EP1657203A2 - Installation de levage guidée avec parachute amorti - Google Patents
Installation de levage guidée avec parachute amorti Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1657203A2 EP1657203A2 EP05024622A EP05024622A EP1657203A2 EP 1657203 A2 EP1657203 A2 EP 1657203A2 EP 05024622 A EP05024622 A EP 05024622A EP 05024622 A EP05024622 A EP 05024622A EP 1657203 A2 EP1657203 A2 EP 1657203A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- basket
- lifting device
- safety gear
- stage
- cabin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66D—CAPSTANS; WINCHES; TACKLES, e.g. PULLEY BLOCKS; HOISTS
- B66D5/00—Braking or detent devices characterised by application to lifting or hoisting gear, e.g. for controlling the lowering of loads
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/02—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators responsive to abnormal operating conditions
- B66B5/04—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators responsive to abnormal operating conditions for detecting excessive speed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B66—HOISTING; LIFTING; HAULING
- B66B—ELEVATORS; ESCALATORS OR MOVING WALKWAYS
- B66B5/00—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators
- B66B5/02—Applications of checking, fault-correcting, or safety devices in elevators responsive to abnormal operating conditions
- B66B5/16—Braking or catch devices operating between cars, cages, or skips and fixed guide elements or surfaces in hoistway or well
- B66B5/18—Braking or catch devices operating between cars, cages, or skips and fixed guide elements or surfaces in hoistway or well and applying frictional retarding forces
Definitions
- the invention relates to a guided lifting device with a stage, a basket or a car according to the preamble of claim 1, ie in particular a lift, and an attenuator and a triggering device for a safety gear to intercept the guided lifting device in case of failure.
- a guided lifting device of the present type therefore comprises at least one guide rail, on which the stage, the basket or the cabin is movably guided, a safety device which is attached directly or indirectly to the stage, the basket or the cabin and a contact surface for a in Direction of movement extending brake rail or for the guide rail, and a triggering device for the safety gear, which cooperates with the safety device at a given unacceptable acceleration of the stage, the basket or the car so that the contact surface thereof in frictional or non-positive contact with the brake rail or the guide rail steps to catch the stage, basket or cabin.
- Known safety devices for such a guided lifting device conventionally operate as a safety catching device according to the wedging principle, in which either a cylindrical locking roller or a safety catch is pressed over the triggering device into a wedge-shaped shaft of a catching housing which is opposite to the direction of movement.
- a safety catching device according to the wedging principle, in which either a cylindrical locking roller or a safety catch is pressed over the triggering device into a wedge-shaped shaft of a catching housing which is opposite to the direction of movement.
- the roller or the wedge comes into contact with the brake rail running through the catching housing, the roller or the wedge according to the self-help principle in the catching housing becomes complete wedged and so braked the stage, the basket or the cab on the brake rail and held.
- a catch wedge is driven as in the locking device in a wedge-shaped shaft to wedge on the brake rail and intercept the stage, the basket or the car;
- a spring-loaded fishing jaw is used on the opposite side of the brake rail, which cooperates with the catch wedge floating.
- the catch wedge runs in the wedge-shaped shaft against a mechanical stop, so that the catching force can be set defined in total defined by a corresponding dimensioning of the spring force of the spring-loaded fishing jaw.
- a safety gear has become known in which a contact surface for frictional or non-positive contact with a brake rail is biased by a mechanical spring against the brake rail, wherein a pressure medium cylinder for compensating the biasing force of the spring is present, to open the safety gear.
- the biasing force of the spring is compensated by the pressure medium cylinder, so that the contact surface is lifted from the brake rail and the movement of the lifting device is released.
- the brake is closed by the spring in the rest position with maximum braking force, so that is guaranteed for safety reasons even in case of failure of all systems that the lifting device is reliably fixed to the brake rail.
- the safety devices in the prior art have in common that their braking force significantly overcompensates the weight of the stage, the basket or the cab when fully loaded, to ensure a reliable catch even when fully loaded.
- this has the consequence that at partial load, especially at low loading of the stage, the basket or the cabin, the braking force generated by the safety gear in case of failure very much higher than necessary, resulting in an undesirable abrupt deceleration.
- EP 0 648 703 B1 it is proposed in EP 0 648 703 B1 to use a pressure regulating valve in the outlet of the pressure medium cylinder, to additionally measure the speed or the deceleration of the stage, the basket or the cabin and to form a control circuit which controls the pressure regulating valve regulates that the braking force of the safety gear is adapted to the respective load condition.
- the triggering of the safety gear takes place here via an electrical control using the signals of a speed sensor as a manipulated variable.
- the problem here is that in case of power failure, the system is not functional.
- such an additional control loop with additional sensors means an additional potential source of error as well as additional outlay during setup and maintenance.
- the present invention is therefore an object of the invention to improve a guided lifting device of the type mentioned in terms of their safety gear to the effect that a simple and reliable way to adapt the braking force of the safety gear to the respective loading condition of the stage, the basket or the car.
- the safety gear is thus additionally provided with an attenuator, which ensures a ramp-like increase in the braking force.
- the ramp is here designed so that a stage, a basket or a car that is not fully loaded, comes to a halt after the activation of the safety gear even before the maximum braking force acts.
- the braking force of the safety gear with an attenuator according to the invention is thus initially adapted to an empty stage, basket or cabin and then steadily increases until the maximum braking force acts, which overcompensates the weight of the stage, the basket or the cabin in fully loaded condition .
- the length of the ramp is inventively chosen so that a lightly loaded stage, basket or cabin already comes to a halt in the rising phase of the brake force ramp, so that in the end not the full braking force to intercept the stage, the basket or the cabin is used. This results in a beneficial gentle catch. Even with a stage, a basket or a cab with full load, the invention offers advantages, since the braking effect of the safety gear not abruptly but gently starts and increases until the stage, the basket or the cabin comes to a standstill.
- the decisive advantage of the invention over the hitherto known solutions for a safety gear and for the load-dependent control of the braking force of the safety gear is in any case that by the ramp-like increase in the braking force of the safety gear due to the attenuator according to the invention and by a correspondingly adapted interpretation of the length of this ramp simplest and more reliable means is achieved that a stage, a basket or a car, which is not fully loaded, is intercepted with significantly lower, adapted braking force, as a stage, a basket or a car with full load.
- the inventively existing attenuator can cause the increase in the braking force of the safety gear in dependence on the distance covered the stage, the basket or the cabin since the triggering of the safety gear; However, this can also be done indirectly by the ramp is selected, for example, depending on the time that has elapsed since the triggering of the safety gear.
- the invention can be used in conventional safety gear with a catch wedge and a catcher housing with wedge-shaped shaft, wherein the attenuator is then implemented so that the shaft is significantly longer than previously executed, in such a way that a not fully loaded stage, basket or cabin comes to a stop before the catch wedge generates its maximum braking force.
- a safety catch device can be "adapted" to the current loading state of the stage, the basket or the cabin.
- the attenuator of the invention may be formed as a mechanical damping of the contact surface, resulting in the application of the contact surface of the brake rail a damped onset of braking force and thereby the ramp according to the invention is generated.
- the invention can be used in a guided lifting device whose safety catch comprises a spring element which biases the contact surface against the brake rail or the guide rail, and an actuating element for compensating the biasing force of the spring element as required and is designed so that the contact surface by driving the Actuator can be employed on the brake rail or the guide rail and parked by this.
- the inventively existing attenuator can easily act on the activation of the actuator and delay this, so that the biasing force of the spring element increases according to the invention ramp-like.
- a force-intensifying transmission kinematics is used in the safety gear, by means of which the spring element acts on the contact surface.
- This translation kinematics can be designed, for example, as a toggle lever translation. Due to the very high gear ratio of a toggle lever translation, a comparatively weak spring element can be used, which requires little installation space. Furthermore, a toggle lever translation has the further advantage that it can be designed so that the gear ratio increases just as quickly or even faster than the spring force of a mechanical spring when relaxing the same decreases. Irregularities on the brake rail no longer have to lead to adverse changes in the braking force.
- the spring element of a safety device designed in this way is preferably a mechanical spring, while the actuating element for compensating the spring force may be a hydraulically or pneumatically actuated piston-cylinder unit.
- a mechanical spring package is not susceptible to interference and thus offers the advantage that the safety gear still works even if the hydraulic system or the pneumatic system fails.
- the inventively existing attenuator can then be advantageously arranged so that it specifically delays the outflow of the pressure medium from the piston-cylinder unit and thereby generates the ramp-like increase in the braking force, ie in particular the spring force of the spring element. It is particularly advantageous if a pressure accumulator for the hydraulic or pneumatic pressure means is present, which dynamically stabilizes the delayed flow of the pressure medium and the associated back pressure.
- the present invention existing attenuator is preferably integrated into the triggering device of the safety gear, so that it is automatically activated as soon as the triggering device responds.
- the attenuator according to the invention can be designed so that it is an inlet for the catching device for interception the stage, the basket or the cabin effluent pressure medium, a drain for this pressure medium and a back pressure valve between the inlet and the drain has.
- the dynamic pressure valve is in this case designed such that it increases the flow rate of the pressure medium after triggering the safety gear from a minimum value to a maximum value, wherein the ramp-like increase of the flow and thus in the end of the braking force of the spring element is selected according to the present invention, that a stage, a basket or a cab comes to a standstill when not fully loaded, before the maximum braking force of the safety gear acts.
- the dynamic pressure valve of such an attenuator can be designed so that the increase in the flow of the pressure medium depends on the distance covered the stage, the basket or the cabin since the triggering of the safety gear.
- This can be achieved in that the dynamic pressure valve is formed by a poppet valve with a control spring acting on it, wherein the counter-bearing of the control spring according to the distance traveled the stage, the basket or the cabin since the release of the safety gear from the seat valve is displaced away.
- the abutment of the control spring can this purpose on a control, which can be used in particular a usable in a governor rope of the guided lifting device actuating rod, are mounted, whereby the path-dependent control of the attenuator mechanically inevitably results.
- a triggering device which is integrated into the damping element of a guided lifting device according to the invention and comprises a control valve actuatable by the control between the inlet and the outlet of the damping element.
- the control valve may be biased by a closing spring in the closed position, so that the triggering device actually only triggers when the governor rope is blocked due to improper acceleration of the stage, the basket or the cabin.
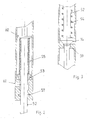
- FIGS. 1 to 3 of an attenuator provided according to the invention in a guided lifting device is used in a safety gear which generates the catch braking force by means of mechanically prestressed spring elements 31, wherein a hydraulic piston-cylinder unit 35 controls the spring force during normal driving operation compensates for these spring elements (Fig. 4).
- the damping member in Figures 1 to 3 also includes the triggering device and comprises a housing 51 which is fixedly connected to the (not shown) cabin of an elevator and tubular and formed at both ends with coaxially arranged, sealed passages 56, 57, through which an actuating rod 52 is running.
- the actuating rod 52 is provided with an upper suspension point 63 and a lower suspension point 64 is provided for a governor rope 16 of the elevator and is accordingly used as part of this governor rope in this.
- the housing 51 is provided in its interior with a partition 59 through which the actuating rod 52 passes. As a result, the housing 51 is divided into an upper 66 and a lower housing space 65.
- the actuating rod 52 is provided with a control valve 14 which, by means of the spring force of a closing spring 54, seals the housing spaces 65 and 66 which are divided by the partition 59.
- An inlet 61 is connected to the piston-cylinder unit 35 of the safety gear, whereas a drain 62 in the tank 1 of the hydraulic system ( Figure 4) leads back.
- the control valve 14 thus closes the drainage of the hydraulic oil from the safety gear and thereby allows a normal operation of the elevator, as long as the actuating rod 52 is not moved relative to the housing 51.
- the closing force of the closing spring 54 is in this case designed so that it is greater than the frictional and inertia forces of the governor cable 16 and the moving parts of the attached thereto (not shown) speed limiter. Only then, when the governor rope 16 is blocked and accordingly the actuating rod 52 is pulled against the force of the closing spring 54 relative to the housing 51 upwards, the control valve 14 is opened. This then allows the drainage of the hydraulic oil from the safety gear, so that the existing there spring 31 can build the braking force to intercept the elevator car.
- a seat valve 53 is arranged in the lower housing space 65, which valve is pretensioned via a control spring 55.
- the poppet valve 53 is provided with a coaxial bore through which the actuating rod 52 extends so that it can be displaced with respect thereto.
- the control spring 55 is supported on a stop collar 60 which is fixedly connected to the actuating rod 52.
- the attenuator shown in Figures 1 to 3 with integrated release device works in the following manner: As soon as an illegal Acceleration of the elevator car is blocked, the governor rope 16 in a conventional manner, whereby the actuating rod 52 is pulled upwards due to the connection with the governor rope in the upper mounting point 63. As a result, the control valve 14 is opened. Now, the hydraulic oil from the piston-cylinder unit 35 in the safety gear via the inlet 61, the seat valve 53 and the drain 62 drain. Here, the effective back pressure due to the initially high bias of the control spring 55 is initially high, so that the spring force of the safety gear due to the back pressure in the piston-cylinder unit 35 initially only minimally acts on the guide rail 42. This setting is adapted to the empty elevator car.
- the actuating rod 52 and with this the stop collar 60 is pulled further and further up, so that the bias of the control spring 55 decreases more and more and the back pressure is reduced. As a result, thereby increases the braking force of the safety gear with increasing braking distance. If the stop collar 60 reaches the abutment surface of the dividing wall 59, then the spring preload of the control spring 55 is released and the back pressure drops to zero. The braking force of the safety gear thus reaches the maximum value. This value depends on the requirements of a catch of a fully loaded elevator car.
- the pressure in the piston-cylinder unit 35 of the safety device is also completely reduced when the stop collar has not yet reached the dividing wall 59 when the car 60 is stationary. so that the braking force after the standstill of the elevator car nonetheless increases to the maximum braking force and the captured car is held so far with maximum braking force.
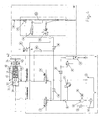
- the block diagram in Figure 4 shows the hydraulic system for the safety gear, which contains a mechanical spring column 31 in a housing 30, which acts via two toggle lever 33 and brake arms 32 on two symmetrically in the manner of a pair of pliers operable brake shoes 34.
- the brake arms 32 are rotatably mounted on the housing 30 for this purpose.
- the two brake shoes 34 each having a bearing surface 45 formed as a brake pad act on a guide rail 42 of the guided lifting device, which simultaneously serves as a brake rail serves.
- the biasing force of the spring column 31 is compensated by means of a piston-cylinder unit, which is designed here as a double-acting hydraulic cylinder 35, if necessary.
- the hydraulic cylinder 35 counteracts the spring column 31 or increases its spring force.
- the hydraulic supply unit which controls the double-acting hydraulic cylinder 35, is summarized in block I in FIG.
- This supply unit consists essentially of a hydraulic tank 1 with a ventilation filter 2, a suction filter 3, a pump 4 with a motor 5, a pump check valve 6, a pressure relief valve 7, two solenoid-operated three / two-way seat valves 11 and 12, a Pressure accumulator 10 with a throttle 8 in the inlet and outlet and an interposed pressure switch 9. Further, in the return from A to B, a throttle 13.
- the pump 4 is normally switched on and off via the pressure switch 9, whereby they the pressure accumulator 10 holds on the required for the compression of the spring column 31 level.
- the brake shoes 34 of the safety gear are opened so that no braking force is generated on the guide rail 42.
- the hydraulic cylinder 35 is printed at port A and connected at port B to the tank line, to which the solenoid valves 11 and 12 are de-energized.
- the force of the spring column 31, which spreads the toggle lever 33 is compensated by the hydraulic force in the piston-side pressure chamber 39 of the hydraulic cylinder 35 and thereby released the toggle 33, whereby the rear legs of the brake lever 32 are pulled inwardly and the brake shoes 34 of the Lift off guide rail 42.
- the piston-side pressure chamber 39 in the hydraulic cylinder 35 is constantly kept under pressure and the spring force compensated.
- the two solenoid valves 11 and 12 of the safety gear are energized, thereby connecting the A port of the piston-side pressure chamber 39 of the hydraulic cylinder 35 via the throttle 13 to the tank 1 and the B port of the rod-side pressure chamber printed by the pump 4 and the pressure accumulator 10.
- the force of the spring column 31 in this case acts together with the force acting in the rod-side pressure chamber hydraulic force on the toggle 33.
- the toggle 33 are spread and thereby pressed apart the brake lever 32, whereby the brake shoes 34 located at the other end on the guide rail 42 are pressed.
- the pressure in the rod-side pressure chamber is maintained again after the stroke via the memory charging circuit.
- the provided in the return from A to tank 1 throttle 13 ensures this for the damping of the switching operation.
- the circuit according to block I thus allows the safety gear in trouble-free normal operation can also be used as a holding brake in the stop.
- the governor rope 16 is blocked, whereby a catch switch 17 is actuated. This interrupts the power supply of the solenoid valves 11 and 12 and the motor pump 4 and 5 by the blocked governor cable 16 also the actuating rod 2 is pulled upwards and thereby the control valve 14 is opened.
- a formed from the seat valve 53 and the control spring 55 back pressure valve 15 is ramped with increasing braking distance, so that via the line A, the hydraulic oil from the piston-side pressure chamber 39 of the hydraulic cylinder 35 via the Back pressure valve 15 and the control valve 14 can flow into the tank 1.
- a throttle valve 19 is additionally provided in the return line.
- a check valve 20 allows regardless of the switching position of the solenoid valve 12 a rod-side suction of hydraulic oil in the hydraulic cylinder 35, so that the catching process can be affected in any case.
- a third solenoid valve 21 is not energized during normal operation as well as during a capture process and therefore open. It rather serves the elevator car after a successful catch by hand to solve again until the triggering device is reset and then can build up without the solenoid valve 21, a pressure in the piston-side pressure chamber of the safety gear.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Maintenance And Inspection Apparatuses For Elevators (AREA)
- Types And Forms Of Lifts (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE202004017587U DE202004017587U1 (de) | 2004-11-12 | 2004-11-12 | Geführte Hebeeinrichtung mit gedämpfter Fangvorrichtung |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1657203A2 true EP1657203A2 (fr) | 2006-05-17 |
| EP1657203A3 EP1657203A3 (fr) | 2008-02-13 |
Family
ID=34089505
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05024622A Withdrawn EP1657203A3 (fr) | 2004-11-12 | 2005-11-11 | Installation de levage guidée avec parachute amorti |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1657203A3 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE202004017587U1 (fr) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016120227A3 (fr) * | 2015-01-30 | 2016-09-22 | Thyssenkrupp Elevator Ag | Frein à rail à assistance hydraulique |
| WO2018050577A1 (fr) | 2016-09-16 | 2018-03-22 | Thyssenkrupp Elevator Ag | Dispositif de freinage d'une installation d'ascenseur |
| WO2020115304A1 (fr) * | 2018-12-07 | 2020-06-11 | Chr. Mayr Gmbh + Co. Kg | Frein de cabine actionné par un fluide sous pression et système de soupape pour commander la fonction de frein d'urgence du frein de cabine actionné par un fluide sous pression d'un système d'ascenseur |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1840068A1 (fr) * | 2006-03-29 | 2007-10-03 | Inventio Ag | Ascenseur comprenant und dispositif de frein de cabine d'ascenseur et méthode de freinage d'une cabine d'ascenseur |
| DE202011051664U1 (de) | 2011-10-18 | 2012-01-13 | Slc Sautter Lift Components Gmbh & Co. Kg | Bremseinrichtung für einen Aufzug |
| DE102014206461A1 (de) | 2014-04-03 | 2015-10-08 | Thyssen Krupp Elevator Ag | Aufzug mit einer Bremsvorrichtung |
| DE102014104865A1 (de) | 2014-04-04 | 2015-10-08 | Thyssenkrupp Ag | Aufzug mit einer Bremsvorrichtung |
| WO2015177234A1 (fr) * | 2014-05-20 | 2015-11-26 | Wittur Holding Gmbh | Dispositif de sécurité pour faire fonctionner un ascenseur |
| CN107739001B (zh) * | 2017-12-01 | 2024-04-09 | 江西工埠机械有限责任公司 | 一种新型安全应急液压制动器 |
| CN108046151B (zh) * | 2017-12-21 | 2023-12-12 | 泰华伟业科技有限责任公司 | 自动限速变阻尼器 |
| CN113562671A (zh) * | 2021-05-19 | 2021-10-29 | 国网河北省电力有限公司石家庄市藁城区供电分公司 | 一种电力检修维护专用升降平台 |
| CN115853931B (zh) * | 2023-03-03 | 2023-05-09 | 太原矿机电气股份有限公司 | 一种限速值可调的限速制动控制系统 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0648703B1 (fr) | 1993-10-18 | 1999-01-20 | Inventio Ag | Système de sécurité par freinage pour cabine d'ascenseur |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1002933B (de) * | 1953-11-13 | 1957-02-21 | Bbc Brown Boveri & Cie | Daempfungseinrichtung fuer Fallgewichts-Sicherheitsbremsen bei Foerdermaschinen |
| DE2932485A1 (de) * | 1979-08-10 | 1981-03-26 | M.A.N. Maschinenfabrik Augsburg-Nürnberg AG, 4200 Oberhausen | Vorrichtung zur seillaengungsdaempfung |
-
2004
- 2004-11-12 DE DE202004017587U patent/DE202004017587U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2005
- 2005-11-11 EP EP05024622A patent/EP1657203A3/fr not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0648703B1 (fr) | 1993-10-18 | 1999-01-20 | Inventio Ag | Système de sécurité par freinage pour cabine d'ascenseur |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016120227A3 (fr) * | 2015-01-30 | 2016-09-22 | Thyssenkrupp Elevator Ag | Frein à rail à assistance hydraulique |
| US9738491B2 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2017-08-22 | Thyssenkrupp Elevator Ag | Hydraulic-boosted rail brake |
| CN107207203A (zh) * | 2015-01-30 | 2017-09-26 | 蒂森克虏伯电梯股份公司 | 液压助力的导轨制动器 |
| CN107207203B (zh) * | 2015-01-30 | 2019-07-05 | 蒂森克虏伯电梯股份公司 | 液压助力的导轨制动器 |
| WO2018050577A1 (fr) | 2016-09-16 | 2018-03-22 | Thyssenkrupp Elevator Ag | Dispositif de freinage d'une installation d'ascenseur |
| DE102016217790A1 (de) | 2016-09-16 | 2018-03-22 | Thyssenkrupp Ag | Bremsvorrichtung für eine Aufzugsanlage |
| US11117782B2 (en) | 2016-09-16 | 2021-09-14 | Tk Elevator Innovation And Operations Gmbh | Force adjusting braking device for an elevator system |
| WO2020115304A1 (fr) * | 2018-12-07 | 2020-06-11 | Chr. Mayr Gmbh + Co. Kg | Frein de cabine actionné par un fluide sous pression et système de soupape pour commander la fonction de frein d'urgence du frein de cabine actionné par un fluide sous pression d'un système d'ascenseur |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1657203A3 (fr) | 2008-02-13 |
| DE202004017587U1 (de) | 2005-01-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1657203A2 (fr) | Installation de levage guidée avec parachute amorti | |
| EP1213248B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'arrêt d'urgence dont la force de freinage est fonction de la déccélération de l'ascenseur | |
| EP1657204A2 (fr) | Installation de levage guidée avec dispositif de retenue et parachute | |
| DE102007015277A1 (de) | Aufzugsanlage mit einer Aufzugskabinenbremseinrichtung und Verfahren zum Bremsen einer Aufzugskabine | |
| EP2483118B1 (fr) | Réglage de jeu dans un système de freinage hydraulique | |
| DE1950040A1 (de) | Druckmittelbetaetigte Bremssysteme | |
| DE102006059840A1 (de) | Adaptive Leerwegreduzierung | |
| EP3608286B1 (fr) | Chariot industriel avec système de levage hydraulique et protection électronique du système de levage contre les dysfonctionnements | |
| EP1400476B1 (fr) | Parachute pour ascenseurs | |
| DE68904047T2 (de) | Sicherheitsbremseinrichtung. | |
| DE3630681C2 (de) | Bremssystem für Förderanlagen | |
| WO1999008029A1 (fr) | Soupape de limitation de pression pilotee | |
| EP0216776A1 (fr) | Systeme de reglage de pression pour un embrayage et/ou un frein a commande hydraulique pour l'arbre d'entrainement d'une presse. | |
| DE19518893C2 (de) | Magnetschienenbremse für ein Schienenfahrzeug | |
| EP3401270A1 (fr) | Commande de fluide, appareil releveur de frein, assemblée de frein | |
| EP3286055B1 (fr) | Dispositif soupape pneumatique actionnable hydrauliquement | |
| DE2646286A1 (de) | Druckuebersetzer | |
| WO2013000666A1 (fr) | Dispositif de compensation destiné à un système de freinage et système de freinage muni dudit dispositif de compensation | |
| DE102013108495B4 (de) | Hebewerk-Bremssystem | |
| DE2102142C3 (de) | Blockiergeschützte Fahrzeugbremsanlage | |
| DE3346999A1 (de) | Insbesondere hydraulische bremsanlage fuer einen ueber einen antrieb bewegbaren teil | |
| DE2717560A1 (de) | Federspeicherbremseinrichtung fuer schienenfahrzeuge | |
| EP1616771B1 (fr) | Tampon pour véhicules ferroviaires | |
| DE3817313A1 (de) | Insbesondere hydraulische bremsanlage fuer einen ueber einen antrieb bewegbaren teil | |
| DE131923C (fr) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK YU |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK YU |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B66D 5/00 20060101ALI20080110BHEP Ipc: B66B 5/04 20060101AFI20060317BHEP |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid | ||
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20080814 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |