EP1286794B2 - Cold rolling machine - Google Patents
Cold rolling machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1286794B2 EP1286794B2 EP01955205A EP01955205A EP1286794B2 EP 1286794 B2 EP1286794 B2 EP 1286794B2 EP 01955205 A EP01955205 A EP 01955205A EP 01955205 A EP01955205 A EP 01955205A EP 1286794 B2 EP1286794 B2 EP 1286794B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- rolling
- cold rolling
- rods
- accordance
- guide
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21H—MAKING PARTICULAR METAL OBJECTS BY ROLLING, e.g. SCREWS, WHEELS, RINGS, BARRELS, BALLS
- B21H5/00—Making gear wheels, racks, spline shafts or worms
- B21H5/02—Making gear wheels, racks, spline shafts or worms with cylindrical outline, e.g. by means of die rolls
- B21H5/027—Making gear wheels, racks, spline shafts or worms with cylindrical outline, e.g. by means of die rolls by rolling using reciprocating flat dies, e.g. racks
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21H—MAKING PARTICULAR METAL OBJECTS BY ROLLING, e.g. SCREWS, WHEELS, RINGS, BARRELS, BALLS
- B21H3/00—Making helical bodies or bodies having parts of helical shape
- B21H3/02—Making helical bodies or bodies having parts of helical shape external screw-threads ; Making dies for thread rolling
- B21H3/06—Making by means of profiled members other than rolls, e.g. reciprocating flat dies or jaws, moved longitudinally or curvilinearly with respect to each other
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21H—MAKING PARTICULAR METAL OBJECTS BY ROLLING, e.g. SCREWS, WHEELS, RINGS, BARRELS, BALLS
- B21H7/00—Making articles not provided for in the preceding groups, e.g. agricultural tools, dinner forks, knives, spoons
- B21H7/14—Making articles not provided for in the preceding groups, e.g. agricultural tools, dinner forks, knives, spoons knurled articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21H—MAKING PARTICULAR METAL OBJECTS BY ROLLING, e.g. SCREWS, WHEELS, RINGS, BARRELS, BALLS
- B21H7/00—Making articles not provided for in the preceding groups, e.g. agricultural tools, dinner forks, knives, spoons
- B21H7/18—Making articles not provided for in the preceding groups, e.g. agricultural tools, dinner forks, knives, spoons grooved pins; Rolling grooves, e.g. oil grooves, in articles
Definitions
- the invention relates to a cold rolling machine according to the preamble of patent claim 1 and a method for cold rolling a workpiece.
- the workpiece to be machined is rotatably tensioned between two tips or other quick-action clamping devices, this workpiece clamping device generally being associated with a feed axis.
- the desired profiling of the workpiece via two synchronously counter-rotating rolling rods, which impinge simultaneously on the workpiece and this initially by frictional engagement and later by positive engagement in rotation.
- the material is in the free spaces of the tool, d. H. displaced by the rolling rods.
- the height of the ground profile of the rolling rod increases in the forming area, so that each tooth of the rolling rod is pressed slightly deeper into the workpiece, as the preceding.
- This non-cutting cold forming of profiles is about thirty times faster than the machining of the profiles.
- Cold rolled workpieces also offer higher strength, better surface finish and high accuracy.
- transverse roll strips provided, which are arranged by linear drives in a direction transverse to the axis of rotation movable.
- the transverse rolling strips are received by an upper support and sub-support, wherein the upper support in a vertical direction above and a sub-support in a vertical direction below the tool chuck are arranged movable.
- the rolling rod For dimensional corrections on the workpiece, it may be necessary to deliver the rolling rod in the radial direction (relative to the workpiece) in order to form the predetermined tread depth. This delivery is done manually via adjusting screws, over which the radial position of the rolling rods is adjustable relative to the workpiece. For this readjustment of the rolling process must be interrupted, so that the productivity of the system is reduced.
- the present invention seeks to provide a cold rolling machine and a method for cold rolling, through which the downtime during production are reduced.
- the cold rolling machine is provided with a feed device with an integrated feed drive, via which the rolling rods can be adjusted during the rolling process in the direction of engagement. That is, each rolling rod is associated with a feed axis, which allows an adjustment of the rolling rods in approximately radial direction with respect to the workpiece to be machined.
- this feed device thus the tread depth can be changed during the rolling process, so that, for example, the desired Endprofiliefe not - as required in the prior art - during a feed movement of the rolling rods, but during several Walzstangenh Claus can be formed, in which the rolling rods are readjusted in the radial direction. This makes it possible to minimize the length of the rolling rod, so that the dimensions of the cold rolling machine remain relatively low.
- the rolling rods can be performed substantially with constant tread depth, so that their production is much easier than in the conventional rolling rods with increasing profile depth in the rolling direction.
- the calibration and relaxation zones described above can be formed by means of small ramps at the end sections of the rolling rods, wherein the region of the rolling rods extending between the ramps is formed essentially with the same profile depth.
- Each of the two rolling rods is in each case assigned a guide carriage, which is displaceable along inclined guides.
- These two inclined guides are employed in a V-shaped manner with respect to one another, so that the radial distance between the rolling rod and the workpiece can be changed by displacing the guide carriage along the associated inclined guide.
- the feed movement is carried out by moving the rolling rod along the wedge-shaped inclined guides, so that by adjusting the rolling rods without tool change a variation of the number of teeth, the rolling of even and odd numbers of teeth, a positioned rolling and the quality optimization of the profile by division correction is possible.
- each guide carriage is assigned its own feed drive, for example a planetary spindle drive.
- feed drive for example a planetary spindle drive.
- suitable drives such as rack drives, ball screw drives or hydraulic drives can be used.
- the structure of the cold rolling machine according to the invention can be further simplified if the free end portions of the guide slide displaceable along the inclined guides are connected via a console on which the drives for the rolling rod device are mounted.
- the inventive concept can be used particularly advantageously in cold rolling machines, the rolling rods are driven in the vertical direction, so that the footprint of the machine according to the invention is minimal.
- the height can be minimized by driving the rolling rods in the horizontal direction.
- the workpiece can be driven via the rolling rods transmitted forces or via its own rotary drive, which is synchronized with the drive of the rolling rods.
- the forming area of the workpiece is subjected to ultrasound.
- ultrasound the flow limit is lowered during the forming process, so that the forming forces are reduced compared to conventional solutions.
- the guide rails supporting the inclined guides are advantageously supported on two spaced support legs of a machine bed, these two support legs are connected to increase the rigidity over cross straps.
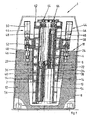
- FIG. 1 shows a section through a cold rolling machine 1, in which two rolling rods 2, 4 in the vertical direction: (with respect to the footprint) are arranged, while a workpiece, not shown, the bearing headstock 6 (only indicated in FIG FIG. 1 ) in the horizontal direction, that is arranged parallel to the support surface.
- the workpiece is rotatably mounted in this headstock 6, wherein via an NC drive, not shown, for example, for feeding or removal of the workpiece from the processing area, before or after the rolling, a shift in the axial direction (perpendicular to the plane) is possible.
- the design of the headstock with a quill and a rear centering differs essentially not from conventional solutions, so that reference is made to the above-mentioned prospectus of the applicant with regard to further details for the sake of simplicity.
- cold rolling machine can be a variety of profiles, such as serrations, threads, running gears, oil grooves, annular grooves, knurls or other special forms in reversing train.
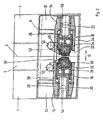
- the control of the cold rolling machine 1 is according to FIG. 2 housed in laterally arranged cabinets 7.
- This extremely compact design with minimal footprint makes it possible to perform the cold rolling machine 1 as a so-called hook machine, which is practically pre-assembled and delivered as a functional unit.
- the illustrated cold rolling machine 1 has a base made of mineral cast, the two upwards (see FIG. 1 ) projecting support legs 10, 12 has. These each have a stepped recess with an in FIG. 1 visible horizontal support surface 14 and a vertical support surface ( FIG. 2 ) 16, on which one of the two support legs 10, 12 overstretching bridge structure 18 is supported. This is in FIG. 2 shown cut and contains essentially the guides and drives for the reciprocating movement of the rolling rods 2, 4th
- the bridge structure 18 carrying the rolling rods 2, 4 has in each case one supporting body 20, 22 attached to the supporting legs 10, 12, which essentially consists of a cast-supporting structure 24, which is designed with a mineral casting filling.
- FIG. 2 can be removed, the two support bodies 20, 22 via a rear transverse tab 26 and a front transverse flap 28 are connected to each other, which extend beyond the area between the two support legs 10, 12.
- the end portions of the front cross-bar 28 are secured to the bearing surfaces of the support legs 10 and 12 formed by the horizontal support surface 14 and the vertical support surface 16.
- Both transverse straps 26, 28 each have a recess 30, 32, through which the workpiece with the associated clamping devices of the headstock 6 (indicated in FIG FIG. 2 ) can be feasible in the editing area.
- FIG. 2 can be removed, are formed on the opposite end surfaces of the two support bodies 20, 22 and the cast-support structure 24 oblique track guides 34, 36 in the form of flat track guides made of plastic, characterized by low friction, high accuracy, long life and optimum Characterize damping behavior.
- oblique track guides 34, 36 in the form of flat track guides made of plastic, characterized by low friction, high accuracy, long life and optimum Characterize damping behavior.
- a guide carriage 38, 40 guided which is designed in the contact area with the two support members 20, 22 with guide legs which engage around the inclined track guide 34, 36.
- the determination of the guide carriage 38, 40 in the transverse direction takes place via a counter guide 42, which engage behind the side surfaces of the flat track guide 36.
- each flat track guide 34, 36 may be, for example, 3 °.
- NC drive 44 which can be embodied, for example, as a planetary spindle drive with servomotor 50.
- a spindle nut 46 is rotatably supported in the support body 22 and 24, while the planetary spindle 48 is mounted in a console of the guide carriage 38 and 40 and connected via a toothed belt with the servo motor 50.
- the planetary spindle 48 is rotated by the fixed spindle nut 46 and transmitted as axial displacement on the guide carriage 38,40 so that they are moved along the inclined track guides 34 and 36, respectively.
- the end faces of the guide carriage 38, 40 remote from the inclined track guides 34, 36 run parallel to the feed axis of the two rolling rods 2, 4, so that the guide slides, 38, 40 in the illustration according to FIG FIG. 1 have an approximately wedge-shaped cross-section.
- the rolling rods 2, 4 facing end surfaces of the guide carriage 38, 40 are also formed as guides 52, 54, along which slides 56, 58 are guided, on which the Wälzstangen 2, 4 are fixed.
- the guides 52, 54 are also executed again as a cast flat rail guides and correspond in terms of structure substantially the inclined guides 34, 36. D. h., The carriages 56, 58 dive with their end face in a U-shaped recess of the associated guide carriage 38, 40, wherein this recess is designed as a sliding guide. The determination of the carriages 56, 58 on the associated guide carriage 38, 40 takes place via a counter guide 60.
- FIG. 1 via the two support legs 10, 12 also extending end portions of the two guide slides 38, 40 each have a bracket 62, in each of which a NC drives 64, 66 is mounted.
- a planetary spindle 48 is (here via a toothed belt 68) ( FIG. 2 ) connected to a servomotor 50 and rotatably mounted in the bracket 62.
- the cooperating with the planetary spindle 48 spindle nut 46 is rotatably mounted in a respective carriage 56, 58, so that upon rotation of the planetary spindle 48, the spindle nut 46 and the associated carriage 56 and 58 along the guide 52 and 54 is moved.
- the planetary spindle 48 passes through an inner bore of the associated carriage 56, 58.
- the two NC drives 64, 66 are driven in such a way that the two rolling rods 2, 4 are offset in the counter-synchronized movements.
- FIG. 3 shows a schematic representation of a rolling rod 2, as used in the cold rolling machine 1 according to the invention FIG. 1 can be used.
- This rolling rod 2 is conventionally made of hardened and ground cold work steel and carries a profiling 70 whose tread depth S is substantially constant along a region T. At the two end portions of the profiling 70 ramps 72 are formed whose length U is substantially less than the length T with constant profiling 70. Due to the substantially constant profiling can be in FIG. 3 shown rolling rod much easier to produce than conventional rolling rods, where the tread depth in the range T is variable. Also the regrinding of in FIG. 3 shown rolling rod is due to the substantially constant tread depth much easier than in the conventional solutions.
- FIG. 1 shows the basic position of the cold rolling machine 1, in which the carriage 58 is in its upper and the carriage 56 in its lower end position.
- the two guide slides 38, 40 are moved via the NC drives 44 into their upper end position, so that the distance between the rolling rods 2, 4 is maximum (minimum profile depth).
- the workpiece is brought over the headstock 6 in its processing position between the two rolling rods 2, 4.
- the two NC drives 64, 66 controlled synchronously and in opposite directions, so that the two rolling rods 2, 4 accumulate in opposite directions on the workpiece and this offset by frictional and positive locking in rotation, wherein the engagement between the workpiece and the two rolling rods. 2 , 4 the forming process takes place.
- the tread depth can be adjusted by a synchronous displacement of the two guide slides 38, 40 along the inclined surfaces 34, 36, wherein the maximum tread depth during a stroke of the rolling rods 2, 4 or during several successive strokes (also in reversing) is formed.
- suitable inclination of the inclined guide 34, 36 and corresponding stroke of the NC drives for example, a tread depth of up to about 5 mm can be produced.
- the rolling process is constantly monitored, so that the rolling process can be optimized by means of variable speed profiles both for the advance of the guide carriages 34, 36 and the carriages 56, 58.
- the mineral casting substructure 8 and the mineral cast-filled support body 20, 22 cause a much better attenuation than conventional constructions.
- the cast mineral substructure makes it possible to integrate all the supply elements, with virtually no additional processing required after casting the substructure.
- the substructure may be formed in a conventional manner by a welded or cast construction in deviation from the above-described embodiment.
- the adjustability of the guide carriages 38, 40 also makes it possible to carry out a division correction during the rolling process, so that the rolling quality is significantly improved over conventional solutions with rolling rods.
- conventional, non-plastic-coated sliding guides rolling guides, for example roller shoes or flat cage guides could alternatively also be used, but these are less favorable than the molded guideways both in terms of load capacities and costs.
- the workpiece is driven by the engagement with the rolling rods 2, 4.
- the workpiece can be assigned its own rotary drive, which is synchronized with the NC drives 64, 66 of the rolling rods, so that the stroke of the rolling rods 2, 4 is synchronized with the rotation of the workpiece to be rolled.
- the forming forces can be reduced when the rolled portion of the workpiece is subjected to ultrasound.
- a suitable ultrasonic head can be integrated into the cold rolling machine.
- Another possibility is to overlay the rotational movement of the workpiece during the rolling process with ultrasonic vibrations. This could be done, for example, by the fact that the above-described rotary drive generates a rotary movement for the workpiece, which is superimposed with high-frequency ultrasound oscillations of low amplitude.
- the Schwingungsbeinsselung the forming process the forming forces can be reduced during the rolling process, so that an increase in the process speed is possible. Due to the reduction in the flow limit, materials that are difficult to form can also be cold-rolled using conventional methods.
- a cold rolling machine in which the rolling rods are preferably arranged in the vertical direction and are adjustable via a feed device during the rolling process in the radial direction with respect to the workpiece to be machined.
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Kaltwalzmaschine gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Patentanspruchs 1 und ein Verfahren zum Kaltwalzen eines Werkstücks.The invention relates to a cold rolling machine according to the preamble of patent claim 1 and a method for cold rolling a workpiece.
Bei derartigen Kaltwalzmaschinen wird das zu bearbeitende Werkstück drehbar zwischen zwei Spitzen oder sonstigen Schnellspannvorrichtungen gespannt, wobei dieser Werkstückspannvorrichtung in der Regel eine Vorschubachse zugeordnet ist. Die gewünschte Profilierung des Werkstücks erfolgt über zwei sich synchron gegenläufig bewegende Walzstangen, die gleichzeitig auf das Werkstück auftreffen und dieses zunächst durch Reibschluß und später durch Formschluß in Drehung versetzen. Dabei wird der Werkstoff in die Freiräume des Werkzeugs, d. h. der Walzstangen verdrängt. Üblicherweise nimmt die Höhe des eingeschliffenen Profils der Walzstange im Umformbereich zu, so daß jeder Zahn der Walzstange etwas tiefer in das Werkstück eingedrückt wird, als der vorangegangene. Nach Erreichen der vollen Profiltiefe kann sich eine Kallibrierzone und eine Entspannungszone anschließen, entlang denen die Geometrie und die Oberflächenqualität des Werkstücks optimiert wird.In such cold rolling machines, the workpiece to be machined is rotatably tensioned between two tips or other quick-action clamping devices, this workpiece clamping device generally being associated with a feed axis. The desired profiling of the workpiece via two synchronously counter-rotating rolling rods, which impinge simultaneously on the workpiece and this initially by frictional engagement and later by positive engagement in rotation. The material is in the free spaces of the tool, d. H. displaced by the rolling rods. Usually, the height of the ground profile of the rolling rod increases in the forming area, so that each tooth of the rolling rod is pressed slightly deeper into the workpiece, as the preceding. Once the full tread depth has been reached, a calibration zone and a relaxation zone can follow, along which the geometry and surface quality of the workpiece is optimized.
Dieses spanlose Kaltformen von Profilen, wie beispielsweise Steckverzahnungen (gerade oder schräg), Spiralverzahnungen, Ölnuten, Gewinde oder Rändel ist ca. dreißig mal schneller als die spanabhebende Bearbeitung der Profile. Kaltgewalzte Werkstücke bieten zudem eine höhere Festigkeit, bessere Oberflächengüte und große Genauigkeit.This non-cutting cold forming of profiles, such as splines (straight or oblique), spiral teeth, oil grooves, threads or knurls is about thirty times faster than the machining of the profiles. Cold rolled workpieces also offer higher strength, better surface finish and high accuracy.
In dem Prospekt "Spezialmaschinenprogramm XK" der Anmelderin wird eine Kaltwalzmaschine vorgestellt, bei der die beiden gegenläufig bewegbaren Walzstangen in Horizontalrichtung angeordnet sind, während die Werkstückachse ebenfalls in Horizontalrichtung quer zur Bewegungsrichtung der Walzstangen angeordnet ist. Nachteilig bei dieser Lösung ist, daß aufgrund der Horizontalanordnung der Walzstangen eine erhebliche Baubreite der Kaltwalzmaschine erforderlich ist. Diese bekannte Maschine hat des weiteren einen hydraulischen Antrieb, dessen Hydraulik-Aggregat sehr viel Platz benötigt.In the brochure "Special Machine Program XK" of the applicant, a cold rolling machine is presented, in which the two counter-rotating rolling rods are arranged in the horizontal direction, while the workpiece axis is also arranged in the horizontal direction transverse to the direction of movement of the rolling rods. A disadvantage of this solution is that due to the horizontal arrangement of the rolling rods a considerable width of the cold rolling machine is required. This known machine also has a hydraulic drive, the hydraulic unit requires a lot of space.
Dieser Nachteil wird durch eine Kaltwalzmaschine gemäß der
Aus der
Es sind Querwalzleisten vorgesehen, welche durch Linearantriebe in einer Richtung quer zur Drehachse bewegbar angeordnet sind. Die Querwalzleisten sind durch einen Obersupport und Untersupport aufgenommen, wobei der Obersupport in einer vertikalen Richtung oberhalb und ein Untersupport in einer vertikalen Richtung unterhalb des Werkzeugfutters bewegbar angeordnet sind.There are transverse roll strips provided, which are arranged by linear drives in a direction transverse to the axis of rotation movable. The transverse rolling strips are received by an upper support and sub-support, wherein the upper support in a vertical direction above and a sub-support in a vertical direction below the tool chuck are arranged movable.
Bei Maßkorrekturen am Werkstück kann es erforderlich sein, zum Ausbilden der vorbestimmten Profiltiefe die Walzstange in Radialrichtung (bezogen auf das Werkstück) zuzustellen. Diese Zustellung erfolgt manuell über Justierschrauben, über die die Radialposition der Walzstangen gegenüber dem Werkstück einstellbar ist. Für diese Nachjustierung muß der Walzvorgang unterbrochen werden, so daß die Produktivität der Anlage verringert ist.For dimensional corrections on the workpiece, it may be necessary to deliver the rolling rod in the radial direction (relative to the workpiece) in order to form the predetermined tread depth. This delivery is done manually via adjusting screws, over which the radial position of the rolling rods is adjustable relative to the workpiece. For this readjustment of the rolling process must be interrupted, so that the productivity of the system is reduced.
. Demgegenüber liegt der Erfindung die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Kaltwalzmaschine und ein Verfahren zum Kaltwalzen zu schaffen, durch die die Stillstandszeiten während der Produktion verringert sind., In contrast, the present invention seeks to provide a cold rolling machine and a method for cold rolling, through which the downtime during production are reduced.
Diese Aufgabe wird hinsichtlich der Kaltwalzmaschine durch die Merkmale des Patentanspruchs 1 und hinsichtlich des Verfahrens durch die Merkmale des Patentanspruchs 11 gelöst.This object is achieved with regard to the cold rolling machine by the features of patent claim 1 and with respect to the method by the features of claim 11.
Erfindungsgemäß wird die Kaltwalzmaschine mit einer Zustelleinrichtung mit integriertem Zustellantrieb versehen, über die die Walzstangen während des Walzvorganges in Eingriffsrichtung verstellbar sind. D. h., jeder Walzstange ist eine Zustellachse zugeordnet, die eine Verstellung der Walzstangen in etwa Radialrichtung mit Bezug zu dem zu bearbeitenden Werkstück ermöglicht. Durch diese Zustelleinrichtung kann somit die Profiltiefe während des Walzvorganges verändert werden, so daß beispielsweise die gewünschte Endprofiltiefe nicht - wie beim Stand der Technik erforderlich - während einer Vorschubbewegung der Walzstangen, sondern während mehreren Walzstangenhüben ausbildbar ist, bei denen die Walzstangen in Radialrichtung nachgestellt werden. Dies ermöglicht es, die Länge der Walzstange zu minimieren, so daß auch die Abmessungen der Kaltwalzmaschine vergleichsweise gering bleiben.According to the invention, the cold rolling machine is provided with a feed device with an integrated feed drive, via which the rolling rods can be adjusted during the rolling process in the direction of engagement. That is, each rolling rod is associated with a feed axis, which allows an adjustment of the rolling rods in approximately radial direction with respect to the workpiece to be machined. By this feed device thus the tread depth can be changed during the rolling process, so that, for example, the desired Endprofiliefe not - as required in the prior art - during a feed movement of the rolling rods, but during several Walzstangenhüben can be formed, in which the rolling rods are readjusted in the radial direction. This makes it possible to minimize the length of the rolling rod, so that the dimensions of the cold rolling machine remain relatively low.
Bei diesem Reversierbetrieb wird daher das Profil mit mehreren Walzstangenhüben ausgebildet, während bei den bekannten Maschinen das Profil mit nur einem Hub gewalzt werden mußte - es liegt auf der Hand, daß das herkömmliche Verfahren eine wesentlich größere Belastung für die Maschine und die Walzstangen darstellt.In this reversing operation, therefore, the profile is formed with several Walzstangenhüben, while in the known machines, the profile had to be rolled with only one stroke - it is obvious that the conventional method represents a much greater burden on the machine and the rolling rods.
Da die Profiltiefe erfindungsgemäß über die Zustelleinrichtung bestimmt wird, können die Walzstangen im Wesentlichen mit gleichbleibender Profiltiefe ausgeführt werden, so daß deren Herstellung wesentlich einfacher als bei den herkömmlichen Walzstangen mit in Walzrichtung größer werdender Profiltiefe ist. Die eingangs beschriebenen Kalibrier- und Entspannungszonen können über kleine Rampen an den Endabschnitten der Walzstangen ausgebildet werden, wobei der sich zwischen den Rampen erstreckende Bereich der Walzstangen im Wesentlichen mit gleichbleibender Profiltiefe ausgebildet ist.Since the tread depth is determined according to the invention via the feed device, the rolling rods can be performed substantially with constant tread depth, so that their production is much easier than in the conventional rolling rods with increasing profile depth in the rolling direction. The calibration and relaxation zones described above can be formed by means of small ramps at the end sections of the rolling rods, wherein the region of the rolling rods extending between the ramps is formed essentially with the same profile depth.
Jeder der beiden Walzstangen ist jeweils ein Führungsschlitten zugeordnet, der entlang von Schrägführungen verschiebbar ist. Diese beiden Schrägführungen sind v-förmig zueinander angestellt, so daß durch Verschieben des Führungsschlittens entlang der zugeordneten Schrägführung der Radialabstand zwischen Walzstange und Werkstück veränderbar ist. D. h., die Zustellbewegung erfolgt durch Verschieben der Walzstange entlang der keilförmig ausgebildeten Schrägführungen, so daß durch Verstellen der Walzstangen ohne Werkzeugwechsel eine Variation der Zähnezahl, das Walzen von geraden und ungerade Zähnezahlen, ein positioniertes Walzen und die Qualitätsoptimierung des Profils durch Teilungskorrektur möglich ist.Each of the two rolling rods is in each case assigned a guide carriage, which is displaceable along inclined guides. These two inclined guides are employed in a V-shaped manner with respect to one another, so that the radial distance between the rolling rod and the workpiece can be changed by displacing the guide carriage along the associated inclined guide. D. h., The feed movement is carried out by moving the rolling rod along the wedge-shaped inclined guides, so that by adjusting the rolling rods without tool change a variation of the number of teeth, the rolling of even and odd numbers of teeth, a positioned rolling and the quality optimization of the profile by division correction is possible.
Die Zustellbewegung läßt sich besonders präzise ausführen, wenn jedem Führungsschlitten ein eigener Zustellantrieb, beispielsweise ein Planetenspindelantrieb zugeordnet ist. Alternativ können auch andere geeignete Antriebe, wie beispielsweise Zahnstangenantriebe, Kugelgewindeantriebe oder hydraulische Antriebe verwendet werden.The feed movement can be carried out particularly precisely if each guide carriage is assigned its own feed drive, for example a planetary spindle drive. Alternatively, other suitable drives, such as rack drives, ball screw drives or hydraulic drives can be used.
Der Aufbau der erfindungsgemäßen Kaltwalzmaschine läßt sich weiter vereinfachen, wenn die freien Endabschnitte der entlang der Schrägführungen verschiebbaren Führungsschlitten über eine Konsole verbunden sind, an der die Antriebe für die Walzstangenvorrichtung gelagert sind.The structure of the cold rolling machine according to the invention can be further simplified if the free end portions of the guide slide displaceable along the inclined guides are connected via a console on which the drives for the rolling rod device are mounted.
Das erfindungsgemäße Konzept läßt sich besonders vorteilhaft bei Kaltwalzmaschinen einsetzen, deren Walzstangen in Vertikalrichtung angetrieben sind, so daß die Aufstellfläche der erfindungsgemäßen Maschine minimal ist. Die Bauhöhe lässt sich durch Antreiben der Walzstangen in Horizontalrichtung minimieren.The inventive concept can be used particularly advantageously in cold rolling machines, the rolling rods are driven in the vertical direction, so that the footprint of the machine according to the invention is minimal. The height can be minimized by driving the rolling rods in the horizontal direction.
Erfindungsgemäß kann das Werkstück über die Walzstangen übertragenen Kräfte oder aber über einen eigenen Drehantrieb angetrieben werden, der mit dem Antrieb der Walzstangen synchronisiert ist.According to the invention, the workpiece can be driven via the rolling rods transmitted forces or via its own rotary drive, which is synchronized with the drive of the rolling rods.
Bei einer vorteilhaften Variante der Erfindung wird der Umformbereich des Werkstückes mit Ultraschall beaufschlagt. Durch diesen Ultraschall wird die Fliesgrenze während des Umformprozesses abgesenkt, so daß die Umformkräfte gegenüber herkömmlichen Lösungen verringert sind.In an advantageous variant of the invention, the forming area of the workpiece is subjected to ultrasound. By this ultrasound, the flow limit is lowered during the forming process, so that the forming forces are reduced compared to conventional solutions.
Die die Führungsschlitten abstützenden Schrägführungen werden vorteilhafterweise an zwei beabstandeten Stützschenkeln eines Maschinenbettes abgestützt, wobei diese beiden Stützschenkel zur Erhöhung der Steifigkeit über Querlaschen verbunden sind.The guide rails supporting the inclined guides are advantageously supported on two spaced support legs of a machine bed, these two support legs are connected to increase the rigidity over cross straps.
Sonstige vorteilhafte Weiterbildungen der Erfindung sind Gegenstand der weiteren Unteransprüche.Other advantageous developments of the invention are the subject of the other dependent claims.
Im folgenden wird ein bevorzugtes Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung anhand schematischer Zeichnungen näher erläutert. Es zeigen:
-
Figur 1 eine schematische Schnittdarstellung einer erfindungsgemäßen Kaltwalzmaschine; -
Figur 2Figur 1 und -
Figur 3 eine schematische Darstellung einer Walzstange ausFigur 1 .
-
FIG. 1 a schematic sectional view of a cold rolling machine according to the invention; -
FIG. 2 a sectional plan view of the cold rolling machineFIG. 1 and -
FIG. 3 a schematic representation of a rolling rodFIG. 1 ,
Durch die erfindungsgemäße Kaltwalzmaschine lassen sich eine Vielzahl von Profilen, beispielsweise Kerbverzahnungen, Gewinde, Laufverzahnungen, Ölnuten, Ringnuten, Rändel oder sonstige Sonderformen auch im Reversierbetrieb ausbilden.By the cold rolling machine according to the invention can be a variety of profiles, such as serrations, threads, running gears, oil grooves, annular grooves, knurls or other special forms in reversing train.
Die Steuerung der Kaltwalzmaschine 1 ist gemäß
Die dargestellte Kaltwalzmaschine 1 hat einen aus Mineralguß hergestellten Unterbau, der zwei nach oben (Ansicht nach
Die die Walzstangen 2, 4 tragende Brückenkonstruktion 18 hat jeweils einen an den Stützschenkeln 10, 12 befestigten Stützkörper 20, 22, der im Wesentlichen aus einer Guß-Tragkonstruktion 24 besteht, die mit einer Mineralgußfüllung ausgeführt ist.The
Wie insbesondere
Wie des Weiteren insbesondere
Wie insbesondere aus
Die Axialverschiebung der beiden Führungsschlitten 38, 40 erfolgt jeweils über einen NC-Antrieb 44, der beispielsweise als Planetenspindelantrieb mit Servomotor 50 ausgeführt sein kann. Dabei ist jeweils eine Spindelmutter 46 drehbar im Stützkörper 22 bzw. 24 gelagert, während die Planetenspindel 48 in einer Konsole des Führungsschlittens 38 bzw. 40 gelagert und über einen Zahnriemen mit dem Servomotor 50 verbunden ist. Je nach Drehrichtung des Servomotors 50 wird die Planetenspindel 48 durch die feststehende Spindelmutter 46 in Drehung versetzt und diese als Axialverschiebung auf die Führungsschlitten 38,40 übertragen, so daß diese entlang der Schrägbahnführungen 34 bzw. 36 verschoben werden.The axial displacement of the two guide slides 38, 40 takes place in each case via an
Die von den Schrägbahnführungen 34, 36 entfernten Stirnflächen des Führungsschlittens 38, 40 verlaufen parallel zur Vorschubachse der beiden Walzstangen 2, 4, so daß die Führungsschlitten, 38, 40 in der Darstellung gemäß
Die Führungen 52, 54 sind ebenfalls wieder als eingegossene Flachbahnführungen ausgeführt und entsprechen hinsichtlich des Aufbaus im Wesentlichen den Schrägführungen 34, 36. D. h., die Schlitten 56, 58 tauchen mit ihrer Stirnfläche in eine u-förmige Ausnehmung des zugeordneten Führungsschlittens 38, 40 ein, wobei diese Ausnehmung als Gleitführung ausgebildet ist. Die Festlegung der Schlitten 56, 58 am zugeordneten Führuhgsschlitten 38, 40 erfolgt über eine Gegenführung 60.The
Die sich in
Diese Walzstange 2 wird in herkömmlicher Weise aus gehärtetem und geschliffenem Kaltarbeitsstahl hergestellt und trägt eine Profilierung 70, dessen Profiltiefe S entlang eines Bereiches T im Wesentlichen gleichbleibend ist. An den beiden Endabschnitten der Profilierung 70 sind Rampen 72 ausgebildet, deren Länge U wesentlich geringer als die Länge T mit gleichbleibender Profilierung 70 ist. Aufgrund der im Wesentlichen gleichbleibenden Profilierung läßt sich die in
Anschließend werden die beiden NC-Antriebe 64, 66 synchron und gegenläufig angesteuert, so daß die beiden Walzstangen 2, 4 gegenläufig auf das Werkstück auflaufen und dieses durch Reib- und Formschluß in Drehung versetzten, wobei durch den Eingriff zwischen Werkstück und den beiden Walzstangen 2, 4 der Umformvorgang erfolgt. Die Profiltiefe kann dabei durch eine synchrone Verschiebung der beiden Führungsschlitten 38, 40 entlang den Schrägflächen 34, 36 eingestellt werden, wobei die maximale Profiltiefe während eines Hubes der Walzstangen 2, 4 oder während mehrerer aufeinanderfolgender Hübe (auch im Reversierbetrieb) ausgebildet wird. Durch geeignete Neigung der Schrägführung 34, 36 und entsprechendem Hub der NC-Antriebe läßt sich beispielsweise eine Profiltiefe von bis zu etwa 5 mm herstellen. Der Walzprozeß wird ständig überwacht, so daß der Walzvorgang durch variable Geschwindigkeitsprofile sowohl für den Vorschub der Führungsschlitten 34, 36 als auch der Schlitten 56, 58 optimierbar ist.Subsequently, the two NC drives 64, 66 controlled synchronously and in opposite directions, so that the two rolling
Durch die über die Brückenkonstruktion 18 miteinander verbundenen Stützschenkel 10, 12 ist eine äußerst steife Maschinenkonstruktion gewährleistet, wobei der Mineralguß Unterbau 8 und die mineralgußgefüllten Stützkörper 20, 22. eine wesentlich bessere Dämpfung als herkömmliche Konstruktionen bewirken. Der Mineralgußunterbau ermöglicht es, alle Versorgungselemente zu integrieren, wobei nach dem Gießen des Unterbaus praktisch keine zusätzliche Bearbeitung erforderlich ist.By connected via the
Die vertikale Ausrichtung der Walzstangen 2, 4 vereinfacht die Kühlmittelabfuhr gegenüber der im Prospekt der Anmelderin offenbarten Lösung erheblich.The vertical orientation of the rolling
Anstelle der genannten Planetenspindelantriebe können selbstverständlich auch andere geeignete Antriebe, wie beispielsweise Kugelgewindetriebe, Zahnstangenantriebe oder hydraulische Antriebe verwendet werden. Der Unterbau kann in Abweichung vom vorbeschriebenen Ausführungsbeispiel auch in herkömmlicher Weise durch eine Schweiß- oder Gußkonstruktion gebildet sein.Of course, other suitable drives, such as ball screws, rack drives or hydraulic drives can be used instead of said planetary spindle drives. The substructure may be formed in a conventional manner by a welded or cast construction in deviation from the above-described embodiment.
Die Verstellbarkeit der Führungsschlitten 38, 40 ermöglicht es des Weiteren, während des Walzvorganges eine Teilungskorrektur durchzuführen, so daß die Walzqualität gegenüber herkömmlichen Lösungen mit Walzstangen erheblich verbessert ist. Anstelle der beschriebenen Gleitführung könnten alternativ auch herkömmliche, nicht kunststoffbeschichtete Gleitführungen, Wälzführungen, beispielsweise Rollenschuhe oder Flachkäfigführungen verwendet werden, die jedoch sowohl hinsichtlich der Tragzahlen als auch der Kosten ungünstiger als die abgeformten Führungsbahnen sind.The adjustability of the
Bei dem vor beschriebenen Ausführungsbeispiel wird das Werkstück durch den Eingriff mit den Walzstangen 2, 4 angetrieben. Bei einer alternativen Variante kann dem Werkstück ein eigener Drehantrieb zugeordnet werden, der mit den NC-Antrieben 64, 66 der Walzstangen synchronisiert ist, so dass der Hub der Walzstangen 2, 4 mit der Drehung des zu walzenden Werkstückes synchronisiert ist.In the embodiment described above, the workpiece is driven by the engagement with the rolling
Die Umformkräfte lassen sich herabsetzen, wenn der gewalzte Bereich des Werkstückes mit Ultraschall beaufschlagt wird. Für diese Ultraschallbeaufschlagung kann ein geeigneter Ultraschallkopf in die Kaltwalzmaschine integriert werden. Eine weitere Möglichkeit besteht darin, die Drehbewegung des Werkstückes während des Walzvorganges mit Ultraschallschwingungen zu überlagen. Dies könnte beispielsweise dadurch erfolgen, dass der vorbeschriebene Drehantrieb für.das Werkstück eine Drehbewegung erzeugt, die mit hochfrequenten Ultraschallschwingungen geringer Amplitude überlagert ist. Durch die Schwingungsbeinflussung des Umformprozesses lassen sich die Umformkräfte während des Walzvorganges verringern, so dass eine Erhöhung der Prozessgeschwindigkeit ermöglicht ist. Aufgrund der Herabsetzung der Fliesgrenze können auch nach konventionellen Methoden schwer umformbare Materialien kaltgewalzt werden.The forming forces can be reduced when the rolled portion of the workpiece is subjected to ultrasound. For this Ultraschallbeaufschlagung a suitable ultrasonic head can be integrated into the cold rolling machine. Another possibility is to overlay the rotational movement of the workpiece during the rolling process with ultrasonic vibrations. This could be done, for example, by the fact that the above-described rotary drive generates a rotary movement for the workpiece, which is superimposed with high-frequency ultrasound oscillations of low amplitude. By the Schwingungsbeinflussung the forming process, the forming forces can be reduced during the rolling process, so that an increase in the process speed is possible. Due to the reduction in the flow limit, materials that are difficult to form can also be cold-rolled using conventional methods.
Offenbart ist eine Kaltwalzmaschine, bei der die Walzstangen vorzugsweise in Vertikalrichtung angeordnet sind und über eine Zustelleinrichtung während des Walzvorganges in Radialrichtung mit Bezug zum zu bearbeitenden Werkstück verstellbar sind.Disclosed is a cold rolling machine, in which the rolling rods are preferably arranged in the vertical direction and are adjustable via a feed device during the rolling process in the radial direction with respect to the workpiece to be machined.
- 11
- KaltwalzmaschineCold Rolling Machine
- 2, 42, 4
- Walzstangerolling bar
- 66
- Spindelstockheadstock
- 77
- Schaltschrankswitch cabinet
- 88th
- Unterbausubstructure
- 10, 1210, 12
- Stützschenkelsupport legs
- 1414
- HorizontalstützflächeHorizontal support surface
- 1616
- VertikalstützflächeVertical support surface
- 1818
- Brückenkonstruktionbridge construction
- 20, 2220, 22
- Stützkörpersupport body
- 2424
- Guß-TragkonstruktionCast supporting structure
- 2626
- hintere Querlascherear cross-strap
- 2828
- vordere Querlaschefront cross strap
- 30, 3230, 32
- Ausnehmungenrecesses
- 34, 3634, 36
- Schrägführungeninclined guides
- 38, 4038, 40
- Führungsschlittenguide carriage
- 4242
- Gegenführungcounter-guide
- 4444
- NC-AntriebNC drive
- 4646
- Spindelmutterspindle nut
- 4848
- Planetenspindelplanetary spindle
- 5050
- Servomotorservomotor
- 52, 5452, 54
- Führungenguides
- 56, 5856, 58
- Schlittencarriage
- 6060
- Klemmkörperclamping bodies
- 6262
- Konsoleconsole
- 64, 6664, 66
- NC-AntriebeNC drives
- 6868
- Zahnriementoothed belt
- 7070
- Profilierungprofiling
- 7272
- Ramperamp
Claims (12)
- A cold rolling machine comprising two profiled rolling rods (2, 4) which are driven in opposite directions and each of which is mounted on a guide (52, 54) by means of a slide (56, 58) and engages with a work-piece that is mounted in rotatable manner between the rolling rods (2, 4), and comprising a feeding device (38, 40; 20, 22) including at least one feed drive (44) with the aid of which the rolling rods (2, 4) are adjustable in a radial direction with respect to the work-piece during the rolling operation, wherein said feeding device includes for each guide (52, 54) a guide block (38, 40), characterised in that this is mounted in displaceable manner on an inclined guide (34, 36), wherein the incline guides (34, 36) associated with the two rolling rods (2, 4) are set in a V-shape relative to one another.
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with Claim 1, wherein a feed drive (44), preferably an NC drive, is associated with each guide block (38, 40).
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with any of the Claims 1 to 2, wherein the free end portions of the guide blocks (38, 40) have a bracket (62) upon which the drives (64, 66) for the rolling rods (2, 4) are mounted.
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with any of the preceding Claims, wherein the guides (52, 54) for the rolling rods (2, 4) are arranged in the vertical direction or in a horizontal direction.
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with any of the claims 1 to 4, wherein the inclined guides (34, 36) are arranged on two supporting legs (10, 12) of a substructure (8).
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with Claim 5, wherein the two supporting legs (10, 12) are interconnected by means of transverse fishplates (26, 28).
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with any of the Claims 1 to 6, wherein a drive which is synchronized with the drive for the rolling rods is associated with the work-piece.
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with any of the Claims 1 to 7, comprising an ultrasonic device by means of which vibrations in the ultrasonic range are adapted to be applied to the rolled area of the work-piece.
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with any of the preceding Claims, characterized in that a rolling rod (2; 4) is provided with a profiling (70) that extends with a constant profile over substantially the entire operative surface of the rolling rod (2; 4).
- A cold rolling machine in accordance with Claim 9, wherein short ramps (72) having a smaller profile depth are formed at the end portions of the profiling (70).
- A method of cold rolling a work-piece which is in effective engagement with two rolling rods (2, 4) that are arranged to be driven in opposite directions, wherein the rolling rods (2, 4) are adjusted during the rolling operation in a radial direction with respect to the work-piece, the rolling rods are each displaceably mounted by guide blocks on an inclined guide and the inclined guides associated with the two rolling rods are set in a V-shape relative to one another.
- A method in accordance with Claim 11, wherein the predetermined profile depth is formed during a plurality of successive strokes of the rolling rods.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE20122205U DE20122205U1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Cold Rolling Machine |
| EP04009469A EP1442808B1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Flat rolling die |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE10028165 | 2000-06-09 | ||
| DE10028165A DE10028165A1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2000-06-09 | Cold rolling machine comprises two profiled rollers moving in opposite directions and each arranged on a guide over a carriage, and an adjusting device having an adjustment drive |
| PCT/DE2001/002119 WO2001094048A1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Cold rolling machine |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04009469A Division EP1442808B1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Flat rolling die |
| EP04009469.0 Division-Into | 2004-04-22 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1286794A1 EP1286794A1 (en) | 2003-03-05 |
| EP1286794B1 EP1286794B1 (en) | 2004-09-22 |
| EP1286794B2 true EP1286794B2 (en) | 2009-12-30 |
Family
ID=7644977
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP01955205A Expired - Lifetime EP1286794B2 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Cold rolling machine |
| EP04009469A Expired - Lifetime EP1442808B1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Flat rolling die |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP04009469A Expired - Lifetime EP1442808B1 (en) | 2000-06-09 | 2001-06-08 | Flat rolling die |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7051565B2 (en) |
| EP (2) | EP1286794B2 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE276846T1 (en) |
| DE (4) | DE10028165A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2001094048A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10259665A1 (en) * | 2002-12-18 | 2004-07-08 | Wemakon Zeulenroda Gmbh | Contra-motion twin-tray roll forming machine tool press has integral hydrostatic spindle drive or electrical linear motor drive |
| DE102004035153A1 (en) * | 2004-07-15 | 2006-02-09 | Ex-Cell-O Gmbh | Rolled steel rod useful in cold rolling, especially in chip-free cold forming includes data selection storage elements for bar-,cold rolling machine-, rolling process- and workpiece parameters |
| DE102004053501B3 (en) | 2004-10-28 | 2006-06-01 | Ex-Cell-O Gmbh | Cold rolling machine and cold rolling process |
| ATE485118T1 (en) * | 2007-08-07 | 2010-11-15 | E W Menn Gmbh & Co Kg | PROFILE ROLLING MACHINE |
| DE102007044283A1 (en) * | 2007-09-07 | 2009-03-12 | Ex-Cell-O Gmbh | Machine tool for producing toothings on workpieces and method for producing a toothing on a workpiece by means of a machine tool |
| US9403206B2 (en) * | 2012-05-23 | 2016-08-02 | U.S. Gear Tools, Inc. | Spline rolling rack and method |
| KR102264766B1 (en) * | 2013-03-21 | 2021-06-14 | 일리노이즈 툴 워크스 인코포레이티드 | Roll forming machine with reciprocating dies and method of forming a pattern on a cylindrical blank |
| DE102013106268A1 (en) * | 2013-06-17 | 2014-12-18 | Thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Ag | Method and device for producing rotationally symmetrical metal components |
| RU2644837C2 (en) * | 2015-11-30 | 2018-02-14 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Челябинский трубопрокатный завод-Инжиниринг" | Method to produce conical thread on pipes by plastic deformation method |
| DE102017113382B3 (en) | 2017-06-19 | 2018-10-18 | Ffg Werke Gmbh | Thread rolling method and thread rolling device for producing a thread |
| DE102017116895A1 (en) | 2017-07-26 | 2019-01-31 | Mag Ias Gmbh | Method and device for producing a toothing on a cylindrical workpiece |
| DE102018113978B3 (en) | 2018-06-12 | 2019-09-05 | Mag Ias Gmbh | Cold rolling machine and method for producing a profile on a workpiece |
| CN112828216A (en) * | 2020-12-30 | 2021-05-25 | 瑞斯恩智能科技(苏州)有限公司 | Efficient gear rolling machine |
| DE102022110872A1 (en) | 2022-05-03 | 2023-11-09 | Osg Ex-Cell-O Gmbh | Tool unit for a cold rolling machine |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE708057C (en) † | 1937-06-20 | 1941-07-11 | Pee Wee Maschinen Und Appbau I | Process for the production of bolt or external threads |
| DE751904C (en) † | 1939-10-26 | 1954-03-01 | Pee Wee Maschinen U Appbau Inh | Device on thread rolling machines with a support that supports the workpiece during operation and is movable perpendicular to the roll axes |
| US3303682A (en) † | 1962-02-01 | 1967-02-14 | Gen Motors Corp | Method and apparatus for cold forming toothed elements |
| US4045988A (en) † | 1976-04-14 | 1977-09-06 | Anderson-Cook Inc. | Rotary forming machine and tool |
| DE3512514A1 (en) † | 1984-07-25 | 1986-01-30 | VEB Kombinat Umformtechnik "Herbert Warnke" Erfurt, DDR 5010 Erfurt | Cross-rolling machine with rectilinearly, hydraulically driven rolling slides |
| EP0123851B1 (en) † | 1983-03-22 | 1988-01-07 | Osg Mfg. Company | Method and apparatus for rolling a cylindrical blank |
| DE29616460U1 (en) † | 1996-09-23 | 1996-12-12 | Linnenbrink Wolfgang | Cold rolling machine |
| EP0894555A2 (en) † | 1997-07-29 | 1999-02-03 | Revue Thommen AG | Profile rolling machine with supporting frame |
| US6047581A (en) † | 1998-02-27 | 2000-04-11 | Anderson Cook, Inc. | Drive system for vertical rack spline-forming machine |
| DE19718257C2 (en) † | 1997-04-30 | 2001-06-07 | Bad Dueben Profilwalzmaschinen | Profile rolling machine for rolling a rotationally symmetrical workpiece with a precise outer profile |
| DE19728669C2 (en) † | 1997-07-04 | 2001-08-23 | Leico Werkzeugmaschb Gmbh & Co | Method and cross rolling machine for forming a rotationally symmetrical hollow body |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US408529A (en) * | 1889-08-06 | Island | ||
| US1460061A (en) * | 1922-02-15 | 1923-06-26 | Hamilton Gavin Shearer | Axle mill |
| US2760388A (en) * | 1953-05-18 | 1956-08-28 | Bethlehem Steel Corp | Two-diameter thread rolling device |
| US3945272A (en) * | 1970-01-30 | 1976-03-23 | Nl Industries Inc. | Thread-rolling method, thread-rolling dies, and method of manufacturing the dies |
| US4037281A (en) * | 1975-03-03 | 1977-07-26 | Litton Systems, Inc. | Fastener manufacturing method |
| SU559759A1 (en) * | 1976-02-23 | 1977-05-30 | Cross-wedge rolling device | |
| US4016738A (en) * | 1976-04-27 | 1977-04-12 | Alexandr Vladimirovich Puchko | Traverse wedge forming machine |
| US4487047A (en) * | 1981-03-02 | 1984-12-11 | Anderson-Cook, Inc. | Thin-wall spline forming |
| US4519231A (en) * | 1983-03-11 | 1985-05-28 | Roth Robert G | Forming machine including drive mechanism having rack and gear synchronization |
| JPS60166136A (en) * | 1984-02-08 | 1985-08-29 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Die fitting stand of form rolling board |
| DE3619631A1 (en) * | 1986-06-11 | 1987-12-17 | Ind Systeme Datentechnik | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CROSS-ROLLING PROFILED ROTATIONAL PROFILES |
| DE4123847C2 (en) * | 1991-07-18 | 1994-08-04 | Beche & Grohs Gmbh | Flat jaw cross rolling machine |
| WO1994003454A1 (en) | 1992-07-29 | 1994-02-17 | E.I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Herbicidal triazinones |
| DE4306742A1 (en) * | 1993-03-04 | 1994-09-08 | Zahnradfabrik Friedrichshafen | Tool and method for the non-cutting production of the external toothing of gear wheels |
| US5950471A (en) * | 1998-02-27 | 1999-09-14 | Anderson-Cook, Inc. | Vertical rack spline forming machine |
| US6301945B1 (en) * | 2000-06-01 | 2001-10-16 | Utica Enterprises, Inc. | Rack slide assembly and machine for rolling splines in a round workpiece |
-
2000
- 2000-06-09 DE DE10028165A patent/DE10028165A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2001
- 2001-06-08 EP EP01955205A patent/EP1286794B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-06-08 DE DE20122205U patent/DE20122205U1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-06-08 DE DE50114694T patent/DE50114694D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-06-08 US US10/297,195 patent/US7051565B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-06-08 EP EP04009469A patent/EP1442808B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-06-08 DE DE50103775T patent/DE50103775D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2001-06-08 WO PCT/DE2001/002119 patent/WO2001094048A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2001-06-08 AT AT01955205T patent/ATE276846T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2006
- 2006-03-27 US US11/389,006 patent/US7353679B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE708057C (en) † | 1937-06-20 | 1941-07-11 | Pee Wee Maschinen Und Appbau I | Process for the production of bolt or external threads |
| DE751904C (en) † | 1939-10-26 | 1954-03-01 | Pee Wee Maschinen U Appbau Inh | Device on thread rolling machines with a support that supports the workpiece during operation and is movable perpendicular to the roll axes |
| US3303682A (en) † | 1962-02-01 | 1967-02-14 | Gen Motors Corp | Method and apparatus for cold forming toothed elements |
| US4045988A (en) † | 1976-04-14 | 1977-09-06 | Anderson-Cook Inc. | Rotary forming machine and tool |
| EP0123851B1 (en) † | 1983-03-22 | 1988-01-07 | Osg Mfg. Company | Method and apparatus for rolling a cylindrical blank |
| DE3512514A1 (en) † | 1984-07-25 | 1986-01-30 | VEB Kombinat Umformtechnik "Herbert Warnke" Erfurt, DDR 5010 Erfurt | Cross-rolling machine with rectilinearly, hydraulically driven rolling slides |
| DE29616460U1 (en) † | 1996-09-23 | 1996-12-12 | Linnenbrink Wolfgang | Cold rolling machine |
| DE19718257C2 (en) † | 1997-04-30 | 2001-06-07 | Bad Dueben Profilwalzmaschinen | Profile rolling machine for rolling a rotationally symmetrical workpiece with a precise outer profile |
| DE19728669C2 (en) † | 1997-07-04 | 2001-08-23 | Leico Werkzeugmaschb Gmbh & Co | Method and cross rolling machine for forming a rotationally symmetrical hollow body |
| EP0894555A2 (en) † | 1997-07-29 | 1999-02-03 | Revue Thommen AG | Profile rolling machine with supporting frame |
| US6047581A (en) † | 1998-02-27 | 2000-04-11 | Anderson Cook, Inc. | Drive system for vertical rack spline-forming machine |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| "Fertigungsverfahren Druckumformen Walzen", DEUTSCHE NORMEN, 2 May 1969 (1969-05-02), BERLIN, pages 1 - 7, XP000675285 † |
| "Profilwalzmaschine mit direkter aktiver Regelung des Walzvorganges", UMFORMTECHNIK, 1993, pages 291 † |
| M.WALTHER U. P. STREHMEL U. B. LORENZ: "Verzahnungswalzen in der Gesamtprozesskette beim Herstellen hohler wellenförmiger Antreibsteile", PROFIROLL TECHNOLOGIES BAD DÜBEN/FRAUNHOFER CHEMNITZ, 2000, CHEMNITZ GERMANY † |
| NÄSER/MEICHSNER: "Technologie des gewindewalzens", FACHBUCHVERLAG, 1959, LEIPZIG † |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20040007034A1 (en) | 2004-01-15 |
| EP1286794B1 (en) | 2004-09-22 |
| US20060162409A1 (en) | 2006-07-27 |
| WO2001094048A1 (en) | 2001-12-13 |
| DE50114694D1 (en) | 2009-03-19 |
| US7051565B2 (en) | 2006-05-30 |
| ATE276846T1 (en) | 2004-10-15 |
| US7353679B2 (en) | 2008-04-08 |
| DE20122205U1 (en) | 2004-09-30 |
| DE10028165A1 (en) | 2001-12-13 |
| EP1442808B1 (en) | 2009-02-04 |
| EP1442808A2 (en) | 2004-08-04 |
| EP1286794A1 (en) | 2003-03-05 |
| EP1442808A3 (en) | 2004-09-29 |
| DE50103775D1 (en) | 2004-10-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1286794B2 (en) | Cold rolling machine | |
| EP2732895B1 (en) | Machine tool for manufacturing profiles | |
| EP0492211B1 (en) | Method for bending hollow metal profiles and apparatus for carrying out this process | |
| DE2612174A1 (en) | RAIL GRINDING MACHINE | |
| DE2612173B2 (en) | Mobile rail grinding machine | |
| EP0021329A1 (en) | Indexing generating method and apparatus for grinding gear teeth | |
| DE3390141C2 (en) | Device for the final machining of a convolution, cut in a cylindrical piece, by finish rolling | |
| EP1722912B1 (en) | Method for the production of profiled stips for joint parts | |
| AT395835B (en) | METHOD FOR PRODUCING A PARALLEL-AXIS ROTARY PISTON MACHINE | |
| DE3601425A1 (en) | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CUTTING EXTRUDED PLASTIC PIPES | |
| EP3609634B1 (en) | Multi-piece rolling tool with floating support and rolling machine | |
| EP0248983B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for rolling profiles in cylindrical work pieces | |
| EP0683001B1 (en) | Method and device to cut rods, tubes and tube ends | |
| DE10212256A1 (en) | Tool for producing tooth profiles is in more than one part and includes base body fixable to carriage of cold-rolling machine, and working body attachable to base body | |
| CH692382A5 (en) | Profile rolling machine with motor frame. | |
| EP3016771B1 (en) | Apparatus for smoothing a toothing system and production process for a toothing system | |
| DE922045C (en) | Machine for rolling inner or outer profiles | |
| DE102018102768B4 (en) | System with a workpiece in the form of a threaded spindle and with a fine machining device | |
| EP3414030B1 (en) | Rolling device for rolling work pieces having a toothing, and associated method | |
| DE19710730B4 (en) | Rolling process and two-roll profile rolling machine for producing pitch profiles with an odd number of turns on rotationally symmetrical workpieces | |
| DE4340162A1 (en) | Method of threaded or smooth rolling of sleeve or bolt shaped metal workpieces | |
| DE102010008027A1 (en) | Machine tool is provided with cold rolling unit, and longitudinal guides movable rod rolling units, where roll bars are provided with outer profile | |
| DE202004012067U1 (en) | Cold metal rolling tool for fabrication of symmetrical metal work piece with straight or angled teeth, spiral teeth with grooves, threads or knurled surfaces | |
| DE102011102793B3 (en) | Method for machining the end faces of workpieces made of wood, plastic and the like | |
| DE3329731A1 (en) | HONAHLE |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20021205 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20031217 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: KREISSIG, BERND Inventor name: OPHEY, LOTHAR, DR. Inventor name: BRUENTRUP, OTTO |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20040922 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50103775 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20041028 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PLAQ | Examination of admissibility of opposition: information related to despatch of communication + time limit deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDOPE2 |
|
| PLBQ | Unpublished change to opponent data |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OPPO |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAQ | Examination of admissibility of opposition: information related to despatch of communication + time limit deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDOPE2 |
|
| PLAR | Examination of admissibility of opposition: information related to receipt of reply deleted |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSDOPE4 |
|
| PLBQ | Unpublished change to opponent data |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OPPO |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: PROFIROLL TECHNOLOGIES GMBH Effective date: 20050422 |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: PROFIROLL TECHNOLOGIES GMBH Effective date: 20050422 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| PLAF | Information modified related to communication of a notice of opposition and request to file observations + time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCOBS2 |
|
| PLAF | Information modified related to communication of a notice of opposition and request to file observations + time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCOBS2 |
|
| PLAF | Information modified related to communication of a notice of opposition and request to file observations + time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCOBS2 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20091230 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20100610 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110608 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 276846 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20110608 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50103775 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: HOEGER, STELLRECHT & PARTNER PATENTANWAELTE MB, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20180626 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50103775 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: HOEGER, STELLRECHT & PARTNER PATENTANWAELTE MB, DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20190608 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190608 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20200623 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20200623 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20200630 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 50103775 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 50103775 Country of ref document: DE Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 50103775 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: OSG EX-CELL-O GMBH, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: EX-CELL-O GMBH, 73054 EISLINGEN, DE |