EP1555309A1 - Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus MItteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs und Wasser - Google Patents
Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus MItteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs und Wasser Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1555309A1 EP1555309A1 EP20040030573 EP04030573A EP1555309A1 EP 1555309 A1 EP1555309 A1 EP 1555309A1 EP 20040030573 EP20040030573 EP 20040030573 EP 04030573 A EP04030573 A EP 04030573A EP 1555309 A1 EP1555309 A1 EP 1555309A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- oil
- ether
- acid
- fuel
- diglycidyl ether
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/146—Macromolecular compounds according to different macromolecular groups, mixtures thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/143—Organic compounds mixtures of organic macromolecular compounds with organic non-macromolecular compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/18—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C10L1/192—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/198—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds homo- or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon to carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by an acyloxy radical of a saturated carboxylic acid, of carbonic acid
- C10L1/1985—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds homo- or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon to carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by an acyloxy radical of a saturated carboxylic acid, of carbonic acid polyethers, e.g. di- polygylcols and derivatives; ethers - esters
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/22—Organic compounds containing nitrogen
- C10L1/234—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/238—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C10L1/2383—Polyamines or polyimines, or derivatives thereof (poly)amines and imines; derivatives thereof (substituted by a macromolecular group containing 30C)
- C10L1/2387—Polyoxyalkyleneamines (poly)oxyalkylene amines and derivatives thereof (substituted by a macromolecular group containing 30C)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/18—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C10L1/192—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/195—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C10L1/196—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derived from monomers containing a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and a carboxyl group or salts, anhydrides or esters thereof homo- or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals each having one carbon bond to carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a carboxyl radical or of salts, anhydrides or esters thereof
- C10L1/1966—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derived from monomers containing a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and a carboxyl group or salts, anhydrides or esters thereof homo- or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals each having one carbon bond to carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by a carboxyl radical or of salts, anhydrides or esters thereof poly-carboxylic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/18—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C10L1/192—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/195—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C10L1/197—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derived from monomers containing a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and an acyloxy group of a saturated carboxylic or carbonic acid
- C10L1/1973—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derived from monomers containing a carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bond and an acyloxy group of a saturated carboxylic or carbonic acid mono-carboxylic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/18—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C10L1/192—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/198—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds homo- or copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon to carbon double bond, and at least one being terminated by an acyloxy radical of a saturated carboxylic acid, of carbonic acid
- C10L1/1981—Condensation polymers of aldehydes or ketones
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/22—Organic compounds containing nitrogen
- C10L1/222—Organic compounds containing nitrogen containing at least one carbon-to-nitrogen single bond
- C10L1/2222—(cyclo)aliphatic amines; polyamines (no macromolecular substituent 30C); quaternair ammonium compounds; carbamates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/22—Organic compounds containing nitrogen
- C10L1/222—Organic compounds containing nitrogen containing at least one carbon-to-nitrogen single bond
- C10L1/224—Amides; Imides carboxylic acid amides, imides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/22—Organic compounds containing nitrogen
- C10L1/234—Macromolecular compounds
- C10L1/236—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derivatives thereof
- C10L1/2364—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds derivatives thereof homo- or copolymers derived from unsaturated compounds containing amide and/or imide groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10L—FUELS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; NATURAL GAS; SYNTHETIC NATURAL GAS OBTAINED BY PROCESSES NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C10G OR C10K; LIQUIFIED PETROLEUM GAS; USE OF ADDITIVES TO FUELS OR FIRES; FIRE-LIGHTERS
- C10L1/00—Liquid carbonaceous fuels
- C10L1/10—Liquid carbonaceous fuels containing additives
- C10L1/14—Organic compounds
- C10L1/28—Organic compounds containing silicon
- C10L1/285—Organic compounds containing silicon macromolecular compounds
Definitions
- the present invention relates to the use of an additive as a demulsifier for Mixtures of middle distillates with vegetable or animal fuel oils and Water.
- Oils obtained from animal or vegetable material are mainly metabolites comprising triglycerides of monocarboxylic acids, eg acids having 10 to 25 carbon atoms, and the formula in which R is an aliphatic radical of 10 to 25 carbon atoms, which may be saturated or unsaturated.
- oils contain glycerides of a number of acids whose Number and variety varies with the source of the oil, and they may additionally Contain phosphoglycerides.
- Such oils can be used in the prior art known methods are obtained.
- Triglycerides Due to the partially unsatisfactory physical properties of the Triglycerides, the technique has gone over to the naturally occurring Triglycerides in fatty acid esters of lower alcohols such as methanol or ethanol convict.
- the prior art also includes mixtures of middle distillates with oils of vegetable or animal origin (in the following also "biofuel oils” called).
- EP-B-0 665 873 discloses a fuel oil composition
- a fuel oil composition comprising a A biofuel comprising a petroleum-based fuel oil and an additive which comprises (a) an oil-soluble ethylene copolymer or (b) a comb polymer or (c) a polar Nitrogen compound or (d) a compound in which at least one in the Substantially linear alkyl group having 10 to 30 carbon atoms with one not polymeric organic radical is connected to at least one linear chain of To provide atoms containing the carbon atoms of the alkyl groups and one or more includes non-terminal oxygen atoms, or (e) one or more of Components (a), (b), (c) and (d).
- Object of this invention was a suitable demulsifier for To find mixtures of middle distillates, biofuel oils and water.
- Another object of the invention is the use of the defined under C) Block copolymer as a demulsifier in mixtures of middle distillate fuel oils with Biofuel oils and water.
- Another object of the invention is a process for the demulsification of Water from mixtures of middle distillate fuel oils with biofuel oils, by adding to the mixtures the above-defined block copolymer.
- middle distillate fuel oils are used as component A. With this designation in particular those mineral oils obtained by distillation of crude oil and boiling in the range of 120 to 450 ° C, for example, kerosene, jet fuel, Diesel and heating oil.
- middle distillates are used which less than 350 ppm sulfur, more preferably less than 200 ppm sulfur in particular less than 50 ppm sulfur and in special cases less than Contain 10 ppm of sulfur.
- These are generally such Middle distillates which have been subjected to a hydrogenating refining, and therefore contain only low levels of polyaromatic and polar compounds.
- these are middle distillates, the 95% distillation points below 370 ° C, in particular 350 ° C and in special cases below 330 ° C.
- the middle distillates preferably have aromatics contents of less than 28% by weight, in particular below 20% by weight.
- biofuel oils are used.
- the biofuel which is often also as “Biodiesel” or “biofuel” is referred to fatty acid alkyl esters Fatty acids having 14 to 24 carbon atoms and alcohols having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Usually a greater proportion of fatty acids contain one, two or three double bonds.
- Rapsölkladyer and especially mixtures containing rapeseed, sunflower and / or soybean oil fatty acid methyl ester.
- oils derived from animal or vegetable material which can be used in the composition of the present invention are rapeseed oil, coriander oil, soybean oil, cottonseed oil, sunflower oil, castor oil, olive oil, peanut oil, corn oil, almond oil, palm kernel oil, coconut oil, soybean oil, Mustard seed oil, beef tallow, bone oil and fish oils.
- Other examples include oils derived from wheat, jute, sesame, shea nut, arachis oil, and linseed oil, and may be derived therefrom by methods known in the art.
- oils can be used, which were obtained from used waste oils, such as cooking oil.
- Rapeseed oil which is a mixture of glycerol partially esterified fatty acids, is preferred because it is available in large quantities and is readily available by squeezing rapeseed.
- sunflower and soybeans and their mixtures with rapeseed oil are preferred.
- lower alkyl esters of fatty acids the following may be considered for example, as commercial mixtures: the ethyl, propyl, butyl and in particular methyl esters of fatty acids having 12 to 22 carbon atoms, for example, lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, Stearic acid, oleic acid, elaidic acid, petroselinic acid, ricinoleic acid, Elaeostearic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, eicosanoic acid, gadoleic acid, Docosanoic or erucic acid, preferably having an iodine value of 50 to 150, especially 90 to 125 have.
- the ethyl, propyl, butyl and in particular methyl esters of fatty acids having 12 to 22 carbon atoms for example, lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, Stearic acid
- Mixtures with particularly advantageous Properties are those that are mainly, i. at least 50% by weight, Methyl esters of fatty acids having 16 to 22 carbon atoms and 1, 2 or 3 Double bonds included.
- the preferred lower alkyl esters of fatty acids are the methyl esters of oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid and erucic acid.
- Component C) is a crosslinked block copolymer prepared by crosslinking from a block copolymer of at least 2 different C 2 to C 4 alkylene oxides.
- the block copolymer may consist of 2, 3, 4 or more blocks.
- the block copolymers used are prepared by sequential polymerization of alkylene oxides (ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, butylene oxide), preferably under alkaline catalysis, as known in the art.
- alkylene oxides ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, butylene oxide
- the base polymer used to make the block copolymer C) has general, a molecular weight of 500 to 100,000 g / mol, preferably 1000 to 60,000, in particular 4000 to 50,000 g / mol. These molecular weights are the Molecular weights before crosslinking.
- crosslinking of the block copolymers used is as in the prior art known by alkaline or acid catalyzed ring opening of di-, tri- or Tetraglycidylethern, by esterification with polybasic carboxylic acids or
- Carboxylic anhydrides or by reaction with polyvalent isocyanates carried out are Carboxylic anhydrides or by reaction with polyvalent isocyanates carried out.
- Suitable crosslinkers are those compounds which are at least 2 Binding sites can bind to the block polymer.
- the following are Crosslinkers listed: bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, butane-1,4-diol diglycidyl ether, Hexane-1,6-diol diglycidyl ether, ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, Cyclohexanedimethanol diglycidyl ether, resorcinol diglycidyl ether, Glycerol diglycidyl ether, glycerol triglycidyl ether, glycerol propoxylate triglycidyl ether, Polyglycerol polyglycidyl ether, p-aminophenol triglycidyl ether, Polypropylene glycol diglycidyl ether, pentaerythritol tetraglycidyl ether, Sorbitol polyglycidyl ether
- the crosslinked block copolymers C) generally have a molecular weight of 1000-200,000 g / mol, preferably 2000-100,000, in particular 4000-50,000 g / mol, measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) against Polystyrene standards in THF.
- GPC gel permeation chromatography
- WZ water number
- DIN EN 12836, to which reference is hereby made To a solvent mixture, which consists of a certain volume Dioxan and Toluene in the ratio 97: 3, and in which the block copolymer sample as a clear Solution, water is added at a temperature of (25 ⁇ 1) ° C until a permanent haze occurs. The number of water is given in milliliters of water, which are needed to get the permanent haze.
- the water number in the crosslinked block copolymer C) is preferably between 6 ml and 25 ml, especially between 6 ml and 17 ml.
- the crosslinked block copolymers C) become the mixtures containing A) and B) in amounts of 0.001 to 5 wt .-%, preferably 0.005 to 1 wt .-% and especially 0.01 added to 0.05 wt .-%. They can be solved as such or also dispersed in solvents, e.g. aliphatic and / or aromatic Hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon mixtures such as e.g.
- they are in animal or animal fuel oil vegetable origin based on fatty acid alkyl esters.
- the crosslinked block copolymers C) can be added to the oil to be added in accordance with State of the art known methods are supplied. If more than one Copolymer component to be used may include such components be introduced together or separately in any combination in the oil.
- the crosslinked block copolymers C) also together with one or more oil-soluble co-additives are used, which already for themselves Properties of crude oils, lubricating oils or fuel oils.
- co-additives are polar compounds that are paraffin-dispersed effect (paraffin dispersants), alkylphenol-aldehyde resins, polymers Cold flow improvers and oil-soluble amphiphiles.
- mixtures of the crosslinked block copolymers C) have proven outstandingly well with copolymers which contain from 10 to 40% by weight of vinyl acetate and from 60 to 90% by weight of ethylene.
- the additives according to the invention are mixed with ethylene / vinyl acetate / vinyl 2-ethylhexanoate terpolymers, ethylene / vinyl acetate / vinyl neononanoate terpolymers and / or ethylene / vinyl acetate / vinyl neodecanoate terpolymers to simultaneously improve flowability and lubricity of mineral oils or mineral oil distillates.
- the terpolymers of vinyl 2-ethylhexanoate, vinyl neononanoate or vinyl neodecanoate contain, in addition to ethylene, 8 to 40% by weight of vinyl acetate and 1 to 40% by weight of the respective long-chain vinyl ester. Further preferred copolymers contain, in addition to ethylene, 10 to 40% by weight of vinyl acetate and optionally 1 to 40% by weight of vinyl esters with C 3 to C 12 -alkyl groups in the ester radical and optionally from 0.5 to 20% by weight of olefins with 3 to 10 C atoms such as isobutylene, diisobutylene, propylene, methylpentene or norbornene.
- paraffin dispersants are preferably low molecular weight or polymeric, oil-soluble compounds having ionic or polar groups, e.g. Amine salts, imides and / or amides.
- Particularly preferred paraffin dispersants contain reaction products of primary and / or secondary fatty amines with 8 to 36 C atoms, especially dicocosfettamine, ditallow fatty amine and distearylamine.
- Paraffin dispersants which have proved particularly suitable by reaction aliphatic or aromatic amines, preferably long-chain aliphatic Amines, with aliphatic or aromatic mono-, di-, tri- or tetracarboxylic acids or their anhydrides are obtained (see US 4 211 534).
- Paraffin dispersants are copolymers of maleic, fumaric and / or itaconic acid or maleic anhydride and other ⁇ , ⁇ -unsaturated compounds which optionally with primary and / or secondary monoalkylamines and / or Aliphatic alcohols can be reacted (see EP-A-0 154 177), which Reaction products of alkenyl spiro-bis-lactones with amines (see EP-A-0 413 279 B1) and, according to EP-A-0 606 055 A2, reaction products of terpolymers based on ⁇ , ⁇ -unsaturated dicarboxylic anhydrides, ⁇ , ⁇ -unsaturated compounds and Polyoxyalkylene ethers of lower unsaturated alcohols.
- esters suitable are derived from polyols having 3 or more OH groups, in particular of glycerol, trimethylolpropane, pentaerythritol and the like Condensation accessible oligomers having 2 to 10 monomer units, e.g. Polyglycerol.
- the polyols are generally containing from 1 to 100 mol of alkylene oxide, preferably 3 to 70, in particular 5 to 50 mol of alkylene oxide reacted per mole of polyol.
- Preferred alkylene oxides are ethylene oxide, propylene oxide and butylene oxide.
- the Alkoxylation is carried out by known methods.
- the fatty acids suitable for the esterification of the alkoxylated polyols preferably have 8 to 50, in particular 12 to 30, especially 16 to 26 C-atoms.
- Suitable fatty acids are, for example, lauric, tridecane, myristic, pentadecane, palmitic, margarine, stearic, isostearic, arachic and behenic, oleic and erucic acid, palmitoleic, myristolein, ricinoleic acid, as well as natural fats and Oils derived fatty acid mixtures.
- Preferred fatty acid mixtures contain more than 50% fatty acids with at least 20 C atoms.
- the fatty acids used for esterification contain double bonds, in particular less than 10%; specifically, they are largely saturated. Under largely saturated here is an iodine value of the fatty acid used of up to 5 g of I per 100 g of fatty acid are understood.
- the esterification can also be carried out starting from reactive derivatives of fatty acids such as esters with lower alcohols (for example methyl or ethyl esters) or anhydrides.
- esters with lower alcohols for example methyl or ethyl esters
- anhydrides for the esterification of the alkoxylated polyols, it is also possible to use mixtures of the above fatty acids with fat-soluble, polybasic carboxylic acids.
- suitable polybasic carboxylic acids are dimer fatty acids, alkenylsuccinic acids and aromatic polycarboxylic acids and derivatives thereof such as anhydrides and C 1 - to C 5 -esters.
- Alkenylsuccinic acids and their derivatives with alkyl radicals having 8 to 200, in particular 10 to 50, carbon atoms are preferred.
- Examples are dodecenyl, octadecenyl and poly (isobutenyl) succinic anhydride.
- the polybasic carboxylic acids are preferably used to lower levels of up to 30 mol%, preferably 1 to 20 mol%, in particular 2 to 10 mol%.
- Ester and fatty acid are used for esterification based on the content Hydroxyl groups on the one hand and carboxyl groups on the other hand in a ratio of 1.5: 1 used to 1: 1.5, preferably 1.1: 1 to 1: 1.1, in particular equimolar.
- the paraffin dispersing effect is particularly pronounced when combined with a Acid excess of up to 20 mol%, especially up to 10 mol%, in particular up to 5 mol% is worked.
- the esterification is carried out by conventional methods.
- the separation of the water of reaction can be carried out by distillation by direct condensation or preferably by azeotropic distillation in the presence of organic solvents, in particular aromatic solvents such as toluene, xylene or higher boiling mixtures such as ® Shellsol A, Shellsol B, Shellsol AB or Solvent Naphtha.
- the esterification is preferably carried out completely, ie for the esterification 1.0 to 1.5 moles of fatty acid are used per mole of hydroxyl groups.
- the acid number of the esters is generally below 15 mg KOH / g, preferably below 10 mg KOH / g, especially below 5 mg KOH / g.
- paraffin dispersants are prepared by reacting compounds containing an acyl group with an amine.
- This amine is a compound of the formula NR 6 R 7 R 8 , in which R 6 , R 7 and R 8 may be identical or different, and at least one of these groups is C 8 -C 36 -alkyl, C 6 - C 36 -cycloalkyl, C 8 -C 36 -alkenyl, in particular C 12 -C 24 -alkyl, C 12 -C 24 -alkenyl or cyclohexyl, and the other groups are either hydrogen, C 1 -C 36 -alkyl, C 2 -C 36 alkenyl, cyclohexyl, or a group of the formulas - (AO) x -E or - (CH 2 ) n -NYZ, where A is an ethylene or propylene group, x is a number from 1 to 50, E Is H, C 1 -C 30 -alkyl
- paraffin dispersants may be admixed with the crosslinked block copolymer C) or added separately to the middle distillate to be added.
- alkylphenol-aldehyde resins are also suitable as paraffin dispersants.
- Alkylphenol-aldehyde resins are known in principle and, for example, in Römpp Chemie Lexikon, 9th edition, Thieme Verlag 1988-92, Volume 4, p 3351ff. described.
- the alkyl or alkenyl radicals of the alkylphenol have 6-24, preferably 8-22, in particular 9-18, carbon atoms. They may be linear or preferably branched, wherein the branch may contain secondary as well as tertiary structural elements.
- alkylphenol-aldehyde resin may also contain up to 20 mole% of phenol units and / or alkylphenols with short alkyl chains, such as e.g. B. butylphenol.
- alkylphenol-aldehyde resin the same or different alkylphenols may be used.
- the aldehyde in the alkylphenol-aldehyde resin has 1 to 10, preferably 1 to 4 Carbon atoms and may carry other functional groups. He is preferably a aliphatic aldehyde, most preferably it is formaldehyde.
- the molecular weight of the alkylphenol-aldehyde resins is preferably 350 to 10,000, in particular 400 to 5000, g / mol. This preferably corresponds to a condensation degree n of from 3 to 40, in particular from 4 to 20.
- the prerequisite here is that the resins are oil-soluble.
- the preparation of the alkylphenol-aldehyde resins is carried out in a known manner basic catalysis, resulting in resol-type condensation products, or by acid catalysis to produce novolac-type condensation products.
- the condensates obtained according to both types are for the invention Compositions suitable.
- the condensation is in the presence of acid catalysts.
- alkylphenol-aldehyde resins For the preparation of the alkylphenol-aldehyde resins, an alkylphenol having 6-24, preferably 8-22, in particular 9-18, C atoms per alkyl group, or mixtures thereof and at least one aldehyde reacted with each other, wherein per mol Alkylphenol compound about 0.5 to 2 mol, preferably 0.7 to 1.3 mol and In particular, equimolar amounts of aldehyde can be used.
- Suitable alkylphenols are in particular n- and iso-hexylphenol, n- and iso-octylphenol, n- and iso-nonylphenol, n- and iso-decylphenol, n- and iso-dodecylphenol, tetradecylphenol, hexadecylphenol, octadecylphenol, eicosylphenol, tripropenylphenol, tetrapropenylphenol and poly (isobutenyl) phenol -C 24th
- the alkylphenols are preferably para-substituted.
- the alkylphenols can have a or more alkyl radicals. Preferably, they are at most 5 mol%, in particular at most 20 mol% and especially at most 40 mol% with more than substituted an alkyl group. Preferably carry at most 40 mol%, in particular at most 20 mol% of the alkylphenols used in the ortho position an alkyl radical.
- the alkylphenols ortho to the hydroxyl group are not tertiary Substituted alkyl groups.
- the aldehyde may be a mono- or dialdehyde and other functional groups like -COOH.
- Particularly suitable aldehydes are formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, Butyraldehyde, glutardialdehyde and glyoxylic acid, preferred is formaldehyde.
- the Formaldehyde may be in the form of paraformaldehyde or in the form of a preferably 20 - 40 wt .-% aqueous formalin solution can be used. It can too corresponding amounts of trioxane are used.
- alkylphenol and aldehyde is usually carried out in the presence of alkaline catalysts, for example alkali metal hydroxides or alkylamines, or of acidic catalysts, for example inorganic or organic acids, such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, sulfonic acid, sulfamido acids or Haloacetic acids, and in the presence of an azeotrope with water organic solvent, for example toluene, xylene, higher aromatics or Mixtures thereof.
- the reaction mixture is heated to a temperature of 90 to 200 ° C, preferably 100 - 160 ° C heated, wherein the resulting reaction water is removed during the reaction by azeotropic distillation.
- Solvent which under the conditions of condensation can not split off any protons remain in the products after the condensation reaction.
- the resins can be directly or after neutralization of the catalyst, optionally after further dilution of the solution with aliphatic and / or aromatic Hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon mixtures, e.g. Petroleum fractions, Kerosene, decane, pentadecane, toluene, xylene, ethylbenzene or solvents such as ® Solvent Naphtha, ® Shellsol AB, ® Solvesso 150, ® Solvesso 200, ® Exxsol, ® ISOPAR and ® Shellsol D types.
- the crosslinked block copolymers C) are used together with comb polymers.
- This term refers to polymers in which hydrocarbon radicals having at least 8, in particular at least 10, carbon atoms are bonded to a polymer backbone.
- they are homopolymers whose alkyl side chains contain at least 8 and in particular at least 10 carbon atoms.
- at least 20%, preferably at least 30% of the monomers have side chains (compare Comb-like Polymers-Structure and Properties, NA Platé and VP Shibaev, J. Polym, Sci Macromolecular Revs 1974, 8, 117 ff).
- Suitable comb polymers are, for example, fumarate / vinyl acetate copolymers (cf., EP 0 153 176 A1), copolymers of a C 6 -C 24 - ⁇ -olefin and an NC 6 -C 22 -alkylmaleimide (compare EP-A-0 320,766), further esterified olefin / maleic anhydride copolymers, polymers and copolymers of ⁇ -olefins, and esterified copolymers of styrene and maleic anhydride.
- fumarate / vinyl acetate copolymers cf., EP 0 153 176 A1
- copolymers of a C 6 -C 24 - ⁇ -olefin and an NC 6 -C 22 -alkylmaleimide compare EP-A-0 320,766
- further esterified olefin / maleic anhydride copolymers polymers
- the mixing ratio (in parts by weight) of the crosslinked block copolymers C) with polymeric cold flow improvers, paraffin dispersants, comb polymers or Resins are each 1: 1000 to 1: 1, preferably 1:10 to 1:50.
- the crosslinked block copolymers C) may be used alone or together with others Additives are used, for. B. with other pour point depressants or Dewatering aids, with corrosion inhibitors, antioxidants, lubricity additives Mud inhibitors, dehazers, and add-ons for lowering the cloud point.
- the testing of the emulsification of additives is carried out according to ASTM D 1094-85.
- a middle distillate with a CFPP of -7 ° C. and its mixture with 5% of the described biofuel (CFPP of the mixture likewise -7 ° C.) with cold flow improvers and block copolymers were investigated Influence of Cold Flow Properties by Block Copolymers example fuel oil copolymers 300 ppm P7 300 ppm P8 300 ppm P7 + 10 ppm P1 300 ppm P8 + 10 ppm P1 65 (V) middle distillate - 22 - 20 - 23 - 20 66 Middle distillate + biofuel - 23 - 21 - 24 - 19
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Liquid Carbonaceous Fuels (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
Abstract
Description
sowie einem kleineren Anteil
Beispiele für Öle, die sich von tierischem oder pflanzlichem Material ableiten, und die in der erfindungsgemäßen Zusammensetzung verwendet werden können, sind Rapsöl, Korianderöl, Sojaöl, Baumwollsamenöl, Sonnenblumenöl, Ricinusöl, Olivenöl, Erdnussöl, Maisöl, Mandelöl, Palmkernöl, Kokosnussöl, Sojaöl, Senfsamenöl, Rindertalg, Knochenöl und Fischöle. Weitere Beispiele schließen Öle ein, die sich von Weizen, Jute, Sesam, Scheabaumnuß, Arachisöl und Leinöl ableiten und können aus diesen nach im Stand der Technik bekannten Verfahren abgeleitet werden. Außerdem können Öle verwendet werden, welche aus gebrauchten Altölen, wie Frittieröl gewonnen wurden. Rapsöl, das eine Mischung von mit Glycerin partiell veresterten Fettsäuren ist, ist bevorzugt, da es in großen Mengen erhältlich ist und in einfacher Weise durch Auspressen von Rapssamen erhältlich ist. Des weiteren sind die ebenfalls weit verbreiteten Öle von Sonnenblumen und Soja sowie deren Mischungen mit Rapsöl bevorzugt.
Zur Veresterung der alkoxylierten Polyole können auch Gemische obiger Fettsäuren mit fettlöslichen, mehrwertigen Carbonsäuren eingesetzt werden. Beispiele für geeignete mehrwertige Carbonsäuren sind Dimerfettsäuren, Alkenylbernsteinsäuren und aromatische Polycarbonsäuren sowie deren Derivate wie Anhydride und C1- bis C5-Ester. Bevorzugt sind Alkenylbernsteinsäuren und deren Derivate mit Alkylresten mit 8 bis 200, insbesondere 10 bis 50 C-Atomen. Beispiele sind Dodecenyl-, Octadecenyl- und Poly(isobutenyl)bernsteinsäureanhydrid. Bevorzugt werden die mehrwertigen Carbonsäuren dabei zu untergeordneten Anteilen von bis zu 30 Mol-%, bevorzugt 1 bis 20 Mol-%, insbesondere 2 bis 10 Mol-% eingesetzt.
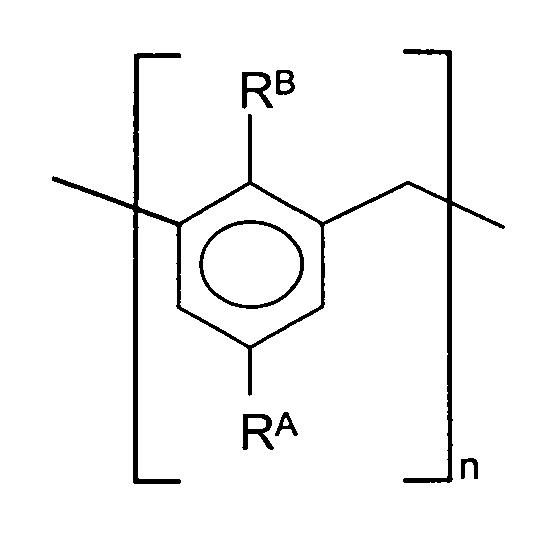
In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Erfindung handelt es sich bei diesen Alkylphenol-Formaldehydharzen um solche, die Oligo- oder Polymere mit einer repetitiven Struktureinheit der Formel sind, worin RA für C4 bis C30-, insbesondere C6- bis C24-Alkyl oder -Alkenyl, RB für OH oder O-(A-O)x-H mit A = C2-C4-Alkylen und x = 1 bis 50, und n für eine Zahl von 2 bis 50, insbesondere 5 bis 40 und speziell 7 bis 12 steht.
- A
- R', COOR', OCOR', R"-COOR' oder OR';
- D
- H, CH3, A oder R;
- E
- H oder A;
- G
- H, R", R"-COOR', einen Arylrest oder einen heterocyclischen Rest;
- M
- H, COOR", OCOR", OR" oder COOH;
- N
- H, R", COOR", OCOR, COOH oder einen Arylrest;
- R'
- eine Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 8-150 Kohlenstoffatomen;
- R"
- eine Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 1 bis 10 Kohlenstoffatomen;
- m
- eine Zahl zwischen 0,4 und 1,0; und
- n
- eine Zahl zwischen 0 und 0,6.
| Analyse des verwendeten Biodiesel | |||
| Öl Nr. | CP | CFPP | |
| E 1 | Rapsölsäuremethylester (RME) | -2,3 | -14°C |
| E 2 | 90% Rapsölsäuremethylester (RME) + 10 % Sojaölsäuremethylester (SojaME) | -2,0 | -8°C |
| C-Kettenverteilung der zur Herstellung der Testöle eingesetzten Fettsäuremethylester (Hauptbestandteile; FI.-% gemäß GC) | ||||||||||
| C16 | C16' | C18 | C18' | C18" | C18" | C20 | C20' | C22 | Σ gesättigt | |
| RME | 4,4 | 0,4 | 1,6 | 57,8 | 21,6 | 8,8 | 1,5 | 0,7 | 0,2 | 7,7 |
| SojaME | 10,4 | 0,1 | 4,1 | 24,8 | 51,3 | 6,9 | 0,5 | 0,4 | 0,4 | 15,4 |
| Charakterisierung der verwendeten Mitteldestillate | ||||
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
| Schwefelgehalt, ppm | 7,9 | 4,9 | 32,0 | 900 |
| Dichte, g/cm3 | 0,8436 | 0,8306 | 0,8348 | 0,8487 |
| Siedebeginn, °C | 209,9 | 143,9 | 209,1 | 203,7 |
| Siedeende, °C | 334,6 | 363,2 | 347,8 | 365,6 |
| Siedebereich (90-20), °C | 63,5 | 87,6 | 83,8 | 94,9 |
| Aromatengehalt, Gew.-% | 25,7 | 16,5 | 20,5 | 29,9 |
| Charakterisierung der Copolymere C | ||
| Polymer | Mw [g/mol] | Wasserzahl [ml] |
| P1 | 3000 | 12,0 |
| P2 | 3400 | 9,1 |
| P3 | 3600 | 7,6 |
| P4 | 3100 | 15,1 |
| P5 | 3300 | 11,8 |
| P6 | 3000 | 14,2 |
| Charakterisierung der Fließverbesserer | |||
| Beispiel | Comonomer(e) | V140 | CH3/100 CH2 |
| P7 | 13,6 Mol-% Vinylacetat | 130 mPas | 3,7 |
| P8 | 13,7 Mol-% Vinylacetat und 1,4 Mol-% Neodecansäurevinylester | 105 mPas | 5,3 |
| P9 | 9,4 Mol-% Vinylacetat | 220 mPas | 6,2 |
| Bewertung der Trennschicht | Bewertung der Phasentrennung | ||
| 1 | Klar und sauber | 1 | Komplette Abwesenheit aller Emulsionen und/oder Abscheidungen in beiden Phasen oder oben auf der Öl-Phase. |
| 1 b | kleine, klare Blasen, die schätzungsweise nicht mehr als 50 % der Trennschicht bedecken. Keine Schlieren, keine Filmbildung oder sonstige Benetzung an der Trennschicht. | ||
| 2 | Wie (1), aber zusätzlich kleine Luftbläschen oder kleine Wassertröpfchen in der Öl-Phase. | ||
| 2 | Schlieren, Filmbildung oder sonstige Benetzung an der Trennschicht | 3 | Emulsionen und/oder Niederschläge in beiden Phasen oder oben auf der Öl-Phase, |
| 3 | Schmaler Saum oder leichte Schaumbildung, oder beides | und/oder Tropfen in der Wasser-Phase oder an der Wandung anhaftend (ausgenommen die | |
| 4 | Dichter Saum oder starke Schaumbildung, oder beides | Wandung über der Öl-Phase). In Klammern gesetzt: Menge der Wasserphase |
| Wirksamkeit von Copolymeren als Demulgator in einer Mischung aus 95 Gew.-% F2 und 5 Gew.-% Biodiesel E1 | |||||||
| Bsp. Nr. | Copolymer | optische Beurteilung | Dosierung Copolymer ppm | ||||
| Trennschicht | Phasentrennung | Öl-Phase | Wasser-Phase | ||||
| 1 (V) | -- | 3-4 | 12 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | -- |
| 2(V) | P7 | 4 | 14 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 3(V) | P8 | 3 | 15 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 4(V) | P9 | 4 | 17 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 5 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 6 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 7 | P3 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 8 | P4 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 9 | P5 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 10 | P6 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 11 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 100 |
| 12 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 13 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 25 |
| 14 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| 15 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 100 |
| 16 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 17 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 25 |
| 18 | P2 | 1* | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| 19 | P4 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 100 |
| 20 | P4 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 21 | P4 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| 22 | P6 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 23 | P6 | 2 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| Wirksamkeit von Copolymeren als Demulgator in einer Mischung aus 95 Gew.-% F2 und 5 Gew.-% Biodiesel E2 | |||||||
| Bsp. Nr. | Copolymer | optische Beurteilung | Dosierung Copolymer ppm | ||||
| Trennschicht | Phasen- trennung | Öl-Phase | Wasser-Phase | ||||
| 24(V) | -- | 3-4 | 14 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | -- |
| 25(V) | P7 | 4 | 13 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 26(V) | P8 | 3 | 17 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 27(V) | P9 | 4 | 16 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 28 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 29 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 30 | P3 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 31 | P4 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 32 | P5 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 33 | P6 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 250 |
| 34 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 100 |
| 35 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 36 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 25 |
| 37 | P1 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| 38 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 100 |
| 39 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 40 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 25 |
| 41 | P2 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| 42 | P4 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 100 |
| 43 | P4 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 44 | P4 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| 45 | P6 | 1b | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 50 |
| 46 | P6 | 2 | 20 ml | 3 | trübe | klar | 10 |
| Beeinflussung der Kaltfließeigenschaften durch Blockcopolymere | |||||
| Beispiel | Brennstofföl | Copolymere | |||
| 300 ppm P7 | 300 ppm P8 | 300 ppm P7 + 10 ppm P1 | 300 ppm P8+ 10 ppm P1 | ||
| 65(V) | Mitteldestillat | - 22 | - 20 | - 23 | - 20 |
| 66 | Mitteldestillat + Biokraftstoff | - 23 | - 21 | - 24 | - 19 |
| Einfluss von Kaltfließverbesserern auf die Emulgierneigung mit und ohne Copolymer C) (hier P1) | ||||||||
| Bsp. | Öl | Kälteadditiv | optische Beurteilung | Dosierung P1 [ppm] | ||||
| Trennschicht | Phasentrennung | Öl-Phase | Wasser-Phase | |||||
| 67(V) | F4 | P7 | 1 b | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | - |
| 68(V) | F4+E1 | P7 | 3 | 14 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | - |
| 69 | F4+E1 | P7 | 1* | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 10 |
| 70 | F4+E1 | P7 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 250 |
| 71 | F4+E2 | P7 | 1 b | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 10 |
| 72 | F4+E2 | P7 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 250 |
| 73(V) | F4 | P8 | 1 b | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | - |
| 74(V) | F4+E1 | P8 | 3 | 13 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | - |
| 75 | F4+E1 | P8 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 10 |
| 76 | F4+E1 | P8 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 250 |
| 77 | F4+E2 | P8 | 1 b | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 10 |
| 78 | F4+E2 | P8 | 1 | 20 ml | 3 | trüb | klar | 250 |
Claims (12)
- Brennstofföl, enthaltend einen größeren Anteil einer Mischung ausA) einem Mitteldestillat-Brennstofföl, undB) einem Biobrennstofföl,
sowie einem kleineren AnteilC) eines öllöslichen, vernetzten Blockcopolymers aus C2- bis C4-Alkylenoxiden. - Brennstofföl nach Anspruch 1, worin das Mischungsverhältnis A) : B) bei 99:1 bis 1:99 liegt.
- Brennstofföl nach Anspruch 1 und/oder 2, worin das Molekulargewicht des vernetzten Bestandteils C) zwischen 1000 und 200.000 g/mol liegt.
- Brennstofföl nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, worin das Blockcopolymer C) eine Wasserzahl von 6 bis 17ml aufweist.
- Brennstofföl nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, worin der Vernetzer ausgewählt ist aus Bisphenol-A-diglycidylether, Butan-1,4-dioldiglycidylether, Hexan-1,6-dioldiglycidylether, Ethylenglykoldiglycidylether, Cyclohexandimethanoldiglycidylether, Resorcindiglycidylether, Glycerindiglycidylether, Glycerintriglycidylether, Glycerinpropoxylattriglycidylether, Polyglycerinpolyglycidylether, p-Aminophenoltriglycidylether, Polypropylenglykoldiglycidylether, Pentaerythrittetraglycidylether, Sorbitolpolyglycidylether, Trimethylolpropantriglycidylether, Castoröltriglycidylether, Diaminobiphenyltetraglycidylether, Sojaölepoxid, Adipinsäure, Maleinsäure, Phthalsäure, Maleinsäureanhydrid, Bernsteinsäureanhydrid, Dodecylbernsteinsäureanhydrid, Phthalsäureanhydrid, Trimellitsäureanhydrid, Pyromellitsäureanhydrid, Dimethoxydimethylsilan, Diethoxydimethylsilan, Toluoldiisoyanat und Diphenylmethandiisocyanat.
- Brennstofföl nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 5, worin der Gehalt der aus A) und B) bestehenden Mischung an C) von 0,001 bis 5 Gew.-% beträgt.
- Brennstofföle nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, welche zusätzlich zu den Bestandteilen A), B) und C) noch mindestens ein Alkylphenol-Formaldehydharz der Formel enthalten, worin RA für C4-C30-Alkyl oder -Alkenyl, RB für OH oder O-(A-O)x-H mit A = C2-C4-Alkylen und x = 1 bis 50, und n für eine Zahl von 2 bis 50 steht.
- Brennstofföle nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 7, welche zusätzlich zu den Bestandteilen A), B) und C) noch mindestens ein Copolymer enthalten, welches neben Ethylen 10 bis 40 Gew.-% Vinylacetat und gegebenenfalls 1 bis 40 Gew.-% Vinylester mit C3- bis C12-Alkylgruppen im Esterrest und gegebenenfalls 0,5 bis 20 Gew.-% Olefine mit 3 bis 10 C-Atomen enthält.
- Brennstofföle nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 8, welche zusätzlich zu den Bestandteilen A), B) und C) noch mindestens ein Aminsalz, Imid oder Amid eines primären und/oder sekundären Fettamins mit 8 bis 36 Kohlenstoffatomen umfassen.
- Brennstofföle nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 9, welche zusätzlich zu den Bestandteilen A), B) und C) noch mindestens ein Copolymer enthalten, welches von Amiden, Imiden und/oder Estern der Maleinsäure, Fumarsäure und/oder Itaconsäure abgeleitet ist.
- Brennstofföle nach einem oder mehreren der Ansprüche 1 bis 10, welche zusätzlich zu den Bestandteilen A), B) und C) noch ein Kammpolymer der Formel enthalten, worin
- A
- R', COOR', OCOR', R"-COOR' oder OR';
- D
- H, CH3, A oder R;
- E
- H oder A;
- G
- H, R", R"-COOR', einen Arylrest oder einen heterocyclischen Rest;
- M
- H, COOR", OCOR", OR" oder COOH;
- N
- H, R", COOR", OCOR, COOH oder einen Arylrest;
- R'
- eine Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 8-150 Kohlenstoffatomen;
- R"
- eine Kohlenwasserstoffkette mit 1 bis 10 Kohlenstoffatomen;
- m
- eine Zahl zwischen 0,4 und 1,0; und
- n
- eine Zahl zwischen 0 und 0,6 bedeuten.
- Verwendung eines Blockcopolymers C) wie in Anspruch 1 definiert zur Demulgierung von Mischungen aus Mitteldestillat-Brennstoffölen, Biobrennstoffölen und Wasser.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004002080A DE102004002080B4 (de) | 2004-01-15 | 2004-01-15 | Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus Mitteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs und Wasser |
| DE102004002080 | 2004-01-15 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1555309A1 true EP1555309A1 (de) | 2005-07-20 |
| EP1555309B1 EP1555309B1 (de) | 2015-10-21 |
Family
ID=34609561
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04030573.2A Expired - Lifetime EP1555309B1 (de) | 2004-01-15 | 2004-12-23 | Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus MItteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs und Wasser |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7815698B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1555309B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2005200651A (de) |
| CA (1) | CA2493178C (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102004002080B4 (de) |
| NO (1) | NO20050180L (de) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090038692A1 (en) * | 2007-08-09 | 2009-02-12 | 21St Century R & D, Llc | Modification of vegetable oils for fuel applications |
| US20110139106A1 (en) | 2007-08-09 | 2011-06-16 | 21St Century R & D, Llc | Modification of fats and oils for fuel and lubricating applications |
| US20090293344A1 (en) * | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-03 | Baker Hughes Incorporated | Process for Removing Water and Water Soluble Contaminants From Biofuels |
| US9127226B2 (en) * | 2008-06-06 | 2015-09-08 | Baker Hughes Incorporated | Process for clarifying biofuels |
| US8962059B1 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2015-02-24 | Superior Oil Company, Inc. | Bio-based oil composition and method for producing the same |
| GB201113392D0 (en) * | 2011-08-03 | 2011-09-21 | Innospec Ltd | Fuel compositions |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3879308A (en) * | 1973-05-14 | 1975-04-22 | Lubrizol Corp | Lubricants and fuels containing ester-containing compositions |
| US4183821A (en) * | 1978-05-26 | 1980-01-15 | Basf Wyandotte Corporation | Heteric/block polyoxyalkylene compounds as crude oil demulsifiers |
| US4398921A (en) * | 1981-11-02 | 1983-08-16 | Ethyl Corporation | Gasohol compositions |
| US4460380A (en) * | 1982-12-27 | 1984-07-17 | Exxon Research & Engineering Co. | Water shedding agents in distillate fuel oils |
| US4551152A (en) * | 1985-04-01 | 1985-11-05 | Texaco Inc. | Alcohol fuel anti-wear additive |
| US4561861A (en) * | 1984-11-01 | 1985-12-31 | Texaco Inc. | Motor fuel composition |
| WO1994010267A1 (en) * | 1992-10-26 | 1994-05-11 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc. | Oil additives and compositions |
| WO2000031216A1 (en) * | 1998-11-23 | 2000-06-02 | Pure Energy Corporation | Diesel fuel composition |
Family Cites Families (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3511882A (en) * | 1964-03-06 | 1970-05-12 | Nalco Chemical Co | Products of reaction of polyoxyalkylene alcohols and di-glycidyl ethers of bis-phenol compounds |
| US3344083A (en) | 1966-03-04 | 1967-09-26 | Petrolite Corp | Process of breaking emulsions |
| DE2227546C3 (de) * | 1972-06-07 | 1979-04-05 | Basf Ag, 6700 Ludwigshafen | Verwendung von oxalkylierten PoIyalkylenpolyaminen zur SchneUentwässening von Rohölen |
| US4211534A (en) * | 1978-05-25 | 1980-07-08 | Exxon Research & Engineering Co. | Combination of ethylene polymer, polymer having alkyl side chains, and nitrogen containing compound to improve cold flow properties of distillate fuel oils |
| DE3300866A1 (de) * | 1983-01-13 | 1984-07-19 | Basf Ag, 6700 Ludwigshafen | Oxalkylierte polyamidoamine, deren herstellung und deren verwendung als erdoelemulsionsspalter |
| DE3405843A1 (de) * | 1984-02-17 | 1985-08-29 | Bayer Ag, 5090 Leverkusen | Copolymere auf basis von maleinsaeureanhydrid und (alpha), (beta)-ungesaettigten verbindungen, ein verfahren zu ihrer herstellung und ihre verwendung als paraffininhibitoren |
| IN163163B (de) * | 1984-02-21 | 1988-08-20 | Exxon Research Engineering Co | |
| JPH0777986B2 (ja) * | 1985-01-31 | 1995-08-23 | 京セラ株式会社 | 炭化珪素質焼結体の製法 |
| DE3640613A1 (de) | 1986-11-27 | 1988-06-09 | Ruhrchemie Ag | Verfahren zur herstellung von ethylen-mischpolymerisaten und deren verwendung als zusatz zu mineraloel und mineraloelfraktionen |
| DE3742630A1 (de) | 1987-12-16 | 1989-06-29 | Hoechst Ag | Polymermischungen fuer die verbesserung der fliessfaehigkeit von mineraloeldestillaten in der kaelte |
| US5196486A (en) * | 1989-03-17 | 1993-03-23 | Nalco Chemical Company | Alkoxylated vinyl polymer demulsifiers |
| US4985046A (en) * | 1989-06-09 | 1991-01-15 | E. I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Process for preparing poly (paraphenylene terephthalamide) fibers dyeable with cationic dyes |
| DE3926992A1 (de) * | 1989-08-16 | 1991-02-21 | Hoechst Ag | Verwendung von umsetzungsprodukten von alkenylspirobislactonen und aminen als paraffindispergatoren |
| DE4136661A1 (de) * | 1991-11-07 | 1993-05-13 | Basf Ag | Erdoelemulsionsspalter |
| US5464549A (en) * | 1991-12-12 | 1995-11-07 | Ethyl Corporation | Oil soluble dispersants suitable for use in fuels and lubricants |
| DE4142579A1 (de) * | 1991-12-21 | 1993-06-24 | Basf Ag | Erdoelemulsionsspalter auf der basis eines alkoxylats und verfahren zur herstellung dieses alkoxylats |
| GB9204709D0 (en) | 1992-03-03 | 1992-04-15 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Additives for oils |
| IL107927A0 (en) * | 1992-12-17 | 1994-04-12 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil soluble ethylene/1-butene copolymers and lubricating oils containing the same |
| DE59404053D1 (de) * | 1993-01-06 | 1997-10-23 | Hoechst Ag | Terpolymere auf Basis von alpha,beta-ungesättigten Dicarbonsäureanhydriden, alpha,beta-ungesättigten Verbindungen und Polyoxyalkylenethern von niederen, ungesättigten Alkoholen |
| GB9303924D0 (en) | 1993-02-26 | 1993-04-14 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Oil additives and compositions |
| US5749923A (en) * | 1993-11-23 | 1998-05-12 | Degussa Aktiengellschaft | Method for bleaching denim textile material |
| DE4418800A1 (de) * | 1994-05-30 | 1995-12-07 | Basf Ag | Verfahren zur Abtrennung vom Wasser aus Rohöl und hierbei verwendete Erdölemulsionsspalter |
| EP0857776B2 (de) * | 1997-01-07 | 2007-05-02 | Clariant Produkte (Deutschland) GmbH | Verbesserung der Fliessfähigkeit von Mineralölen und Mineralöldestillaten unter Verwendung von Alkylphenol-Aldehydharzen |
| GB9827366D0 (en) * | 1998-12-11 | 1999-02-03 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc | Macromolecular materials |
| DE50011064D1 (de) * | 2000-01-11 | 2005-10-06 | Clariant Gmbh | Mehrfunktionelles Additiv für Brennstofföle |
-
2004
- 2004-01-15 DE DE102004002080A patent/DE102004002080B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-12-23 EP EP04030573.2A patent/EP1555309B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2005
- 2005-01-12 NO NO20050180A patent/NO20050180L/no unknown
- 2005-01-13 JP JP2005006739A patent/JP2005200651A/ja not_active Withdrawn
- 2005-01-14 CA CA2493178A patent/CA2493178C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2005-01-14 US US11/036,693 patent/US7815698B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3879308A (en) * | 1973-05-14 | 1975-04-22 | Lubrizol Corp | Lubricants and fuels containing ester-containing compositions |
| US4183821A (en) * | 1978-05-26 | 1980-01-15 | Basf Wyandotte Corporation | Heteric/block polyoxyalkylene compounds as crude oil demulsifiers |
| US4398921A (en) * | 1981-11-02 | 1983-08-16 | Ethyl Corporation | Gasohol compositions |
| US4460380A (en) * | 1982-12-27 | 1984-07-17 | Exxon Research & Engineering Co. | Water shedding agents in distillate fuel oils |
| US4561861A (en) * | 1984-11-01 | 1985-12-31 | Texaco Inc. | Motor fuel composition |
| US4551152A (en) * | 1985-04-01 | 1985-11-05 | Texaco Inc. | Alcohol fuel anti-wear additive |
| WO1994010267A1 (en) * | 1992-10-26 | 1994-05-11 | Exxon Chemical Patents Inc. | Oil additives and compositions |
| WO2000031216A1 (en) * | 1998-11-23 | 2000-06-02 | Pure Energy Corporation | Diesel fuel composition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE102004002080B4 (de) | 2007-03-29 |
| US7815698B2 (en) | 2010-10-19 |
| EP1555309B1 (de) | 2015-10-21 |
| CA2493178C (en) | 2013-07-09 |
| US20050155282A1 (en) | 2005-07-21 |
| CA2493178A1 (en) | 2005-07-15 |
| NO20050180D0 (no) | 2005-01-12 |
| DE102004002080A1 (de) | 2005-09-01 |
| JP2005200651A (ja) | 2005-07-28 |
| NO20050180L (no) | 2005-07-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69532917T2 (de) | Kraftölzusammensetzung mit polyoxyalkylenen | |
| DE69903545T2 (de) | Ölzusammensetzungen | |
| EP1541664B1 (de) | Brennstofföle aus Mitteldestillaten und Ölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs mit verbesserten Kälteeigenschaften | |
| EP2516605A2 (de) | Multifunktionelle kälteadditive für mitteldestillate mit verbesserter fliessfähigkeit | |
| EP1801187B2 (de) | Detergenzadditive enthaltende Mineralöle mit verbesserter Kältefliessfähigkeit | |
| DE10319028B4 (de) | Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus Mitteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs | |
| EP1380634B1 (de) | Oxidationsstabilisierte Schmieradditive für hochentschwefelte Brennstofföle | |
| DE102004024532B4 (de) | Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus Mitteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs und Wasser | |
| EP1446464A2 (de) | Additive für schwefelarme mineralöldestillate, umfassend einen ester eines alkoxylierten polyols und ein alkylphenol-aldehydharz | |
| DE69926887T2 (de) | Zusätze und ölzusammensetzungen | |
| EP1555309B1 (de) | Demulgatoren für Mischungen aus MItteldestillaten mit Brennstoffölen pflanzlichen oder tierischen Ursprungs und Wasser | |
| EP1621600B1 (de) | Mineralöle mit verbesserter Leitfähigkeit und Kältefliessfähigkeit | |
| EP1380633B1 (de) | Verwendung von öligen Flüssigkeiten zur Verbesserung der Oxidationsstabilität der Brennstofföle | |
| DE102005045134B4 (de) | Alkylphenol-Aldehydharze, diese enthaltende Zusammensetzungen zu Verbesserung der Kältefließfähigkeit und Schmierfähigkeit von Brennstoffölen sowie deren Verwendung | |
| EP4127106B1 (de) | Zusammensetzungen und verfahren zur dispergierung von paraffinen in schwefelarmen brennstoffölen | |
| DE102005020264B4 (de) | Additive für schwefelarme Mineralöldestillate, umfassend Aromaten, welche eine Hydroxygruppe, eine Methoxygruppe und eine Säurefunktion tragen | |
| DE10252973A1 (de) | Oxidationsstabilisierte Schmieradditive für hochentschwefelte Brennstofföle | |
| DE102005061465B4 (de) | Detergenzadditive enthaltende Mineralöle mit verbesserter Kältefließfähigkeit | |
| DE10252972A1 (de) | Oxidationsstabilisierte ölige Flüssigkeiten auf Basis pflanzlicher oder tierischer Öle | |
| DE19739272A1 (de) | Additiv zur Paraffindispergierung in Mineralölen und Mineralöldestillaten |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR LV MK YU |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: CLARIANT PRODUKTE (DEUTSCHLAND) GMBH |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060120 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20061204 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20150608 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502004015058 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20151021 Year of fee payment: 12 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20151021 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20151030 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502004015058 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20160530 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20160722 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502004015058 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20161223 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20170831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170102 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161223 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20161223 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170701 |