WO2011093408A1 - 通信システム及び携帯通信装置、並びに通信システム用サーバー - Google Patents
通信システム及び携帯通信装置、並びに通信システム用サーバー Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011093408A1 WO2011093408A1 PCT/JP2011/051663 JP2011051663W WO2011093408A1 WO 2011093408 A1 WO2011093408 A1 WO 2011093408A1 JP 2011051663 W JP2011051663 W JP 2011051663W WO 2011093408 A1 WO2011093408 A1 WO 2011093408A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- mobile communication
- communication device
- information
- search request
- server
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W8/00—Network data management
- H04W8/005—Discovery of network devices, e.g. terminals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04M—TELEPHONIC COMMUNICATION
- H04M1/00—Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers
- H04M1/72—Mobile telephones; Cordless telephones, i.e. devices for establishing wireless links to base stations without route selection
- H04M1/724—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones
- H04M1/72403—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for local support of applications that increase the functionality
- H04M1/72409—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for local support of applications that increase the functionality by interfacing with external accessories
- H04M1/72412—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for local support of applications that increase the functionality by interfacing with external accessories using two-way short-range wireless interfaces
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/80—Services using short range communication, e.g. near-field communication [NFC], radio-frequency identification [RFID] or low energy communication
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04M—TELEPHONIC COMMUNICATION
- H04M1/00—Substation equipment, e.g. for use by subscribers
- H04M1/72—Mobile telephones; Cordless telephones, i.e. devices for establishing wireless links to base stations without route selection
- H04M1/724—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones
- H04M1/72448—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for adapting the functionality of the device according to specific conditions
- H04M1/72451—User interfaces specially adapted for cordless or mobile telephones with means for adapting the functionality of the device according to specific conditions according to schedules, e.g. using calendar applications
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a technique for managing a plurality of portable communication devices and assisting (supporting) when searching for a group of portable communication devices as needed.
- Patent Document 1 a lost emblem with information recorded in advance is possessed by a person who is a lost child and a guardian of the entrant, and information on the lost emblem is obtained by a portable terminal possessed by a hall attendant or a guardian when the lost child occurs.
- a lost child support method is disclosed in which reading, lost child protection information and lost child notification are transmitted to a management server by e-mail, and the lost child is searched and protected by sending and receiving e-mail between the management server and the portable terminal.
- Patent Document 1 is effective in a theme park and the like because a lost child emblem is distributed in advance, but is inconvenient in daily life.
- the technique disclosed in Patent Document 1 requires a lost child to be protected and needs to be picked up by a guardian, and is insufficient for assistance when searching for an unprotected lost child.
- An object of this invention is to provide the communication system and portable communication apparatus which are useful for the assistance at the time of searching for an undiscovered lost child etc., and the server for communication systems.
- the invention for solving the above-described problems includes a plurality of first portable communication devices having short-range wireless communication means capable of directly communicating with other portable communication devices, and short-range wireless capable of directly communicating with other portable communication devices.
- a second mobile communication device having communication means; and a server for storing information relating to the plurality of first mobile communication devices, wherein the plurality of first mobile communication devices have the respective short-range wireless communication means.
- communicating with the second mobile communication device to acquire at least identification information of the second mobile communication device, storing the acquired identification information in association with the acquired time, and
- the server obtains a search request for a communication device
- the server transmits information related to the search request to the plurality of first mobile communication devices, and receives information related to the search request.
- the first portable communication device transmits information about the second portable communication device that is the subject of the search request to the server, a communication system.
- the plurality of first mobile communication devices that have received information about the second mobile communication device that is the target of the search request uses the respective short-range wireless communication means to perform the search request. If communication with the second portable communication device that is the target of the search request is established and communication with the second portable communication device that is the target of the search is established, the search request is the target. It is preferable that at least identification information of the second portable communication device is acquired and transmitted to the server.
- a plurality of second portable communication devices having short-range wireless communication means capable of directly communicating with other portable communication devices are provided, and the plurality of second portable communication devices include the short-range wireless communication means. And communicating with another second mobile communication device to acquire at least identification information of the other second mobile communication device, storing the acquired identification information in association with the acquired time, and the server
- the plurality of first mobile communication devices is configured to transmit the information to at least one of the plurality of second mobile communication devices.
- the plurality of second portable communication devices that have transmitted information related to the search request and received information related to the search request include information about the second portable communication device that is the target of the search request.
- the server obtains information about the second mobile communication device that is the target of the search request from the plurality of second mobile terminal devices via the first mobile communication terminal. It is preferable.
- the server when the server transmits information related to the search request to the plurality of first mobile communication devices, the plurality of first mobile communication devices are associated with the plurality of second second communication devices.
- the plurality of second mobile communication devices that have transmitted information related to the search request to the mobile communication device and received the information related to the search request are information about the second mobile communication device that is the target of the search request. Is preferably transmitted to the first mobile communication terminal associated with itself.
- communication using the short-range wireless communication means is periodically executed for a predetermined time.
- communication using the short-range wireless communication means is executed based on a reference time transmitted from the plurality of second mobile communication devices and a base station accessible by the plurality of first mobile communication devices. It is preferable that
- the first mobile communication device or the second mobile communication device that has transmitted information about the second mobile communication device that is the target of the search request is the target of the search request, respectively. If communication with the second mobile communication device that is the target of the search request is established, at least one of the second mobile communication devices that are the target of the search request is established. It is preferable to acquire and transmit identification information.
- the first portable communication device that has acquired the identification information transmits the acquired information to the server
- the second portable communication device that has acquired the identification information is the first portable communication device associated with the first portable communication device. It is preferable to transmit the acquired information to a communication device or the server.
- the plurality of second mobile communication devices have position information detection means for detecting their own positions, and the plurality of first mobile communication devices and the plurality of second mobile communication devices are respectively If there is position information obtained by the position information detecting means together with identification information of the second portable communication device that is the target of the search request, the position information is acquired together and transmitted. It is preferable to do.
- At least the first mobile communication device that has acquired the identification information transmits the acquired information to the server, and the second mobile communication device that has acquired the identification information and the location information is associated with itself.
- the acquired information is transmitted to the first portable communication device or the server.
- the invention for solving the above-described problem is a mobile communication device used when collectively managing a plurality of mobile communication devices, and is capable of directly communicating with a first communication means capable of communicating with a server and other mobile communication devices.
- the second communication means, a storage unit for storing information, and the second communication means are used to communicate with another mobile communication device to acquire at least identification information of the other mobile communication device, and the acquired time
- the mobile communication device associated with the mobile communication device is related to the search request.
- the invention for solving the above-described problem is a mobile communication device associated with each of a plurality of mobile communication devices managed in a group, and is directly connected to a first communication means capable of communicating with a server and other mobile communication devices. While communicating with another portable communication device using the second communication means capable of communication, a storage unit for storing information, and using the second communication means to obtain at least identification information of the other portable communication device, When the information related to the search request of the mobile communication device associated with the mobile communication device to be managed in a group is received from the mobile communication device associated with the mobile communication device associated with the acquired time and stored in the storage unit, And a control unit that transmits information about the mobile communication device targeted for the search request via the first communication unit.
- the invention for solving the above-described problem is a mobile communication device used when collectively managing a plurality of mobile communication devices, and is capable of directly communicating with a first communication means capable of communicating with a server and other mobile communication devices. If information about a search request for a mobile communication device associated with a second communication means, a storage unit that stores information, and a mobile communication device that is collectively managed is acquired, the mobile communication device that is the target of the search request If the communication with the mobile communication device that is the target of the search request can be established, control means for acquiring identification information and position information of the mobile communication device that is the target of the search request, Is a portable communication device.
- the invention for solving the above-described problem is a server that collectively manages a plurality of portable communication devices, and is associated with a storage unit that stores information on the plurality of portable communication devices and a portable communication device that is collectively managed.
- Mobile information communication device for collective management the information regarding the search request is transmitted to the plurality of mobile communication devices, and the information regarding the search request is received.
- a communication system server comprising: a processing unit that acquires information about the mobile communication device that is a target of the search request from the mobile communication device that has received the information related to the search request from the mobile communication device that is collectively managed. It is.
- the processing unit transmits search support information to a mobile communication device that has transmitted information related to the search request after acquiring information about the mobile communication device that is the target of the search request. Is preferable.
- the present invention can provide a communication system, a portable communication device, and a communication system server useful for assisting in searching for an undiscovered lost child or the like.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of a communication system according to the present embodiment.
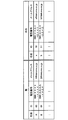
- FIG. 2 is an information table showing an example of information of the parent mobile communication device managed by the server included in the communication system according to the present embodiment.
- FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram showing a correspondence relationship between information on the parent portable communication device and information on the child portable communication device.
- FIG. 4 is a device configuration diagram of the parent portable communication device.
- FIG. 5 is a device configuration diagram of the portable communication device for children.
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing each step of information collection processing executed by the communication system.
- FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram of timing for executing short-range wireless communication in the information collection process.
- FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram of timing for executing short-range wireless communication in the information collection process.
- FIG. 9 is a conceptual diagram of short-range wireless communication executed in the information collection process.
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the server of the communication system.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the parent mobile communication device of the communication system.
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the child mobile communication device of the communication system.
- FIG. 13 is an explanatory diagram of search support processing.
- FIG. 14 is an explanatory diagram of search support processing.
- FIG. 15 is a conceptual diagram of search support information transmitted to the search request source.
- FIG. 16 is an explanatory diagram of search support processing according to a modification of the present embodiment.
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the server of the communication system.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the parent mobile communication device of the communication system.
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart
- FIG. 17 is a conceptual diagram of search support information transmitted to search target information or a search request source.
- FIG. 18 is a flowchart illustrating each process of search support processing according to the second embodiment, which is executed by the parent mobile communication device.
- FIG. 19 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing according to the second embodiment, which is executed by the child mobile communication device.
- a mobile phone is taken as an example of a mobile communication device.
- the application target of the present invention is not limited to a mobile phone.
- a personal handyphone system (PHS) or a PDA (Personal Data having a communication function) is provided. Assistant).
- a portable communication device such as a crime prevention terminal or a child's mobile phone is purchased in a lump for the whole school or the whole local government for crime prevention.
- short distance wireless communication technology such as Bluetooth is used to assist in searching for an undiscovered lost child.
- the parent mobile communication device is collectively managed by a server or the like, and short-range wireless communication is performed between the parent mobile communication device that is collectively managed and the corresponding child mobile communication device.
- the location information of the mobile communication device of the child is periodically acquired and stored in the mobile communication device or the server.
- the position of the stored mobile communication device of the child Use information to help find undiscovered lost children.
- the parent mobile communication device and the child mobile communication device are always associated with each other, using this correspondence, only the parent mobile communication device is collectively managed to prevent leakage of the child's personal information. Reduce as much as possible.
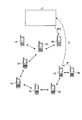
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a communication system according to the present embodiment.
- a communication system 100 shown in FIG. 1 collectively manages a plurality of mobile communication devices (first mobile communication devices) 1A, 1B, and the like. Then, when there is a search request for the mobile communication devices (second mobile communication devices) 2a, 2b, etc. associated with each of the plurality of mobile communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. that are collectively managed, Helps (supports) the search for whereabouts of the search request.
- the communication system 100 includes a plurality of mobile communication devices 1A, 1B, etc., a plurality of mobile communication devices 2a, 2b, etc., and a server 3.
- the plurality of first mobile communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. are mobile communication devices used by a parent, and are hereinafter referred to as parent mobile communication devices.
- the plurality of second mobile communication devices 2a, 2b, etc. are mobile communication devices used by children, and are hereinafter referred to as child mobile communication devices.
- the same alphabet corresponds to the parent-child relationship, with the upper case representing the parent and the lower case representing the child.
- the parent portable communication device 1A is used for the parent A, and the child a of the parent A uses the child portable communication device 2a.
- the alphabets attached to the reference numerals 1 and 2 representing the mobile communication device are added for convenience in order to identify the respective mobile communication devices.
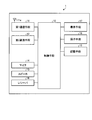
- the server 3 includes a processing unit 3C, a storage unit 3M, and an input / output unit (IO) 3I.
- the server 3 is connected to the base station 5 via the communication control device 4 connected to the input / output unit 3I.
- the base station 5 receives radio waves from the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. and the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b, etc., or the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. and the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b. Sending radio waves to etc.
- the base station 5 includes an antenna 5A and reference time generation means 5C that generates a reference time.
- the reference time generating means 5C is obtained from, for example, a GPS (Global Positioning System) clock, that is, a transmitter that transmits a time acquired from an atomic clock mounted on a GPS satellite, or a reference station that transmits a time for a radio clock. There is something that sends the time.
- the communication control device 4 controls information conversion and transmission / reception control between the base station 5 and the server 3.
- the processing unit 3C included in the server 3 is a computer such as an MPU (Micro Processing Unit) that controls the operation of the server 3 to exhibit the functions of the server 3.
- the storage unit 3M performs group management in the communication system 100 transmitted from the parent mobile communication devices 1A, 1B, etc., the parent mobile communication devices 1A, 1B, etc., and the child mobile communication devices 2a, 2b, etc. Information (position information, time information, etc.) and the like of the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B and the like and the corresponding child portable communication devices 2a, 2b are stored and accumulated.
- the storage unit 3M is a secondary storage device such as an HDD (Hard Disc Drive) device.
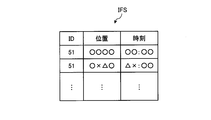
- FIG. 2 is an information table showing an example of information of the parent portable communication device managed by the server included in the communication system according to the present embodiment.
- the information table 6 stored in the storage unit 3M describes information related to a plurality of parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, and the like. Since the storage unit 3M is a component of the server 3, it can be understood that the server 3 stores information related to the plurality of parent portable communication devices 1A and 1B. As shown in FIG. 2, information related to a plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 ⁇ / b> A, 1 ⁇ / b> B, etc. stored in the information table 6 includes name (parent name), ID (device IDs of the parent portable communication devices 1 ⁇ / b> A, 1 ⁇ / b> B, etc.). ), Phone number, email address, etc.
- FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram showing a correspondence relationship between information on the parent portable communication device and information on the child portable communication device.
- the correspondence between the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B and the like and the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b, etc. corresponds to the parent-child relationship between the parent A and the child a.
- the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. are always associated with the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b, etc.
- the communication system 100 performs group management by storing only information related to the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B and the like in the server 3 (more specifically, the storage unit 3M).
- the server 3 can directly access the parent mobile communication devices 1A and 1B using information described in the information table 6, for example, an e-mail address.
- the server 3 since the server 3 does not store information related to the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b, etc., the server 3 accesses the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b, etc. via the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. Will do.
- the server 3 does not have information regarding the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b and the like, and cannot directly access the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b. It is possible to reduce the risk of information leaking from the communication devices 2a and 2b. As a result, the communication system 100 can effectively suppress the leakage of the child's personal information.
- Each of the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. is associated with each of the child portable communication devices 2a, 2b, etc.
- the server 3 stores only information related to the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc., and the parent portable communication devices 1A, 1B, etc. are directly managed in a collective manner. 2b and the like are also indirectly managed by the server 3 as a group. There may be a case where a plurality of child portable communication devices are associated with one parent portable communication device, and a plurality of parent portable communication devices are associated with one child portable communication device. Sometimes.
- the former is, for example, a relationship between a parent portable communication device of one parent and a portable communication device for a plurality of children's children
- the latter is, for example, for a parent's parent portable communication device and a child of a child. It is a relationship with a portable communication device.
- FIG. 4 is a device configuration diagram of the parent portable communication device.
- FIG. 5 is a device configuration diagram of the portable communication device for children.
- the parent portable communication device 1 includes a control unit 10, a storage unit 13, a first communication unit 11 to which a terminal antenna 11 a is connected, a second communication unit 12, a microphone 14, a speaker 15, and a receiver 16. Display means 17 and operation means 18.
- the child mobile communication device 2 is the same as the parent mobile communication device 1 except that the location information detection means 19 is added to the parent mobile communication device 1. Only the parent portable communication device 1 will be described.
- the control means 10 has a function of comprehensively controlling the overall operation of the parent portable communication device 1. That is, the control unit 10 controls the operations of the first communication unit 11, the second communication unit 12, the display unit 17, and the like so that various processes of the parent mobile communication device 1 are executed in an appropriate procedure.
- Various processes of the parent mobile communication device 1 include, for example, voice calls performed via a circuit switching network, creation and transmission / reception of e-mails, browsing of the Internet Web (World Wide Web) site, and search support Communication and information gathering.
- the control unit 10 executes processing based on a program (for example, an operating system program, an application program, etc.) stored in the storage unit 13 or an operation input by the operation unit (for example, operation key) 18. Further, the control means 10 executes processing of an audio signal input to the microphone 14 and the receiver 16 and an audio signal output from the speaker 15.
- the display means (for example, a liquid crystal panel) 17 causes the display panel to display a video corresponding to the video data supplied from the control means 10 and an image corresponding to the image data.
- the control means 10 is composed of, for example, a microprocessor unit (MPU: Micro Processing Unit), and the parent portable communication device 1 described above according to a procedure instructed by software for executing search support processing according to the present embodiment.
- the various processes are executed. That is, the control unit 10 sequentially reads instruction codes from an operating system program, an application program, or the like stored in the storage unit 13 and executes processing.
- the storage means 13 stores software and data used for processing by the control means 10.
- the storage means 13 stores information collected for search support.
- the computer program and temporary data used in the software processing process are temporarily stored in the work area assigned to the storage unit 13 by the control unit 10.
- the storage means 13 is, for example, a non-volatile storage device (non-volatile semiconductor memory such as ROM: Read Only Memory, hard disk device, etc.), or a readable / writable storage device (for example, SRAM: Static Random Access Memory, DRAM: Dynamic Random Access Memory).
- the first communication means 11 establishes a radio signal line by a CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) method or the like with the base station via a channel assigned by the base station, and with the base station 5 shown in FIG. Perform telephone communication and information communication.
- the first communication means 11 can access the server 3 shown in FIG. 1 via the base station 5 and exchange information between them.
- the second communication means 12 is a short-range wireless communication means, and can directly perform wireless information communication between portable communication devices and exchange information at a distance of several meters to several tens of meters.
- the parent mobile communication device 1 can realize both communication between mobile communication devices via a base station and direct communication between mobile communication devices not via a base station.
- the position information detection means 19 included in the child mobile communication device 2 shown in FIG. 5 detects, for example, a position from a GPS satellite and acquires position information of a plurality of base stations. To detect the position of.
- the position information is detected.
- the means 19 may read the position information stored in the IC tag and detect its own position.
- the own position detected by the position information detection means 19 is stored in, for example, the storage means 13, or the control means 10 via the second communication means 12 for the other portable communication device 2 for children and the parent shown in FIG. Or transmitted to the mobile communication device 1.
- a group of a plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 and a plurality of child portable communication devices 2 is referred to as a group management terminal group. Further, when the parent mobile communication device 1 and the child mobile communication device 2 in the group management terminal group are not distinguished, they are referred to as in-group terminal devices as necessary.
- the search support process includes an information collection process and a search support process.
- the communication system 100 performs information collection processing and search support processing to support searching for an undiscovered lost child or the like.
- the parent mobile communication device 1 or the child mobile communication device 2 acquires location information other than itself, and stores its own information corresponding to the acquired time. This is processing to be stored in the means 13 or the server 3.
- the position information of the mobile communication device 2 for a child to be searched is extracted from the accumulated position information, for example, the request source of the search request (search This is a process for assisting in searching for a lost child or the like by sending it to the requester.
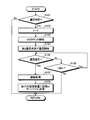
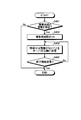
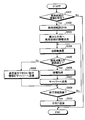
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing each step of information collection processing executed by the communication system.
- 7 and 8 are explanatory diagrams of timing for executing short-range wireless communication in the information collection process.
- FIG. 9 is a conceptual diagram of short-range wireless communication executed in the information collection process.
- the information collection process is not always executed, but is periodically executed for a predetermined time.
- the power consumption of the parent portable communication device 1 and the child portable communication device 2 becomes intense. For this reason, an increase in power consumption is suppressed by periodically executing a predetermined time information collection process. If power consumption does not become a problem, the information collection process may be executed at all times. In this case, since more information is obtained, in the search for an undiscovered lost child or the like, the accuracy of specifying the search target is improved.
- the second communication means 12 communicates with another portable communication device. However, at the time of communication, it is necessary that communication ports between communication targets be open. For this reason, in the communication system 100, when the communication time comes, the plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 that are collectively managed and the child portable communication devices 2 associated therewith are ready to communicate simultaneously. Need to be.
- step S101 the control means 10 of each parent portable communication device 1 and the control means 10 of the child portable communication device 2 determine whether or not the communication time in the information collection processing has come. To do. At this time, each control means 10 acquires the reference time generating means 5C of the base station 5 shown in FIG. 1 via the first communication means 11, and determines whether or not the communication time has come.
- the communication time is, for example, every minute, and the communication time is, for example, 1 to 15 seconds. That is, in the information collection process, the plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 and the child portable communication device 2 associated therewith communicate with each other for a predetermined time every second using the second communication means 12. To get. By doing in this way, the group management terminal group can be surely communicated at a predetermined time, so that it is possible to suppress power consumption and reduce information collection omission.
- step S101, No If the control means 10 of the terminal device in each group determines that it is not the communication time (step S101, No), the process returns to START.
- the control means 10 of each intra-group terminal apparatus determines that it is the communication time (step S101, Yes)
- step S102 the control means 10 of each intra-group terminal apparatus sets the elapsed time t to zero.
- step S103 the control means 10 of each intra-group terminal device starts counting the elapsed time t, and then proceeds to step S104, using the second communication means 12 of each intra-group terminal device, Communication with the terminal device in the group is started.
- step S105 the control means 10 of each intra-group terminal device determines whether communication with another intra-group terminal device has been established.
- the control means 10 of each intra-group terminal apparatus determines that communication has not been established (No at Step S105)
- the process proceeds to Step S106.
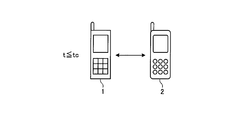
- step S106 the control means 10 of the intra-group terminal device that has not established communication determines whether or not the elapsed time t is equal to or shorter than the communicable time tc.
- the communicable time tc is a time during which communication by the second communication means 12 is possible after the communication time is reached in the information collection process, and is set to 1 to 15 seconds, for example. That is, in the information collection process, the time from the communication time to the communicable time tc is a time during which communication by the second communication unit 12 is possible.
- step S106 When the control means 10 of the in-group terminal device that has not established communication determines that t ⁇ tc is satisfied (step S106, Yes), the control means 10 of the in-group terminal device that has not established communication does not satisfy t ⁇ tc. Communication by the second communication means 12 is attempted until tc is reached.
- step S106, No When the control means 10 of the intra-group terminal device with which communication has not been established determines that t> tc (step S106, No), the process returns to START and starts the information collection process again.
- step S105 When the control means 10 of each intra-group terminal apparatus determines that communication has been established (step S105, Yes), the process proceeds to step S107, and the control means 10 of the intra-group terminal apparatuses established with the respective second At least identification information of the intra-group terminal device to be communicated is acquired via the communication means 12.
- the identification information is information for identifying the parent portable communication device 1 and the child portable communication device 2, and is, for example, a device ID.
- the position information is information indicating the position of the parent mobile communication device 1 or the child mobile communication device 2 at the time of information acquisition, and is, for example, latitude and longitude, an address, or the like.
- the position information is detected by the position information detection means 19 of the child mobile communication device 2.
- step S107 the control means 10 between the intra-group terminal devices with which communication has been established, after acquiring the identification information and the position information, communicates with another intra-group terminal device if the communicable time tc has not elapsed.
- the identification information and the position information may be acquired by establishing.
- step S106 communication is possible between in-group terminal devices (in this example, between the parent portable communication device 1 and the child portable communication device 2) until the communicable time tc elapses.
- step S106 communication with another intra-group terminal device is attempted.
- the communicable time tc elapses, communication between the intra-group terminal devices (in this example, between the parent portable communication device 1 and the child portable communication device 2) is not performed, and the step In S106, communication with other intra-group terminal devices is not attempted.
- a predetermined time communication available time tc
- the parent portable communication device 1A can establish communication with the parent portable communication device 1C and the child portable communication device 2b.
- the identification information and the position information are transmitted / received to / from each other selected according to ().
- the parent portable communication device 1B since the parent portable communication device 1B can establish communication with the child portable communication device 2a, the parent portable communication device 1B transmits and receives identification information and position information to and from each other.
- the second communication means 12 which is a short-range wireless communication means is used.
- CA1 shown in FIG. 9 is a communicable range of the second communication unit 12 included in the parent portable communication device 1A
- CA2 is a communicable range of the second communication unit 12 included in the child portable communication device 2a.
- the communicable ranges CA1 and CA2 are within a circle having a radius of several meters to several tens of meters.
- the child mobile communication device 2b does not belong to any of the communicable ranges CA1 and CA2.
- the other party with whom communication has been established exists within a circle with a radius of several meters to several tens of meters centered on itself. Therefore, even if the intra-group terminal device cannot acquire the position information of the communication partner, if the position information of itself is known, the position information of the communication partner can be estimated from the position information. For example, the position of the communication partner can be estimated from the own position within a circle whose radius is the communicable distance of the second communication means 12. Further, if the parent mobile communication device 1 or the like has a function capable of estimating the direction of the transmission source from the direction of the received radio wave, the direction in which the communication partner exists can also be estimated.
- the process proceeds to step S108, and the control unit 10 of the intra-group terminal device that acquired the identification information and the position information acquires the acquired identification information and the position information. And stored in the storage unit 13 or transmitted to the server 3 via the first communication unit 11.
- the control unit 10 of the intra-group terminal device stores at least the acquired identification information in the storage unit 13 in association with the acquired time or through the first communication unit 11.
- the control unit 10 of the intra-group terminal apparatus estimates the position information of the communication partner from its own position information and stores it in the storage unit 13 in association with the time when the identification information is acquired. You may transmit to the server 3 via the 1st communication means 11.
- the information collection process is completed by the above-described steps. Note that the information collection process is periodically executed every time a predetermined communication start time arrives. Next, the operation support process will be described.
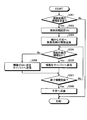
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing each step of the search support process executed by the server of the communication system.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the parent mobile communication device of the communication system.
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the child mobile communication device of the communication system.
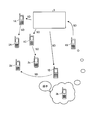
- 13 and 14 are explanatory diagrams of search support processing.
- FIG. 15 is a conceptual diagram of search support information transmitted to the search request source.
- the search support process is triggered by the fact that the server 3 of the communication system 100 shown in FIG. 1 has received a search request. In the case of searching for a lost child or the like, the search request is transmitted from the parent mobile communication device 1 to the server 3, for example.
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing each step of the search support process executed by the server of the communication system.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing executed by the parent mobile communication device of the communication system.
- FIG. 12 is
- the parent mobile communication device 1 ⁇ / b> B transmits a search request SD for the corresponding child mobile communication device 2 b to the server 3.
- the search request SD is by e-mail, but may be by a predetermined operation on the operation means 18 or by voice.
- step S201 The search support process of the server 3 described here is executed by the processing unit 3C of the server 3 shown in FIG. 1, and the collected information is stored in the storage unit 3M.
- step S201 the server 3 determines whether or not there is a search request SD, that is, whether or not the search request SD is received.
- step S201, No the search support process ends.
- the plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 and the plurality of child portable communication devices 2 collectively managed by the server 3 periodically execute the above-described information collection processing.
- step S201 determines that the search request SD has been received (step S201, Yes)
- the process proceeds to step S202, and the server 3 turns on the search request setting.
- this search request setting is ON, support for searching for a lost child or the like by the communication system 100 is executed.
- step S203 the server 3 transmits the search request SD to a plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 (1A, 1C, 1D in the example shown in FIG. 13) that are collectively managed.
- the search request SD is transmitted via the communication control device 4 and the base station 5 shown in FIG.
- the parent mobile communication device 1 acquires the search request SD via the first communication means 11 shown in FIG.
- the server 3 includes a plurality of parent portable communication devices 1 (1A, 1C, and 1D in the example shown in FIG. 14) that are collectively managed, and child mobile phones that are associated with them.
- Information (search target information) about the child mobile communication device 2b (referred to as search target if necessary) from the communication device 2 (2a, 2c, 2d in the example shown in FIG. 14)
- search target Information about the search target is information transmitted from the parent portable communication device 1 or the child portable communication device 2, and these are information on the intra-group terminal device (in-group terminal information) stored in the storage unit 13. ).
- the intra-group terminal information is collected by the above-described information collecting process and stored in the respective parent portable communication device 1 and child portable communication device 2. Are associated with each other).
- the intra-group terminal information is obtained by associating identification information and position information of the intra-group terminal device with these acquisition times.
- the intra-group terminal information is obtained by direct short-range wireless communication between the parent portable communication device 1 and the child portable communication device 2 with a parent or child portable communication device different from itself in the information collecting process. This is identification information and position information of different parent or child portable communication devices.
- the intra-group terminal information may or may not include identification information, position information, and the like of the search target. However, even in the latter case, the information that the parent or child portable communication device that generated the intra-group terminal information did not encounter the search target within the communicable range of the second communication means 12 is obtained. . For this reason, the information that the identification information or the position information of the search target is not included in the intra-group terminal information is also the search target information IF.
- the search target information IF includes both intra-group terminal information and information that the search target identification information, position information, and the like are not included in the intra-group terminal information.
- the search target information IF is acquired, and the collected server 3 creates search support information IFS shown in FIG. 14 from the collected search target information IF and transmits it to the search request source.
- step S204 the server 3 searches the collected search target information IF with the device ID of the search target, identifies identification information and position information about the child mobile communication device 2b that is the target of the search request SD, the position Information about the time when the information was acquired is extracted. Even if the search target information IF does not include identification information or position information about the search target, the parent or child mobile communication device that generated the search target information IF does not encounter the search target. Information is obtained.
- the server 3 creates search support information IFS as shown in FIG. 15 and transmits it to the search request source, that is, the parent mobile communication device 1B that has transmitted the search request SD. If no identification information or position information about the search target is obtained from the collected search target information IF, that is, only information that the search target information IF does not include the identification information or position information of the search target If only the information is obtained, the search support information IFS is that no trace of the search target could be found within the group management.
- the ID in the search support information IFS corresponds to the device ID (51, see FIG. 3) of the child mobile communication device 2b that is the search target.
- the server 3 may create the search support information IFS every time a predetermined time has elapsed after receiving the search request SD, or may create the search support information IFS after collecting a predetermined amount of information. Good.
- step S205 the server 3 determines whether or not the search support process is complete.
- the termination condition may be, for example, when the server 3 receives the search request SD and a predetermined time has elapsed, or may be a case where the server 3 has received information that the search target has been found. It is good.
- the server 3 determines that the search support processing termination condition is not satisfied (No in step S205)
- the server 3 continues to collect the intra-group terminal information and to create and transmit the search support information IFS.
- step S206 sets the search request to OFF, and this information, that is, the information to end the search support process.
- the search support processing of the parent mobile communication device 1 described here is executed by the control means 10 of the parent mobile communication device 1 shown in FIG.
- the control unit 10 of the parent mobile communication device 1 determines whether or not the information related to the search request SD transmitted by the server 3 in step S203 described above has been received and acquired.
- the information related to the search request SD includes at least identification information (for example, device ID) of the search target (in this example, the mobile communication device 2b for children).
- step S301, No the search support process of the parent mobile communication device 1 ends.
- the control means 10 determines that the information related to the search request SD has been acquired (step S301, Yes)
- the control means 10 turns on the search request setting in step S302.
- This search request setting is unique to the parent portable communication device 1, and when it is ON, support for searching for a lost child or the like by the communication system 100 is executed.
- the control means 10 may notify the speaker 15 or the display means 17 to that effect.
- the owner of the parent mobile communication device 1 knows that the search request SD has been made, and can also participate in the search or directly transmit information to the search request source. The search efficiency for lost children is improved.
- step S303 the control means 10 of the parent portable communication device 1 transmits information related to the search request SD to the child portable communication device 2 corresponding to itself.
- the parent portable communication device 1A is a child portable communication device 2a
- the parent portable communication device 1D is a child portable communication device 2d
- the parent portable communication device 1C is a child portable communication device 2c.
- information on the search request SD is transmitted.
- the control means 10 of each parent portable communication device 1A, 1C, 1D shown in FIG. 14 stores the search target information in each storage means 13 based on the information related to the search request SD. It is determined whether or not it is accumulated.
- step S304 If the control means 10 determines that there is information to be searched (step S304, Yes), the process proceeds to step S305. Then, the control means 10 of the parent portable communication device 1 transmits the search target information IF stored in the storage means 13 to the server 3 via the first communication means 11 shown in FIG. 14). In this case, based on information related to the search request SD (for example, the device ID of the search target), information obtained from the search target is extracted from the intra-group terminal information stored in the storage unit 13 and obtained from the search target. Only the information may be transmitted to the server 3. By doing so, it is possible to reduce the load when the server 3 creates the search support information IFS in step S204 of FIG.
- information related to the search request SD for example, the device ID of the search target
- the information comprised only by search object is transmitted to the server 3, compared with the case where search object information IF is transmitted to the server 3, information amount can be reduced. This is preferable because the communication time between the parent portable communication device 1 and the server 3 is shortened, and the line occupation time can be shortened.
- step S304 when the control means 10 determines that there is no information to be searched (step S304, No), the process proceeds to step S306. Then, the control means 10 of the parent portable communication device 1 transmits information indicating that there is no information to be searched to the server 3 via the first communication means 11 shown in FIG. 4 as the search target information IF. In this way, the search target information IF is transmitted from the parent mobile communication device 1 in step S305 or step S306.
- step S305 or step S306 the process proceeds to step S307.
- the control means 10 such as the parent mobile communication devices 1A and 1C receives information from the server 3 to end the search support process, and determines whether or not it has been acquired. If the control means 10 determines that the information to end the search support process has not been acquired (No at Step S307), Steps S304 to S306 are repeated until the information is received and acquired.
- the parent mobile communication device 1 may receive the search target information IF transmitted from the corresponding child mobile communication device 2 as described later.
- the control means 10 stores it in the storage means 13. If the parent mobile communication device 1 has not received the information indicating that the search support process is to be terminated, the process returns to step S304. At this time, the control means 10 has the received search target information IF in the storage means 13. It is determined whether or not to perform, and the subsequent steps are executed.
- step S307 When it is determined that the control means 10 has received information indicating that the search support process is to be ended (step S307, Yes), the process proceeds to step S308.
- step S308 the control means 10 of the parent mobile communication device 1 that has received the information to end the search support process passes the information to the child mobile communication device 2 corresponding to itself via the first communication means 11. To send. Then, the control means 10 turns off the search request setting. Thereby, support for searching for a lost child or the like by the communication system 100 is not executed, and only the above-described information collection processing is executed. Next, the search support process of the child mobile communication device 2 will be described.
- the search support process of the child mobile communication device 2 described here is executed by the control means 10 of the child mobile communication device 2 shown in FIG.
- the control means 10 of the child mobile communication device 2 determines whether or not the information related to the search request SD transmitted by the parent mobile communication device 1 in step S303 described above has been acquired.
- the information related to the search request SD includes at least identification information (for example, device ID) of the search target (in this example, the mobile communication device 2b for children).
- the search support process of the child mobile communication device 2 ends.
- the control means 10 determines that the information about the search request SD has not been acquired (No at Step S401)
- the search support process of the child mobile communication device 2 ends.
- the control means 10 determines that the information related to the search request SD has been acquired (step S401, Yes)
- the process proceeds to step S402, and the control means 10 turns on the search request setting.
- This search request setting is unique to the child mobile communication device 2, and when it is ON, support for searching for a lost child or the like by the communication system 100 is executed.
- the control unit 10 may cause the speaker 15 or the display unit 17 to notify that effect.
- the control means 10 of the child mobile communication device 2 obtains the intra-group terminal information stored in the storage means 13 or the information that there is no search target information, that is, the search target information IF. Then, the data is transmitted to the parent portable communication device 1 or the server 3 corresponding to itself via the first communication means 11 (see FIG. 14).
- the search target information IF is transmitted to the parent portable communication device 1, there is no connection between the child portable communication device 2 and the server 3, so that the security of the child portable communication device 2 is maintained higher, which is preferable.
- the server 3 can quickly acquire the search target information IF.
- the information obtained from the search target is extracted from the intra-group terminal information accumulated in the storage means 13 and obtained from the search target. Only the information may be transmitted to the parent portable communication device 1 or the server 3. This point is as described in the search support processing of the parent mobile communication device 1. If the child mobile communication device 2 transmits the search target information IF directly to the server 3, the processing load on the parent mobile communication device 1 is reduced as compared with the case of transmitting the search target information IF to the server 3 via the parent mobile communication device 1. Therefore, it is preferable.
- step S404 the control means 10 such as the child mobile communication devices 2a and 2c determines whether or not information indicating that the search support processing is to be terminated is received from the parent mobile communication devices 1A and 1B. To do.
- step S403 is repeated until the information is received.
- control means 10 determines that the information indicating that the search support processing is to be ended has been received (Yes in step S404), the control means 10 of the child mobile communication device 2 that has received the information indicating that the search support processing is to be ended. Turns off the search request setting. Thereby, support for searching for a lost child or the like by the communication system 100 is not executed, and only the above-described information collection processing is executed.
- identification information, position information, and the like acquired from the parent and child mobile communication devices by short-range communication are stored in association with the acquired time.
- the server collects identification information and the like stored in a plurality of parent and child mobile communication devices as search target information. Then, by searching for the search target from the collected search target information, the server extracts search target identification information and position information, time information when the position information was acquired, etc., and creates search support information To do. Since this search support information can know the position information of the search target in time series, it is possible to know what trajectory the search target has followed.
- the search target when transmitting the search target information, if the identification information of the parent or child mobile communication device to be transmitted is added, the search target is close to any parent or child mobile communication device. You can also know if you were in. Furthermore, if you add your own identification information, even if there is no location information for the search target, you can listen to the situation at that time from the owner of the mobile communication device for parents or children that was near the search target. it can. This also provides clues for the search. Further, in the present embodiment, only information related to the parent mobile communication device is stored in the server for group management, and the child mobile communication devices are indirectly group-managed by the correspondence of the parent-child relationship. As a result, leakage of the child's personal information can be reduced as much as possible. In the future, if a pet collar equipped with a communication function appears, searching for undiscovered stray puppies and stray kittens can be performed by the same method as in this embodiment.
- FIG. 16 is an explanatory diagram of search support processing according to a modification of the present embodiment.
- FIG. 17 is a conceptual diagram of search support information transmitted to search target information or a search request source.
- the parent mobile communication device 1 and the child mobile communication device 2 transmit the search target information IF, they attempt communication with the search target, respectively.
- the search target is established, at least identification information of the search target is acquired and transmitted as the search target information IF.
- the parent mobile communication device 1 and the child mobile communication device 2 that have received and acquired the information related to the search request SD transmit the search target information IF to the server 3, and then receive the second communication.
- the short distance wireless communication is executed using the means 12.
- the short-range wireless communication may be performed periodically for a certain period of time as in the information collection process described above.
- the parent mobile communication device 1D acquires at least identification information (identification information and position information in the present modification) of the child portable communication device 2b via the second communication unit 12.
- the parent mobile communication device 1D transmits the acquired identification information and the like of the child mobile communication device 2b to the server 3 as the search target information IF as shown in FIG.
- the server is directly connected to the server via the parent mobile communication device 1C. 3 to send.
- the server 3 that has acquired the search target information IF from the parent mobile communication device 1D creates search support information IFS using this, and sends it to the parent mobile communication device 1B that is the search request source. Send.
- the search support information IFS is the same as the search target information IF as shown in FIG.
- the communication target of the short-range wireless communication of the parent portable communication device or the child portable communication device may be only the child portable communication device 2b that is the search target.
- the search information IF stored in the storage means 13 of the parent portable communication device 1 or the child portable communication device 2 is transmitted to the server 3 or the like, and the parent portable communication device 1 and the child are also transmitted.
- Mobile communication device 2 tries to access the search target.
- the search efficiency for undiscovered lost children and the like can be improved, and the search for undiscovered lost children and the like can be performed more reliably.
- the search target information IF transmitted to the server 3 is not information accumulated for a certain period of time, the amount of information can be reduced as compared with the case where the search target information IF stored in the storage means 13 is transmitted. .
- the communication time between the parent portable communication device 1 and the server 3 is shortened, and the line occupation time can be shortened.
- the communication object of the short-distance communication using the 2nd communication means 12 can be specified based on the information regarding search request SD, when a communication object cannot be discovered, it does not need to perform acquisition of information. Thereby, power consumption can be further suppressed.
- FIG. 18 is a flowchart illustrating each process of search support processing according to the second embodiment, which is executed by the parent mobile communication device.
- FIG. 19 is a flowchart showing each step of search support processing according to the second embodiment, which is executed by the child mobile communication device.
- the search support processing according to the present embodiment does not execute the information collection processing, receives information related to the search request SD, and the acquired parent mobile communication device 1 and acquired child mobile communication device 2 Try to communicate. When communication with the search target is established, at least identification information of the search target is acquired and transmitted as the search target information IF.
- Search support processing according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 18, 19, 16, 17, and the like.
- the search support process of the server 3 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
- Step S501 to S503 of the search support process for the parent mobile communication device are the same as steps S301 to S303 of the search support process for the parent mobile communication device according to the first embodiment.
- step S504 the control means 10 such as the parent portable communication devices 1A and 1C shown in FIG. 16 tries to communicate with the child portable communication device 2b to be searched using the second communication means 12, respectively.
- step S505 the control means 10 such as the parent portable communication devices 1A and 1C determines whether or not communication with the child portable communication device 2b has been established.
- the control means 10 determines that communication with the child mobile communication device 2b has been established (step S505, Yes)
- the process proceeds to step S506.
- the control means 10 acquires at least identification information (identification information and position information in this embodiment) of the child portable communication device 2b via the second communication means 12.
- the control means 10 of the parent portable communication device 1D is connected to the child portable communication device 2b.
- At least identification information (in this embodiment, identification information and position information) is acquired.
- the control unit 10 transmits the acquired information on the child mobile communication device 2b to the server 3 as the search target information IF.
- step S508 the process returns to step S505, and if the control means 10 determines that communication with the child mobile communication device 2b has not been established (No in step S505), the process proceeds to step S508. And the control means 10 of such a parent portable communication device uses the information that the communication with the search target cannot be established as the search target information IF to the server 3 via the first communication means 11 shown in FIGS. Send. As described above, the search target information IF is transmitted to the server 3 in step S506 and step S507 or step S508. When step S507 or step S508 ends, the process proceeds to step S509.
- Step S509 and step S510 are basically the same as step S307 and step S308 of the search support process of the parent mobile communication device according to the first embodiment, but in step S509, the control means 10 ends the search support process. If it is determined that the information to the effect is not acquired (No at Step S509), Steps S504 to S508 are repeated. Next, search support processing for the mobile communication device for children will be described.
- Step S601 and step S602 are the same as step S401 and step S402 of the search support process of the child mobile communication device according to the first embodiment.
- step S603 the control means 10 such as the child portable communication devices 2a and 2c shown in FIG. 16 tries to communicate with the child portable communication device 2b to be searched using the second communication means 12, respectively.
- step S604 the control means 10 such as the child mobile communication devices 2a and 2c determines whether or not communication with the child mobile communication device 2b has been established.
- the control means 10 determines that communication with the child mobile communication device 2b has been established (step S604, Yes)
- the process proceeds to step S605.
- the control means 10 acquires at least identification information (identification information and position information in this embodiment) of the child portable communication device 2b via the second communication means 12.
- step S606 the control unit 10 transmits the acquired information of the child mobile communication device 2b to the parent mobile communication device 1 or the server 3 as the search target information IF.
- step S604 if the control means 10 determines that communication with the child mobile communication device 2b has not been established (step S604, No), the process proceeds to step S607.
- the control means 10 of such a portable communication device for children uses the information that the communication with the search target cannot be established as the search target information IF, and the corresponding parent via the first communication means 11 shown in FIGS.
- the search target information IF is transmitted to the server 3 in step S605 and step S606 or step S607.
- step S606 or step S607 ends, the process proceeds to step S608.
- Step S608 is basically the same as step S404 of the search support process of the parent mobile communication device according to the first embodiment. However, in step S608, the control unit 10 obtains information indicating that the search support process is ended. If it is determined that it has not been performed (No at Step S608), Steps S603 to S607 are repeated if it is determined No.
- the communication with the search target is attempted by short-range communication using the second communication means 12 and communication with the search target is established.
- Obtain and send to server 3. This eliminates the need for information collection processing, which can significantly reduce power consumption.
- the communication object of the short-distance communication using the 2nd communication means 12 can be specified based on the information regarding search request SD, when a communication object cannot be discovered, it does not need to perform acquisition of information. Thereby, power consumption can be further suppressed.
- the search target information IF transmitted to the server 3 is not information accumulated for a certain period of time, it is compared with the case where the search target information IF stored in the storage unit 13 is transmitted as in the first embodiment. Thus, the amount of information can be reduced. This is preferable because the communication time between the parent portable communication device 1 and the server 3 is shortened, and the line occupation time can be shortened.
- the communication system, the portable communication device, and the communication system server according to the present invention are useful for searching for an undiscovered lost child or the like.
Abstract
子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等の捜索依頼をサーバー3が取得したら、サーバー3は、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に対して捜索依頼に関する情報を送信する。親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等は、自身に対応付けられている子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等に捜索依頼に関する情報を送信するとともに、捜索依頼の対象となっている子供用携帯通信装置についての情報をサーバー3に送信する。捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等は、自身に対応付けられた親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に、捜索依頼の対象となっている子供用携帯通信装置についての情報を送信する。
Description
本発明は、複数の携帯通信装置を管理するとともに、必要に応じて一群の携帯通信装置の行方を捜索する際の手助け(支援)をする技術に関する。
迷子が発生したときに、携帯電話機を使用して迷子の捜索を支援する技術がある。例えば、特許文献1には、予め情報の記録された迷子ワッペンを入場者の迷子対象者および保護者に所持させ、迷子発生時に、会場係員や保護者が所持する携帯端末により迷子ワッペンの情報を読み取り、迷子保護情報や迷子届を電子メールで管理サーバへ送信し、管理サーバと前記携帯端末との間の電子メールの授受によって前記迷子を探索して保護する迷子支援方法が開示されている。
特許文献1に開示された技術は、迷子ワッペンを予め配布するため、テーマパーク等では有効であるが、日常生活においては不便である。また、特許文献1に開示された技術は、迷子が保護され、保護者が引き取りに行くことが必要であり、保護されていない迷子を捜索する際の支援には不十分である。本発明は、未発見の迷子等を捜索する際の支援に有用な通信システム及び携帯通信装置、並びに通信システム用サーバーを提供することを目的とする。
上述した課題を解決するための発明は、他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な短距離無線通信手段を有する複数の第1携帯通信装置、並びに他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な短距離無線通信手段を有する第2携帯通信装置と、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に関する情報を記憶するサーバーと、を有し、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、それぞれの前記短距離無線通信手段を用いて、前記第2携帯通信装置と通信して、前記第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、当該取得した識別情報を、取得した時間と対応付けて記憶し、前記第2携帯通信装置の捜索依頼を前記サーバーが取得したら、前記サーバーは、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した第1携帯通信装置は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置についての情報を前記サーバーに送信する、通信システムである。
前記発明において、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置についての情報を受信した前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、それぞれの前記短距離無線通信手段を用いて、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置との通信を試み、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置との通信が確立できたら、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得して前記サーバーに送信する、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な短距離無線通信手段を有する複数の第2携帯通信装置を備え、前記複数の第2携帯通信装置は、それぞれの前記短距離無線通信手段を用いて、他の第2携帯通信装置と通信して、他の第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、当該取得した識別情報を、取得した時間と対応付けて記憶し、前記サーバーが、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信したら、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、前記複数の第2携帯通信装置のうちの少なくとも一つに対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した前記複数の第2携帯通信装置は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を前記第1携帯通信端末に送信し、前記サーバーは、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を、前記第1携帯通信端末を介して前記複数の第2携帯端末装置から得る、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、前記サーバーが、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信したら、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、自身に対応付けられている前記複数の第2携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した前記複数の第2携帯通信装置は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を、自身と対応づいている前記第1携帯通信端末に送信する、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、前記短距離無線通信手段を用いた通信は、定期的に、所定の時間実行される、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、前記短距離無線通信手段を用いた通信は、前記複数の第2携帯通信装置及び前記複数の第1携帯通信装置がアクセス可能な基地局から発信される基準時間に基づいて実行される、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を送信した、前記第1携帯通信装置又は前記第2携帯通信装置は、それぞれ、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置との通信を試み、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置との通信が確立できたら、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得して送信する、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、前記識別情報を取得した第1携帯通信装置は、取得した情報を前記サーバーに送信し、前記識別情報を取得した第2携帯通信装置は、前記自身に対応付けられた第1携帯通信装置、又は前記サーバーに取得した情報を送信する、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、複数の第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも一部は、自身の位置を検出する位置情報検出手段を有し、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置及び複数の第2携帯通信装置は、それぞれ、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置の識別情報と共に前記位置情報検出手段によって得られた位置情報がある場合は、当該位置情報をあわせて取得して送信することを特徴とする、ことが好ましい。
前記発明において、少なくとも前記識別情報を取得した第1携帯通信装置は、取得した情報を前記サーバーに送信し、前記識別情報及び前記位置情報を取得した第2携帯通信装置は、自身に対応付けられた第1携帯通信装置、又は前記サーバーに取得した情報を送信する、ことが好ましい。
上述した課題を解決するための発明は、複数の携帯通信装置を集団管理する際に用いる携帯通信装置であり、サーバーと通信可能な第1通信手段と、他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な第2通信手段と、情報を記憶する記憶部と、前記第2通信手段を用いて他の携帯通信装置と通信して、当該他の携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、取得した時間と対応付けて前記記憶部へ記憶させ、団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を受信したら、自身に対応付けられている携帯通信装置に前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信するとともに、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を、前記第1通信手段を介して前記サーバーへ送信する制御手段と、を含む、携帯通信装置である。
上述した課題を解決するための発明は、集団管理される複数の携帯通信装置とそれぞれ対応付けられた携帯通信装置であり、サーバーと通信可能な第1通信手段と、他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な第2通信手段と、情報を記憶する記憶部と、前記第2通信手段を用いて他の携帯通信装置と通信して、当該他の携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、取得した時間と対応付けて前記記憶部へ記憶させ、集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を、自身に対応付けられている携帯通信装置から受信すると、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を、前記第1通信手段を介して送信する制御手段と、を含む、携帯通信装置である。
上述した課題を解決するための発明は、複数の携帯通信装置を集団管理する際に用いる携帯通信装置であり、サーバーと通信可能な第1通信手段と、他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な第2通信手段と、情報を記憶する記憶部と、集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を取得したら、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置との通信を試み、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置との通信が確立できたら、捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置の識別情報及び位置情報を取得する制御手段と、を含む、携帯通信装置である。
上述した課題を解決するための発明は、複数の携帯通信装置を集団管理するサーバーであり、前記複数の携帯通信装置に関する情報を記憶する記憶部と、集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を取得したら、前記複数の携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した、集団管理される携帯通信装置、及び当該集団管理される携帯通信装置から前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した携帯通信装置から、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を取得する処理部と、を含む、通信システム用サーバーである。
前記発明において、前記処理部は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を取得した後に、前記捜索依頼に関する情報を発信した携帯通信装置に対して、捜索支援情報を送信する、ことが好ましい。
本発明は、未発見の迷子等を捜索する際の支援に有用な通信システム及び携帯通信装置、並びに通信システム用サーバーを提供できる。
以下、本発明につき図面を参照しつつ詳細に説明する。なお、以下の説明により本発明が限定されるものではない。また、以下の説明における構成要素には、当業者が容易に想定できるもの、実質的に同一のもの、いわゆる均等の範囲のものが含まれる。以下においては、携帯通信装置の一例として、携帯電話機を取り上げるが、本発明の適用対象は携帯電話機に限定されるものではなく、例えば、PHS(Personal Handyphone System)や通信機能を有するPDA(Personal Data Assistant)であってもよい。
(実施形態1)
例えば、防犯のために防犯端末や子供用携帯電話等の携帯通信装置を学校全体、あるいは自治体全体で一括して購入するケースが想定される。このような場合に、本実施形態では、Bluetooth等の短距離無線通信技術を利用して、未発見の迷子を捜索する場合等の支援をするものである。すなわち、本実施形態では、親の携帯通信装置をサーバー等で集団管理するとともに、集団管理される親の携帯通信装置とそれぞれに対応する子供の携帯通信装置との間で、短距離無線通信を利用して定期的に子供の携帯通信装置の位置情報を取得し、携帯通信装置あるいはサーバーに蓄積しておく。そして、集団管理される親の携帯通信装置と対応する携帯通信装置を有する子供が迷子等になった場合であって、その捜索依頼があった場合は、蓄積された子供の携帯通信装置の位置情報により、未発見の迷子等の捜索を支援する。また、親の携帯通信装置と子供の携帯通信装置とは、常に対応付けられるので、この対応関係を利用して、親の携帯通信装置のみを集団管理することにより、子供の個人情報の漏洩をできる限り低減する。
例えば、防犯のために防犯端末や子供用携帯電話等の携帯通信装置を学校全体、あるいは自治体全体で一括して購入するケースが想定される。このような場合に、本実施形態では、Bluetooth等の短距離無線通信技術を利用して、未発見の迷子を捜索する場合等の支援をするものである。すなわち、本実施形態では、親の携帯通信装置をサーバー等で集団管理するとともに、集団管理される親の携帯通信装置とそれぞれに対応する子供の携帯通信装置との間で、短距離無線通信を利用して定期的に子供の携帯通信装置の位置情報を取得し、携帯通信装置あるいはサーバーに蓄積しておく。そして、集団管理される親の携帯通信装置と対応する携帯通信装置を有する子供が迷子等になった場合であって、その捜索依頼があった場合は、蓄積された子供の携帯通信装置の位置情報により、未発見の迷子等の捜索を支援する。また、親の携帯通信装置と子供の携帯通信装置とは、常に対応付けられるので、この対応関係を利用して、親の携帯通信装置のみを集団管理することにより、子供の個人情報の漏洩をできる限り低減する。
図1は、本実施形態に係る通信システムの概略構成を示す図である。図1に示す通信システム100は、複数の携帯通信装置(第1携帯通信装置)1A、1B等を集団管理する。そして、通信システム100は、集団管理される複数の携帯通信装置1A、1B等それぞれに対応付けられた携帯通信装置(第2携帯通信装置)2a、2b等の捜索依頼があった場合には、捜索依頼の対象となっているものの行方を捜索する際の手助け(支援)をするものである。
図1に示すように、通信システム100は、複数の携帯通信装置1A、1B等と、複数の携帯通信装置2a、2b等と、サーバー3と、を有する。本実施形態において、複数の第1携帯通信装置1A、1B等は、親が使用する携帯通信装置であり、以下においては親用携帯通信装置という。複数の第2携帯通信装置2a、2b等は、子供が使用する携帯通信装置であり、以下においては子供用携帯通信装置という。親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等と子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等とは、同じアルファベットが親子関係に対応しており、大文字が親、小文字が子供を表す。例えば、親用携帯通信装置1Aは親Aに使用されるものであり、親Aの子供aが子供用携帯通信装置2aを使用する。このように、携帯通信装置を表す符号1、2に付されるアルファベットは、それぞれの携帯通信装置を識別するために便宜上付されたものである。
サーバー3は、処理部3Cと、記憶部3Mと、入出力部(IO)3Iとを有している。サーバー3は、入出力部3Iに接続される通信制御装置4を介して基地局5に接続される。基地局5は、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等や子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等からの電波を受信したり、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等や子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等へ電波を発信したりする。基地局5は、アンテナ5Aと基準時刻を生成する基準時刻生成手段5Cとを有する。基準時刻生成手段5Cは、例えば、GPS(Global Positioning System)時計、すなわち、GPS用衛星に搭載される原子時計から取得した時刻を発信するものや、電波時計用の時刻を発信する基準局から取得した時刻を発信するものがある。通信制御装置4は、基地局5とサーバー3との間で、情報の変換や送受信の制御等を司るものである。
サーバー3が有する処理部3Cは、サーバー3の動作を制御して、サーバー3の機能を発揮させるものであり、MPU(Micro Processing Unit)等のコンピュータである。記憶部3Mは、複数の親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に関する情報や、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等や子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等から送信された、通信システム100で集団管理される親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等及びこれらに対応する子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等の情報(位置情報、時間情報等)等を記憶し、蓄積する。記憶部3Mは、例えば、HDD(Hard Disc Drive)装置等の二次記憶装置である。
図2は、本実施形態に係る通信システムが有するサーバーが管理する親用携帯通信装置の情報の一例を示す情報テーブルである。記憶部3Mが記憶する情報テーブル6は、複数の親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に関する情報が記述される。記憶部3Mは、サーバー3の構成要素であるので、サーバー3が、複数の親用携帯通信装置1A、1Bに関する情報を記憶していると把握することができる。図2に示すように、情報テーブル6に記憶される複数の親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に関する情報は、名前(親の名前)、ID(親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等の装置ID)、電話番号、メールアドレス等である。
図3は、親用携帯通信装置の情報と子供用携帯通信装置の情報との対応関係を示す概念図である。親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等と子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等との対応関係は、親Aとその子供aとの親子関係に対応する。このため、通信システム100において、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等と子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等とは常に対応付けられる。本実施形態において、通信システム100は、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に関する情報のみをサーバー3(より具体的には記憶部3M)に記憶させて、集団管理する。
サーバー3は、情報テーブル6に記述される情報、例えば、メールアドレスを用いて親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に直接アクセスできる。一方、サーバー3は、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等に関する情報は記憶していないため、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等を介して、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等に対してアクセスすることになる。このように、本実施形態において、サーバー3は、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等に関する情報を有しておらず、また、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2bへ直接アクセスはできないため、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2bの情報が漏洩するおそれを低減できる。これによって、通信システム100は、子供の個人情報の漏洩を効果的に抑制することができる。
それぞれの親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等とそれぞれの子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等とは対応付けられる。サーバー3には、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に関する情報のみが記憶されて、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等が直接集団管理されるが、上記の対応により、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2b等もサーバー3によって、間接的に集団管理されることになる。なお、1台の親用携帯通信装置に対して、複数台の子供用携帯通信装置が対応付けられる場合もあり、1台の子供用携帯通信装置に複数台の親用携帯通信装置が対応付けられる場合もある。前者は、例えば、一方の親の親用携帯通信装置と複数人の子供の子供用携帯通信装置との関係であり、後者は、例えば、両親の親用携帯通信装置と一人の子供の子供用携帯通信装置との関係である。次に、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等及び子供用携帯通信装置2a、2bの構成を説明する。
図4は、親用携帯通信装置の装置構成図である。図5は、子供用携帯通信装置の装置構成図である。親用携帯通信装置1は、制御手段10と、記憶手段13と、端末アンテナ11aが接続される第1通信手段11と、第2通信手段12と、マイク14と、スピーカ15と、レシーバ16と、表示手段17と、操作手段18とを有する。図5に示すように、子供用携帯通信装置2は、親用携帯通信装置1に位置情報検出手段19を付加した点以外は親用携帯通信装置1と同様なので、位置情報検出手段19以外については、親用携帯通信装置1についてのみ説明する。
制御手段10は、親用携帯通信装置1の全体的な動作を統括的に制御する機能を有する。すなわち、制御手段10は、親用携帯通信装置1の各種の処理が適切な手順で実行されるように、第1通信手段11や第2通信手段12や表示手段17等の動作を制御する。親用携帯通信装置1の各種の処理としては、例えば、回線交換網を介して行われる音声通話、電子メールの作成及び送受信、インターネットのWeb(World Wide Web)サイトの閲覧や、捜索支援のための通信や情報収集等がある。
制御手段10は、記憶手段13に記憶されているプログラム(例えば、オペレーティングシステムプログラム、アプリケーションプログラム等)や、操作手段(例えば、操作キー)18によって入力された操作に基づいて処理を実行する。また、制御手段10は、マイク14やレシーバ16に入力される音声信号やスピーカ15から出力される音声信号の処理を実行する。表示手段(例えば、液晶パネル)17は、制御手段10から供給される映像データに応じた映像や画像データに応じた画像を表示パネルに表示させる。
制御手段10は、例えば、マイクロプロセッサユニット(MPU:Micro Processing Unit)で構成され、本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理を実行するためのソフトウェアで指示された手順にしたがって上述した親用携帯通信装置1の各種の処理を実行する。すなわち、制御手段10は、記憶手段13に記憶されるオペレーティングシステムプログラムやアプリケーションプログラム等から命令コードを順次読み込んで処理を実行する。
記憶手段13には、制御手段10での処理に利用されるソフトウェアやデータが記憶されている。また、記憶手段13には、捜索支援のために収集された情報が記憶される。なお、ソフトウェアの処理過程で用いられるコンピュータプログラムや一時的なデータは、制御手段10によって記憶手段13に割り当てられた作業領域へ一時的に記憶される。記憶手段13は、例えば、不揮発性の記憶デバイス(ROM:Read Only Memory等の不揮発性半導体メモリ、ハードディスク装置等)や、読み書き可能な記憶デバイス(例えば、SRAM:Static Random Access Memory、DRAM:Dynamic Random Access Memory)等で構成される。
第1通信手段11は、基地局によって割り当てられるチャネルを介し、基地局との間でCDMA(Code Division Multiple Access)方式などによる無線信号回線を確立し、図1に示す基地局5との間で電話通信及び情報通信を行う。第1通信手段11は、基地局5を介して、図1に示すサーバー3にアクセスして、両者間で情報のやり取りをすることができる。第2通信手段12は、短距離無線通信手段であり、数m~数十mの距離で、携帯通信装置間で直接無線情報通信を行い、情報のやり取りをすることができる。このように、親用携帯通信装置1は、基地局を介した携帯通信装置間における通信と、基地局を介さない携帯通信装置間における直接通信との両方を実現することができる。
図5に示す子供用携帯通信装置2が有する位置情報検出手段19は、例えば、GPS衛星からの信号を取得して自身の位置を検出したり、複数の基地局の位置情報を取得して自身の位置を検出したりする。また、例えば、公園や電柱等の位置情報を記憶させたICタグを、当該公園や電柱等に取り付けておき、その子供用携帯通信装置2がそのICタグの近傍にきたときに、位置情報検出手段19が当該ICタグに記憶されている位置情報を読み出して、自身の位置を検出してもよい。位置情報検出手段19が検出した自身の位置は、例えば、記憶手段13に記憶されたり、制御手段10が第2通信手段12を介して他の子供用携帯通信装置2や図4に示す親用携帯通信装置1に送信したりする。
次に、本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理を説明する。これは、通信システム100によって実現される。以下においては、複数の親用携帯通信装置1及び複数の子供用携帯通信装置2の群を、集団管理端末群という。また、集団管理端末群の中における親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2を区別しない場合、必要に応じて群内端末装置という。
本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理は、情報収集処理と、捜索支援処理とを含んでいる。通信システム100は、情報収集処理と、捜索支援処理とを実行して、未発見の迷子等の捜索を支援する。情報収集処理は、迷子等の捜索依頼が発生する前に、親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2が、自身以外の位置情報を取得し、取得した時間に対応させて自身の記憶手段13やサーバー3に蓄積しておく処理である。捜索支援処理は、迷子等の捜索依頼があった場合には、蓄積された位置情報から、捜索対象の子供用携帯通信装置2の位置情報を抽出して、例えば、捜索依頼の依頼元(捜索依頼元)に送信することにより、迷子等の捜索の支援をする処理である。
図6は、通信システムが実行する情報収集処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。図7、図8は、情報収集処理において短距離無線通信を実行するタイミングの説明図である。図9は、情報収集処理で実行される短距離無線通信の概念図である。本実施形態において、情報収集処理は、常時実行される訳ではなく、定期的に、所定の時間実行される。常時情報収集処理を実行すると、親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2の電力の消費が激しくなる。このため、定期的に、所定の時間情報収集処理を実行することにより、電力の消費の増加を抑制する。なお、電力の消費が問題にならない場合は、常時情報収集処理を実行してもよい。この場合、得られる情報が多くなるので、未発見の迷子等の捜索においては、捜索対象の特定精度が向上する。
情報収集処理においては、第2通信手段12で他の携帯通信装置と通信するが、通信時においては、通信対象同士の通信ポートが開いている必要がある。このため、通信システム100においては、通信時刻になったら、集団管理されている複数の親用携帯通信装置1及びこれらに対応付けられた子供用携帯通信装置2が同時に通信可能な状態になっている必要がある。
情報収集処理を実行するにあたり、ステップS101において、それぞれの親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10及び子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10は、情報収集処理における通信時刻になったか否かを判定する。このとき、それぞれの制御手段10は、第1通信手段11を介して、図1に示す基地局5の基準時刻生成手段5Cを取得し、通信時刻になったか否かを判定する。通信時刻は、例えば、1分毎とし、通信時間は、例えば、1秒~15秒とする。すなわち、情報収集処理において、複数の親用携帯通信装置1及びこれらに対応付けられた子供用携帯通信装置2は、第2通信手段12を用いて、毎分毎に所定時間、通信して情報を取得する。このようにすることで、集団管理端末群は、決まった時刻に確実に通信可能な状態となるので、電力の消費を抑制できるとともに、情報の収集漏れを低減できる。
各群内端末装置の制御手段10が通信時刻でないと判定した場合(ステップS101、No)、STARTに戻る。各群内端末装置の制御手段10が通信時刻であると判定した場合(ステップS101、Yes)、ステップS102へ進み、各群内端末装置の制御手段10は、経過時間tを0に設定する。そして、ステップS103において、各群内端末装置の制御手段10は、経過時間tのカウントを開始してから、ステップS104に進み、各群内端末装置の第2通信手段12を用いて、他の群内端末装置との通信を開始する。
ステップS105において、各群内端末装置の制御手段10は、他の群内端末装置との通信が確立したか否かを判定する。各群内端末装置の制御手段10が、通信は確立していないと判定した場合(ステップS105、No)、ステップS106へ進む。ステップS106において、通信の確立していない群内端末装置の制御手段10は、経過時間tが通信可能時間tc以下か否かを判定する。通信可能時間tcは、情報収集処理において、通信時刻になってから第2通信手段12による通信が可能となる時間であり、例えば、1秒~15秒に設定される。すなわち、情報収集処理においては、通信時刻から通信可能時間tcの間が、第2通信手段12による通信が可能となる時間となる。
通信の確立していない群内端末装置の制御手段10が、t≦tcであると判定した場合(ステップS106、Yes)、通信の確立していない群内端末装置の制御手段10は、t≦tcとなるまで第2通信手段12による通信を試みる。通信の確立していない群内端末装置の制御手段10が、t>tcであると判定した場合(ステップS106、No)、STARTに戻り、再び情報収集処理を開始する。
各群内端末装置の制御手段10が、通信は確立したと判定した場合(ステップS105、Yes)、ステップS107へ進み、通信が確立した群内端末装置同士の制御手段10は、それぞれの第2通信手段12を介して通信対象の群内端末装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得する。本実施形態では、識別番号及び位置情報の両方を取得する。ここで識別情報とは、親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2を識別するための情報であり、例えば、装置IDである。位置情報は、情報取得時における親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2の位置を示す情報であり、例えば、緯度及び経度や、住所等である。位置情報は、子供用携帯通信装置2の位置情報検出手段19によって検出される。位置情報も取得することにより、迷子等の捜索支援においては、捜索依頼の対象となっている子供用携帯通信装置2の位置や軌跡を特定するのに極めて有効であるため、識別情報のみを取得するよりも好ましい。ステップS107において、通信が確立した群内端末装置同士の制御手段10は、識別情報及び位置情報を取得した後、通信可能時間tcが経過していなければ、さらに別の群内端末装置と通信を確立して、識別情報及び位置情報を取得してもよい。
本実施形態では、図7に示すように、通信可能時間tcが経過するまでは、群内端末装置間(この例では親用携帯通信装置1と子供用携帯通信装置2間)で通信が可能となるとともに、ステップS106においては、他の群内端末装置と通信を試みることになる。そして、図8に示すように、通信可能時間tcが経過すると、群内端末装置間(この例では親用携帯通信装置1と子供用携帯通信装置2間)での通信はしないこととし、ステップS106においては、他の群内端末装置との通信は試みない。このように、本実施形態では、情報収集処理における通信を開始する時刻から所定の時間(通信可能時間tc)を、第2通信手段12を用いた短距離無線通信に割り当てることで、群内端末装置の電力消費を抑制する。
図9に示す例では、例えば、親用携帯通信装置1Aは親用携帯通信装置1C及び子供用携帯通信装置2bと通信が確立できるので、所定の優先順位(例えば、先に通信が確立した方)にしたがって選択された方との間で互いに識別情報及び位置情報を送受信する。また、親用携帯通信装置1Bは子供用携帯通信装置2aと通信が確立できるので、両者間で互いに識別情報及び位置情報を送受信する。
情報収集処理では、短距離無線通信手段である第2通信手段12を用いる。図9に示すCA1は、親用携帯通信装置1Aが有する第2通信手段12の通信可能範囲であり、CA2は、子供用携帯通信装置2aが有する第2通信手段12の通信可能範囲である。例えば、第2通信手段12の通信可能距離は数m~数十mなので、通信可能範囲CA1、CA2は、半径数m~数十mの円内となる。図9に示す例では、子供用携帯通信装置2bがいずれの通信可能範囲CA1、CA2にも属していない。情報収集処理に短距離無線通信手段を用いることにより、通信が確立した相手は、自身を中心とした半径数m~数十mの円内に存在していることになる。したがって、群内端末装置が通信相手の位置情報を取得できない場合であっても、自身の位置情報が分かれば、その位置情報から通信相手の位置情報を推定することができる。例えば、通信相手の位置は、自身の位置から第2通信手段12の通信可能距離を半径とする円内と推定することができる。また、親用携帯通信装置1等が、受信する電波の方向から、発信元の方向を推定できる機能を有していれば、通信相手が存在する方向も推定できる。
群内端末装置の識別情報及び位置情報が取得されたら、ステップS108に進み、識別情報及び位置情報を取得した群内端末装置の制御手段10は、取得した識別情報及び位置情報を、取得した時刻と対応付けて記憶手段13に記憶させるか、第1通信手段11を介してサーバー3へ送信する。位置情報を通信相手から取得できなかった場合、群内端末装置の制御手段10は、少なくとも取得した識別情報を取得した時刻と対応付けて記憶手段13に記憶させるか、第1通信手段11を介してサーバー3へ送信する。この場合、上述したように、群内端末装置の制御手段10は、自身の位置情報から通信相手の位置情報を推定し、識別情報を取得した時刻と対応付けて記憶手段13に記憶させるか、第1通信手段11を介してサーバー3へ送信してもよい。上述した各工程により、情報収集処理は終了する。なお、情報収集処理は、所定の通信開始時刻が到来する毎に、定期的に実行される。次に、操作支援処理を説明する。
図10は、通信システムのサーバーが実行する捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。図11は、通信システムの親用携帯通信装置が実行する捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。図12は、通信システムの子供用携帯通信装置が実行する捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。図13、図14は、捜索支援処理の説明図である。図15は、捜索依頼元に送信される捜索支援情報の概念図である。捜索支援処理は、図1に示す通信システム100のサーバー3が、捜索依頼を受信したことをトリガーとして開始する。迷子等の捜索の場合は、捜索依頼は、例えば、親用携帯通信装置1からサーバー3に送信される。図13に示す例では、親用携帯通信装置1Bが、これに対応する子供用携帯通信装置2bの捜索依頼SDをサーバー3に送信している。本実施形態において、捜索依頼SDは電子メールによるものであるが、操作手段18に対する所定の操作や、音声によるものであってもよい。
[サーバーの捜索支援処理]
ここで説明するサーバー3の捜索支援処理は、図1に示すサーバー3の処理部3Cが実行し、収集した情報は記憶部3Mが記憶する。ステップS201において、サーバー3は、捜索依頼SDがあったか否か、すなわち、捜索依頼SDを受信したか否かを判定する。捜索依頼SDを受信していないとサーバー3が判断した場合(ステップS201、No)、捜索支援処理は終了する。この場合、サーバー3が集団管理する複数の親用携帯通信装置1及び複数の子供用携帯通信装置2は、上述した情報収集処理を定期的に実行する。
ここで説明するサーバー3の捜索支援処理は、図1に示すサーバー3の処理部3Cが実行し、収集した情報は記憶部3Mが記憶する。ステップS201において、サーバー3は、捜索依頼SDがあったか否か、すなわち、捜索依頼SDを受信したか否かを判定する。捜索依頼SDを受信していないとサーバー3が判断した場合(ステップS201、No)、捜索支援処理は終了する。この場合、サーバー3が集団管理する複数の親用携帯通信装置1及び複数の子供用携帯通信装置2は、上述した情報収集処理を定期的に実行する。
捜索依頼SDを受信したとサーバー3が判断した場合(ステップS201、Yes)、ステップS202へ進み、サーバー3は、捜索依頼設定をONにする。この捜索依頼設定がONである場合には、通信システム100による迷子等の捜索の支援が実行される。次に、ステップS203へ進み、サーバー3は、集団管理している複数の親用携帯通信装置1(図13に示す例では、1A、1C、1D)に、捜索依頼SDを送信する。捜索依頼SDは、図1に示す通信制御装置4及び基地局5を介して送信される。親用携帯通信装置1は、図4に示す第1通信手段11を介して捜索依頼SDを取得する。
次に、ステップS204に進む。サーバー3は、図14に示すように、集団管理している複数の親用携帯通信装置1(図14に示す例では、1A、1C、1D)、及びこれらに対応付けられている子供用携帯通信装置2(図14に示す例では、2a、2c、2d)から、捜索依頼の対象となっている子供用携帯通信装置2b(必要に応じて捜索対象という)についての情報(捜索対象情報)IFを取得して、収集する。捜索対象についての情報は、親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2から送信される情報であり、これらは記憶手段13に蓄積されている、群内端末装置の情報(群内端末情報)を含む情報である。
群内端末情報は、上述した情報収集処理で収集され、それぞれの親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2に蓄積されている、群内端末装置の情報(少なくとも識別情報をその取得時間と対応付けたもの)である。本実施形態において、群内端末情報は、群内端末装置の識別情報及び位置情報をこれらの取得時間と対応付けたものである。
群内端末情報は、情報収集処理において、親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2が自身とは異なる親用又は子供用携帯通信装置と直接短距離無線通信することによって得られた前記異なる親用又は子供用携帯通信装置の識別情報や位置情報である。群内端末情報の中には、捜索対象の識別情報や位置情報等が含まれている場合もあり、また含まれていない場合もある。しかし、後者であっても、その群内端末情報を生成した親用又は子供用携帯通信装置は、第2通信手段12の通信可能範囲内で捜索対象とは遭遇しなかったという情報が得られる。このため、群内端末情報に捜索対象の識別情報や位置情報等が含まれていないという情報も、捜索対象情報IFとなる。したがって、捜索対象情報IFは、群内端末情報及び群内端末情報に捜索対象の識別情報や位置情報等が含まれていないという情報の両方を含む。ステップS204において、捜索対象情報IFを取得し、収集したサーバー3は、収集した捜索対象情報IFから図14に示す捜索支援情報IFSを作成して、捜索依頼元へ送信する。
サーバー3は、ステップS204において、収集した捜索対象情報IFを捜索対象の装置IDで検索して、捜索依頼SDの対象となっている子供用携帯通信装置2bについての識別情報や位置情報、当該位置情報が取得された時間についての情報等を抽出する。なお、捜索対象情報IFに、捜索対象についての識別情報や位置情報等が含まれていない場合でも、その捜索対象情報IFを生成した親用又は子供用携帯通信装置が捜索対象とは遭遇しなかったという情報が得られる。
サーバー3は、図15に示すような捜索支援情報IFSを作成し、捜索依頼元、すなわち、捜索依頼SDを送信した親用携帯通信装置1Bに送信する。収集された捜索対象情報IFから捜索対象についての識別情報や位置情報等がまったく得られなかった場合、すなわち、捜索対象情報IFに捜索対象の識別情報や位置情報等が含まれていないという情報のみしか得られなかった場合、捜索支援情報IFSは、集団管理の範囲内において捜索対象の痕跡は発見できなかったというものになる。なお、捜索支援情報IFS中のIDは、捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bの装置ID(51、図3参照)に対応する。サーバー3は、捜索依頼SDを受信してから所定の時間が経過する毎に捜索支援情報IFSを作成してもよいし、所定量の情報が収集されてから捜索支援情報IFSを作成してもよい。
次に、ステップS205へ進み、サーバー3は、捜索支援処理の終了条件か否かを判定する。終了条件は、例えば、サーバー3が捜索依頼SDを受信して所定時間が経過した場合としてもよいし、捜索対象が発見されたという情報をサーバー3が受信した場合としてもよいし、他の条件としてもよい。サーバー3が、捜索支援処理の終了条件は成立していないと判定した場合(ステップS205、No)、サーバー3は群内端末情報の収集と、捜索支援情報IFSの作成及び送信とを継続する。サーバー3が、捜索支援処理の終了条件は成立したと判定した場合(ステップS205、Yes)、ステップS206へ進み、捜索依頼設定をOFFとして、この情報、すなわち、捜索支援処理を終了するという情報を、それぞれの親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等に送信する。この捜索依頼設定がOFFである場合には、通信システム100による迷子等の捜索の支援が実行されず、上述した情報収集処理のみが実行される。次に、親用携帯通信装置1の捜索支援処理を説明する。
[親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理]
ここで説明する親用携帯通信装置1の捜索支援処理は、図4に示す親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10が実行する。ステップS301において、親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10は、上述したステップS203でサーバー3が送信した捜索依頼SDに関する情報を受信して、取得したか否かを判定する。捜索依頼SDに関する情報は、少なくとも捜索対象(この例では、子供用携帯通信装置2b)の識別情報(例えば、装置ID)を含む。
ここで説明する親用携帯通信装置1の捜索支援処理は、図4に示す親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10が実行する。ステップS301において、親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10は、上述したステップS203でサーバー3が送信した捜索依頼SDに関する情報を受信して、取得したか否かを判定する。捜索依頼SDに関する情報は、少なくとも捜索対象(この例では、子供用携帯通信装置2b)の識別情報(例えば、装置ID)を含む。
制御手段10が、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を受信していないと判定した場合(ステップS301、No)、親用携帯通信装置1の捜索支援処理は終了する。制御手段10が、図13に示すように、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得したと判定した場合(ステップS301、Yes)、ステップS302において、制御手段10は、捜索依頼設定をONにする。この捜索依頼設定は、親用携帯通信装置1に固有のものであり、これがONである場合には、通信システム100による迷子等の捜索の支援が実行される。なお、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得した場合、制御手段10は、スピーカ15や表示手段17に、その旨の報知をさせてもよい。これによって、親用携帯通信装置1の所有者は、捜索依頼SDがあったことを知ることになり、自身も捜索に加わったり、捜索依頼元に直接情報を伝えたりすることができるので、未発見の迷子等の捜索効率が向上する。
次に、ステップS303へ進み、親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10は、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を、自身に対応する子供用携帯通信装置2へ送信する。図13に示す例では、親用携帯通信装置1Aは子供用携帯通信装置2aに、親用携帯通信装置1Dは子供用携帯通信装置2dに、親用携帯通信装置1Cは子供用携帯通信装置2cに、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を送信する。その後、ステップS304へ進み、図14に示す、それぞれの親用携帯通信装置1A、1C、1Dの制御手段10は、捜索依頼SDに関する情報に基づいて、捜索対象の情報がそれぞれの記憶手段13に蓄積されているか否かを判定する。
捜索対象の情報があると制御手段10が判定した場合(ステップS304、Yes)、ステップS305へ進む。そして、そのような親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10は、記憶手段13に蓄積されている捜索対象情報IFを、図4に示す第1通信手段11を介してサーバー3へ送信する(図14参照)。この場合、捜索依頼SDに関する情報(例えば、捜索対象の装置ID)に基づいて、記憶手段13に蓄積されている群内端末情報から、捜索対象から得た情報を抽出して、捜索対象から得た情報のみをサーバー3へ送信してもよい。このようにすれば、図10のステップS204において、サーバー3が捜索支援情報IFSを作成する際の負荷を軽減できる。また、捜索対象のみで構成される情報をサーバー3へ送信すれば、捜索対象情報IFをサーバー3へ送信する場合と比較して情報量を低減できる。これによって、親用携帯通信装置1とサーバー3との通信時間も短くなり、回線の占有時間を短縮できるので好ましい。
ステップS304に戻り、捜索対象の情報がないと制御手段10が判定した場合(ステップS304、No)、ステップS306へ進む。そして、そのような親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10は、捜索対象の情報がないという情報を捜索対象情報IFとして、図4に示す第1通信手段11を介してサーバー3へ送信する。このように、ステップS305又はステップS306で、捜索対象情報IFが親用携帯通信装置1から送信される。
ステップS305又はステップS306が終了したら、ステップS307へ進む。ステップS307において、親用携帯通信装置1A、1C等の制御手段10は、サーバー3から捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信し、取得したか否かを判定する。制御手段10が、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を取得していないと判定した場合(ステップS307、No)、当該情報を受信し、取得するまで、ステップS304~ステップS306を繰り返す。
親用携帯通信装置1は、後述するように、対応する子供用携帯通信装置2から送信される捜索対象情報IFを受信することがある。親用携帯通信装置1が子供用携帯通信装置2から捜索対象情報IFを受信した場合、制御手段10は記憶手段13に記憶させる。捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を親用携帯通信装置1が受信していない場合、ステップS304に戻るが、このとき、制御手段10は、受信された捜索対象情報IFが記憶手段13に存在するか否かを判定し、以後のステップを実行することになる。
制御手段10が、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信したと判定した場合(ステップS307、Yes)、ステップS308へ進む。ステップS308において、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信した親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10は、当該情報を、自身に対応する子供用携帯通信装置2に第1通信手段11を介して送信する。そして、制御手段10は、捜索依頼設定をOFFにする。これによって、通信システム100による迷子等の捜索の支援が実行されず、上述した情報収集処理のみが実行される。次に、子供用携帯通信装置2の捜索支援処理を説明する。
[子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理]
ここで説明する子供用携帯通信装置2の捜索支援処理は、図5に示す子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10が実行する。ステップS401において、子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10は、上述したステップS303で親用携帯通信装置1が送信した捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得したか否かを判定する。捜索依頼SDに関する情報は、少なくとも捜索対象(この例では、子供用携帯通信装置2b)の識別情報(例えば、装置ID)を含む。
ここで説明する子供用携帯通信装置2の捜索支援処理は、図5に示す子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10が実行する。ステップS401において、子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10は、上述したステップS303で親用携帯通信装置1が送信した捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得したか否かを判定する。捜索依頼SDに関する情報は、少なくとも捜索対象(この例では、子供用携帯通信装置2b)の識別情報(例えば、装置ID)を含む。
制御手段10が、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得していないと判定した場合(ステップS401、No)、子供用携帯通信装置2の捜索支援処理は終了する。制御手段10が、図13に示すように、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得したと判定した場合(ステップS401、Yes)、ステップS402に進み、制御手段10は、捜索依頼設定をONにする。この捜索依頼設定は、子供用携帯通信装置2に固有のものであり、これがONである場合には、通信システム100による迷子等の捜索の支援が実行される。なお、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を取得した場合、制御手段10は、スピーカ15や表示手段17に、その旨の報知をさせてもよい点は上述した通りである。
次に、ステップS403に進み、子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10は、記憶手段13に蓄積されている群内端末情報、あるいは捜索対象の情報がないという情報、すなわち、捜索対象情報IFを、自身に対応する親用携帯通信装置1又はサーバー3へ、第1通信手段11を介して送信する(図14参照)。捜索対象情報IFを親用携帯通信装置1へ送信する場合、子供用携帯通信装置2とサーバー3との接続はないので、子供用携帯通信装置2のセキュリティはより高く保たれるので、好ましい。一方、サーバー3へ送信する場合、親用携帯通信装置1を介する必要はないので、サーバー3は、捜索対象情報IFを迅速に取得できる。
この場合、ステップS401で受信し、取得した捜索依頼SDに関する情報に基づいて、捜索対象から得た情報を、記憶手段13に蓄積されている群内端末情報から抽出して、捜索対象から得た情報のみを親用携帯通信装置1又はサーバー3へ送信してもよい。この点は、親用携帯通信装置1の捜索支援処理で説明した通りである。子供用携帯通信装置2が、捜索対象情報IFを直接サーバー3へ送信すれば、親用携帯通信装置1を介してサーバー3へ送信するよりも、親用携帯通信装置1の処理負荷が軽減するので好ましい。
次に、ステップS404へ進み、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2c等の制御手段10は、親用携帯通信装置1A、1B等から捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信したか否かを判定する。制御手段10が、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信していないと判定した場合(ステップS404、No)、当該情報を受信するまで、ステップS403を繰り返す。
制御手段10が、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信したと判定した場合(ステップS404、Yes)、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を受信した子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10は、捜索依頼設定をOFFにする。これによって、通信システム100による迷子等の捜索の支援が実行されず、上述した情報収集処理のみが実行される。
本実施形態では、近距離通信により親用及び子供用携帯通信装置から取得した識別情報や位置情報等を、取得した時間と対応付けて蓄積する。そして、迷子等の捜索依頼があった場合には、複数の親用及び子供用携帯通信装置に蓄積された識別情報等を捜索対象情報としてサーバーが収集する。そして、サーバーが、収集された捜索対象情報から、捜索対象について検索することにより、捜索対象の識別情報や位置情報、当該位置情報が取得された時間情報等を抽出して、捜索支援情報を作成する。この捜索支援情報は、捜索対象の位置情報を時系列で知ることができるので、捜索対象がどのような軌跡をたどったかを知ることができる。
また、捜索対象情報を送信する際に、送信する親用あるいは子供用携帯通信装置の自身の識別情報を付加するようにすれば、捜索対象がどのような親用あるいは子供用携帯通信装置の近くにいたのかも知ることができる。さらに、自身の識別情報を付加すれば、捜索対象の位置情報がない場合でも、捜索対象の近くにあった親用あるいは子供用携帯通信装置の所有者から、その当時の状況を聴取することができる。これによって、捜索の手がかりを得ることもできる。さらに、本実施形態では、サーバーに、親用携帯通信装置に関する情報のみを記憶して集団管理し、親子関係の対応により、子供用携帯通信装置を間接的に集団管理する。これによって、子供の個人情報の漏洩をできる限り低減することができる。なお、将来、ペットの首輪に通信機能を搭載したものが登場すると、未発見の迷子犬や迷子猫等の捜索も、本実施形態と同様の手法で捜索することができる。
(変形例)
図16は、本実施形態の変形例に係る捜索支援処理の説明図である。図17は、捜索対象情報あるいは捜索依頼元に送信される捜索支援情報の概念図である。本変形例に係る捜索支援処理は、親用携帯通信装置1及び子供用携帯通信装置2が、捜索対象情報IFを送信した後に、それぞれ、捜索対象との通信を試みる。そして、捜索対象との通信が確立できたら、捜索対象の少なくとも識別情報を取得して、捜索対象情報IFとして送信する。
図16は、本実施形態の変形例に係る捜索支援処理の説明図である。図17は、捜索対象情報あるいは捜索依頼元に送信される捜索支援情報の概念図である。本変形例に係る捜索支援処理は、親用携帯通信装置1及び子供用携帯通信装置2が、捜索対象情報IFを送信した後に、それぞれ、捜索対象との通信を試みる。そして、捜索対象との通信が確立できたら、捜索対象の少なくとも識別情報を取得して、捜索対象情報IFとして送信する。
図16に示す例において、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を受信し、取得した親用携帯通信装置1及び子供用携帯通信装置2は、捜索対象情報IFをサーバー3へ送信した後に、それぞれの第2通信手段12を用いて短距離無線通信を実行する。短距離無線通信は、上述した情報収集処理と同様に、定期的に、一定時間実行すればよい。
この例においては、捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信が確立できているのは、親用携帯通信装置1Dである。したがって、親用携帯通信装置1Dは、第2通信手段12を介して、子供用携帯通信装置2bの少なくとも識別情報(本変形例では、識別情報及び位置情報)を取得する。
その後、親用携帯通信装置1Dは、取得した子供用携帯通信装置2bの識別情報等を、図16に示すような捜索対象情報IFとしてサーバー3へ送信する。なお、例えば、子供用携帯通信装置2c等が捜索対象との通信を確立し、捜索対象の識別情報等を捜索対象情報IFとして送信する場合、親用携帯通信装置1Cを介して、又は直接サーバー3へ送信する。
図16に示す例において、親用携帯通信装置1Dから捜索対象情報IFを取得したサーバー3は、これを用いて、捜索支援情報IFSを作成し、捜索依頼元である親用携帯通信装置1Bに送信する。サーバー3が受信した捜索対象情報IFが単一である場合、図17に示すように、捜索支援情報IFSは、捜索対象情報IFと同一になる。
本変形例において、捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信が確立されなかった子供用携帯通信装置2dや親用携帯通信装置1C等については、通信が確立された対象との間で情報のやり取りをする必要はない。また、情報をやり取りしても、それをサーバー3へ送信する必要もない。なお、図16では、捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信が確立されなかった子供用携帯通信装置2dや親用携帯通信装置1C等は、親用携帯通信装置1Dやサーバー3に捜索対象情報IFを送信していない。さらに、親用携帯通信装置や子供用携帯通信装置の短距離無線通信の通信対象を、捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bのみとしてもよい。
本変形例は、親用携帯通信装置1や子供用携帯通信装置2の記憶手段13に蓄積された捜索対象情報IFがサーバー3等へ送信された後においても、親用携帯通信装置1及び子供用携帯通信装置2が捜索対象とのアクセスを試みる。これによって、未発見の迷子等の捜索効率が向上するとともに、より確実に未発見の迷子等の捜索を遂行することができる。また、サーバー3へ送信される捜索対象情報IFは、ある程度の期間、蓄積された情報ではないので、記憶手段13に蓄積された捜索対象情報IFを送信する場合と比較して情報量を低減できる。これによって、親用携帯通信装置1とサーバー3との通信時間も短くなり、回線の占有時間を短縮できるので好ましい。また、捜索依頼SDに関する情報に基づいて、第2通信手段12を用いた近距離通信の通信対象を特定できるので、通信対象が発見できない場合には、情報の取得を実行しないでもよい。これによって、電力消費をさらに抑制できる。
(実施形態2)
図18は、親用携帯通信装置が実行する、実施形態2に係る捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。図19は、子供用携帯通信装置が実行する、実施形態2に係る捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理は、情報収集処理を実行せず、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を受信し、取得した親用携帯通信装置1及び子供用携帯通信装置2は、それぞれ、捜索対象との通信を試みる。そして、捜索対象との通信が確立できたら、捜索対象の少なくとも識別情報を取得して、捜索対象情報IFとして送信する。図18、図19、図16、図17等を用いて、本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理を説明する。本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理において、サーバー3の捜索支援処理は実施形態1と同様である。
図18は、親用携帯通信装置が実行する、実施形態2に係る捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。図19は、子供用携帯通信装置が実行する、実施形態2に係る捜索支援処理の各工程を示すフローチャートである。本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理は、情報収集処理を実行せず、捜索依頼SDに関する情報を受信し、取得した親用携帯通信装置1及び子供用携帯通信装置2は、それぞれ、捜索対象との通信を試みる。そして、捜索対象との通信が確立できたら、捜索対象の少なくとも識別情報を取得して、捜索対象情報IFとして送信する。図18、図19、図16、図17等を用いて、本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理を説明する。本実施形態に係る捜索支援処理において、サーバー3の捜索支援処理は実施形態1と同様である。
[親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理]
この捜索支援処理は、図4に示す親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10が実行する。親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS501~ステップS503は、実施形態1に係る親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS301~ステップS303と同様である。ステップS504において、図16に示す親用携帯通信装置1A、1C等の制御手段10は、それぞれ第2通信手段12を用いて捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を試みる。
この捜索支援処理は、図4に示す親用携帯通信装置1の制御手段10が実行する。親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS501~ステップS503は、実施形態1に係る親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS301~ステップS303と同様である。ステップS504において、図16に示す親用携帯通信装置1A、1C等の制御手段10は、それぞれ第2通信手段12を用いて捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を試みる。
ステップS505に進み、親用携帯通信装置1A、1C等の制御手段10は、それぞれ子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立したか否かを判定する。制御手段10が、子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立したと判定した場合(ステップS505、Yes)、ステップS506へ進む。そして、制御手段10は、第2通信手段12を介して、子供用携帯通信装置2bの少なくとも識別情報(本実施形態では、識別情報及び位置情報)を取得する。図16に示す例では、親用携帯通信装置1Dが、子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立しているので、親用携帯通信装置1Dの制御手段10が、子供用携帯通信装置2bの少なくとも識別情報(本実施形態では、識別情報及び位置情報)を取得する。そして、ステップS507へ進み、制御手段10は、取得した子供用携帯通信装置2bの情報を捜索対象情報IFとしてサーバー3へ送信する。
次に、ステップS505へ戻り、制御手段10が、子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立していないと判定した場合(ステップS505、No)、ステップS508へ進む。そして、そのような親用携帯通信装置の制御手段10は、捜索対象と通信を確立できないという情報を捜索対象情報IFとして、図4、図5に示す第1通信手段11を介してサーバー3へ送信する。このように、ステップS506及びステップS507、あるいはステップS508で、捜索対象情報IFがサーバー3へ送信される。ステップS507又はステップS508が終了したら、ステップS509へ進む。ステップS509、ステップS510は、実施形態1に係る親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS307、ステップS308と基本的に同様であるが、ステップS509において、制御手段10が、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を取得していないと判定した場合(ステップS509、No)、ステップS504~ステップS508が繰り返される。次に、子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理を説明する。
[子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理]
子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理は、図5に示す子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10が実行する。ステップS601、ステップS602は、実施形態1に係る子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS401、ステップS402と同様である。ステップS603において、図16に示す子供用携帯通信装置2a、2c等の制御手段10は、それぞれ第2通信手段12を用いて捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を試みる。
子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理は、図5に示す子供用携帯通信装置2の制御手段10が実行する。ステップS601、ステップS602は、実施形態1に係る子供用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS401、ステップS402と同様である。ステップS603において、図16に示す子供用携帯通信装置2a、2c等の制御手段10は、それぞれ第2通信手段12を用いて捜索対象である子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を試みる。
そして、ステップS604に進み、子供用携帯通信装置2a、2c等の制御手段10は、それぞれ子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立したか否かを判定する。制御手段10が、子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立したと判定した場合(ステップS604、Yes)、ステップS605へ進む。そして、制御手段10は、第2通信手段12を介して、子供用携帯通信装置2bの少なくとも識別情報(本実施形態では、識別情報及び位置情報)を取得する。そして、ステップS606へ進み、制御手段10は、取得した子供用携帯通信装置2bの情報を捜索対象情報IFとして親用携帯通信装置1又はサーバー3へ送信する。
次に、ステップS604へ戻り、制御手段10が、子供用携帯通信装置2bとの通信を確立していないと判定した場合(ステップS604、No)、ステップS607へ進む。そして、そのような子供用携帯通信装置の制御手段10は、捜索対象と通信を確立できないという情報を捜索対象情報IFとして、図4、図5に示す第1通信手段11を介して対応する親用携帯通信装置1又はサーバー3へ送信する。このように、ステップS605及びステップS606、あるいはステップS607で、捜索対象情報IFがサーバー3へ送信される。ステップS606又はステップS607が終了したら、ステップS608へ進む。ステップS608は、実施形態1に係る親用携帯通信装置の捜索支援処理のステップS404と基本的に同様であるが、ステップS608において、制御手段10が、捜索支援処理を終了する旨の情報を取得していないと判定した場合(ステップS608、No)には、Noと判定された場合には、ステップS603~ステップS607が繰り返される。
本実施形態では、捜索依頼SDが発生してから、第2通信手段12を用いた近距離通信により、捜索対象と通信を試み、捜索対象との通信が確立したら、捜索対象の識別情報等を取得して、サーバー3へ送信する。これによって、情報収集処理が不要になるので、電力消費を大幅に抑制することができる。また、捜索依頼SDに関する情報に基づいて、第2通信手段12を用いた近距離通信の通信対象を特定できるので、通信対象が発見できない場合には、情報の取得を実行しないでよい。これによって、電力消費をさらに抑制できる。さらに、サーバー3へ送信される捜索対象情報IFは、ある程度の期間、蓄積された情報ではないので、実施形態1のように、記憶手段13に蓄積された捜索対象情報IFを送信する場合と比較して情報量を低減できる。これによって、親用携帯通信装置1とサーバー3との通信時間も短くなり、回線の占有時間を短縮できるので好ましい。
以上のように、本発明に係る通信システム及び携帯通信装置、並びに通信システム用サーバーは、未発見の迷子等の捜索に有用である。
1、1A、1B、1C、1D 親用携帯通信装置
2、2a、2b、2c、2d 子供用携帯通信装置
3 サーバー
3C 処理部
3M 記憶部
3I 入出力部
4 通信制御装置
5 基地局
5C 基準時刻生成手段
6 情報テーブル
10 制御手段
11 第1通信手段
12 第2通信手段
13 記憶手段
19 位置情報検出手段
100 通信システム
2、2a、2b、2c、2d 子供用携帯通信装置
3 サーバー
3C 処理部
3M 記憶部
3I 入出力部
4 通信制御装置
5 基地局
5C 基準時刻生成手段
6 情報テーブル
10 制御手段
11 第1通信手段
12 第2通信手段
13 記憶手段
19 位置情報検出手段
100 通信システム
Claims (15)
- 他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な短距離無線通信手段を有する複数の第1携帯通信装置、並びに他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な短距離無線通信手段を有する第2携帯通信装置と、
前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に関する情報を記憶するサーバーと、を有し、
前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、それぞれの前記短距離無線通信手段を用いて、前記第2携帯通信装置と通信して、前記第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、当該取得した識別情報を、取得した時間と対応付けて記憶し、
前記第2携帯通信装置の捜索依頼を前記サーバーが取得したら、前記サーバーは、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、
前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した第1携帯通信装置は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置についての情報を前記サーバーに送信する、
通信システム。 - 前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置についての情報を受信した前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、
それぞれの前記短距離無線通信手段を用いて、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置との通信を試み、
前記捜索依頼の対象となっている前記第2携帯通信装置との通信が確立できたら、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得して前記サーバーに送信する、
請求項1に記載の通信システム。 - さらに、他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な短距離無線通信手段を有する複数の第2携帯通信装置を備え、
前記複数の第2携帯通信装置は、それぞれの前記短距離無線通信手段を用いて、他の第2携帯通信装置と通信して、他の第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、当該取得した識別情報を、取得した時間と対応付けて記憶し、
前記サーバーが、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信したら、
前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、前記複数の第2携帯通信装置のうちの少なくとも一つに対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、
前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した前記複数の第2携帯通信装置は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を前記第1携帯通信端末に送信し、
前記サーバーは、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を、前記第1携帯通信端末を介して前記複数の第2携帯端末装置から得る、
請求項1又は請求項2に記載の通信システム。 - 前記サーバーが、前記複数の第1携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信したら、
前記複数の第1携帯通信装置は、自身に対応付けられている前記複数の第2携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、
前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した前記複数の第2携帯通信装置は、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を、自身と対応づいている前記第1携帯通信端末に送信する、
請求項3に記載の通信システム。 - 前記短距離無線通信手段を用いた通信は、
定期的に、所定の時間実行される、
請求項4に記載の通信システム。 - 前記短距離無線通信手段を用いた通信は、
前記複数の第2携帯通信装置及び前記複数の第1携帯通信装置がアクセス可能な基地局から発信される基準時間に基づいて実行される、
請求項5に記載の通信システム。 - 前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置についての情報を送信した、前記第1携帯通信装置又は前記第2携帯通信装置は、
それぞれ、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置との通信を試み、
前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置との通信が確立できたら、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得して送信する、
請求項4から6のいずれか1項に記載の通信システム。 - 前記識別情報を取得した第1携帯通信装置は、取得した情報を前記サーバーに送信し、
前記識別情報を取得した第2携帯通信装置は、前記自身に対応付けられた第1携帯通信装置、又は前記サーバーに取得した情報を送信する、
請求項7に記載の通信システム。 - 複数の第2携帯通信装置の少なくとも一部は、自身の位置を検出する位置情報検出手段を有し、
前記複数の第1携帯通信装置及び複数の第2携帯通信装置は、それぞれ、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている第2携帯通信装置の識別情報と共に前記位置情報検出手段によって得られた位置情報がある場合は、当該位置情報をあわせて取得して送信することを特徴とする、
請求項4から8のいずれか1項に記載の通信システム。 - 少なくとも前記識別情報を取得した第1携帯通信装置は、
取得した情報を前記サーバーに送信し、前記識別情報及び前記位置情報を取得した第2携帯通信装置は、自身に対応付けられた第1携帯通信装置、又は前記サーバーに取得した情報を送信する、
請求項7に記載の通信システム。 - 複数の携帯通信装置を集団管理する際に用いる携帯通信装置であり、
サーバーと通信可能な第1通信手段と、
他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な第2通信手段と、
情報を記憶する記憶部と、
前記第2通信手段を用いて他の携帯通信装置と通信して、当該他の携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、取得した時間と対応付けて前記記憶部へ記憶させ、
集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を受信したら、自身に対応付けられている携帯通信装置に前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信するとともに、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を、前記第1通信手段を介して前記サーバーへ送信する制御手段と、
を含む、
携帯通信装置。 - 集団管理される複数の携帯通信装置とそれぞれ対応付けられた携帯通信装置であり、
サーバーと通信可能な第1通信手段と、
他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な第2通信手段と、
情報を記憶する記憶部と、
前記第2通信手段を用いて他の携帯通信装置と通信して、当該他の携帯通信装置の少なくとも識別情報を取得するとともに、取得した時間と対応付けて前記記憶部へ記憶させ、
集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を、自身に対応付けられている携帯通信装置から受信すると、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を、前記第1通信手段を介して送信する制御手段と、
を含む、
携帯通信装置。 - 複数の携帯通信装置を集団管理する際に用いる携帯通信装置であり、
サーバーと通信可能な第1通信手段と、
他の携帯通信装置と直接通信可能な第2通信手段と、
情報を記憶する記憶部と、
集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を取得したら、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置との通信を試み、
前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置との通信が確立できたら、捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置の識別情報及び位置情報を取得する制御手段と、
を含む、
携帯通信装置。 - 複数の携帯通信装置を集団管理するサーバーであり、
前記複数の携帯通信装置に関する情報を記憶する記憶部と、
集団管理される携帯通信装置に対応付けられた携帯通信装置の捜索依頼に関する情報を取得したら、前記複数の携帯通信装置に対して前記捜索依頼に関する情報を送信し、
前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した、集団管理される携帯通信装置、及び当該集団管理される携帯通信装置から前記捜索依頼に関する情報を受信した携帯通信装置から、前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を取得する処理部と、
を含む、
通信システム用サーバー。 - 前記処理部は、
前記捜索依頼の対象となっている携帯通信装置についての情報を取得した後に、前記捜索依頼に関する情報を発信した携帯通信装置に対して、捜索支援情報を送信する、
請求項14に記載の通信システム用サーバー。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/575,087 US9185201B2 (en) | 2010-01-27 | 2011-01-27 | Communication system and mobile communication device, and server for communication system |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010-016066 | 2010-01-27 | ||
| JP2010016066A JP5679670B2 (ja) | 2010-01-27 | 2010-01-27 | 通信システム及び携帯通信装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011093408A1 true WO2011093408A1 (ja) | 2011-08-04 |
Family
ID=44319391
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/051663 WO2011093408A1 (ja) | 2010-01-27 | 2011-01-27 | 通信システム及び携帯通信装置、並びに通信システム用サーバー |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9185201B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5679670B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2011093408A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20140130952A (ko) * | 2013-05-02 | 2014-11-12 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 전자 장치에서 근거리 통신을 이용하여 신호를 전송하기 위한 장치 및 방법 |
| US9565527B1 (en) * | 2013-12-19 | 2017-02-07 | Securus Technologies, Inc. | Location-based services for exigent circumstances |
| JP6427386B2 (ja) * | 2014-03-18 | 2018-11-21 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | 通信システム、携帯端末および位置管理方法 |
| KR102218646B1 (ko) * | 2014-10-22 | 2021-02-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 페어링 장치 및 그 방법 |
| JP6296510B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-28 | 2018-03-20 | 株式会社ナスカ | 移動物体の位置検索登録システム |
| EP3249957B1 (en) * | 2015-02-16 | 2020-01-08 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Method, apparatus and system for acquiring location information of target object |
| JP2016184306A (ja) * | 2015-03-26 | 2016-10-20 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 保護支援システム、保護支援サーバー及び保護端末 |
| JP6194441B1 (ja) * | 2015-11-17 | 2017-09-13 | 株式会社リキッド・デザイン・システムズ | 対象者発見支援システム及び対象者情報発信装置 |
| JP6703737B2 (ja) | 2016-06-20 | 2020-06-03 | 株式会社音力発電 | 制御システム |
| JP6300878B1 (ja) * | 2016-10-11 | 2018-03-28 | 洋彰 船橋 | 管理対象端末、サーバ、携帯電話装置、携帯情報端末プログラム、携帯電話装置プログラム及び位置管理システム |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004355349A (ja) * | 2003-05-29 | 2004-12-16 | Hitachi Ltd | 探索支援システム |
| JP2006211014A (ja) * | 2005-01-25 | 2006-08-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 捜索支援システム |
| JP2006270629A (ja) * | 2005-03-24 | 2006-10-05 | Fujitsu Ltd | 探索を中継する携帯端末、探索方法、および探索プログラム |
| JP2008206025A (ja) * | 2007-02-22 | 2008-09-04 | Nec Corp | 携帯端末探索システム、携帯端末 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003092578A (ja) * | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-28 | Fujitsu Ltd | 管理装置、処理装置、装置、およびプログラム |
| US7848704B2 (en) * | 2005-03-04 | 2010-12-07 | Broadcom Corporation | Location system for bluetooth enabled devices |
| JP2007011555A (ja) | 2005-06-29 | 2007-01-18 | Nec Corp | 迷子支援方法および装置 |
| JP4466661B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-02 | 2010-05-26 | 株式会社カシオ日立モバイルコミュニケーションズ | 携帯端末装置及びプログラム |
-
2010
- 2010-01-27 JP JP2010016066A patent/JP5679670B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2011
- 2011-01-27 US US13/575,087 patent/US9185201B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2011-01-27 WO PCT/JP2011/051663 patent/WO2011093408A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004355349A (ja) * | 2003-05-29 | 2004-12-16 | Hitachi Ltd | 探索支援システム |
| JP2006211014A (ja) * | 2005-01-25 | 2006-08-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 捜索支援システム |
| JP2006270629A (ja) * | 2005-03-24 | 2006-10-05 | Fujitsu Ltd | 探索を中継する携帯端末、探索方法、および探索プログラム |
| JP2008206025A (ja) * | 2007-02-22 | 2008-09-04 | Nec Corp | 携帯端末探索システム、携帯端末 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5679670B2 (ja) | 2015-03-04 |
| JP2011154571A (ja) | 2011-08-11 |
| US20120295638A1 (en) | 2012-11-22 |
| US9185201B2 (en) | 2015-11-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5679670B2 (ja) | 通信システム及び携帯通信装置 | |
| KR100992163B1 (ko) | 휴대단말장치, 원격통지방법 및 프로그램을 기록한기록매체 | |
| JP6019544B2 (ja) | 無線通信システムおよび加入者情報管理装置 | |
| EP2883370B1 (en) | Information processing terminal, information processing method, program, and information storage medium | |
| US20090002237A1 (en) | Method and device for determining a position of a portable electronic device | |
| JP5187975B2 (ja) | 捜索支援システム | |
| CN102740294A (zh) | 终端装置和通信方法、信息处理装置、方法和系统 | |
| JP2006267057A (ja) | 位置検出システム、携帯端末、位置検出方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2008172635A (ja) | 通信システム及び携帯通信端末 | |
| JP6386254B2 (ja) | 捜索支援プログラム、捜索支援システム及び捜索支援の方法 | |
| WO2010093348A1 (en) | Wireless device for receiving calls to automatically transmit messages of current device location | |
| JP2017097750A (ja) | 測位システム、無線タグ装置およびその測位方法 | |
| JP2012070082A (ja) | 構内無線システム | |
| JP2004297334A (ja) | 位置情報測定端末装置、および無線タグによる位置情報測定方法、ならびにプログラム | |
| JP3926746B2 (ja) | 携帯情報端末、無線通信システム及びリンク確立方法 | |
| CN101854585A (zh) | 一种带电子栅栏的子母机定位的方法及其装置 | |
| JP5102232B2 (ja) | 端末装置、位置情報制御方法および位置情報制御システム | |
| EP2654354B1 (en) | Providing a current position while reducing an overall power consumption | |
| JP2015142241A (ja) | 無線通信システム、無線端末および無線通信方法 | |
| JP2019213070A (ja) | 位置探索システムおよび位置探索方法 | |
| JP2008159005A (ja) | 携帯端末、混雑情報収集サーバ、及び混雑状況把握方法 | |
| WO2013046817A1 (ja) | 情報処理装置 | |
| CN111277944A (zh) | 一种定位方法及定位设备 | |
| CN201750561U (zh) | 一种带电子栅栏的子母机定位的装置 | |
| JP2007257534A (ja) | 異常報知端末及び管理装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11737119 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13575087 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11737119 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |