EP2711088B1 - Film-coating nozzle, coating device and coating method - Google Patents
Film-coating nozzle, coating device and coating method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2711088B1 EP2711088B1 EP12786423.9A EP12786423A EP2711088B1 EP 2711088 B1 EP2711088 B1 EP 2711088B1 EP 12786423 A EP12786423 A EP 12786423A EP 2711088 B1 EP2711088 B1 EP 2711088B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- coating
- nozzle
- groove
- film
- liquid material
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 title claims description 115
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 title claims description 110
- 239000007888 film coating Substances 0.000 title claims description 16
- 238000009501 film coating Methods 0.000 title claims description 16
- 239000011344 liquid material Substances 0.000 claims description 75
- 210000005239 tubule Anatomy 0.000 claims description 64
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 28
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 14
- 230000007480 spreading Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005219 brazing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004519 grease Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009499 grossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010422 painting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/02—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C5/00—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work
- B05C5/02—Apparatus in which liquid or other fluent material is projected, poured or allowed to flow on to the surface of the work the liquid or other fluent material being discharged through an outlet orifice by pressure, e.g. from an outlet device in contact or almost in contact, with the work
- B05C5/0254—Coating heads with slot-shaped outlet
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05B—SPRAYING APPARATUS; ATOMISING APPARATUS; NOZZLES
- B05B1/00—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means
- B05B1/14—Nozzles, spray heads or other outlets, with or without auxiliary devices such as valves, heating means with multiple outlet openings; with strainers in or outside the outlet opening
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C—APPARATUS FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05C13/00—Means for manipulating or holding work, e.g. for separate articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D—PROCESSES FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D1/00—Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials
- B05D1/26—Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials performed by applying the liquid or other fluent material from an outlet device in contact with, or almost in contact with, the surface
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a nozzle, a coating device, and a coating method for coating a liquid material in the form of a film, having a uniform thickness, on a surface of a coating target over a wide region.
- a device for coating a liquid material in the form of a film, having a uniform thickness, on a surface of a coating target over a wide region such as for coating, e.g., a resist liquid in manufacturing of electric and electronic products, or for coating, e.g., a phosphor paste in manufacturing of display devices
- a slit nozzle including a single elongate gap formed therein and a comb-shaped nozzle including a plurality of tubules arranged on a straight line at narrow intervals.
- Those nozzles are advantageous in finishing the coating with a smaller number of times of nozzle movements.
- those nozzles have drawbacks that pressure in the nozzle is not held uniform and an amount of the coated material varies due to, e.g., the difference in distances from an inflow opening to individual outflow openings of the nozzle or the presence of flow resistance at each outflow opening.
- Various techniques have been proposed up to date with intent to eliminate the variation in the amount of the coated material and to realize the coating in a uniform thickness.
- Patent Document 1 relates to an extrusion type nozzle used to coat a coating liquid on a surface of one or more coating targets traveling in a belt-like discrete or continuous form. More specifically, Patent Document 1 discloses an extrusion type nozzle including two stages of manifolds for spreading a coating liquid in a direction of width, and two stages of slits for rectifying the coating liquid, wherein one of the two stages of slits, which is disposed on the inflow side of the coating liquid is formed of a replaceable member, and the member is replaced with an optimum member for each coating operation depending on, e.g., viscosity of the coating liquid, thereby realizing uniform coating.
- Patent Document 2 relates to a device for forming a protective film on a painting surface in an external appearance of a vehicular body, and it discloses such a technique that, in the case of forming a smooth protective film by jetting out a water soluble paint to a target surface from a nozzle device, which includes many fine holes arranged on a line, at a short distance under comparatively low pressure, while utilizing a flattening property of the paint on the target surface, tip openings of the fine holes include portions communicating with each other to form a paint jetted out from the nozzle device into a thin film, thereby coating a smooth protective film.
- a fluid ejection channel structure including multiple stages of branching portions to branch flow channels in a region from one inflow opening to a plurality of ejection ports, wherein a horizontal width of a compartment defining the branching portion in an upper stage is set to be greater than a distance between inlets of adjacent branching portions in a lower stage, adjacent compartments in upper and lower stages are communicated with each other through a tubular channel arranged at a center of the branching portion on the lower stage side, and the tubular channel is formed in length shorter than lengths of the branching portions in the upper and lower stages, thus making total lengths of individual branched channels substantially equal to one another and making pressure losses of the fluid passing through all the branched channels substantially equal to one another such that amounts of the fluid ejected through the individual ejection ports are held uniform with high accuracy (Patent Document 3).
- Patent Document 4 discloses a liquid application apparatus which applies a liquid to an objective region.
- the apparatus includes a trap having an opening from which the liquid linearly appears, a feeder to feed the liquid to the trap, and an operation unit to position the trap on the objective region and bring the linearly appeared liquid at the trap into contact with the objective region, thereby linearly applying the liquid to the objective region.
- the apparatus is capable of linearly applying the liquid in a uniform thickness to the objective region.
- the slit nozzle includes only one elongate gap, pressure for pushing out the liquid material is not uniformly exerted on the slit nozzle, thus causing a problem that the slit nozzle may deform from a weak portion or may break in the worst case.
- the above-mentioned problem is more frequently caused because comparatively high pressure is exerted. If the above-described deformation of the slit nozzle occurs, the coating amount would be changed as a matter of course, and a coated film having a uniform thickness could not be obtained.
- Patent Document 2 Aiming to solve the above-mentioned problem with the slit nozzle, it is conceivable to employ such a comb-shaped nozzle as disclosed in Patent Document 2.
- the comb-shaped nozzle disclosed in Patent Document 2 is not satisfactory as a means for obtaining a painted film having a uniform thickness for the reason that the paint is jetted out in the form of an irregular thin film, and that smoothing of the painted film is based on fluidity of the paint after the coating.
- Patent Document 2 includes no suggestions with respect to the problem of the pressure loss, which may arise with the provision of the fine holes.
- Patent Document 3 is adapted for forming a multiplicity of parallel lines, for example, by applying the phosphor paste into a recess of a substrate surface, and it does not include a nozzle for coating a film.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a film-coating technique which can make uniform amounts of inflows through all of flow channels communicating with an ejection port, which can minimize the influence of an application gap, and which can coat a film with higher precision than in the past.
- a film-coating nozzle comprising branching blocks having a branched channel structure, a tip member having an ejection port formed to be wide in a longitudinal direction, and a tube section including a plurality of tubules having tubule inflow openings that communicate with the branched channel structure, and tubule outflow openings that communicate with the ejection port of the tip member, wherein the branching blocks include multiple stages of branching portions each of which provides a chamber to branch a flow channel communicating with an inflow opening, the flow channels branched by the branching portions in the same stage having equal lengths up to outflow openings thereof, the tip member has a groove that constitutes the ejection port, and a length S of an end surface of the ejection port in a transverse direction is longer than an internal diameter D of the tubule outflow openings, the tubule outflow openings being disposed at substantially equal intervals in an innermost surface of the groove, and the branching blocks and
- a length W of the end surface of the ejection port in the longitudinal direction is longer than a distance between the tubule outflow openings that are disposed at opposite ends of the innermost surface of the groove.
- a length of the groove in the transverse direction is gradually increased from the innermost surface of the groove toward the end surface of the ejection port.
- a sectional shape of the groove taken in the transverse direction is trapezoidal, and the tubule outflow openings are positioned on a vertical center line of the sectional shape of the groove.
- a sectional shape of the groove taken in the transverse direction is semi-circular or semi-elliptic, and the tubule outflow openings are positioned on a vertical center line of the sectional shape of the groove.
- the length S of the end surface of the ejection port in the transverse direction is 1.2 to 2.5 times the internal diameter D of the tubule outflow openings.
- a coating device comprising the film-coating nozzle according to any one of the first to sixth aspects of the present invention, a tank for storing a liquid material, an ejection valve for controlling supply or stop of the liquid material, which is supplied from the tank, with respect to the nozzle, a work table on which a coating target is placed, and a moving mechanism for moving the nozzle and the coating target placed on the work table relative to each other.
- the coating device further comprises an adjustment mechanism including a base member to which the nozzle is fixed, a rotary shaft disposed in a central portion of the base member, a mounting member for rotatably supporting the rotary shaft, and an adjustment screw disposed on the mounting member.
- a coating device comprising the film-coating nozzle according to the first aspect of the present invention, a tank for storing a liquid material, an ejection valve for controlling supply or stop of the liquid material, which is supplied from the tank, with respect to the nozzle, a work table on which a coating target is placed, and a moving mechanism for moving the nozzle and the coating target placed on the work table relative to each other, the coating device further comprising an adjustment mechanism that includes a base member for fixedly holding the branching blocks and/or the tip member in a coupled state, a rotary shaft disposed in a central portion of the base member, a mounting member for rotatably supporting the rotary shaft, and an adjustment screw disposed on the mounting member.
- the tank is provided in plural number, and the coating device further comprises a selector valve for selectively switching over communication with one of the tanks to be used.
- the coating device further comprises a pump disposed between the ejection valve and the selector valve.
- the pump is a positive displacement pump.
- a coating method of coating a liquid material by employing the film-coating nozzle according to any one of the first to sixth aspects of the present invention, while a coating target and/or the nozzle is moved by a moving mechanism.
- a highly-viscous liquid material is coated in form of a film.
- the present invention because of including not only the branched channel structure capable of distributing the liquid material in uniform amounts, but also the plural tubules, which are supplied with the liquid material in uniform amounts through the branched channels, and the groove serving to restore pressure, it is possible to minimize the influence of a variation in the application gap, and to coat a film in a more uniform thickness than in the past.
- a nozzle configuration can be easily changed just by modifying the modules depending on a size change of the coating target. Washing of the individual sections is also facilitated.
- the inflow side of the nozzle is called the "upper” side
- the ejection side is called the “lower” side
- a longitudinal direction of branching blocks 3 to 5 and a tip member 12 is called a "direction of longitudinal width”
- a transverse direction thereof is called a "direction of depth” in some cases.
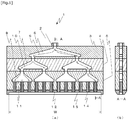
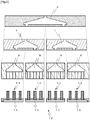
- Fig. 1 is a sectional view of an entire structure of a nozzle according to the present invention.
- Fig. 1(a) is a front view
- Fig. 1(b) is a sectional view taken along a line A-A in Fig. 1(a) , looking in a direction denoted by arrow.
- a nozzle 1 of the present invention includes a branching block 3 in a first stage, a branching block 4 in a second stage, and a branching block 5 in a third stage.
- the nozzle 1 has one nozzle inlet 2 and twelve tubules 14 each having an ejection opening.
- the nozzle 1 is structured such that a liquid material 43 flowing into the nozzle 1 through the one nozzle inlet 2 is branched in each of the three stages of branching portions (branching chambers), and are ejected after flowing into a groove 15 through the total twelve tubules 14, which are disposed side by side on a straight line.
- the number of stages of branching blocks is just required to be two or more, and it may be four or five, for example.
- the branching chamber constituting the branching portion is provided, and the plural tubules 14 are communicated with the branching chambers. Therefore, the number of the tubules 14 is set to be at least four, preferably six or more, and more preferably eight or more.
- the liquid material 43 having entered through the one nozzle inlet 2 is branched into two even flows 9, having a substantially equal length, in a branching portion (branching chamber) 6 that is provided in the branching block 3 in the first stage.
- the liquid materials 43 branched in the first stage are each further branched into two even flows 10, having a substantially equal length, in each of two branching portions 7 that are provided in the branching block 4 in the second stage.
- the liquid materials 43 branched in the second stage are each further branched into three even flows 11, having a substantially equal length, in each of four branching portions 8 that are provided in the branching block 5 in the third stage.
- the branched liquid materials flow into the tubules 14, which are grouped in units of three and which are communicated with the four branching portions 8 that are provided in the branching block 5 in the third stage, and then flow out to the groove 15, and ejected.
- the branched flows have the same length in all branching portions provided in the same branching block.
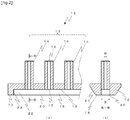
- Fig. 2 is an enlarged partial sectional view of a tip portion of the nozzle according to the present invention. Specifically, Fig. 2(a) is a front view, and Fig. 2(b) is a sectional view taken along a line B-B in Fig. 2(a) , looking in a direction denoted by arrow.
- a nozzle tip member 12 in the present invention includes a tube section 13 including the plural tubules 14, and an elongate groove 15 communicating with the tube section 13 to merge the branched liquid materials 43 together.
- Respective inflow openings 16 of the tubules 14 constituting the tube section 13 communicate with the branching portions 8 provided in the branching block 5 in the third stage of a branched channel structure, which is made up of the branching blocks 3 to 5.
- respective ends of the tubules 14 at their outflow openings 17 are fitted to the tip member 12 having the groove 15, and are fixed to the tip member 12 by employing, e.g., a brazing alloy, a solder, or an adhesive.
- the tubule ends may be fixed through "close fitting" without using the adhesive or the like.
- tubules 14 defining the outflow openings 17 are positioned in flush with an innermost surface 19 of the groove 15.
- the tubules 14 are arranged in plural number at substantially equal intervals on a straight line in the longitudinal direction, thereby constituting the tube section 13.
- the tubules 14 are preferably arranged at predetermined intervals from the viewpoint of providing a spreading effect in the direction of longitudinal width. However, if the tubules 14 are too far spaced from each other, a film could not be formed.
- the tubules 14 are arranged such that the distance between centerlines of the adjacent tubules 14, each having an internal diameter D, is about 4 to 12 times the internal diameter D.
- each tubule 14 in the present invention is, for example, ⁇ 0.3 to 1.0 mm, and the thickness of a coated film is, for example, 20 to 500 ⁇ m.
- the groove 15 has a rectangular shape that is elongate in the longitudinal direction, and it defines a rectangular parallelepiped space that is surrounded by the innermost surface 19 with which the tube section 13 communicates, and by inner walls 22 and 23.
- the groove 15 constitutes a spreading portion that acts to spread a space defined by the outflow opening of each tubule 14.
- outer lateral surfaces of the tip member 12 extending in the longitudinal direction have inclined surfaces 21, and the tip member 12 is formed into a tapered shape by the two inclined surfaces 21 and 21.
- a tip end surface 18 is formed as a horizontal surface between each inclined surface 21 and the groove 15.
- inner surfaces of the tip member 12 extending in the transverse direction are formed by the inner walls 23, which are relatively thick and which specify a length W of the groove 15 in the direction of longitudinal width. It is, however, to be noted that the length W of the groove 15 in the direction of longitudinal width is set so as to provide a rather broad space occupying most of the tip member 12, and the walls of the tip member 12 are not so thick as to form a narrow slit nozzle.
- the length W of the groove 15 in the direction of longitudinal width is preferably set to be longer than the distance between the tubules 14 positioned at both ends in the direction of longitudinal width. This aims to enable pressure to restore with the arrangement of providing spreading spaces in the direction of longitudinal width at both the longitudinal ends of the groove 15 as well.
- the inner walls 23 specifying the length W of the groove 15 in the direction of longitudinal width may be each formed to have an inclined surface or a stepwise or curved surface (see later description related to the inner walls 22 specifying a length S of the groove 15 in the transverse direction).
- the groove 15 is formed in a way to provide a spreading space not only in the direction of longitudinal width, but also in the direction of depth. More specifically, the groove 15 is formed such that a length S of the groove in the transverse direction is greater than the internal diameter D of the tubule (i.e., D ⁇ S) (see Fig. 2(b) ). With such an arrangement, the liquid material 43 delivered from the branching portion 8 to flow out through the tubule 14 is caused to temporarily spread in the groove 15 before being ejected toward a coating target 29, whereby pressure lost in the tubule 14 is restored to some extent.
- a sectional shape of the groove 15, taken in the transverse direction, is preferably line-symmetrical with respect to the centerline of the tubule 14 having the internal diameter D such that the liquid material spreads uniformly in an entire space of the groove 15.
- the length S of the groove 15 in the transverse direction and the internal diameter D of the tubule are changed as appropriate depending on physical property values of the liquid material 43 used, the desired coating shape, and so on, the length S of the groove 15 in the transverse direction is, for example, preferably about 1.2 to about 2.5 times and more preferably about 1.5 to about 2.0 times the internal diameter D of the tubule.
- the internal diameter of the outflow opening 17 is taken as a reference.
- the tubule 14 is thinnest among all the flow channels including the branching portions (6, 7 and 8), and flow resistance is maximum in the tubule 14.
- the plural tubules 14 are arrayed in the longitudinal direction of the tip member 12, forces exerted by supply pressure is distributed.
- the nozzle 1 of the present invention is able to eject the liquid material without causing, e.g., deformation.
- the nozzle of the present invention can be used to coat the liquid material having viscosity of 300 to 500000 mPa ⁇ s, for example, it is particularly preferable to coat the liquid material having high viscosity.
- high viscosity implies a viscosity of 50000 mPa ⁇ s or more and preferably 100000 mPa ⁇ s or more.
- Fig. 3 is an explanatory view to explain a state under coating.
- reference symbol 24 denotes a moving direction of the nozzle 1.
- Fig. 3(a) represents the case of the prior-art slit nozzle.
- the liquid material 43 to be ejected is delivered from a pool 25 to pass through a slit ( ⁇ ), and is directly ejected to the coating target 29.
- Fig. 3(b) represents the case of the present invention.
- the liquid material 43 to be ejected is delivered from the branching portion to pass through the tubule 14 ( ⁇ ), and is ejected to the coating target 29 after having spread in the groove 15 ( ⁇ ).
- an application gap G there is a gap G (hereinafter referred to as an "application gap G") between the tip end of the nozzle 1 and the coating target 29.
- the application gap G may vary due to the influences of, e.g., flatness of the coating target 29 and parallelism of a moving mechanism 31. If the application gap G increases or decreases, the liquid material 43 sandwiched between the tip surface of the nozzle 1 and the surface of the coating target 29 is pulled or pushed. Correspondingly, pressure in the inside ( ⁇ , ⁇ ) of the liquid material falls or rises.
- the flow of the liquid material is caused to slightly spread in the groove 15 ( ⁇ ), thus allowing the pressure to restore to some extent. Thereafter, the liquid material flows out to the outside ( ⁇ ). Accordingly, the pressure in the inside ( ⁇ ) of the liquid material sandwiched between the nozzle and the coating target increases, but the increase of the pressure is not so abrupt.
- the coating amount is stabilized and the film thickness becomes uniform even if the application gap varies due to the influences of, e.g., flatness of the coating target and parallelism of the moving mechanism.
- the groove 15 is formed such that the length S of the groove in the transverse direction is greater than the internal diameter D of the tubule (i.e., D ⁇ S).
- the length S of the groove in the transverse direction may be increased finally at a most-downstream end surface 20 that defines an ejection port.
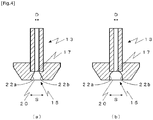
- Fig. 4 illustrates modifications in that case.
- Fig. 4(a) illustrates the groove 15 having a trapezoidal shape in section taken in the transverse direction.
- an angle formed by each of inner walls 22a and 22b having flat surfaces changes depending on the length S of the groove in the transverse direction and the internal diameter D of the tubule, it is, for example, preferably 90 degrees or less and more preferably 60 degrees or less.
- Fig. 4(b) illustrates the groove15 having a semi-circular or semi-elliptic shape in section taken in the transverse direction.
- the inner walls 22a and 22b are just needed to have such shapes as gradually increasing the distance between them in the transverse direction, the inner walls 22a and 22b are preferably formed as smooth (flat or curved) surfaces.
- the inner walls 22a and 22b are preferably formed in shapes not causing contraction of area midway a portion ranging from the outflow opening 17 of the tubule to the end surface of the groove. This is because such shapes are easier to obtain with working and do not make flows in the groove 15 complicated.
- the flow of the liquid material is allowed to more gently spread, whereby the pressure can be restored while the pressure loss can be held smaller.
- the nozzle 1 of the present invention can be constituted in a modular structure depending on varieties of the branching portions (6, 7 and 8).
- Figs. 5 and 6 are each an explanatory view to explain an example of the modular structure of the nozzle according to the present invention.
- Fig. 5 illustrates an example of the modular structure in which one or more branching portions (6, 7 and 8) having equal lengths of the branched flows (9, 10 and 11) per stage are formed as one-piece integral branching blocks (3, 4 and 5), respectively.
- the branching blocks (3, 4 and 5) constitute modules for each branching stage.
- the modules (3, 4 and 5) are coupled to each other using fastening members (not illustrated).
- the fastening members are, e.g., screws or bolts.
- each module may be fixed to, e.g., a plate-like member serving as a base.
- positioning pins are preferably disposed to avoid the flow channels from displacing in mutual connection when the modules are coupled or fixed, thus allowing the modules to be properly positioned with ease.
- a sealing member is disposed at a flow-channel connecting portion of each module in order to prevent leakage of the liquid material.
- Fig. 6 illustrates another example of the modular structure in which the branching portions (6, 7 and 8) are each constituted as one integral module.
- the modular structure of Fig. 6 can also be said as a modular structure per minimum unit.
- the tip member 12 is divided into modules corresponding to the divided modules 5 in the lowermost stage.
- the modules are coupled to each other using fastening members (not illustrated), or are each fixed to a plate-like member serving as a base.
- a positioning pin, a sealing member, etc. are further disposed in a similar manner to that in the above example.
- the modules constituting the opposite ends of the tip member 12 are different in shape of the groove 15 from the other modules.
- the inner walls 23 specifying the longitudinal width of the groove 15 have to be provided in those modules constituting the opposite ends of the tip member 12.
- the thicknesses of sidewalls of the modules constituting opposite ends of the stage are different from those of sidewalls of the other modules.
- Such a difference in the thicknesses of the sidewalls is intended to make respective widths of the stages equal to each other when the stages are directly coupled to each other.
- the nozzle in the modular structure as described above, when the size of the coating target is changed, it is possible to easily change the nozzle configuration just by changing combination of the modules, and to facilitate cleaning of the nozzle.
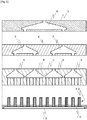
- Fig. 7 is a partial sectional view of the adjustment mechanism capable of being attached to the nozzle 1 of the present invention. Specifically, Fig. 7(a) is a front view, and Fig. 7(b) is a partial side sectional view.
- a rotary shaft 37 is disposed substantially in a central portion of a nozzle structure 44 including the modules (6, 7 and 8) that are fixed to a base plate 36, and the rotary shaft 37 is inserted into a bearing 38 that is fixed to a mounting plate 39.
- the base plate 36 and the mounting plate 39 are not fixed to each other such that the base plate 36 and the nozzle structure 44, fixed to the base plate 36, are freely rotatable. Therefore, the nozzle structure 44 is rotatable as a whole about the axis in the up and down direction and about the axis perpendicular to the axis in the direction of longitudinal width (i.e., to an axis perpendicular to the drawing sheet of Fig.
- Two adjustment screws 40 are attached to the mounting plate 39 with one screw disposed at each of the right and left sides. By moving each of the screws forward and backward (as denoted by reference symbol 42), an amount through which an upper surface of the base plate 36 is pushed down is adjusted to rotate the nozzle structure 44 through a minute angle, thereby adjusting the inclination of the nozzle 1.
- the adjustment screw one provided with a scale like a micrometer head is advantageous in enabling an adjustment amount to be confirmed and recorded, and in facilitating the adjustment operation.
- the above-described nozzle of the present invention can be applied to various types of coating devices for coating a film on a workpiece, such as a coating device including an XYZ driving mechanism to move the nozzle and the workpiece relative to each other, a gantry type device in which a frame including the nozzle provided thereon is moved relative to a fixed workpiece, and a coating device for applying a liquid material from the nozzle, which is fixedly positioned, to be coated on a continuously conveyed workpiece.
- a coating device including an XYZ driving mechanism to move the nozzle and the workpiece relative to each other
- a gantry type device in which a frame including the nozzle provided thereon is moved relative to a fixed workpiece
- a coating device for applying a liquid material from the nozzle which is fixedly positioned, to be coated on a continuously conveyed workpiece.
- a coating device according to Example is to coat an adhesive or a filler for use in optical bonding in which a protective glass and a liquid crystal display are directly bonded to each other to improve viewability.
- Fig. 8 is an explanatory view to explain an example of configuration of the coating device according to Example.
- the coating device 26 includes a tank 27 for storing the liquid material 43, an ejection valve 28 for controlling whether the liquid material 43 supplied from the tank 27 is supplied to the nozzle 1 of the present invention or stopped, the nozzle 1 of the present invention, a work table 30 on which the coating target 29 is placed, and a moving mechanism 31 for moving the nozzle 1 of the present invention and the coating target 29 placed on the work table 30 relative to each other.
- the tank 27 is a pressure vessel that supplies the liquid material 43 upon receiving a compressed gas supplied thereto.
- the liquid material 43 stored in this Example has viscosity of 1500 to 100000 mPa ⁇ s, for example.
- plural (two) tanks are prepared to be alternately used such that the operation may be continued without stopping the device each time the liquid material 43 is replenished. While, in this Example, a selector valve 33 is provided for selection of one of the tanks 27 to be used, a single tank 27 may be prepared instead.
- a pump 34 is disposed between the selector valve 33 and the ejection valve 28 such that the liquid material 43 is supplied without supplying the compressed gas to the tank 27, or while supplying the compressed gas thereto.
- the pump 34 used here is preferably, for example, a positive displacement pump such as a syringe pump, a diaphragm pump, a vane pump, or a gear pump.
- the positive displacement pump By employing the positive displacement pump, the liquid material 43 can be supplied in a fixed amount, and the amount of the ejected liquid material can be controlled with high precision.
- the ejection valve 28 is to control whether the liquid material 43 supplied from the tank 27 is supplied to the nozzle 1 of the present invention or stopped.
- the amount of the ejected liquid material is controlled by controlling an open time of the ejection valve 28.
- the nozzle 1 used here is the nozzle that is described in the above embodiment and that is illustrated in Figs. 1 and 2 .
- the number of stages for branching the flow channels, the number of the branching portions, the number of the tubules 14, and the length of the groove 15 in the direction of longitudinal width can be changed as appropriate depending on the size of the coating target 29 and the desired coating shape.
- the internal diameter of the tubule 14 is, for example, ⁇ 0.6 mm.
- the work table 30 is used for placing and fixing the coating target 29 onto it.
- the coating target 29 is firmly fixed in place with attraction through vacuuming or with abutment using a positioning pin such that the coating target 29 is not displaced when the work table 30 is relatively moved.
- the moving mechanism 31 is to move the nozzle 1 and the coating target 29 placed on the work table 30 relative to each other in any of directions denoted by reference symbol 32.
- the moving mechanism 31 may be any of the type moving only the nozzle 1, the type moving only the work table 30, and the type moving both the nozzle 1 and the work table 30 individually.
- an XYZ robot is employed as the moving mechanism 31.
- the present invention can be applied to the technique for uniformly coating the liquid material on the surface of the coating target over a wide range. More specifically, the present invention can be applied to, for example, the cases of coating a resist liquid, etc. in manufacturing of electric and electronic products, coating a phosphor paste, etc. in manufacturing of display devices, coating a super view resin (SVR) to bond a protective cover, etc. used in a flat display panel, coating an encapsulation material to encapsulate an entire surface of an organic EL panel, and coating heat-radiating grease.
- SVR super view resin
- nozzle 2 nozzle inlet 3: branching block (module) in first stage 4: branching block (module) in second stage 5: branching block (module) in third stage 6: branching portion (module) in first stage 7: branching portion (module) in second stage 8: branching portion (module) in third stage 9: branched flow in first stage 10: branched flow in second stage 11: branched flow in third stage 12: tip member 13: tube section 14: tubule 15: groove 16: inflow opening of tubule 17: outflow opening of tubule 18: tip end surface 19: innermost surface (surface with which the tube section communicates) 20: end surface of ejection port 21: inclined surface 22: inner wall (transverse direction) 23: inner wall (longitudinal direction) 24: nozzle moving direction 25: pool 26: coating device 27: tank 28: ejection valve 29: coating target 30: work table 31: moving mechanism 32: moving direction 33: selector valve 34: pump 35: adjustment mechanism 36: base plate (base member)
Landscapes
- Coating Apparatus (AREA)
- Nozzles (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011109047A JP5702223B2 (ja) | 2011-05-16 | 2011-05-16 | 膜状塗布ノズル、塗布装置および塗布方法 |
| PCT/JP2012/061335 WO2012157434A1 (ja) | 2011-05-16 | 2012-04-27 | 膜状塗布ノズル、塗布装置および塗布方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2711088A1 EP2711088A1 (en) | 2014-03-26 |
| EP2711088A4 EP2711088A4 (en) | 2015-02-25 |
| EP2711088B1 true EP2711088B1 (en) | 2020-01-15 |
Family
ID=47176769
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12786423.9A Active EP2711088B1 (en) | 2011-05-16 | 2012-04-27 | Film-coating nozzle, coating device and coating method |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2711088B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5702223B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR102006009B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN103596700B (ja) |
| ES (1) | ES2774224T3 (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI533935B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2012157434A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022184636A1 (en) * | 2021-03-01 | 2022-09-09 | Single Technologies Ab | Liquid handling means for performing assays |
Families Citing this family (30)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5702223B2 (ja) * | 2011-05-16 | 2015-04-15 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 膜状塗布ノズル、塗布装置および塗布方法 |
| JP6121203B2 (ja) * | 2013-03-13 | 2017-04-26 | 東レエンジニアリング株式会社 | 塗布器、パターン塗布装置およびパターン塗布方法 |
| JP6142268B2 (ja) * | 2013-05-28 | 2017-06-07 | 兵神装備株式会社 | 吐出幅可変装置、及び吐出装置 |
| JP6068271B2 (ja) | 2013-06-10 | 2017-01-25 | 東レ株式会社 | 塗布器、及び塗布装置 |
| KR102218589B1 (ko) * | 2013-06-20 | 2021-02-23 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 수지 도포 장치, 그 방법 및 이를 이용한 수지층 형성방법 |
| JP2015013272A (ja) | 2013-07-08 | 2015-01-22 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 塗布装置及び塗布方法 |
| JP6466845B2 (ja) | 2013-08-30 | 2019-02-06 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 板状積層体の製造方法および装置 |
| DE102014212940A1 (de) * | 2014-07-03 | 2016-01-07 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Modul, System und Verfahren zum Auftragen eines viskosen Mediums auf eine Oberfläche und Verfahren zum Herstellen des Moduls |
| JP2016111302A (ja) * | 2014-12-10 | 2016-06-20 | 株式会社Screenホールディングス | 基板処理装置 |
| JP6385864B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-18 | 2018-09-05 | 株式会社東芝 | ノズルおよび液体供給装置 |
| JP6877877B2 (ja) * | 2016-01-26 | 2021-05-26 | ノードソン コーポレーションNordson Corporation | ノズル |
| CN107398365B (zh) * | 2017-08-02 | 2019-03-12 | 东南大学 | 一种洒水车喷头 |
| CN108097538A (zh) * | 2018-02-01 | 2018-06-01 | 安徽东旭康图太阳能科技有限公司 | 光伏组件的打胶系统及打胶方法 |
| JP6554580B1 (ja) * | 2018-05-22 | 2019-07-31 | 日東電工株式会社 | 塗工膜形成方法 |
| KR102116534B1 (ko) | 2018-06-25 | 2020-05-28 | 주식회사 에이치에스하이테크 | 기판 세정용 노즐 및 그 제조 방법 |
| CN109433695B (zh) * | 2018-10-23 | 2019-08-23 | 广东顺德蓝导电器科技有限公司 | 高温高压蒸汽清洁机 |
| IT201800009720A1 (it) * | 2018-10-23 | 2020-04-23 | Isopan Spa | Dispositivo di erogazione di un liquido |
| IT201800020614A1 (it) * | 2018-12-20 | 2020-06-20 | Isopan S P A | Dispositivo per l'erogazione di un liquido |
| CN109721254B (zh) * | 2019-02-21 | 2021-01-01 | 深圳市华星光电技术有限公司 | 喷嘴以及涂布装置 |
| JP7513285B2 (ja) | 2019-04-27 | 2024-07-09 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 積層面材の製造方法および装置 |
| CN109967309A (zh) * | 2019-05-08 | 2019-07-05 | 绍兴索顿电子科技有限公司 | 一种专用高分子疏水材料的上料设备 |
| JP7213142B2 (ja) * | 2019-05-24 | 2023-01-26 | 花王株式会社 | 発熱体の製造方法 |
| JP7377641B2 (ja) * | 2019-07-31 | 2023-11-10 | タツモ株式会社 | 塗布ノズル及び塗布装置 |
| JP7170936B2 (ja) * | 2020-08-04 | 2022-11-14 | 株式会社東芝 | 塗布装置及び塗布方法 |
| JP6847566B1 (ja) * | 2020-10-01 | 2021-03-24 | 中外炉工業株式会社 | 塗布装置及び塗布方法 |
| CN112873585B (zh) * | 2021-01-12 | 2023-01-20 | 上海新昇半导体科技有限公司 | 晶棒带锯机喷嘴 |
| CN217140968U (zh) * | 2022-03-14 | 2022-08-09 | 宁德时代新能源科技股份有限公司 | 涂布模头和电池极片的涂布装置 |
| CN114985211B (zh) * | 2022-08-01 | 2022-10-25 | 潍坊市昌威交通工程有限公司 | 一种组合式高压热熔喷涂头 |
| CN115716027A (zh) * | 2022-11-30 | 2023-02-28 | 安徽环速自动化科技有限公司 | 一种用于直线导轨加工的润滑油均匀涂覆装置 |
| CN116550548A (zh) * | 2023-05-19 | 2023-08-08 | 苏州迪泰奇自动化科技有限公司 | 多支路宽幅出胶嘴 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS59109273A (ja) * | 1982-12-15 | 1984-06-23 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 回転塗布装置用ノズル |
| JPH0598625A (ja) * | 1991-04-08 | 1993-04-20 | Tatsumi Kogyo Kk | オイルフエンス形槽 |
| JP3277214B2 (ja) * | 1992-02-05 | 2002-04-22 | 株式会社スギノマシン | 急拡大型液中ジェット噴射用ノズル |
| CA2098784A1 (en) * | 1992-07-08 | 1994-01-09 | Bentley Boger | Apparatus and methods for applying conformal coatings to electronic circuit boards |
| JPH08224503A (ja) | 1995-02-21 | 1996-09-03 | Alloy Koki Kk | 塗装方法および装置 |
| JPH09206649A (ja) * | 1996-01-31 | 1997-08-12 | Sony Corp | 接着剤塗布装置 |
| JPH11290746A (ja) * | 1998-04-07 | 1999-10-26 | Musashi Eng Co Ltd | 流体の吐出路構造 |
| JP2002052731A (ja) * | 2000-08-09 | 2002-02-19 | Mimaki Engineering Co Ltd | インクジェットプロッタ |
| JP2002370057A (ja) | 2001-06-13 | 2002-12-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | エクストルージョン型ノズルおよび塗布装置 |
| JP2006084975A (ja) * | 2004-09-17 | 2006-03-30 | Fujitsu Display Technologies Corp | 液晶表示装置の製造方法及び液晶滴下装置 |
| JP4037861B2 (ja) | 2004-11-11 | 2008-01-23 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 流体の吐出路構造 |
| JP4509763B2 (ja) * | 2004-12-15 | 2010-07-21 | エムケー精工株式会社 | 気液混合流噴射装置 |
| US8163120B2 (en) * | 2005-01-28 | 2012-04-24 | Emulsion Technology Co., Ltd. | Adhesive for production of IC card, process for producing IC card, and IC card |
| US9302301B2 (en) * | 2006-12-19 | 2016-04-05 | Spraying Systems Co. | Automated tank cleaning and monitoring device |
| CN101623684A (zh) * | 2008-07-07 | 2010-01-13 | 中信国安盟固利新能源科技有限公司 | 用于锂离子电池极片的涂膜方法和涂膜设备 |
| JP5583526B2 (ja) * | 2009-09-17 | 2014-09-03 | 日本発條株式会社 | 液剤塗布装置 |
| JP5702223B2 (ja) * | 2011-05-16 | 2015-04-15 | 武蔵エンジニアリング株式会社 | 膜状塗布ノズル、塗布装置および塗布方法 |
-
2011
- 2011-05-16 JP JP2011109047A patent/JP5702223B2/ja active Active
-
2012
- 2012-04-27 EP EP12786423.9A patent/EP2711088B1/en active Active
- 2012-04-27 WO PCT/JP2012/061335 patent/WO2012157434A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2012-04-27 ES ES12786423T patent/ES2774224T3/es active Active
- 2012-04-27 CN CN201280023279.4A patent/CN103596700B/zh active Active
- 2012-04-27 KR KR1020137033271A patent/KR102006009B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2012-05-14 TW TW101117040A patent/TWI533935B/zh active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022184636A1 (en) * | 2021-03-01 | 2022-09-09 | Single Technologies Ab | Liquid handling means for performing assays |
| US12044693B2 (en) | 2021-03-01 | 2024-07-23 | Single Technologies Ab | Liquid handling means for performing assays using plate-like liquid contacting means with force controlling element |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2012157434A1 (ja) | 2012-11-22 |
| EP2711088A1 (en) | 2014-03-26 |
| EP2711088A4 (en) | 2015-02-25 |
| JP2012239930A (ja) | 2012-12-10 |
| CN103596700B (zh) | 2016-12-28 |
| ES2774224T3 (es) | 2020-07-17 |
| TW201302314A (zh) | 2013-01-16 |
| KR20140024921A (ko) | 2014-03-03 |
| JP5702223B2 (ja) | 2015-04-15 |
| KR102006009B1 (ko) | 2019-07-31 |
| CN103596700A (zh) | 2014-02-19 |
| TWI533935B (zh) | 2016-05-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2711088B1 (en) | Film-coating nozzle, coating device and coating method | |
| EP2454010B1 (en) | Metering system with variable volumes | |
| KR102394822B1 (ko) | 슬릿 코터 | |
| CA2683574C (en) | Hybrid hot melt adhesive or other thermoplastic material dispensing system | |
| EP2582470B1 (en) | Distribution manifold with multiple dispensing needles | |
| CN103331232B (zh) | 涂布喷头、具有该涂布喷头的涂布装置及其涂布方法 | |
| JP2006334483A (ja) | 塗布装置 | |
| KR101980283B1 (ko) | 슬롯 다이 코터 및 이를 구비한 구강 용해 필름 제조 장치 | |
| CN102006943B (zh) | 液体材料的排出装置及其涂布装置 | |
| KR20110039180A (ko) | 커튼 코터 | |
| US9044764B2 (en) | Device for applying viscous media | |
| JP6269215B2 (ja) | 液体噴射ヘッド及び液体噴射装置 | |
| JP5759058B1 (ja) | 微量流体流出方法および微量流体ディスペンサ | |
| US8961720B2 (en) | Method for guiding and bonding strands to a substrate | |
| JP2013046886A (ja) | パターン形成装置 | |
| JP4723417B2 (ja) | 接着材塗布装置 | |
| JP2013099738A (ja) | カーテンコーター | |
| KR20170015289A (ko) | 액체 재료 적하 장치 및 방법 | |
| CN108698406B (zh) | 流体喷射器 | |
| JP6376329B2 (ja) | 液体噴射ヘッド及び液体噴射装置 | |
| US20240191729A1 (en) | Metering module | |
| JP2013052379A (ja) | 塗布装置 | |
| US20230347648A1 (en) | An actuator component for a droplet ejection head and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2023057618A (ja) | 塗布ノズル | |
| BR112018016269B1 (pt) | Ejetor de fluido para a ejeção de volumes discretos de ejetante e método para a ejeção de volumes discretos de ejetante |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20131213 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| A4 | Supplementary search report drawn up and despatched |
Effective date: 20150123 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B05B 1/14 20060101ALI20150119BHEP Ipc: B05D 1/26 20060101ALI20150119BHEP Ipc: B05C 5/02 20060101AFI20150119BHEP |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20181022 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20190808 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602012067294 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1224692 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20200215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SK Ref legal event code: T3 Ref document number: E 33754 Country of ref document: SK |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2774224 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20200717 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200607 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200415 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200515 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200415 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200416 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602012067294 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1224692 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20201016 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200430 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200427 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200430 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20200430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200430 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200427 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20200115 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230519 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240419 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240418 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240524 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20240419 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Payment date: 20240423 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240424 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240425 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20240418 Year of fee payment: 13 |