EP0981035B1 - Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement - Google Patents
Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0981035B1 EP0981035B1 EP99115443A EP99115443A EP0981035B1 EP 0981035 B1 EP0981035 B1 EP 0981035B1 EP 99115443 A EP99115443 A EP 99115443A EP 99115443 A EP99115443 A EP 99115443A EP 0981035 B1 EP0981035 B1 EP 0981035B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- heat exchanger
- exhaust
- flat tubes
- gas
- flow ducts
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D9/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall
- F28D9/0031—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other
- F28D9/0043—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other the plates having openings therein for circulation of at least one heat-exchange medium from one conduit to another
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D7/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary tubular conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall
- F28D7/0008—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary tubular conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one medium being in heat conductive contact with the conduits for the other medium
- F28D7/0025—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary tubular conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one medium being in heat conductive contact with the conduits for the other medium the conduits for one medium or the conduits for both media being flat tubes or arrays of tubes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D9/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall
- F28D9/0031—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other
- F28D9/0037—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary plate-like or laminated conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits for one heat-exchange medium being formed by paired plates touching each other the conduits for the other heat-exchange medium also being formed by paired plates touching each other
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D21/00—Heat-exchange apparatus not covered by any of the groups F28D1/00 - F28D20/00
- F28D21/0001—Recuperative heat exchangers
- F28D21/0003—Recuperative heat exchangers the heat being recuperated from exhaust gases
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F2250/00—Arrangements for modifying the flow of the heat exchange media, e.g. flow guiding means; Particular flow patterns
- F28F2250/10—Particular pattern of flow of the heat exchange media
- F28F2250/104—Particular pattern of flow of the heat exchange media with parallel flow
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F2250/00—Arrangements for modifying the flow of the heat exchange media, e.g. flow guiding means; Particular flow patterns
- F28F2250/10—Particular pattern of flow of the heat exchange media
- F28F2250/108—Particular pattern of flow of the heat exchange media with combined cross flow and parallel flow
Definitions
- the invention relates to an exhaust gas heat exchanger with pairs of bowl-shaped Heat exchanger plates; forms each pair of bowl-shaped heat exchanger plates a flow channel for cooling water by using the peripheral flange are mirrored assembled and connected so that the edge flange of the a heat exchanger plate on one side and the edge flange on the other Heat exchanger plate is directed to the opposite side, as well as with openings in the heat exchanger plates, which lie on a common line to form the collecting and distribution channel for the cooling water and with between the above-mentioned flow channels arranged further flow channels for the exhaust gas.
- This exhaust gas heat exchanger is known from EP 677 715.
- the known exhaust gas heat exchanger can be regarded as disadvantageous because breakthroughs on the exhaust side caused by corrosion lead to the mixing of the exhaust gas with the cooling water. Since the exhaust gases contain very aggressive substances, the possibility of rusting through is not far away. Therefore, the heat exchanger plates, the corrugated fins and the connecting pieces are made of stainless steel in the document mentioned, but this increases the costs. In addition, despite this measure, there is no guarantee that mixing will not happen, since even the stainless steel plates, if they are not the highest quality, can be attacked, at least in the vicinity of the soldered connections. Especially since there is a constant effort to reduce the sheet thickness of the heat exchanger plates.
- the required housing which surrounds the heat exchanger.
- the exhaust gas heat exchanger is constructed in the so-called document in a so-called rod-plate construction and has an outer housing. This otherwise advantageous construction has the disadvantage that the number of individual parts and the number and length of the soldered connections are quite large, which increases the risk that soldering errors can occur.
- the object of the invention is to further reduce the manufacturing costs in the exhaust gas heat exchanger specified in the preamble and also to ensure greater security against mixing of the exhaust gas with the cooling water, with at the same time low pressure loss on the exhaust side.
- the solution according to the invention results from the characterizing part of patent claim 1.
- the problem is solved by the skillful combination of features which may be known individually in heat exchanger construction, the inventors having recognized that their novel interaction leads to an inventive exhaust gas heat exchanger in which the exhaust gas is cooled with liquid.
- the exhaust gas heat exchanger is designed in a housingless design, that the flow channels formed from shell-shaped heat exchanger plates are provided for the cooling water and that the flow channels for the exhaust gas arranged therebetween are approximately straight flat tubes which open at opposite ends in tube sheets to which the Exhaust pipe is connected.
- the tube sheets have a diameter that is at least partially larger than the subsequent cross-sectional dimension of the heat exchanger.
- the tube sheets are preferably circular parts, as a result of which the production and connection of the likewise round exhaust pipe can be carried out more easily.
- the flue gas pipe can be connected to the heat exchanger using screws, clamps or clamping rings.
- At least one type of flow channel has a corrugated or similarly structured surface. The corrugated surface structure sufficiently ensures that, in the event of rusting, the exhaust gas can escape to the atmosphere and not easily get into the cooling water.
- the pressure loss on the exhaust side is extremely low because the associated flow channels have no deflections and because the tube sheets are kept so large that this requirement can be met. Furthermore, the distributor and the collecting space for the cooling water are arranged in projecting areas of the bowl-shaped heat exchanger plates, which are outside the cross section of the flat tubes. This also makes a contribution to reducing the pressure loss on the exhaust side, because the distributor and collection space are therefore not in the flow area of the exhaust gases and do not impede their flow.
- the manufacturing costs are reduced in that the water-cooled exhaust gas heat exchanger according to the invention only has to be made of stainless steel on the exhaust side - that is, the flat tubes and the tube sheets - while all other parts can be made of aluminum.
- the water-cooled exhaust gas heat exchanger from EP 677 715 is made entirely of stainless steel.
- the proposed exhaust gas heat exchanger therefore also has a lower weight. Furthermore, a contribution to lowering the manufacturing costs can be seen in the fact that the water-cooled exhaust gas heat exchanger, as stated above, is provided in a housing-free design.
- the external flow channels are cooling water channels, so that the radiant heat of the heat exchanger is reduced, which is not insignificant in exhaust gas heat exchangers because of the high exhaust gas temperatures.
- the bowl-shaped heat exchanger plates, which form the flow channels for the cooling water have inward corrugated support knobs in their corrugated surface, which are soldered at their apex to the same support knobs of the adjacent heat exchanger plate.
- the flat tubes that carry the exhaust gas can either be drawn tubes or flat tubes welded with a longitudinal seam, or they can be formed from two half-shells that are soldered together on the peripheral edge flange. Punched or rolled inner inserts can be arranged in the flat tubes, which are soldered to the tubes in order to promote heat exchange and to increase the stability.
- the wall of the flat tubes has a wave-like structure.
- the wave peaks and valleys run in the longitudinal direction of the flat tubes.
- there are projecting and angled sections on their edge flange which interlock and serve to correctly position two half-shells to form a flat tube. These sections are comparable to those on the edge flange of the heat exchanger plates. Openings are punched out in the tube sheets, which are adapted to the cross section of the flat tubes and which have passages which are either directed towards the exhaust gas line or towards the interior of the heat exchanger.
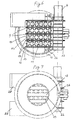
- FIG. 5 shows the view from the direction of the clamping ring 26 of the embodiment from FIGS. 1, 2 and 4.
- inner inserts 24 in the flat tubes 8 have been completely dispensed with.
- the walls of the flat tubes 8 consisting of two half-shells 8/1 and 8/2 were formed with a distinct wave-like structure 22.
- the wave crests and the wave troughs here run in the longitudinal direction of the flat tubes 8 or the flow channels 14.
- the heat exchanger plates 6 are preferably also included formed a smooth surface, apart from the embossed knobs 11.
- This embodiment is particularly suitable for exhaust gas heat exchangers because the risk of clogging of the flat tubes 8 by deposits is significantly lower.
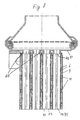
- FIG. 7 shows the view belonging to the exemplary embodiment in FIG. 6 from the direction of the clamping ring 26.
- the longitudinal wave-like structure 22 of the flow channels 14 is also evident from this illustration.
- the longitudinal section in FIG. 8 also belonging to this embodiment shows that the undulating structure 22 ends in front of the tube sheet 13.
- the passages 25 on the tube plate 13 were made towards the heat exchanger and the flat tubes 8 were plugged with their ends onto these passages 25
- FIG. 8 shows another connection to the exhaust pipe, not shown.
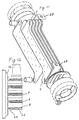
- FIG. 9 can be interpreted as a cross section in FIG. 3. It differs from FIG. 4 in that welded or drawn flat tubes 8 have been used here. Furthermore, the attachment was selected with the aid of a connecting flange 27, as is also shown in FIG. 3. 10 differs from the exemplary embodiment in FIG. 9 in that in FIG. 10 the passages 25 on the tube sheet 13 are directed towards the exhaust gas line, while in FIG. 9 the passages 25 point towards the heat exchanger.
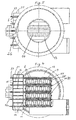
- FIG. 11 shows an exemplary embodiment in which the overhanging regions 7, in which the collecting and distribution spaces 20, 21 are arranged, are located on opposite sides of the heat exchanger. Therefore, two different types of heat exchanger plates 6 must be used here.
- Fig. 12 shows a partial longitudinal section, similar to Fig. 8, but in which the heat exchanger plates 6 have a corrugated surface structure 22 in order to achieve greater security against mixing of exhaust gas and cooling water.
- the flat tubes 8 have also been used in the passages 25 of the tube sheet 13.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Heat-Exchange Devices With Radiators And Conduit Assemblies (AREA)
- Gas Separation By Absorption (AREA)
- Separation By Low-Temperature Treatments (AREA)
- Exhaust Gas After Treatment (AREA)
Claims (8)
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement (1) avec des paires de plaques d'échangeur de chaleur (6) en forme de coquilles, chaque paire de plaques d'échangeur de chaleur (6) en forme de coquilles forme un canal de circulation (9) pour l'eau de refroidissement, du fait qu'elles sont réunies et assemblées de façon symétrique sur la bride de bord périphérique de manière telle que la bride de bord d'une première plaque d'échangeur de chaleur (6) est orientée vers un côté et que la bride de bord de l'autre plaque d'échangeur de chaleur (6) est orientée vers le côté- opposé, ainsi qu'avec des ouvertures dans les plaques d'échangeur de chaleur, qui se situent sur une ligne commune pour former le canal de collecte et de distribution pour l'eau de refroidissement, et avec d'autres canaux de circulation (14) pour les gaz d'échappement disposés entre les canaux de circulation précités,
caractérisé en ce que l'échangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement (1) refroidi par un liquide est réalisé selon le mode sans caisson,
en ce que les plaques d'échangeur de chaleur (6) présentent des régions saillantes (7), qui se trouvent à l'extérieur de la section transversale des canaux de circulation (14) pour les gaz d'échappement et qui forment dans ces régions (7) la chambre de distribution et de collecte pour l'eau de refroidissement, en ce que les canaux de circulation (14) pour les gaz d'échappement sont des tubes plats (8), qui s'étendent sensiblement en ligne droite à travers l'échangeur de chaleur et qui débouchent en des endroits opposés dans des fonds à tubes (13),
et en ce que les parois d'au moins un des deux types de canaux de circulation (9; 14) présentent une structure de surface (22) telle que le contact de pleine surface entre les canaux de circulation (9 et 14) soit exclu. - Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que les canaux de circulation (9) pour l'eau de refroidissement présentent une structure de surface sensiblement ondulée.
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant les revendications 1 et 2, caractérisé en ce que lès tubes plats (8) formant les canaux de circulation (14) pour les gaz d'échappement sont de préférence constitués d'acier allié et présentent des pièces intérieures ondulées (24) et sont des tubes plats (8) soit étirés soit soudés ou sont fabriqués à partir de deux demi-coquilles (8/1; 8/2) et assemblés l'un à l'autre sur la bride de bord.
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que les tubes plats (8) respectivement les canaux de circulation (14) comportent des parois ondulées, dans lesquelles les crêtes et les vallées des ondulations sont disposées dans le sens de l'axe longitudinal des tubes plats (8).
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que, sur la bride de bord des demi-coquilles (8/1; 8/2) formant les tubes plats (8) et/ou sur la bride de bord (23) des plaques d'échangeur de chaleur (6) en forme de coquilles sont disposées des parties saillantes et coudées (12), qui s'engagent l'une dans l'autre lors de l'assemblage des plaques d'échangeur de chaleur (6) et qui servent pour le positionnement correct des deux demi-coquilles l'une par rapport à l'autre.
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que les fonds à tubes (13) sont constitués d'acier allié et sont de préférence des pièces rondes, avec un diamètre tel que les fonds à tubes (13) dépassent au moins en partie au-delà de la dimension de la section transversale de l'échangeur de chaleur qui s'y raccorde.
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que les plaques d'échangeur de chaleur (6) sont de préférence constituées d'aluminium et présentent des bosses d'appui (11), qui se touchent après l'assemblage et qui sont assemblées aux points de contact.
- Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement suivant l'une quelconque des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que la ligne centrale de l'échangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement (1) orientée dans le sens des tubes plats (8) et la conduite de gaz d'échappement sont situées sur une ligne sensiblement droite ou faiblement incurvée au moins à proximité de l'entrée et de la sortie.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19836889A DE19836889A1 (de) | 1998-08-14 | 1998-08-14 | Abgaswärmetauscher |
| DE19836889 | 1998-08-14 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0981035A2 EP0981035A2 (fr) | 2000-02-23 |
| EP0981035A3 EP0981035A3 (fr) | 2000-06-07 |
| EP0981035B1 true EP0981035B1 (fr) | 2003-06-11 |
Family
ID=7877538
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99115443A Expired - Lifetime EP0981035B1 (fr) | 1998-08-14 | 1999-08-05 | Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0981035B1 (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE242860T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19836889A1 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2201604T3 (fr) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102597680A (zh) * | 2009-08-31 | 2012-07-18 | 法雷奥热系统公司 | 热交换器 |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19846518B4 (de) * | 1998-10-09 | 2007-09-20 | Modine Manufacturing Co., Racine | Wärmetauscher, insbesondere für Gase und Flüssigkeiten |
| DE10147555B4 (de) | 2001-09-26 | 2014-01-30 | Behr Gmbh & Co. Kg | Vorrichtung zum Befestigen eines Abgas-Wärmeübertragers |
| DE10214467A1 (de) | 2002-03-30 | 2003-10-09 | Modine Mfg Co | Abgaswärmetauscher für Kraftfahrzeuge |
| US6892803B2 (en) * | 2002-11-19 | 2005-05-17 | Modine Manufacturing Company | High pressure heat exchanger |
| JP4166591B2 (ja) | 2003-02-13 | 2008-10-15 | カルソニックカンセイ株式会社 | 熱交換器 |
| FR2855602A1 (fr) * | 2003-05-27 | 2004-12-03 | Valeo Thermique Moteur Sa | Echangeur de chaleur a plaques, notamment refroidisseur des gaz d'echappement recircules |
| US7108054B2 (en) | 2003-09-11 | 2006-09-19 | Honeywell International, Inc. | Heat exchanger |
| DE10359806A1 (de) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-14 | Modine Manufacturing Co., Racine | Wärmeübertrager mit flachen Rohren und flaches Wärmeübertragerrohr |
| DE102004036020A1 (de) * | 2004-07-23 | 2006-02-16 | Behr Gmbh & Co. Kg | Wärmeübertrager, insbesondere Kondensator |
| DE102005053924B4 (de) | 2005-11-11 | 2016-03-31 | Modine Manufacturing Co. | Ladeluftkühler in Plattenbauweise |
| ATE472708T1 (de) * | 2006-02-17 | 2010-07-15 | Schilling Heinz Kg | Vorrichtung und verfahren zur thermischen stromerzeugung |
| JP2008038723A (ja) | 2006-08-04 | 2008-02-21 | Toyota Motor Corp | 排気系熱交換器の支持構造 |
| FR2906017B1 (fr) | 2006-09-19 | 2012-12-21 | Valeo Systemes Thermiques | Echangeur de chaleur, en particulier refroidisseur d'air de suralimentation. |
| US8424592B2 (en) | 2007-01-23 | 2013-04-23 | Modine Manufacturing Company | Heat exchanger having convoluted fin end and method of assembling the same |
| US20090250201A1 (en) | 2008-04-02 | 2009-10-08 | Grippe Frank M | Heat exchanger having a contoured insert and method of assembling the same |
| GB2461854A (en) * | 2008-07-11 | 2010-01-20 | Stephen John Heard | Heat exchange unit for cooling engine exhaust emissions |
| DE102009010039B4 (de) | 2009-02-21 | 2012-09-20 | Modine Manufacturing Co. | Wärmetauscher |
| US10697706B2 (en) | 2012-09-25 | 2020-06-30 | Modine Manufacturing Company | Heat exchanger |
| CN113244698B (zh) * | 2021-05-12 | 2023-03-24 | 天能电池集团(安徽)有限公司 | 一种用于皮帽机负压排气管的余酸收集装置 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3537513A (en) * | 1968-03-11 | 1970-11-03 | Garrett Corp | Three-fluid heat exchanger |
| US4310960A (en) * | 1973-04-16 | 1982-01-19 | The Garrett Corporation | Method of fabrication of a formed plate, counterflow fluid heat exchanger and apparatus thereof |
| JPS6186590A (ja) * | 1984-10-03 | 1986-05-02 | Hisaka Works Ltd | 熱交換器 |
| US4681155A (en) * | 1986-05-01 | 1987-07-21 | The Garrett Corporation | Lightweight, compact heat exchanger |
| GB2211283B (en) * | 1987-10-20 | 1992-04-15 | Rolls Royce Plc | Heat exchanger |
| JP3359946B2 (ja) * | 1993-03-04 | 2002-12-24 | 東京ラヂエーター製造株式会社 | 積層型熱交換器 |
| DE4403144C3 (de) * | 1994-02-02 | 2002-05-29 | Laengerer & Reich Gmbh & Co | Plattenwärmeaustauscher |
| DE9406197U1 (de) * | 1994-04-14 | 1994-06-16 | Behr Gmbh & Co | Wärmetauscher zum Kühlen von Abgas eines Kraftfahrzeugmotors |
| DE29616354U1 (de) * | 1996-09-19 | 1997-01-09 | Laengerer & Reich Gmbh & Co | Abgaswärmetauscher |
-
1998
- 1998-08-14 DE DE19836889A patent/DE19836889A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1999
- 1999-08-05 EP EP99115443A patent/EP0981035B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-08-05 DE DE59905912T patent/DE59905912D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-08-05 AT AT99115443T patent/ATE242860T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-08-05 ES ES99115443T patent/ES2201604T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102597680A (zh) * | 2009-08-31 | 2012-07-18 | 法雷奥热系统公司 | 热交换器 |
| CN102597680B (zh) * | 2009-08-31 | 2014-06-11 | 法雷奥热系统公司 | 热交换器 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE242860T1 (de) | 2003-06-15 |
| EP0981035A2 (fr) | 2000-02-23 |
| DE19836889A1 (de) | 2000-02-17 |
| EP0981035A3 (fr) | 2000-06-07 |
| ES2201604T3 (es) | 2004-03-16 |
| DE59905912D1 (de) | 2003-07-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0981035B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur pour gaz d'échappement | |
| DE3872162T2 (de) | Honigwaben-koerper. | |
| DE2946804C2 (fr) | ||
| EP1816425B1 (fr) | Échangeur thermique de gaz d'échappement dans un agencement de recyclage des gaz d'échappement | |
| DE60219538T2 (de) | Wärmetauscher | |
| EP0772018B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur pour le refroidissement de gaz d'échappement | |
| EP0881447B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur et dispositif d'échange de chaleur pour véhicule automobile | |
| DE3423736C2 (fr) | ||
| EP0152560B1 (fr) | Matrice pour réacteur catalytique pour purifier des gaz d'échappement | |
| CH655385A5 (de) | Waermeaustauscher. | |
| DE2657307A1 (de) | Rohrbuendel fuer einen waermetauscher | |
| DE2951352C2 (de) | Flachrohr-Wärmetauscher | |
| DE4403144C3 (de) | Plattenwärmeaustauscher | |
| DE10328846C5 (de) | Wärmetauscher | |
| DE19709601A1 (de) | Plattenwärmeübertrager | |
| EP0990868B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur | |
| EP1788320B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur | |
| WO2012159958A1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur à lamelles | |
| DE3834822A1 (de) | Waermetauscher | |
| DE2536657B2 (de) | Wärmeaustauscher zum Vorwärmen von Verbrennungsluft für insbesondere ölbeheizte Industrieöfen | |
| DE69903895T2 (de) | Wärmetauscher | |
| DE3148941C2 (de) | Wassergekühlter Ölkühler für Verbrennungskraftmaschinen | |
| EP3730890A1 (fr) | Échangeur de chaleur à plaques | |
| DE10236665B4 (de) | Gas-Flüssigkeits-Wärmetauscher und damit ausgerüsteter Boiler | |
| EP0177904B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour l'échange de chaleur entre deux gaz en flux croisé |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20000516 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20020425 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030611 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030611 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59905912 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20030717 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030805 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030805 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030805 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030831 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030831 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030831 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030911 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030911 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20030911 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20031007 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *MODINE MFG CY Effective date: 20030831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2201604 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20040312 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20110907 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20110808 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20110830 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20110827 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20110830 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20110824 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20110819 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: V1 Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: EUG |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20120805 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130301 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120806 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20130430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120805 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120805 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59905912 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20131021 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120806 |