WO2013069676A1 - Procédé de fabrication d'un article à capacité d'absorption d'eau - Google Patents
Procédé de fabrication d'un article à capacité d'absorption d'eau Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013069676A1 WO2013069676A1 PCT/JP2012/078825 JP2012078825W WO2013069676A1 WO 2013069676 A1 WO2013069676 A1 WO 2013069676A1 JP 2012078825 W JP2012078825 W JP 2012078825W WO 2013069676 A1 WO2013069676 A1 WO 2013069676A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- area
- web
- guide roll
- polymer particles
- water
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15617—Making absorbent pads from fibres or pulverulent material with or without treatment of the fibres
- A61F13/15658—Forming continuous, e.g. composite, fibrous webs, e.g. involving the application of pulverulent material on parts thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F2013/530481—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having superabsorbent materials, i.e. highly absorbent polymer gel materials
- A61F2013/530489—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium having superabsorbent materials, i.e. highly absorbent polymer gel materials being randomly mixed in with other material
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a method for producing a water-absorbent article suitable for use as an absorbent body or disposable wipes in a body fluid-absorbing wearing article such as a disposable diaper.
- a water-absorbing pad in which superabsorbent polymer particles are interposed between sheet pieces in which at least one of the two sheet pieces is water-permeable is known.
- an absorbent sheet described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2009-131510 is a sheet in which superabsorbent polymer particles are contained between an upper sheet and a lower sheet, and the upper sheet and the lower sheet In the non-joined part surrounded by the joined part, the pocket is formed by the upper sheet and the lower sheet, and the superabsorbent polymer particles are accommodated in the pocket.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles are movable within the pockets.
- the subject of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a water-absorbent article that can solve such problems.
- the present invention is intended to provide highly water-absorbing polymer particles between opposing surfaces of the two sheet pieces in which at least one of the two overlapping sheet pieces is water permeable. It is a manufacturing method of a water-absorbing article having a first zone interposed and a second zone in which the opposing surfaces are joined to each other and surround the first zone.
- the features of the present invention are as follows. That is, the first web and the second web, which are continuous bodies of the two sheet pieces, are continuously run in the machine direction.
- the first web the superabsorbent polymer particles are supplied to the facing surface of the portion corresponding to the first section, while the portion of the second web corresponding to the first section and the second section is supplied.
- a hot melt adhesive is applied to the opposite surface.
- the composite web is sequentially brought into contact with a plurality of guide rolls that rotate so as to cause the composite web to travel in the machine direction, and the first guide roll located on the upstream side in the machine direction among the plurality of guide rolls;
- the direction of the travel direction of the composite web between the second guide roll adjacent to the first guide roll on the downstream side in the machine direction is set to the direction of the travel direction of the composite web toward the first guide roll. Change the angle in the range of 30-180 degrees.
- the range of the angle is less than 90 degrees.
- the composite web is sequentially brought into contact with the first guide roll, the second guide roll, and a third guide roll adjacent to the second guide roll on the downstream side.
- the range of the angle is less than 90 degrees between the first roll and the second roll, and the composite web is caused to run downhill or uphill, and the second roll and the third roll Between the rolls, the composite web is caused to run so as to have an upward slope or a downward slope.
- the first zone contains the superabsorbent polymer particles in a mass ratio of 30-300 g / m 2 .
- the application amount of the hot melt adhesive per unit area in the second area is the same as the application amount of the hot melt adhesive per unit area in the first area. is there.
- the application amount of the hot melt adhesive per unit area in the second area is larger than the application amount of the hot melt adhesive per unit area in the first area.
- a plurality of the first areas are formed in the water absorbent article.
- each of the two sheet pieces is water permeable.
- the sheet piece that is water permeable is a hydrophilic nonwoven fabric formed of thermoplastic synthetic fibers.
- one of the two sheet pieces is water permeable, the other is either impermeable or hardly permeable, and the superabsorbent polymer particles are It is joined to the sheet piece which is either impermeable or hardly permeable.
- the angle between the composite web that travels toward the first guide roll and the composite web that travels from the first guide roll toward the second guide roll is 30.
- the composite web can be brought into close contact with the first guide roll.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles that are not bonded to the first web or the second web in the first section of the composite web and are accumulated locally in the first section are such that the composite web is on the peripheral surface of the first guide roll.
- the contact starts, the accumulated state collapses and is subjected to the action of spreading inside the first area.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles can be uniformly distributed in the first zone of the composite web, in other words the first zone of the water-absorbent article.
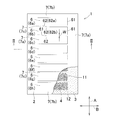
- FIG. 3 The partially broken top view of a water absorbing article.
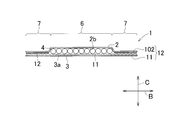
- wire cut surface of FIG. The figure which shows an example of the manufacturing process of a water absorptive article.
- the elements on larger scale of FIG. The figure similar to FIG. 3 which shows an example of an embodiment.
- the article 1 includes an upper layer sheet 2 that is water permeable, a lower layer sheet 3 that is either water permeable, poorly water permeable, or water impermeable, and superabsorbent polymer particles 4.
- superabsorbent polymer 4 various known polymers can be mentioned as will be apparent to those skilled in the art.
- the article 1 also includes a plurality of first areas 6 in which the upper sheet 2 and the lower sheet 3 are separated from each other and the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are joined to the lower sheet 3, and the upper sheet 2 and the lower sheet 3 A second region 7 that is joined.
- That the lower layer sheet 3 is water permeable means that the lower layer sheet 3 can easily pass water in the same manner as the upper layer sheet 2, and that the lower layer sheet 3 is hardly water permeable means that the upper layer sheet 2 and Means that the lower layer sheet 3 is in a state of not allowing water to permeate as much as the upper layer sheet 2.
- the lower layer sheet layer 3 is impermeable to water in comparison with the upper layer sheet 2. Is in a state of substantially not transmitting.
- any one of a water-permeable material, a hardly water-permeable material, and a water-impermeable material is adopted for the lower layer sheet 3.
- the diameter of the superabsorbent polymer particle 4 is exaggerated in order to clearly show the presence of the superabsorbent polymer particle 4 described later.
- the first zone 6 is surrounded by the second zone 7 and forms a water absorbing zone by including the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 as the water absorbing material.
- the first zone 6 is a superabsorbent polymer.
- the particles 4 preferably at a rate of 30-300g / m 2, more preferably contains a proportion of 40-280g / m 2.
- region 6 it has joined to the lower layer sheet 3 via the hot melt adhesive 11 for polymer particle fixation uniformly apply
- the first area 6 is an area that may contain superabsorbent polymer particles that are not bonded to the lower layer sheet 3, and the first area 6 may be included between the lower layer sheet 3 and the upper layer sheet 2.
- the upper limit of the total amount of superabsorbent polymer particles that can be produced is 400 g / m 2 .
- the lower layer sheet 3 and the upper layer sheet 2 are not joined, but in the manufacturing process of the article 1 (see FIGS. 3 and 4), it is extremely unintended.
- the upper layer sheet 2 may be bonded to the lower layer sheet 3 with a small area.
- the second region 7 is a super absorbent polymer particle 4 when the super absorbent polymer particle 4 contained in the first region 6 is not joined to the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 and can move freely.
- Including the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 up to a mass of up to 20 g / m 2 which is not intended in the manufacturing process of the upper layer sheet 2 and article 1, except for the superabsorbent polymer particles 4. It is also a region that forms a substantially non-water-absorbing region.
- the mass (g / m 2 ) of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 is the first per unit area of the lower layer sheet 3.
- the area 6 is less than the mass (g / m 2 ) of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 included in one area 6.
- the upper layer sheet 2 and the lower layer sheet 3 are joined via the hot melt adhesive 12 for sealing.
- the peel strength of both sheets 2 and 3 can be improved by further welding the upper layer sheet 2 and the lower layer sheet 3 that are joined as described above.
- the upper layer sheet 2 and the lower layer sheet 3 in the second area 7 are not peeled even during use of the article 1.
- the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 applied so as to overlap in the second area 7 and the second hot melt adhesive 102 (see FIGS. 3 and 4) described later. Forms a hot-melt adhesive 12 for sealing, and the upper-layer sheet 2 and the lower-layer sheet 3 are joined via the hot-melt adhesive 12 for sealing.
- the hot melt adhesive in the article 1 a conventional one in this kind of article can be used.
- the article 1 in the illustrated example is made to be long in the vertical direction A.
- first sections 6, that is, water absorption areas, indicated by reference numerals 6a-6h.
- Each of the first areas 6a-6h has a perimeter 61 that defines its planar shape.
- the periphery 61 of the first areas 6 adjacent in the vertical direction A includes opposite side portions 62 that face each other in the vertical direction A and extend in the horizontal direction B.
- opposite side portions 62 facing each other in the longitudinal direction A and extending in the lateral direction B are indicated by reference numerals 62a and 62b.
- the second area 7 is on both sides of the article 1 and extends in the longitudinal direction A.
- the side edges 7 a extend in the longitudinal direction A.
- An intermediate portion 7c extending between the adjacent first areas 6 and extending in the lateral direction B is provided.
- the longitudinal direction A of the article 1 is aligned with the front-rear direction of the diaper, and the central portion of the longitudinal direction A is a diaper.
- the upper layer sheet 2 is formed of a water-permeable sheet piece and is directed to the skin of the diaper wearer.
- the use of the article 1 improves the possibility of obtaining various effects.
- urine excreted by the wearer passes through the upper layer sheet 2 in the first section 6 and is absorbed by the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 so that it does not flow.
- the diaper by fixing the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 to the lower layer sheet 3 formed of the hardly water-permeable or water-impermeable sheet piece, the wearer's crotch can be changed even if the posture of the wearer changes variously.
- the distribution state of the highly water-absorbing polymer particles 4 in the part is always constant, and no bias occurs in the first area 6.
- the article 1 urine can be permeated in a wide area of the upper layer sheet 2 and absorbed in a wide area of the first area 6.
- the distribution of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 is biased inside the first section 6.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are unevenly distributed locally in the first section 6, and the article 1 has a uniform thickness.
- the article 1 does not press the wearer's skin locally. Incidentally, the state that the article 1 is not uniform in thickness becomes prominent when the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 swell after absorbing urine.
- the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 is applied to the lower layer sheet 3 and not applied to the upper layer sheet 2, so that the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 is applied to the upper layer sheet 2.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 fixed to the lower layer sheet 3 prevent the upper layer sheet 2 from approaching and joining to the lower layer sheet 3 to which the hot melt adhesive 11 for fixing polymer particles is applied, This prevents the article 1 from being poorly flexible by bonding the upper sheet 2 to the lower sheet 3.
- a plurality of intermediate portions 7c that are parallel to each other as shown in the drawing act so that the article 1 can be easily bent in the longitudinal direction A.
- the width W of the intermediate portion 7c acting in this way is preferably 2-15 mm.
- the upper layer sheet 2 includes a sheet piece of a water-permeable nonwoven fabric formed of thermoplastic synthetic fibers and subjected to a hydrophilic treatment, for example, an SMS formed of polypropylene fibers.
- a sheet piece of nonwoven fabric spunbond-meltblown-spunbond nonwoven fabric
- Spunbonded nonwoven fabric to each other the mass of 10-12g / m 2, which is interposed meltblown nonwoven having a mass of 0.5-2g / m 2 between having a mass of 4-5g / m 2 is one example of the SMS nonwoven fabric
- the lower layer sheet 3 may be a non-woven sheet piece made of hydrophobic thermoplastic synthetic fiber and hardly or water-impermeable.
- the 10-13g / m 2 which is interposed meltblown nonwoven having a mass of 0.5-2g / m 2 between the spunbonded nonwoven fabric to each other with a mass of 4-6 g / m 2 formed of polypropylene fibers
- a sheet piece of SMS nonwoven fabric having a mass and poor water permeability can be used.
- the lower layer sheet 3 is also formed of a water-impermeable sheet piece formed of a plastic film such as a polyethylene film having a thickness of 0.01 to 0.03 mm, or a water-impermeable plastic film and a thermoplastic synthetic fiber.
- a water-impermeable sheet piece that is a laminate with a water-permeable or hardly water-permeable nonwoven fabric.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are bonded to the nonwoven fabric so that the nonwoven fabric is inside the article 1 and the water-impermeable plastic film is outside the article 1, and from the fiber gap in the nonwoven fabric. It is preferable to stop leakage of body fluid with a plastic film.
- the highly water-absorbing polymer particles 4 have various water absorption speeds, and those having a constant water absorption speed can be used alone, or those having different water absorption speeds can be mixed and used.
- a water absorption rate of about 30 seconds according to the VORTEX method defined in JIS K 7224 can be used with the upper limit of 400 g / m 2 for the first zone 6.
- the amount of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 used is preferably adjusted in consideration of the size of the section of the first section 6 and the usage pattern of the article 1. It is preferable to use the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 having a small amount of components eluted with respect to urine. This is because components that elute from the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 when they are in contact with urine may increase the viscosity of the urine and increase discomfort when the urine touches the skin.
- the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 is applied to the lower layer sheet 3 in the first area 6 in order to fix the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 to the lower layer sheet 3. It may be applied also to the lower layer sheet 3.
- the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 is applied at a mass ratio of 1-12 g / m 2 so as to be uniformly distributed over the entire upper surface 3a of the lower layer sheet 3.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 fixed to the lower layer sheet 3 in the first area 6 are not covered with the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 so that the entire surface thereof is covered with the hot melt adhesive for fixing polymer particles. It is preferable that the agent 11 reduces the coating amount per unit area as much as possible.
- the hot melt adhesive 11 for fixing polymer particles can also be applied to the lower layer sheet 3 so as to be intermittently distributed like dots or beads, or continuously covers the entire first area 6. It can also be applied. However, in any case, the surface of the superabsorbent polymer particle 4 is bonded to the upper surface 3a while the portion facing the upper surface 3a of the lower layer sheet 3 is covered with the hot melt adhesive 11 for fixing the polymer particles. It is preferable that the portion facing the lower surface 2b (see FIG. 2) is in a state in which urine can be rapidly absorbed without being covered with the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11.
- the hot melt adhesive 12 for sealing is added at a rate of 5-30 g / m 2 with respect to the hot melt adhesive 11 for fixing polymer particles applied to the lower layer sheet 3 located in the second area 7 and the lower layer sheet 3.
- the second hot melt adhesive 102 shown in FIG. By adjusting the application amount of the hot melt adhesive between the first area 6 and the second area 7 in this way, the hot melt adhesive 11 for fixing polymer particles is highly absorbent in the first area 6. While the surface of each of the polymer particles 4 is widely covered to avoid affecting the water absorption amount and the water absorption speed of the highly water-absorbing polymer particles 4, in the second area 7, only the hot melt adhesive 11 for fixing the polymer particles is used.
- the additional use of the second hot melt adhesive 102 can prevent the peeling.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 that are not fixed to the lower sheet 3 are present in the first zone 6, the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are moved from the first zone 6 to the second zone 6.
- the upper sheet through the hot-melt adhesive 12 for sealing that is continuous or substantially continuous along the periphery of the first area 6 so that it can be prevented from moving to 7 2 and the lower layer sheet 3 are preferably joined.
- the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 and the second hot melt adhesive 102 used in this way can be the same or those that adhere well to each other.
- the function as the sealing hot-melt adhesive 12 can be achieved only by the polymer particle fixing adhesive 11 applied to the second area 7, the second hot-melt adhesive 102 in FIG. 4 is unnecessary. Become. In this case, the application amount per unit area of the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 may be the same in the first area 6 and the second area 7.
- Each dimension of the first area 6 in the longitudinal direction A and the lateral direction B in the article 1 when used for a diaper is a diaper.
- An appropriate value can be set in accordance with the size of.
- the dimension in the vertical direction A and the dimension in the horizontal direction B can be set in a range of 25 to 250 mm. It is preferable that the number of sections of the first area 6 in such a dimension is 5-15.
- the width of the side edge 7a and the end edge 7b of the second area 7 is preferably 5-40 mm.
- the dimension in the longitudinal direction A of the intermediate part 7c is preferably 3-30 mm.
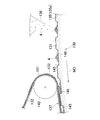
- FIG. 3 and 4 are an example of a process diagram when the article 1 is continuously manufactured, and a partial enlarged view of the suction drum 130 in the process diagram.
- the first web 131 which is a continuous body of the upper layer sheet 2 is supplied toward the peripheral surface 135 of the suction drum 130 from the right side of the drawing.
- the first web 131 that is in close contact with the peripheral surface 135 by the pressing action by the guide roll 141 and the suction action that works from the peripheral surface 135 toward the inside of the suction drum 130 is a polymer set above the suction drum 130.
- Superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are supplied from the particle supply device 136.
- the second web 132 which is a continuous body of the lower layer sheet 3 is continuously supplied to the peripheral surface 135 of the suction drum 130 via the guide roll 142.
- the first hot melt adhesive 101 is applied to one surface of the second web 132 by a first coater 121 provided on the upstream side of the suction drum 130.
- the second hot melt adhesive 102 is applied onto a part of the first hot melt adhesive 101 already applied by the second coater 122 provided on the downstream side of the first coater 121.
- the first web 131 to which the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are supplied and the second web 132 to which the first and second hot melt adhesives 101 and 102 are applied are on the peripheral surface 135 of the suction drum 130.
- the composite web 137 is formed by joining and joining via the first hot melt adhesive 101 and the second hot melt adhesive 102.
- the composite web 137 advances in the machine direction MD and is separated from the suction drum 130, and is then pressed by a pair of first guide rolls 161 that also serve as a press roll, and is at least a part of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4.
- the first hot melt adhesive 101 come into contact with each other, and the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are fixed to the second web 132 through the first hot melt adhesive 101.
- the composite web 137 separated from the first press roll 143 enters between the pair of first guide rolls 161 in a substantially horizontal state, and the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are bonded to the first hot melt adhesive.
- the first hot melt adhesive 101 is the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 in the article 1, but the one that overlaps the second hot melt adhesive 102 is integrated with the second hot melt adhesive 102.
- the sealing hot melt adhesive 12 in the article 1 is formed.
- FIG. 4 shows a state where the first web 131 and the second web 132 merge to form the composite web 137, and the suction drum 130 is shown in a partial cross-sectional view.
- a plurality of recesses 145 are formed in the circumferential surface 135 of the suction drum 130 so as to be arranged in the circumferential direction.
- the planar shape of each of the recesses 145 corresponds to the planar shape of each of the first areas 6 arranged in the longitudinal direction A in FIG.
- the depth of the recess 145 is set to such an extent that a single supply amount of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 supplied intermittently from the polymer supply device 136 can be accommodated.
- the composite web 137 that has passed through the first guide roll 161 proceeds in the machine direction MD, reaches the cutter 138 via the second guide roll 162, and is intermittently cut by the cutter 138, and the individual articles 1 and become.
- Both the first guide roll 161 and the second guide roll 162 are driven and rotated so that the composite web 137 travels in the machine direction MD, or are freely rotatable.
- the vehicle is inclined so that the direction of the machine direction MD is a downward slope. That is, the second roll 162 indicated by the solid line is at a position where the intersection angle ⁇ is about 30 degrees.
- the second roll 162 indicated by an imaginary line is in a position when the intersection angle ⁇ is about 120 degrees.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 to be supplied to the recesses 145 of the suction drum 130 are first positioned on the bottom surface 146 of the recesses 145. It is difficult to uniformly distribute the web 131. Also in the first zone 6 (see FIG. 1) formed when the first web 131 and the second web 132 merge and pass through the first press roll 143, the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are uniformly distributed. It is difficult to distribute it. In the first zone 6, the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are unevenly distributed downstream in the machine direction MD, and the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are present on the first hot melt adhesive 101 applied to the second web 132. There may be many parts that have not yet been joined. In the first zone 6, the unevenly distributed portion of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 may be thicker than the other portions.
- the composite web 137 when the direction in which the composite web 137 travels on the first guide roll 161 is changed by the angle ⁇ , the composite web 137 is in close contact with the peripheral surface of at least one of the pair of first guide rolls 161.
- the highly water-absorbing polymer particles 4 that are unevenly distributed are pushed to the upstream side in the machine direction MD in the first section 6 and are widely and uniformly distributed in the first section 6. It becomes possible.
- the upper guide roll 161 can be omitted.
- the composite web 137 passing through the first guide roll 161 toward the second guide roll 162 is inclined as shown in the illustrated example, the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 that are unevenly distributed in the first section 6 are provided. However, it may move down the slope to promote uniform distribution of the superabsorbent polymer particles 4. It is also possible for the composite web 137 to travel in a manner of an upward slope between the first guide roll 161 and the second guide roll 162.
- a third guide roll 163 is provided on the downstream side of the second guide roll 162.
- the composite web 137 that has left the suction drum 130 (see FIG. 3) travels in the machine direction MD. However, the composite web 137 travels horizontally between the first guide roll 161 and the second guide roll 162.
- the crossing angle ⁇ is less than 90 degrees and the traveling direction is a downward slope.
- the 2nd guide roll 162 and the 3rd guide roll 162 it exists in the aspect from which the direction to drive
- the composite web 137 is run in this way, the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 that are inside the first section 6 and are not bonded to the first hot melt adhesive 101 and are movable are combined with each other.
- the first hot melt adhesive 101 is uniformly distributed in both the longitudinal direction A and the lateral direction B with respect to each of the first area 6 and the second area 7. Although it can be in the state of being applied intermittently, it can also be in the state of being applied continuously in at least one of the vertical direction A and the horizontal direction B. Therefore, there is no special rule in selecting the model of the first coater 121 for applying the first hot melt adhesive 101, and the same applies to the second coater 122 for applying the second hot melt adhesive 102. It is. However, in the article 1, the hot melt adhesives 11 and 12 are continuous between the polymer particle fixing hot melt adhesive 11 in the first section 6 and the sealing hot melt adhesive 12 in the second section 7.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 When the polymer particle fixing hot-melt adhesive 11 is applied in such a manner so as to reach every corner of the first area 6, the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 also reach every corner of the first area 6. Become.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 can be distributed along the opposite side portion 62 immediately inside the opposite side portion 62 of the first area 6.
- the superabsorbent polymer particles 4 are preferably distributed so as to cover almost the entire upper surface 3a (see FIG.
- the hot melt adhesive can be applied to a necessary portion of the upper layer sheet 2 in the steps of FIGS. .
- the shape of the article 1 there is no particular provision for the shape of the article 1, the shape of the first section 6, and the number of sections formed by the first section 6, and appropriate changes can be made to these shapes and numbers in the illustrated example.
- the shape of the second area 7 can be changed so that the article 1 in FIG. 1 can be divided into two or three in the lateral direction B of the first area 6. 3 and 5, the composite web 137 when it is separated from the suction drum 130 can be run in a state intersecting with the horizontal, in addition to running horizontally as in the illustrated example.
- the number of guide rolls that are positioned downstream of the suction drum 130 and used to change the direction in which the composite web 137 travels.
- the guide roll may be connected to the drive device and may be rotated, or may be a free roll that is not connected to the drive device and can be freely rotated.
- the ordering in the first, second and third guide rolls 161, 162 and 163 means the order of the guide rolls arranged in the machine direction, and does not mean the order adjacent to the suction drum 130. That is, in the manufacturing method according to the present invention, an appropriate roll can be interposed between the suction drum 130 and the first guide roll 161 if necessary in assembling the manufacturing process.
- the article 1 obtained by the manufacturing method according to the present invention is not limited to disposable diapers, but is used in combination with diapers and diaper covers, urine absorbing pads, incontinence patient pants. It can be used as a urine absorption pad for use together.
- the article 1 can also be used as a wipe for absorbing and treating water and other water-absorbing articles.
- a water-permeable sheet piece is used as the lower layer sheet 3. It can be used, or a sheet piece of poor water permeability or water impermeability can be used.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
L'invention concerne un procédé de fabrication d'un article à capacité d'absorption d'eau, au moyen duquel des particules polymères à haute capacité d'absorption d'eau ne seront pas distribuées localement de façon inégale. Dans une étape de fabrication d'une sangle composite (137) qui est un corps continu de l'article à capacité d'absorption d'eau ayant une première section dans laquelle des particules polymères à haute capacité d'absorption d'eau (4) sont interposées entre deux morceaux de feuille superposés, et une seconde section qui entoure la première section, l'angle entre un premier rouleau de guidage (161) qui est situé sur le côté amont dans un sens machine (MD) parmi des rouleaux de guidage pour permettre à la sangle composite (137) de se déplacer dans le sens machine (MD) et un second rouleau de guidage (162) qui est adjacent au premier rouleau de guidage (161) sur le côté aval dans le sens machine (MD) est amené à varier à l'intérieur d'une plage de 30-180 ° par rapport à l'orientation du sens de déplacement de la sangle composite (137), l'orientation du sens de déplacement de la sangle composite (137) étant dirigée vers le premier rouleau de guidage (161).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011244854A JP5734164B2 (ja) | 2011-11-08 | 2011-11-08 | 吸水性物品の製造方法 |
| JP2011-244854 | 2011-11-08 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013069676A1 true WO2013069676A1 (fr) | 2013-05-16 |
Family
ID=48290050
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2012/078825 WO2013069676A1 (fr) | 2011-11-08 | 2012-11-07 | Procédé de fabrication d'un article à capacité d'absorption d'eau |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5734164B2 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2013069676A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2966472A1 (fr) | 2014-11-28 | 2016-06-02 | Unicharm Corporation | Procede pour former des pieces serties sur un corps continu d'element d'ame ayant des faisceaux de fibres, et dispositif de formation |
| CA2968428C (fr) | 2014-11-28 | 2018-04-03 | Unicharm Corporation | Procede de formation de parties serties dans un corps continu d'element en bande ayant des paquets de fibres, et dispositif de formation |
| ITUB20154187A1 (it) | 2015-10-06 | 2016-01-06 | Fameccanica Data Spa | Procedimento ed apparecchiatura per la produzione di una struttura assorbente |
| JP7411439B2 (ja) * | 2020-02-21 | 2024-01-11 | 花王株式会社 | 複合シートの製造方法 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005059579A (ja) * | 2003-07-31 | 2005-03-10 | Livedo Corporation | シート状体の製造方法および装置並びにシート状体を用いた使い捨て吸収性物品の製造方法 |
| JP2010063815A (ja) * | 2008-09-12 | 2010-03-25 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収体 |
-
2011
- 2011-11-08 JP JP2011244854A patent/JP5734164B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2012
- 2012-11-07 WO PCT/JP2012/078825 patent/WO2013069676A1/fr active Application Filing
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005059579A (ja) * | 2003-07-31 | 2005-03-10 | Livedo Corporation | シート状体の製造方法および装置並びにシート状体を用いた使い捨て吸収性物品の製造方法 |
| JP2010063815A (ja) * | 2008-09-12 | 2010-03-25 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収体 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5734164B2 (ja) | 2015-06-10 |
| JP2013099429A (ja) | 2013-05-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2012101934A1 (fr) | Article absorbant en forme de tampon | |
| JP5769432B2 (ja) | パッド形態を有する吸水性物品 | |
| JP5328273B2 (ja) | 体液吸収性物品 | |
| KR100819367B1 (ko) | 초박형 흡수 시트체, 초박형 흡수 시트체를 구비한 일회용흡수성 물품 및 초박형 흡수 시트체의 제조 장치 | |
| JP5383589B2 (ja) | 体液吸収体及びその製造方法 | |
| JP4638087B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5517290B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5318747B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| WO2010050376A1 (fr) | Structure d'absorption de fluide pour article portable | |
| KR20090083375A (ko) | 흡수성 물품 | |
| JP6360540B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| CA2587581A1 (fr) | Serviette hygienique | |
| WO2013069676A1 (fr) | Procédé de fabrication d'un article à capacité d'absorption d'eau | |
| JP4972384B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2013078369A (ja) | 使い捨て着用物品 | |
| JP6932887B2 (ja) | 軽失禁用吸収性物品 | |
| JP3776014B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品およびその製造方法 | |
| JP5939806B2 (ja) | 吸水性物品 | |
| JP2013042881A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5577906B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品用シートの製造方法、吸収性物品用シート及び吸収性物品 | |
| JP2020116154A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2020116153A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2021053239A (ja) | 吸収体及び該吸収体を備えた吸収性物品 | |
| JP2017225604A (ja) | 吸収性物品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12848138 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 12848138 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |