EP1537337B1 - Dispositif de servocommande hautement dynamique a soupapes - Google Patents
Dispositif de servocommande hautement dynamique a soupapes Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1537337B1 EP1537337B1 EP03807769A EP03807769A EP1537337B1 EP 1537337 B1 EP1537337 B1 EP 1537337B1 EP 03807769 A EP03807769 A EP 03807769A EP 03807769 A EP03807769 A EP 03807769A EP 1537337 B1 EP1537337 B1 EP 1537337B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- valve
- bushing
- drive device
- highly dynamic
- sleeve
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000005355 Hall effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003319 supportive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B13/00—Details of servomotor systems ; Valves for servomotor systems
- F15B13/02—Fluid distribution or supply devices characterised by their adaptation to the control of servomotors
- F15B13/04—Fluid distribution or supply devices characterised by their adaptation to the control of servomotors for use with a single servomotor
- F15B13/0401—Valve members; Fluid interconnections therefor
- F15B13/0402—Valve members; Fluid interconnections therefor for linearly sliding valves, e.g. spool valves
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T137/00—Fluid handling
- Y10T137/8158—With indicator, register, recorder, alarm or inspection means
- Y10T137/8225—Position or extent of motion indicator
- Y10T137/8242—Electrical
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T137/00—Fluid handling
- Y10T137/8593—Systems
- Y10T137/86493—Multi-way valve unit
- Y10T137/86574—Supply and exhaust
- Y10T137/86622—Motor-operated
- Y10T137/8663—Fluid motor
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T137/00—Fluid handling
- Y10T137/8593—Systems
- Y10T137/86493—Multi-way valve unit
- Y10T137/86574—Supply and exhaust
- Y10T137/8667—Reciprocating valve
- Y10T137/86694—Piston valve
- Y10T137/8671—With annular passage [e.g., spool]
Definitions
- the invention relates to a highly dynamic servo-valve control device with a tax-containing in a base body sleeve and a tax-containing in the body tax-carrying slide, wherein at least one of the control edges of the slider is designed to be displaceable relative to a control edge of the sleeve, wherein the slide and the sleeve to each other the servo valve control device comprises a primary drive device and a high frequency drive device, wherein the primary drive device comprises at least one pilot valve which influences the movement of the sleeve or the slide.
- Highly dynamic servo-valve control devices are known from the prior art. These servo-valve control devices are used in the prior art to control or regulate flow rates and / or pressures in hydraulic systems. In order to change volume flows, control cross sections are changed via a movement of control edges, for example on a slide and with the aid of a direct or indirect drive.
- Valve control is disclosed in British Patent GB 677,672A. From the European patent application EP 1 098 101 A2 a further valve control device is known. U.S. Patent 4,205,590 A also discloses another valve control device, as does U.S. Patent 4,333,387 A.
- Directly controlled valves include electromechanical converters, proportional solenoids, linear motors, plunger coils or piezoelectric transducers. Pilot-operated valves are indirectly operated drives, such as mechanical-hydraulic converters, spool valves, nozzle baffle plates and jet pipes. High dynamic servo valve control devices include both direct and pilot operated valves.
- control cross sections are bounded by two control edges, wherein the prior art, an active, i. in its position variable control edge, such as on the slider and a passive, i. fixed control edge, about on the sleeve includes.
- the achievable frequency of the servo-valve control device is specified in the existing cases via a drive of the slide and an associated drive or control electronics.
- the high-frequency drive device comprises a piezoelectric element or a plunger coil.
- the servo-valve control device comprises a sleeve position determining device for determining a position of the sleeves relative to a position of the slider. In such an embodiment, it is possible to determine the exact position of slide to sleeve and accordingly to operate the servo-valve control device.
- the sleeve position determining device comprises an eddy current sensor.
- a non-contact eddy current sensor is wear-free and robust. Also, it is extremely resistant to corrosion, which increases the longevity of the servo-valve control device.
- the servo-valve control device has an absolute position determining device for determining the position of the sleeve and slide in relation to the main body, the exact position of sleeve and slide can be advantageously determined in this variant in this variant. This allows avoiding drift of sleeve and slider in the body. Thus, a fault-free operation of the servo-valve control device is made possible even over long periods of use. An absolute measurement is only necessary if the slide and sleeve are pilot-operated.
- the sleeve position determining device or the absolute position determining device comprises an eddy current sensor, a Hall effect sensor, or an inductive displacement transducer (LVDT). Since, for example, the use of the property that a movement of electrons in the magnetic field is influenced, and a resulting deflection as voltage on the Hall effect sensor can be tapped off, this has the advantage that this is very large magnetic fields can be measured and the measuring range of Hall effect sensors is significantly larger than other sensors.
- the use of known measuring sensors in the sleeve position determining device or the absolute position determining device is particularly advantageous in this variant, since costs and troubles are avoided in the procurement of the corresponding sensors.
- the servo-valve control device comprises at least one pilot valve controlling the movement of the sleeve and a pilot valve controlling the movement of the slide. It is thus used for slide and sleeve drive side robust and particularly small-sized elements.
- the servo-valve control device comprises at least one high-frequency drive device.
- a high frequency drive device has the significant advantage of having very short response times.
- the high-frequency drive device controls at least one displacement of the sleeve. This minimizes the response time of the sleeve in the control.
- the high-frequency drive device has a high inherent momentum and a low lift
- the primary drive device has a low inherent dynamics and a large stroke.
- the high-frequency drive device complements the primary drive device in terms of its own dynamics and speed increase in the expression, particularly fast control times become possible.
- the combination of high dynamics / short stroke and medium (low) dynamics / long stroke results in a high speed gain.
- the high-frequency drive device has a low momentum and a large stroke, and the primary drive means a high momentum and has a small stroke, so in a further variant, an exchange of high-frequency drive device elements with primary drive device elements is possible.
- the advantage of a particularly fast control of the individual components of the servo-valve control device is nevertheless maintained.
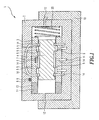
- the servo-valve control device 1 is shown in a section.
- the servo-valve control device 1 comprises a base body 2 in which a sleeve 3 is mounted.
- the sleeve 3 has control edges 5.
- the control edges 5 are pronounced inside the sleeve 3.
- a slide 4 In the interior of the sleeve 3, a slide 4, with a pronounced on the circumference of the control edges 5 displaceable within the sleeve 3 pronounced.
- Through the sleeve 3 pass through openings.
- the passage openings 14 are connected to passage openings 14 in the base body 2.
- the sleeve 3 is designed displaceable via a high-frequency drive device 11 in this embodiment.
- the high-frequency drive device 11 pushes the sleeve 3 in one direction.
- the high-frequency drive device 11 comprises a piezoelectric element 13.
- the piezoelectric element 13 has the advantage of a very fast response and pushes the sleeve 3 in one direction.
- a return movement is effected by a spring 20.
- the spool 4 is moved by pressurized liquids either in one direction or the other.
- the liquids are conveyed by pilot valves 12 to one side or the other of the slide 4 from a prime mover 10.
- the pilot valves 12 are supplied via the primary drive device 10, which has supply channels for the liquid supply to the pilot valves 12, preferably with an incompressible liquid.
- the supply channels are connected to the pilot valves.
- supportive also offers the use of the spring 20.
- the position of the slider 4 in the sleeve 3 is determined by an incorporated in the sleeve 3 eddy current sensor 7, which is part of a sleeve position determining means 6.
- the housing 2 and an absolute position determining device 8 is incorporated.
- the Hall effect sensor 9 is thus located between the housing 2 and sleeve 3.
- the sleeve position determination device 6 and the absolute position determination device 8 comprise further sensors known from the prior art.
- the primary drive device 10 and the high-frequency drive device 11 also use standard known elements from the prior art.
- the movement of the sleeve 3 via a force flow through a transmission medium such as an incompressible fluid, e.g. Oil advantageously reachable, wherein the movement of the slider 4 is also achieved via a transmission medium, such as an incompressible liquid such as oil.
- a transmission medium such as an incompressible fluid, e.g. Oil
- the two transmission media are controlled separately from each other. However, the possibility of a predefined forced coupling between the two transmission media can also be used.
- the slide can be designed to be displaceable in both directions by the action of the transmission medium alone.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Servomotors (AREA)
- Electrically Driven Valve-Operating Means (AREA)
- Fluid-Driven Valves (AREA)
- Magnetically Actuated Valves (AREA)
Claims (9)
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) avec une douille (3) contenue dans un corps de base (2) et comprenant des bords de commande et avec un registre (4) contenu dans le corps de base (2) et comprenant des bords de commande, au moins un des bords de commande (5) du registre (4) étant conçu pour être mobile par rapport à un bord de commande (5) de la douille (3), le registre (4) et aussi la douille (3) étant conçus pour être mobiles en sens mutuellement opposés et par rapport au corps de base (2), le dispositif de servocommande de vannes (1) comprenant un dispositif d'entraînement primaire (10) et un dispositif d'entraînement à haute fréquence (11) et le dispositif d'entraînement primaire (10) comprenant au moins une vanne pilote (12) qui exerce une influence sur le mouvement de la douille (3) ou du registre (4), caractérisé en ce que le dispositif d'entraînement à haute fréquence (11) comprend un élément piézoélectrique (13) ou une bobine plongeante.
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de servocommande de vannes (1) comprend un dispositif de détermination de la position de la douille (6) servant à déterminer une position de la douille (3) dans une relation avec une position du registre (4).
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de détermination de la position de la douille (6) comprend un capteur à courant de Foucault (7).
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de servocommande de vannes (1) comprend un dispositif de détermination de la position absolue (8) servant à déterminer la position de la douille (3) et du registre (4) en relation avec le corps de base (2).
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de détermination de la position de la douille (6) ou le dispositif de détermination de la position absolue (8) comprend un capteur à courant de Foucault, un capteur à effet Hall (9) ou un capteur de déplacement inductif (LVDT).
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de servocommande de vannes (1) comprend au moins une vanne pilote (12) qui commande le mouvement de la douille (3) ou une vanne pilote (12) qui commande le mouvement du registre (4).
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 6, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif à haute fréquence (11) commande au moins un déplacement de la douille (3).
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 7, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif d'entraînement à haute fréquence (11) présente une forte dynamique propre et une faible course et en ce que le dispositif d'entraînement primaire (10) présente une faible dynamique propre et une course importante.
- Dispositif de servocommande de vannes à forte dynamique (1) selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 8, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif d'entraînement à haute fréquence (11) présente une faible dynamique propre et une course importante et en ce que le dispositif d'entraînement primaire (10) présente une forte dynamique propre et une faible course.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE2002141977 DE10241977B4 (de) | 2002-09-11 | 2002-09-11 | Hochdynamische Servo-Ventilsteuervorrichtung |
| DE10241977 | 2002-09-11 | ||
| PCT/EP2003/008550 WO2004033921A1 (fr) | 2002-09-11 | 2003-08-01 | Dispositif de servocommande hautement dynamique a soupapes |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1537337A1 EP1537337A1 (fr) | 2005-06-08 |
| EP1537337B1 true EP1537337B1 (fr) | 2006-06-14 |
Family
ID=31969060
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03807769A Expired - Lifetime EP1537337B1 (fr) | 2002-09-11 | 2003-08-01 | Dispositif de servocommande hautement dynamique a soupapes |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7721758B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP1537337B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP4198115B2 (fr) |
| AU (1) | AU2003250203A1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE10241977B4 (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2004033921A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100535486C (zh) * | 2008-03-11 | 2009-09-02 | 浙江大学 | 压电晶体驱动高速开关阀 |
| US20100148098A1 (en) * | 2008-10-03 | 2010-06-17 | Toliusis Vytautas J | Directly piloted valve assembly |
| JP5212035B2 (ja) * | 2008-11-14 | 2013-06-19 | 株式会社Ihi | 弁装置及びサーボ弁 |
| US8678033B2 (en) * | 2010-03-24 | 2014-03-25 | Eaton Corporation | Proportional valve employing simultaneous and hybrid actuation |
| KR101161802B1 (ko) * | 2010-10-15 | 2012-07-04 | 한국도키멕유공압 주식회사 | 유압서보밸브 튜닝시스템 |
| US9592905B2 (en) * | 2014-11-03 | 2017-03-14 | Hamilton Sunstrand Corporation | Fuel intelligent crossfeed valve for detecting leakage in aircraft fuel tanks |
| DE102016214252A1 (de) | 2016-08-02 | 2018-02-08 | Festo Ag & Co. Kg | Ventilbetätigungssystem |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE802298C (de) * | 1948-10-09 | 1951-02-08 | Elektro Mechanik G M B H | Hydraulische Schiebersteuerung mit Vorsteuerung |
| GB677672A (en) * | 1949-06-08 | 1952-08-20 | Gen Motors Corp | Improved reciprocable fluid-control valve |
| US4205590A (en) * | 1978-02-06 | 1980-06-03 | Moog Inc. | Positive feedback mechanism for servocontroller of fluid operated actuator |
| US4333387A (en) * | 1978-03-21 | 1982-06-08 | Bertea Corporation | Anti-jam hydraulic servo valve |
| US4907615A (en) * | 1987-11-05 | 1990-03-13 | Schenck Pegasus Corporation | High frequency response servovalve with electrical position feedback element structure and method |
| DE19711781C2 (de) * | 1997-03-12 | 2000-05-31 | Pepperl & Fuchs | Vorrichtung zur Positionserfassung eines beweglich angeordneten Magneten zum Erzeugen eines magnetischen Feldes durch eine Wandung aus ferromagnetischem Material hindurch, insbesondere Stellantrieb mit bewegbarem Stellglied |
| DE19841660C2 (de) * | 1998-09-11 | 2003-07-10 | Audi Ag | Anordnung zum berührungslosen Messen von Ventilbewegungen bei Brennkraftmaschinen |
| US6179107B1 (en) * | 1999-11-08 | 2001-01-30 | General Motors Corporation | Trim valve for a fluid operated friction torque transmitting device |
| US6789570B2 (en) * | 2001-04-23 | 2004-09-14 | Hydraforce, Inc. | Hydraulic valve with a position sensor |
| US7422033B2 (en) * | 2004-12-16 | 2008-09-09 | Husco International, Inc. | Position feedback pilot valve actuator for a spool control valve |
-
2002
- 2002-09-11 DE DE2002141977 patent/DE10241977B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2003
- 2003-08-01 JP JP2004542282A patent/JP4198115B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-08-01 AU AU2003250203A patent/AU2003250203A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2003-08-01 DE DE50303863T patent/DE50303863D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-08-01 US US10/527,204 patent/US7721758B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2003-08-01 EP EP03807769A patent/EP1537337B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-08-01 WO PCT/EP2003/008550 patent/WO2004033921A1/fr active Application Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005538331A (ja) | 2005-12-15 |
| WO2004033921A1 (fr) | 2004-04-22 |
| US7721758B2 (en) | 2010-05-25 |
| DE10241977A1 (de) | 2004-04-01 |
| DE10241977B4 (de) | 2006-01-26 |
| US20070079879A1 (en) | 2007-04-12 |
| EP1537337A1 (fr) | 2005-06-08 |
| DE50303863D1 (de) | 2006-07-27 |
| JP4198115B2 (ja) | 2008-12-17 |
| AU2003250203A1 (en) | 2004-05-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2209998B1 (fr) | Vanne de distribution à commande pilote, destinée en particulier à commander un vérin de commande d'une turbomachine | |
| EP2425159A1 (fr) | Vanne papillon proportionnelle | |
| DE3506053A1 (de) | Schaltmagnet fuer gleichstrom zum antrieb eines ventilgliedes | |
| EP1537337B1 (fr) | Dispositif de servocommande hautement dynamique a soupapes | |
| EP3181967B1 (fr) | Soupape | |
| EP3446014B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'actionnement pour un piston de commande d'une soupape hydraulique | |
| DE4446860A1 (de) | Regelventil | |
| DE102012210799A1 (de) | Hydraulische Steuervorrichtung mit Volumenstromsensor für jedes Stellglied | |
| EP2702460B1 (fr) | Vanne pneumatique et son usage pour un consommateur connecté | |
| WO2011000515A1 (fr) | Ensemble à soupape | |
| DE2618874C3 (de) | Elektrohydraulisches Servoventil | |
| EP0504465A1 (fr) | Transducteur fluidique à entraînement piézo-électrique | |
| DE4135822C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung eines hydraulischen Signals entsprechend einem elektrischen Signal | |
| DE102012103636A1 (de) | Bidirektionales Durchflusssteuerventil | |
| EP0528103B2 (fr) | Dispositif de commande électro-hydraulique | |
| WO2011003210A1 (fr) | Système pour préparer une section transversale d'étranglement variable pour un flux de fluide | |
| EP0388635B1 (fr) | Dispositif de commande électrohydraulique | |
| DE3708570C2 (de) | Elektrohydraulische Einrichtung zum Betätigen eines in einer Gehäusebohrung verschiebbaren kolbenartigen Teils | |
| DE2416235A1 (de) | Drucksteuerventil | |
| DE3810139C2 (fr) | ||
| DE4125818C2 (de) | Düse-Prallplatte-System für ein Druckregelventil | |
| EP0049714B1 (fr) | Servomoteur à asservissement commandé par des moyens électro-magnétiques | |
| DE2515134A1 (de) | Hydraulisches proportionalventil mit elektromagnetischer steuerung | |
| DE3743345A1 (de) | Proportional arbeitendes druckbegrenzungsventil | |
| EP0825349B1 (fr) | Valve de commande directionnelle et proportionnelle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20050217 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): CH DE IT LI |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE IT LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: BOVARD AG PATENTANWAELTE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50303863 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20060727 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20070315 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Owner name: MOOG GMBH Free format text: MOOG GMBH#HANNS-KLEMM-STRASSE 28#71034 BOEBLINGEN (DE) -TRANSFER TO- MOOG GMBH#HANNS-KLEMM-STRASSE 28#71034 BOEBLINGEN (DE) |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50303863 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: DR. JOSTARNDT & KOLLEGEN, DE Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50303863 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: FLEUCHAUS & GALLO PARTNERSCHAFT MBB, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50303863 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: FLEUCHAUS & GALLO PARTNERSCHAFT MBB, DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20160823 Year of fee payment: 14 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20160819 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170831 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170801 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50303863 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: WITHERS & ROGERS LLP, DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20190822 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 50303863 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20210302 |