WO2011034021A1 - 無線基地局及び移動通信方法 - Google Patents
無線基地局及び移動通信方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011034021A1 WO2011034021A1 PCT/JP2010/065724 JP2010065724W WO2011034021A1 WO 2011034021 A1 WO2011034021 A1 WO 2011034021A1 JP 2010065724 W JP2010065724 W JP 2010065724W WO 2011034021 A1 WO2011034021 A1 WO 2011034021A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- data channel
- base station
- radio base
- uplink data
- channel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0001—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff
- H04L1/0002—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff by adapting the transmission rate
- H04L1/0003—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff by adapting the transmission rate by switching between different modulation schemes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0001—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff
- H04L1/0006—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff by adapting the transmission format
- H04L1/0007—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff by adapting the transmission format by modifying the frame length
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0001—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff
- H04L1/0009—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff by adapting the channel coding
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0001—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff
- H04L1/0023—Systems modifying transmission characteristics according to link quality, e.g. power backoff characterised by the signalling
- H04L1/0026—Transmission of channel quality indication
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/1607—Details of the supervisory signal
- H04L1/1671—Details of the supervisory signal the supervisory signal being transmitted together with control information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/12—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel
- H04L1/16—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using return channel in which the return channel carries supervisory signals, e.g. repetition request signals
- H04L1/18—Automatic repetition systems, e.g. Van Duuren systems
- H04L1/1867—Arrangements specially adapted for the transmitter end
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/20—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received using signal quality detector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/10—Scheduling measurement reports ; Arrangements for measurement reports
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W72/00—Local resource management
- H04W72/20—Control channels or signalling for resource management
- H04W72/23—Control channels or signalling for resource management in the downlink direction of a wireless link, i.e. towards a terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/04—Error control
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W28/00—Network traffic management; Network resource management
- H04W28/02—Traffic management, e.g. flow control or congestion control
- H04W28/06—Optimizing the usage of the radio link, e.g. header compression, information sizing, discarding information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/08—Access point devices
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a radio base station and a mobile communication method.
- TBS table usable TBSs are defined for each number of resource blocks.
- MCS Modulation and Coding Scheme, combination of modulation scheme and coding rate
- TF Transmission Format
- the case where the maximum TBS defined in the above TBS table is selected is the case where the peak rate is realized.
- the throughput characteristics when the transmission format (TF # 26) corresponding to the maximum TBS is used that is, the TBS table is deteriorated.
- the peak rate determined by the maximum TBS specified in the above cannot be realized.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to provide a radio base station and a mobile communication method capable of realizing a high-speed peak rate without degrading throughput characteristics. To do.
- a first feature of the present invention is a radio base station configured to transmit a downlink data signal to a mobile station via a downlink data channel, the channel in the downlink data channel from the mobile station Adjusting the received channel quality information based on a channel quality information receiving unit configured to receive quality information and a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the downlink data channel
- a channel quality information adjusting unit configured in the above, a selectable transport format number determining unit that determines a selectable maximum transport block size based on the number of mobile stations in each scheduling unit period, and the adjusted To the channel quality information and the determined maximum transport block size that can be selected Based on the transmission format response, and summarized in that comprises a modulation scheme and a selection unit configured to select a coding rate applied to each resource blocks of the downlink data channel.
- a second feature of the present invention is a radio base station configured to transmit a downlink data signal to a mobile station via a downlink data channel, from the mobile station to a channel in the downlink data channel Adjusting the received channel quality information based on a channel quality information receiving unit configured to receive quality information and a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the downlink data channel
- a third feature of the present invention is a radio base station configured to transmit a downlink data signal to a mobile station via a downlink data channel, the channel in the downlink data channel from the mobile station. Adjusting the received channel quality information based on a channel quality information receiving unit configured to receive quality information and a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the downlink data channel A channel quality information adjustment unit configured in the above, a measurement unit configured to measure an error rate in the downlink data channel, and the selectable based on the measured error rate in the downlink data channel A calculator configured to calculate a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size; Select a modulation scheme and a coding rate to be applied to each resource block in the downlink data channel based on the transmitted channel quality information and the calculated transmission format corresponding to the selectable maximum transport block size
- the gist of the invention is to include a selection unit configured to do so.
- a fourth feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method for transmitting a downlink data signal from a radio base station to a mobile station via a downlink data channel, wherein the mobile station transmits to the radio base station, Transmitting the channel quality information in the downlink data channel, and the radio base station adjusts the received channel quality information based on a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the downlink data channel Determining the maximum selectable transport block size based on the number of mobile stations in each scheduling unit period, and adjusting the channel quality information adjusted by the radio base station. And the downlink based on the determined transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected. And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource block in Tachaneru.
- a fifth feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method for transmitting a downlink data signal from a radio base station to a mobile station via a downlink data channel, wherein the mobile station transmits to the radio base station, Transmitting the channel quality information in the downlink data channel, and the radio base station adjusts the received channel quality information based on a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the downlink data channel
- the radio base station Inputting a transmission format corresponding to a selectable maximum transport block size to the radio base station as an external setting parameter, the radio base station adjusting the channel quality information and Based on the input transmission format corresponding to the selectable maximum transport block size, the lower And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource blocks in the data channel.
- a sixth feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method for transmitting a downlink data signal from a radio base station to a mobile station via a downlink data channel, wherein the mobile station transmits to the radio base station, Transmitting the channel quality information in the downlink data channel, and the radio base station adjusts the received channel quality information based on a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the downlink data channel Measuring the error rate in the downlink data channel, calculating a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the measured error rate in the downlink data channel, The radio base station determines the adjusted channel quality information and the calculated maximum transposable Based on the transmission format corresponding to the heat block size, and summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource blocks of the downlink data channel.
- a seventh feature of the present invention is a radio base station configured to receive an uplink data signal from a mobile station via an uplink data channel, and configured to calculate quality in the uplink data channel.
- a quality adjustment unit configured to adjust the calculated quality in the uplink data channel based on a reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the uplink data channel;
- a selectable transport format number determination unit that determines a maximum selectable transport block size based on the number of mobile stations in each scheduling unit period, and the quality in the adjusted uplink data channel and the determined selectable Based on the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size
- a selection unit configured to select a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource block in said uplink data channel.
- An eighth feature of the present invention is a radio base station configured to receive an uplink data signal from a mobile station via an uplink data channel, and configured to calculate quality in the uplink data channel.
- a quality adjustment unit configured to adjust the calculated quality in the uplink data channel based on a reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the uplink data channel;
- a transmission format corresponding to the selectable maximum transport block size is acquired as an external setting parameter, and the quality in the adjusted uplink data channel and the acquired transmission format corresponding to the selectable maximum transport block size are acquired.
- For each resource block in the uplink data channel And summarized in that it includes a selection unit configured to select a modulation scheme applied to and the coding rate.
- a ninth feature of the present invention is a radio base station configured to receive an uplink data signal from a mobile station via an uplink data channel, and configured to calculate quality in the uplink data channel.
- a quality adjustment unit configured to adjust the calculated quality in the uplink data channel based on a reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the uplink data channel; Based on the measurement unit configured to measure the error rate in the uplink data channel and the measured error rate in the uplink data channel, a transmission format corresponding to the selectable maximum transport block size is calculated.
- a calculation unit configured to perform the quality and calculation in the adjusted uplink data channel.
- a selection configured to select a modulation scheme and a coding rate to be applied to each resource block in the uplink data channel based on a transmission format corresponding to the selected maximum transport block size It is made a summary.
- a tenth feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method for transmitting an uplink data signal from a mobile station to a radio base station via an uplink data channel, the step of calculating quality in the uplink data channel, A step in which the radio base station adjusts the calculated quality in the uplink data channel based on a reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted through the uplink data channel; and the radio base station performs each scheduling unit period Determining a selectable maximum transport block size based on the number of mobile stations in the radio base station, and the radio base station adjusting the quality in the uplink data channel and the determined selectable maximum transport block Each resource in the uplink data channel based on the transmission format corresponding to the size And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to the lock.
- An eleventh feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method for transmitting an uplink data signal from a mobile station to a radio base station via an uplink data channel, the step of calculating quality in the uplink data channel, The wireless base station adjusts the calculated quality in the uplink data channel based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the uplink data channel, and the wireless base station as an external setting parameter
- the step of inputting a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected, and the quality of the uplink data channel adjusted by the radio base station and the input maximum transport block that can be selected Based on the transmission format corresponding to the size, each resource in the uplink data channel And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to over the scan block.
- a twelfth feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method for transmitting an uplink data signal from a mobile station to a radio base station via an uplink data channel, the step of calculating quality in the uplink data channel,
- the radio base station adjusts the calculated quality in the uplink data channel based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted through the uplink data channel, and measures the error rate in the uplink data channel Calculating a transmission format corresponding to the selectable maximum transport block size based on the measured error rate in the uplink data channel, and adjusting the uplink data channel by the radio base station And the calculated maximum transport block size Based on the transmission format, and summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource block in said uplink data channel.
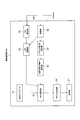
- FIG. 1 is an overall configuration diagram of a mobile communication system according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a functional block diagram of a radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention. It is a figure which shows an example of the TBS table used with the mobile communication system which concerns on the 1st Embodiment of this invention. It is a figure which shows an example of the throughput characteristic in the mobile communication system which concerns on the 1st Embodiment of this invention.
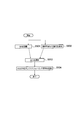
- 5 is a flowchart showing an operation of the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention. It is a functional block diagram of the radio base station which concerns on the example 1 of a change of the 1st Embodiment of this invention.
- FIG. 10 is a functional block diagram of a radio base station according to Modification 1 of the second embodiment of the present invention.
- Mobile communication system according to the first embodiment of the present invention A mobile communication system according to a first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
- the mobile communication system according to the present embodiment is an LTE mobile communication system.
- the radio base station eNB A downlink data signal is transmitted via PDSCH (Physical Downlink Shared Channel, downlink data channel), and a downlink control signal is transmitted via PDCCH (Physical Downlink Control Channel, downlink control channel).
- PDSCH Physical Downlink Shared Channel
- PDCCH Physical Downlink Control Channel
- the mobile station UE transmits an uplink data signal to the radio base station eNB via a PUSCH (Physical Uplink Shared Channel, uplink data channel), and a PUCCH (Physical Uplink Control Channel, uplink). And an uplink control signal is transmitted via the control channel.
- PUSCH Physical Uplink Shared Channel, uplink data channel
- PUCCH Physical Uplink Control Channel
- the mobile station UE uses “ACK / NACK”, which is delivery confirmation information indicating a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the PDSCH, as the uplink control signal, CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) in the PDSCH, Channel quality information).
- ACK / NACK delivery confirmation information indicating a delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal transmitted via the PDSCH, as the uplink control signal, CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) in the PDSCH, Channel quality information).
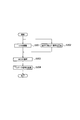
- the radio base station eNB includes a CQI receiving unit 11, an ACK / NACK / DTX determining unit 12, a CQI adjusting unit 13, an eNB scheduler 14, an MCS selecting unit 15, and a PDSCH generating unit 16. And a transmission unit 17.
- the CQI receiving unit 11 is configured to receive the CQI in the PDSCH transmitted by the mobile station UE via the PUCCH.
- the ACK / NACK / DTX determination unit 12 receives an acknowledgment result (ACK) for the downlink data signal transmitted to the mobile station UE via the PDSCH based on the acknowledgment information transmitted by the mobile station UE via the PUCCH. / NACK / DTX).
- ACK acknowledgment result
- the CQI adjusting unit 13 offsets the CQI received by the CQI receiving unit 11 based on the delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal determined by the ACK / NACK / DTX determining unit 12. It is comprised so that it may add and adjust.
- the CQI adjusting unit 13 is configured to adjust the CQI received by the CQI receiving unit 11 according to (Equation 1).
- CQIadjust CQIreceived + CQIoffset (Formula 1)
- CQIadjust is a CQI adjusted by the CQI adjusting unit 13
- CQIreceived is a CQI received by the CQI receiving unit 11
- CQIoffset is an offset amount given by (Equation 2).
- BLERtarget is a parameter indicating a target BLER (Block Error Rate) in PDSCH
- ⁇ adj is a parameter indicating a CQI adjustment range.
- the CQI adjustment unit 13 determines that the acknowledgment result for the downlink data signal is “NACK” by the ACK / NACK / DTX determination unit 12 , The offset amount of the CQI is decreased by “ ⁇ adj ⁇ (1 ⁇ BLERtarget)”.
- the CQI adjustment unit 13 determines that the delivery confirmation result for the downlink data signal is “DTX” by the ACK / NACK / DTX determination unit 12 The CQI offset amount is not changed.
- the eNB scheduler 14 is configured to perform scheduling in PDSCH and scheduling in PUSCH.
- the eNB scheduler 14 is configured to determine a mobile station UE that is a target for transmitting a downlink data signal and a radio resource (for example, a resource block in the PDSCH) for transmitting the downlink data signal. ing.
- the eNB scheduler 14 is configured to determine a mobile station UE that can transmit an uplink data signal and a radio resource (for example, a resource block in PUSCH) for transmitting the uplink data signal.
- a radio resource for example, a resource block in PUSCH
- the MCS selection unit 15 performs the transmission for each resource block in the PDSCH based on the transmission format corresponding to the CQI adjusted by the CQI adjustment unit 13 and the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF that can be selected). MCS (combination of modulation scheme and coding rate) to be applied, that is, a transmission format is selected.
- the MCS selection unit 15 may be configured to select a transmission format corresponding to the CQI adjusted by the CQI adjustment unit 13 from the transmission formats corresponding to the maximum selectable transport block size. .
- the MCS selection unit 15 is configured to acquire a transmission format number corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF # that can be selected) as the external setting parameter.
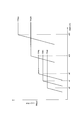
- Fig. 3 shows the "TBS table” specified in "Table 7.1.1.7.2.1-1" of TS36.213 of 3GPP.
- ITBS is a TBS index corresponding to TF #
- NPRB is the number of resource blocks
- the numbers in the table are transport block sizes.
- the MCS selection unit 15 acquires “TF # 25”, “TF # 26”, and the like as the number of the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF # that can be selected). It is configured as follows.
- FIG. 4 shows the relationship between SINR and throughput when each transmission format TF # 0 to TF # 26 is used.
- the LTE mobile communication system is configured such that the coding rate applied in the PDSCH increases as the TBS (TF #) applied in the PDSCH increases, and thus the required power in the PDSCH. Is configured to be large.
- the LTE mobile communication system is configured such that the smaller the TBS (TF #) applied in the PDSCH, the smaller the coding rate applied in the PDSCH, and thus the required power in the PDSCH is small. It is comprised so that it may become.
- the LTE mobile communication system is configured such that there is a large difference between the coding rate in TF # 25 and the coding rate in TF # 26. Therefore, even in a wireless environment (SINR state) in which communication is impossible at the coding rate in TF # 26, the radio base station eNB receives ACK continuously in a state where TF # 25 is used.
- SINR state wireless environment
- TF # 26 is selected, and transmission of the downlink data signal always fails, resulting in a problem that the throughput deteriorates.
- TF # 25 a transmission format number corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected for the radio base station eNB.
- the PDSCH generation unit 16 is configured to generate a downlink data signal to be transmitted via the PDSCH based on the MCS (transmission format) selected by the MCS selection unit 15.
- the transmission unit 17 is configured to transmit the downlink data signal generated by the PDSCH generation unit 16 to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDSCH.
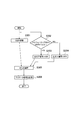
- the radio base station eNB determines from the mobile station UE via the PUCCH based on the delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted via the PDSCH. Adjust received CQI.
- step S102 the radio base station eNB acquires a transmission format number corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF # that can be selected) as an external setting parameter.
- step S103 the radio base station eNB selects an MCS (transmission format) based on the transmission format corresponding to the adjusted CQI and the selectable maximum transport block size.
- MCS transmission format
- step S104 the radio base station eNB transmits a downlink data signal addressed to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDSCH using the selected MCS (transmission format).
- throughput characteristics are deteriorated by using MCS (transmission format) having a high coding rate that deteriorates reception characteristics in a specific wireless environment by simple control with little development impact. It can be avoided.
- MCS transmission format
- Modification 1 With reference to FIG.6 and FIG.7, the mobile communication system which concerns on the modification 1 of the 1st Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated.
- the mobile communication system according to the first modification will be described by focusing on differences from the mobile communication system according to the first embodiment described above.
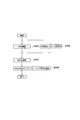
- the radio base station eNB according to the first modification includes the PDSCH error rate measurement unit 21 and the selectable TF number calculation in addition to the configuration of the radio base station eNB according to the first embodiment described above. Part 22 is provided.
- the PDSCH error rate measurement unit 21 determines the PDSCH such as BLER (error rate) in the PDSCH based on the acknowledgment result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal determined by the ACK / NACK / DTX determination unit 12. Is configured to measure an index (metric value) indicating reception quality.
- BLER error rate
- the PDSCH error rate measurement unit 21 may be configured to measure the BLER for the top Z MCSs in the measurement interval Y seconds for each measurement period X seconds as the metric value.
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 is based on the metric value such as BLER in the PDSCH measured by the PDSCH error rate measurement unit 21, and the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum selectable TF number). TF) is calculated.
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 may determine that a transmission format (for example, a transmission format specified by TF # 26) in which the metric value is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold cannot be selected.
- a transmission format for example, a transmission format specified by TF # 26
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 may determine that a transmission format in which the metric value is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value cannot be selected until the next measurement interval ends.
- the MCS calculation unit 15 sets the transmission format corresponding to the CQI adjusted by the CQI adjustment unit 13 and the maximum selectable transport block size calculated by the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 (that is, the maximum selectable TF). Based on this, MCS (combination of modulation scheme and coding rate) to be applied to each resource block in the PDSCH, that is, a transmission format is selected.
- the radio base station eNB determines from the mobile station UE via the PUCCH based on the delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted via the PDSCH. Adjust received CQI.
- the radio base station eNB calculates a transmission format number corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF # that can be selected) based on the measured BLER in the PDSCH.
- the radio base station eNB selects an MCS (transmission format) based on the transmission format corresponding to the adjusted CQI and the calculated maximum transport block size that can be selected.
- step S204 the radio base station eNB transmits a downlink data signal addressed to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDSCH using the selected MCS (transmission format).
- the mobile communication system According to the mobile communication system according to the first modification, it is possible to avoid the use of MCS that cannot communicate with a mobile station UE in an environment with poor reception quality or a mobile station UE with poor decoding performance, Degradation can be avoided.
- Modification 2 With reference to FIG. 8, a mobile communication system according to Modification 2 of the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
- the mobile communication system according to the second modification will be described by focusing on differences from the mobile communication system according to the first embodiment described above.
- the MCS selection unit 15 is configured to determine a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe (each scheduling unit period).
- the number of mobile stations UE may be, for example, the number of mobile stations UE with which RRC connection is established in each subframe (that is, “RRC connected UE”), or in a Non-DRX state. Or the number of mobile stations UE for which data is present in the buffer, or the number of mobile stations UE for which scheduling is calculated. Alternatively, it may be the number of mobile stations UE determined to be actually assigned a shared channel.
- the mobile station UE that is the target of the scheduling calculation refers to a mobile station UE that may be assigned a shared channel in each subframe, and the mobile station that is actually assigned the shared channel. It may include both the UE and the mobile station UE that was not actually assigned a shared channel.
- the MCS selection unit 15 determines that a plurality of mobile stations UE are subjected to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), the number of the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected Is determined as “TF # 25”, and it is determined that only one mobile station UE is subject to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), transmission corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected The format number may be determined to be “TF # 26”.
- the MCS selection unit 15 determines the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the number of instantaneous mobile stations UE in each subframe (each scheduling unit period). Alternatively, the maximum transport block size that can be selected may be determined based on the average number of mobile stations UE.
- the MCS selection unit 15 may determine the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the average value of the number of mobile stations UE per second, or the minimum value of the number of mobile stations UE per second Alternatively, the maximum transport block size that can be selected may be determined based on the maximum value.
- the radio base station eNB determines from the mobile station UE via the PUCCH based on the delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted via the PDSCH. Adjust received CQI.
- step S302 the radio base station eNB determines whether or not a plurality of mobile stations UE are subjected to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period).
- the radio base station eNB determines that a plurality of mobile stations UE are subject to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), in step S303, the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected Is determined as “TF # 25”.
- the radio base station eNB determines that only one mobile station UE has been subject to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period)
- the radio base station eNB supports the maximum transport block size that can be selected in step S304.
- the transmission format number to be determined is determined as “TF # 26”.
- step S305 the radio base station eNB selects an MCS (transmission format) based on the transmission format corresponding to the adjusted CQI and the determined maximum transport block size that can be selected.
- MCS transmission format
- step S306 the radio base station eNB transmits a downlink data signal addressed to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDSCH using the selected MCS (transmission format).
- the peak rate is really important for one mobile in a subframe. Only when the station UE performs communication.
- the peak rate is not realized in each mobile station UE.
- the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that causes characteristic degradation is selected. By prohibiting, it is possible to avoid degradation of throughput, that is, degradation of cell capacity.
- the mobile communication system according to the second modification when only one mobile station UE performs communication in one subframe, it is a quiet time, and when TF # 26 is selected, Even in an erroneous reception environment, since the cell capacity is not affected, a slight deterioration in characteristics can be tolerated. Therefore, the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size is allowed to be selected.
- the peak rate can be realized by selecting TF # 26 as well. Is possible.
- the first feature of the present embodiment is a radio base station eNB configured to transmit a downlink data signal to the mobile station UE via PDSCH (downlink data channel), and from the mobile station UE, Received based on a CQI receiver 11 configured to receive CQI (channel quality information) in PDSCH and a delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for a downlink data signal transmitted via PDSCH.
- PDSCH downlink data channel
- Selectable TF number for calculating the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe (scheduling unit period) and the CQI adjusting unit 13 configured to adjust the CQI Determination unit 22 and transmission corresponding to adjusted CQI and selectable maximum transport block size
- the MCS selection unit 15 configured to select a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource block in the PDSCH.
- the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe described above is the number of mobile stations UE (RRC connected UE) in which an RRC connection is established in each subframe, Non-DRX status ,
- the mobile station UE that is the target of the calculation of scheduling is a mobile station UE that may be assigned a shared channel in each subframe, and the mobile station UE that is actually assigned the shared channel It may include both the station UE and the mobile station UE that was not actually assigned a shared channel.
- a second feature of the present embodiment is a radio base station eNB configured to transmit a downlink data signal to the mobile station UE via PDSCH (downlink data channel), from the mobile station UE, Received based on a CQI receiver 11 configured to receive CQI (channel quality information) in PDSCH and a delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for a downlink data signal transmitted via PDSCH.
- the CQI adjustment unit 13 configured to adjust the CQI and the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected as an external setting parameter, and the adjusted CQI and the acquired selectable Each resource in the PDSCH is based on the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size.
- the MCS selection unit 15 configured to select a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to the scan block.
- the third feature of the present embodiment is a radio base station eNB configured to transmit a downlink data signal to the mobile station UE via PDSCH (downlink data channel), from the mobile station UE, Received based on the CQI receiving unit 11 configured to receive CQI (channel quality information) in the PDSCH and a delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted via the PDSCH.
- PDSCH downlink data channel
- the PDSCH error rate measurement unit 21 configured to measure the BLER (error rate) in the PDSCH, and the measured BLER in the PDSCH Configured to calculate the transmission format corresponding to the maximum selectable transport block size
- a selectable TF number calculating unit 22 a modulation scheme to be applied to each resource block in the PDSCH based on the adjusted CQI and the transmission format corresponding to the calculated maximum selectable transport block size, and
- the gist is to include an MCS selection unit 15 configured to select a coding rate.
- a fourth feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method for transmitting a downlink data signal from the radio base station eNB to the mobile station UE via the PDSCH, where the mobile station UE is connected to the radio base station eNB. Transmitting the CQI in the PDSCH, and adjusting the received CQI based on a delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted from the radio base station eNB through the PDSCH; The radio base station eNB calculates a maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe, and the radio base station eNB uses the adjusted CQI and the calculated selectable Suitable for each resource block in the PDSCH based on the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate to.
- the number of mobile stations UE in each sub-frame mentioned above is the number of mobile stations UE (RRC Connected UE) in which RRC connection is established in each sub-frame, Non-DRX state , The number of mobile stations whose data is present in the buffer, the number of mobile stations UE subject to scheduling calculation, or the mobile station UE determined to be actually assigned a shared channel
- the mobile station UE that is the target of the calculation of scheduling is a mobile station UE that may be assigned a shared channel in each subframe, and the mobile station UE that is actually assigned the shared channel It may include both the station UE and the mobile station UE that was not actually assigned a shared channel.
- a fifth feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method for transmitting a downlink data signal from the radio base station eNB to the mobile station UE via the PDSCH, where the mobile station UE is connected to the radio base station eNB. Transmitting the CQI in the PDSCH, and adjusting the received CQI based on a delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted from the radio base station eNB through the PDSCH; , A step of inputting a transmission format corresponding to a maximum transport block size that can be selected to the radio base station eNB as an external setting parameter, and the radio base station eNB, the adjusted CQI and the input selectable Each resource block in the PDSCH based on the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied for.
- a sixth feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method for transmitting a downlink data signal from the radio base station eNB to the mobile station UE via the PDSCH, where the mobile station UE is connected to the radio base station eNB. Transmitting the CQI in the PDSCH, and adjusting the received CQI based on a delivery confirmation result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the downlink data signal transmitted from the radio base station eNB through the PDSCH; Measuring a BLER in the PDSCH, calculating a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the measured BLER in the PDSCH, and the radio base station eNB comprising the adjusted CQI and Based on the transmission format corresponding to the calculated maximum selectable transport block size.
- Mobile communication system according to the second embodiment With reference to FIG.9 and FIG.10, the mobile communication system which concerns on the 2nd Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated.
- the mobile communication system according to the present embodiment will be described by focusing on differences from the mobile communication system according to the first embodiment described above.
- the radio base station eNB includes an SIR calculation unit 31, a reception unit 32, an SIR adjustment unit 33, an eNB scheduler 14, an MCS selection unit 15, a PDCCH generation unit 34, and a transmission unit 17. It is equipped with.
- the SIR calculation unit 31 is configured to calculate the quality in PUSCH such as SIR (Signal-to-Interference Ratio) in PUSCH.
- the SIR calculation unit 31 may calculate the quality using “Sounding Reference signal (SRS)”, or may calculate the quality using “Demodulation RS” multiplexed on the PUSCH. .
- SRS Sounding Reference signal
- the receiving unit 32 is configured to receive an uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH by the mobile station UE and receive an uplink control signal transmitted via the PUCCH by the mobile station UE.
- the SIR adjustment unit 33 is configured to adjust the SIR in the calculated PUSCH based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH.
- the SIR adjustment unit 33 is configured to adjust the SIR calculated by the SIR calculation unit 31 according to (Equation 3).
- SIRadjust SIRmeasured + SIRoffset (Formula 3)
- SIRadjust is the SIR adjusted by the SIR adjusting unit 33
- SIRmeasured is the SIR measured by the SIR receiving unit 31
- SIRoffset is the offset amount given by (Equation 4).
- BLERtarget is a parameter indicating a target BLER (Block Error Rate) in PUSCH
- ⁇ adj is a parameter indicating an adjustment range of SIR.
- the SIR adjustment unit 33 sets the SIR offset amount to “ ⁇ adj”. It is configured to increase by “ ⁇ BLERtarget”.
- the SIR adjustment unit 33 sets the SIR offset amount. It is configured to decrease by “ ⁇ adj ⁇ (1 ⁇ BLERtarget)”.
- the SIR adjusting unit 33 receives the above-described uplink data signal by the receiving unit 32 when the receiving unit 32 has not successfully received the above-described uplink control signal. When it is determined that the result is “DTX”), the SIR offset amount is not changed.
- the MCS selection unit 15 performs, for each resource block in the PUSCH, based on the transmission format corresponding to the SIR adjusted by the SIR adjustment unit 33 and the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF that can be selected). MCS (combination of modulation scheme and coding rate) to be applied, that is, a transmission format is selected.
- the MCS selection unit 15 may be configured to select a transmission format corresponding to the SIR adjusted by the SIR adjustment unit 33 from the transmission formats corresponding to the maximum selectable transport block size. .
- the MCS selection unit 15 is configured to acquire a transmission format number corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF # that can be selected) as the external setting parameter.
- the PDCCH generation unit 34 is configured to generate a downlink control signal to be transmitted via the PDCCH.
- the PDCCH generation unit 34 is configured to include the MCS (transmission format) selected by the MCS selection unit 15 as a scheduling signal in the downlink control signal transmitted via the PDCCH.
- MCS transmission format
- the transmission unit 17 is configured to transmit the downlink control signal (scheduling signal) generated by the PDCCH generation unit 34 to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDCCH.
- step S401 the radio base station eNB calculates a SIR in the PUSCH using the Demodulation RS or the Sounding RS, and receives a reception result (ACK for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH). / NACK / DTX), the calculated SIR in the PUSCH is adjusted.
- step S402 the radio base station eNB acquires a transmission format number (that is, selectable maximum TF #) corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected as an external setting parameter.
- the radio base station eNB selects an MCS (transmission format) to be applied to the resource block in the PUSCH based on the adjusted SIR and the transmission format corresponding to the maximum selectable transport block size. .
- the radio base station eNB transmits a downlink control signal including the selected MCS (transmission format) as a scheduling signal to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDCCH.
- throughput characteristics are deteriorated by using MCS (transmission format) having a high coding rate that deteriorates reception characteristics in a specific wireless environment by simple control with little development impact. It can be avoided.
- MCS transmission format
- Modification 1 With reference to FIG.11 and FIG.12, the mobile communication system which concerns on the modification 1 of the 2nd Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated.
- the mobile communication system according to the first modification will be described by focusing on differences from the mobile communication system according to the second embodiment described above.
- the radio base station eNB according to the first modification includes, in addition to the configuration of the radio base station eNB according to the first embodiment described above, a PUSCH error rate measurement unit 41 and a selectable TF number calculation. Part 22 is provided.
- the PUSCH error rate measurement unit 41 is an index (metric value) indicating reception quality in PUSCH such as BLER (error rate) in PUSCH based on the reception result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the above uplink data signal by the reception unit 32. ) Is configured to measure.
- the PUSCH error rate measurement unit 41 may be configured to measure the BLER for the top Z MCSs within the measurement interval Y seconds as the metric value for every measurement period X seconds.
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 determines the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the metric value such as BLER in the PUSCH measured by the PUSCH error rate measurement unit 41 (that is, the maximum selectable TF number). TF) is calculated.
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 may determine that a transmission format (for example, a transmission format specified by TF # 26) in which the metric value is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold cannot be selected.
- a transmission format for example, a transmission format specified by TF # 26
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 may determine that a transmission format in which the metric value is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value cannot be selected until the next measurement interval ends.
- the MCS calculation unit 15 sets the transmission format corresponding to the SIR adjusted by the SIR adjustment unit 33 and the maximum selectable transport block size calculated by the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 (that is, the maximum selectable TF). Based on this, MCS (combination of modulation scheme and coding rate) to be applied to each resource block in PUSCH, that is, a transmission format is selected.
- step S501 the radio base station eNB calculates the SIR in the PUSCH, and calculates based on the reception result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH. Adjust SIR in PUSCH.
- the radio base station eNB calculates a transmission format number corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected (that is, the maximum TF # that can be selected) based on the measured BLER in the PUSCH.
- the radio base station eNB applies MCS (transmission format) to be applied to the resource block in the PUSCH based on the transmission format corresponding to the adjusted SIR and the calculated maximum transport block size that can be selected. Select.
- MCS transmission format
- the radio base station eNB transmits a downlink control signal including the selected MCS (transmission format) as a scheduling signal to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDCCH.
- the mobile communication system According to the mobile communication system according to the first modification, it is possible to avoid the use of MCS that cannot communicate with a mobile station UE in an environment with poor reception quality or a radio base station eNB with poor decoding performance, and throughput characteristics Can be avoided.
- Modification 2 With reference to FIG. 13, a mobile communication system according to Modification 2 of the second embodiment of the present invention will be described. Hereinafter, the mobile communication system according to the second modification will be described by focusing on differences from the mobile communication system according to the second embodiment described above.
- the MCS selection unit 15 is configured to determine a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe (each scheduling unit period).
- the number of mobile stations UE may be, for example, the number of mobile stations UE with which RRC connection is established in each subframe (that is, “RRC connected UE”), or in a Non-DRX state. Or the number of mobile stations UE for which data is present in the buffer, or the number of mobile stations UE for which scheduling is calculated. Alternatively, it may be the number of mobile stations UE determined to be actually assigned a shared channel.
- the mobile station UE that is the target of the scheduling calculation refers to a mobile station UE that may be assigned a shared channel in each subframe, and the mobile station that is actually assigned the shared channel. It may include both the UE and the mobile station UE that was not actually assigned a shared channel.
- the MCS selection unit 15 determines that a plurality of mobile stations UE are subjected to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), the number of the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected Is determined as “TF # 25”, and it is determined that only one mobile station UE is subject to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), transmission corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected The format number may be determined to be “TF # 26”.
- the MCS selection unit 15 determines the maximum selectable transport block size based on the number of instantaneous mobile stations in each subframe (each scheduling unit period). The maximum selectable transport block size may be determined based on the average number of mobile stations.
- the MCS selection unit 15 may determine the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the average value of the number of mobile stations per second.
- the MCS selection unit 15 may determine the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the minimum value or the maximum value of the number of mobile stations per second.
- step S601 the radio base station eNB calculates the SIR in the PUSCH and calculates based on the reception result (ACK / NACK / DTX) for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH. Adjust SIR in PUSCH.
- step S602 the radio base station eNB determines whether or not a plurality of mobile stations UE are subjected to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period).
- the radio base station eNB determines that a plurality of mobile stations UE have been subject to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), in step S603, the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected Is determined as “TF # 25”.
- the radio base station eNB determines that only one mobile station UE has been subject to scheduling calculation in each subframe (each scheduling unit period), in step S604, the radio base station eNB supports the maximum transport block size that can be selected.
- the transmission format number to be determined is determined as “TF # 26”.
- step S605 the radio base station eNB applies MCS (transmission format) to be applied to the resource block in the PUSCH based on the transmission format corresponding to the adjusted SIR and the determined maximum transport block size that can be selected. Select.
- MCS transmission format
- step S606 the radio base station eNB transmits a downlink control signal including the selected MCS (transmission format) as a scheduling signal to the scheduled mobile station UE via the PDCCH.
- MCS transmission format
- the mobile communication system when a plurality of mobile stations UE perform communication in one subframe, selection of a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that causes characteristic degradation is prohibited. Thus, it is possible to avoid the deterioration of throughput, that is, the deterioration of cell capacity.
- the mobile communication system according to the second modification when only one mobile station UE performs communication in one subframe, it is a quiet time, and when TF # 26 is selected, Even in an erroneous reception environment, since the cell capacity is not affected, a slight deterioration in characteristics can be tolerated. Therefore, the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size is allowed to be selected.
- the peak rate can be realized by selecting TF # 26 in a reception environment where no error occurs even when TF # 26 is selected. It becomes possible.
- a first feature of the present embodiment is a radio base station eNB configured to receive an uplink data signal from a mobile station UE via a PUSCH (uplink data channel), and the SIR (quality) in the PUSCH is A SIR calculating unit 31 configured to calculate, and a SIR adjusting unit 33 configured to adjust the SIR in the calculated PUSCH based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH.
- PUSCH uplink data channel
- a selectable TF number determination unit 22 that calculates a maximum selectable transport block size based on the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe (scheduling unit period), an adjusted SIR, and a calculated selectable PUSCH based on the transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size And summarized in that comprises the MCS selection unit 15 configured to select a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to each resource block.
- the number of mobile stations UE in each subframe described above is the number of mobile stations UE (RRC connected UE) in which an RRC connection is established in each subframe, Non-DRX status ,
- the mobile station UE that is the target of the calculation of scheduling is a mobile station UE that may be assigned a shared channel in each subframe, and the mobile station UE that is actually assigned the shared channel It may include both the station UE and the mobile station UE that was not actually assigned a shared channel.
- the second feature of the present embodiment is a radio base station eNB configured to receive an uplink data signal from a mobile station UE via a PUSCH (uplink data channel), and the SIR (quality) in the PUSCH is A SIR calculating unit 31 configured to calculate, and a SIR adjusting unit 33 configured to adjust the SIR in the calculated PUSCH based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH. And a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected as an external setting parameter, and PUSCH based on the adjusted SIR and the transmission format corresponding to the acquired maximum transport block size that can be selected Modulation scheme and code to be applied to each resource block And summarized in that comprises the MCS selection unit 15 configured to select the rate.
- a third feature of the present embodiment is a radio base station eNB configured to receive an uplink data signal from a mobile station UE via a PUSCH (uplink data channel), and the SIR (quality) in the PUSCH is A SIR calculating unit 31 configured to calculate, and a SIR adjusting unit 33 configured to adjust the SIR in the calculated PUSCH based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH. And a PUSCH measurement unit 41 configured to measure the BLER (error rate) in the PUSCH, and a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected is calculated based on the measured BLER in the PUSCH.
- BLER error rate
- the selectable TF number calculation unit 22 configured as described above and the adjusted S MCS selection configured to select a modulation scheme and coding rate to apply to each resource block in PUSCH based on R and a transmission format corresponding to the calculated maximum selectable transport block size
- the gist of the present invention is to include the unit 15.
- a fourth feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method for transmitting an uplink data signal from the mobile station UE to the radio base station eNB via the PUSCH, and the radio base station eNB calculates the SIR in the PUSCH.
- the number of mobile stations UE in each sub-frame mentioned above is the number of mobile stations UE (RRC Connected UE) in which RRC connection is established in each sub-frame, Non-DRX state , The number of mobile stations whose data is present in the buffer, the number of mobile stations UE subject to scheduling calculation, or the mobile station UE determined to be actually assigned a shared channel
- the mobile station UE that is the target of the calculation of scheduling is a mobile station UE that may be assigned a shared channel in each subframe, and the mobile station UE that is actually assigned the shared channel It may include both the station UE and the mobile station UE that was not actually assigned a shared channel.
- a fifth feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method for transmitting an uplink data signal from a mobile station UE to a radio base station eNB via a PUSCH, in which the radio base station eNB calculates an SIR in the PUSCH.
- the radio base station eNB adjusts the SIR in the calculated PUSCH based on the reception result of the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH, and the radio base station eNB as an external setting parameter
- Inputting a transmission format corresponding to the maximum selectable transport block size, and the radio base station eNB based on the adjusted SIR and the transmission format corresponding to the input maximum selectable transport block size Modulation scheme and code to be applied to each resource block in PUSCH And summarized in that a step of selecting the rate.
- a fifth feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method for transmitting an uplink data signal from a mobile station UE to a radio base station eNB via a PUSCH, in which the radio base station eNB calculates an SIR in the PUSCH.
- the radio base station eNB adjusts the SIR in the calculated PUSCH based on the reception result for the uplink data signal transmitted via the PUSCH, the step of measuring the BLER in the PUSCH, and A step of calculating a transmission format corresponding to the maximum transport block size that can be selected based on the BLER in PUSCH, and the radio base station eNB supports the adjusted SIR and the calculated maximum transport block size that can be selected Each resource in the PUSCH based on the transmission format to be And summarized in that a step of selecting a modulation scheme and coding rate applied to the lock.
- radio base station eNB and the mobile station UE described above may be implemented by hardware, may be implemented by a software module executed by a processor, or may be implemented by a combination of both. .
- Software modules include RAM (Random Access Memory), flash memory, ROM (Read Only Memory), EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM), EEPROM (Electronically Erasable and Programmable, Removable ROM, and Hard Disk). Alternatively, it may be provided in a storage medium of an arbitrary format such as a CD-ROM.
- Such a storage medium is connected to the processor so that the processor can read and write information from and to the storage medium. Further, such a storage medium may be integrated in the processor. Such a storage medium and processor may be provided in the ASIC. Such an ASIC may be provided in the radio base station eNB or the mobile station UE. Further, the storage medium and the processor may be provided as a discrete component in the radio base station eNB or the mobile station UE.
- the present invention it is possible to provide a radio base station and a mobile communication method capable of realizing a high-speed peak rate without degrading throughput characteristics.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/496,058 US8743728B2 (en) | 2009-09-15 | 2010-09-13 | Radio base station and mobile communication method |
| CN201080041025.6A CN102598768B (zh) | 2009-09-15 | 2010-09-13 | 无线基站和移动通信方法 |
| EP10817134.9A EP2480023A4 (en) | 2009-09-15 | 2010-09-13 | RADIO BASE STATION AND MOBILE COMMUNICATION PROCESS |
| IN2579CHN2012 IN2012CN02579A (enExample) | 2009-09-15 | 2010-09-13 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009213668A JP5031009B2 (ja) | 2009-09-15 | 2009-09-15 | 無線基地局及び移動通信方法 |
| JP2009-213668 | 2009-09-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011034021A1 true WO2011034021A1 (ja) | 2011-03-24 |
Family
ID=43758625
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2010/065724 Ceased WO2011034021A1 (ja) | 2009-09-15 | 2010-09-13 | 無線基地局及び移動通信方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8743728B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2480023A4 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5031009B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102598768B (enExample) |
| IN (1) | IN2012CN02579A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2011034021A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013139044A1 (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | Nokia Corporation | Method and apparatus for re-interpreting channel state information |
| WO2013149573A1 (zh) * | 2012-04-01 | 2013-10-10 | 华为技术有限公司 | 传输信号的方法、网络设备和用户设备 |
| CN104170450A (zh) * | 2012-03-16 | 2014-11-26 | 株式会社Ntt都科摩 | 无线基站、用户终端、无线通信方法以及无线通信系统 |
| US10200839B2 (en) * | 2014-03-21 | 2019-02-05 | Alcatel Lucent | Method and apparatus for low cost machine type communication |
| WO2019095315A1 (en) * | 2017-11-17 | 2019-05-23 | Zte Corporation | Methods, apparatus and systems for determining a transport block size in a wireless communication |
Families Citing this family (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012050329A2 (ko) * | 2010-10-11 | 2012-04-19 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 무선 접속 시스템에서 상향링크 데이터 재전송 시 상향링크 제어정보 전송 방법 및 장치 |
| CN102752874B (zh) * | 2011-04-22 | 2016-08-24 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 物理下行共享信道的调度方法及装置 |
| CN102265543B (zh) * | 2011-06-10 | 2014-03-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | 修正信道质量指示值的方法和设备 |
| CN104094661B (zh) * | 2011-12-29 | 2018-01-19 | 意大利电信股份公司 | 无线通信网络的调度算法 |
| JP5642102B2 (ja) * | 2012-03-27 | 2014-12-17 | ソフトバンクモバイル株式会社 | Ofdm伝送システムにおける受信装置及び無線通信制御方法 |
| US9584288B2 (en) | 2012-03-28 | 2017-02-28 | Nec Corporation | Communication channel quality estimating method, wireless communications system, base station, and program |
| CN103378935B (zh) * | 2012-04-27 | 2018-04-27 | 广州世炬网络科技有限公司 | 一种基于反馈歧义调整下行相关参数的方法 |
| US9374191B2 (en) | 2012-05-17 | 2016-06-21 | Apple Inc. | Outer loop link adaptation for device resumption |
| US20150236808A1 (en) * | 2012-09-25 | 2015-08-20 | Telefonaktiebolaget L M Ericsson (Publ) | Method and apparatus for radio link adaptation for flexible subframe communications |
| CN104081819B (zh) * | 2012-10-18 | 2021-06-01 | 华为技术有限公司 | 资源的调度方法及装置 |
| CN103905102B (zh) * | 2012-12-27 | 2017-02-08 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 协作多点数据传输方法及基站 |
| KR20150082448A (ko) | 2013-01-03 | 2015-07-15 | 인텔 코포레이션 | 개선된 채널 품질 정보 피드백 기술 |
| US10432370B2 (en) * | 2013-01-14 | 2019-10-01 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Transmission and processing of higher order modulation |
| JP5852616B2 (ja) | 2013-01-29 | 2016-02-03 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | ユーザ端末、無線基地局及び適応変調符号化方法 |
| US9219569B2 (en) * | 2013-03-09 | 2015-12-22 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method and apparatus for optimizing rate control based on packet aggregation considerations |
| WO2014146280A1 (zh) * | 2013-03-21 | 2014-09-25 | 华为终端有限公司 | 数据传输方法、基站及用户设备 |
| PT2830345T (pt) | 2013-03-21 | 2019-09-17 | Huawei Device Co Ltd | Método de transmissão de dados, estação de base e equipamento de utilizador |
| US20150139000A1 (en) * | 2013-11-18 | 2015-05-21 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Adjustment of cqi based on fading condition |
| CN104980247B (zh) * | 2014-04-04 | 2019-11-22 | 北京三星通信技术研究有限公司 | 自适应调整调制编码方式和参考信号图样的方法、基站、终端和系统 |
| CN107667483A (zh) * | 2015-06-09 | 2018-02-06 | 瑞典爱立信有限公司 | 具有对csi‑rs产生的干扰的预测的外环链路适配 |
| DE102015109951B4 (de) * | 2015-06-22 | 2021-10-21 | Apple Inc. | Verfahren und Vorrichtungen zum Bereitstellen einer robusten Datenkommunikation zwischen einem Client und einem Server |
| GB2552307A (en) * | 2016-07-12 | 2018-01-24 | Tcl Communication Ltd | Methods and devices for link adaptation under conditions of intermittent interference in wireless communication systems |
| US20180035409A1 (en) * | 2016-07-28 | 2018-02-01 | Nokia Solutions And Networks Oy | Mitigation of rate matching errors in a wireless network |
| WO2018049562A1 (zh) * | 2016-09-13 | 2018-03-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | 自适应调制编码的方法和基站 |
| KR102142363B1 (ko) * | 2016-09-28 | 2020-08-07 | 후지쯔 가부시끼가이샤 | 기지국 장치, 단말 장치, 무선 통신 시스템 및 무선 통신 시스템 제어 방법 |
| CN108270470B (zh) * | 2016-12-30 | 2021-02-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种数据传输的方法及发送端设备、接收端设备 |
| CN113890676A (zh) * | 2017-03-24 | 2022-01-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种信道质量指示反馈的方法及设备 |
| US10750482B2 (en) * | 2017-08-11 | 2020-08-18 | Mediatek Singapore Pte. Ltd. | Uplink control channel design for high reliability transmission in mobile communications |
| CN107483156B (zh) * | 2017-08-23 | 2020-09-18 | 北京佰才邦技术有限公司 | 资源分配方法、装置及系统 |
| WO2019189119A1 (ja) * | 2018-03-27 | 2019-10-03 | 日本電気株式会社 | 無線通信装置、データ受信方法及びプログラム |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005086304A (ja) * | 2003-09-05 | 2005-03-31 | Fujitsu Ltd | 無線通信装置 |
| JP2005318470A (ja) * | 2004-04-30 | 2005-11-10 | Ntt Docomo Inc | 無線基地局装置及び無線通信制御方法 |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2391431A (en) * | 2002-07-30 | 2004-02-04 | Fujitsu Ltd | Adaptive modulation and coding method |
| JP2004343524A (ja) * | 2003-05-16 | 2004-12-02 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 基地局、移動局、通信システムおよび通信方法 |
| CN101379753B (zh) * | 2006-02-03 | 2012-06-27 | Lg电子株式会社 | 无线通信系统中基于反馈信息发送至少一个子分组的方法 |
| JP4760547B2 (ja) * | 2006-06-02 | 2011-08-31 | 日本電気株式会社 | 無線基地局装置およびスケジューリング方法 |
| BRPI0713665B1 (pt) * | 2006-06-19 | 2019-11-26 | Ntt Docomo Inc | método de comunicação de rádio, estação base, estação móvel e chip de ci |
| CN101132227B (zh) * | 2006-08-23 | 2012-01-25 | 电信科学技术研究院 | 一种无线通信信道质量的监控方法及系统 |
| US8068427B2 (en) * | 2006-09-27 | 2011-11-29 | Qualcomm, Incorporated | Dynamic channel quality reporting in a wireless communication system |
| CN101207553B (zh) * | 2006-12-18 | 2010-12-08 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 一种高速下行分组接入业务中确定传输块大小的方法 |
| KR20080073196A (ko) * | 2007-02-05 | 2008-08-08 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Mimo 시스템에서 효율적인 채널 품질 정보 전송 방법 |
| EP2117245A4 (en) * | 2007-03-01 | 2014-01-01 | Ntt Docomo Inc | BASIC STATION EQUIPMENT AND COMMUNICATION CONTROL METHOD |
| CN101159951B (zh) * | 2007-11-08 | 2013-03-20 | 重庆重邮信科通信技术有限公司 | Td-scdma系统hsdpa信道质量指示计算方法 |
| US8275408B2 (en) * | 2008-08-27 | 2012-09-25 | Qualcomm, Incorporated | Power control in a wireless communication system |
-
2009
- 2009-09-15 JP JP2009213668A patent/JP5031009B2/ja active Active
-
2010
- 2010-09-13 IN IN2579CHN2012 patent/IN2012CN02579A/en unknown
- 2010-09-13 EP EP10817134.9A patent/EP2480023A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2010-09-13 CN CN201080041025.6A patent/CN102598768B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-09-13 WO PCT/JP2010/065724 patent/WO2011034021A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2010-09-13 US US13/496,058 patent/US8743728B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005086304A (ja) * | 2003-09-05 | 2005-03-31 | Fujitsu Ltd | 無線通信装置 |
| JP2005318470A (ja) * | 2004-04-30 | 2005-11-10 | Ntt Docomo Inc | 無線基地局装置及び無線通信制御方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| "3rd Generation Partnership Project;Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Evolved universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA);Physical layer procedures(Release8)", 3GPP TS36.213, V8.7.0, May 2009 (2009-05-01), pages 25 - 33, XP050377562 * |
| See also references of EP2480023A4 * |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104170450A (zh) * | 2012-03-16 | 2014-11-26 | 株式会社Ntt都科摩 | 无线基站、用户终端、无线通信方法以及无线通信系统 |
| CN104170450B (zh) * | 2012-03-16 | 2018-06-05 | 株式会社Ntt都科摩 | 无线基站、用户终端、无线通信方法以及无线通信系统 |
| WO2013139044A1 (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2013-09-26 | Nokia Corporation | Method and apparatus for re-interpreting channel state information |
| US9345015B2 (en) | 2012-03-23 | 2016-05-17 | Nokia Technologies Oy | Method and apparatus for re-interpreting channel state information |
| WO2013149573A1 (zh) * | 2012-04-01 | 2013-10-10 | 华为技术有限公司 | 传输信号的方法、网络设备和用户设备 |
| US10200839B2 (en) * | 2014-03-21 | 2019-02-05 | Alcatel Lucent | Method and apparatus for low cost machine type communication |
| WO2019095315A1 (en) * | 2017-11-17 | 2019-05-23 | Zte Corporation | Methods, apparatus and systems for determining a transport block size in a wireless communication |
| CN111373710A (zh) * | 2017-11-17 | 2020-07-03 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 无线通信中确定传输块大小的方法、装置和系统 |
| CN111373710B (zh) * | 2017-11-17 | 2021-09-24 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | 无线通信中确定传输块大小的方法、装置和系统 |
| US11638251B2 (en) | 2017-11-17 | 2023-04-25 | Zte Corporation | Methods, apparatus and systems for determining a transport block size in a wireless communication |
| US11991674B2 (en) | 2017-11-17 | 2024-05-21 | Zte Corporation | Methods, apparatus and systems for determining a transport block size in a wireless communication |
| US12294981B2 (en) | 2017-11-17 | 2025-05-06 | Zte Corporation | Methods, apparatus and systems for determining a transport block size in a wireless communication |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102598768A (zh) | 2012-07-18 |
| CN102598768B (zh) | 2014-12-10 |
| JP5031009B2 (ja) | 2012-09-19 |
| US20120207054A1 (en) | 2012-08-16 |
| EP2480023A1 (en) | 2012-07-25 |
| IN2012CN02579A (enExample) | 2015-08-21 |
| US8743728B2 (en) | 2014-06-03 |
| EP2480023A4 (en) | 2016-03-30 |
| JP2011066545A (ja) | 2011-03-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5031009B2 (ja) | 無線基地局及び移動通信方法 | |
| JP3796212B2 (ja) | 基地局装置及び送信割り当て制御方法 | |
| CN102265689B (zh) | 无线基站以及通信控制方法 | |
| US7539497B2 (en) | Obtaining channel quality information in a wireless communication network | |
| US8971271B2 (en) | Methods and network nodes for scheduling transmission | |
| US10200907B2 (en) | Systems and methods for dynamic uplink and downlink rate assignment in a wireless communication network | |
| US20090239590A1 (en) | Uplink Scheduling in a Cellular System | |
| EP3314794B1 (en) | Method and base station for selecting a transport format | |
| CN113841449B (zh) | 用于超可靠低时延通信上行链路的资源选择 | |
| US8897284B2 (en) | Radio base station | |
| EP1826922A1 (en) | Mobile communication system, mobile station, and radio base station | |
| CN103155655A (zh) | 上行链路功率控制 | |
| CN107534512A (zh) | 限定解码余量的多等级ack | |
| JP5170483B2 (ja) | 物理アップリンク共有チャネルの送信パワー制御方法及びシステム | |
| JP4734404B2 (ja) | 無線基地局及び通信制御方法 | |
| JP2007536866A (ja) | 確認応答をマッピングするarq通信システム及び方法 | |
| CN101106403B (zh) | 一种调整hspa下行物理信道发射功率的方法和装置 | |
| EP2810507B1 (en) | Methods and network nodes for scheduling transmission | |
| US20240323994A1 (en) | Method, apparatus and system relating to determining a target quality | |
| EP2408231A1 (en) | Wireless base station | |
| CN102412945A (zh) | 物理混合重传指示信道的功率配置方法 | |
| CN107342839A (zh) | 链路自适应调整方法及装置 | |
| EP3633893A1 (en) | Method and device for transmitting configuration information, and method and device for receiving configuration information | |
| KR101582392B1 (ko) | 신뢰할 수 있는 제어 채널 성능을 위한 방법 및 장치 | |
| CN109819455A (zh) | 一种上行选阶方法、用户终端和基站 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201080041025.6 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 10817134 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2579/CHENP/2012 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2010817134 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2010817134 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13496058 Country of ref document: US |