EP0917954B1 - Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Erstellen eines Einzelpositionbezugwertes in einem Druckprozess - Google Patents
Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Erstellen eines Einzelpositionbezugwertes in einem Druckprozess Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0917954B1 EP0917954B1 EP98121184A EP98121184A EP0917954B1 EP 0917954 B1 EP0917954 B1 EP 0917954B1 EP 98121184 A EP98121184 A EP 98121184A EP 98121184 A EP98121184 A EP 98121184A EP 0917954 B1 EP0917954 B1 EP 0917954B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- unit
- speed
- drive shaft
- position reference
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41F—PRINTING MACHINES OR PRESSES
- B41F13/00—Common details of rotary presses or machines
- B41F13/004—Electric or hydraulic features of drives
- B41F13/0045—Electric driving devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41F—PRINTING MACHINES OR PRESSES
- B41F13/00—Common details of rotary presses or machines
- B41F13/08—Cylinders
- B41F13/10—Forme cylinders
- B41F13/12—Registering devices
Definitions
- the present invention relates generally to position determination in Printing systems and a control system for a printing press, the Relative positions of drive units in the press controls.
- a conventional printing press usually consists of a series of Printing units.
- the relative positions of drive shafts of these printing units must be accurately regulated to ensure accurate registration of the various To ensure printing units so that errors, such as printing register errors, Web tension errors, web-to-web register errors and / or signature section errors can be prevented. Such errors occur at high Print speeds increased.
- each group of printing units has a drive unit with an input shaft with an output shaft of an electric motor for this Group is connected and driven by this.
- a Speed control unit generates a speed control signal to control the speed of rotation of the Output shaft of the electric motor.
- Other groups of printing units as well as not printing points in the printing press can also have drive units.
- a drive unit of the machine for "master drive” is determined, the one Receives signal that the desired speed of through the printing press shows the running paper web. This signal of the desired speed is sent to the Speed control element of the master drive for controlling the speed of the Drive shaft of the master drive sent. Signals the actual speed and position the drive shaft of the master drive are displayed on the others, as “slave drives” designated drive units transmitted.
- the speed controller of everyone Follower unit sends a speed control signal based on the actual position of the Drive shafts of the slave drives and the drive shaft of the master drive are based on the Electric motor of the slave drive, which causes the drive shaft of each Follower follows the speed and position of the drive shaft of the master drive.
- the drive shaft of each slave drive unit is in the same position and has the same speed as the drive shaft of the master drive unit.
- DE 41 37 979 describes a drive for a printing press with several Printing units, the individual printing units or printing unit groups are mechanically decoupled from each other, each printing unit or each Printing unit group is assigned a drive motor and being on each Printing unit or at each printing unit group a device for speed and / or Rotation angle determination is arranged. It is also a device for Angle control is provided, which is a permissible angular deviation of the individual printing units or printing unit groups from a given Angle setpoint dimensioned such that it at least in the angular position at handing over a sheet is minimal.
- the respective Angular position of two printing units fed to a microcomputer which continue from a setpoint specification a speed setpoint and one Receives the angle setpoint at which the sheet transfer is to take place, the Microcomputer based on an angular difference between the given Angle setpoint and the angular positions of the printing units torque setpoints calculated such that the permissible angular deviation of the respective Printing units of the specified target value at the sheet transfer is minimal.
- DD 115 069 discloses a method for starting register control on printing presses with several printing units, whereby the position of elements, for example, gears on at least two printing units by pulse generators is sampled, the phase position or phase shift of a pulse opposite the other pulse, the reference pulse, electronically according to size and direction is determined and the determined value for adjusting an actuator is evaluated becomes.
- a synchronous controller includes normally a resolver to the angular position of the drive shaft of the Convert slave drive into an electrical output signal. The position of the The slave drive shaft relative to the position of the master drive shaft will then be in correspondence of the electrical output signal generated by the synchronous regulator.
- Control devices with control compensation such as "Forced control”, “Speed setpoint” and “dp / dt pilot control” are also known.
- a "Type-3" controller can be used, the one Position error signal (i.e., a difference in the positions of the slave shaft and the master drive shaft) double integrated.
- a regulator is issued in US 5,049,798 on September 17, 1991.
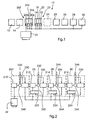
- Fig. 1 shows a conventional printing machine 10 with feed mechanisms 12 and 14, one Group 207 of printing units 200 - 206 and a group 23 of printing units 16 - 22, a dryer 24, cooling units 25 and 26 and folding units 28 and 30.
- Each of the Printing unit groups 207 and 23 and folding units 28 and 30 have one Drive unit. From a master reference signal source 32 a signal, i. H. on Speed command signal generated that the drive unit of group 207 a displays the desired press speed.
- the drive unit of the Group 207 is designated as the master drive unit.
- Those belonging to group 23 other drive units and the folding units 28 and 30 are used as subsequent printing units designated that follow the position and speed of the master printing unit.
- FIGS Groups 207 and 23 shows details regarding the internal components of the drive units in FIGS Groups 207 and 23 and the folding units 28 and 30 and connections between the Drive units and the control reference signal source 32.
- the Control reference signal source 32 incoming speed command signal in Speed control element 210 of the master drive unit entered in group 207, to control the speed of motor 260.
- the speed command signal can be an analog or a digital signal.
- a position encoder 230 determines the Actual position value of a drive shaft 240, which is from the motor 260 of the master drive unit is driven.
- the Position encoder 230 since the position information output from the position encoder 230 can be used to determine speed information, the Position encoder 230 alternatively also an actual value to the Send speed controller 210 back to ensure that the actual speed the drive shaft 240 of the master drive unit of the desired one Speed corresponds.
- the speeds and positions of the drive shafts 242-246 of the Follower units are controlled to match speed and position the drive shaft 240 of the master drive unit are adapted. This is through Using the speed of the drive shaft 240 of the master drive unit together with the feedback regarding the positions of the drive shafts 242-248 of the slave drive units relative to the position of the drive shaft 240 of the Master drive unit achieved.
- the slave drive units have motors 262-266 that are Drive drive shafts 242-246.
- Position encoders 232-236 determine the actual positions of the drive shafts 242-246 and send corresponding feedback signals to Controllers 222-226, which indicate the specific positions.
- that of the Position encoders 232-236 produce information for determining both the Speeds as well as the positions of the corresponding drive shafts 242-246 be used.
- the output signal generated by the position encoder 230 that the Indicates actual position of the drive shaft 240 of the master drive unit is considered a Reference position signal to the controllers 222-226 of the slave drive units of the Printing unit group 23 and sent to the folding units 28 and 30, as shown in Fig. 2.
- the controllers 222-226 compare the output signal of the position encoder 230 Master drive unit with the output signals of the position encoder 232-236 and send on the basis of this comparison command signals to the speed controllers 212-216, to control the speed of motors 262-266 such that the Drive shafts 242-246 of the slave drive units of the speed and position of the Drive shaft 240 follow the master drive unit.
- this produces one Impulse for every angular increment of the rotating drive shaft 240 Master drive. So while the drive shaft is rotating, the Position encoder 230 a stream of pulses.
- the position encoder 230 Number of pulses generated during a time interval indicates by what amount the drive shaft 240 has changed position during this time interval.
- the Average speed during the time interval can be determined effortlessly by the value of the position change by the duration of the time interval is divided.
- the angular increase corresponding to a pulse is fixed so that the Position encoder 230 generates 2,048 pulses during each complete revolution.
- the position encoder 230 is monitored and the pulses generated by it become counted by means of a counter, not shown.
- the counter usually jumps to Completion of one turn back to zero after counting up to 2,048. In some designs there is a different number of pulses per revolution decisive and in other versions the counter jumps less frequently than after to zero every revolution.
- the position encoders 232-236 are the same like the position encoder 230.
- the positions of the encoders 230-236 can be synchronized by simultaneously setting the corresponding counter to zero be reset, e.g. B. when the paper web with slower and constant speed through the printing press.
- the meters are inside or near the corresponding position encoder.
- controllers 222-226 for synchronizing the speeds and Positions of the drive shafts of the slave drive units with those of the Drive shaft 240 of the master drive unit are designed, they can not be used are used for problems caused by mechanical malfunctions or control errors on the Drive shaft 240 of the master drive unit arise. Such control errors will arise the. Transfer drive units and there is a tendency that these errors to repeat. Thus, a control error on the master drive shaft can affect the function of the Very badly affect slave drive units. In the event of major faults, the controller performance interrupted or endangered, so that problems in printing, e.g. B. by Register errors can occur.
- the present invention relates to a method and an apparatus which make it possible to trouble-free speed and position reference signals on drive units in one Printing machine, e.g. B. printing units to send.
- a device for controlling the printing process of a printing press a first and at least a second drive unit with a respective motor and one respective drive shaft; a first and at least a second position encoder, which each determine the actual position of the respective drive shaft and at least one Generate position encoder signal; a first and at least a second Speed control unit which control the speed of the respective drive shaft; and
- a first controller is characterized in that the device is a single position reference value unit having at least one single position reference signal based on the desired printing press speed that is generated free by the printing operation triggered disturbances, and sends to the first and at least second controller, the Controller to the respective speed control unit on the single position reference signal and send a control signal based on the respective position encoder signal, and that the Single position reference signal and the position encoder signals each a number of pulses include.
- a single position reference value unit receives a signal that the displays the desired speed of a web running through the printing press.
- the Single position reference value unit generates signals that have a correct reference speed and represent an error-free reference position and which the printing press drive units, for.
- the same Reference signals can be sent to all drive units. Alternatively, separate reference signals can be used be generated for each drive unit and between the individual, for the different Drive signals generated by reference signals can cause inaccuracies Error correction circuits are corrected.
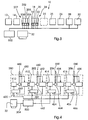
- Fig. 3 shows an embodiment of a printing press, in which elements that with those of the printing press shown in Fig. 1 are identical to the same Reference signs have been identified. According to the embodiments of the present invention is not one of the printing units of a printing press Leitdruckwerk marked. As shown in Fig. 3, is a single position reference value unit 500 provided by a master reference signal source 32 a Received signal representing the desired printing press speed and a Send single position reference signal to each printing unit. In contrast to that in the 1 and 2, the printing presses shown have each of the printing units 200-206 and 16-22 and each of the folding units 28 and 30 has a separate drive unit.
- FIGS. 3 and 4 is a drive unit for has any printing unit, it is self-evident to the person skilled in the art that the invention also in a printing press with only one drive unit for all printing units or for any group of printing units can be realized.
- a single drive unit for a group of printing units can be controlled in the same way as one Drive unit for a single printing unit in the described here Embodiments is controlled.
- Fig. 4 shows details of the printing machine of Fig. 3, i.e. H. internal components of the Printing units 200-206 and connections between these printing units, the Single position reference value unit 500. and the master reference signal source 32. In contrast to the components shown in FIG.
- the Drive unit 2 is the drive unit for the printing unit 200 equipped with a regulator 420; thus the inner construction is this Drive unit the same as that shown in the other printing units 202-206 Drive units.
- Each of the controllers 420-426 in the printing units 200-206 receives this Single position reference signal from the single position reference value unit 500.
- the Single position reference signal can be an analog or a digital signal.
- the speeds and positions of the drive shafts 440-446 of the drive units are controlled so that they are displayed by the single position reference signal Adjust the reference speed and position using the Reference speed, along with feedback regarding the positions of the Drive shafts 440-446 of the drive units relative to the reference position.
- the drive units have motors 460-466 which the Drive drive shafts 440-446.
- Position encoders 430-436 determine the actual positions of the drive shafts 440-446 and send corresponding feedback signals to controllers 420-426, which indicate the particular positions.
- the information output from position encoders 430-436 for both determination the speeds as well as the positions of the corresponding ones Drive shafts 440-446 can be used.
- the controllers 420-426 compare that Single position reference signal with the output of position encoders 430-436 and transmit based on this comparison command signals to the Speed control units 410-416 for controlling the speed of the Motors 460-466, so that the drive shafts 440-446 of the drive units of the by the Single position reference signal follow displayed speed and position. Consequently the drive shafts 440-446 are affected by temporary mechanical disturbances in the Print operation not affected.
- the printing units 16-22 and the folding units 28 and 30 are of the same configuration and offer the same advantages.
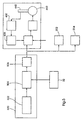
- Fig. 5 shows a second embodiment of the invention with an exemplary internal configuration of the single position reference value unit 500 which one Vibration generator 502, a divider / multiplier 504 and a filter / amplifier device 506 includes.
- the vibrator 502 generates one Time signal corresponding to that received from the control reference signal source 32 Signal that represents the desired press speed, divided or is multiplied.
- the filter / amplifier device 506 filters noise from the Divider / multiplier 504 output signal and sends the resultant Single position reference signal to the controllers of the printing units.
- the filter / amplifier device 506 also amplifies the signal in each of the users desired way so that it is compatible with the controls in the printing units.
- the Single position reference value unit 500 can be realized by only electronic components are used, they can be a solid state device or be an analog device.
- Each pulse of that output from the single position reference value unit 500 Single position reference signal represents an angular increase by which there is a Drive shaft must move.
- the angle increase has a predetermined value. Consequently indicates the number of times in the single position reference signal within a time interval impulses indicate a change in the reference position during this time interval and the frequency of the pulses indicates a reference speed or Reference angular velocity.
- FIG. 5 shows in the printing unit 200 a counter / scanner 508 which is connected to the controller 420 and to position encoder 430 and can be used to adjust the Processing ability of the controller 420 to supplement and / or information from To provide position encoders 430 in a more useful form.
- the counter / scanner 508 can, for example, generate a signal that corresponds to the number of position increases which the drive shaft 440 has moved during a time interval, i. H. the Displays the number of position changes during the time interval.
- Controller 420 includes a counter (not shown) that is used by the single position reference value unit 500 received impulses counts with those of the Counter / sampler 508 counted pulses can be compared to one possible Phase difference between the reference position and the position of the drive shaft 440 determine.
- the counter can also be inside the divider / multiplier 504 mounted in the single position reference value unit 500 be so that the signal output of unit 500 is a pulse number.
- Controller 420 can also received a delay compensation signal to unwanted To compensate for signal delays or inaccuracies occurring in the system.
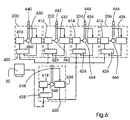
- Fig. 6 shows a third embodiment of the invention, the configuration of the Single position reference value unit 600 which includes one motor 668, one Drive shaft 648, a position encoder 638, a speed control unit 618 and includes a controller 628.
- the internal construction of the single position reference unit 600 is similar to that shown in the printing units 200-206 of FIG. 4, but with a few differences.
- the drive shaft 648 is not one of the Processes in the printing press and therefore no undesirable mechanical malfunctions in the operation of the printing press, for example Blanket washes, subjected.
- the drive shaft 648 can e.g. B. with a Operation process (not shown) connected, the straightforward, predictable Has behavioral characteristics and is free from transition disorders, the problems could cause in machine operation.
- controller 628 receives that desired speed command signal indicating printing press speed from the lead reference signal source.
- this is from position encoder 638 output signal is the single position reference signal which is sent to the controllers 420-426 Printing units 200-206 is sent.
- Motor 668 can operate independently of others in the Printing machine used motors can be selected. For example, the Motor 668 can be smaller than motors 460-466 and an auxiliary motor.
- the controller 628 of the single position reference value unit 600 controls the Speed control unit 618 in that by means of a Speed feedback the speed of the drive shaft 648 as precise as possible is maintained to indicate the desired speed.
- regulators 420-426 regulate the respective Speed control units of the printing units 200-206 in such a way that the Drive shafts 440-446 the speed and position of drive shaft 648 accurately consequences.
- Fig. 7 shows a fourth embodiment of the invention.
- the unit position reference value unit actually consists of components that are within the regulator located, and from connections between the controllers. That is, each of the controls internally generates a single position reference signal which is based on the Speed command signal from the master reference signal source 32 based.
- each Controller becomes the single position reference signal with the drive shaft speed and the position information obtained from the position encoder of the corresponding one Printing unit is generated, compared. Based on this comparison, the Regulator sends a command signal to a corresponding speed control unit is input so that the drive shaft by the single position reference signal displayed reference speed and position follows.
- printing unit 200 is selected as a standard unit and that of whose position encoder 430 output signal 700 is from everyone else Printing units used as a standard to which the single position reference signal each of the printing units is periodically adjusted. According to the embodiments the single position reference signals are corrected at one time or standardized if the printing unit chosen as standard does not suffer from transitional faults is influenced.
- This concept can also be used, for example, when the invention is in an existing printing press is integrated, which is due to original structural Restrictions do not apply to the same single position reference signal on all their drive units can transmit.
- FIG. 8 shows the internal construction of controller 822 of FIG. 7.
- a vibrator 800 generates a timing signal in a manner similar to that in FIG. 5 Single position reference value unit 500 shown.
- the time signal is sent to a divider / multiplier unit 802 sent the the time signal that is on the by the Routing reference signal source 32 received via line 304 Speed command signal based, divided or multiplied, and that too Pulses of the divided or multiplied time signal counts.
- a Signal setting unit 804 filters noise from the pulse count signal from the divider / multiplier 802 is output, and amplifies the signal accordingly.
- the Signal setting unit 804 can also set the signal so that it matches the Standard signal 700 is synchronized.
- the one output from the signal setting unit 804 Signal is a single position reference signal for the print engine 202 and is turned on Position register 808 sent.
- Position register 808 also receives a signal from counter 806; this signal indicates the number of pulses detected by the Received counter 806 from position encoder 432.
- the counter 806 may receive a signal generate the number of position increments by which the drive shaft 442 has moved during a time interval, d. H. the number of position changes displays during the time interval.
- Position register 808 compares that from counter 806 and from Signal setting unit 804 sent signals.
- the signals represent a change the position of the drive shaft 442 and a change in the reference position during a Time interval and also show the reference speed and the speed the drive shaft 442. Based on this comparison, this creates Position register 808 a command signal that is sent to the speed control unit 412 is sent as is more well known according to the general principles Control functions take place and for example in the controller 22 of that shown in FIG. 2 Printing machine of the prior art is realized.
- An exemplary implementation of a circuit to correct or Standardizing the single position reference signal generated in controller 822 a counter 818, a comparator 812, an error detector 810, one Error compensator 814 and a correction value limiter 816.
- counter 818 functions in the same way as counter / scanner 508 in FIG. 5 and counter 806.
- the printing group 200 is selected as the standard printing group.
- counter 818 detects the pulses and received from the position encoder 430 of the standard printing unit 200 generates a signal representing the number of position increments by which the Drive shaft 440 has moved during a time interval, i.e. the number of Displays changes in position during the time interval.
- the signal output from counter 818 and the single position reference signal from of the signal setter 804 are input to the comparator 812 which is the compares the two signals and generates an error signal on the basis of this comparison.
- the signal output by the comparator 812 is fed into the error detector 810 entered the presence and magnitude of the error between (a) the output signal counter 818, i. H. the position and speed of the drive shaft 440 the standard print engine 200, as indicated by the position encoder 430, and (b) the Reference speed and position as determined by the signal setting unit 804 output single position reference signal shown, detected.
- the error detector 810 generates a signal indicating the particular error and the signal is converted into a Error compensator 814 input, which generates a control signal, which the Signal setter 804 causes the single position reference signal to be corrected or to the position and speed of the drive shaft 440 of the Standard printing unit 200 to adapt.
- a correction value limiter 816 can be used with the Error compensator 814 and the signal adjuster 804 are connected to the Correction process by restricting the output signal of the error compensator 814 slow it down.
- controller 822 can Contain counter 806 and position register 808 and an output signal from Position encoder 432 and another output signal from the Receive signal setter 804.
- Components like that Vibration generator 800, the divider / multiplier 802, the Signal setting unit 804, the comparator 812, the error detector 810, the Error compensator 814, correction value limiter 816 and counter 818 can be on can be arranged anywhere as long as they remain correctly connected and the output of the signal setting unit 804 to the controller 822, the routing reference signal 304 to the Divider / multiplier 802 passes and the standard position encoder signal 700 to counter 818.
- the other printing units 204, 206 can be of the same construction and in be operated in the same way as the printing unit 202. If the configuration of the FIG. 8, for example, for the prior art printing machine shown in FIG. 2 is to be used, the printing group 23 and the folding units 28 and 30 2 may have the same construction as the printing unit 202.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Inking, Control Or Cleaning Of Printing Machines (AREA)
Description
- Fig. 1
- ein Blockdiagramm einer Druckmaschine des oben beschriebenen Standes der Technik;
- Fig. 2
- ein Blockdiagramm, das die interne Konstruktion einiger Elemente der in Fig. 1 dargestellten Druckmaschine zeigt;
- Fig. 3
- ein Blockdiagramm einer Druckmaschine gemäß einem ersten Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung;
- Fig. 4
- ein Blockdiagramm, das die interne Konstruktion einiger in Fig. 3 dargestellten Druckwerke zeigt;
- Fig. 5
- ein Blockdiagramm einer Druckmaschine gemäß einem zweiten Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung;
- Fig. 6.
- ein Blockdiagramm einer Druckmaschine gemäß einem dritten Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung;
- Fig. 7
- ein Blockdiagramm einer Druckmaschine gemäß einem vierten Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung;
- Fig. 8
- ein Blockdiagramm, das die interne Konstruktion von in Fig. 7 dargestellten Reglern zeigt.
- 16
- Druckwerk (Fig. 1)
- 18
- Druckwerk
- 20
- Druckwerk
- 22
- Druckwerk
- 28
- Falzeinheit
- 30
- Falzeinheit
- 32
- Leitbezugssignalquelle
- 200
- Druckwerk (Fig. 7)
- 202
- Druckwerk
- 204
- Druckwerk
- 206
- Druckwerk
- 230
- Positionskodierer (Fig. 2)
- 410
- Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (Fig. 4)
- 412
- Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit
- 414
- Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit
- 416
- Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit
- 420
- Regler
- 422
- Regler
- 424
- Regler
- 426
- Regler
- 430
- Positionskodierer
- 432
- Positionskodierer
- 434
- Positionskodierer
- 436
- Positionskodierer
- 440
- Antriebswelle
- 442
- Antriebswelle
- 444
- Antriebswelle
- 446
- Antriebswelle
- 460
- Motor
- 462
- Motor
- 464
- Motor
- 466
- Motor
- 500
- Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (Fig. 5)
- 502
- Schwingungserzeuger
- 504
- Dividier-/Multipliziereinheit
- 506
- Filterverstärkereinheit
- 508
- Zähler/Abtaster
- 600
- Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (Fig. 6)
- 618
- Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit
- 628
- Regler
- 638
- Positionskodierer
- 648
- Antriebswelle
- 668
- Motor
- 700
- Signal des Positionskodierers 430 (Fig. 7)
- 720
- Regler
- 724
- Regler
- 726
- Regler
- 800
- Schwingungserzeuger (Fig. 8)
- 802
- Dividier-/Multipliziereinheit
- 804
- Signaleinstelleinheit
- 806
- Zähler
- 808
- Positionsregister
- 810
- Fehlerdetektor
- 812
- Komparator
- 814
- Fehlerkompensator
- 816
- Korrekturwert-Begrenzer
- 818
- Zähler
- 822
- Regler
Claims (20)
- Vorrichtung zur Steuerung des Druckprozesses einer Druckmaschine mit einer ersten und mindestens einer zweiten Antriebseinheit mit einem jeweiligen Motor (460-468) und einer jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-448); einem ersten und mindestens einem zweiten Positionscodierer (430-436, 638), welche jeweils die Ist-Position der jeweiligen Antriebswelle bestimmen und mindestens ein jeweiliges Positionskodierer-Signal erzeugen;
einer ersten und mindestens einer zweiten Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (410-416, 618), die die Geschwindigkeit der jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446, 648) steuern; und
einem ersten Regler (420-426, 628, 720-726, 822),
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Vorrichtung eine Einzelposition-Bezugwert-Einheit (500) aufweist, die mindestens ein Einzelposition-Bezugssignal auf der Basis der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit erzeugt, das frei von durch den Druckbetrieb ausgelösten Störungen ist, und an den ersten und mindestens zweiten Regler (420-426, 628, 720-726, 822) sendet, wobei die Regler (420-426, 628, 720-726, 822) an die jeweilige Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (410-416, 618) ein auf dem Einzelposition-Bezugssignal und dem jeweiligen Positionskodierer-Signal basierendes Steuersignal senden, und daß das Einzelposition-Bezugssignal und die Positionskodierer-Signale (430-436, 638) jeweils eine Anzahl von Impulsen umfassen. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Einzelposition-Bezugssignal mindestens ein Bezugsgeschwindigkeitssignal und ein Bezugspositionssignal umfaßt. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1 oder 2,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit einen Schwingungserzeuger (502) zum Erzeugen eines Bezugssignals und eine Frequenz-Dividiereinheit (504) zum Dividieren des auf der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basierenden Bezugssignals umfaßt. - Vorrichtung nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die erste und die mindestens zweite Antriebseinheit ferner jeweils einen Zähler (508) umfaßt, der mit dem jeweiligen ersten und mindestens zweiten Positionskodierer (430-436) und dem jeweiligen ersten und mindestens zweiten Regler (420-426) operativ verbunden ist, um während einer Abtastzeit eine Änderung der Position der jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446) zu erfassen. - Vorrichtung nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das von dem jeweiligen ersten und mindestens zweiten Regler (420-426) erzeugte Steuersignal auch auf einem Verzögerungsausgleichssignal für eine Signalpfadverbindung zwischen der Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) und dem jeweiligen ersten und mindestens zweiten Regler (420-426) basiert. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet,daß die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) folgendes umfaßt:einen von der Druckmaschine getrennten Motor (460) mit einer Abtriebswelle;eine Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (410), durch die die Geschwindigkeit der Abtriebswelle gesteuert wird;einen Positionskodierer (430), der ein die Position der Abtriebswelle anzeigendes Signal erzeugt, wobei das Positionskodierer-Signal das Einzelposition-Bezugssignal ist;und einen Regler (420), der ein Steuersignal, das auf dem Einzelposition-Bezugssignal und der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basiert, an die Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit sendet. - Vorrichtung nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß ferner eine Leitbezugssignalquelle (32) vorgesehen ist, um ein die gewünschte Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit darstellendes Signal an die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) zu senden. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 7,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das von der Leitbezugssignalquelle erzeugte Signal ein digitales Signal ist. - Vorrichtung nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) ein elektronischer Baukörper ist. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) eine Vielzahl von auf der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basierten Einzelposition-Bezugssignalen erzeugt, und daß die Vorrichtung ferner umfaßt:eine Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten (460-466) mit einer jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446); eine Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (410), die die Geschwindigkeit der Antriebswelle (440) steuert; einen Positionskodierer (430), der ein die Position der Antriebswelle (440) anzeigendes Signal erzeugt; und einen Regler (720), der ein Steuersignal an die Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit sendet, das auf dem Signal des Positionskodierers und auf mindestens einem der Vielzahl von Einzelposition-Bezugssignalen basiert. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 10,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) mindestens einen Fehlerkorrektur-Schaltkreis umfaßt, um mindestens eines der Einzelposition-Bezugssignale, die auf dem Output eines Positionskodierers einer aus einer Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten designierten Antriebseinheit basiert sind, zu korrigieren. - Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 10 oder 11,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß eine von der Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten (460-466) als Leitantriebseinheit designiert ist und andere der Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten (460-466) als Folgeantriebseinheiten designiert sind; und
daß die Einzelposition-Bezugswert-Einheit (500) für jede der Folgeantriebseinheiten folgendes umfaßt:einen Schwingungserzeuger (502), der ein Signal erzeugt;eine Frequenz-Dividiereinheit (504), die durch Dividieren des Schwingungserzeuger-Signals, das auf der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basiert, ein Signal erzeugt;eine Impuls-Addier-/Subtrahiereinheit zum Erzeugen des Einzelposition-Bezugssignals durch Ändern der Anzahl der Impulse in dem von der Frequenz-Dividiereinheit (504) erzeugten Signal;ein Komparator (812), der das von der Impuls-Addier-/Subtrahiereinheit erzeugte Einzelposition-Bezugssignal mit dem von dem Positionskodierer der Leitantriebseinheit erzeugten Signal vergleicht und auf der Basis dieses Vergleichs ein Signal erzeugt;ein Fehlerdetektor (810), der einen Fehler zwischen dem von der Impuls-Addier/Subtrahiereinheit erzeugten Einzelposition-Bezugssignal und dem von dem Positionskodierer der Leitantriebseinheit erzeugten Signal erfaßt; undeine Fehlerkorrektureinheit, die auf der Basis des erfaßten Fehlers ein Steuersignal zur Steuerung der Impuls-Addier-/Subtrahiereinheit erzeugt. - Verfahren zum Steuern des Druckprozesses einer Druckmaschine, mit den folgenden Schritten:Bestimmen der Position einer jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446) einer ersten und mindestens einer zweiten Antriebseinheit (460-466) der Druckmaschine mit einem jeweiligen Positionskodierer (430-436, 638) und Senden eines jeweiligen Positionskodierer-Signals an einen Regler (420-426, 628, 720-726, 822); undSteuern der Drehzahl der jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446) mit einer jeweiligen Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (410-416, 618),
gekennzeichnet durchErzeugen eines auf der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basierten Einzelposition-Bezugssignals, das frei von durch den Druckbetrieb ausgelösten Störungen ist, und eine Anzahl von Impulsen umfaßt;Senden des Einzelpositions-Bezugssignals an jeweilige Regler (420-426, 628, 720-726, 822); und - Verfahren nach Anspruch 13,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Schritt des Erzeugens des Einzelposition-Bezugssignals folgendes umfaßt:Senden eines jeweiligen Signals auf der Basis des Einzelposition-Bezugssignals und des jeweiligen, eine Anzahl von Impulsen umfassenden Positionskodierer-Signals an die jeweilige Geschwindigkeitssteuereinheit (410-416, 618).Erzeugen eines Zeitsignals mit einer vorbestimmten Frequenz;Dividieren des auf der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basierten Zeitsignals;Ausfiltern von Lärm aus dem Zeitsignal; undVerstärken des Zeitsignals. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 13 oder 14,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dieses ferner den Schritt des Feststellens einer Änderung der Position der jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446) während einer Abtastzeit umfaßt. - Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 13 bis 15,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Steuern der Drehzahl der jeweiligen Antriebswelle (440-446) auch auf einem Verzögerungsausgleichssignal basiert. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 13,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Erzeugen eines Einzelposition-Bezugssignals folgendes umfaßt:Bestimmen der Position einer von der Druckmaschine getrenntenAntriebswelle (440-446);Erzeugen des Einzelposition-Bezugssignals auf der Basis der bestimmten Antriebswellenposition; undSteuern der Drehzahl der Antriebswelle (440-446) auf der Basis des Einzelposition-Bezugssignals und der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 13,
gekennzeichnet durch
Bestimmen der Antriebswellenposition einer jeden einer Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten (460-466);
Erzeugen mindestens eines auf der gewünschten Druckmaschinengeschwindigkeit basierten Einzelposition-Bezugssignals für jede der Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten (460-466); und
Steuern der Geschwindigkeit einer jeden Antriebswelle auf der Basis der bestimmten Antriebswellenposition und des mindestens einen Einzelposition-Bezugssignals. - Verfahren nach Anspruch 18,
dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dieses ferner den Schritt des Korrigierens des mindestens einen Einzelposition-Bezugssignals, das auf der bestimmten Antriebswellenposition einer aus einer Vielzahl von Antriebseinheiten (460-466) designierten Antriebseinheit basiert, umfaßt. - Rollenrotationsdruckmaschine,
gekennzeichnet durch
eine Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 12.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US975710 | 1997-11-21 | ||
| US08/975,710 US5894802A (en) | 1997-11-21 | 1997-11-21 | Method and apparatus for establishing an isolated position reference in a printing operation |
Publications (4)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0917954A2 EP0917954A2 (de) | 1999-05-26 |
| EP0917954A3 EP0917954A3 (de) | 2000-03-15 |
| EP0917954B1 true EP0917954B1 (de) | 2003-03-19 |
| EP0917954B2 EP0917954B2 (de) | 2008-10-15 |
Family
ID=25523301
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP98121184A Expired - Lifetime EP0917954B2 (de) | 1997-11-21 | 1998-11-13 | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Erstellen eines Einzelpositionbezugwertes in einem Druckprozess |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5894802A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0917954B2 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPH11216849A (de) |
| CN (1) | CN1106285C (de) |
| DE (2) | DE59807532D1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10104795B4 (de) * | 2001-02-02 | 2007-07-05 | Siemens Ag | Drehzahlabhängige Sollwertkorrektur bei elektrisch geregelten Slaveantrieben |
| DE10117454A1 (de) * | 2001-04-06 | 2002-10-17 | Rexroth Indramat Gmbh | Verfahren zur Registerregelung |
| US6823792B2 (en) * | 2001-07-26 | 2004-11-30 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Multi-motor drive and method for driving a printing press |
| US6722279B2 (en) * | 2001-12-05 | 2004-04-20 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Device and corresponding method for rapid image data transfer in printing presses |
| DE102004007069A1 (de) * | 2004-02-13 | 2005-08-25 | Goss International Montataire S.A. | Rotationselement einer Druckmaschine, mit einem Encoder |
| US7109670B1 (en) * | 2005-05-25 | 2006-09-19 | Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. | Motor drive with velocity-second compensation |
| US7187142B2 (en) * | 2005-05-25 | 2007-03-06 | Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. | Motor drive with velocity noise filter |
| DE102005048472A1 (de) * | 2005-10-07 | 2007-04-12 | Bosch Rexroth Ag | Rotationsdruckmaschine und Verfahren des Betriebs einer Rotationsdruckmaschine |
| US7965397B2 (en) * | 2006-04-06 | 2011-06-21 | Xerox Corporation | Systems and methods to measure banding print defects |
| FR2911969B1 (fr) * | 2007-01-31 | 2009-08-07 | Goss Int Montataire Sa | Dispositif de controle d'une presse rotative. |
| US8690461B2 (en) * | 2009-09-21 | 2014-04-08 | Goss International Americas, Inc. | System and method for controlling a multi-drive printing press |
| US8640617B2 (en) | 2009-10-07 | 2014-02-04 | Goss International Americas, Inc. | Multi-drive printed product processing device with verified feedback control |
| US10279584B2 (en) * | 2010-07-27 | 2019-05-07 | Goss International Americas, Inc. | Observation-enhanced virtual master system for a printing press |
| CN106364157B (zh) * | 2016-09-30 | 2018-07-10 | 武汉菲仕运动控制系统有限公司 | 一种印铁机控制系统 |
| EP3672808B1 (de) * | 2017-08-21 | 2024-07-10 | manroland sheetfed GmbH | Regelung von druckmaschinen mit mehreren hauptantriebsmotoren |
| WO2021021078A1 (en) | 2019-07-26 | 2021-02-04 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Synchronizing multiple printing presses |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4322744A1 (de) * | 1993-07-08 | 1995-01-19 | Baumueller Nuernberg Gmbh | Elektrisches Antriebssystem zur Verstellung von einem oder mehreren dreh- und/oder verschwenkbaren Funktionsteilen in Geräten und Maschinen, Antriebsanordnung mit einem Winkellagegeber und Druckmaschine |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3845366A (en) * | 1971-07-22 | 1974-10-29 | Fincor Inc | Integrated drive system |
| DD115069A1 (de) * | 1974-10-15 | 1975-09-12 | ||
| DE2613600A1 (de) * | 1976-03-30 | 1977-10-06 | Siemens Ag | Drehzahlregelung fuer eine bahnfoerdernde maschine |
| US4271379A (en) * | 1978-12-29 | 1981-06-02 | Harris Corporation | Web fed printing press motor control |
| US4495583A (en) * | 1982-06-04 | 1985-01-22 | Harris Graphics Corporation | Apparatus and method for encoding positions of web press machines |
| US4495582A (en) * | 1982-06-04 | 1985-01-22 | Harris Graphics Corporation | Control system for pre-setting and operation of a printing press and collator |
| US4839814A (en) * | 1985-01-29 | 1989-06-13 | Moore Business Forms, Inc. | Size independent modular web processing line and modules |
| AU8326287A (en) * | 1986-10-31 | 1988-05-25 | Quad/Tech, Inc. | Improved cutoff control system |
| US4901577A (en) * | 1988-04-28 | 1990-02-20 | World Color Press, Inc. | Apparatus for detecting splices in the web of a printing press |
| US5049798A (en) * | 1990-03-13 | 1991-09-17 | Harris Graphics Corporation | Control apparatus |
| JP2720584B2 (ja) * | 1990-07-20 | 1998-03-04 | 株式会社安川電機 | サーボシステムの同調位相制御装置 |
| US5490243A (en) * | 1990-12-13 | 1996-02-06 | F3 Software Corporation | Data processing system for multi-platform print control and electronic data fill |
| US5243408A (en) * | 1991-07-17 | 1993-09-07 | P. H. Glatfelter Company | Method and apparatus for detecting web discontinuities |
| DE4137979B4 (de) * | 1991-11-19 | 2004-05-06 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Antrieb für eine Druckmaschine mit mindestens zwei mechanisch voneinander entkoppelten Druckwerken |
| US5481971A (en) * | 1991-11-19 | 1996-01-09 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Drive for a printing press with a plurality of printing units |
| US5615609A (en) * | 1995-08-21 | 1997-04-01 | The Lawrence Paper Company | System and method for controlling AC motor driven multi-unit printing press |
-
1997
- 1997-11-21 US US08/975,710 patent/US5894802A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1998
- 1998-11-13 DE DE59807532T patent/DE59807532D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-11-13 DE DE19852436A patent/DE19852436A1/de not_active Ceased
- 1998-11-13 EP EP98121184A patent/EP0917954B2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-11-20 JP JP10331317A patent/JPH11216849A/ja active Pending
- 1998-11-20 CN CN98125106A patent/CN1106285C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4322744A1 (de) * | 1993-07-08 | 1995-01-19 | Baumueller Nuernberg Gmbh | Elektrisches Antriebssystem zur Verstellung von einem oder mehreren dreh- und/oder verschwenkbaren Funktionsteilen in Geräten und Maschinen, Antriebsanordnung mit einem Winkellagegeber und Druckmaschine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1106285C (zh) | 2003-04-23 |
| EP0917954B2 (de) | 2008-10-15 |
| EP0917954A3 (de) | 2000-03-15 |
| CN1239689A (zh) | 1999-12-29 |
| US5894802A (en) | 1999-04-20 |
| JPH11216849A (ja) | 1999-08-10 |
| DE59807532D1 (de) | 2003-04-24 |
| EP0917954A2 (de) | 1999-05-26 |
| DE19852436A1 (de) | 1999-05-27 |
| HK1022125A1 (en) | 2000-07-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0917954B1 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Erstellen eines Einzelpositionbezugwertes in einem Druckprozess | |
| EP0812682B1 (de) | Antrieb für eine Druckmaschine | |
| DE10243454B4 (de) | Antriebsvorrichtung einer Bearbeitungsmaschine | |
| DE69701481T2 (de) | Rotationsdruckmachine | |
| EP0452704A2 (de) | Druckmaschinenanlage | |
| DE60127034T2 (de) | Synchrone Regelung mit automatischen Registerfunktionen für das Schneiden und Drucken | |
| EP0993698B2 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum dezentralen betrieb bzw aufbau einer winkelgenauen gleichlaufregelung in einem mehrmotorenantriebssystem | |
| DE69113979T2 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Regeln der Phase in einem Druckrollenantriebsystem für Wellpappendruckmaschinen. | |
| EP1211070B2 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Synchronisation von an mehreren Einheiten ablaufenden Prozessen | |
| DE19781048B4 (de) | Druckeinrichtung | |
| DE60035464T2 (de) | Netzwerksteuerungssystem für Rotationsdruckmaschinen | |
| EP1373992B1 (de) | Verfahren zum synchronisierten betrieb von maschinen mit durch einzelantriebe angetriebenen achsen | |
| DE69926980T2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Synchronisierungsregelung | |
| EP0747216B1 (de) | Steuerung für eine Druckmaschine | |
| EP1372965B1 (de) | Verfahren zur registerregelung | |
| EP1531992B1 (de) | Antriebsvorrichtung und ein verfahren zur steuerung eines aggregates einer druckmaschine | |
| DE3781814T2 (de) | Registerkontrolle fuer kombinierte druck- und schneidmaschinen. | |
| DE60126013T2 (de) | Synchrone Regelung von Rotationsdruckmaschinen | |
| WO1998039838A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur aufrechterhaltung eines winkelgenauen gleichlaufs einzelner vernetzter antriebe eines dezentralen antriebssystems | |
| DE10259494A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Steuern einer Druckmaschine | |
| EP1779504B1 (de) | Anordnung zum antrieb eines lastelementes | |
| EP0692377B2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum synchronen Antreiben von Druckmaschinenkomponenten | |
| EP1987951A2 (de) | Druckmaschine und Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Druckmaschine | |
| DE10208791C5 (de) | Druckmaschinenantriebssystem | |
| DE102006014526B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Reduzierung von periodischen Drehwinkel-Lagedifferenzen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19981113 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20010110 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20030319 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59807532 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20030424 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: MAN ROLAND DRUCKMASCHINEN AG Effective date: 20031219 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: GOSS INTERNATIONAL AMERICAS, INC. |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: KIRKER & CIE SA |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20081015 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: AEN Free format text: AUFRECHTERHALTUNG DES PATENTES IN GEAENDERTER FORM |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20101124 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20121113 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20121113 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20131127 Year of fee payment: 16 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20131118 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20141128 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141130 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20150731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59807532 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160601 |