EP0617153B1 - Process to influence the movement of a weft yarn drawn from a storage bobbin to the weft inserting device of a loom and loom to carry out the process - Google Patents
Process to influence the movement of a weft yarn drawn from a storage bobbin to the weft inserting device of a loom and loom to carry out the process Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0617153B1 EP0617153B1 EP93810220A EP93810220A EP0617153B1 EP 0617153 B1 EP0617153 B1 EP 0617153B1 EP 93810220 A EP93810220 A EP 93810220A EP 93810220 A EP93810220 A EP 93810220A EP 0617153 B1 EP0617153 B1 EP 0617153B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- weft
- compressed
- yarn
- compressed air
- weft insertion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 23
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims description 43
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims description 43
- 238000009941 weaving Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 claims 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002268 wool Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D47/00—Looms in which bulk supply of weft does not pass through shed, e.g. shuttleless looms, gripper shuttle looms, dummy shuttle looms
- D03D47/34—Handling the weft between bulk storage and weft-inserting means
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for influencing the movement of a weft thread which is to be drawn off from a supply spool and runs against a weft insertion device of a weaving machine, in particular a projectile weaving machine, and which is transferred in each weaving cycle for a weft insertion to a weft insertion member penetrating the shed, the weft thread being passed through a compressed air nozzle arranged between the supply reel and the weft insertion device is additionally accelerated, is retracted by a predetermined length after each weft insertion by a deflecting element movable transversely to the weft insertion direction and locally deflected from an essentially stretched thread path into a loop-like angled thread path and out of this during a subsequent weft insertion is in each case returned against the stretched thread path.
- the invention further relates to a weaving machine for carrying out the method.
- a loom of the type mentioned at the beginning of EP-A-0 155 432 contains a nozzle arrangement with a compressed air nozzle for accelerating and a compressed air nozzle for braking the between the supply spool and the deflecting element Weft insertion device to be supplied, and a compressed air nozzle arranged between the deflection element and the weft insertion device for transferring the weft thread to the insertion member.
- the nozzle of the known arrangement intended to accelerate the weft thread is pressurized with compressed air during most of the weft insertion process in order to prevent the weft thread from being pulled off by the insertion element alone.
- the compressed air supply to this acceleration nozzle is shut off and compressed air is applied to the brake nozzle acting in the opposite direction.
- the thread transfer nozzle is only activated before the weft insertion in order to insert the end of the weft thread to be gripped into the insertion element.
- the known embodiment with the acceleration nozzle which is effective essentially throughout the entire weft insertion period, requires a relatively complex arrangement and control of the compressed air supply and has a relatively high compressed air requirement.
- the object of the invention is to provide a method for the controlled feeding of the weft thread to the weft insertion device, which is further developed in this regard, and a correspondingly simplified weaving machine, which allows gentle guiding of the weft thread to be fed to the weft insertion device with less effort than before and through the one sudden stress on the weft thread, in particular when returning the deflected weft thread length against the stretched thread path is avoided.
- the weft thread is only accelerated during the relatively short initial phase, which is critical for a sudden load, by a correspondingly short supply of compressed air. It has been shown that in this way, with a minimal compressed air requirement and with a simple nozzle arrangement, possibly with a single compressed air nozzle, a reliable return of the weft thread into the optimal stretch position for the weft insertion is guaranteed, the thread tension in the weft thread to be inserted only during a precise definable and variable time period is influenced according to different parameters. Accordingly, the occurrence of a "stretching blow" when stretching the deflected weft thread length can be prevented and thus an inadmissible stress on the weft thread can be avoided.
- the weaving machine according to the invention for performing the method is the subject of claim 7.
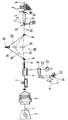
- a weft 1 is drawn off from a stationary weft supply spool 2, which is arranged outside the loom 4 of the loom formed by warp threads 3.
- the weft thread 1 running out of the supply spool 2 is wound onto a drum store 5, drawn off overhead in the axial direction and guided through a thread brake 7, a compressed air nozzle 6 and a deflection device 10 into a weft insertion device 11.
- the deflection device 10 contains two fixed guide eyelets 8, 8 'and a deflection element 16 arranged movably between them and adjustable transversely to the weft insertion direction , shown a projectile 14 provided with a weft thread clip 13.
- the projectile 14 can be fired into the shed 4 by a striking lever 15, the weft thread 1 being inserted.
- the projectile 14 is braked and pushed back into a thread release position by a defined amount.
- the weft thread 1 is deflected by the deflecting element 16 from a substantially stretched thread path 1a shown in dash-dotted lines into a loop path-like thread path 1b also shown in dash-dotted lines, so that the weft thread 1 is held taut in the shed 4. Then the weft thread 1 is knocked on in a known manner by a weaving leaf (not shown) in the tip of the shed 4 on the fabric 18 formed there and cut off by a pair of scissors 17 on the weft side.
- the end of the weft thread 1 that remains outside the shed 4 is then, as is also known, returned by the thread clamp 12 from the area of the scissors 17 into the position shown and for a subsequent weaving cycle to be transferred to another Projectile 14 ready.
- the weft thread 1 is further deflected by the deflecting element 16 out of the thread path 1b into the angled thread path 1c shown with solid lines and is kept tensioned accordingly.
- the weaving cycles can each be determined in a known manner by one revolution of a control shaft 20 of the weaving machine, from which the drives and control functions of all units of the weaving machine are derived.
- the compressed air nozzle 6 is connected via a control valve 21, which can be triggered like a trigger, to a compressed air supply line 22, which is provided with a pressure gauge 23 and is connected to a compressed air source, not shown.
- the control valve 21 can be adjusted in any manner, as shown via an electromagnetic actuating device, depending on the respective angular position of the control shaft 20 between a blocking position shown which blocks the compressed air supply to the compressed air nozzle 6 and a flow position which releases the compressed air supply.
- the control valve 21 is held in the blocking position for most of the weaving cycle and can only be adjusted to the flow position by means of a switching segment 24 indicated in the drawing, during a precisely definable fraction of the weaving cycle, which corresponds to a partial rotation of the control shaft 20 by an angle of rotation ⁇ .
- the switching segment 24, which extends over an angle of rotation ⁇ approximately 90 °, corresponds to an initial phase of the weft insertion process, in which the projectile 14 is shot into the shed 4 and which comprises at least part of the time period in which the deflection element 16 is out the deflected thread web 1c is returned against the stretched thread web 1a.
- the compressed air nozzle 6 is supplied only during this defined initial phase by means of a relatively high pressure, for example approximately 2 to 3 bar Compressed air is applied so that the section 1 'of the weft thread 1 located upstream of the guide eyelet 8 is additionally accelerated during the return movement of the deflecting element 16 into the position 16' shown in broken lines by a strong compressed air blast in the weft insertion direction according to arrow 9. This prevents the weft thread 1 from being impermissibly stressed by a "stretching stroke" when the thread path 1c is stretched out.
- a relatively high pressure for example approximately 2 to 3 bar Compressed air is applied so that the section 1 'of the weft thread 1 located upstream of the guide eyelet 8 is additionally accelerated during the return movement of the deflecting element 16 into the position 16' shown in broken lines by a strong compressed air blast in the weft insertion direction according to arrow 9.
- the start and duration of the time period provided for the application of the compressed air nozzle 6 are variable within an adjustment range given by the design and the performance data of the weaving machine and can take place within the weaving cycle, e.g. according to the yarn material to be processed, adapted to the respective conditions.
- the compressed air supply to the compressed air nozzle 6 can be controlled so that the maximum air pressure provided for the additional acceleration of the weft thread 1 essentially only in the second half of that for the return of the deflecting element 16 or Weft thread 1 is effective against the thread path 1a certain period. Accordingly, it can be achieved that the section 1 ′ of the weft thread 1 located upstream of the guide eyelet 8 is accelerated from the rest position to the desired speed only shortly before the stretched position of the weft thread 1 is reached, and thus an abrupt stress on the weft thread 1 is avoided at the crucial point in time.
- the pressure of the compressed air provided for the additional acceleration of the weft thread 1 can expediently be built up essentially during the first half of the period of time intended for the return of the weft thread 1 against the thread path 1a.
- the section 1 'of the weft thread 1 located upstream of the guide eyelet 8 can thus move from the rest position to the desired speed, regardless of the section 1' 'located downstream of the guide eyelet 8' which is already in motion due to the projectile 14 being fired be accelerated.
- the start of the compressed air supply can be varied within a period of time within a period of time before the start of the time period provided for the return of the weft thread 1 against the thread path 1a, as determined by the time the projectile 14 was fired predetermined fraction, e.g. 10% of the time period mentioned or a rotation angle ⁇ of approximately 0 to 10 ° of the control shaft 20 corresponds.
- a balanced loading of the weft thread 1 during the weft insertion process can be achieved by the compressed air supply to the compressed air nozzle 6 is controlled that the section 1 'of the weft thread 1 located upstream of the guide eyelet 8 is in each case pre-accelerated to a speed which is a predetermined fraction, for example half, of the speed of the section 1' located downstream of the guide eyelet 8 'and accelerated by the projectile 14 'corresponds to the weft thread 1.
- a second compressed air nozzle in addition to the compressed air nozzle 6 blowing in the weft insertion direction (arrow 9), a second compressed air nozzle, not shown, which blows in the opposite direction can also be provided, which, in a known manner, for braking the weft thread 1 during an end phase of the weft insertion process, for example Compressed air can be applied via a correspondingly controllable control valve.
- the thread brake 7 can optionally be omitted or, e.g. for the processing of fine weft yarns, only as an organ for holding and releasing the weft thread 1 and controlled in certain angular sections of the weaving cycle.
- the compressed air nozzle 6 and the brake nozzle can also be arranged in a combined, common unit, which can be controlled separately from one another.
- thread brake 7 between the compressed air nozzle 6 and the deflection device 10 is arranged.
- the invention can also be used for weaving machines with another weft insertion element, for example a rapier belt.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Looms (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft ein Verfahren zum Beeinflussen der Bewegung eines von einer Vorratsspule abzuziehenden, gegen eine Schusseintragseinrichtung einer Webmaschine, insbesondere einer Projektilwebmaschine, verlaufenden Schussfadens, der jeweils in einem Webzyklus für einen Schusseintrag an ein das Webfach durchsetzendes Schusseintragsorgan übergeben wird, wobei der Schussfaden jeweils durch eine zwischen der Vorratsspule und der Schusseintragseinrichtung angeordnete Druckluftdüse zusätzlich beschleunigt wird, nach jedem Schusseintrag durch ein quer zur Schusseintragsrichtung bewegliches Umlenkelement um eine vorbestimmte Länge zurückgezogen und örtlich aus einer im wesentlichen gestreckt verlaufenden Fadenbahn in eine schlaufenartig abgewinkelte Fadenbahn ausgelenkt und aus dieser bei einem folgenden Schusseintrag jeweils gegen die gestreckt verlaufende Fadenbahn zurückgeführt wird.The invention relates to a method for influencing the movement of a weft thread which is to be drawn off from a supply spool and runs against a weft insertion device of a weaving machine, in particular a projectile weaving machine, and which is transferred in each weaving cycle for a weft insertion to a weft insertion member penetrating the shed, the weft thread being passed through a compressed air nozzle arranged between the supply reel and the weft insertion device is additionally accelerated, is retracted by a predetermined length after each weft insertion by a deflecting element movable transversely to the weft insertion direction and locally deflected from an essentially stretched thread path into a loop-like angled thread path and out of this during a subsequent weft insertion is in each case returned against the stretched thread path.
Ferner betrifft die Erfindung eine Webmaschine zur Durchführung des Verfahrens.The invention further relates to a weaving machine for carrying out the method.
Eine aus der EP-A-0 155 432 bekannte Webmaschine der eingangs genannten Art enthält zwischen der Vorratsspule und dem Umlenkelement eine Düsenanordnung mit einer Druckluftdüse zum Beschleunigen und einer Druckluftdüse zum Abbremsen des der Schusseintragseinrichtung zuzuführenden Schussfadens, sowie eine zwischen dem Umlenkelement und der Schusseintragseinrichtung angeordnete Druckluftdüse zum Uebergeben des Schussfadens an das Eintragsorgan. Die zum Beschleunigen des Schussfadens bestimmte Düse der bekannten Anordnung wird während des grössten Teils des Schusseintragsvorganges mit Druckluft beaufschlagt, um ein Abziehen des Schussfadens allein durch das Eintragsorgan zu vermeiden. Gegen Ende des Schusseintragsvorganges, wenn das Eintragsorgan zu der Fangseite der Webmaschine gelangt, wird die Druckluftzufuhr zu dieser Beschleunigungsdüse abgestellt und die in die entgegengesetzte Richtung wirkende Bremsdüse mit Druckluft beaufschlagt. Die Fadenübergabedüse wird jeweils nur vor dem Schusseintrag aktiviert, um das zu ergreifende Ende des Schussfadens in das Eintragsorgan einzuführen. Die bekannte Ausführung mit der im wesentlichen während der ganzen Schusseintragsdauer wirksamen Beschleunigungsdüse erfordert eine relativ aufwendige Anordnung und Steuerung der Druckluftversorgung und weist einen relativ hohen Druckluftbedarf auf. Bei Webmaschinen mit hoher Schusseintragsleistung kann zudem beim Zurückführen der schlaufenartig ausgelenkten Schussfadenlänge gegen die Strecklage, insbesondere beim Ausstrecken des ständig durch die Beschleunigungsdüse und durch das Schusseintragsorgan beschleunigten Schussfadenabschnitts, ein "Streckschlag" auftreten, der bei der Verarbeitung von empfindlichem Garnmaterial, z.B. Wolle, zu einem Schussfadenbruch führen kann.A loom of the type mentioned at the beginning of EP-A-0 155 432 contains a nozzle arrangement with a compressed air nozzle for accelerating and a compressed air nozzle for braking the between the supply spool and the deflecting element Weft insertion device to be supplied, and a compressed air nozzle arranged between the deflection element and the weft insertion device for transferring the weft thread to the insertion member. The nozzle of the known arrangement intended to accelerate the weft thread is pressurized with compressed air during most of the weft insertion process in order to prevent the weft thread from being pulled off by the insertion element alone. Towards the end of the weft insertion process, when the entry member reaches the catching side of the weaving machine, the compressed air supply to this acceleration nozzle is shut off and compressed air is applied to the brake nozzle acting in the opposite direction. The thread transfer nozzle is only activated before the weft insertion in order to insert the end of the weft thread to be gripped into the insertion element. The known embodiment with the acceleration nozzle, which is effective essentially throughout the entire weft insertion period, requires a relatively complex arrangement and control of the compressed air supply and has a relatively high compressed air requirement. In looms with a high weft insertion rate, when the loop-length deflected weft length is returned against the stretched position, in particular when the weft section that is constantly accelerated by the acceleration nozzle and by the weft insertion member, a "stretch stroke" can occur which occurs when processing sensitive yarn material, e.g. wool can cause a weft break.
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, ein insbesondere in dieser Hinsicht weiter entwickeltes Verfahren zum gesteuerten Zuführen des Schussfadens an die Schusseintragseinrichtung und eine entsprechend vereinfachte Webmaschine zu schaffen, die mit geringerem Aufwand als bisher eine schonende Führung des der Schusseintragseinrichtung zuzuführenden Schussfadens gestattet und durch die eine schlagartige Beanspruchung des Schussfadens, insbesondere beim Zurückführen der ausgelenkten Schussfadenlänge gegen die gestreckte Fadenbahn, vermieden wird.The object of the invention is to provide a method for the controlled feeding of the weft thread to the weft insertion device, which is further developed in this regard, and a correspondingly simplified weaving machine, which allows gentle guiding of the weft thread to be fed to the weft insertion device with less effort than before and through the one sudden stress on the weft thread, in particular when returning the deflected weft thread length against the stretched thread path is avoided.
Diese Aufgabe wird gemäss der Erfindung durch die im kennzeichnenden Teil des Patentanspruchs 1 angegebenen Merkmale gelöst.This object is achieved according to the invention by the features specified in the characterizing part of patent claim 1.
Durch das erfindungsgemässe Verfahren wird der Schussfaden nur während der relativ kurzen, für eine schlagartige Beanspruchung kritischen Anfangsphase, durch eine entsprechend kurzzeitige Druckluftzufuhr, zusätzlich beschleunigt. Es hat sich gezeigt, dass auf diese Weise, bei minimalem Druckluftbedarf und mit einer einfachen Düsenanordnung, gegebenenfalls mit einer einzigen Druckluftdüse, eine sichere Rückführung des Schussfadens in die für den Schusseintrag optimale Strecklage gewährleistet wird, wobei die Fadenspannung im einzutragenden Schussfaden nur während einer genau definierbaren und nach verschiedenen Parametern variierbaren Zeitspanne beeinflusst wird. Entsprechend kann die Entstehung eines "Streckschlags" beim Ausstrecken der ausgelenkten Schussfadenlänge verhindert und damit eine unzulässige Beanspruchung des Schussfadens vermieden werden.With the method according to the invention, the weft thread is only accelerated during the relatively short initial phase, which is critical for a sudden load, by a correspondingly short supply of compressed air. It has been shown that in this way, with a minimal compressed air requirement and with a simple nozzle arrangement, possibly with a single compressed air nozzle, a reliable return of the weft thread into the optimal stretch position for the weft insertion is guaranteed, the thread tension in the weft thread to be inserted only during a precise definable and variable time period is influenced according to different parameters. Accordingly, the occurrence of a "stretching blow" when stretching the deflected weft thread length can be prevented and thus an inadmissible stress on the weft thread can be avoided.
Die erfindungsgemässe Webmaschine zur Durchführung des Verfahrens ist Gegenstand des Anspruchs 7.The weaving machine according to the invention for performing the method is the subject of
Ausgestaltungen des Erfindungsgegenstandes sind in den abhängigen Ansprüchen angegeben.Embodiments of the subject matter of the invention are specified in the dependent claims.
Weitere Einzelheiten ergeben sich aus der folgenden Beschreibung eines in der Zeichnung schematisch dargestellten Ausführungsbeispiels der Erfindung, in Verbindung mit den Ansprüchen. Die einzige Figur der Zeichnung zeigt einige für die Erfindung wesentliche Teile einer Projektil-Webmaschine.Further details emerge from the following description of an exemplary embodiment of the invention shown schematically in the drawing, in conjunction with the claims. The only figure in the drawing shows some parts of a projectile weaving machine that are essential to the invention.
Bei der dargestellten Webmaschine wird ein Schussfaden 1 von einer ortsfesten Schussfaden-Vorratsspule 2 abgezogen, die ausserhalb des durch Kettfäden 3 gebildeten Webfachs 4 der Webmaschine angeordnet ist. Der von der Vorratsspule 2 ablaufende Schussfaden 1 wird auf einen Trommelspeicher 5 aufgewickelt, von diesem in axialer Richtung über Kopf abgezogen und durch eine Fadenbremse 7, eine Druckluftdüse 6 und eine Umlenkvorrichtung 10 in eine Schusseintragseinrichtung 11 geführt. Die Umlenkvorrichtung 10 enthält zwei feststehende Führungsösen 8, 8' und ein zwischen diesen beweglich angeordnetes, quer zur Schusseintragsrichtung verstellbares Umlenkelement 16. In der Schusseintragseinrichtung 11 wird das Ende des Schussfadens 1 jeweils durch eine Uebergabedüse oder, wie darstellt, eine Fadenklemme 12 an ein Schusseintragsorgan, darstellungsgemäss ein mit einer Schussfadenklammer 13 versehendes Projektil 14, übergeben. Das Projektil 14 kann in bekannter Weise durch einen Schlaghebel 15 in das Webfach 4 geschossen werden, wobei der Schussfaden 1 eingetragen wird. Auf der nicht dargestellten Fangseite der Webmaschine wird das Projektil 14 abgebremst und um ein definiertes Mass in eine Fadenlösestellung zurückgeschoben.In the loom shown, a weft 1 is drawn off from a stationary
Während der Rückschiebebewegung des Projektils 14 wird der Schussfaden 1 durch das Umlenkelement 16 aus einer strichpunktiert dargestellten, im wesentlichen gestreckten Fadenbahn 1a in eine ebenfalls strichpunktiert dargestellte, schlaufenartig abgewinkelte Fadenbahn 1b ausgelenkt, so dass der Schussfaden 1 im Webfach 4 gespannt gehalten wird. Hierauf wird der Schussfaden 1 in bekannter Weise durch ein nicht dargestelltes Webeblatt in der Spitze des Webfaches 4 an das dort gebildete Gewebe 18 angeschlagen und durch eine schussseitige Schere 17 abgeschnitten. Das ausserhalb des Webfaches 4 verbleibende Ende des Schussfadens 1 wird hierauf, wie ebenfalls bekannt, durch die Fadenklemme 12 aus dem Bereich der Schere 17 in die dargestellte Stellung zurückgeführt und für einen folgenden Webzyklus zur Uebergabe an ein weiteres Projektil 14 bereitgehalten. Während dieser Rückführbewegung der Fadenklemme 12 wird der Schussfaden 1 durch das Umlenkelement 16 aus der Fadenbahn 1b in die mit vollen Linien dargestellte abgewinkelte Fadenbahn 1c weiter ausgelenkt und entsprechend gespannt gehalten.During the push-back movement of the
Die Webzyklen können in bekannter Weise je durch eine Umdrehung einer Steuerwelle 20 der Webmaschine bestimmt sein, von der die Antriebe und Steuerfunktionen aller Aggregate der Webmaschine abgeleitet werden. Die Druckluftdüse 6 ist über ein triggerartig ansteuerbares Steuerventil 21 an eine Druckluft-Zuführleitung 22 angeschlossen, die mit einem Manometer 23 versehen und mit einer nicht dargestellten Druckluftquelle verbunden ist. Das Steuerventil 21 kann in beliebiger Weise, darstellungsgemäss über eine elektromagnetische Stelleinrichtung, in Abhängigkeit von der jeweiligen Winkelstellung der Steuerwelle 20 zwischen einer dargestellten, die Druckluftzufuhr zur Druckluftdüse 6 sperrenden Sperrstellung und einer die Druckluftzufuhr freigebenden Durchflussstellung verstellt werden. Das Steuerventil 21 wird während des grössten Teils des Webzyklus in der Sperrstellung gehalten und ist nur während eines genau definierbaren Bruchteils des Webzyklus, der einer Teilumdrehung der Steuerwelle 20 um einen Drehwinkel α entspricht, über ein in der Zeichnung angedeutetes Schaltsegment 24 in die Durchflussstellung verstellbar.The weaving cycles can each be determined in a known manner by one revolution of a
Das Schaltsegment 24, das sich darstellungsgemäss über einen Drehwinkel α = ca. 90° erstreckt, entspricht einer Anfangsphase des Schusseintragsvorganges, in welcher das Projektil 14 in das Webfach 4 eingeschossen wird und welche mindestens einen Teil des Zeitabschnitts umfasst, in dem das Umlenkelement 16 aus der ausgelenkten Fadenbahn 1c gegen die gestreckte Fadenbahn 1a zurückgeführt wird. Entsprechend wird die Druckluftdüse 6 nur während dieser definierten Anfangsphase durch die mit einem relativ hohen Druck - z.B. ca. 2 bis 3 bar - zugeführte Druckluft beaufschlagt, so dass der stromaufwärts der Führungsöse 8 gelegene Abschnitt 1' des Schussfadens 1 während der Rückführbewegung des Umlenkelementes 16 in die strichpunktiert dargestellte Stellung 16' durch einen kräftigen Druckluftstoss in Schusseintragsrichtung gemäss Pfeil 9 zusätzlich beschleunigt wird. Dadurch wird vermieden, dass der Schussfaden 1 beim Ausstrecken der Fadenbahn 1c durch einen "Streckschlag" unzulässig beansprucht wird. Wenn das Umlenkelement 16 nach der Teilumdrehung der Steuerwelle 20 um den Drehwinkel α seine Stellung 16' im Bereich der Fadenbahn 1a erreicht hat, wird das Steuerventil 21 in die Sperrstellung zurückgestellt und die Druckluftzufuhr während des restlichen Teils des Webzyklus gesperrt, in welchem der Schussfaden 1 ausschliesslich durch das Projektil 14 vom Trommelspeicher 5 abgezogen, in das Webfach 4 eingetragen und schliesslich, in einer Endphase des Schusseintragsvorganges, durch Betätigung der Fadenbremse 7 abgebremst wird.The
Beginn und Dauer des zur Beaufschlagung der Druckluftdüse 6 vorgesehenen Zeitabschnitts sind innerhalb eines durch die Bauart und die Leistungsdaten der Webmaschine gegebenen Verstellbereichs variabel und können innnerhalb des Webzyklus, z.B. entsprechend dem zu verarbeitenden Garnmaterial, an die jeweiligen Verhältnisse angepasst werden. Der für die Beaufschlagung der Druckluftdüse 6 massgebende Drehwinkel α der Steuerwelle 20 kann daher innerhalb bestimmter Grenzen beliebig, z.B. innerhalb eines Bereichs von α = 60° bis 120°, frei gewählt und dem jeweiligen Bewegungsbereich des Umlenkelements zwischen den Stellungen 16 und 16' entsprechend genau eingestellt werden.The start and duration of the time period provided for the application of the
Die Druckluftzufuhr zur Druckluftdüse 6 kann nach einer Ausführungsform so gesteuert werden, dass der für die zusätzliche Beschleunigung des Schussfadens 1 vorgesehene maxiamale Luftdruck im wesentlichen erst in der zweiten Hälfte des für das Zurückführen des Umlenkelements 16 bzw. des Schussfadens 1 gegen die Fadenbahn 1a bestimmten Zeitabschnitts wirksam ist. Entsprechend kann erreicht werden, dass der stromaufwärts der Führungsöse 8 gelegene Abschnitt 1' des Schussfadens 1 erst kurz vor dem Erreichen der Strecklage des Schussfadens 1 aus der Ruhelage auf die gewünschte Geschwindigkeit vorbeschleunigt und damit im entscheidenden Zeitpunkt eine schlagartige Beanspruchung des Schussfadens 1 vermieden wird.According to one embodiment, the compressed air supply to the
Der für die zusätzliche Beschleunigung des Schussfadens 1 vorgesehene Druck der Druckluft kann zweckmässigerweise im wesentlichen während der ersten Hälfte des für das Zurückführen des Schussfadens 1 gegen die Fadenbahn 1a bestimmten Zeitabschnitts aufgebaut werden. Während dieser Teilphase kann somit der stromaufwärts der Führungsöse 8 gelegene Abschnitt 1' des Schussfadens 1 - unabhängig von dem bereits durch den Abschuss des Projektils 14 in Bewegung befindlichen, stromabwärts der Führungsöse 8' gelegenen Abschnitt 1'' - aus der Ruhelage auf die gewünschte Geschwindigkeit vorbeschleunigt werden.The pressure of the compressed air provided for the additional acceleration of the weft thread 1 can expediently be built up essentially during the first half of the period of time intended for the return of the weft thread 1 against the thread path 1a. During this partial phase, the section 1 'of the weft thread 1 located upstream of the
Zur Beeinflussung des Druckaufbaues in der Druckluftdüse 6 kann nach einer Ausführungsform der Beginn der Druckluftzufuhr zeitlich vor dem durch den Zeitpunkt des Abschusses des Projektils 14 bestimmten Beginn des für das Zurückführen des Schussfadens 1 gegen die Fadenbahn 1a vorgesehenen Zeitabschnitts innerhalb einer Zeitspanne variiert werden, die einem vorbestimmten Bruchteil, z.B. 10%, des genannten Zeitabschnitts bzw. einem Drehwinkel β von ca. 0 bis 10° der Steuerwelle 20 entspricht.In order to influence the pressure build-up in the
Nach einer Ausführungsform der Erfindung, an einer Webmaschine mit einer Schusseintragsgeschwindigkeit, die z.B. 40 m/sec betragen kann, ist eine ausgeglichene Beanspruchung des Schussfadens 1 während des Schusseintragsvorganges dadurch erzielbar, dass die Druckluftzufuhr zur Druckluftdüse 6 so gesteuert wird, dass der stromaufwärts der Führungsöse 8 gelegene Abschnitt 1' des Schussfadens 1 jeweils auf eine Geschwindigkeit vorbeschleunigt wird, die einem vorbestimmten Bruchteil, z.B. der Hälfte, der Geschwindigkeit des durch das Projektil 14 beschleunigten, stromabwärts der Führungsöse 8' gelegenen Abschnitts 1'' des Schussfadens 1 entspricht.According to one embodiment of the invention, on a weaving machine with a weft insertion speed, which can be, for example, 40 m / sec, a balanced loading of the weft thread 1 during the weft insertion process can be achieved by the compressed air supply to the
Eine schonende Beanspruchung des Schussfadens 1 kann ferner dadurch erzielt werden, dass die Druckluftzufuhr zur Druckluftdüse 6 so gesteuert wird, dass die zur Vorbeschleunigung des Abschnitts 1' des Schussfadens 1 vorgesehene Geschwindigkeit der Druckluft im wesentlichen innerhalb des ersten Drittels des für das Zurückführen des Schussfadens 1 gegen die Fadenbahn 1a vorgesehenen Zeitabschnitts, beim dargestellten Beispiel nach einer Teilumdrehung des Steuerwelle 20 um einen Drehwinkel Gamma = ca. 25° nach dem Abschuss des Projektils 14, erreicht wird.A gentle loading of the weft thread 1 can also be achieved in that the compressed air supply to the
Nach einer abgewandelten Ausführungsform kann, zusätzlich zu der in Schusseintragsrichtung (Pfeil 9) blasenden Druckluftdüse 6, auch eine in die entgegengesetzte Richtung blasende, nicht dargestellte zweite Druckluftdüse vorgesehen sein, welche in bekannter Weise zur Bremsung des Schussfadens 1 während einer Endphase des Schusseintragsvorganges, etwa über ein entsprechend ansteuerbares Steuerventil, mit Druckluft beaufschlagbar ist. Dabei kann gegebenenfalls die Fadenbremse 7 weggelassen oder , z.B. für die Verarbeitung feiner Schussgarne, lediglich als Organ zum Festhalten und Freigeben des Schussfadens 1 beibehalten und in bestimmten Winkelabschnitten des Webzyklus entsprechend angesteuert werden. Die Druckluftdüse 6 und die Bremsdüse können auch - voneinander getrennt ansteuerbar - in einem kombinierten, gemeinsamen Aggregat angeordnet sein.According to a modified embodiment, in addition to the
Es ist auch eine Ausführung möglich, bei der die Fadenbremse 7 zwischen der Druckluftdüse 6 und der Umlenkvorrichtung 10 angeordnet ist. Ferner ist die Erfindung auch für Webmaschinen mit einem anderen Schusseintragsorgan, z.B. einem Greiferband, verwendbar.An embodiment is also possible in which the
Claims (8)
- A method of influencing the motion of a weft yarn (1)
which has to be drawn off a stock bobbin (2) and runs towards a weft insertion mechanism (11) of a loom, in particular a projectile loom, and at any given time in a weaving cycle is transferred for a weft insertion to a weft insertion member (14) which passes through the shed (4), where the weft yarn (1) is additionally accelerated at any given time by a compressed-air nozzle arranged between the stock bobbin (2) and the weft insertion mechanism (11), and after the weft insertion is drawn back by a predetermined length by a deflector element (16) movable transversely to the direction of weft insertion (arrow 9) and deflected locally from a yarn path (1a) running essentially stretched into a yarn path (1c) cranked like a loop, and upon a following weft insertion is returned from the latter at any given time towards the yarn path (1a) running stretched,
characterized in that for the additional acceleration of the weft yarn (1) at any given time within a predetermined fraction of the weaving cycle which corresponds with a starting phase of the weft insertion process which comprises at least one part of a certain period intended for the return of the weft yarn (1) from the cranked yarn path (1c) towards the yarn path (1a) running essentially stretched, the compressed air nozzle is acted upon by compressed air, and that after this return of the weft yarn (1) the compressed-air feed to the compressed-air nozzle (6) is blocked during the remaining part of the weaving cycle. - A method as in Claim 1, characterized in that
the compressed-air feed to the compressed-air nozzle (6) is so controlled that a maximum pressure of the compressed air, foreseen for the additional acceleration of the weft yarn (1), is effective essentially in the second half of the period intended for returning the weft yarn (1) towards the yarn path (1a) running stretched. - A method as in Claim 1 or 2, characterized in that
the pressure of the compressed air, foreseen for the additional acceleration of the weft yarn (1), becomes built up essentially during the first half of the period intended for returning the weft yarn (1) towards the yarn path (1a) running stretched. - A method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterized in that with respect to time the start of the compressed-air feed to the compressed-air nozzle (6) is effected before the start of the period which is intended for the return of the weft yarn (1) towards the stretched yarn path (1a), within a time interval which corresponds with a predetermined fraction, e.g., 10% of the aforesaid period. - A method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterized in that the compressed-air feed to the compressed-air nozzle (6) is so controlled that a portion (1') of the weft yarn (1) laid upstream of the deflector element (16) is accelerated to a speed which corresponds with a predetermined fraction, e.g., half the speed of a portion (1") of the weft yarn (1) which is laid downstream of the deflector element (16) and accelerated by the weft insertion member (14). - A method as in Claim 5, characterized in that
the compressed-air feed to the compressed-air nozzle (6) is so controlled that the speed of the compressed air foreseen for the preacceleration of the portion (1') of yarn laid upstream of the deflector element (16) is reached essentially within the first third of the period foreseen for returning the weft yarn (1) towards the stretched yarn path (1a). - A loom for the performance of the method as in
one of the preceding Claims, characterized in that the compressed air nozzle (6) is connected to a control valve (21) which is only intended for brief activation within the predetermined fraction of the weaving cycle and at the start of the weft insertion process is adjustable from a blocking position blocking a compressed air feed into a flow position releasing the compressed air feed to the cmpressed air nozzle, and into the blocking position after the starting phase of the weft insertion process determined by the return of the deflector element (16) towards the yarn path (1a) running stretched, and adopts this blocking position until the next weft insertion. - A loom as in Claim 7, characterized in that
in the case of a weaving cycle determined in each case by one revolution of a control shaft (20) the fraction of this weaving cycle predetermined for the activation of the compressed air nozzle (6) corresponds with a partial revolution of the control shaft (20) through an angle of rotation (α) of from about 60° to 120°, e.g., 90°.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP93810220A EP0617153B1 (en) | 1993-03-26 | 1993-03-26 | Process to influence the movement of a weft yarn drawn from a storage bobbin to the weft inserting device of a loom and loom to carry out the process |
| DE59304128T DE59304128D1 (en) | 1993-03-26 | 1993-03-26 | Method for influencing the movement of a weft thread to be drawn off from a supply spool and running against a weft insertion device of a weaving machine and weaving machine for carrying out the method |
| US08/184,317 US5423355A (en) | 1993-03-26 | 1994-01-21 | Method and apparatus for limiting stresses in weft yarn advancing towards a weft insertion mechanism |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP93810220A EP0617153B1 (en) | 1993-03-26 | 1993-03-26 | Process to influence the movement of a weft yarn drawn from a storage bobbin to the weft inserting device of a loom and loom to carry out the process |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0617153A1 EP0617153A1 (en) | 1994-09-28 |
| EP0617153B1 true EP0617153B1 (en) | 1996-10-09 |
Family
ID=8214941
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP93810220A Expired - Lifetime EP0617153B1 (en) | 1993-03-26 | 1993-03-26 | Process to influence the movement of a weft yarn drawn from a storage bobbin to the weft inserting device of a loom and loom to carry out the process |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5423355A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0617153B1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE59304128D1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19611320C2 (en) * | 1996-03-22 | 1999-05-20 | Dornier Gmbh Lindauer | Method and device for pneumatically supporting the insertion and tensioning of a weft thread in weaving machines |
| DE59707877D1 (en) * | 1997-11-28 | 2002-09-05 | Sulzer Textil Ag Rueti | Method and device for inserting a weft thread in a row shed loom |
| DE102010044127B3 (en) * | 2010-11-18 | 2011-12-29 | Lindauer Dornier Gesellschaft Mit Beschränkter Haftung | Gripper head for the entry of weft threads on a rapier loom and a rapier loom with such a gripper head |
| JP5229351B2 (en) * | 2011-05-06 | 2013-07-03 | 株式会社豊田自動織機 | Weft storage device in loom |
| JP5273205B2 (en) * | 2011-05-27 | 2013-08-28 | 株式会社豊田自動織機 | Weft storage device in loom |
| DE102012208158B3 (en) * | 2012-05-15 | 2013-09-05 | Lindauer Dornier Gmbh | Air jet loom with a device for compressed air supply |
| SE1650986A1 (en) * | 2016-07-06 | 2018-01-07 | Iro Ab | Weft yarn feeding arrangement with motor drive |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH654601A5 (en) * | 1982-04-07 | 1986-02-28 | Sulzer Ag | Weft thread tensioning device for weaving machines, especially gripper pojectile weaving machines. |
| EP0155432A1 (en) * | 1984-03-23 | 1985-09-25 | GebràDer Sulzer Aktiengesellschaft | Loom |
| EP0189497B1 (en) * | 1985-01-28 | 1988-08-24 | GebràDer Sulzer Aktiengesellschaft | Arrangement for the insertion of at least one weft thread into looms |
| EP0389410A1 (en) * | 1989-03-17 | 1990-09-26 | Sulzer RàTi Ag | Weft threading system for a loom |
| US5199468A (en) * | 1990-06-21 | 1993-04-06 | Sulzer Brothers Limited | Weft yarn clearing device |
-
1993
- 1993-03-26 DE DE59304128T patent/DE59304128D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1993-03-26 EP EP93810220A patent/EP0617153B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1994
- 1994-01-21 US US08/184,317 patent/US5423355A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US5423355A (en) | 1995-06-13 |
| DE59304128D1 (en) | 1996-11-14 |
| EP0617153A1 (en) | 1994-09-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0605531B1 (en) | Power loom and insertion brake for power looms | |
| DE69107536T2 (en) | Device for tension regulation and withdrawal of weft yarn in weaving machines. | |
| EP0475892A1 (en) | Yarn brake for looms | |
| DE10244694B4 (en) | Method for holding a weft thread in the region of a main nozzle of a jet loom and jet loom for carrying out the method | |
| EP1440193B1 (en) | Yarn processing system | |
| EP0155432A1 (en) | Loom | |
| EP0617153B1 (en) | Process to influence the movement of a weft yarn drawn from a storage bobbin to the weft inserting device of a loom and loom to carry out the process | |
| DE19611320C2 (en) | Method and device for pneumatically supporting the insertion and tensioning of a weft thread in weaving machines | |
| DE9420562U1 (en) | Ribbon loom | |
| EP1038061B1 (en) | Storage device | |
| EP0963470B1 (en) | Measuring delivery device | |
| DE60200740T2 (en) | Apparatus for attenuating the unwinding of yarn turns from the cylinder to form the weft supply in weft feeding apparatus for jet looms | |
| EP0445489A1 (en) | Weft measuring device for a loom | |
| DE10213639C1 (en) | Method and device for feeding a clamped weft thread to a gripper of a weaving machine | |
| EP0022226B1 (en) | Jet loom | |
| EP1576219B1 (en) | Device and method for stretching | |
| EP0155431A1 (en) | Process for weft insertion in looms, and loom for realising this process | |
| DE2752094A1 (en) | Pneumatic weft yarn inserter - has torsion spring controlled guide deflecting yarn from its rectilinear path to prevent retraction of yarn inserted into shed | |
| DE4008864A1 (en) | Airjet looms - have automatic device to reduce weft breaks on weft insertion | |
| DE3345627A1 (en) | DEVICE FOR INSERTING A WIDE THREAD IN THE COMPARTMENT OF A WEAVING MACHINE | |
| EP1606442B1 (en) | Weaving machine, particularly a ribbon weaving machine | |
| EP0390730A1 (en) | Yarn-feeding device, yarn-feeding nozzle for such a device and their use | |
| DE102023205630B3 (en) | METHOD FOR FORMING A LOOP-SHAPED SEWING EDGE ON A RAPPER WEAVING MACHINE AND RAPPER WEAVING MACHINE | |
| CH508074A (en) | Weft yarn feeder for a loom | |
| EP1699959A1 (en) | Device for picking up a section of a weft thread |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19950301 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19951219 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): DE |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59304128 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19961114 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20040305 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20051001 |