JP6717242B2 - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6717242B2 JP6717242B2 JP2017047334A JP2017047334A JP6717242B2 JP 6717242 B2 JP6717242 B2 JP 6717242B2 JP 2017047334 A JP2017047334 A JP 2017047334A JP 2017047334 A JP2017047334 A JP 2017047334A JP 6717242 B2 JP6717242 B2 JP 6717242B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- type semiconductor
- semiconductor layer
- type
- region
- trench
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 516
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims description 220
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 240
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 59
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 58
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 49
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 37
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 37
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 28
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 26
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 24
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 23
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 21
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 20
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 20
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 18
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 17
- JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium nitride Chemical compound [Ga]#N JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 15
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 12
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 10
- 229910002601 GaN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 7
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 6
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000000231 atomic layer deposition Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000001004 secondary ion mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- PIGFYZPCRLYGLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Aluminum nitride Chemical compound [Al]#N PIGFYZPCRLYGLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RNQKDQAVIXDKAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminum gallium Chemical compound [Al].[Ga] RNQKDQAVIXDKAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium atom Chemical compound [In] APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N AsGa Chemical compound [As]#[Ga] JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910004205 SiNX Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium Chemical compound [Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AUCDRFABNLOFRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N alumane;indium Chemical compound [AlH3].[In] AUCDRFABNLOFRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052790 beryllium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ATBAMAFKBVZNFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N beryllium atom Chemical compound [Be] ATBAMAFKBVZNFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000005465 channeling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002109 crystal growth method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000994 depressogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002542 deteriorative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- AJNVQOSZGJRYEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N digallium;oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Ga+3].[Ga+3] AJNVQOSZGJRYEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010292 electrical insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- -1 for example Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052735 hafnium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium atom Chemical compound [Hf] VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CJNBYAVZURUTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium(iv) oxide Chemical compound O=[Hf]=O CJNBYAVZURUTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);zirconium(4+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Zr+4] RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000005268 plasma chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tellanylidenegermanium Chemical compound [Te]=[Ge] JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001928 zirconium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/41741—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices for vertical or pseudo-vertical devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/26—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/263—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/265—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation
- H01L21/2654—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation in AIIIBV compounds
- H01L21/26546—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation in AIIIBV compounds of electrically active species
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
- H01L29/0623—Buried supplementary region, e.g. buried guard ring
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0684—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions
- H01L29/0692—Surface layout
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/0852—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate of DMOS transistors
- H01L29/0856—Source regions
- H01L29/086—Impurity concentration or distribution
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/0852—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate of DMOS transistors
- H01L29/0856—Source regions
- H01L29/0865—Disposition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1095—Body region, i.e. base region, of DMOS transistors or IGBTs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66674—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/66712—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/66734—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with a step of recessing the gate electrode, e.g. to form a trench gate electrode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7813—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with trench gate electrode, e.g. UMOS transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/20—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only AIIIBV compounds
- H01L29/2003—Nitride compounds
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Description
本発明の第1の形態は、トレンチゲート構造を有する半導体装置であって、n型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体層と、前記第1のn型半導体層の上に形成されており、p型不純物を含むp型半導体層と、前記p型半導体層を貫通して、前記第1のn型半導体層に至るまで落ち込んだトレンチと、前記トレンチの表面を覆い、絶縁体により形成された絶縁膜と、前記絶縁膜を介して前記トレンチに形成されたゲート電極と、前記p型半導体層の上に第2のn型半導体層があり、前記第2のn型半導体層の上に形成されたソース電極と、前記第1のn型半導体層に対して、前記p型半導体層とは反対側に形成されたドレイン電極と、を備え、前記第1のn型半導体層は、p型不純物をn型不純物よりも多く含むp型不純物含有領域を備え、前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記p型半導体層および前記トレンチの底面外周と接し、前記第1のn型半導体層と前記p型半導体層との積層方向から見たときに、前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記ソース電極の少なくとも一部と重ならない位置にあり、かつ、前記トレンチの底面外周と重なる位置にあり、前記積層方向から見たときに、前記p型不純物含有領域と重なる位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度は、前記p型不純物含有領域と重ならない位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度よりも小さい、半導体装置である。
また、本発明の第2の形態は、トレンチゲート構造を有する半導体装置であって、n型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体層と、前記第1のn型半導体層の上に形成されており、p型不純物を含むp型半導体層と、前記p型半導体層を貫通して、前記第1のn型半導体層に至るまで落ち込んだトレンチと、前記トレンチの表面を覆い、絶縁体により形成された絶縁膜と、前記絶縁膜を介して前記トレンチに形成されたゲート電極と、前記p型半導体層の上に第2のn型半導体層があり、前記第2のn型半導体層の上に形成されたソース電極と、前記第1のn型半導体層に対して、前記p型半導体層とは反対側に形成されたドレイン電極と、を備え、前記第1のn型半導体層は、p型不純物をn型不純物よりも多く含むp型不純物含有領域を備え、前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記p型半導体層および前記トレンチの底面外周と接し、前記第1のn型半導体層と前記p型半導体層との積層方向から見たときに、前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記ソース電極の少なくとも一部と重ならない位置にあり、かつ、前記トレンチの底面外周と重なる位置にあり、前記第2のn型半導体層は、前記p型半導体層に備えられたn型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体領域であり、前記積層方向から見たときに、前記第1のn型半導体領域は、前記トレンチの底面外周及び前記p型不純物含有領域と重なり、前記積層方向から見たときに、前記トレンチの底面外周と重ならず、前記第1のn型半導体領域よりもn型不純物濃度が小さい第2のn型半導体領域を備え、前記積層方向から見たときに、前記第1のn型半導体領域と重なる位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度は、前記第2のn型半導体領域と重なる位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度よりも小さい、半導体装置である。本発明は以下の形態としても実現できる。
A−1.半導体装置の構成
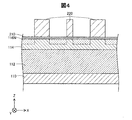
図1は、第1実施形態における半導体装置100の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。半導体装置100は、窒化ガリウム(GaN)を用いて形成されたGaN系の半導体装置である。半導体装置100は、トレンチゲート構造を有する。本明細書において、「トレンチゲート構造」とは、半導体層にトレンチを形成し、その中にゲート電極の少なくとも一部が埋め込まれている構造を言う。本実施形態では、半導体装置100は、縦型トレンチMISFET(Metal-Insulator-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor)である。本実施形態では、半導体装置100は、電力制御に用いられ、パワーデバイスとも呼ばれる。
第1実施形態の半導体装置100において、n型半導体層112とp型半導体層114との積層方向(Z軸方向)から見たとき、p型不純物含有領域118は、トレンチ122の底面BS2外周と重なる位置にある。このため、第1実施形態の半導体装置100によれば、トレンチ122の底面外周付近に電界が集中することを抑制できることにより、半導体装置100の耐圧を向上させることができる。
図3は、第1実施形態における半導体装置100の製造方法を示す工程図である。まず、製造者は、基板110を準備する(工程P100)。本実施形態では、基板110は、窒化ガリウム(GaN)から形成されている。
〈イオン注入条件〉
・1回目
加速電圧:50keV
ドーズ量:5.0×1014cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
・2回目
加速電圧:100keV
ドーズ量:5.0×1014cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
<熱処理の条件>
雰囲気ガス:窒素
加熱温度:1150℃
加熱時間:4分
A−4−1.第1評価試験
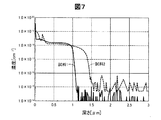
第1評価試験では、n型不純物のイオン注入とp型不純物含有領域118の形成との関係を評価した。第1評価試験には、以下の試料を用いた。具体的には、試験者は、まず、第1実施形態と同じ方法により、基板110を準備して(工程P105)、結晶成長を行った(工程P110)。その後、試験者は、p型半導体層114の上に、マグネシウム(Mg)濃度を1×1019cm−3とし、厚みを0.1μmとしたp+型半導体層を形成した。そして、試験者は、第1実施形態と同じ方法により、イオン注入(工程P120)及び熱処理(工程P130)を行った。
第2評価試験では、イオン注入(工程P120(図3))におけるケイ素(Si)のドーズ量を変化させることによるp型不純物含有領域118の深さへの影響を評価した。第2評価試験において、試験者は、互いにイオン注入条件が異なる試料3及び試料4を用意した。具体的には、試験者は、まず、窒化ガリウム(GaN)基板(ケイ素濃度:1.0×1018cm−3)に、n型窒化ガリウム層(ケイ素濃度:1.0×1016cm−3、厚み:1μm)と、p型窒化ガリウム層(マグネシウム濃度:4.0×1018cm−3、厚み:1μm)とをこの順に結晶成長させた。その後、試験者は、イオン注入条件以外は、第1実施形態の製造法と同じ方法により活性化アニール(工程P130)まで行うことにより試料を作製した。ここで、試料3,4におけるイオン注入条件を以下に示す。
〈試料3のイオン注入条件〉
・1回目
加速電圧:50keV
ドーズ量:5.0×1014cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
・2回目
加速電圧:100keV
ドーズ量:5.0×1014cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
〈試料4のイオン注入条件〉
・1回目
加速電圧:50keV
ドーズ量:1.0×1015cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
・2回目
加速電圧:100keV
ドーズ量:1.0×1015cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
第3評価試験では、イオン注入(工程P120(図3))後の活性化アニール(工程P130)の有無によるp型不純物含有領域118への影響を評価した。第3評価試験において、試験者は、試料5及び試料6を用意した。試験者は、イオン注入条件及び活性化アニールの有無以外は、第2評価試験と同じ方法により試料の作製を行った。試料5は、活性化アニールを行わなかった試料であり、試料6は、活性化アニールを行なった試料である。ここで、試料5,6におけるイオン注入条件を以下に示す。
〈イオン注入条件〉
加速電圧:50keV
ドーズ量:5×1014cm−2
注入角度:9°
温度:25℃
第4評価試験は、トレンチ122とp型不純物含有領域118との位置関係による電界強度及びオン抵抗への影響を評価した。第4評価試験において、試験者は、第1実施形態と同じ方法で作製した試料7と、トレンチ122の深さDtを変化させた試料8とを作製した。なお、試料7,8については、それぞれWdiを0.0μm、0.2μm、0.4μm、0.6μm、0.8μm、1.0μm、1.4μmのものについて作製した。
<試料7の条件>
トレンチ122の深さDt:1.0μm(Ddi:0.3μm)
p型不純物含有領域118トレンチ122と重なる幅をWdi:0.0μm〜1.4μm
トレンチ122の幅をWt:2.0μm
<試料8の条件>
トレンチ122の深さDt:1.2μm(Ddi:0.1μm)
p型不純物含有領域118トレンチ122と重なる幅をWdi:0.0μm〜1.4μm
トレンチ122の幅をWt:2.0μm
図12は、第2実施形態における半導体装置200の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。第2実施形態の半導体装置200は、第1実施形態の半導体装置100と比較して、(i)半導体装置100のn型半導体領域116の代わりに第1のn型半導体領域116A及び第2のn型半導体領域116Bを備え、(ii)半導体装置100のp型不純物含有領域118の代わりに第1のp型不純物含有領域118A及び第2のp型不純物含有領域118Bを備えている点が異なるが、それ以外は同じである。
図13は、第3実施形態における半導体装置300の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。第3実施形態の半導体装置300は、第2実施形態の半導体装置200と比較して、(i)半導体装置200の第1のn型半導体領域116A及び第2のn型半導体領域116Bの代わりにn型半導体領域116C及びn型半導体領域116Dを備え、(ii)半導体装置200の第1のp型不純物含有領域118A及び第2のp型不純物含有領域118Bの代わりにp型不純物含有領域118C及びp型不純物含有領域118Dを備えている点が異なるが、それ以外は同じである。
図14は、第4実施形態における半導体装置400の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。第4実施形態の半導体装置400は、第3実施形態の半導体装置300と比較して、(i)ソース電極141とp型半導体層114とが接する部分にあるn型半導体領域116Cの変わりにn型半導体領域116Eを備え、(ii)n型半導体領域116Eの下方に、p型不純物含有領域118Cではなくp型不純物含有領域118Eが形成されている点が異なるが、それ以外は同じである。第4実施形態の半導体装置400においても、第1実施形態の半導体装置100と同様に、半導体装置の耐圧を向上させつつ、ドレイン・ソース間の容量が高くなることを抑制できる。また、n型半導体領域116Eのn型不純物濃度をn型半導体領域116Cよりも高くすることにより、n型半導体領域116Eとソース電極141との接触抵抗を低くできるため、オン抵抗を低くできる。
本発明は、上述の実施形態や実施例、変形例に限られるものではなく、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の構成で実現することができる。例えば、発明の概要の欄に記載した各形態中の技術的特徴に対応する実施形態、実施例、変形例中の技術的特徴は、上述の課題の一部または全部を解決するために、あるいは、上述の効果の一部または全部を達成するために、適宜、差し替えや、組み合わせを行うことが可能である。また、その技術的特徴が本明細書中に必須なものとして説明されていなければ、適宜、削除することが可能である。
110…基板
112…n型半導体層
114…p型半導体層
115…p型半導体層
116…n型半導体領域
116A…第1のn型半導体領域
116B…第2のn型半導体領域
116C…n型半導体領域
116D…n型半導体領域
116N…イオン注入領域
118…p型不純物含有領域
118A…第1のp型不純物含有領域
118B…第2のp型不純物含有領域
118C…p型不純物含有領域
118D…p型不純物含有領域
118E…p型不純物含有領域
121…コンタクトホール
122…トレンチ
130…絶縁膜
141…ソース電極
142…ゲート電極
143…ドレイン電極
144…ボディ電極
200…半導体装置
210…膜
220…マスク
240…キャップ膜
300…半導体装置
400…半導体装置
BS1…底面
BS2…底面
Claims (7)
- トレンチゲート構造を有する半導体装置であって、
n型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体層と、
前記第1のn型半導体層の上に形成されており、p型不純物を含むp型半導体層と、
前記p型半導体層を貫通して、前記第1のn型半導体層に至るまで落ち込んだトレンチと、
前記トレンチの表面を覆い、絶縁体により形成された絶縁膜と、
前記絶縁膜を介して前記トレンチに形成されたゲート電極と、
前記p型半導体層の上に第2のn型半導体層があり、前記第2のn型半導体層の上に形成されたソース電極と、
前記第1のn型半導体層に対して、前記p型半導体層とは反対側に形成されたドレイン電極と、を備え、
前記第1のn型半導体層は、p型不純物をn型不純物よりも多く含むp型不純物含有領域を備え、
前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記p型半導体層および前記トレンチの底面外周と接し、
前記第1のn型半導体層と前記p型半導体層との積層方向から見たときに、
前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記ソース電極の少なくとも一部と重ならない位置にあり、かつ、前記トレンチの底面外周と重なる位置にあり、
前記積層方向から見たときに、
前記p型不純物含有領域と重なる位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度は、前記p型不純物含有領域と重ならない位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度よりも小さい、
半導体装置。 - 請求項1に記載の半導体装置であって、
前記積層方向から見たときに、前記p型不純物含有領域が、前記トレンチと重なる幅をWdiとし、前記積層方向から見たときの前記トレンチの幅をWtとしたとき、
Wdiは、前記絶縁膜の厚みの2倍以上であって、Wtの2/3倍未満である、半導体装置。 - 請求項1または請求項2に記載の半導体装置であって、
前記p型半導体層のp型不純物濃度は、前記ソース電極と接する面のほうが、前記第1のn型半導体層と接する面よりも高い、半導体装置。 - 請求項1から請求項3のいずれか1項に記載の半導体装置であって、
前記第2のn型半導体層は、前記p型半導体層に備えられたn型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体領域であり、
前記積層方向から見たときに、
前記第1のn型半導体領域は、前記トレンチの底面外周及び前記p型不純物含有領域と重なる、半導体装置。 - 請求項4に記載の半導体装置であって、さらに、
前記積層方向から見たときに、前記トレンチの底面外周と重ならず、前記第1のn型半導体領域よりもn型不純物濃度が小さい第2のn型半導体領域を備える、半導体装置。 - 請求項5に記載の半導体装置であって、
前記積層方向の深さは、前記第1のn型半導体領域のほうが、前記第2のn型半導体領域よりも深い、半導体装置。 - トレンチゲート構造を有する半導体装置であって、
n型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体層と、
前記第1のn型半導体層の上に形成されており、p型不純物を含むp型半導体層と、
前記p型半導体層を貫通して、前記第1のn型半導体層に至るまで落ち込んだトレンチと、
前記トレンチの表面を覆い、絶縁体により形成された絶縁膜と、
前記絶縁膜を介して前記トレンチに形成されたゲート電極と、
前記p型半導体層の上に第2のn型半導体層があり、前記第2のn型半導体層の上に形成されたソース電極と、
前記第1のn型半導体層に対して、前記p型半導体層とは反対側に形成されたドレイン電極と、を備え、
前記第1のn型半導体層は、p型不純物をn型不純物よりも多く含むp型不純物含有領域を備え、
前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記p型半導体層および前記トレンチの底面外周と接し、
前記第1のn型半導体層と前記p型半導体層との積層方向から見たときに、
前記p型不純物含有領域は、前記ソース電極の少なくとも一部と重ならない位置にあり、かつ、前記トレンチの底面外周と重なる位置にあり、
前記第2のn型半導体層は、前記p型半導体層に備えられたn型不純物を含む第1のn型半導体領域であり、
前記積層方向から見たときに、前記第1のn型半導体領域は、前記トレンチの底面外周及び前記p型不純物含有領域と重なり、
前記積層方向から見たときに、前記トレンチの底面外周と重ならず、前記第1のn型半導体領域よりもn型不純物濃度が小さい第2のn型半導体領域を備え、
前記積層方向から見たときに、
前記第1のn型半導体領域と重なる位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度は、前記第2のn型半導体領域と重なる位置の前記p型半導体層における前記p型不純物の平均濃度よりも小さい、半導体装置。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017047334A JP6717242B2 (ja) | 2017-03-13 | 2017-03-13 | 半導体装置 |
| CN201810193710.9A CN108574001B (zh) | 2017-03-13 | 2018-03-09 | 半导体装置 |
| US15/916,790 US10177234B2 (en) | 2017-03-13 | 2018-03-09 | Semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017047334A JP6717242B2 (ja) | 2017-03-13 | 2017-03-13 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018152455A JP2018152455A (ja) | 2018-09-27 |
| JP2018152455A5 JP2018152455A5 (ja) | 2019-06-27 |
| JP6717242B2 true JP6717242B2 (ja) | 2020-07-01 |
Family
ID=63445040
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017047334A Active JP6717242B2 (ja) | 2017-03-13 | 2017-03-13 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10177234B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6717242B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN108574001B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7279587B2 (ja) * | 2018-09-25 | 2023-05-23 | 豊田合成株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| DE102020202053A1 (de) * | 2020-02-19 | 2021-08-19 | Robert Bosch Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Mosfet mit sättigungskontakt und verfahren zum bilden eines mosfet mit sättigungskontakt |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000269518A (ja) * | 1999-03-18 | 2000-09-29 | Toshiba Corp | 電力用半導体素子及び半導体層の形成方法 |
| JP2004134547A (ja) * | 2002-10-10 | 2004-04-30 | Hitachi Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP4450241B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-20 | 2010-04-14 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2010021176A (ja) * | 2008-07-08 | 2010-01-28 | Nec Electronics Corp | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2012069797A (ja) * | 2010-09-24 | 2012-04-05 | Toyota Motor Corp | 絶縁ゲート型トランジスタ |
| US20130164895A1 (en) * | 2011-12-12 | 2013-06-27 | Maxpower Semiconductor, Inc. | Trench-Gated Power Devices with Two Types of Trenches and Reliable Polycidation |
| JP2015072999A (ja) * | 2013-10-02 | 2015-04-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置 |
| JP6428489B2 (ja) * | 2014-09-16 | 2018-11-28 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| WO2016042738A1 (ja) * | 2014-09-16 | 2016-03-24 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US9825126B2 (en) * | 2014-10-20 | 2017-11-21 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Semiconductor device |
| JP6354525B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-06 | 2018-07-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2016181617A (ja) * | 2015-03-24 | 2016-10-13 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP6367760B2 (ja) * | 2015-06-11 | 2018-08-01 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 絶縁ゲート型スイッチング装置とその製造方法 |
-
2017
- 2017-03-13 JP JP2017047334A patent/JP6717242B2/ja active Active
-
2018
- 2018-03-09 US US15/916,790 patent/US10177234B2/en active Active
- 2018-03-09 CN CN201810193710.9A patent/CN108574001B/zh active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US10177234B2 (en) | 2019-01-08 |
| CN108574001A (zh) | 2018-09-25 |
| CN108574001B (zh) | 2021-02-19 |
| JP2018152455A (ja) | 2018-09-27 |
| US20180261673A1 (en) | 2018-09-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10153356B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device | |
| US10256323B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device including an n type semiconductor region formed in a p type semiconductor layer | |
| US9548204B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, manufacturing method of the same and method of suppressing decrease of flat band voltage | |
| US10510833B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP2016111253A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP6183310B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2018166150A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法及び半導体装置の終端構造 | |
| US10879376B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP6717242B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US10854454B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| US9852925B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| TWI546958B (zh) | Gold and oxygen semi - high electron mobility transistor | |
| US10153352B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP5448530B2 (ja) | 電界効果トランジスタ | |
| JP6693020B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US10170564B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device and semiconductor device | |
| JP2016225426A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP7017152B2 (ja) | 半導体装置とその製造方法 | |
| US20230134698A1 (en) | Apparatus and method to control threshold voltage and gate leakage current for gan-based semiconductor devices | |
| JP7120886B2 (ja) | スイッチング素子の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190426 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190523 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200128 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200324 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200512 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200525 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6717242 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |