JP2006505015A - マルチドメイン垂直配向液晶ディスプレー - Google Patents
マルチドメイン垂直配向液晶ディスプレー Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006505015A JP2006505015A JP2004550336A JP2004550336A JP2006505015A JP 2006505015 A JP2006505015 A JP 2006505015A JP 2004550336 A JP2004550336 A JP 2004550336A JP 2004550336 A JP2004550336 A JP 2004550336A JP 2006505015 A JP2006505015 A JP 2006505015A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- display
- vertical alignment
- liquid crystal
- domain vertical
- domain
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 95
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 27
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 27
- 239000012788 optical film Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 44
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 31
- 239000004988 Nematic liquid crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004737 colorimetric analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1337—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1337—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers
- G02F1/133707—Structures for producing distorted electric fields, e.g. bumps, protrusions, recesses, slits in pixel electrodes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/137—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells characterised by the electro-optical or magneto-optical effect, e.g. field-induced phase transition, orientation effect, guest-host interaction or dynamic scattering
- G02F1/139—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells characterised by the electro-optical or magneto-optical effect, e.g. field-induced phase transition, orientation effect, guest-host interaction or dynamic scattering based on orientation effects in which the liquid crystal remains transparent
- G02F1/1393—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells characterised by the electro-optical or magneto-optical effect, e.g. field-induced phase transition, orientation effect, guest-host interaction or dynamic scattering based on orientation effects in which the liquid crystal remains transparent the birefringence of the liquid crystal being electrically controlled, e.g. ECB-, DAP-, HAN-, PI-LC cells
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09G—ARRANGEMENTS OR CIRCUITS FOR CONTROL OF INDICATING DEVICES USING STATIC MEANS TO PRESENT VARIABLE INFORMATION
- G09G3/00—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes
- G09G3/20—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters
- G09G3/34—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters by control of light from an independent source
- G09G3/36—Control arrangements or circuits, of interest only in connection with visual indicators other than cathode-ray tubes for presentation of an assembly of a number of characters, e.g. a page, by composing the assembly by combination of individual elements arranged in a matrix no fixed position being assigned to or needed to be assigned to the individual characters or partial characters by control of light from an independent source using liquid crystals
- G09G3/3611—Control of matrices with row and column drivers
- G09G3/3614—Control of polarity reversal in general
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Control Of Indicators Other Than Cathode Ray Tubes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims (51)
- マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーに於いて、該ディスプレーが、
液晶ディスプレーデバイスであるが、該デバイスの各画素に付随するフリンジ場を備える該デバイスを具備しており、該各画素内の該フリンジ場が、該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創るために該液晶チルト方向を制御するよう実質的に使われることを特徴とする該ディスプレー。 - 該液晶チルト方向がマルチドメイン垂直配向ドメインプロフアイルを創るよう駆動スキームにより制御されることを特徴とする請求項1の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該駆動スキームが列反転駆動スキーム、行反転駆動スキーム、又は画素反転駆動スキームであることを特徴とする請求項2のマルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該画素反転駆動スキームが4ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項3の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該列反転及び該行反転駆動スキームが2ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項3の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 隣接画素内への延びからの該フリンジ場を減じるか又は取り除くために更に境界線を具備することを特徴とする請求項3の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該境界線が基準電圧に保持されることを特徴とする請求項6の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該基準電圧が大地電位であることを特徴とする請求項7の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該ディスプレーの視野角を改善するために更に光学補償膜を具備することを特徴とする請求項1の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該光学補償膜が負の複屈折異方性光学膜であることを特徴とする請求項9の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該光学膜が一軸性膜又は2軸性膜であることを特徴とする請求項9の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーが単色液晶ディスプレー、カラーディスプレー、マルチドメイン均質(平行)液晶ディスプレー、マルチドメインツイステッドネマチック液晶ディスプレー、透過型液晶ディスプレー、反射型液晶ディスプレー、トランスフレクチブ型液晶ディスプレー、又は混成配向ネマチック液晶ディスプレーであることを特徴とする請求項1の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創る方法に於いて、該方法が、
液晶ディスプレーデバイスであるが、該デバイスの各画素に付随するフリンジ場を有する該液晶ディスプレーデバイス内で、該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創るために該フリンジ場を使って、各画素内の該液晶のチルト方向を実質的に制御する過程を具備することを特徴とする該方法。 - 制御する過程がマルチドメイン垂直配向ドメインプロフアイルを創る駆動スキームを備えることを特徴とする請求項13の該方法。
- 該駆動スキームが列反転駆動スキーム、行反転駆動スキーム、又は画素反転スキームであることを特徴とする請求項14の該方法。
- 該画素反転駆動スキームが4ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項15の該方法。
- 該列反転駆動スキーム又は該行反転駆動スキームが2ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項15の該方法。
- 更に、隣接画素内への延びからの該フリンジ場を減じる又は取り除く過程を具備することを特徴とする請求項15の該方法。
- 該フリンジ場を減じる又は取り除く過程が該隣接画素の間に境界線を設置する過程を有することを特徴とする請求項18の該方法。
- 該境界線が基準電圧に保持されることを特徴とする請求項19の該方法。
- 該基準電圧が大地電位であることを特徴とする請求項20の該方法。
- 該ディスプレーの該視野角を改善するために更に光学補償膜を該ディスプレーに付加する過程を具備することを特徴とする請求項13の該方法。
- 該光学補償膜が負の複屈折異方性光学膜であることを特徴とする請求項22の該方法。
- 該光学膜が一軸性膜又は二軸性膜であることを特徴とする請求項22の該方法。
- 該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーが単色液晶ディスプレー、カラーディスプレー、マルチドメイン均質(平行)液晶ディスプレー、マルチドメインツイステッドネマチック液晶ディスプレー、透過型液晶ディスプレー、反射型液晶ディスプレー、トランスフレクチブ型液晶ディスプレー、又は混成配向ネマチック液晶ディスプレーであることを特徴とする請求項13の該方法。
- マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーに於いて、該ディスプレーが、
第1基盤及び第2基盤と、
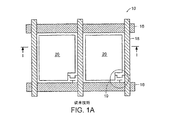
交点が複数の画素を形成する、該第2基盤上に形成された複数の行及び複数の列と、
該第1基盤及び第2基盤の間に配置された液晶材料と、を具備しており、液晶分子は垂直配向を有しておりそして該第1基盤及び第2基盤の間に電場が印加された時各画素は付随フリンジ場を有しており、該ディスプレーは又、
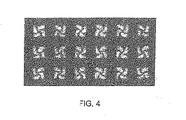
各画素に付随した該フリンジ場を使って該液晶分子のチルトされた配向を実質的に提供するための制御器を具備することを特徴とする該ディスプレー。 - 該制御器がマルチドメイン垂直配向ドメインプロフアイルを創るために駆動スキームを使用することを特徴とする請求項26の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該駆動スキームが列反転駆動スキーム、行反転駆動スキーム、又は画素反転駆動スキームであることを特徴とする請求項27の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該画素反転駆動スキームが4ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項28の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該列反転及び該行反転駆動スキームが2ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項28の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 隣接画素内への延びからの該フリンジ場を減じる又は取り除くために境界線を更に具備することを特徴とする請求項28の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該境界線が基準電圧に保持されることを特徴とする請求項31の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該基準電圧が大地電位であることを特徴とする請求項32の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該ディスプレーの該視野角を改善するために光学補償膜を更に具備することを特徴とする請求項26の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該光学補償膜が負の複屈折異方性光学膜であることを特徴とする請求項34の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該光学膜が一軸性膜又は二軸性膜であることを特徴とする請求項34の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- 該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーが単色液晶ディスプレー、カラーディスプレー、マルチドメイン均質液晶ディスプレー、マルチドメインツイステッドネマチック液晶ディスプレー、マルチドメイン平行液晶ディスプレー、透過型液晶ディスプレー、反射型液晶ディスプレー、トランスフレクチブ型液晶ディスプレー、又は混成配向ネマチック液晶ディスプレーであることを特徴とする請求項26の該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレー。
- マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創る方法に於いて、該方法が、
第1基盤及び第2基盤を提供する過程と、
該第2基盤上に複数の画素を形成する過程と、
該第1及び第2基盤間に液晶材料を配置する過程と、を具備しており、液晶材料は垂直配向を有しており、該第1基盤及び該第2基盤の間に電場が印加された時各画素は付随フリンジ場を有しており、該方法は又、
各画素に付随する該フリンジ場を使って該液晶分子のチルトされた配向を実質的に制御する過程を具備することを特徴とする該方法。 - 制御する過程がマルチドメイン垂直配向ドメインプロフアイルを創るために駆動スキームを備えることを特徴とする請求項38の該方法。
- 該駆動スキームが列反転駆動スキーム、行反転駆動スキーム、又は画素反転駆動スキームであることを特徴とする請求項39の該方法。
- 該画素反転駆動スキームが4ドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項40の該方法。
- 該列反転及び該行反転駆動スキームが2ドメインマルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーを創ることを特徴とする請求項40の該方法。
- 隣接画素内への延びからの該フリンジ場を減じる又は取り除く過程を具備することを特徴とする請求項40の該方法。
- 該フリンジ場を減じる又は取り除く過程が該隣接画素間に境界線を設置する過程を備えることを特徴とする請求項43の該方法。
- 該境界線が基準電圧に保持されることを特徴とする請求項44の該方法。
- 該基準電圧が大地電位であることを特徴とする請求項45の該方法。
- 該ディスプレーの該視野角を改善するために更に光学補償膜を付加する過程を具備することを特徴とする請求項38の該方法。
- 該光学補償膜が負の複屈折異方性光学膜であることを特徴とする請求項47の該方法。
- 該光学膜が一軸性膜又は二軸性膜であることを特徴とする請求項47の該方法。
- 該マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーが単色液晶ディスプレー、カラーディスプレー、マルチドメイン均質(平行)液晶ディスプレー、マルチドメインツイステッドネマチック液晶ディスプレー、透過型液晶ディスプレー、反射型液晶ディスプレー、トランスフレクチブ型液晶ディスプレー、又は混成配向ネマチック液晶ディスプレーであることを特徴とする請求項38の該方法。
- マルチドメイン垂直配向ディスプレーに於いて、該ディスプレーが、
各画素に付随するフリンジ場を使って該ディスプレー各画素内の該LCチルト方向を実質的に制御するための手段を具備することを特徴とする該ディスプレー。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US42362102P | 2002-11-01 | 2002-11-01 | |
| PCT/US2003/034680 WO2004042462A1 (en) | 2002-11-01 | 2003-10-31 | Multi-domain vertical alignment liquid crystal display |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006505015A true JP2006505015A (ja) | 2006-02-09 |
| JP2006505015A5 JP2006505015A5 (ja) | 2006-12-14 |
Family
ID=32312691
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004550336A Withdrawn JP2006505015A (ja) | 2002-11-01 | 2003-10-31 | マルチドメイン垂直配向液晶ディスプレー |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20040201807A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2006505015A (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20050067216A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN1708724A (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2003284384A1 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW200428067A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2004042462A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4217170B2 (ja) * | 2004-01-28 | 2009-01-28 | 株式会社 日立ディスプレイズ | 液晶表示装置およびその駆動方法 |
| TWI307992B (en) * | 2005-06-30 | 2009-03-21 | Delta Electronics Inc | Dual fan and motor thereof |
| US20070200986A1 (en) * | 2005-12-29 | 2007-08-30 | Ong Hiap L | Contrast ratio and viewing angle improvement for a TN- LCD |
| TWI340268B (en) | 2006-03-31 | 2011-04-11 | Wintek Corp | Multi-domain lcd |
| US20080225212A1 (en) * | 2007-03-13 | 2008-09-18 | Ong Hiap L | Pixel designs for multi-domain vertical alignment liquid crystal display |
| US9063357B2 (en) * | 2007-03-20 | 2015-06-23 | Jabil Circuit, Inc. | Method for despeckling in laser display systems |
| JP4978786B2 (ja) * | 2007-07-30 | 2012-07-18 | ソニー株式会社 | 液晶表示装置 |
| TWI369530B (en) * | 2007-09-19 | 2012-08-01 | Wintek Corp | Multi-domain liquid crystal display |
| TWI377419B (en) * | 2007-10-04 | 2012-11-21 | Wintek Corp | Multi-domain liquid crystal display and array substrate thereof |
| KR101390768B1 (ko) * | 2007-10-10 | 2014-05-02 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | 액정표시장치 |
Family Cites Families (54)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6327010B1 (en) * | 1992-02-03 | 2001-12-04 | Merck Patent Gesellschaft Mit Beschrankter Haftung | Electrooptical system |
| JP2502802B2 (ja) * | 1990-10-15 | 1996-05-29 | インターナシヨナル・ビジネス・マシーンズ・コーポレーシヨン | 液晶表示装置 |
| SG50586A1 (en) * | 1991-07-26 | 2000-05-23 | Rolic Ag | Liquid crystal display cell |
| US5858784A (en) * | 1991-12-17 | 1999-01-12 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Expression of cloned genes in the lung by aerosol- and liposome-based delivery |
| TW255017B (ja) * | 1991-12-26 | 1995-08-21 | Toshiba Co Ltd | |
| US5504604A (en) * | 1992-01-22 | 1996-04-02 | Nec Corporation | Liquid crystal display elements with opposite twist domains aligned in the same direction on one substrate |
| DE69318865T2 (de) * | 1992-03-03 | 1998-12-10 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Kadoma, Osaka | Verdrillt-nematische Flüssigkristall-Anzeigevorrichtung mit aktiver Matrix |
| US5309264A (en) * | 1992-04-30 | 1994-05-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Liquid crystal displays having multi-domain cells |
| JP2693368B2 (ja) * | 1993-06-29 | 1997-12-24 | スタンレー電気株式会社 | 液晶表示素子とその製造方法 |
| US5576854A (en) * | 1993-11-12 | 1996-11-19 | Hughes-Jvc Technology Corporation | Liquid crystal light valve projector with improved contrast ratio and with 0.27 wavelength compensation for birefringence in the liquid crystal light valve |
| US5550661A (en) * | 1993-11-15 | 1996-08-27 | Alliedsignal Inc. | Optical phase retardation film |
| US5623354A (en) * | 1994-02-10 | 1997-04-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Liquid crystal display with multi-domains |
| US5864376A (en) * | 1994-04-21 | 1999-01-26 | Nec Corporation | LCD of a selected twist angle through an LC material of a selected chiral pitch |
| JP2643835B2 (ja) * | 1994-06-06 | 1997-08-20 | 日本電気株式会社 | 液晶表示装置およびその駆動方法 |
| JP3044681B2 (ja) * | 1994-06-08 | 2000-05-22 | 富士写真フイルム株式会社 | 液晶表示装置 |
| US5710611A (en) * | 1994-11-17 | 1998-01-20 | Nec Corporation | Liquid crystal display apparatus preventing image on screen from influences of disclination line |
| US5818560A (en) * | 1994-11-29 | 1998-10-06 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Liquid crystal display and method of preparing the same |
| JP3544572B2 (ja) * | 1995-02-01 | 2004-07-21 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 液晶パネルおよび液晶表示装置 |
| US5831700A (en) * | 1995-05-19 | 1998-11-03 | Kent State University | Polymer stabilized four domain twisted nematic liquid crystal display |
| JPH0968706A (ja) * | 1995-09-01 | 1997-03-11 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 液晶表示素子 |
| US5610743A (en) * | 1995-10-30 | 1997-03-11 | United Microelectronics Corporation | Liquid crystal display including concentric shapes and radial spokes which has an improved viewing angle |
| US5726723A (en) * | 1996-01-31 | 1998-03-10 | Technology Research International Corporation | Sub-twisted nematic liquid crystal display |
| KR100225910B1 (ko) * | 1996-04-04 | 1999-10-15 | 구자홍 | 액정표시장치(liquid crystal display device) |
| KR100244710B1 (ko) * | 1997-04-18 | 2000-02-15 | 김영환 | 액정 표시 장치 |
| JP3966614B2 (ja) * | 1997-05-29 | 2007-08-29 | 三星電子株式会社 | 広視野角液晶表示装置 |
| GB9713981D0 (en) * | 1997-07-03 | 1997-09-10 | Sharp Kk | Optical device |
| US5907380A (en) * | 1997-10-30 | 1999-05-25 | International Business Machines Corporation | Liquid crystal cell employing thin wall for pre-tilt control |
| JPH11212107A (ja) * | 1998-01-26 | 1999-08-06 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | アクティブマトリクス型液晶表示装置およびその駆動方法ならびにその製造方法 |
| US5953091A (en) * | 1998-04-09 | 1999-09-14 | Ois Optical Imaging Systems, Inc. | Multi-domain LCD and method of making same |
| US6124907A (en) * | 1998-04-24 | 2000-09-26 | Ois Optical Imaging Systems, Inc. | Liquid crystal display with internal polarizer and method of making same |
| JP3301381B2 (ja) * | 1998-04-28 | 2002-07-15 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 液晶表示素子 |
| US6335776B1 (en) * | 1998-05-30 | 2002-01-01 | Lg. Philips Lcd Co., Ltd. | Multi-domain liquid crystal display device having an auxiliary electrode formed on the same layer as the pixel electrode |
| KR100357213B1 (ko) * | 1998-07-23 | 2002-10-18 | 엘지.필립스 엘시디 주식회사 | 멀티도메인 액정표시소자 |
| KR20000009518A (ko) * | 1998-07-25 | 2000-02-15 | 노봉규 | 광시야각을 갖는 수직배향 액정표시소자 |
| US6057902A (en) * | 1998-08-05 | 2000-05-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | Pixels for wide viewing angle liquid crystal display |
| KR100299381B1 (ko) * | 1998-08-24 | 2002-06-20 | 박종섭 | 고개구율 및 고투과율을 갖는 액정표시장치 및 그 제조방법 |
| KR100313949B1 (ko) * | 1998-11-11 | 2002-09-17 | 엘지.필립스 엘시디 주식회사 | 멀티도메인액정표시소자 |
| US6061115A (en) * | 1998-11-03 | 2000-05-09 | International Business Machines Incorporation | Method of producing a multi-domain alignment layer by bombarding ions of normal incidence |
| US6426786B1 (en) * | 1999-06-01 | 2002-07-30 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method of homeotropic alignment or tilted homeotropic alignment of liquid crystals by single oblique evaporation of oxides and liquid crystal display device formed thereby |
| US6504592B1 (en) * | 1999-06-16 | 2003-01-07 | Nec Corporation | Liquid crystal display and method of manufacturing the same and method of driving the same |
| US6256080B1 (en) * | 1999-06-23 | 2001-07-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Self-aligned structures for improved wide viewing angle for liquid crystal displays |
| US6400440B1 (en) * | 1999-06-23 | 2002-06-04 | International Business Machines Corporation | Passive liquid crystal display having pre-tilt control structure and light absorbent material at a center |
| US6313896B1 (en) * | 1999-08-31 | 2001-11-06 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for forming a multi-domain alignment layer for a liquid crystal display device |
| TW548475B (en) * | 1999-11-18 | 2003-08-21 | Ind Tech Res Inst | Fabrication method of homeotropic aligned LCD structure and the bump structure |
| US6636289B2 (en) * | 2000-04-19 | 2003-10-21 | Lg.Philips Lcd Co., Ltd. | In-plane switching LCD panel with multiple domains and rubbing directions symetric about a line |
| US6549257B2 (en) * | 2000-05-22 | 2003-04-15 | Industrial Technology Research Institute | Structure of a multi-domain wide viewing angle liquid crystal display |
| JP4499254B2 (ja) * | 2000-07-27 | 2010-07-07 | ソニー株式会社 | 液晶表示素子 |
| KR100720093B1 (ko) * | 2000-10-04 | 2007-05-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 액정 표시 장치 |
| KR100601454B1 (ko) * | 2000-10-04 | 2006-07-14 | 엘지.필립스 엘시디 주식회사 | 멀티 도메인 액정표시장치 및 그 제조방법 |
| TW562976B (en) * | 2000-11-27 | 2003-11-21 | Au Optronics Corp | Pixel structure in liquid crystal display |
| KR100448046B1 (ko) * | 2000-12-05 | 2004-09-10 | 비오이 하이디스 테크놀로지 주식회사 | 반사형 프린지 필드 구동 모드 액정 표시 장치 |
| TW571165B (en) * | 2000-12-15 | 2004-01-11 | Nec Lcd Technologies Ltd | Liquid crystal display device |
| TW588171B (en) * | 2001-10-12 | 2004-05-21 | Fujitsu Display Tech | Liquid crystal display device |
| US7016001B2 (en) * | 2002-03-14 | 2006-03-21 | Hannstar Display Corp. | MVA-LCD device with color filters on a TFT array substrate |
-
2003
- 2003-10-31 AU AU2003284384A patent/AU2003284384A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2003-10-31 CN CNA2003801022084A patent/CN1708724A/zh active Pending
- 2003-10-31 JP JP2004550336A patent/JP2006505015A/ja not_active Withdrawn
- 2003-10-31 WO PCT/US2003/034680 patent/WO2004042462A1/en active Application Filing
- 2003-10-31 KR KR1020057007714A patent/KR20050067216A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2003-10-31 TW TW092130416A patent/TW200428067A/zh unknown
- 2003-10-31 US US10/698,968 patent/US20040201807A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2006
- 2006-07-20 US US11/489,770 patent/US20070013849A1/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2004042462A1 (en) | 2004-05-21 |
| AU2003284384A1 (en) | 2004-06-07 |
| US20070013849A1 (en) | 2007-01-18 |
| KR20050067216A (ko) | 2005-06-30 |
| US20040201807A1 (en) | 2004-10-14 |
| CN1708724A (zh) | 2005-12-14 |
| TW200428067A (en) | 2004-12-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Hanaoka et al. | 40.1: A new MVA‐LCD by polymer sustained alignment technology | |
| US6930739B2 (en) | Liquid crystal device | |
| US20070013849A1 (en) | Multi-domain vertical alignment liquid crystal display | |
| US6573965B1 (en) | Multi-domain wide viewing angle liquid crystal display having slits on electrodes and bumps above the slits | |
| US20070195251A1 (en) | Systems for displaying images involving alignment liquid crystal displays | |
| JP3108768B2 (ja) | Tn液晶表示素子 | |
| US20040105062A1 (en) | Wide-viewing angle display device and fabrication method for thereof | |
| US20080266499A1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| CN101429437A (zh) | 用于液晶显示器的基片以及使用该基片的液晶显示器 | |
| WO2010137386A1 (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| US7995887B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic device using the same | |
| JPH06160878A (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| JPH0822023A (ja) | 液晶表示素子とその製造方法 | |
| WO2010055633A1 (ja) | 液晶表示装置及び液晶表示装置の製造方法 | |
| JPH11174481A (ja) | 表示装置 | |
| Kataoka et al. | 39.4: A New MVA‐LCD with Jagged Shaped Pixel Electrodes | |
| JP3324606B2 (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| JP2000356775A (ja) | 液晶表示素子とその製造方法 | |
| US20050128400A1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| CN101989011A (zh) | 液晶显示元件 | |
| US20030011734A1 (en) | Multi-domain liquid crystal display having bump structures with non-parallel boundaries | |
| Tien et al. | P‐164: Novel Pixel Design of Multi‐Domain Polymer Sustained Alignment LCD Technology with Improved Mura Performance | |
| JP3099817B2 (ja) | 液晶表示装置 | |
| JP4075542B2 (ja) | 液晶表示素子 | |
| JP3586446B2 (ja) | 液晶表示装置及びその駆動方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20060915 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20060915 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20060915 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061027 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20061027 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20080313 |