US8080703B2 - Dressing - Google Patents
Dressing Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US8080703B2 US8080703B2 US10/536,422 US53642205A US8080703B2 US 8080703 B2 US8080703 B2 US 8080703B2 US 53642205 A US53642205 A US 53642205A US 8080703 B2 US8080703 B2 US 8080703B2
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- dressing
- indentations
- adhesive
- pattern
- skin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime, expires
Links
- 238000007373 indentation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 109
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 72
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 71
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 47
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 206010052428 Wound Diseases 0.000 description 20
- 208000027418 Wounds and injury Diseases 0.000 description 20
- 210000003127 knee Anatomy 0.000 description 13
- 230000002250 progressing effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- 206010040844 Skin exfoliation Diseases 0.000 description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000005299 abrasion Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 6
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000013508 migration Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005012 migration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000037303 wrinkles Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000002310 elbow joint Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000416 hydrocolloid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 210000000629 knee joint Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000002803 maceration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000037081 physical activity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002035 prolonged effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000002874 Acne Vulgaris Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000003643 Callosities Diseases 0.000 description 1
- QDHHCQZDFGDHMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloramine Chemical compound ClN QDHHCQZDFGDHMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GHXZTYHSJHQHIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorhexidine Chemical compound C=1C=C(Cl)C=CC=1NC(N)=NC(N)=NCCCCCCN=C(N)N=C(N)NC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 GHXZTYHSJHQHIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010011985 Decubitus ulcer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 201000004624 Dermatitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010020649 Hyperkeratosis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000006877 Insect Bites and Stings Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 240000008790 Musa x paradisiaca Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000018290 Musa x paradisiaca Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 102000057297 Pepsin A Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000284 Pepsin A Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000004210 Pressure Ulcer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 201000004681 Psoriasis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000006981 Skin Abnormalities Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000028990 Skin injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000004142 Trypsin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000631 Trypsin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 240000008042 Zea mays Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000005824 Zea mays ssp. parviglumis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000002017 Zea mays subsp mays Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010000496 acne Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006978 adaptation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001464 adherent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000844 anti-bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108010072041 arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000010668 atopic eczema Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000003899 bactericide agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003385 bacteriostatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003287 bathing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960003260 chlorhexidine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000005822 corn Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003974 emollient agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940088598 enzyme Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920005570 flexible polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000035876 healing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002458 infectious effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical compound II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004807 localization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940111202 pepsin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006149 polyester-amide block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006264 polyurethane film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001902 propagating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011321 prophylaxis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003378 silver Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000008961 swelling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000699 topical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012588 trypsin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009736 wetting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/10—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads specially adapted for fingers, hands or arms; Finger-stalls; Nail-protectors
- A61F13/101—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads specially adapted for fingers, hands or arms; Finger-stalls; Nail-protectors for the elbow, e.g. decubitus ulcer bandages
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/00987—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing non-adhesive dressings or bandages
- A61F13/00991—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing non-adhesive dressings or bandages for treating webs, e.g. for moisturising, coating, impregnating or applying powder
- A61F13/00995—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing non-adhesive dressings or bandages for treating webs, e.g. for moisturising, coating, impregnating or applying powder for mechanical treatments
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/02—Adhesive bandages or dressings
- A61F13/023—Adhesive bandages or dressings wound covering film layers without a fluid retention layer
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/02—Adhesive bandages or dressings
- A61F13/0246—Adhesive bandages or dressings characterised by the skin-adhering layer
- A61F13/025—Adhesive bandages or dressings characterised by the skin-adhering layer having a special distribution arrangement of the adhesive
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/06—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads specially adapted for feet or legs; Corn-pads; Corn-rings
- A61F13/061—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads specially adapted for feet or legs; Corn-pads; Corn-rings for knees
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F2013/00089—Wound bandages
- A61F2013/00314—Wound bandages with surface treatments
- A61F2013/00327—Wound bandages with surface treatments to create projections or depressions in surface
Definitions
- the present invention relates to dressings, in particular dressings for covering a portion of the anatomical surface of a living being, a method for preparing such dressings, and a method of treating a portion of the anatomical surface of a living being, especially a joint or a protruding part of the body.
- dressings for the treatment or prevention of wounds or pressure sores or even unbroken skin are essentially flat dressings, which are sufficiently mouldable to be applied to flat or slightly curved areas of the body.
- Such flat dressings are not very suitable for applying on protruding parts of the body or joints e.g. heels or especially elbows or knees having not only a very pronounced curvature but also being subject to constant bending which often causes wrinkling and focusing of stresses in the dressing often causing slipping of the adhesive and unintended detachment of the dressing.
- WO 93/00056 discloses that a skin-friendly dressing having grooves or ditches surrounding a central part of the dressing has a high degree of flexibility.
- the ditches are surrounding a central part of the adhesive.
- EP patent No. 0 768 071 discloses a wound dressing especially for use in the sacrum area, said dressing having one or more linear depressions that assist a user in applying, flexing or folding the dressing and that the dressing may have two sets of spaced parallel depressions forming a grid which is useful in the wound assessment.
- the thickness of the adhesive layer at the base of the depressions should at least be as great as the thickness of the border portion of the adhesive layer.
- GB patent No. 1,075,939 discloses an adhesive bandage having a thermoplastic top film provided with embossments in order to allow passage of water vapour though the film.
- Non-adherent dressing comprising a film which contains depressions over the wound contacting area which depressions contain a viscous pharmaceutical composition which is suitable for topical application.
- the depressions may be in the form of a pattern of conical depressions.
- WO 99/36017 discloses a dressing comprising a substantially water-impervious layer and a skin-friendly adhesive having a pattern of indentations, which diminishes or disappears when the dressing is moisturised.
- the grooves are stated to have a depth of at least 25% and more preferred at least 50% of the thickness of the dressing and it is stated that the pattern may increase the flexibility of the dressing.
- U.S. Pat. No. 5,356,372 discloses an occlusive pressure-reducing wound dressing consisting of an occlusive wound contacting layer and a pressure-reducing layer and it is claimed that the pressure-reducing layer has a contour for adapting to curved body surfaces.
- the top surface comprises a plurality of elevated domains and lowered domains providing a lower overall resistance to larger applied compressive force.
- the lowered domains between the elevated domains provide valleys extending across the pressure-reducing layer in substantially right-angled relationship to each other so that the bending of the relatively thick foam in a multiplicity of directions is facilitated.
- DE 42 03 130 discloses a medical dressing, the surface of which in certain areas has been embossed so that the embossed areas are transparent.
- the embossed fraction of the dressing is greater than 20% of the surface for enabling a sufficient transparency to inspect the below wound and skin.
- DE 42 03 130 shows different embossment patterns all showing linear indentations progressing in several directions and is silent with respect to the disadvantages of such lines.
- the flexibility of a dressing is important, with respect to the shape, the size and the adhesive of the dressing, not only in use but also during the application.
- a dressing on a part of the body that is frequently bent such as the inner or outer side of a joint or inside a hand, or a protruding part of the body or a part of the body having a double curvature such as the inter digital area flexibility is a very important property as the dressing must be able to adapt to the contour of the skin surface and to follow movements without slipping the skin or exposing the skin to significant stress causing pain or unpleasant feeling and during use a sufficient flexibility enabling the dressing to follow the movement of the underlying skin is decisive for obtaining a long wear time and for reducing the risk of migration of humidity from a wound or an abrasion to neighbouring areas which may cause maceration of the skin or leakage at the edge of the dressing.
- the present invention relates to a dressing for covering a portion of the anatomical surface of a living being, said dressing being able to adhere to the skin, and/or a wound, said dressing comprising a backing layer and a layer of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin, and said dressing having a pattern of indentations.
- the invention also relates to a method for preparing a dressing comprising a backing layer and a layer of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin, which dressing has a pattern of indentations.
- the invention relates to a method of treating a portion of the anatomical surface of a living being, especially a protruding part of the body.
- FIG. 1 shows a top view of an embodiment of a dressing of the invention
- FIG. 2 shows a top view of another embodiment of a dressing of the invention
- FIG. 3 shows in an enlarged scale a sectional view of the embodiment of FIG. 2 along the line A-A,
- FIG. 4 shows a top view of a further embodiment of a dressing of the invention
- FIG. 5 shows a top view of a still further embodiment of a dressing of the invention
- FIG. 6 shows the localisation of a release liner with respect to the Section A-A in FIG. 5 ,
- FIG. 7 shows in an enlarged scale a sectional view of the embodiment of FIG. 5 along the line A-A
- FIG. 8 shows in an enlarged scale a sectional view of the embodiment of FIG. 5 along the line B-B
- FIG. 9 shows in a further enlarged scale a detail in the area marked C in FIG. 8 .
- the present invention relates to a dressing for covering a portion of the anatomical surface of a living being, said dressing being able to adhere to the skin, and/or a wound, said dressing comprising a backing layer and a layer of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin, and said dressing having a pattern of indentations wherein the indentations are in the form of a pattern of connected indentations not being linear and progressing in at least three main directions.
- the pattern of indentations of a dressing according to the present invention covers all the central surface of the dressing providing flexibility to all of the surface of the dressing and not only to the distal part thereof.
- the dressing of the invention is suitable for covering blisters, cuts, graces and abrasions and other skin injuries especially on a part of the body that is frequently bent such as a joint, e.g. heels, knuckles, elbows or knees, or inside a hand, on a protruding part of the body such as the tip of a finger or toe, or on a part of the body having a double curvature such as the inter digital area or other parts of the body that are stressed by movements as it has a high capability of adapting to the specific site during application and then, when applied, a high capability of following movements of the skin like a second skin.
- a joint e.g. heels, knuckles, elbows or knees, or inside a hand
- a protruding part of the body such as the tip of a finger or toe
- a part of the body having a double curvature such as the inter digital area or other parts of the body that are stressed by movements as it has a high capability of
- a dressing of the invention is preferably large enough to cover abrasions on both knees and elbows, large enough to anchor well at both or several sides of the joint, and yet preferably small enough to be applied with one hand when applying on an elbow.
- the pattern of indentations progressing in at least three directions allows maximum flexibility and it allows the dressing to bend in the pattern of indentations without introducing stress to the adhesive material and reducing the risk of peeling of the dressing from the skin.
- the effect is believed to be supported by the non-linearity and number of the indentations, which distributes the stress introduced when bending and stretching a joint rather than focussing the stress along the edge or rectilinear indentations, which might initiate formation of a fold or peeling of the dressing.
- the indentations are in the form of a symmetrical pattern providing a more controlled spacing of the general directions of progression of the indentations.
- the indentations are in the form of a honeycomb pattern in which the indentations are relatively narrow grooves defining a pattern of adhesive areas having the maximum thickness of the dressing and being of essentially hexagonal shape.
- the angled propagation of the indentations is believed to distribute the stress rather than to focus the same and thus to prevent formation of folds which might open for peeling of the dressing at the edge or expose the adhesive and cause adhesion to e.g. clothes.
- the high flexibility is achieved as a consequence of the combination of the size of the parts of the pattern, i.e. separate hexagonal shape of the adhesive areas between the indentations, the distance between the separate pattern parts, the thickness of the overall adhesive layer and the thickness of the adhesive layer in the pattern.
- the distance between the areas between the indentations i.e. the width of the indentations
- the width of the indentations is in the magnitude of from about 0.2 to about 3 millimeters, e.g. 0.5-2 millimeters, suitably 1.2 millimeters providing a suitable flexibility.
- the size of the adhesive areas between the indentations is from 2 to 25 millimeters, more preferred from 2 to 16 millimeters and preferably from 2 to 12 millimeters.
- the pattern of indentations progressing in at least three directions should not provide any lines of sight across the dressing in any direction for avoiding focussing of stress along such lines of the indentations.
- the total area of the indentations is below 20% of the total surface of the dressing, suitably below 18% providing a sufficient flexibility combined with high security against formation of wrinkles or leakages.
- indentations being wider at the top end and narrower at the bottom e.g. having a trapezoidal cross-section.
- the indentations are in the form of a pattern in which the indentations are relatively thin grooves defining a pattern of adhesive areas having the maximum thickness of the dressing and being of essentially circular shape.
- the indentations are suitably made from the side of the backing layer in which case it is simple to add a step for effecting the impression in a conventional line for producing medical dressings.
- this embodiment provides an uninterrupted adhesive surface facing the skin to be covered which is pertinent for obtaining a protection against migration of humidity from a wound or an abrasion to neighbouring parts of the skin or to the edge of the dressing. Still further, an uninterrupted adhesive surface facing the skin will not give rise to unpleasant feeling during physical activity due to “opening and closing” of the indentations which may cause pinching or pain.
- the indentations have depth of at least two thirds of the total thickness of the dressing. In accordance with a preferred embodiment the indentations have depth of at least 75% of the total thickness of the dressing, more preferred up to 90% and even exceeding 90% of the total thickness of the dressing.
- the dressing may be considered as a number of thick parts connected by thinner bridging parts.
- the bridging parts are preferably sufficiently large and present in a sufficient number to allow stress originated from movement of an elbow or knee joint to be relaxed without proceeding from one thick part to the next.
- the thickness of the dressing at the bottom of the indentations of a dressing of the invention is below 0.5 millimetres e.g. from 0.05 to 0.4 millimetres, suitably form 0.1 to 0.3 millimetres providing a suitable flexibility.
- a dressing of the invention is provided with zones of small thickness stopping the propagation of the peeling and enabling cutting off a part of the edge along the indentations.
- pattern may also offer further advantages as the zones will prevent/slow down the propagation of swelling of a hydrocolloid from to reach the whole dressing, and to reach the edge and cause slip of the dressing, and also provide an additional stability and comfort due to the discontinuous attachment to the skin surface.
- the dressing of the invention is especially suitable for use on hands or feet or on a joint such as a heel, a knee, an elbow, or a knuckle, preferably a knee, an elbow, or a knuckle.
- the backing layer is a substantially water-impervious film which protects the adhesive from being adversely affected when the wearer is bathing or in case of incidental wetting of the area and especially when the adhesive is water absorbing.
- the backing layer is a film showing a low surface friction for reducing the stress transferred to the skin due to physical activity of the user as a dressing covered by clothing will move relatively to the dressing. Such stress may cause a rolling up of the edge or even slippage of the grip between the dressing and the skin reducing the wear time.
- a border zone of the dressing is free of indentations for providing a sealing preventing e.g. dust and infectious matter from entering an injured part of the skin covered by the dressing.
- the outer periphery of the dressing is preferably bevelled in analogy with the disclosure of U.S. Pat. No. 4,867,748 or U.S. Pat. No. 5,133,821 in order to reduce the risk of “rolling-up” the edge of the dressing reducing the wear-time.
- the edge is preferably bevelled so that the thickness adjacent to the edge does not exceed about 30% of the maximum thickness of the dressing, more preferred not exceeding 25% of the maximum thickness for dressings having a maximum thickness above about 0.7 millimetres, whereas the thickness adjacent to the edge for dressings having a maximum thickness below about 0.5 millimetres preferably does not exceed about 50% of the maximum thickness of the dressing.
- the thickness of the adhesive in the bottom of the pattern of indentations is less than the thickness of the beveled edge which provides for a very flexible area for contacting the protruding part of the body.
- the dressing of the invention may be in one embodiment of the invention in the form of individual dressings as indicated above having a bevelled edge.
- the dressing is in the form of a long strip of dressing having bevelled edges. This embodiment is suitable for tailoring individual dressings by cutting a suitable length of the strip. It is preferred to cut in the bottom of the indentations, as a tailored dressing having relatively thin edges reducing the risk of “rolling-up” of the edge is then obtained.
- Such broader indentations may in accordance with a further embodiment of the invention be applied to individual dressings for enabling a custom cutting of the dressing to the specific site where the dressing is to be used.
- the broader indentations may thus e.g. follow the outer contour of the dressing, enabling a reduction of the size of the dressing without losing the advantage of a predetermined shape such as a “banana”-shape.
- the invention furthermore relates in a further aspect to a method for preparing a dressing comprising a backing layer and a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin and a backing layer, which dressing has a pattern of indentations not being linear and progressing in at least three main directions.
- the method includes providing a supply of dressing having a backing layer and a layer of skin friendly adhesive, placing the dressing in a press together with a mould having a surface corresponding to the desired pattern of indentations and providing a sufficient pressure to provide the desired pattern of indentations.
- the method of the invention may be carried out in a conventional stepwise manner or the mould may have a continuous surface corresponding to the desired pattern of indentations for producing individual dressings or dressings in the form of a continuous long strip of dressings as described above.
- a mould having a continuous surface may e.g. be located on a roller in a manner known per se.
- the invention in a third aspect relates to a method of treating a portion of the anatomical surface of a living being comprising applying a dressing for covering the portion of the anatomical surface of a living being, said dressing being able to adhere to the skin of a living being and said dressing comprising a backing layer and a skin-friendly adhesive, which dressing comprises a pattern of indentations wherein the indentations are in the form of a pattern of connected indentations not being linear and progressing in at least three main directions.
- a dressing of the invention may preferably be sterilised for avoiding the risk of causing infections when applied to skin areas having broken skin.
- the dressing is sterilised, if the dressing is applied to non-broken skin, e.g. on an elbow for preventing and protecting against abrasion which is also considered an aspect of the present invention.
- the skin-friendly adhesive may be any skin-friendly adhesive known per se for production of medical articles, which are to be adhered to human skin, preferably an adhesive comprising hydrocolloids or other moisture absorbing constituents for prolonging the time of use.
- the adhesive may suitably be of the type disclosed in U.S. Pat. Nos. 4,231,369, 4,367,732, 4,867,748, and 5,714,225. Especially preferred are the adhesives disclosed in U.S. Pat. Nos. 4,367,732, and 5,714,225.
- the dressing of the invention may in one embodiment of the invention be in the form of a mono-phase adhesive, i.e. made from one adhesive component or in accordance with another embodiment of the invention be in the form of a two-zone adhesive, e.g. of the general type disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,714,225, i.e. a part of or all of the adhesive areas of the dressing having maximum thickness being constituted by more than one type of adhesive.
- a water impervious layer or film may be of any suitable material known per se for use in the preparation of wound dressings e.g. a foam, a non-woven layer or a polyurethane, polyethylene, polyester or polyamide film.
- a thinner backing layer or film than is normally used when preparing medical dressings, an improved stretchability and adaptability is obtained at the same time as the modulus is reduced.
- the water impervious layer or film is preferably a low-friction flexible polymer film reducing the risk of unwanted stress in the area of the crack impeding the healing of a crack on a very exposed site.
- a suitable material for use as water impervious layer is a film conventionally used as backing layer in the preparation of wound dressings, suitably having a thickness of about 30 microns.
- An especially suitable material for use as a water impervious film is a polyurethane film.
- a preferred low friction film material is disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,643,187.
- a preferred thickness of this film may be below 20 microns, more preferred about 12-18 microns, e.g. about 15 microns, thus resulting in a significant decrease of the modulus, compared to a film that is normally used when preparing medical dressings.
- An improved stretchability and adaptability is obtained at the same time as the modulus is reduced.
- the thickness of the film must be chosen in consideration of the pressure used in the production process in order to avoid a rupture of the film along the indentations when removing the dressing.
- a dressing of the invention is optionally covered in part or fully by one or more release liners or cover films to be removed before or during application.
- a protective cover or release liner may for instance be siliconized paper. It does not need to have the same contour as the dressing, e.g. a number of dressings may be attached to a larger sheet of protective cover.
- the protective cover is not present during the use of the dressing of the invention and is therefore not an essential part of the invention.
- the dressing of the invention may comprise one or more “non touch” grip(s) known per se for applying the dressing to the skin without touching the adhesive layer.
- a non-touch grip is not present after application of the dressing.
- it is suitable to have 2 or 3 or even 4 “non-touch” grips.
- a dressing of the invention with components for treatment or prophylaxis of formation of wounds and/or skin abnormalities, e.g. with emollients or an active constituent e.g. retinoids for treating or preventing formation of psoriasis, eczema, callous skin, corns, insect bites, acne or blisters.
- the dressing of the invention may also contain medicaments such as bacteriostatic or bactericide compounds, e.g. iodine, iodopovidone complexes, chloramine, chlorohexidine, silver salts, zinc or salts thereof, tissue-healing enhancing agents, e.g.
- RGD tripeptides and the like enzymes for cleansing of wounds, e.g. pepsin, trypsin and the like, pain relieving agents, or agents having a cooling effect which is also considered an aspect of the invention.
- agents are preferably enclosed in a part of the adhesive.
- FIG. 1 shows a top view of an embodiment of a dressing 1 of the invention, said dressing being able to adhere to the skin, and/or a wound on a protruding part of the body, said dressing comprising a backing layer 2 and a layer of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin and a backing layer, said dressing having a pattern 3 of indentations progressing in three main directions a, b, and c wherein the indentations are in the form of a pattern of connected indentations in the form of si nuisancedal indentations progressing in at least three main directions.
- the dressing has a border zone 4 being free of indentations.
- FIG. 2 shows a top view of another embodiment of a dressing 10 of the invention, said dressing being able to adhere to the skin, and/or a wound on a protruding part of the body, said dressing comprising a backing layer 11 and a layer 12 of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin and a backing layer, said dressing having a pattern 13 of indentations progressing in three main directions a, b, and c wherein the indentations are in the form of a pattern of connected indentations defining a pattern of adhesive areas 14 having the maximum thickness of the dressing and being of essentially circular shape.
- the dressing has a border zone 15 being free of indentations.
- FIG. 3 shows in an enlarged scale a sectional view of the embodiment of FIG. 2 along the line A-A, and more clearly showing the adhesive areas 14 having the maximum thickness of the dressing and the indentations 13 .
- the rim 16 is shown having a bevel leaving a relatively thin edge 17 .
- the top film layer 11 is shown as well as a release liner 18 .
- FIG. 4 shows a top view of a further and preferred embodiment of a dressing 20 of the invention said dressing being able to adhere to the skin, and/or a wound on a protruding part of the body, said dressing comprising a backing layer 21 and a layer of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin and a backing layer, said dressing having a pattern 22 of indentations wherein the indentations are in the form of a pattern of connected indentations progressing in three main directions a, b, and c defining a pattern of adhesive areas 24 having the maximum thickness of the dressing and being of essentially hexagonal shape.
- the dressing has a border zone 23 being free of indentations.
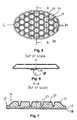
- FIG. 5 shows a top view of a another preferred embodiment of a dressing 30 of the invention said dressing being able to adhere to the skin, and/or a wound on a protruding part of the body, said dressing comprising a backing layer 31 and a layer of a skin-friendly adhesive for adhering to the skin and a backing layer, said dressing having a pattern 32 of indentations wherein the indentations are in the form of a pattern of connected indentations progressing in three main directions, a pattern of adhesive areas 34 having the maximum thickness of the dressing and being of essentially hexagonal shape.
- the dressing has a border zone 33 being free of indentations.
- FIG. 6 shows schematically a section of the embodiment of FIG. 5 along the line C-C showing the release liner and a fold 35 of a non-touch feature allowing gripping and removing the release liner 38 without touching the adhesive surface.
- FIG. 7 shows in an enlarged scale a sectional view of the embodiment of FIGS. 5 and 6 along the line A-A, and more clearly showing the adhesive areas 34 having the maximum thickness of the dressing and the indentations 33 .
- the indentations are wider at the top end and narrower at the bottom end.
- the rim is shown having a bevel 36 leaving a relatively thin edge 37 .
- the top film layer 31 is shown as well as a release liner 38 . Between the release-liner 38 and the adhesive 34 the fold 35 is seen.
- FIG. 8 shows in an enlarged scale a sectional view along the line B-B of the embodiment of FIG. 5 showing an adhesive areas 34 and two indentations 33
- FIG. 9 shows in a further enlarged scale a detail of the indentation area marked C in FIG. 8 showing and indentation 33 between two adhesive areas 34 and the release liner 38 and more clearly the thickness 39 of the dressing at the bottom of the indentations.
- Dressings of the invention were made from blanks comprising a backing layer and a layer of skin-friendly adhesive as disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 4,367,732 using a press and using a mould made from aluminium and having a surface corresponding to the desired pattern of indentations.
- the width of the indentations was about 1 millimetre and the transverse measurement of the areas between the indentations was about 5 millimetres.
- the mould was then suitably closed using a pressure of up to 10-40 metric tons at a temperature of about 90-110° C. for 1-3 seconds. Controls were prepared using identical blanks but only impressing a bevelled edge.
- dressings of the invention were tested on a volunteer for covering an elbow and compared with a corresponding dressing without indentations.
- the dressing of the invention showed a much longer wearing time of 10-12 days as opposed to about 4 days for the control.
- the dressings were of the embodiment as shown in FIG. 4 and were tested on healthy volunteers in a screening test.
- the dressings according to this invention showed an extended wear time when applied to the elbow or the knee as compared to the controls.
- the wear time of the dressings of the invention (A) was found to be clearly longer than the wear time of the controls (B).
- the results are summarized in the below Table 1 stating the percentage of dressings still being in service.
- a dressing of the invention provides prolonged wear time and a substantial better feeling for the user when the dressing is applied, which is believed to be ascribed to the great flexibility of the dressing allowing the dressing to follow all the movements of the user perfectly.
- the applying of the dressing according to the invention on the parts of the body mentioned above is easier compared with a dressing according to the prior because of the flexing feature of the dressing.
- Dressings corresponding to the dressing of the invention tested in Example 1 but having the indentations at the adhesive surface for contacting the skin instead of in the surface covered by the backing layer were prepared.
- the dressings were tested on two volunteers for covering the bend (cubital area) of an elbow and both test persons reported that the feeling was utmost uncomfortable due to pinching effects.
- Dressings according to the invention as tested in Example 1 were tested on volunteers on the palm of the hand and compared to controls as in example 1.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
- Adhesive Tapes (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DKPA200201824 | 2002-11-26 | ||
| DK200201824 | 2002-11-26 | ||
| DKPA200201824 | 2002-11-26 | ||
| PCT/DK2003/000806 WO2004047695A1 (en) | 2002-11-26 | 2003-11-25 | A dressing |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20060064049A1 US20060064049A1 (en) | 2006-03-23 |
| US8080703B2 true US8080703B2 (en) | 2011-12-20 |
Family
ID=32337942
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/536,422 Expired - Lifetime US8080703B2 (en) | 2002-11-26 | 2003-11-25 | Dressing |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8080703B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1565137B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP4891547B2 (de) |
| AU (1) | AU2003281987A1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2537299T3 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2004047695A1 (de) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100324511A1 (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2010-12-23 | Hollister Incorporated | Ostomy faceplate having moldable adhesive wafer with diminishing surface undulations |
| US20110034849A1 (en) * | 2009-08-06 | 2011-02-10 | Andrell Cooks | Contoured eye patch |
| USD686735S1 (en) | 2010-05-28 | 2013-07-23 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc | Medical patch |
| USD686734S1 (en) * | 2010-01-28 | 2013-07-23 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | Medical patch |
| USD698928S1 (en) | 2010-11-05 | 2014-02-04 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | Medical patch |
| US9314378B2 (en) | 2009-10-14 | 2016-04-19 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | Method and apparatus for manufacturing adhesive patch |
| US9358256B2 (en) | 2013-07-11 | 2016-06-07 | Links Medical Products, Inc. | Gap-patterned foam dressing and method of making same |
| US20160270965A1 (en) * | 2012-11-15 | 2016-09-22 | Colopast A?S | A wound dressing |
| US11690933B2 (en) | 2016-06-10 | 2023-07-04 | Sentient Foams Limited | Absorbent aliphatic polyurethane foam product |
| US20240382348A1 (en) * | 2023-05-18 | 2024-11-21 | Catherine Ross STOLL | Hydrocolloid heel patch and methods |
| US12472089B2 (en) | 2020-12-23 | 2025-11-18 | Coloplast A/S | Ostomy product adhesive securing member |
Families Citing this family (44)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8741335B2 (en) | 2002-06-14 | 2014-06-03 | Hemcon Medical Technologies, Inc. | Hemostatic compositions, assemblies, systems, and methods employing particulate hemostatic agents formed from hydrophilic polymer foam such as Chitosan |
| EP1401352B1 (de) | 2001-06-14 | 2012-03-21 | Kenton W. Gregory | Verfahren zur herstellung von chitosan-wundauflagen |
| US7083818B2 (en) * | 2002-08-16 | 2006-08-01 | Apio, Inc. | Party tray |
| US7884258B2 (en) * | 2004-04-13 | 2011-02-08 | Boehringer Technologies, L.P. | Wound contact device |
| US7951124B2 (en) * | 2004-04-13 | 2011-05-31 | Boehringer Technologies, Lp | Growth stimulating wound dressing with improved contact surfaces |
| MX2007007744A (es) * | 2004-12-23 | 2007-08-17 | Hemcon Inc | Barreras, sistemas, y metodos antimicrobianos formados a partir de estructuras polimericas hidrofilicas tales como quitosana. |
| SE0500061L (sv) | 2005-01-11 | 2006-07-12 | Moelnlycke Health Care Ab | Tätande filmförband |
| US20080275327A1 (en) * | 2005-03-09 | 2008-11-06 | Susanne Holm Faarbaek | Three-Dimensional Adhesive Device Having a Microelectronic System Embedded Therein |
| US9204957B2 (en) | 2005-03-17 | 2015-12-08 | Hemcon Medical Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for hemorrhage control and or tissue repair |
| US8415523B2 (en) * | 2005-04-16 | 2013-04-09 | Aalnex, Inc. | Secondary wound dressings for securing primary dressings and managing fluid from wounds, and methods of using same |
| US8067662B2 (en) | 2009-04-01 | 2011-11-29 | Aalnex, Inc. | Systems and methods for wound protection and exudate management |
| US7745683B2 (en) * | 2005-04-16 | 2010-06-29 | Aalnex, Inc. | Deformable and conformable wound protecting apparatus and its method of application |
| JP4510084B2 (ja) * | 2005-05-10 | 2010-07-21 | ピアック株式会社 | さかむけ用粘着保護部材およびその製造方法 |
| GB2425961B (en) * | 2005-05-12 | 2009-11-11 | Lrc Products | Improved bunion cushion |
| FR2890854B1 (fr) * | 2005-09-22 | 2008-09-12 | Thuasne Soc Par Actions Simpli | Dispositif, bande et vetement de traitement d'affections tissulaires cutanees et sous-cutanees et de reparation sportive, et leur procede de fabrication. |
| JP2009509574A (ja) * | 2005-09-26 | 2009-03-12 | コロプラスト アクティーゼルスカブ | 被覆材 |
| US8586818B2 (en) | 2005-12-15 | 2013-11-19 | Aalnex, Inc. | Wound shield |
| US7863495B2 (en) | 2006-01-12 | 2011-01-04 | Aalnex, Inc. | Dressing substrate |
| US7601129B2 (en) * | 2005-12-15 | 2009-10-13 | Aalnex, Inc. | Wound shield and warming apparatus and method |
| US7622629B2 (en) | 2005-12-15 | 2009-11-24 | Aalnex, Inc. | Wound shield for exudate management |
| US7816577B2 (en) | 2006-02-13 | 2010-10-19 | Aalnex, Inc. | Wound shield |
| CA2653175A1 (en) | 2006-05-23 | 2007-12-06 | Providence Health System-Oregon D/B/A Providence St. Vincent Medical Cen Ter | Systems and methods for introducing and applying a bandage structure within a body lumen or hollow body organ |
| SE0601536L (sv) * | 2006-07-11 | 2008-01-12 | Moelnlycke Health Care Ab | Spolförband |
| GB0624658D0 (en) | 2006-12-11 | 2007-01-17 | Medical Device Innovations Ltd | Electrosurgical ablation apparatus and a method of ablating biological tissue |
| GB0710846D0 (en) * | 2007-06-06 | 2007-07-18 | Bristol Myers Squibb Co | A wound dressing |
| EP2240143B1 (de) * | 2008-01-18 | 2014-03-05 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Hydrogele mit verjüngtem rand |
| CN102076364B (zh) | 2008-05-02 | 2014-07-02 | 普罗维登斯医疗卫生系统-俄勒冈州D/B/A普罗维登斯圣文森特医疗中心 | 创伤敷裹装置和方法 |
| EP2278949B1 (de) | 2008-05-30 | 2016-07-06 | KCI Licensing, Inc. | Lineare wundverschlusspolster mit reduziertem druck und entsprechende systeme |
| US8188331B2 (en) * | 2008-05-30 | 2012-05-29 | Kci Licensing, Inc. | See-through, reduced-pressure dressings and systems |
| WO2010036682A2 (en) * | 2008-09-24 | 2010-04-01 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Hydrogels with release element |
| EP2340002B1 (de) | 2008-10-06 | 2015-03-25 | Providence Health System - Oregon | Medizinische schaumvorrichtungen und verfahren |
| WO2010051073A1 (en) | 2008-10-29 | 2010-05-06 | Kci Licensing, Inc. | Reduced-pressure, abdominal treatment systems and methods |
| US8252971B2 (en) * | 2009-07-16 | 2012-08-28 | Aalnex, Inc. | Systems and methods for protecting incisions |
| US8623047B2 (en) | 2010-04-30 | 2014-01-07 | Kci Licensing, Inc. | System and method for sealing an incisional wound |
| US20140142490A1 (en) * | 2011-07-08 | 2014-05-22 | Mölnlycke Health Care Ab | Self-adhesive wound care product |
| EP3508182A1 (de) | 2011-07-14 | 2019-07-10 | Smith & Nephew PLC | Wundverband und verfahren zur behandlung |
| ES2573784T3 (es) | 2011-09-30 | 2016-06-10 | Coloplast A/S | Apósito adhesivo |
| JP6300241B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-02 | 2018-03-28 | ケーシーアイ ライセンシング インコーポレイテッド | 超薄ドレープフィルムと厚みのある接着剤コーティングとを有する医療用ドレープ |
| ES2921990T3 (es) | 2014-09-10 | 2022-09-05 | Bard Inc C R | Apósito protector para un dispositivo médico colocado en la piel |
| EP3448331B1 (de) * | 2016-04-29 | 2025-11-26 | Hollister Incorporated | Stomagürtel |
| GB201609954D0 (en) | 2016-06-07 | 2016-07-20 | Monty Stephanie | A dressing |
| WO2021224698A1 (en) * | 2020-05-05 | 2021-11-11 | Kci Licensing, Inc. | Tissue interface for negative pressure and instillation therapy |
| CN113576757A (zh) * | 2021-09-03 | 2021-11-02 | 军事科学院系统工程研究院卫勤保障技术研究所 | 一种壳聚糖聚合物敷料 |
| CN119074386B (zh) * | 2024-11-06 | 2025-02-25 | 山东百多安医疗器械股份有限公司 | 一种智能化多模态仿生交互式创伤修复装置及其制备方法 |
Citations (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1075939A (en) | 1964-10-28 | 1967-07-19 | Smith & Nephew | Improvements in and relating to adhesive surgical and other tapes, plasters, bandages, dressings and the like |
| US3835992A (en) * | 1972-10-24 | 1974-09-17 | J Adams | Bandage dispensing package |
| US4231369A (en) | 1977-05-24 | 1980-11-04 | Coloplast International A/S | Sealing material for ostomy devices |
| US4260443A (en) * | 1978-10-20 | 1981-04-07 | Grain Processing Corporation | Laminated absorbent process |
| US4367732A (en) | 1980-12-05 | 1983-01-11 | Coloplast A/S | Skin barrier |
| EP0256893A2 (de) | 1986-08-20 | 1988-02-24 | SMITH & NEPHEW plc | Wundverband, seine Herstellung und Verwendung |
| US4798604A (en) | 1985-08-24 | 1989-01-17 | Smith And Nephew Associated Companies P.L.C. | Contoured film |
| US4867748A (en) | 1986-10-17 | 1989-09-19 | Coloplast A/S | Dressing with hydrocolloid |
| WO1990010424A1 (en) | 1989-03-16 | 1990-09-20 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Absorbent devices and precursors therefor |
| EP0409587A1 (de) | 1989-07-19 | 1991-01-23 | JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER PRODUCTS, INC. | Filmpflaster mit niedriger Reibung |
| WO1991010415A2 (en) | 1990-01-10 | 1991-07-25 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Coverstock |
| US5133821A (en) * | 1990-11-19 | 1992-07-28 | Jensen Ole R | Method for contouring hydrocolloid wound dressings |
| CA2060702A1 (en) | 1991-02-06 | 1992-08-07 | Tokyo Eizai Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Dressing |
| WO1993000056A1 (en) | 1991-06-24 | 1993-01-07 | Coloplast A/S | A bandage or dressing for covering wounds |
| GB2276087A (en) | 1993-03-08 | 1994-09-21 | Ultra Lab Ltd | Wound dressings |
| US5356372A (en) | 1993-12-01 | 1994-10-18 | Ludlow Corporation | Occlusive pressure-reducing wound dressing |
| US5505720A (en) * | 1991-06-12 | 1996-04-09 | Mcneil-Ppc, Inc. | Melt blown menstrual pad for application to the body |
| EP0768071A1 (de) | 1995-10-10 | 1997-04-16 | JENSEN, Ole Roger | Wundverband mit einer Linienvertiefungen aufweisenden, hydrokolloidenthaltenden und mit einem Film versehenen Klebstoffschicht |
| US5633007A (en) * | 1993-07-21 | 1997-05-27 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Surgical dressing |
| US5643187A (en) | 1992-01-17 | 1997-07-01 | Coloplast A/S | Dressing |
| US5714225A (en) | 1993-01-15 | 1998-02-03 | Coloplast A/S | Skin plate product |
| US5782787A (en) * | 1993-02-15 | 1998-07-21 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Moisture-responsive absorbent wound dressing |
| US5902260A (en) * | 1997-03-14 | 1999-05-11 | Hollister Incorporated | Thin film wound dressing with stretchable foraminous backing layer |
| WO1999036017A1 (en) | 1998-01-15 | 1999-07-22 | Coloplast A/S | A dressing |
| JP2002035196A (ja) | 2000-07-21 | 2002-02-05 | Kineshio:Kk | 身体接着布 |
| US6713659B2 (en) * | 1998-06-09 | 2004-03-30 | Beiersdorf Ag | Self-adhesive bandage |
| US6969548B1 (en) * | 1999-08-30 | 2005-11-29 | Goldfine Andrew A | Impact absorbing composite |
-
2003
- 2003-11-25 ES ES03773593.3T patent/ES2537299T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-11-25 EP EP03773593.3A patent/EP1565137B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-11-25 WO PCT/DK2003/000806 patent/WO2004047695A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2003-11-25 JP JP2004554244A patent/JP4891547B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-11-25 US US10/536,422 patent/US8080703B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-11-25 AU AU2003281987A patent/AU2003281987A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1075939A (en) | 1964-10-28 | 1967-07-19 | Smith & Nephew | Improvements in and relating to adhesive surgical and other tapes, plasters, bandages, dressings and the like |
| US3835992A (en) * | 1972-10-24 | 1974-09-17 | J Adams | Bandage dispensing package |
| US4231369A (en) | 1977-05-24 | 1980-11-04 | Coloplast International A/S | Sealing material for ostomy devices |
| US4260443A (en) * | 1978-10-20 | 1981-04-07 | Grain Processing Corporation | Laminated absorbent process |
| US4367732A (en) | 1980-12-05 | 1983-01-11 | Coloplast A/S | Skin barrier |
| US4798604A (en) | 1985-08-24 | 1989-01-17 | Smith And Nephew Associated Companies P.L.C. | Contoured film |
| US4990144A (en) | 1986-08-20 | 1991-02-05 | Smith And Nephew Associated Companies Plc | Medicating impressed film wound dressing |
| EP0256893A2 (de) | 1986-08-20 | 1988-02-24 | SMITH & NEPHEW plc | Wundverband, seine Herstellung und Verwendung |
| US4867748A (en) | 1986-10-17 | 1989-09-19 | Coloplast A/S | Dressing with hydrocolloid |
| WO1990010424A1 (en) | 1989-03-16 | 1990-09-20 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Absorbent devices and precursors therefor |
| US5328450A (en) * | 1989-03-16 | 1994-07-12 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Absorbent devices and precursors therefor |
| EP0409587A1 (de) | 1989-07-19 | 1991-01-23 | JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER PRODUCTS, INC. | Filmpflaster mit niedriger Reibung |
| US5012801A (en) | 1989-07-19 | 1991-05-07 | Johnson & Johnson Consumer Products, Inc. | Low friction film dressing |
| WO1991010415A2 (en) | 1990-01-10 | 1991-07-25 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Coverstock |
| US5133821A (en) * | 1990-11-19 | 1992-07-28 | Jensen Ole R | Method for contouring hydrocolloid wound dressings |
| EP0573708A1 (de) | 1990-11-19 | 1993-12-15 | Hollister Incorporated | Formgebungsmethode für Hydrokolloidverbände |
| CA2060702A1 (en) | 1991-02-06 | 1992-08-07 | Tokyo Eizai Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Dressing |
| DE4203130A1 (de) | 1991-02-06 | 1992-08-13 | Tokyo Eizai Lab | Haftverbandstoff |
| US5505720A (en) * | 1991-06-12 | 1996-04-09 | Mcneil-Ppc, Inc. | Melt blown menstrual pad for application to the body |
| WO1993000056A1 (en) | 1991-06-24 | 1993-01-07 | Coloplast A/S | A bandage or dressing for covering wounds |
| US5486158A (en) * | 1991-06-24 | 1996-01-23 | Coloplast A/S | Grooved hydrocolloidal dressing |
| US5643187A (en) | 1992-01-17 | 1997-07-01 | Coloplast A/S | Dressing |
| US5714225A (en) | 1993-01-15 | 1998-02-03 | Coloplast A/S | Skin plate product |
| US5782787A (en) * | 1993-02-15 | 1998-07-21 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Moisture-responsive absorbent wound dressing |
| GB2276087A (en) | 1993-03-08 | 1994-09-21 | Ultra Lab Ltd | Wound dressings |
| US5633007A (en) * | 1993-07-21 | 1997-05-27 | Smith & Nephew Plc | Surgical dressing |
| US5356372A (en) | 1993-12-01 | 1994-10-18 | Ludlow Corporation | Occlusive pressure-reducing wound dressing |
| US5704905A (en) * | 1995-10-10 | 1998-01-06 | Jensen; Ole R. | Wound dressing having film-backed hydrocolloid-containing adhesive layer with linear depressions |
| EP0768071A1 (de) | 1995-10-10 | 1997-04-16 | JENSEN, Ole Roger | Wundverband mit einer Linienvertiefungen aufweisenden, hydrokolloidenthaltenden und mit einem Film versehenen Klebstoffschicht |
| US5902260A (en) * | 1997-03-14 | 1999-05-11 | Hollister Incorporated | Thin film wound dressing with stretchable foraminous backing layer |
| WO1999036017A1 (en) | 1998-01-15 | 1999-07-22 | Coloplast A/S | A dressing |
| US6713659B2 (en) * | 1998-06-09 | 2004-03-30 | Beiersdorf Ag | Self-adhesive bandage |
| US6969548B1 (en) * | 1999-08-30 | 2005-11-29 | Goldfine Andrew A | Impact absorbing composite |
| JP2002035196A (ja) | 2000-07-21 | 2002-02-05 | Kineshio:Kk | 身体接着布 |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8211073B2 (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2012-07-03 | Hollister Incorporated | Ostomy faceplate having moldable adhesive wafer with diminishing surface undulations |
| US20100324511A1 (en) * | 2009-06-17 | 2010-12-23 | Hollister Incorporated | Ostomy faceplate having moldable adhesive wafer with diminishing surface undulations |
| US20110034849A1 (en) * | 2009-08-06 | 2011-02-10 | Andrell Cooks | Contoured eye patch |
| US9314378B2 (en) | 2009-10-14 | 2016-04-19 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | Method and apparatus for manufacturing adhesive patch |
| USD686734S1 (en) * | 2010-01-28 | 2013-07-23 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | Medical patch |
| USD686735S1 (en) | 2010-05-28 | 2013-07-23 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc | Medical patch |
| USD698928S1 (en) | 2010-11-05 | 2014-02-04 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | Medical patch |
| US20160270965A1 (en) * | 2012-11-15 | 2016-09-22 | Colopast A?S | A wound dressing |
| US9913759B2 (en) * | 2012-11-15 | 2018-03-13 | Coloplast A/S | Wound dressing |
| RU2651125C2 (ru) * | 2012-11-15 | 2018-04-18 | Колопласт А/С | Повязка на рану |
| US9358256B2 (en) | 2013-07-11 | 2016-06-07 | Links Medical Products, Inc. | Gap-patterned foam dressing and method of making same |
| US11690933B2 (en) | 2016-06-10 | 2023-07-04 | Sentient Foams Limited | Absorbent aliphatic polyurethane foam product |
| US12472089B2 (en) | 2020-12-23 | 2025-11-18 | Coloplast A/S | Ostomy product adhesive securing member |
| US20240382348A1 (en) * | 2023-05-18 | 2024-11-21 | Catherine Ross STOLL | Hydrocolloid heel patch and methods |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006507065A (ja) | 2006-03-02 |
| US20060064049A1 (en) | 2006-03-23 |
| JP4891547B2 (ja) | 2012-03-07 |
| WO2004047695A1 (en) | 2004-06-10 |
| ES2537299T3 (es) | 2015-06-05 |
| EP1565137B1 (de) | 2015-02-25 |
| AU2003281987A1 (en) | 2004-06-18 |
| EP1565137A1 (de) | 2005-08-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8080703B2 (en) | Dressing | |
| AU2020201604B2 (en) | Adhesive film bandage for medical compression | |
| AU755828B2 (en) | A dressing | |
| JP3100149B2 (ja) | 低摩擦フイルム包帯 | |
| JP2010508061A (ja) | 高い柔軟性を有する縁部と硬化性縁部層とを有するサージカルドレープ | |
| US12336887B2 (en) | Medical dressing | |
| JPH0838543A (ja) | 適合性絆創膏 | |
| GB2451877A (en) | Adhesive bandage | |
| HK1032192B (en) | A dressing | |
| HK1020857A (en) | A permanently deformable dressing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: COLOPLAST A/S, DENMARK Free format text: ASSIGNMENT OF ASSIGNORS INTEREST;ASSIGNOR:MARCUSSEN, JAN;REEL/FRAME:017123/0990 Effective date: 20050503 |
|
| STCF | Information on status: patent grant |
Free format text: PATENTED CASE |
|
| FPAY | Fee payment |
Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment |
Free format text: PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 8TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1552); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment |
Free format text: PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 12TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1553); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment: 12 |