EP1069265A2 - Dispositif d'autorisation d'entrée et dispositif d'autorisation combinée d'entrée et d'utilisateur - Google Patents
Dispositif d'autorisation d'entrée et dispositif d'autorisation combinée d'entrée et d'utilisateur Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1069265A2 EP1069265A2 EP00109565A EP00109565A EP1069265A2 EP 1069265 A2 EP1069265 A2 EP 1069265A2 EP 00109565 A EP00109565 A EP 00109565A EP 00109565 A EP00109565 A EP 00109565A EP 1069265 A2 EP1069265 A2 EP 1069265A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- base station
- code
- bypass path
- transmitter
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 238000013475 authorization Methods 0.000 title claims description 17
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 50
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 abstract description 15
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 19
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000001934 delay Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000015654 memory Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011017 operating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000029305 taxis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C9/00309—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C9/00309—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks
- G07C2009/00365—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks in combination with a wake-up circuit
- G07C2009/00373—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks in combination with a wake-up circuit whereby the wake-up circuit is situated in the lock
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C9/00309—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks
- G07C2009/00507—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks keyless data carrier having more than one function
- G07C2009/00531—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated with bidirectional data transmission between data carrier and locks keyless data carrier having more than one function immobilizer
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/00174—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys
- G07C2009/00753—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated by active electrical keys
- G07C2009/00769—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated by active electrical keys with data transmission performed by wireless means
- G07C2009/00793—Electronically operated locks; Circuits therefor; Nonmechanical keys therefor, e.g. passive or active electrical keys or other data carriers without mechanical keys operated by active electrical keys with data transmission performed by wireless means by Hertzian waves
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C2209/00—Indexing scheme relating to groups G07C9/00 - G07C9/38
- G07C2209/08—With time considerations, e.g. temporary activation, valid time window or time limitations
Definitions
- the invention relates to a control system and method for Control at least one function of an object where Measures to prevent unauthorized use or Access to the object are met.
- the invention relates also an access control and driving authorization facility for a motor vehicle.
- the base station checks the response code signal received with regard to its justification, for example by comparison a code information contained in the response code signal with a stored reference code information. With authorization the desired function is carried out, such as unlocking the motor vehicle doors or that Release the immobilizer.
- Such a system can pose security problems result, for example by unauthorized eavesdropping and manipulation wireless communication between motor vehicles and code transmitter.
- a control device of functions of an object in particular the access and Driver authorization control for a motor vehicle known (DE 196 32 025 C2), in which the communication duration of the question-answer dialog measured and with a predetermined maximum duration is compared.
- the signal delays are compared to the computing times very little, so that increased Make signal runtimes not noticeable and therefore not can serve as protection against manipulation by unauthorized persons.
- the invention has for its object to a control system create that through increased security against unauthorized Attempted use distinguishes without making major Interventions in the system are required.
- the invention is a method according to claim 8 provided an improvement over that offers unauthorized execution of the associated function.
- Transmitted signal and the reception of these parts determined, i.e. it becomes the system response time to determine, so to speak the distance between the code transmitter and the object-side Base station measured.
- This measurement preferably takes place from energy-related or logical, system-related Reasons take place in the base station, however, depending after system design, can also be adopted by the encoder.
- the evaluation circuit measures in this Fall the time between signal transmission and reception at least one or more marked sections or parts of the signals and compares these time periods in the simplest case with a predetermined reference period, which entitle to receive the signal back from a Sufficient code transmitter located close to the motor vehicle due to an unauthorized remote access of the above influences are usually exceeded becomes.
- the base station is designed such that it only executes or releases the desired function if at least the specially marked parts of the signals have been received within the specified period of time.
- System component generating response signal here the code transmitter
- transmitter amplifier and / or antenna Processing operations with a view to receiving a Interrogation signal, the detection and evaluation of the interrogation signal, the generation / calculation of a response signal and the Sending the same are conditional, is preferably that System component generating response signal (here the code transmitter) equipped with a bypass path, at least over the bypassing a marked portion of the received signal its own evaluation circuit directly to the transmitter (transmitter amplifier and / or antenna) can be conducted and thus almost sent back to the sending component without delay becomes.
- the corresponding parts are almost without delay, apart of the short group duration, reflected (transparency mode of the code provider).
- the delay time between sending and then receiving a signal is essentially only due to running time, so that a distance measurement to a certain extent between the base station and the code transmitter takes place.
- An additional analog or digital processing of the original signal would result in additional processing times with them, which are much longer than the signal propagation time in free space.
- the bypass path is preferably a controllable one Provide switches so that the bypass path is only temporary direct forwarding of parts of the received Signals to the transmitter causes, but can otherwise be switched off and thus the signal communication (and the energy content) of the received signal is not impaired.
- the component equipped with the bypass path is received signal not only to the bypass path, but can also create its own evaluation circuit at the same time this the received signal on correct, for the concerned Check the component's intended code and if the code is correct (or code information) possibly an additional one Signal, for example a pulse or a pulse train, to the one sent and sent via the bypass path Append signal.
- This allows a further increase in Tamper-proof, e.g. versus using fake Transponders.
- the one that generates the question code signal Component or additional impulses, or that Question code signal with itself from pulse to pulse or signal to Signal changing field strength, pulse duration or frequency or sequence or pulse / pause ratio.
- the component generating the question code signal in the form of corresponding field strength, pulse length or frequency differences back so an additional security parameter is available from the one that generates the question code signal Component by comparing the received field strength, Pulse length or frequency curve with the expected Course is evaluated.
- the encoder can for example from the transmitter unit during the vehicle locking process information is sent to the customer transmit frequency to be used in the subsequent opening or starting process signals, to which the encoder then adjusts itself.
- the transmitter is the code transmitter is set to the correct frequency, so that the impulses passed through the bypass path almost over the right frequency or channel without delay without settling or the like, be returned.
- the base station may be due to this considerable time delay that of one before The code transmitter located in the signal is clearly returned by a signal supplied via unauthorized remote access, for example by specifying a time window for the response signal distinguish that when the arrival via the remote query route greatly delayed or distorted response signal supplied is already closed again, so this response signal is rejected as late.
- next transmission frequency to be selected can also be another signal parameter, for example the amplitude, type of modulation or the like from the base station be ordered.
- the invention can generally not only in the control of Access control function or immobilizer function, but also with others, only if there is a legitimate one Key functions to be performed, and also in general the authorization-relevant control of non-vehicle-related Functions of objects, e.g. access control to houses, apartments, offices, hotels, parking garages, Garages or the like are used.
- the invention is described below using the exemplary embodiment an access control and driving authorization device for a motor vehicle based on the single figure explained. However, the invention cannot be applied to only one Motor vehicle, but also used in other objects for which an authorization must be proven, to object-specific functions, such as access to the object Taxes.
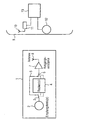
- the control system for a motor vehicle includes a portable one Code transmitter or an electronic "key" that one Transmitter 7, 8 and a receiver 2.
- the code encoder can be designed as a card (smart card) or in any other way and serves as an identification transmitter, which after receipt a response code signal automatically from a request signal sends back. Therefore, the code encoder is in the following as Transponder 1 called.
- the response code signal contains one a carrier frequency modulated for the transponder 1 characteristic binary code information.
- the transponder 1 has a schematically illustrated reception circuit with the receiver 2, the radio frequency signals recorded via an antenna and possibly after demodulation to a computing unit (controller) 4, which transmits the received and processed demodulated question code signal, in particular decodes, and examines whether it is an attached to the transponder 1 directed question code signal of a vehicle-side fixed attached control device (base station 14). Is if this is the case, the computing unit 4 generates using the response code signal and / or stored information and / or a mathematical algorithm a code information that with an output amplifier / modulator 7 of a carrier frequency is modulated and via an antenna 8 as a response code signal is sent out.
- the signal processing in the computing unit 4 requires one Duration that is significantly longer than the signal propagation times between base station 14 and transponder 1, which at wireless transmission of the signals. So only that pure signal propagation times measured for wireless transmission and thus a distance from the transponder 1 to the base station 14 can be determined, the transponder 1 has one Bypass path 5 as a bypass of the computing unit 4 in the form a continuous line (hereinafter referred to as bypass path 5 referred to), via which the receiver 2 directly with the Output amplifier 7 is connected.
- a controllable switch 3, 6 arranged, depending on Can be switched to the bypass path as needed.
- the Receiving circuit 2 is either by using switch 3 Input of the computing unit 4 or connected to the bypass path 5, whereas the switch 6 the input of the output amplifier 7 either with the bypass path 5 or with the Output of the computing unit 4 connects.
- the switches 3, 6 are preferably designed and constructed as a semiconductor switch controlled synchronously by the computing unit 4 such that they are either in the position shown or connected to the input and output of the computing unit 4 are.
- the receiving circuit 2 also permanently connected to the input of the computing unit 4 his.
- the switch 3 can then be omitted entirely or arranged in this way be either bypassing 5 with this one Connection line between the receiving circuit 2 and the Computing unit 4 connects or the bypass path 5 selectively disconnects from this connecting line.
- the output of the computing unit 4 can also be fixed with the Input of the output amplifier 7 may be connected, the Bypass path 5 then via switch 6 either additionally connected to the input of the output amplifier 7 or from this is separated.
- the control system of the schematically represented motor vehicle 9 contains a transmission unit 12, which is connected to a motor vehicle, for example attached to the outside or inside mirror Antenna 10 can send signals, and a receiving unit 12 for receiving externally supplied signals, in particular Response code signals from one of the access control or driving authorization devices assigned to the motor vehicle Transponders 1.
- the transmitting and receiving unit 11, 12 is with a control device 13 for controlling transmission and reception of signals, generation and evaluation of signals and for Control vehicle-specific functions, for example a central locking system or an immobilizer system, connected.
- the transmitting and receiving unit 11, 12 and the control unit 13 form the base station 14.
- An access signal is used for access control (for example, operating the door handle or another Switch on the outside of the motor vehicle) a question code signal triggered and via the transmitter unit 11 with her Antenna 10 emitted. If there is a transponder 1 in the area is present and via his receiving group 2 the question code signal receives, it is checked in the computing unit 4, whether it's actually the question code signal for this Transponder 1 is intended. If so, generated the computing unit 4 a defined response code signal, the sent back to the receiving unit 12 via the antenna 8 becomes.
- the response code signal contains encrypted code information, which is checked in the base station 14 for authorization becomes. If the response code signal is justified, it will be shown below described runtime analysis and if necessary then access by unlocking door locks enables.
- the same process takes place to release the immobilizer and start the internal combustion engine.
- An ignition start switch is used for the question-answer dialog. Consequently the motor vehicle can be used, i.e. the driving operation is released.
- the same operating procedure also applies the control of another vehicle-specific function, for example user-specific settings of seats or mirrors, or release of use from mobile phone or internet in the motor vehicle too.
- the Switches 3 and 6 temporarily switched so that one or several marked or marked parts or sections (hereinafter referred to as check bits) of the question code signal directly to the transmitter 7, 8, while at least the remaining parts of the question code signal of the computing unit 4 are supplied.
- the check bits are one or more bits of a binary (encoded) Information contained in the question code signal as one Carrier frequency is present modulated or the one separately binary information transmitted by the question code signal is.
- This coding can change continuously according to a fixed random principle.
- the base station measures the transit times of the test bits, namely from transmission to receipt of the test bits.
- the base station 14 is designed so that the time the transmission of a signal via the transmission unit 11 and the Receipt of a response signal detected via the receiving unit 12 (especially the check bits relevant for the runtime). So there is a real-time measurement in the base station 14 instead of starting with sending test bits by base station 14 and the end by receiving the corresponding test bits given by the base station 14 is.
- the runtime of the check bits i.e. from transmission by the transmission unit 11 until reception by the receiving unit 12 is measured and with a maximum permissible reference term compared. Only if the runtime of the check bits is within the reference term and the code information entitles functions are controlled in the motor vehicle.
- the reference running time is determined during an initialization phase (for example at the end of the assembly line during the manufacture of the motor vehicle) in such a way that the running time of a signal is measured, which is sent to a transponder 1 that is at a fixed, short distance from the motor vehicle and is transmitted directly from it A tolerance value (for example 50%) is then added to the measured transit time value (possibly averaged over several measurements).
- the reference transit time thus obtained is much smaller than a transit time taking into account the processing time in the computing unit of the transponder 1.
- the maximum permissible reference term is in one configuration without bypass path 5 dimensioned so that a response code signal from a place far from the motor vehicle Transponder 1 is recognized as not permitted. So if that Response code signal via an unauthorized remote access to the remotely located transponder 1 is requested, result themselves much longer terms, so the sum of all Time delays are significantly greater than with one nearby or transponder 1 located in the motor vehicle.
- the transponder 1 should be used in a motor vehicle a maximum of only a few meters from the motor vehicle his. Only then should access be possible.
- the direct electrical connection between the receiving circuit (s) 2 (the number of receiving channels depends, for example on the number of channels or frequency bands ab, which can be covered by the identity provider) and the Output stage 7, 8 is from the computing unit 4 by appropriate Position of switches 3, 6 controlled.
- switches 3 and 6 are in the idle state a switching state in which the input of the computing unit 4 is directly connected to the receiving circuit 2 and the output the computing unit 4 to the input of the output amplifier 7 connected. If now the base station 14 via the transmitter unit 11 sends out a question code signal to the Transponder 1 is directed, so the beginning of the question code signal recognized by the computing unit 4.
- the transponder 1, i.e. the computing unit 4 and its switches controlled by it 3, 6 are synchronized so they arrive on time of the check bits in the transparency mode and after switch back the check bits.
- the computing unit can then - starting with the first bit or start bit of the received binary information - switch 3 and 6 synchronously switch at the times specified by position / position and / or length and / or number of test bits so that the test bits are routed via the bypass path and immediately sent back in.
- the transponder 1 is then (during the bypass) in a so-called transparency mode. At least the other parts of the question code signal are fed to the computing unit 4 in order to form the answer code signal with the help of the question code signal.
- the evasion process advantageously takes place within a running, possibly encrypted data stream, namely within the question code signal and the answer code signal from. Then it is difficult for unauthorized persons recognize where the check bits are, how big they are and how many there are.
- a start signal can also be sent through first that the computing unit 4 is synchronized.
- the start signal can have one or more short pings that are considered as check bits and sent back directly become. Then the actual question code signal sent and then the response code signal are generated.
- the pings can also be sent out after the question code signal However, there may be interference with the response code signal come as the pings instantaneous and the response code signal due to the processing time in the computing unit are sent out with a delay by transponder 1.
- the base station 14 determines the time period between transmission the respective check bits and their return and compares this time period with the reference time period.
- the computing unit 4 switches the switches 3 and 6 in such a way that the check bits are routed through the bypass path.
- the Switches 3 and 6 can also be designed so that the Check bits both via the bypass path and in parallel are fed to the computing unit 4.
- the base station 14 triggers test bits to perform the desired function off, for example unlocking the motor vehicle doors or starting the engine.
- control system can also be designed such that the computing unit 4 after receiving the first question code signal first sends the response code signal back to base station 14 and only then switches 3 and 6 into the position shown switches, after which the base station 14 or the Check bits for determining the response time until receipt the response impulses generated.
- the computing unit 4 can then be designed so that there is a additional pulse train or a single pulse generated and this to the through the bypass path 5 Check bits for additional identification confirmation attached.
- the base station 14 can also be designed such that it the transmitted test bits in their field strength, pulse duration or frequency varies according to a predetermined scheme. This "Modulation" remains in transponder 1 during transmission receive the bypass path 5 so that the over the exit circuit 7, 8 returned pulses also this modulation contain. In this case, the base station 14 additionally measures the varied parameter, i.e. the field strength, pulse length and / or frequency change and only accepts pulse trains, that change in the expected way.
- This "Modulation" remains in transponder 1 during transmission receive the bypass path 5 so that the over the exit circuit 7, 8 returned pulses also this modulation contain.
- the base station 14 additionally measures the varied parameter, i.e. the field strength, pulse length and / or frequency change and only accepts pulse trains, that change in the expected way.
- Correction factors dependent on field strength can also be transferred to runtime differences due to large dynamic differences to be able to compensate.
- the above The specified security measures can then be carried out simultaneously with the actual Code exchanges take place, which is an unauthorized manipulation even more difficult. So the question code signal with the check bits for example at 125 kHz and the response code signal and the test bits are returned at 433 MHz.
- the transponder 1 has several frequency bands on the transmission side or sweep at least several channels within a band can, it is designed for example in PLL technology and can optionally have a plurality of for different Output circuits designed for frequencies or channels 7, 8 have.
- the transmitter and receiver unit also open the motor vehicle side are then also for several frequency bands or multiple channels within a band.
- This can be used to advantage in that that the base station 14 the transmission frequency used in each case or changes the channel used and the transponder 1 the transmission frequency or channel to be used in advance, for example, by means of a corresponding code signal communicates. This allows maintaining a proper one Communication between the base station 14 and the Transponder 1.
- the base station 14 can make the transmission frequency dependent, for example, on the respective input code or another code segment, for example a secret key, so that a constant frequency change, for example dependent on the bit status or the checksum or the like, results. Since only the base station 14 knows the codes and thus the new frequency to be used in each case, only the connected receiver can also carry out the correct frequency jump. This makes unauthorized eavesdropping difficult. The previous one Communicate "can of course also apply to the position / length / number of check bits.
- base station 14 shares this Transponder 1 during a locking process of the motor vehicle in the form of a code signal with which frequency at the next contact, namely with the access control authorization query the next time you try to open the door, will be used.
- the transponder 1 can then on set this new frequency and at the next communication send on this frequency.
- Remote query means remains the one to be used next Frequency unknown.
- the transponder 1 it is also possible for the transponder 1 to be active the frequency to be used and the frequency change defined and the base station 14 over it in the form of code signals informed.
- the route that is routed via the bypass path 5 immediately returned signal with that from the computing unit 4 overlay the upcoming transmission signal so that interference effects, Zero crossing fluctuations and thus phase changes, as well Mixing frequencies occur at the receiving unit 12 that of the base station 14 can be detected (e.g. via a Phase comparison or an interference pattern evaluation). This enables an even more precise measurement of the delay times / running times that have occurred up to a distance measurement.
- the question code signal and the answer code signal are code signals, which each have a binary information that one Carrier signal are modulated.
- the binary information points many bit positions.
- By encrypting the code signal changes with every new encryption process.
- the code information can precede or succeed several bits that may be required for secure data transmission become.
- the code information comes with an expected and target code information generated or stored at the receiving end compared.
- Question code signal for the invention is to be understood as a signal that contains encoded information and the check bits (even if the check bits are sent sooner or later) and serves as a request to send the answer code signal.
- Answer code signal to understand a signal that has both code information and the check bits, even if these parts arrive at the respective receiver at different times.
- This code information becomes a carrier signal with the carrier frequency of 125 kHz modulated.
- the code information for example, beginning with the 20th bit position - three check bits (corresponds to a duration of about 750 ⁇ s) marked.
- the average throughput time (duration) of the check bits starting with the sending of the question code signal and ending with receiving the check bits immediately in transparency mode were sent back by transponder 1, amounts in the case of a transponder 1 arranged close to the motor vehicle about 20 ⁇ s (due to the running time at 125 KHz or 433 MHz).
- the value 25 ⁇ s could serve as a reference runtime if 5 ⁇ s added as a safety tolerance. So if a term is measured for the test bits of less than 25 ⁇ s, so the authorized code information of the transponder 1 required to have the desired functions in the motor vehicle to execute.
- multiple check bits could also be used be arranged in the question code signal, for example a Check bit starting at the 20th bit position with the number of 3 Bits and starting at the 43rd bit position with the number of 2 Bits. If the runtimes of the check bits are shorter than the reference term and also the two lengths of 3 bits and 2 with a corresponding time interval to each other and would be correctly captured at the right time, so would the response code signal recognized as justified with regard to its check bits.
- the computing unit 4 is advantageously a microprocessor trained with associated memories.
- the control unit is also 13 as a microprocessor with associated memories educated.
- the transit time measurement can be done by a separate Unit. Likewise, the runtime measurement be made by the microprocessor.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Lock And Its Accessories (AREA)
- Electric Propulsion And Braking For Vehicles (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19930460 | 1999-07-01 | ||
| DE19930460 | 1999-07-01 | ||
| DE10012110 | 2000-03-13 | ||
| DE10012110 | 2000-03-13 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1069265A2 true EP1069265A2 (fr) | 2001-01-17 |
| EP1069265A3 EP1069265A3 (fr) | 2004-01-21 |
Family
ID=26004812
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00109565A Withdrawn EP1069265A3 (fr) | 1999-07-01 | 2000-05-04 | Dispositif d'autorisation d'entrée et dispositif d'autorisation combinée d'entrée et d'utilisateur |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6353776B1 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP1069265A3 (fr) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102016215934A1 (de) | 2016-08-24 | 2018-03-01 | Continental Automotive Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Bestimmung einer Laufzeit und/oder eines Abstands zwischen mehreren Transceivern, insbesondere für ein Fahrzeugs-Zugangs- und/oder Start-System |
Families Citing this family (54)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19957536C2 (de) * | 1999-11-30 | 2003-04-03 | Siemens Ag | Diebstahlschutzsystem für ein Kraftfahrzeug und Verfahren zum Betreiben eines Diebstahlschutzsystems |
| JP4727892B2 (ja) * | 2000-03-09 | 2011-07-20 | シーメンス アクチエンゲゼルシヤフト | 例えばid発生器を検出するための送受信方法 |
| DE10114876A1 (de) * | 2001-03-26 | 2002-10-17 | Siemens Ag | Identifikationssystem zum Nachweis einer Berechtigung für den Zugang zu einem Objekt oder die Benutzung eines Objekts, insbesondere eines Kraftfahrzeugs |
| US7325250B1 (en) * | 2001-07-09 | 2008-01-29 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Method and apparatus for preventing radio communication system access by an unauthorized modem |
| JP3941620B2 (ja) * | 2001-08-31 | 2007-07-04 | 株式会社デンソーウェーブ | Idタグ内蔵電子機器 |
| DE10151034B4 (de) * | 2001-10-16 | 2004-02-05 | Siemens Ag | Diebstahlschutzsystem, Verfahren zum Betreiben eines Diebstahlschutzsystems und Komponenten eines Diebstahlschutzsystems |
| US20030172295A1 (en) * | 2002-03-01 | 2003-09-11 | Onspec Electronics, Inc. | Device and system for allowing secure identification of an individual when accessing information and a method of use |
| EP1378864A1 (fr) * | 2002-07-05 | 2004-01-07 | EM Microelectronic-Marin SA | Procédé de controle d'accès d'un objet portable personnalisé à un espace déterminé, et objet portable pour la mise en oeuvre du procédé |
| JP4178285B2 (ja) * | 2002-08-09 | 2008-11-12 | 豊丸産業株式会社 | 遊技機 |
| JP2004084258A (ja) * | 2002-08-26 | 2004-03-18 | Toyomaru Industry Co Ltd | 施錠システム、遊技機及び装置管理システム |
| DE10255880A1 (de) * | 2002-11-29 | 2004-06-09 | Philips Intellectual Property & Standards Gmbh | Elektronisches Kommunikationssystem und Verfahren zum Erkennen einer Relais-Attacke auf dasselbe |
| US20040232228A1 (en) * | 2003-05-20 | 2004-11-25 | Gotfried Bradley L. | Monitoring system |
| US6923370B2 (en) * | 2003-05-20 | 2005-08-02 | Bradley L. Gotfried | Access system |
| US6888445B2 (en) * | 2003-05-20 | 2005-05-03 | Bradley L. Gotfried | Vehicle identification system |
| US20050005167A1 (en) * | 2003-07-02 | 2005-01-06 | Kelly Thomas J. | Systems and methods for providing security operations in a work machine |
| US7983820B2 (en) * | 2003-07-02 | 2011-07-19 | Caterpillar Inc. | Systems and methods for providing proxy control functions in a work machine |
| US7532640B2 (en) | 2003-07-02 | 2009-05-12 | Caterpillar Inc. | Systems and methods for performing protocol conversions in a machine |
| US20050002354A1 (en) * | 2003-07-02 | 2005-01-06 | Kelly Thomas J. | Systems and methods for providing network communications between work machines |
| US7516244B2 (en) * | 2003-07-02 | 2009-04-07 | Caterpillar Inc. | Systems and methods for providing server operations in a work machine |
| US7650509B1 (en) * | 2004-01-28 | 2010-01-19 | Gordon & Howard Associates, Inc. | Encoding data in a password |
| TW200534531A (en) * | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-16 | Aisin Seiki | Vehicle mounted radio device |
| US20060290473A1 (en) * | 2005-06-27 | 2006-12-28 | Honeywell International Inc. | ID tags with Frequency diversity |
| US20070162626A1 (en) * | 2005-11-02 | 2007-07-12 | Iyer Sree M | System and method for enhancing external storage |
| US20070194881A1 (en) | 2006-02-07 | 2007-08-23 | Schwarz Stanley G | Enforcing payment schedules |
| US7876894B2 (en) * | 2006-11-14 | 2011-01-25 | Mcm Portfolio Llc | Method and system to provide security implementation for storage devices |
| US20080174446A1 (en) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-07-24 | Lear Corporation | Multi-channel passive vehicle activation system |
| US20080288782A1 (en) * | 2007-05-18 | 2008-11-20 | Technology Properties Limited | Method and Apparatus of Providing Security to an External Attachment Device |
| US20080181406A1 (en) * | 2007-01-30 | 2008-07-31 | Technology Properties Limited | System and Method of Storage Device Data Encryption and Data Access Via a Hardware Key |
| US20090046858A1 (en) * | 2007-03-21 | 2009-02-19 | Technology Properties Limited | System and Method of Data Encryption and Data Access of a Set of Storage Devices via a Hardware Key |
| US20080184035A1 (en) * | 2007-01-30 | 2008-07-31 | Technology Properties Limited | System and Method of Storage Device Data Encryption and Data Access |
| US9026267B2 (en) | 2007-03-09 | 2015-05-05 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems of selectively enabling a vehicle by way of a portable wireless device |
| JP4394132B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-19 | 2010-01-06 | 株式会社日本自動車部品総合研究所 | 電子キーシステム |
| DE102007022100B4 (de) * | 2007-05-11 | 2009-12-03 | Agco Gmbh | Kraftfahrzeugsteuergerätedatenübertragungssystem und -verfahren |
| US20080288703A1 (en) * | 2007-05-18 | 2008-11-20 | Technology Properties Limited | Method and Apparatus of Providing Power to an External Attachment Device via a Computing Device |
| JP2010011061A (ja) * | 2008-06-26 | 2010-01-14 | Nippon Soken Inc | 無線通信システム |
| DE102008050988A1 (de) * | 2008-09-01 | 2010-03-04 | Gerd Reime | Identifikationselement mit einem optischen Transponder |
| US8581712B2 (en) | 2008-12-12 | 2013-11-12 | Gordon * Howard Associates, Inc . | Methods and systems related to establishing geo-fence boundaries |
| US8659404B2 (en) | 2008-12-12 | 2014-02-25 | Gordon Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to establishing geo-fence boundaries and collecting data |
| US8018329B2 (en) | 2008-12-12 | 2011-09-13 | Gordon * Howard Associates, Inc. | Automated geo-fence boundary configuration and activation |
| US8686841B2 (en) | 2008-12-12 | 2014-04-01 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to activating geo-fence boundaries and collecting location data |
| US8581711B2 (en) | 2011-03-22 | 2013-11-12 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems of rule-based intoxicating substance testing associated with vehicles |
| US8781900B2 (en) | 2011-09-09 | 2014-07-15 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Method and system of providing information to an occupant of a vehicle |
| US9665997B2 (en) | 2013-01-08 | 2017-05-30 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Method and system for providing feedback based on driving behavior |
| JP5721754B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-28 | 2015-05-20 | オムロンオートモーティブエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 通信システム及び通信装置 |
| US9061645B2 (en) | 2013-02-15 | 2015-06-23 | Clever Devices, Ltd | Methods and apparatus for transmission control of a transit vehicle |
| JP6174341B2 (ja) * | 2013-03-11 | 2017-08-02 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 通信システム、及びチューナ並びに設定方法 |
| US9378480B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2016-06-28 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to asset identification triggered geofencing |
| US9035756B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2015-05-19 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to remote tamper detection |
| US9840229B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2017-12-12 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to a remote tamper detection |
| US8928471B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2015-01-06 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to remote tamper detection |
| US9013333B2 (en) | 2013-06-24 | 2015-04-21 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | Methods and systems related to time triggered geofencing |
| DE102014200116A1 (de) * | 2014-01-08 | 2015-07-09 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Freigabe von Funktionen eines Steuergerätes |
| US9701279B1 (en) | 2016-01-12 | 2017-07-11 | Gordon*Howard Associates, Inc. | On board monitoring device |
| DE102017004620A1 (de) * | 2016-07-04 | 2018-01-04 | Sew-Eurodrive Gmbh & Co Kg | Sicherheitseinrichtung und Verfahren zum Betreiben eines Systems |
Family Cites Families (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE610902C (de) * | 1935-03-19 | Karl Julius Gaitzsch | Vogelbadehaeuschen fuer Zimmervoegel | |
| US5787174A (en) * | 1992-06-17 | 1998-07-28 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Remote identification of integrated circuit |
| US5777580A (en) * | 1992-11-18 | 1998-07-07 | Trimble Navigation Limited | Vehicle location system |
| US5629693A (en) * | 1993-11-24 | 1997-05-13 | Trimble Navigation Limited | Clandestine location reporting by a missing vehicle |
| US6181253B1 (en) * | 1993-12-21 | 2001-01-30 | Trimble Navigation Limited | Flexible monitoring of location and motion |
| DE4409167C1 (de) * | 1994-03-17 | 1995-06-29 | Siemens Ag | Schlüssellose Zugangskontrolleinrichtung |
| US5729697A (en) * | 1995-04-24 | 1998-03-17 | International Business Machines Corporation | Intelligent shopping cart |
| US5812065A (en) * | 1995-08-14 | 1998-09-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Modulation of the resonant frequency of a circuit using an energy field |
| US5828693A (en) * | 1996-03-21 | 1998-10-27 | Amtech Corporation | Spread spectrum frequency hopping reader system |
| DE19615339A1 (de) * | 1996-04-18 | 1997-10-23 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Ag | Verfahren zum Einstellen von individuellen Funktionen eines Fahrzeugs |
| US5929777A (en) * | 1996-05-16 | 1999-07-27 | Mci World Com, Inc. | Radio activated personal infrared distress beacon |
| DE19632025C2 (de) * | 1996-08-08 | 1998-07-23 | Daimler Benz Ag | Authentikationseinrichtung mit elektronischer Authentikationskommunikation |
| GB9723743D0 (en) * | 1997-11-12 | 1998-01-07 | Philips Electronics Nv | Battery economising in a communications system |
| US6249227B1 (en) * | 1998-01-05 | 2001-06-19 | Intermec Ip Corp. | RFID integrated in electronic assets |
| US6252544B1 (en) * | 1998-01-27 | 2001-06-26 | Steven M. Hoffberg | Mobile communication device |
| DE19941428B4 (de) * | 1998-09-02 | 2015-09-10 | Marquardt Gmbh | Schließsystem, insbesondere für ein Kraftfahrzeug |
| DE19846803C1 (de) * | 1998-10-10 | 2000-09-07 | Daimler Chrysler Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung der Zugangsberechtigung zu einem motorangetriebenen Fahrzeug |
| DE10029170A1 (de) * | 1999-06-25 | 2000-12-28 | Marquardt Gmbh | Schließsystem, insbesondere für ein Kraftfahrzeug |
-
2000
- 2000-05-04 EP EP00109565A patent/EP1069265A3/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 2000-07-03 US US09/609,507 patent/US6353776B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102016215934A1 (de) | 2016-08-24 | 2018-03-01 | Continental Automotive Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Bestimmung einer Laufzeit und/oder eines Abstands zwischen mehreren Transceivern, insbesondere für ein Fahrzeugs-Zugangs- und/oder Start-System |
| US11343076B2 (en) | 2016-08-24 | 2022-05-24 | Continental Automotive Gmbh | Method and apparatus for determining a propagation delay and/or a distance between multiple transceivers, particularly for a vehicle-entry and/or starting system |
| DE102016215934B4 (de) | 2016-08-24 | 2024-02-29 | Continental Automotive Technologies GmbH | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Bestimmung einer Laufzeit und/oder eines Abstands zwischen mehreren Transceivern, insbesondere für ein Fahrzeugs-Zugangs- und/oder Start-System |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6353776B1 (en) | 2002-03-05 |
| EP1069265A3 (fr) | 2004-01-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1069265A2 (fr) | Dispositif d'autorisation d'entrée et dispositif d'autorisation combinée d'entrée et d'utilisateur | |
| EP0980800B1 (fr) | Dispositif de protection anti-vol pour un véhicule automobile et procédé de mise en oeuvre d'un tel dispositif | |
| DE60107512T2 (de) | Sicherheitssystem | |
| DE112019001472T5 (de) | Authentisierungssystem | |
| DE10148830B4 (de) | Verfahren und System zur Authentifizierung eines ersten Sende-/Empfangsgeräts gegenüber einem zu diesem entfernt angeordneten zweiten Sende-/Empfangsgerät | |
| DE102017210523B3 (de) | Verfahren zum Betreiben einer passiven funkbasierten Schließvorrichtung und passive funkbasierte Schließvorrichtung | |
| DE102011075886B3 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Zugangs- und/oder Startverifizierung. | |
| EP3580731A1 (fr) | Procédé de fonctionnement d'un système d'authentification et système d'authentification | |
| WO2002054353A1 (fr) | Systeme d'identification pour detecter une autorisation d'acces a un objet ou d'utilisation d'un objet, notamment d'un vehicule automobile | |
| EP1041224A2 (fr) | Dispositif et procédé de libération d'un système de sécurité, en particulier d'un système d'accès pour véhicule automobile | |
| DE19926748A1 (de) | Funktionskontrollsystem, insbesondere Zugangskontrollsystem, und Verfahren zur Funktionssteuerung | |
| EP1972511A1 (fr) | Système de contrôle d'accès | |
| DE10143727B4 (de) | Im Fahrzeug mitgeführtes Schlüsselprüfsystem mit Prüfungshistorienspeicher | |
| WO2021023465A1 (fr) | Système de fermeture, en particulier pour un véhicule | |
| EP1081000B1 (fr) | Dispositif de sécurité | |
| EP0891607B1 (fr) | Procede d'exploitation d'un dispositif de telecommande et telecommande | |
| DE10112573C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Initialisieren eines Diebstahlschutzsystems für ein Kraftfahrzeug | |
| EP1006248A1 (fr) | Dispositif de contrôle d'accès commandé à distance, en particulier pour un véhicule à moteur et transpondeur portable associé | |
| EP1849665A2 (fr) | Architecture de système pour keyless-go-system | |
| DE102015107640A1 (de) | Zugangs-und Fahrberechtigungssystem mit erhöhter Sicherheit gegen Relaisangriffe auf die Transpondingschnittstelle Teil - II | |
| EP0999103A2 (fr) | Dispositif d'identification d'un utilisateur | |
| EP1254042B1 (fr) | Procede permettant de faire fonctionner un systeme antivol pour vehicule et systeme antivol associe | |
| EP0923054A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour vérifier le droit d'usage de dispositifs de contrÔle d'accès | |
| DE112020000635T5 (de) | Authentifizierungssystem und Authentifizierungsverfahren | |
| DE19832204B4 (de) | Verfahren zum Durchführen einer schlüssellosen Zugangsberechtigungskontrolle bei einem Kraftfahrzeug |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: 7E 05B 49/00 B Ipc: 7B 60R 25/04 B Ipc: 7G 07C 9/00 A |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20040719 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): DE FR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20060322 |