063488A (ja) | 2017-03-30 |
| JP2020014226A (ja) | 2020-01-23 |
| JP6272980B2 (ja) | 2018-01-31 |
| JP2018078634A (ja) | 2018-05-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6786558B2 (ja) | アプリケーション状態変化通知プログラム及びその方法 | |
| JP6585740B2 (ja) | ネットワーク接続システム及びその方法 | |
| US10616120B2 (en) | Service layer southbound interface and quality of service | |
| JP5637471B2 (ja) | サービス制御方法およびシステム、発展型ノードb、ならびにパケットデータネットワークゲートウェイ | |
| JP2017098962A5 (enExample) | ||
| CN104145451B (zh) | 报文处理方法、深度包检测请求网元和深度包检测设备 | |
| CN111052677B (zh) | 用于对在通信网络的切片上路由的应用的数据收费的方法 | |
| CN104995962A (zh) | 网络接入选择方法和终端 | |
| US20140376470A1 (en) | Policy and charging control (pcc) for nat64 and dns64 | |
| JP2017063488A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP2018078634A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP6137848B2 (ja) | ネットワーク通信システム | |
| EP3641248B1 (en) | Traffic optimization device, communication system, traffic optimization method, and program | |
| JP2016034116A (ja) | 経路設定装置、経路設定方法、経路設定プログラムおよび通信システム | |
| WO2017088163A1 (zh) | 一种信息内容传输方法和装置 | |
| WO2025209357A1 (zh) | 一种通信方法及装置 | |
| JP2016034117A (ja) | 経路設定装置、経路設定方法、経路設定プログラムおよび通信システム | |
| JP2018102004A (ja) | 通信システム | |
| JP2017123617A (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、およびプログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14844457 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2015536635 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14844457 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |