EP1471326B1 - Commutateur électrique pour fusée de projectile, ledit commutateur étant actionné par pression de gaz - Google Patents
Commutateur électrique pour fusée de projectile, ledit commutateur étant actionné par pression de gaz Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1471326B1 EP1471326B1 EP04002749A EP04002749A EP1471326B1 EP 1471326 B1 EP1471326 B1 EP 1471326B1 EP 04002749 A EP04002749 A EP 04002749A EP 04002749 A EP04002749 A EP 04002749A EP 1471326 B1 EP1471326 B1 EP 1471326B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- gas
- pressure switch
- switching piston
- contact
- switch according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims description 51
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000003380 propellant Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000012811 non-conductive material Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005553 drilling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005474 detonation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002360 explosive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003746 feather Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- ORQBXQOJMQIAOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N nobelium Chemical compound [No] ORQBXQOJMQIAOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000565 sealant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F42—AMMUNITION; BLASTING
- F42C—AMMUNITION FUZES; ARMING OR SAFETY MEANS THEREFOR
- F42C19/00—Details of fuzes
- F42C19/06—Electric contact parts specially adapted for use with electric fuzes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F42—AMMUNITION; BLASTING
- F42B—EXPLOSIVE CHARGES, e.g. FOR BLASTING, FIREWORKS, AMMUNITION
- F42B3/00—Blasting cartridges, i.e. case and explosive
- F42B3/006—Explosive bolts; Explosive actuators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F42—AMMUNITION; BLASTING
- F42C—AMMUNITION FUZES; ARMING OR SAFETY MEANS THEREFOR
- F42C15/00—Arming-means in fuzes; Safety means for preventing premature detonation of fuzes or charges
- F42C15/28—Arming-means in fuzes; Safety means for preventing premature detonation of fuzes or charges operated by flow of fluent material, e.g. shot, fluids
- F42C15/30—Arming-means in fuzes; Safety means for preventing premature detonation of fuzes or charges operated by flow of fluent material, e.g. shot, fluids of propellant gases, i.e. derived from propulsive charge or rocket motor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H35/00—Switches operated by change of a physical condition
- H01H35/24—Switches operated by change of fluid pressure, by fluid pressure waves, or by change of fluid flow
Definitions
- the invention relates to a gas pressure switch for an ignition and safety device of an ammunition according to the features indicated in the preamble of claim 1.
- Munitions Ignition and Safety Devices require two physically independent release mechanisms to enable firing circuits.
- a spin-stabilized projectile for example, the launch acceleration and the projectile spin are used for this purpose.
- plain tube ammunition for example, 120 mm HE ammunition, however, a spin-dependent release mechanism can not be used.
- a gas pressure switch for an ignition and security device of an ammunition is from the FR 2 070 544 A known.
- the gas pressure switch has a shear-off locking pin, which holds a switching piston until it reaches a defined gas pressure in the rest position and shears when reaching the defined gas pressure, whereby the control piston is free and can be moved into its contact position.
- Same principle is the FR 1 417 132 A removable.
- the invention is based essentially on the idea to perform the gas pressure switch as an assembly that is designed as a "switching element" once and preferably has the form of a screw which is obliquely screwed from the back into the projectile tail of a corresponding ammunition.
- the gas pressure switch comprises a displaceable in the direction of the longitudinal axis of the switch switch piston, which is secured in its rest position by a perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the switch arranged locking pin against unintentional displacement.
- This locking pin is designed and arranged such that the control piston can not be damaged or moved in case of transport loads occurring and rough handling of the ammunition.
- the locking pin is preferably sealed on the side facing the charge space by a membrane of a plastic material which is welded to the housing of the gas pressure switch.
- the membrane presses against the head side of the control piston. As soon as the gas pressure has reached a predetermined value, the locking pin shears off and the switching piston is displaced axially into a sealing seat. During this displacement, the switching piston closes with its lower end two contacts, which forward a signal for ignition release. The plastically deformable membrane also causes the switching piston is held in its contact position, so that the contacts then remain securely closed.
- the gas pressure switch according to the invention represents a crucial securing element for the firing and safety system of a projectile.
- the gas pressure switch Before the single switching operation, the gas pressure switch is safely electrically opened until a predetermined pressure (for example 345 bar) is reached. The switching function takes place only when this defined pressure is exceeded. Within about 15 milliseconds after this pressurization, the switch is then closed and remains closed until the detonation of the explosive charge without bouncing. When the gas pressure switch is stored, it remains securely in its open position even after 15 years and meets all functional requirements.
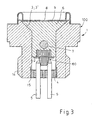
- Fig.1 illustrates the installation of a gas pressure switch 1 according to the invention in the rear-side region of a smooth-tube projectile, preferably HE projectile 114, wherein the gas pressure switch 1 has the shape of a hexagonal screw.
- This hex screw 1 is screwed through a thread 14 in a bore of the bullet tail 17 and the screw receptacle sealed by a sealing ring 22.
- the propellant charge of the projectile 114 is located in a manner known per se in a propellant charge shell 18. Since the projectile shown here is a wing-stabilized projectile, hinged tail wings 19 are arranged on the projectile tail 17.
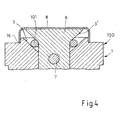
- the gas pressure switch 1 ( Fig.2 and 3 ) comprises a housing 100 made of stainless steel, which is designed in its outer shape like a hexagon screw. Inside the housing 100, a cylindrical bore 2 is arranged, which is designed as a conical countersinking 3 towards the upper end and with respect to a guided in the bore 2 control piston 6, which has a corresponding conical surface 3 'in the region of the countersink 3, with a sealing seat forms the sealing surfaces 3 and 3 '. As Figure 4 can be seen, between the sealing surfaces 3 and 3 'additionally an annular damping element 101 made of a plastic material (eg tin or lead) may be arranged.
- a plastic material eg tin or lead
- the housing 100 of the gas pressure switch 1 is provided on the outside with a fine thread 14 in the lower area, with the aid of which the gas pressure switch 1 is screwed into the projectile 114 and by means of the metallic sealing ring 22 (FIGS. Fig.1 ) is sealed.
- the switching piston 6 is surrounded on the upper side by a hat-shaped, plastically deformable and welded to the switch housing 100 hat-shaped membrane 8 and is connected on its underside with a contact device 60 which consists essentially of a pin-shaped element 11, which is a ceramic insert with gold-plated contact surfaces 10 acts.
- the pin-shaped element 11, which is arranged in an electrically insulated manner on the switching piston 6, is fastened in the region 13 by means of a retaining ring 12 (which is welded to the switching piston 6, for example, by means of laser light).
- the gas pressure switch 1 may be a provided with the gas pressure switch ammunition body in a corresponding weapon and the control piston 6 in Fig.2 take shown rest position.
- the pin-shaped element 11 of the contact device 60 is pressed between the two housing-fixed contact pins 5 and electrically connects them together, so that a signal for ignition release to the corresponding (not shown) device is forwarded.
- the gold-plated contact points of arranged on the control piston 6 ceramic insert 11 and the contact pins 5 guarantee a perfect transfer function of the signal.
- the membrane 8 Since the membrane 8 is plastically deformed by the gas pressure, it remains in the "everted” state, so that it the switching piston 6 in the lower closed position ( FIG. 3 ) positively fixed and the gas pressure switch 1 remains securely closed.
- the gas pressure switch 1 according to the invention is gas-tight, if it is pressurized with pressures up to 6,500 bar up to 15 milliseconds. It has proved to be useful if not only the carrier 4 in the region 15, but also the metallic membrane 8 are welded to the housing 100 in the region 16.
- the Figure 5 and 6 show a second embodiment of a gas pressure switch according to the invention, which is substantially in the Fig.2 and 3 illustrated gas pressure switch differs in that the designated 60 'contact device is not made of a ceramic insert with metallized contact surfaces, but of a metallic contact pin 102 which is connected to a plunger 102'.
- the plunger 102 ' is held by an in the switching piston 6 holding device 103 made of an insulating material, preferably glass.
- the switching pin 102 has a diameter and a shape that are selected such that it is in the contact position of the switching piston 6 (FIG. Figure 6 ) in the contact pins 5 "clawed".
- FIG. 7 and 8th illustrated gas pressure switch differs from that in the Fig.2 and 3 illustrated gas pressure switch substantially by the designated 60 "contact device.
- the switching piston 6 in its displacement from its rest position ( Figure 7 ) in his contact position ( Figure 8 ) causes a displacement of the contact device 60 "via a plan formed bottom side 105.
- the contact device 60 "consists of a printed circuit board arrangement comprising four printed circuit boards 106-109 which adjoin one another axially, wherein the first printed circuit board 106 facing the housing-fixed contact pins 5 is intended to effect a centering of the contact pins 5.
- the second printed circuit board 107 adjoining the first printed circuit board 106 is provided with bores 110 which are arranged above the contact pins 5 and in the rest position of the switching piston 6 (FIG. Figure 7 ) have a relation to the diameter of the contact pins 5 smaller diameter.
- the second circuit board 107 is followed by a third circuit board 108, which is provided with two sleeve-shaped metallic receptacles 104, which are electrically conductively connected to one another via a copper coating 115.
- the position of the two receptacles 104 in the third circuit board 108 is selected such that upon displacement of the control piston 6 from its rest to its contact position, the two housing-fixed contact pins 5 are pressed into one of the two sleeve-shaped receptacles 104.
- a fourth circuit board 109 connects to the upper side, which abuts against the end face 105 of the control piston 6 and on the end face 112 of the third printed circuit board 108, to a movement of the circuit board assembly 60 "in the rest position of the control piston 6 (FIG. Figure 7 ) to prevent.
- the locking pin 7 When this gas pressure switch is acted upon by a defined gas pressure, the locking pin 7 in turn shears off and the actuating piston 6 pushes down the entire printed circuit board arrangement 60 "via the fourth printed circuit board 109.
- the contact pins 5 are pressed through the bores 110 of the second printed circuit board 107 and the sleeve-shaped receivers 104 of the third printed circuit board 108 slide over the contact pins 5 so that the gas pressure switch is closed, since the individual printed circuit boards 106-109 are insulated from the housing 100 of the gas pressure switch, between the elements of the printed circuit board assembly 60 "and the housing 100 no electrically conductive connection.
- the housing-fixed contacts not only rigid, but also be resiliently connected to the housing 100 of the gas pressure switch.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Switches Operated By Changes In Physical Conditions (AREA)
- Emergency Lowering Means (AREA)
Claims (17)
- Commutateur à pression de gaz (1) pour un dispositif d'allumage et de sécurité de munition, comprenant- un boîtier (100) et un piston de commutation (6) pouvant être déplacé, lors de son utilisation conforme, par les gaz de la charge propulsive de la munition, d'une position de repos dans une position de contact, lequel piston, sur son côté opposé aux gaz de la charge propulsive, est connecté à un dispositif de contact (60-60"), qui dans la position de contact du piston de commutation (6), relie électriquement l'une à l'autre au moins deux broches de contact (5) fixées au boîtier,- une broche de sécurité cisaillable (7), qui maintient le piston de commutation (6) dans sa position de repos jusqu'à l'obtention d'une pression de gaz prédéterminée, et qui se cisaille à l'obtention de la pression de gaz définie, de sorte que le piston de commutation (6) puisse alors être déplacé dans sa position de contact,caractérisé en ce que- le piston de commutation (6), sur son côté extérieur tourné vers les gaz de la charge propulsive, est entouré par une membrane (8) déformable plastiquement et connectée au boîtier (100) du commutateur à pression de gaz (1), qui, à l'obtention d'une pression de gaz prédéterminée, presse contre le piston de commutation (6) et maintient le piston de commutation (6) dans cette position après qu'il ait atteint sa position de contact.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que le piston de commutation (6) et le boîtier (100) du commutateur à pression de gaz (1) présentent des faces d'étanchéité (3 ; 3') qui se déplacent l'une vers l'autre lors du déplacement du piston de commutation (6) de la position de repos dans la position de contact.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que le piston de commutation (6) et le boîtier (100) du commutateur à pression de gaz (1) présentent des faces d'étanchéité coniques (3 ; 3') pour réaliser l'étanchéité.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 2 ou 3, caractérisé en ce qu'un élément d'amortissement (101) de forme annulaire en matière plastique est disposé entre les faces d'étanchéité (3 ; 3') du piston de commutation (6) et du boîtier (100).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 4, caractérisé en ce que l'élément d'amortissement (101) est en étain ou en plomb.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de contact (60 ; 60') comprend un élément en forme de broche (11 ; 102), qui, lors du déplacement du piston de commutation (6) de sa position de repos dans sa position de contact, est pressé contre les deux broches de contact (5) fixées au boîtier et relie celles-ci électriquement l'une à l'autre.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 6, caractérisé en ce que l'élément en forme de broche (11) du dispositif de contact (60) est un insert en céramique avec de préférence des faces de contact dorées.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 7, caractérisé en ce que l'insert en céramique (11) est connecté fixement au piston de commutation (6).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 6, caractérisé en ce que l'élément en forme de broche (102) du dispositif de contact (60') est une broche de commutation métallique (102), qui est maintenue directement ou par le biais d'un poussoir (102') en matériau non conducteur de l'électricité par un dispositif de fixation (103) en un matériau non conducteur de l'électricité, disposé dans le piston de commutation (6).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 9, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de fixation (103) de la broche de commutation (102) est en verre.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de contact (60") est constitué d'un agencement de carte de circuits imprimés (60") qui comprend deux logements (104) en forme de douille connectés électriquement l'un à l'autre, de telle sorte que lors du déplacement du piston de commutation (6) de sa position de repos dans sa position de contact, les deux broches de contact (5) fixées au boîtier soient à chaque fois pressées dans l'un des logements (104) en forme de douille.
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 11, caractérisé en ce que l'agencement de carte de circuits imprimés (60") est un module séparé se raccordant au piston de commutation (6), le piston de commutation (6), lors de son déplacement sur son côté inférieur (105) réalisé sous forme plane, provoquant un déplacement correspondant de l'agencement de carte de circuits imprimés (60").
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon la revendication 11 ou 12, caractérisé en ce que l'agencement de carte de circuits imprimés (60") se compose d'au moins quatre cartes de circuits imprimés (106-109) se raccordant axialement les unes aux autres, une première carte de circuits imprimés (106) tournée vers les broches de contact (5) fixées au boîtier, qui provoque un centrage des broches de contact (5), une deuxième carte de circuits imprimés (107) avec des alésages (110) qui présentent un plus petit diamètre que le diamètre des broches de contact (5), afin d'éviter un contact entre les logements en forme de douille (104) et les broches de contact (5) dans la position de repos du piston de commutation (6), une troisième carte de circuits imprimés (108) avec les logements en forme de douille (104) et une quatrième carte de circuits imprimés (109), qui s'applique aux côtés frontaux (105, 112) du piston de commutation (6) et de la troisième carte de circuits imprimés (108), afin d'éviter un déplacement de l'agencement de carte de circuits imprimés (60") dans la position de repos du piston de commutation (6).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 13, caractérisé en ce que les broches de contact (5) présentent des pointes dorées (21) au niveau des points de contact du dispositif de contact (60-60") associé au piston de commutation (6).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 14, caractérisé en ce que les broches de contact (5) sont disposées de manière isolée dans un support (4) et le support (4) est connecté par le biais d'un filetage et soudé de manière étanche aux gaz au boîtier (100) du commutateur à pression de gaz (1).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 15, caractérisé par une construction en forme de vis, qui peut être vissée obliquement depuis le côté arrière dans un culot de projectile (17).
- Commutateur à pression de gaz selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 16, caractérisé en ce que la membrane (8) est réalisée en forme de chapeau et est soudée au boîtier (100).
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10319265 | 2003-04-26 | ||
| DE10319265 | 2003-04-26 | ||
| DE10354012A DE10354012B4 (de) | 2003-04-26 | 2003-11-19 | Gasdruckschalter für eine Zünd- und Sicherungseinrichtung einer Munition |
| DE10354012 | 2003-11-19 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1471326A1 EP1471326A1 (fr) | 2004-10-27 |
| EP1471326B1 true EP1471326B1 (fr) | 2010-04-07 |
Family
ID=32963541
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04002749A Expired - Lifetime EP1471326B1 (fr) | 2003-04-26 | 2004-02-07 | Commutateur électrique pour fusée de projectile, ledit commutateur étant actionné par pression de gaz |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7150228B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP1471326B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP4541747B2 (fr) |
| IL (1) | IL161577A (fr) |
| NO (1) | NO329475B1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8239699B2 (en) * | 2009-06-26 | 2012-08-07 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for performing energy-efficient network packet processing in a multi processor core system |
| KR101473897B1 (ko) * | 2013-04-26 | 2014-12-17 | 이노크린 주식회사 | 비폭발성 고체 또는 액체를 이용한 폭발물 |
| US9470498B1 (en) * | 2014-09-05 | 2016-10-18 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Army | High pressure isolated latching safety switch device |
| US10510504B2 (en) * | 2017-12-08 | 2019-12-17 | Eagle Technology, Llc | Force amplified low pressure depth activated switch |
| CN114508975B (zh) * | 2022-02-15 | 2023-10-13 | 南京理工大学 | 降低剪切断面摩擦影响的引信刚性保险惯性运动机构 |
Family Cites Families (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2458478A (en) | 1943-04-10 | 1949-01-04 | Riehard L Maneval | Setback switch |
| US2873681A (en) | 1945-02-03 | 1959-02-17 | Charles C Lauritsen | Fuze |
| US2674946A (en) * | 1950-06-14 | 1954-04-13 | Bofors Ab | Control device for an electric circuit |
| US2721913A (en) * | 1950-07-17 | 1955-10-25 | Jr Raymond C Kent | Shock and static pressure discriminating switch |
| US2931874A (en) * | 1953-10-08 | 1960-04-05 | Audley B Leaman | Explosive switch |
| US3698323A (en) * | 1955-12-23 | 1972-10-17 | Us Army | Explosive operated switch for bomb fuzing system |
| FR79714E (fr) * | 1959-11-06 | 1963-01-11 | Soc Tech De Rech Ind | Perfectionnements à l'amorçage électrique des projectiles à charge creuse |
| US3167018A (en) | 1962-03-19 | 1965-01-26 | Aeronca Mfg Corp | Missile safety and arming circuit |
| US3248504A (en) | 1962-10-08 | 1966-04-26 | Atlas Chem Ind | Connecting switch |
| US3155800A (en) * | 1963-01-02 | 1964-11-03 | Genisco Technology Corp | Single action temperature sensitive electrical switch including camming means for a plunger retaining member |
| FR1417132A (fr) * | 1964-04-14 | 1965-11-12 | Charbonnages De France | Nouveau dispositif de court-circuitage de conducteurs électriques |
| US3275770A (en) * | 1965-02-26 | 1966-09-27 | Sinclair Research Inc | Explosion pressure responsive switch |
| US3500279A (en) | 1968-07-26 | 1970-03-10 | Us Navy | Exploding bridgewire operated switch |
| US3601057A (en) * | 1969-02-11 | 1971-08-24 | Gibbs Mfg And Research Corp | Arming switch |
| FR2070544A5 (fr) * | 1969-12-09 | 1971-09-10 | Serat | |
| US3675579A (en) * | 1970-02-25 | 1972-07-11 | Us Navy | Pressure actuated safety and arming device |
| US3991649A (en) * | 1975-06-27 | 1976-11-16 | Networks Electronic Corporation | Pyrotechnic wire cutter |
| US4150266A (en) | 1977-01-27 | 1979-04-17 | Networks Electronic Corp. | Miniature pyrotechnic squib switch, single pole, normally open |
| DE2755322A1 (de) | 1977-12-12 | 1979-06-13 | Dynamit Nobel Ag | Elektrischer schalter mit wenigstens einem polpaar |
| JPS573000A (en) * | 1980-06-06 | 1982-01-08 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Flying object |
| US4339638A (en) * | 1980-10-15 | 1982-07-13 | Mcdonnell Douglas Corporation | Electrical switch |
| US4527025A (en) | 1983-02-02 | 1985-07-02 | Networks Electronic Corp. | Miniature delay switch |
| US4852494A (en) * | 1987-11-16 | 1989-08-01 | Williams Robert A | Explosively actuated switch |
| FR2633385B1 (fr) | 1988-06-23 | 1990-08-31 | France Etat Armement | Systeme de securite et d'armement pour projectile utilisant la pression des gaz de combustion |
| FR2679697B1 (fr) | 1991-07-25 | 1994-05-20 | Giat Industries | Contacteur electrique a commande pyrotechnique. |
| US5131328A (en) * | 1991-12-13 | 1992-07-21 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Safety and arming system for tube launched projectile |
-
2004
- 2004-02-07 EP EP04002749A patent/EP1471326B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2004-03-09 NO NO20041025A patent/NO329475B1/no not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2004-04-16 JP JP2004121492A patent/JP4541747B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-04-22 US US10/829,278 patent/US7150228B2/en active Active
- 2004-04-22 IL IL161577A patent/IL161577A/en active IP Right Grant
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| NO20041025L (no) | 2004-10-27 |
| EP1471326A1 (fr) | 2004-10-27 |
| US20050188877A1 (en) | 2005-09-01 |
| US7150228B2 (en) | 2006-12-19 |
| NO329475B1 (no) | 2010-10-25 |
| JP2004325067A (ja) | 2004-11-18 |
| IL161577A (en) | 2008-11-03 |
| IL161577A0 (en) | 2004-09-27 |
| JP4541747B2 (ja) | 2010-09-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0164732B1 (fr) | Dispositif de génération d'un nuage fausse cible, notamment nuage infrarouge | |
| DE2443793A1 (de) | Kombiniertes anzuendhuetchen | |
| DE2907308C2 (de) | Geschoß mit mindestens einem ausstoßbaren Tochtergeschoß | |
| DE2227104A1 (de) | Geschoss oder rakete mit aufklappbarem leitwerk | |
| EP1471326B1 (fr) | Commutateur électrique pour fusée de projectile, ledit commutateur étant actionné par pression de gaz | |
| DE2838381C2 (de) | Sicherheitsvorrichtung für Zündvorrichtungen | |
| EP3767223B1 (fr) | Système, en particulier grenade à main | |
| DE10354012B4 (de) | Gasdruckschalter für eine Zünd- und Sicherungseinrichtung einer Munition | |
| EP0156763A1 (fr) | Méthode et dispositif pour augmenter l'énergie dans une amorce électromagnétique | |
| CH674078A5 (fr) | ||
| EP0341543A1 (fr) | Cartouche à balle pour fusil | |
| EP2872850B1 (fr) | Grenade, notamment grenade de 40 mm | |
| EP0731331A2 (fr) | Dispositif de lancement pour missiles autopropulsés, en particulier pour roquettes d'artillerie | |
| EP0116322B1 (fr) | Fusée de tête | |
| EP0129679B1 (fr) | Fusée de proximitée adaptable sur un projectile | |
| DE3717458A1 (de) | Pyrotechnisches kraftelement | |
| DE2842882C3 (de) | Aufschlagzünder mit einer Zündkapsel | |
| EP1357349B1 (fr) | Cartouche | |
| DE2002288A1 (de) | Mechanische Zuendvorrichtung | |
| DE10039911B4 (de) | Ausstoßvorrichtung zum Ausstoßen von Submunitionskörpern aus einem Geschoß | |
| WO2011128234A1 (fr) | Disjoncteur pour ligne d'alimentation | |
| DE19540863B3 (de) | Zündvorrichtung | |
| DE102021123375A1 (de) | Zündvorrichtung für eine Munition, insbesondere eine Mittelkalibermunition und zugehöriges Verfahren zum Zünden oder zur Selbstzerlegung einer Munition, insbesondere einer Mittelkalibermunition | |
| DE2148197C3 (de) | Zünder für Zündpatronen von Trennvorrichtungen für Minenverankerungsleinen | |
| DE1578495C3 (de) | Aufschlagzünder für Geschosse mit verzögerter Zündung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20041009 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB LI |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: RHEINMETALL WAFFE MUNITION GMBH |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20070524 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: RHEINMETALL WAFFE MUNITION GMBH |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: E. BLUM & CO. AG PATENT- UND MARKENANWAELTE VSP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502004010986 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20100520 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20110110 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20210224 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20210217 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20210219 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20210217 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 502004010986 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20220207 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220228 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220207 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220901 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220228 |