EP2379332B1 - Verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates - Google Patents
Verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2379332B1 EP2379332B1 EP09768083.9A EP09768083A EP2379332B1 EP 2379332 B1 EP2379332 B1 EP 2379332B1 EP 09768083 A EP09768083 A EP 09768083A EP 2379332 B1 EP2379332 B1 EP 2379332B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- ink
- carrier
- color
- printed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Not-in-force
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J2/00—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed
- B41J2/005—Typewriters or selective printing mechanisms characterised by the printing or marking process for which they are designed characterised by bringing liquid or particles selectively into contact with a printing material
- B41J2/01—Ink jet
- B41J2/135—Nozzles
- B41J2/14—Structure thereof only for on-demand ink jet heads
- B41J2/14016—Structure of bubble jet print heads
- B41J2/14161—Structure having belt or drum with holes filled with ink
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for printing a substrate, wherein the color is transferred from a color carrier to the substrate according to a predetermined pattern by energy is introduced by a device for introducing energy through the ink carrier in the color, wherein the color carrier and the Do not touch the substrate. Furthermore, the invention relates to a printing machine, comprising a color carrier, which is coatable with a paint Jerusalemschudruckenden, and a device for introducing energy into the ink, wherein the device for introducing energy is arranged so that the energy in a pressure range on the Color remote from the color carrier can be introduced so that color is transmitted in a field of application of energy from the ink carrier to a substrate to be printed.
- a method for printing on a substrate, in which drops of paint are thrown from a color-coated carrier onto a substrate to be printed is for example off US-B 6,241,344 known.
- energy is introduced by the carrier into the ink on the carrier at the position where the substrate is to be printed.
- a part of the color evaporates, so that it dissolves from the carrier.
- Due to the pressure of the evaporating paint the ink droplet thus dissolved is thrown onto the substrate. Directed penetration of energy can be transferred in this way, the color corresponding to a pattern to be printed on the substrate.
- the necessary energy for transferring the color is introduced, for example, by a laser.
- the carrier on which the paint is applied for example, is a circulating belt, on which by means of a coating device in front of the printing area color is applied.
- the laser is located inside the circulating belt, so that the laser acts on the carrier on the side facing away from the paint.
- a corresponding printing machine is still for example also off US 5,021,808 known. Again, color is applied from a reservoir with an applicator on a circulating belt, which is within the circulating belt, a laser through which the ink is evaporated at predetermined positions and is thrown onto the substrate to be printed.
- the tape is made of a transparent material for the laser.
- the circulating belt to be coated with an absorption layer in which the laser light is absorbed and converted to heat, thus vaporizing the paint at the deployment position of the laser.
- EP 0 947 324 A1 For example, a printing method is known in which color is transferred from a carrier to a substrate with a laser. In addition, an electrostatic field can be applied.
- the application of the paint on the flexible support is generally carried out by rolling mills, wherein a roller immersed in a paint-containing reservoir and the color is transferred by means of the roller on the flexible support.
- the object of the present invention is to provide a method and a printing press for printing a substrate, in which inexact edges and edges in the printed image are reduced or avoided.
- the object is achieved by a method for printing a substrate, in which color is transferred from a color carrier to the substrate according to a predetermined pattern by energy from a device for introducing energy through the ink carrier is introduced into the color, wherein the color carrier and do not touch the substrate.
- the substrate is placed in an electric field so that a charge field is generated on the surface of the substrate, wherein the substrate is first discharged and then charged.
- the charge field can be both homogeneous and heterogeneous.
- a heterogeneous charge field may have a gradient or according to the be formed on the pattern to be printed.
- the charge field is preferably homogeneous.
- an improvement of the printed image is achieved.
- more exact edges and edges can be produced than on a substrate to which no homogeneous charge field is impressed on the surface.
- the improvement of the printed image is achieved despite the printing gap at which the color is transferred from the carrier to the substrate, which initially leads to disordered field lines.
- the nip is the gap between the ink carrier and the substrate, in which the ink is transferred from the ink carrier to the substrate.
- the substrate is introduced into the electric field before transferring the ink.
- a voltage may be applied or a current applied.
- the voltage can be applied touching or non-contact.
- the voltage is applied by applying an electrode to the substrate.
- the inserted electrode can cover only a part or the entire width of the substrate to be printed. It is preferred if the electrode covers the entire width of the substrate.
- a rod electrode along which the substrate is guided. This can be done both touching and non-contact.
- the electrode does not touch the substrate.
- the substrate to be printed to generate the homogeneous charge field at the surface by the application of the voltage or the transfer of the current substantially homogeneously discharged.
- the substrate is discharged by applying a current, it is possible to dissipate the charge directly or indirectly.
- Suitable circuits with which the charge can be discharged are known to the person skilled in the art.
- a discharge potential or a ground potential is applied to the substrate. This reduces the potential on the surface of the substrate. In order to discharge the substrate, the discharge potential is smaller than the potential of the substrate to be discharged. Suitable methods for discharging the substrate by applying a voltage are also known to those skilled in the art.
- the substrate is substantially homogeneously charged by applying the voltage or transmitting the current.
- the application of the voltage or the transmission of the current can be carried out in any manner known to those skilled in the art.
- a voltage source or a current source is connected to the substrate for this purpose.
- the substrate for discharging a homogeneous charge field on the surface is first discharged and then charged.
- Discharging and charging can be carried out as previously described.
- the discharging it is possible for the discharging to take place by applying a voltage and charging by transmitting a current, or discharging by transmitting a current and charging by applying a voltage.
- both the discharging and the charging it is also possible for both the discharging and the charging to take place by applying a voltage or transmitting a current.
- the substrate to be printed and the ink carrier in the printing area have a printing gap in the range from 0 to 2 mm, in particular in the range from 0.01 to 1 mm.
- the smaller the printing gap between the ink carrier and the substrate to be printed the less the drop expands when it strikes the substrate to be printed, and the more uniform the printed image remains.
- it is also important to the substrate to be printed does not touch the color-coated flexible support so that ink is not transferred from the flexible support to the substrate to be printed in undesired places.
- pressure range refers to the region in which energy is introduced into the ink, a part of the ink evaporates and a color drop is thereby transferred to the substrate to be printed.
- the energy is preferably introduced focused into the color by the flexible carrier.
- the size of the point to which the energy to be introduced is focused corresponds to the size of the transferred Point depending on the substrate.
- points to be transferred have a diameter in the range of about 20 ⁇ m to about 200 ⁇ m.
- the size of the point to be transferred may differ depending on the substrate to be printed and the printed product produced therewith. For example, it is possible to choose a larger focus, especially in the production of printed circuit boards.
- printed matters in which a font is displayed generally small printing dots are preferred for producing a clear typeface. Even when printing images and graphics, it is advantageous to print as small dots as possible to create a clear image.
- a flexible carrier is preferably used.
- the ink carrier which is coated with the ink to be printed, designed band-shaped.
- the color carrier is a film.
- the thickness of the ink carrier is preferably in the range of 1 .mu.m to about 500 .mu.m, in particular in the range of 10 .mu.m to 200 .mu.m. It is advantageous to carry out the ink carrier as possible in a small thickness, so that the energy introduced by the ink carrier is not scattered in the ink carrier and so a clean print image is generated.
- transparent polymer films are suitable, for example, for the energy used.
- a laser is preferably used as energy used to vaporize the ink and transfer it to the substrate to be printed.
- Advantage of a laser is that the laser beam used can be bundled to a very small cross-section. A targeted energy input is thus possible.
- a suitable absorber is contained in the ink, which absorbs the laser light and converts it into heat.
- the color carrier is coated with a corresponding absorber or is made of such an absorber or contains such an absorber, which absorbs the laser light and converts it into heat.
- the ink carrier is made of a transparent material for the laser radiation and the absorber, which converts the laser light into heat, is included in the color.
- Suitable absorbers are, for example, carbon black, metal nitrites or metal oxides.
- Suitable lasers which can be used to introduce energy into the paint are, for example, fiber lasers operating in the fundamental mode.
- any printing ink known to the person skilled in the art is suitable.
- liquid colors usually included used liquid paints at least one solvent and color-forming solids, for example pigments.
- the paint contains, for example, a solvent and electrically conductive particles dispersed in the solvent.
- a printed circuit board can be printed with the ink used.
- the color also contains an additive that absorbs the laser radiation and converts it into heat.
- the substrate to be printed is preferably paper.
- any other substrate can also be printed by the method according to the invention.
- plastics such as plastic films, metal foils or composite films can be printed.
- plastic films, metal foils or composite films are used, for example, for packaging.
- the method is suitable for printing on printed circuit boards.
- the substrate to be printed is usually any printed circuit board substrate known to those skilled in the art.
- the printed circuit substrate can be both solid and flexible.
- a suitable printing press comprises a color carrier coated with a paint to be printed, and a device for introducing energy into the ink, wherein the device for introducing energy is arranged so that the energy in a printing area on the side facing away from the color Ink carrier can be introduced so that color is transferred in an area of influence of energy from the ink carrier to a substrate to be printed.
- a voltage source or a current source is furthermore included.
- Any voltage source or current source known to those skilled in the art is suitable as a voltage source or as a current source for generating the electric field.
- the voltage source or the current source generally comprises a first electrode, which in a first embodiment can be contacted with the substrate.
- the contact of the electrode with the substrate takes place, for example, by contact.
- the voltage source or the current source comprises a first electrode, via which voltage is applied to the substrate in a contactless manner by applying an electric field or a current is transmitted to the substrate.
- the electrode extends over the entire width of the substrate.
- the electrode when the electrode contacts the substrate for applying the voltage or transmitting the current, the electrode is preferably applied to the substrate over the entire width. If the voltage is applied without contact or the current is transmitted without contact, it is preferred if the distance between the substrate and the electrode is constant over the entire length of the electrode in order to achieve the homogeneous charge distribution at the surface of the substrate.
- the first electrode contacts the substrate over the entire width
- this is preferably formed in the form of a rod.
- the electrode may have, for example, a circular or a rectangular cross-section. However, any other cross section of the electrode is possible.
- the electrode may also be formed with an oval cross section or a polygonal cross section with any number of corners.
- a plate as the electrode, for example. Even when using a plate, it is advantageous if the electrode extends over the entire width of the substrate, so that the generated charge field is homogeneous at the surface of the substrate.
- the material for the electrode any, known in the art, electrically conductive material is suitable.
- comb-shaped or brush-shaped electrodes are also suitable, wherein the comb-shaped or brush-shaped electrodes preferably also cover the substrate over the entire width.
- the voltage source comprises a second electrode, which is also contactable with the substrate.
- the first electrode to one side of the substrate and the second electrode to the other side of the substrate, so that a current flows through the substrate. In this way, a homogeneous charge field can likewise be generated on the surface of the substrate.
- the device for introducing energy is, as already described above, preferably a laser.
- the ink carrier which is coatable with the ink to be printed, is preferably a flexible carrier.
- the ink carrier is stored in a suitable device.
- the color carrier which is coated with paint
- the color-coated ink carrier is then unwound and passed over the printing area in which is transferred by means of the device for introducing energy color to the substrate to be printed.
- the ink carrier is rewound, for example, again on a roll, which can then be brought to disposal.
- the ink carrier is formed as a circulating belt.
- ink is applied to the ink carrier with a suitable applicator before it reaches the printing position, ie the point at which the ink is transferred from the ink carrier to the substrate to be printed with the aid of the energy input. After printing, some of the ink has been transferred from the ink carrier to the substrate. As a result, there is no more homogeneous color film on the color carrier. Thus, for a next printing operation, it is necessary to re-coat the ink carrier with ink. This is done the next time the corresponding position on the paint application device.
- the paint located on the ink carrier Before a subsequent application of ink to the ink carrier, it is advantageous to first remove the paint located on the ink carrier before a subsequent application of ink to the ink carrier.
- the removal of the paint can be done for example by means of a roller or a squeegee. If a roll is used to remove the paint, it is possible that the same roll is used, with which the color is applied to the ink carrier. For this purpose, it is advantageous if the rotational movement of the roller of the movement of the ink carrier is directed opposite. The color removed from the ink carrier can then be returned to the ink supply.
- a roller is provided for removing the paint, it is of course also possible that a roller for removing the paint is provided and a roller for applying paint.
- the ink is to be removed from the ink carrier with a squeegee, any doctor known to those skilled in the art can be used.
- the ink carrier by means of a counter roll against the applicator roll, with which the ink is applied to the ink carrier, or the role with which the ink is removed from the ink carrier, or the squeegee that removes the ink from the ink carrier is pressed.
- the back pressure is adjusted so that the color is substantially completely removed, but it does not cause damage to the color carrier.
- the printing press comprises a tensioning device in order to tension the ink carrier.
- a tensioning device in order to tension the ink carrier.
- tensioning the ink carrier any distortion waves occurring in the ink carrier are smoothed.
- a homogeneous surface in the printing area can be achieved.
- Different gap widths, which arise for example by waves in the ink carrier, are thus prevented and the printed image is thereby improved.
- a suitable tensioning device comprises at least two guide elements arranged on both sides of the device for introducing energy.
- guide elements are, for example, tensioners, air cushions or stationary rods.
- the tensioning device comprises a guide element permeable to the energy used.
- the guide element which is permeable to the energy used is in this case directly at the pressure area. This means that the guide element is positioned between the device for introducing energy and the flexible carrier, so that the energy with which the ink is vaporized from the carrier to the substrate must be passed through the guide element.
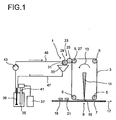
- the single figure shows a schematic representation of an inventively designed printing machine.
- a printing machine 1 comprised a color carrier 3, which is designed as an endless belt in the embodiment shown here and is guided around a plurality of deflection rollers 5. On the ink carrier 3, a color for printing a substrate 7 is applied.
- energy is introduced through the ink carrier 3 in the paint in a pressure range.
- a part of the color evaporates, whereby a drop of paint is thrown onto the substrate 7.
- a laser 11 is suitable as energy that is introduced into the paint.
- Suitable lasers 11 which can be used to introduce energy into the paint are, for example, fiber lasers which are operated in the ground mode.
- the ink carrier 3 In order to replace the transferred by means of the laser 11 to the substrate 7 color, the ink carrier 3, as shown by the arrow 13, moves around the pulleys 5.
- the transport direction 13 of the ink carrier 3 in the printing area 9 is preferably However, since a pressure gap 15 is generally formed between the substrate 7 to be printed and the ink carrier 3, it is also possible for the ink carrier 3 to move in the opposite direction to the transport direction of the substrate 7. It is also possible that color carrier 3 and substrate 7 have different speeds. Preferably, however, the speed of the ink carrier 3 and the substrate 7 is rectified and the same size. In the embodiment shown here, the substrate 7 and the ink carrier 3 are moved in the same direction.
- the transport direction of the substrate 7 is shown by an arrow 17. If a multiple printing is desired, ie that a line is printed several times, it is advantageous if the ink carrier 3 moves at a greater speed than the substrate. 7
- the printing press 1 in the embodiment illustrated here comprises a discharge device 19 and a charging device 21.
- the discharge device 19 any power source or voltage source known to those skilled in the art can be used.
- a charging device 21 any, known in the art power source or voltage source can be used.
- the current can be transmitted contactless or by contact both in the discharge device 19 and in the charging device 21.
- the application of a voltage can also be done contactless or by contact.
- the discharge device 19 or the charging device 21 comprises at least one electrode.
- the electrode can be designed, for example, rod-shaped. In this case, the electrode preferably extends over the entire width of the substrate 7 to be printed. A defined counterelectrode is not required.
- any component of the printing machine can be used for example as a counter electrode.
- first and a second electrode it is also possible to provide a first and a second electrode.
- the current transmission or the application of the voltage is preferably carried out by contact of the electrodes with the substrate 7 to be printed.
- the electrodes are preferably applied opposite to the substrate in order to produce a homogeneous charge field.
- the electrodes can be arranged laterally on the substrate 7 to be printed or, alternatively, on the upper side and the lower side of the substrate 7 to be printed.
- a discharge device 19 and a charging device 21 instead of employing a discharge device 19 and a charging device 21, it is also possible to provide either a discharge device 19 or a charging device 21, around the homogeneous charge field on the surface of the substrate 7 to produce. It is also possible, for example, to provide a plasma treatment of the substrate 7 in place of the charging device 21 before the paint is applied to the substrate 7.
- the ink that is printed on the substrate 7 in the printing area 9 is applied to the ink carrier 3 with an applicator 23.
- the applicator 23 in the embodiment shown here comprises an applicator roll 25 with which the ink is applied to the ink carrier 3.
- the contact pressure required for applying the ink is realized by a counter-roller 27, which also serves as a deflection roller 5 for the ink carrier 3.
- a Einfetzze 29 With the help of a Einfärbewalze 29, the color is applied to the applicator roll 25.
- the inking roller 29 is inked in the embodiment shown here via a Einärbeschild 31.
- the inking roller 29 can also be coated with ink by any other device known to the person skilled in the art.
- the inking roller 29 it is thus possible, for example, for the inking roller 29 to be immersed in a reservoir of paint and thus to be coated with paint. It is also possible that the inking roller 29 is dispensed with and only one application roller 25 is provided. Also, more than two rollers may be provided to apply the ink to the ink carrier 3.
- a drip catcher 33 is provided in the embodiment shown here. Trapped by the drip 33 color is passed back into a reservoir 35 containing the color.
- the color contained in the reservoir 35 can be added as needed from a solvent tank 37 solvent. This is necessary, for example, to replace evaporating solvent from the reservoir 35. Also can be supplemented from the solvent tank 37 solvent, which evaporates from the color which is applied to the ink carrier 3, and with the help of the applicator roller 25 after printing again removed from this and fed back into the reservoir 35.
- an agitator 39 is further preferably provided.
- agitator 39 is any, known in the art agitator.
- any stirrer may be provided. Suitable stirrers are, for example, propeller stirrers, disk stirrers, lattice stirrers, smooth stirrers, anchor stirrers or radial stirrers.
- the amount of solvent that has to be metered from the solvent tank 37 into the storage tank 35 can be determined, for example, by measuring the viscosity of the paint in the storage tank 35.
- About the viscometer 41 is then the amount of solvent to be dosed determined.
- the viscometer 41 is equipped with an automatic dosage for the solvent.
- the paint is transported by a circulation pump 43 through a supply line 45 to Einärbeschild 31.
- the ink is then applied to the inking roller 29 with the inking label 31. Excess paint drips back into the drip 33 and runs from there via a return line 47 back into the reservoir 35th
- color not transferred to the substrate 7 is removed again from the ink carrier 3 after printing with the aid of the applicator roll 25.
- the direction of rotation of the applicator roller 25 is opposite to the transport direction 13 of the ink carrier 3. The removed by means of the applicator roll 25 from the ink carrier 3 color is stripped by means of the inking roller 29 of the applicator roll 25 and drips into the drip 33, from which it is conveyed via the return line 47 back into the reservoir 35.
Landscapes
- Printing Methods (AREA)
- Ink Jet (AREA)
- Printers Or Recording Devices Using Electromagnetic And Radiation Means (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09768083.9A EP2379332B1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2009-12-14 | Verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP08171921 | 2008-12-17 | ||
| EP09768083.9A EP2379332B1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2009-12-14 | Verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates |
| PCT/EP2009/067022 WO2010069901A1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2009-12-14 | Verfahren und druckmaschine zum bedrucken eines substrates |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2379332A1 EP2379332A1 (de) | 2011-10-26 |
| EP2379332B1 true EP2379332B1 (de) | 2014-02-26 |
Family
ID=41627887
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09768083.9A Not-in-force EP2379332B1 (de) | 2008-12-17 | 2009-12-14 | Verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20110310205A1 (es) |
| EP (1) | EP2379332B1 (es) |
| JP (1) | JP5764495B2 (es) |
| CN (1) | CN102317078B (es) |
| ES (1) | ES2456491T3 (es) |
| TW (1) | TWI517984B (es) |
| WO (1) | WO2010069901A1 (es) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101673639B1 (ko) | 2009-03-24 | 2016-11-22 | 바스프 에스이 | 열교환기용 열자기 성형체 제조를 위한 인쇄 방법 |
| WO2011026852A1 (de) | 2009-09-04 | 2011-03-10 | Basf Se | Zusammensetzung zum drucken von elektroden |
| KR101789838B1 (ko) | 2009-09-04 | 2017-10-25 | 바스프 에스이 | 전도체 트랙을 인쇄하기 위한 조성물 및 태양 전지를 제조하기 위한 방법 |
| KR20130008554A (ko) | 2010-02-17 | 2013-01-22 | 바스프 에스이 | 태양 전지들 간의 전기 전도성 결합을 생성시키는 방법 |
| JP6126489B2 (ja) * | 2013-07-29 | 2017-05-10 | キヤノン株式会社 | 記録素子基板、記録ヘッド及び記録装置 |
| DE102013215638A1 (de) * | 2013-08-08 | 2015-02-12 | Krones Ag | Vorrichtung zum Bedrucken von Behältern |
| DE102017203817A1 (de) * | 2017-03-08 | 2018-09-13 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Energiespeichersystem, Verwendung eines Energiespeichersystems, Ladevorrichtung, System und Verfahren zum Laden eines Energiespeichers |
| EP3743287B1 (en) | 2018-01-27 | 2022-07-20 | HELIOSONIC GmbH | Laser printing process |
| WO2019175056A1 (en) | 2018-03-12 | 2019-09-19 | Altana Ag | Laser printing process |
| US11999181B2 (en) | 2019-09-10 | 2024-06-04 | Heliosonic Gmbh | Laser induced transfer printing process |
Family Cites Families (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3745586A (en) * | 1971-07-01 | 1973-07-10 | Rca Corp | Laser writing |
| US4320408A (en) * | 1978-10-06 | 1982-03-16 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Method of forming electrostatic image |
| JPS5667267A (en) * | 1979-11-08 | 1981-06-06 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Ink jet recording system |
| JPS57174268A (en) * | 1981-04-20 | 1982-10-26 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Ink jet printer |
| JPS61127357A (ja) * | 1984-11-26 | 1986-06-14 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | インクジエツト記録装置 |
| JPS61272163A (ja) * | 1985-05-28 | 1986-12-02 | Nec Corp | ミストバブルインクジエツト |
| DE3702643A1 (de) | 1986-02-10 | 1987-08-13 | Toshiba Kawasaki Kk | Tintenstrahlschreiber sowie schreibkopf und schreibkopfkassette dafuer |
| JPH0661937B2 (ja) * | 1986-05-27 | 1994-08-17 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | インクジエツト記録装置 |
| JPH0199856A (ja) * | 1987-10-12 | 1989-04-18 | Seiko Epson Corp | 画像形成装置 |
| JPH0259350A (ja) * | 1988-08-25 | 1990-02-28 | Ricoh Co Ltd | インクジェット記録装置 |
| JP3104326B2 (ja) * | 1991-10-17 | 2000-10-30 | ミノルタ株式会社 | 画像記録装置 |
| JPH05131633A (ja) * | 1991-11-13 | 1993-05-28 | Minolta Camera Co Ltd | 記録方法 |
| WO1995035212A1 (en) * | 1994-06-17 | 1995-12-28 | Natural Imaging Corporation | Electrohydrodynamic ink jet printer and printing method |
| CN1126849A (zh) * | 1995-03-20 | 1996-07-17 | 株式会社日立制作所 | 成象方法和装置 |
| JPH08207283A (ja) * | 1995-10-25 | 1996-08-13 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 液体噴射記録ヘッド |
| JPH09207376A (ja) * | 1996-02-07 | 1997-08-12 | Sharp Corp | 画像形成装置 |
| RU2088411C1 (ru) | 1996-02-19 | 1997-08-27 | Сергей Николаевич Максимовский | Способ печати и печатающее устройство для его осуществления |
| JP3163249B2 (ja) * | 1996-03-14 | 2001-05-08 | シャープ株式会社 | 画像記録装置 |
| WO1998030395A1 (fr) * | 1997-01-08 | 1998-07-16 | Kabushiki Kaisha Tec | Imprimante a jet d'encre |
| JPH11138773A (ja) | 1997-11-10 | 1999-05-25 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | 画像形成方法および画像形成装置 |
| JP2004230709A (ja) * | 2003-01-30 | 2004-08-19 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | インクジェット式記録装置 |
| US20070097162A1 (en) * | 2003-08-08 | 2007-05-03 | Konica Minolta Holdings, Inc. | Liquid ejection apparatus, liquid ejection method, and method for forming wiring pattern of circuit board |
| JP2006184403A (ja) * | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 定着装置 |
| JP2007007949A (ja) * | 2005-06-29 | 2007-01-18 | Fujifilm Holdings Corp | 活性エネルギー硬化型インクジェット記録装置及びその記録方法 |
-
2009
- 2009-12-14 CN CN200980156594.2A patent/CN102317078B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-12-14 WO PCT/EP2009/067022 patent/WO2010069901A1/de active Application Filing
- 2009-12-14 ES ES09768083.9T patent/ES2456491T3/es active Active
- 2009-12-14 EP EP09768083.9A patent/EP2379332B1/de not_active Not-in-force
- 2009-12-14 US US13/140,530 patent/US20110310205A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2009-12-14 JP JP2011541371A patent/JP5764495B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-12-17 TW TW098143451A patent/TWI517984B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102317078B (zh) | 2014-05-28 |
| JP2012512067A (ja) | 2012-05-31 |
| TWI517984B (zh) | 2016-01-21 |
| JP5764495B2 (ja) | 2015-08-19 |
| US20110310205A1 (en) | 2011-12-22 |
| CN102317078A (zh) | 2012-01-11 |
| TW201033022A (en) | 2010-09-16 |
| EP2379332A1 (de) | 2011-10-26 |
| WO2010069901A1 (de) | 2010-06-24 |
| ES2456491T3 (es) | 2014-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2379332B1 (de) | Verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates | |
| EP2379335B1 (de) | Verfahren und druckmaschine zum bedrucken eines substrates | |
| EP2385900B1 (de) | Druckmaschine sowie verfahren zum bedrucken eines substrates | |
| DE102013109636B4 (de) | Integriertes beschichtungssystem | |
| WO1994004364A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum befeuchten einer bedruckten und anschliessend thermsich getrockneten, bewegten materialbahn | |
| DE102012212751B4 (de) | Verfahren, vorrichtung und systeme zum verteilen von strahlenhärtbarer geltinte | |
| DE102015104321A1 (de) | Verfahren, Applikationsvorrichtung und Druckvorrichtung zum Applizieren einer Folie | |
| WO2002018142A1 (de) | Anlage zur kontinuierlichen herstellung bedruckter textilbänder, insbesondere bedruckter etikettenbänder | |
| WO2010069902A1 (de) | Verfahren und druckmaschine zum bedrucken eines substrats | |
| EP2474210B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von elektrisch leitfähigen oberflächen | |
| DE102014224276B4 (de) | Verfahren zum hochpräzisen Drucken von Strukturen auf Oberflächen sowie Substrat mit einer eine gedruckte Struktur aufweisenden Oberfläche | |
| WO2007085384A1 (de) | Verfahren zum tintenstrahldrucken mit lichthärtender tinte | |
| DE102015204980A1 (de) | Druckmaschine mit zumindest einem Selektivtrockner und ein Verfahren zur zumindest teilweisen Trocknung eines Bedruckstoffs | |
| EP3917780B1 (de) | Verfahren und druckmaschine jeweils zum bedrucken eines metallischen bedruckstoffes | |
| WO2013185920A2 (de) | Verfahren zum indirekten auftragen von druckflüssigkeit auf einen bedruckstoff | |
| DE102012024393A1 (de) | Verfahren zum indirekten Auftragen von Druckflüssigkeit auf einen Bedruckstoff | |
| EP2155499B1 (de) | Druckmaschine und druckverfahren hierfür | |
| WO2008087196A1 (de) | Verfahren zum übertragen von strukturinformationen und vorrichtung hierfür | |
| DE102009003445B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Bedrucken einer Bahn | |
| DE102020120411B4 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Bedrucken eines Aufzeichnungsträgers mit einem Druckgerät | |
| DE102013001825A1 (de) | Verfahren zum indirekten Auftragen von Druckflüssigkeit auf einen Bedruckstoff | |
| DE102012004634A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Erzeugen einer Schicht auf einem Substrat | |
| DE102008007228B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Erzeugen mindestens eines Druckbildes auf einem Bildträger | |
| DE10139822B4 (de) | Thermografische Druckeinrichtung und thermografisches Druckverfahren | |
| DE102006057969A1 (de) | Zentraltrockner für mehrere Auftragswerke |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20110718 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20121105 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20130917 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 653326 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20140315 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502009008860 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20140410 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2456491 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20140422 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140626 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140526 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140626 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502009008860 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20141127 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502009008860 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20141127 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20141214 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20141214 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20150831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141214 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141231 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141231 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141231 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 653326 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20141214 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141214 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140527 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20091214 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20170228 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20170127 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502009008860 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20180703 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20190703 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20171215 |