EP0971191A2 - Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases - Google Patents
Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0971191A2 EP0971191A2 EP99111709A EP99111709A EP0971191A2 EP 0971191 A2 EP0971191 A2 EP 0971191A2 EP 99111709 A EP99111709 A EP 99111709A EP 99111709 A EP99111709 A EP 99111709A EP 0971191 A2 EP0971191 A2 EP 0971191A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- gas
- heated gas
- heated
- admixing
- cooler
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F26—DRYING
- F26B—DRYING SOLID MATERIALS OR OBJECTS BY REMOVING LIQUID THEREFROM
- F26B23/00—Heating arrangements
- F26B23/02—Heating arrangements using combustion heating
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for treating goods by means of a heated gas according to the preamble of claim 1 and a device according to the preamble of claim 8.
- a treatment of goods by means of heated gases takes place in different industrial machining processes, e.g. when drying wet or solvent-based products in drying plants, when curing paintwork or molded parts in the oven or when storing cold sensitive goods in Warehouses.
- a combination of storage and drying takes place in the large ones Drying rooms in which ceramic workpieces (e.g. refractory blocks for Construction of float glass pools, porcelain or high voltage insulators) often over Weeks to be dried.
- the heatable rooms mentioned as examples must be used to achieve a uniform temperature distribution targeted and even with the heated Gas flow. This is usually used accordingly dimensioned blowers.
- the air in the Circulation using moving air fans that move air out of the room, circulating air called, suction and elsewhere - after heating and cleaning if necessary - feed again.
- the high ones usually required Air volumes require the use of powerful fans, so that In order to save performance, the pressure losses in the air recirculation system are constructive must be minimized. This is done by using the flow cross sections for the Circulated air flows selected as large as possible and distributing units such as air baffles, Chokes etc. can be avoided.
- a dryer is from the brochure of H. Krantz Textiltechnik GmbH "K M 16" 4/94 for drying textile webs on several floors with a transport device for the web, with two fields, each with two superimposed Chambers and two circulating air devices per chamber with one circulating air fan, a pressure chamber that extends over several floors from the pressure chamber outgoing nozzle boxes on each floor above and below the Goods web are arranged side by side, a suction chamber and one in the Intake chamber protruding gas heating with a surface burner is known. By the burner gas emanating from such a surface burner becomes one Relatively uniform mixture of the burner gas with the recirculating air total height of the chambers achieved.
- the object of the invention is to provide a method for treating goods by means of a heated gas according to the preamble of claim 1 and a device to develop according to the preamble of claim 8, in which a uniform temperature distribution of the heated gas without high pressure losses is achieved in the flow path.
- the inventive method on the treatment of sheet or plate-shaped material in a recirculating air process in one Dryer can be used with several floors, so that in all floors of the dryer Drying air of the same temperature is supplied.
- heated gas is at least a point-shaped inlet is fed to a cooler gas and the thus formed heated gas is fed to the goods to be treated via a blower.
- the heated method is used according to the invention Gas in the area of the punctiform inlet mixed with an admixing gas, the admixing gas through a part of the flow behind the Blower located heated gas is formed.
- the mix in the area of punctiform inlet can be directly at or in front of the punctiform inlet take place, the point-shaped inlet as such being essentially retained, but it can also be arranged directly after the punctiform inlet Mixing device take place.
- the pure heated gas is not used in the method according to the invention supplied to the cooler gas, but a mixture that is as homogeneous as possible heated gas and admixing gas.
- the admixing gas consists of heated gas, it has a lower temperature than the heated gas.
- the mixture of heated Gas and admixing gas are therefore correspondingly cooler than the pure heated gas.
- the removal of the admixing gas from the one behind the fan warmed gas also has the advantages that, firstly, no separate gas must be provided and secondly the pressure of the - already existing - Blower for returning the admixing gas and mixing it with the heated gas is used. As a result, the existing systems and Procedure to be carried out change effort for the conversion to the method according to the invention minimized.
- the mixture of heated gas and admixing gas after punctiform inlet distributed in the vertical direction.
- Such a distribution is for that heated gas known from the prior art and advantageous when in Vertical gas flow is required for the treatment of the goods.
- a less hot mixture of heated gas and admixing gas and in addition a larger volume is present in the vertical distribution hardly any disturbing thermal effects and the result of Distribution is significantly more homogeneous.
- the cooler gas is in which the heated gas is let in, wholly or partly from circulating air.
- the gas is closed under circulating air understand which is supplied as heated gas to the goods to be treated was cooled and after it had acted on the goods and if necessary also with removing products.
- Such a procedure therefore works the recirculation principle, i.e. a cycle of the treatment used Gases, and therefore achieves a corresponding energy and gas savings.
- the heated gas is preferably hot air or the burner gas a gas or oil burner.
- gases are advantageous because of their Properties often used as heat sources in the prior art and are characterized by a naturally relatively high temperature. The one from this Problems resulting from high temperature are caused by the Method according to the invention effectively avoided.
- Claim 5 relates specifically to a method in which sheet or plate-shaped goods are dried on several levels using the air-circulation method, wherein, in at least one stage, heated gas as drying air is supplied to the good by a circulating air fan serving as a blower, via a pressure chamber and nozzle boxes connected to the pressure chamber and arranged on each floor above and possibly below the good, and wherein circulating air as cooler gas in one Suction chamber merged with heated gas and the drying air is supplied to the good again via the recirculation fan, the pressure chamber and the nozzle boxes.
- This known method is characterized according to the invention in that part of the drying air is returned as admixing gas from the pressure chamber into the suction chamber, mixed with the heated gas and this mixture is then fed to the circulating air.
- the mixture of heated gas and returned drying air has a larger volume and a lower temperature than the heated gas and is easier to mix with the circulating air to a drying air of homogeneous temperature.
- drying air is created, the temperature of which remains constant over the height of the suction chamber. A temperature gradient caused by heated gas rising due to the thermals is avoided.
- the goods transported through the dryer on floors are evenly dried.
- the heated gas to a Temperature from 160 to 220 ° C, the cooler gas to a temperature from 80 to 150 ° C and the heated gas at a temperature of about 2000 ° C. are preferably returned such an amount of admixing gas that the Temperature of the mixture of heated gas and admixing gas a temperature of 300 to 500 ° C, in particular from 350 to 450 ° C. With one Mixing temperature, the production of heated gas has become more homogeneous Temperature proved to be particularly simple.
- a proportion of 7 to 25%, in particular 10, attributed in accordance with claim 7 up to 20% of the heated gas as an admixing gas represents a mixture of heated Gas and cooler gas of homogeneous temperature safely.
- the invention also relates to a device for treating goods by means of a heated gas according to the preamble of claim 8, which a Has treatment room and a heating room.
- the treatment room can be of a very general form and e.g. as a separate chamber to the Connect the heating room or completely surround the heating room.
- the heating room has an inlet for a cooler gas, at least one punctiform inlet for the supply of heated gas into the cooler gas, one Heated gas outlet and a blower located at the outlet and is connected with its pressure side to the treatment room.
- the arrangement of the Blower at the exit of the heating room is done so that with the blower Gas can be pumped out of the heating room through the outlet.
- the fan can also form the outlet.
- the device is characterized in that the Heating room also a mixing device, which in the area of point-shaped inlet of the heated gas is arranged, and a Mixed gas supply line, which from the pressure side of the fan to the Mixer leads, contains.
- the arrangement of the mixing device can directly or before the punctiform inlet, the punctiform inlet as such remains essentially intact, but it can also be used directly after the point entry.
- the heated gas a cooler admixing gas can be added. This causes a drop in Temperature and an increase in volume one and the subsequent Mixing with the cooler gas in the heating room is significant steadier instead.
- the admixing gas can be via the mixed gas supply line from the pressure side of the Blower can be tapped. This has the advantage that the blower pressure is used, so no further structural measures or facilities are necessary to give the admixing gas the required pressure. In addition there is no need to provide any additional gas for the admixture as a existing gas is taken anyway.
- the heating room contains a distribution device which is arranged directly behind the point-shaped inlet for the heated gas and the extends in the horizontal and / or preferably in the vertical direction.
- the Extension preferably takes place approximately up to the limits of the Heating room so that the mixture is introduced as well as possible can be made from heated gas and admixing gas into the cooler gas.
- the punctiform in the device according to the invention Inlet designed as a burner, the flame tube protrudes into the heating room.
- This device is characterized in that the mixing device by a Outer tube that at least partially envelops the flame tube, and through inside this outer tube on the circumference distributed openings in the flame tube in this enveloped area is formed. This allows the admixing gas over the circumference of the flame tube flow evenly into the flame tube.
- Such Mixing device is structurally relatively simple, so that even existing burners can be retrofitted with this.
- the arrangement of the outer tube and the openings in the flame tube according to Claim 11 in the initial region of the burner gas in the flow direction Flame tube provides the longest possible mixing section between burner gas and Mixing gas safe.
- the mixed gas supply line is one in this device Connection line between his pressure chamber and the flame tube of his Brenner trained.
- the device is in accordance with a method claims 1 to 7 suitable.
- the device can be used as a dryer can be used to dry goods. From the pressure chamber you can use With the help of the connecting line, simply heated gas (drying air) to the burner lead back. Through the mouth of the connecting line in the flame tube, the Connection line can be arranged completely within the device.
- the starting point of the connecting line at the pressure chamber according to Providing claim 15 in the central region of the pressure chamber ensures in the pressure chamber a uniform flow of the drying air into the Nozzle boxes.
- the invention is initially generalized using a schematic illustration of a first example in Figure 1 explained.
- the invention is further illustrated schematically on the basis of one in FIGS. 2 to 4 illustrated second example of a dryer for a textile web explained.
- Figures 2 to 4 essentially show a side next to the web arranged suction chamber of a circulating air device of the dryer.
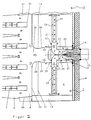
- Figure 2 is a Section through the central axis of a burner arranged in the suction chamber perpendicular to the transport levels of the web, d. H. parallel to the width of the Dryer.
- Figure 3 is a view from the dryer wall in the direction of Goods web on a nozzle box of the air recirculation device and shows the location of one Filters and a cross flow fan.
- Figure 4 is a section parallel to the Transport levels of the web.
- Figure 1 shows a device for treating goods by means of heated gas with a treatment room 50 and a heating room 51.
- the Heating room 51 has an inlet 52 for a cooler gas, at least one point inlet 53 for supplying heated gas to the cooler gas and an outlet 54 for heated gas.
- the punctiform inlet 53 for heated gas can be on a wall of the heating space 50 or in its Inside.
- a heat source for example a burner
- the Outlet the punctiform inlet 53 for heated gas into the heating space 51 forms.
- the inlet 52 for the cooler gas is at the front in the flow direction End and outlet 54 for heated gas at the rear end of the Warming room 51, i.e. they lie one on top of the other at these two ends across from.
- the device also has a blower 55, which at the outlet 54 of the Heating room 51 is arranged and its suction point with the Heating room 51 and its pressure side with the treatment room 50 connected is.
- the fan 55 is a cross flow fan formed, which forms the outlet 54 of the heating chamber 51.
- the device has a mixing device 56, 57, which in the Area of the punctiform inlet 53 for the heated gas is arranged, and a mixed gas supply line 58, which from the pressure side of the blower 55 to the Mixing device 56, 57 leads.
- the one located inside the heating space 51 is Burner a gas burner with a flame tube 56, the open end of the Flame tube 56 forms the punctiform inlet 56.
- the flame tube 56 is of one additional outer tube 57 envelops and has openings within the envelope on.
- the mixing device is activated by the flame tube 56 provided with openings and the enveloping outer tube 57, the mixed gas supply line 58 to the Outer tube 57 is connected.
- the openings in the flame tube 56 are preferably arranged in the initial region of the flame tube 56.
- the mixing device is in front of the punctiform inlet 53 arranged.
- the scope of the invention also includes mixing devices which are arranged immediately behind the punctiform inlet 53.
- a distribution device 59 is connected to the punctiform inlet 53 extends vertically and / or horizontally into the heating space 51 and over the Extension has openings.
- the device described e.g. drying wet goods or hardening ceramic workpieces.
- the only indicated treatment room 50 be trained accordingly.
- it can be sent to the Heating space 51 can then be arranged behind it in the direction of flow or completely surround it.
- cooler gas through the inlet 52 Heating room 51 supplied.
- This gas can preferably be Circulating air from a cycle, act.
- the heating room 51 is the cooler Gas heated gas, namely fed burner gas.
- the gases leave the Heating space 51 at the outlet 54 via the fan 55 as a heated gas, the serves the treatment of the goods.
- the heated gas can be hot air or that Burner gas from a gas or oil burner.
- the burner gas is first fed through a mixing device 56, 57 a cooler admixing gas mixed in compared to the fuel gas.
- the Mixing gas is thereby via a mixed gas supply line 58 on the pressure side of the Blower 55 taken from the flow of the heated gas.
- the outer tube 57 and the openings in the flame tube 56 together act as a mixing device for the Burner gas and the admixing gas. This lowers the temperature of the mixture of burner gas and admixing gas compared to the burner gas, and the volume the mixture to be introduced into the cooler gas increases, so that the subsequent mixing with the cooler gas takes place homogeneously.
- the mixture of burner gas and admixing gas leaves via a point Inlet 53 the mixing device 56, 57 and is by means of the distribution device 59th evenly introduced into the flow of the cooler gas.
- the dryer has a cuboid housing a field, as well as a multi-day stenter frame with a tension chain, Guide rails and deflection wheels trained transport device.
- the field of this dryer is in two superimposed chambers 2, 3 divided.
- the lower chamber 2 extends over four floors, i. H. About four Transport levels of the web 1, and the upper chamber 3 over two more, in the drawing, not shown, transport levels of the web 1.
- each of the chambers 2, 3 there are two circulating air devices, each with its own Intake side connected to a suction chamber 4 recirculation fan in Longitudinal direction of the dryer, d. H. in or against the direction of transport of the web 1, arranged one behind the other.
- the suction chambers 4 with the circulating air fans are alternately on the sides of the dryer next to the web 1, d. H. Next the edges of the superimposed sections of the web 1, arranged.
- Exhaust air space 5 is formed between the web 1 and a housing wall 6.
- the exhaust air spaces 5 each open into the suction chamber 4 of the filter 7 neighboring air recirculation device.
- a recirculation device in addition to the recirculation fan and filter 7, one connected to the pressure side of the air circulation fan, between Suction chamber 4 and web 1 arranged as a pressure box 8 formed Pressure chamber and nozzle boxes 9 and one arranged in the suction chamber 4 Heating device with a burner 10.
- the nozzle boxes 9 are next to each other on each floor above and below the web 1 are arranged and extend over the maximum width of the web 1.
- the nozzle boxes 9 of a circulating air device and the nozzle boxes 9 of the two Adjacent circulating air devices closely follow in the longitudinal direction of the dryer on top of each other, so that the sections of the web 1 except for spaces between the nozzle boxes 9 completely from the nozzle boxes 9 above and below are covered.
- the circulating air fans are cross-flow fans 11 formed and extend over both chambers 2, 3.
- the suction chamber 4 is formed by a housing base 12 and a chamber 2 and 3 separating chamber bottom 13 and through the housing wall 6, the filter 7, a chamber wall 14, a baffle 15, the suction area of the Cross-flow fan 11 separates from the pressure area and the cross-flow fan 11 limited.
- the chamber wall 14 extends from perpendicular to the housing wall 6 arranged filter 7 first parallel to the housing wall 6 and then at an angle to the housing wall 6, in front of which the cross-flow fan 11 is arranged, to. It abuts the baffle plate 15. Near the filter 7, the chamber wall 14 an exhaust air duct 17.
- the burner 10 is approximately at half the height of the chamber 2 in the area of Suction chamber 4 installed in the insulated housing wall 6. Inside the Intake chamber 4, burner 10 has one attached to housing wall 6 Flame tube 18 on. Before the insulation of the housing wall 6 is in the area of Attachment of the flame tube 18 an insulating plate 19 is provided.
- the flame tube 18 has three sections 20, 21 and 22. In the area of the Housing wall 6 abutting section 20, the length of a quarter to one Corresponds to one third of the length of the flame tube 18, the flame tube 18 is perforated.
- the perforation is separated by a few mm, for example 2 mm, arranged circular openings with a diameter of 5 to 20 mm, for example of 10 mm.
- second section 21 of the flame tube 18 is an in Starting position horizontal, with one behind it in the direction of flow Axis 23 arranged gas distribution flap 24.
- gas distribution flap 24 In Flow direction subsequent to the gas distribution flap 24 are in the Flame tube 18 each have an up and down curved baffle 25, each in a distributor pipe 26, namely in its first section 27, opens out.
- the Manifolds 26 extend upward from the flame tube 18 and below.
- At the first rectangular section 27 there is a constant cross section in each case a second section 28 flanged.
- the second section 28 of each The distributor tube 26 tapers, as can be seen in FIG. 3, parallel to the longitudinal wall of the Dryer on the side facing away from the crossflow fan 11 or downward.
- the second section 28 has one over almost its entire length opening 29 directed toward cross-flow fan 11.
- the length of the second Section 21 of the flame tube 18 is approximately half the length of the Flame tube 18.
- the third section 22 of the flame tube 18 is on the opening 29 opposite side slightly tapered inwards.
- the pressure box 8 has a bottom wall 30, a top wall 31, one for Material web 1 directed, vertical side wall 32 with openings for the Nozzle boxes 9 and a side wall 33 running obliquely to the housing wall 6 on.
- the sloping part of the chamber wall 14 and the side wall 33 of the pressure box 8 run approximately parallel.
- a mixed gas feed line designed as a connecting line 34, leads from the pressure box 8 through the chamber wall 14 to the burner 10.
- the connecting line 34 has two connecting sections 35, 36 and a starting from the pressure box 8 Outer tube 37 on.
- the outer tube 37 envelops the flame tube 18 and is together attached to the housing wall 6 with the flame tube 18.
- the diameter of the Round outer tube 37 is about 1.1 to 1.5 times, for example 1.3 times the diameter of the flame tube 18.
- the connecting portions 36 and 35 of the outer tube 37 of the Connecting line 34 are, as can be seen in Figure 4, obliquely to the longitudinal direction of the Dryer, arranged and open at an almost right angle in the mine sloping side wall 33 in the print box 8.
- the Connecting section 36 leads from the outer tube 37 to an opening in the Chamber wall 14 and the following connecting section 35 of the connecting line 34 from the opening 28 of the chamber wall to the pressure box 8. Both Connecting sections 35, 36 are attached to the chamber wall 14.
- the lower chamber 2 are corresponding Circulating air devices arranged.
- An inventive Device can be used as a dryer for drying material webs from other Materials such as paper, plastic, metal or as a dryer for drying Building material parts, for example tarpaulin.
- the transport device can as a meandering transport device or parallel in several floors Transport device be formed.
- the textile web 1 is transported in several by means of the transport device Floors, in this example run from bottom to top through the dryer.
- the of the Goods web 1, circulating air (called exhaust air in the priority application) flows through an exhaust air space 5 and a filter 7 into the suction chamber 4, from which a Part is withdrawn via the exhaust air duct 17 as exhaust air and in which the rest Recirculated air is heated to drying air using hot burner gas.
- the cross-flow fan 11 sucks the drying air out of the suction chamber 4 and guides them to the web 1 over the print box 8 and the nozzle boxes 9 again.
- a portion of 7 to 25%, especially 10 to 20% of the drying air is over the connecting line 34 is withdrawn from the pressure box 9 and under pressure in the suction chamber 4 is returned to the flame tube 18 of the burner.
- the Drying air flows out of the outer tube 37 of the connecting line 34 through the Perforation of the flame tube 18 distributed over the circumference of the flame tube in the Flame tube 18 in which the burner gas is mixed with the drying air.
- This Mixture emerges from the openings 29 of the distributor pipes 26 over almost the entire Height of the chambers 2 and corresponding to the chamber 3 and is in one large area mixed with the recirculated air.
- the amount of returned drying air is adjusted so that the Mixture of burner gas and drying air at a temperature of 300 to 500 ° C, in particular from 350 to 450 ° C.
- a temperature of the circulating air of 150 ° C and a temperature of the burner gas of about 2000 ° C Return a proportion of approximately 20% of the drying air to a temperature of Mixture of burner gas and drying air set at 400 ° C.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Drying Of Solid Materials (AREA)
Abstract
Description
wobei ferner in mindestens einer Stufe erwärmtes Gas als Trocknungsluft durch einen als Gebläse dienenden Umluftventilator über eine Druckkammer und an die Druckkammer angeschlossene, in jeder Etage oberhalb und ggf. unterhalb des Gutes angeordnete Düsenkästen dem Gut zugeführt wird, und wobei Umluft als kühleres Gas in einer Ansaugkammer mit erhitztem Gas zusammengeführt und als Trocknungsluft über den Umluftventilator, die Druckkammer und die Düsenkästen dem Gut erneut zugeführt wird. Dieses bekannte Verfahren ist erfindungsgemäß dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß ein Teil der Trocknungsluft als Zumischgas aus der Druckkammer in die Ansaugkammer zurückgeführt, mit dem erhitzten Gas gemischt und diese Mischung anschließend der Umluft zugeführt wird . Die unter Druck zurückgeführte Trocknungsluft höherer Temperatur als die der Umluft führt bei Mischung mit dem erhitzten Gas (z.B. einem heißen Brennergas) zu einer Mischung homogener Temperatur. Die Mischung aus erhitztem Gas und zurückgeführter Trocknungsluft hat ein größeres Volumen und eine niedrigere Temperatur als das erhitzte Gas und läßt sich einfacher mit der Umluft zu einer Trocknungsluft homogener Temperatur mischen. Insbesondere entsteht eine Trocknungsluft, deren Temperatur über die Höhe der Ansaugkammer gleichbleibt. Ein Temperaturgefälle durch aufgrund der Thermik aufsteigendes erhitztes Gas wird vermieden. Die in Etagen durch den Trockner transportierten Güter werden gleichmäßig getrocknet.
- 1
- Warenbahn
- 2
- untere Kammer
- 3
- obere Kammer
- 4
- Ansaugkammer
- 5
- Abluftraum
- 6
- Gehäusewand
- 7
- Filter
- 8
- Druckkasten
- 9
- Düsenkasten
- 10
- Brenner
- 11
- Querstromventilator
- 12
- Gehäuseboden
- 13
- Kammerboden
- 14
- Kammerwand
- 15
- Leitblech
- 16
- -
- 17
- Abluftkanal
- 18
- Flammrohr
- 19
- isolierplatte
- 20
- erster Abschnitt des Flammrohres
- 21
- zweiter Abschnitt des Flammrohres
- 22
- dritter Abschnitt des Flammrohres
- 23
- Achse
- 24
- Gasverteilungsklappe
- 25
- Leitblech
- 26
- Verteilerrohr
- 27
- erster Abschnitt des Verteilerrohres
- 28
- zweiter Abschnitt des Verteilerrohres
- 29
- Öffnung im Verteilerrohr
- 30
- Bodenwand des Düsenkastens
- 31
- Deckenwand des Düsenkastens
- 32
- Seitenwand des Düsenkastens
- 33
- Seitenwand des Düsenkastens
- 34
- Verbindungsleitung
- 35
- Verbindungsabschnitt der Verbindungsleitung
- 36
- Verbidnungsabschnitt der Verbindungsleitung
- 37
- Außenrohr
- 38
- Öffnung in der Kammerwand
- 50
- Behandlungsraum
- 51
- Erwärmungsraum
- 52
- Einlaß
- 53
- punktförmiger Einlaß
- 54
- Auslaß
- 55
- Gebläse
- 56
- Flammrohr
- 57
- Außenrohr
- 58
- Mischgaszuleitung
- 59
- Verteilvorrichtung
Claims (15)
- Verfahren zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases, wobeia) erhitztes Gas an mindestens einem punktförmigen Einlaß einem kühleren Gas zur Erzeugung eines erwärmten Gases zugeführt wird,b) das erwärmte Gas, weiches das zusammengeführte erhitzte und kühlere Gas enthält, über ein Gebläse den zu behandelnden Gütern zugeführt wird,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daßc) das erhitzte Gas im Bereich des punktförmigen Einlasses mit einem Zumischgas gemischt wird, wobeid) ein Teil des sich in Strömungsrichtung hinter dem Gebläse befindlichen erwärmten Gases als Zumischgas zurückgeführt wird. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Mischung aus erhitztem Gas und Zumischgas nach dem punktförmigen Einlaß in vertikaler Richtung verteilt wird. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 oder 2,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das kühlere Gas in Teilschritt a) ganz oder teilweise aus Umluft besteht. - Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3,bei dem das erhitzte Gas Wasserdampf oder das Brennergas eines Gasoder Ölbrenners ist.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4,
wobei bahn- oder plattenförmige Güter in mehreren Etagen im Umluftverfahren getrocknet werden,
wobei ferner in mindestens einer Stufe erwärmtes Gas als Trocknungsluft durch einen als Gebläse dienenden Umluftventilator über eine Druckkammer und an die Druckkammer angeschlossene, in jeder Etage oberhalb und ggf. unterhalb des Gutes angeordnete Düsenkästen, dem Gut zugeführt wird,
und wobei Umluft als kühleres Gas in einer Ansaugkammer mit erhitztem Gas zusammengeführt und als Trocknungsluft über den Umluftventilator, die Druckkammer und die Düsenkästen dem Gut erneut zugeführt wird,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daßein Teil der Trocknungsluft als Zumischgas aus der Druckkammer (8) in die Ansaugkammer (4) zurückgeführt, mit dem erhitzten Gas gemischt und diese Mischung anschließend der Umluft zugeführt wird. - Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 5,bei dem eine Temperatur des erwärmten Gases von 160 bis 220°C, eine Temperatur des kühleren Gases von 80 bis 150°C und eine Temperatur des erhitzten Gases von etwa 2000°C eingestellt wird,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daßdurch die Menge des zugeführten Zumischgases eine Temperatur der Mischung aus erhitztem Gas und Zumischgas von 300 bis 500°C, insbesondere von 350 bis 450°C, eingestellt wird. - Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der als Zumischgas zurückgeführte Teil des erwärmten Gases 7 bis 25 %, insbesondere 10 bis 20 % des gesamten erwärmten Gases beträgt. - Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases, aufweisend einen Behandlungsraum (50) und einen Erwärmungsraum (51) mita) einem Einlaß (52) für ein kühleres Gas,b) mindestens einem punktförmigen Einlaß (53) für die Zuführung von erhitztem Gas in das kühlere Gas,c) einem Auslaß (54) für erwärmtes Gas,d) einem Gebläse (55), welches am Auslaß angeordnet ist und mit seiner Druckseite mit dem Behandlungsraum verbunden ist,
gekennzeichnet durche) eine Mischeinrichtung (20, 37, 56, 57), welche im Bereich des punktförmigen Einlasses (10, 53) für das erhitzte Gas angeordnet ist, undf) eine Mischgaszuleitung (34, 58), welche von der Druckseite des Gebläses (11, 55) zu der Mischeinrichtung (37, 56, 57) geführt ist. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 8,
wobei der Erwärmungsraum (51) eine Verteilvorrichtung (26, 59) enthält, welche direkt hinter dem punktförmigen Einlaß (53) für das erhitzte Gas angeordnet ist und die sich vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung erstreckt. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 8 oder 9, wobei der punktförmige Einlaß als Brenner ausgebildet ist, dessen Flammrohr in den Erwärmungsraum ragt,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Mischeinrichtung durch ein Außenrohr (37, 57), das das Flammrohr (18, 56) zumindest teilweise umhüllt, und durch Öffnungen im Flammrohr (18, 56) in diesem umhüllten Bereich gebildet wird. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 10,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Öffnungen im Anfangsbereich des Flammrohres (18, 56) angeordnet sind. - Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 10 oder 11 zum Trocknen von bahn- oder plattenförmigem Gut in mehreren Etagen,mit einer Transportvorrichtung für das Gut,mit mindestens einer Umluftvorrichtung mit einem als Gebläse dienenden Umluftventilator, mit einer Druckkammer, die sich über mehrere Etagen erstreckt, mit von der Druckkammer ausgehenden Düsenkästen, die in jeder Etage oberhalb und ggf. unterhalb der Transportebenen des Gutes nebeneinander angeordnet sind,und mit einer als Erwärmungsraum dienenden Ansaugkammer
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Mischgaszuleitung als Verbindungsleitung (34) zwischen der Druckkammer (8) und der Mischeinrichtung ausgebildet ist. - Vorrichtung nach den Ansprüchen 12 und 10,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Außenrohr (37) als Teil der Verbindungsleitung (34) ausgebildet ist. - Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 11 oder 12, bei dem die Verteilvorrichtung durch am Endbereich des Flammrohres angeordnete, senkrecht zu den Transportebenen verlaufende, sich über die gesamte Höhe der Druckkammer erstreckende, mit Öffnungen versehene Verteilerrohre gebildet wird,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daßdas Außenrohr (37) das Flammrohr (18) vollständig umhüllt und die Verteilerrohre (26) durch das Außenrohr (37) ragen. - Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 10 bis 14, wobei die Druckkammer durch einen zwischen Warenbahn und Ansaugkammer angeordneten Druckkasten gebildet wird,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Verbindungsleitung (34) vom mittleren Bereich des Druckkastens (8) ausgeht.
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19830664 | 1998-07-09 | ||
| DE19830664 | 1998-07-09 | ||
| DE19918102 | 1999-04-22 | ||
| DE19918102A DE19918102A1 (de) | 1998-07-09 | 1999-04-22 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0971191A2 true EP0971191A2 (de) | 2000-01-12 |
| EP0971191A3 EP0971191A3 (de) | 2001-12-12 |
| EP0971191B1 EP0971191B1 (de) | 2005-02-09 |
Family
ID=26047291
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99111709A Expired - Lifetime EP0971191B1 (de) | 1998-07-09 | 1999-06-17 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0971191B1 (de) |
| KR (1) | KR100413867B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE289051T1 (de) |
| PT (1) | PT971191E (de) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1316221C (zh) * | 2002-12-25 | 2007-05-16 | 乐金电子(天津)电器有限公司 | 烘干机的空气供应通道 |
| CN100343608C (zh) * | 2002-12-25 | 2007-10-17 | 乐金电子(天津)电器有限公司 | 干燥器的空气供应管道 |
| CN109225775A (zh) * | 2018-11-06 | 2019-01-18 | 江苏大族展宇新能源科技有限公司 | 锂电池涂布机用一体化烘箱 |
| CN109539250A (zh) * | 2018-10-30 | 2019-03-29 | 西安交通大学 | 一种低氮燃烧器及其内置式再循环烟气引入装置 |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7596882B2 (en) | 2004-05-13 | 2009-10-06 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | Treater oven for manufacturing prepreg |
| KR100668696B1 (ko) * | 2004-05-13 | 2007-01-15 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | 프리프레그 제조용 트리터 오븐 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH99095A (de) * | 1921-08-08 | 1923-05-01 | Scherhag Andreas | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Warmluft. |
| FR648100A (fr) * | 1927-10-25 | 1928-12-05 | Krantz Shone H | Rameuse-sécheuse |
| US2541332A (en) * | 1947-11-05 | 1951-02-13 | Campbell Bowen | Portable drier |
| US3057611A (en) * | 1960-02-15 | 1962-10-09 | Bjerkan Engineering Service In | Burner-blower combination for grain dryers |
| FR1471324A (fr) * | 1966-03-05 | 1967-03-03 | Appareil de chauffage associé à une installation de séchage utilisable pour le séchage des fruits, du houblon et de produits analogues | |
| DE2164860A1 (de) * | 1971-12-27 | 1973-06-28 | Kroenert Max Maschf | Duesentrockner |
| DK462875A (da) * | 1974-10-25 | 1976-04-26 | Claas Maschf Gmbh Geb | Torretromle til gronhost |
| US4147115A (en) * | 1977-09-14 | 1979-04-03 | Leppert Alfred M | Incinerator with gas generation |
| GB1583199A (en) * | 1977-12-01 | 1981-01-21 | Whiteley Ltd E Gordon | Cloth drying apparatus |
| FR2514118A1 (fr) * | 1981-10-07 | 1983-04-08 | Arnal Louis | Procede de chauffage d'articles devant subir un traitement thermique tels que des pieces en beton, installation pour sa mise en oeuvre et appareil de combustion formant un produit industriel nouveau |
| DE4405819A1 (de) * | 1994-02-03 | 1995-08-10 | Manfred Baumkoetter | Anordnung und Verfahren zur Erzeugung von Warmluft/Druckluft |
-
1999
- 1999-06-17 AT AT99111709T patent/ATE289051T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-06-17 EP EP99111709A patent/EP0971191B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-06-17 PT PT99111709T patent/PT971191E/pt unknown
- 1999-07-09 KR KR10-1999-0027716A patent/KR100413867B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1316221C (zh) * | 2002-12-25 | 2007-05-16 | 乐金电子(天津)电器有限公司 | 烘干机的空气供应通道 |
| CN100343608C (zh) * | 2002-12-25 | 2007-10-17 | 乐金电子(天津)电器有限公司 | 干燥器的空气供应管道 |
| CN109539250A (zh) * | 2018-10-30 | 2019-03-29 | 西安交通大学 | 一种低氮燃烧器及其内置式再循环烟气引入装置 |
| CN109539250B (zh) * | 2018-10-30 | 2019-12-24 | 西安交通大学 | 一种低氮燃烧器及其内置式再循环烟气引入装置 |
| CN109225775A (zh) * | 2018-11-06 | 2019-01-18 | 江苏大族展宇新能源科技有限公司 | 锂电池涂布机用一体化烘箱 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| PT971191E (pt) | 2005-06-30 |
| KR100413867B1 (ko) | 2004-01-07 |
| EP0971191B1 (de) | 2005-02-09 |
| ATE289051T1 (de) | 2005-02-15 |
| KR20000011611A (ko) | 2000-02-25 |
| EP0971191A3 (de) | 2001-12-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE4324488C2 (de) | Verfahren und Heißluft-Trockner zur Trocknung beschichteter Oberflächen | |
| DE4326877C1 (de) | Verfahren zum Trocknen von Platten und Trockner | |
| EP0706021A1 (de) | Trockner für eine Lackieranlage | |
| DE2637646A1 (de) | Anwaermofen | |
| EP0264637B1 (de) | Durchlauftrockner für Materialbahnen, insbesondere Offset-Trockner | |
| DE102016001893A1 (de) | Brennereinheit und Vorrichtung zum Temperieren von Gegenständen | |
| DE1604901A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Lackieren von Draehten | |
| EP2225044B2 (de) | Kühlvorrichtung und verfahren zum kühlen von gegenständen aus einer beschichtungseinrichtung | |
| DE4436713B4 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Trocknung der Oberflächen eines Gegenstandes | |
| DE3390176C2 (de) | Kombination eines Ofens und eines Rauchveraschers und Verfahren f}r deren Betrieb | |
| EP0971191B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases | |
| DE2735075C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Trocknen einer kontinuierlich bewegten Warenbahn | |
| DE8434317U1 (de) | Bestrahlungseinheit in form eines portals, insbesondere als trocken- und einbrennkanal fuer die automobilindustrie | |
| DE19735322A1 (de) | Durchlauflufttrocknungsanlage | |
| EP0869323A2 (de) | Trockner für eine Materialbahn mit Abgasrezirkulation | |
| EP2601467B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur wärmebehandlung einer textilen warenbahn | |
| DE69221740T2 (de) | Verfahren zum Trocknen von perforierten Ziegelsteinen und Vorrichtung zum Durchführen des Verfahrens. | |
| EP2519796B1 (de) | Vorrichtung und verfahren zur wärmebehandlung von kontinuierlich geförderten flächengebilden | |
| DD212414A1 (de) | Kuehlkanal fuer mit schokoladenmasse oder aehnlichen massen ueberzogene artikel | |
| DE19918102A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Behandeln von Gütern mittels eines erwärmten Gases | |
| DE19538364C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Schnellerwärmung von Metall-Preßbolzen | |
| EP1262726A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Behandlung von textilen Warenbahnen | |
| DE10242944B4 (de) | Trockner für Gegenstände, insbesondere für Fahrzeugkarosserien, sowie Verfahren zum Betreiben eines solchen Trockners | |
| EP0063642B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Heissluft-Trocknung von Textilgut | |
| DE3434906C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Vorwärmen von metallischem Gut |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT PT |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: SUCKER-MUELLER-HACOBA GMBH & CO. |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20020612 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT DE FR GB IT PT |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: MOENUS TEXTILMASCHINEN GMBH |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT PT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59911577 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20050317 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20050531 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20050607 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20050525 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20050429 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20050729 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20051110 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060617 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20061218 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: MM4A Free format text: LAPSE DUE TO NON-PAYMENT OF FEES Effective date: 20061218 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20060617 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20070228 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20070628 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060630 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20080625 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20080623 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080617 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100101 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090617 |