EP0505812B1 - Procédé de séparation d'air à basse température - Google Patents
Procédé de séparation d'air à basse température Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0505812B1 EP0505812B1 EP92104008A EP92104008A EP0505812B1 EP 0505812 B1 EP0505812 B1 EP 0505812B1 EP 92104008 A EP92104008 A EP 92104008A EP 92104008 A EP92104008 A EP 92104008A EP 0505812 B1 EP0505812 B1 EP 0505812B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- stream
- sub
- stage
- pressure
- work
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04248—Generation of cold for compensating heat leaks or liquid production, e.g. by Joule-Thompson expansion
- F25J3/04284—Generation of cold for compensating heat leaks or liquid production, e.g. by Joule-Thompson expansion using internal refrigeration by open-loop gas work expansion, e.g. of intermediate or oxygen enriched (waste-)streams
- F25J3/0429—Generation of cold for compensating heat leaks or liquid production, e.g. by Joule-Thompson expansion using internal refrigeration by open-loop gas work expansion, e.g. of intermediate or oxygen enriched (waste-)streams of feed air, e.g. used as waste or product air or expanded into an auxiliary column
- F25J3/04303—Lachmann expansion, i.e. expanded into oxygen producing or low pressure column
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04006—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit
- F25J3/04012—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit by compression of warm gaseous streams; details of intake or interstage cooling
- F25J3/04018—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit by compression of warm gaseous streams; details of intake or interstage cooling of main feed air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04006—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit
- F25J3/04012—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit by compression of warm gaseous streams; details of intake or interstage cooling
- F25J3/04024—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit by compression of warm gaseous streams; details of intake or interstage cooling of purified feed air, so-called boosted air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04006—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit
- F25J3/04078—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit providing pressurized products by liquid compression and vaporisation with cold recovery, i.e. so-called internal compression
- F25J3/0409—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit providing pressurized products by liquid compression and vaporisation with cold recovery, i.e. so-called internal compression of oxygen
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04006—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit
- F25J3/04078—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit providing pressurized products by liquid compression and vaporisation with cold recovery, i.e. so-called internal compression
- F25J3/04103—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit providing pressurized products by liquid compression and vaporisation with cold recovery, i.e. so-called internal compression using solely hydrostatic liquid head
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04006—Providing pressurised feed air or process streams within or from the air fractionation unit
- F25J3/04109—Arrangements of compressors and /or their drivers
- F25J3/04115—Arrangements of compressors and /or their drivers characterised by the type of prime driver, e.g. hot gas expander
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04151—Purification and (pre-)cooling of the feed air; recuperative heat-exchange with product streams
- F25J3/04157—Afterstage cooling and so-called "pre-cooling" of the feed air upstream the air purification unit and main heat exchange line
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04151—Purification and (pre-)cooling of the feed air; recuperative heat-exchange with product streams
- F25J3/04187—Cooling of the purified feed air by recuperative heat-exchange; Heat-exchange with product streams
- F25J3/04193—Division of the main heat exchange line in consecutive sections having different functions
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04406—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air using a dual pressure main column system
- F25J3/04412—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air using a dual pressure main column system in a classical double column flowsheet, i.e. with thermal coupling by a main reboiler-condenser in the bottom of low pressure respectively top of high pressure column
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2215/00—Processes characterised by the type or other details of the product stream
- F25J2215/50—Oxygen or special cases, e.g. isotope-mixtures or low purity O2
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2240/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for expanding of process streams
- F25J2240/02—Expansion of a process fluid in a work-extracting turbine (i.e. isentropic expansion), e.g. of the feed stream
- F25J2240/10—Expansion of a process fluid in a work-extracting turbine (i.e. isentropic expansion), e.g. of the feed stream the fluid being air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2245/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for recycling of process streams
- F25J2245/40—Processes or apparatus involving steps for recycling of process streams the recycled stream being air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2270/00—Refrigeration techniques used
- F25J2270/04—Internal refrigeration with work-producing gas expansion loop
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S62/00—Refrigeration
- Y10S62/939—Partial feed stream expansion, air
Definitions
- the invention relates to a process for the low-temperature extraction of air, in which feed air is compressed, cleaned, cooled and divided into several partial streams into the pressure stage and into the low-pressure stage of a two-stage rectification device, the feed air being brought to approximately the pressure stage pressure in a first compressor stage Cleaning stage is cleaned by adsorption and then divided into a first and a second partial stream, the first partial stream is fed to the pressure stage and the second partial stream is expanded while performing work and is fed to the low-pressure stage, the work obtained in the expansion of the second partial stream to compress a process stream, in particular air is used.
- DE-A-3643359 shows such a method, in which both partial flows are fed downstream of the cleaning stage to a main heat exchanger, the warm end of which has approximately ambient temperature.
- the second partial flow is cooled to a lower temperature in the main heat exchanger before it is relieved of pressure.
- the work gained during the expansion is used exclusively to compress the second partial flow.
- One of the relevant methods of GB-A-1520103 is to bring the total air upstream of the cleaning stage from ambient temperature into indirect heat exchange with the total air downstream of the cleaning stage .
- the invention is therefore based on the object of specifying a method, which has a high efficiency and in particular a more cost effective air purification.
- This object is achieved in that the second partial stream is heated to above ambient temperature in indirect heat exchange against compressed feed air before the work-relieving expansion and in that the process stream, for the compression of which work obtained in the expansion of the second partial stream is used, is not equal to the second partial stream .
- the process according to the invention makes it possible to treat the entire feed air in a single cleaning stage, namely under pressure stage pressure.
- the investment costs and the high operating costs for an additional low-pressure cleaning stage are eliminated.
- the excess compression energy that is put into the second partial flow can be recovered in a turbine partly as mechanical work and partly converted into cold.
- the work is usually given completely and directly to a compressor by mechanical coupling, but additionally or alternatively, a generator can also be driven.
- a generator can also be driven.
- the second partial flow is previously warmed to above ambient temperature . In this way, heat can be extracted from compressed compressed air cheaply.
- a product or an intermediate product flow can flow through the compressor driven by the turbine. In general, it is most convenient to use the work gained from work relaxation to compress feed air.
- cooling can be generated in the process by branching off a third partial stream downstream of the adsorption, post-compressing in a second compressor stage, then cooling, relieving work and feeding it into the low-pressure stage, with work obtained during the work-relieving expansion of the third partial stream to post-compress the third Partial flow is used in the second compressor stage. In this case, pressure that is not required is also used to generate process cooling.
- the invention provides two variants for the transfer of work and cold:
- the feed air must be pre-cooled anyway. It generally leaves a cooler operated with cooling water of approximately 25 ° C. and a temperature of approximately 35 ° C. and must be brought to approximately 10 ° C. to 15 ° C. for the adsorption in the cleaning stage. This is generally accomplished by an external refrigeration system or by cold cooling water taken from an evaporative cooler operated with dry nitrogen. This pre-cooling can now be at least partially carried out by the cleaned second partial flow, so that the costs for the refrigeration system are reduced or the nitrogen is available for other tasks.
- work gained in the work-relieving expansion of the second partial flow is used in a third compressor stage for post-compression of the third partial flow.
- This third compressor stage is preferably connected upstream of the second compressor stage and serves to increase the pressure difference during the expansion of the third partial flow. It is also expedient if, in addition or as an alternative, a fourth partial flow is branched off downstream of the cleaning stage, subsequently compressed in a fourth compressor stage, then cooled, decompressed and fed into the pressure stage, with work obtained in the work-relieving relaxation of the second partial flow to recompress the fourth partial flow in the fourth compressor stage is used.
- the relief of the fourth partial flow is generally brought about by a throttle valve.
- third and the fourth partial flow are post-compressed in a common third compressor stage.
- the third and fourth compressor stages are implemented as a single machine relatively inexpensively.
- a second type of transfer of the heat to the second partial stream is that the heating of the second partial stream prior to its expansion by indirect heat exchange with the third and / or fourth partial stream after the compression in the third or fourth compressor stage is carried out.
- This measure makes it possible to achieve a particularly favorable adaptation of the flows to the inlet temperature of the main heat exchanger by cooling the partial flow or streams that are subsequently compressed.
- the cold available before the second partial flow enters the expansion turbine is used particularly efficiently at this point.
- Post-compression of the fourth partial flow above the pressure column pressure is particularly advantageous if oxygen is to be obtained under increased pressure in the process.
- liquid oxygen is led out of the low-pressure stage, brought to pressure and evaporated in indirect heat exchange with the post-compressed fourth partial flow.
- the part of the air available under a higher pressure column pressure is used here for an energetically favorable production of pressurized oxygen.
- the oxygen is pressurized in liquid form (either by a pump or by utilizing a hydrostatic potential) and then evaporated under the increased pressure.
- the high-pressure air condenses in counterflow to the evaporating oxygen and emits latent heat.
- the indirect heat exchange is preferably carried out in the main heat exchanger block through which the other feed and product flows also flow.
- the invention also relates to a device for the low-temperature extraction of air according to claim 11 .
- air separation plants more than 100,000 Nm3 / h, preferably more than 200,000 Nm3 / h, most preferably between 200,000 and 400,000 Nm3 / h separation air
- the advantages of the invention are particularly evident.
- Use in the context of GUD (combined cycle) plants or plants for steel production (eg COREX process) is also advantageous.
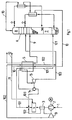
- FIGS. 1 and 2 show schematically in FIGS. 1 and 2.
- the same reference numerals are used in both drawings for analog process steps.
- atmospheric air is drawn in via a line 1 from a first compressor stage 2 and compressed to a pressure of 5 to 10 bar, preferably about 5.65 bar, and cooled to 5 to 25 ° C., preferably about 12 ° C. and freed of impurities such as water, carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons in a cleaning stage 4 filled with a molecular sieve.
- the feed air is branched into a first partial flow 101 and a second partial flow 102.
- the first partial stream 101 is cooled in the main heat exchanger 5 against product streams and fed into the pressure stage 7 of a conventional two-stage rectification column 6.
- Gaseous oxygen 9 and gaseous nitrogen 10 are taken from the low-pressure stage 8 (working pressure 1.2 to 1.6 bar, preferably about 1.3 bar) and heated in the main heat exchanger 5 to about ambient temperature.
- the nitrogen can be used to regenerate the molecular sieve of cleaning stage 4 (line 11) and / or also for other purposes, for example for cooling cooling water in an evaporative cooler, via line 12.
- the second partial flow 102 is heated in a heat exchanger 3 against the compressed feed air, expanded in a turbine 13, cooled and blown into the low-pressure stage 8.
- the feed air flow is additionally cooled between heat exchanger 3 and cleaning stage 4 (not shown in the drawing), for example by indirect heat exchange with water cooled by evaporative cooling.
- a third partial flow 103 is also branched off downstream of the cleaning stage 4, further compressed in a second compressor 14, cooled to an average temperature in the main heat exchanger 5 and then expanded in a turbine 15 for generating cooling.
- the work obtained when releasing the partial flow is mechanically transferred to the second compressor 14.
- the relaxed third partial flow 103 is introduced into the low-pressure stage 8 together with the relaxed and cooled second partial flow 102.
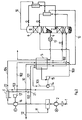
- FIG. 2 shows an exemplary embodiment for a second variant of the method.
- the second partial flow is branched off at a branch point 21 from the first partial flow 101, warmed in the heat exchanger 3 'and relaxed in the turbine 13'.
- the work obtained is transferred to a third compressor 16.
- the third partial flow is compressed in the third compressor to a pressure of at least 15 bar, preferably about 20 to 50 bar, and then cooled in the heat exchanger 3 'against the second partial flow 102 before it relaxes, before the second secondary compressor 14 coupled to the turbine 15 reached.
- a fourth partial flow 104 is branched off from the third partial flow (22), cooled in the main heat exchanger 5 and throttled into the pressure stage 7.
- oxygen is evaporated, which was taken from line 9 of the low-pressure stage and brought to a pressure of at least 4 bar, preferably 20 to 100 bar, in a pump 17.
- the high pressure air in the fourth partial flow condenses almost completely during the heat exchange and is fed into the pressure stage 7 above the first partial flow 101.
- the process with direct feed of feed air to the low pressure stage proves to be economically advantageous if a purity of 85 to 98% is to be achieved in the product oxygen (lines 23 and 24 in the exemplary embodiment). If, for example, an oxygen purity of 96% is desired, up to 35% of the feed air can be fed directly into the low-pressure stage via the second and third partial streams 102, 103 without significantly reducing the oxygen yield.
Claims (12)
- Procédé de séparation d'air à basse température, dans lequel l'air de charge (1) est comprimé (2), purifié (4), refroidi (5), divisé en plusieurs courants partiels et introduit à l'étage de pression (7) et à l'étage à basse pression (8) d'un dispositif de rectification (6) à deux étages, où :- l'air de charge (1) est amené dans un premier étage de compresseur (2) à approximativement la pression à l'étage de pression, est purifié par adsorption à un étage de purification (4) et ensuite, divisé en un premier (101) et un deuxième (102) courants partiels,- le premier courant partiel (101) est conduit à l'étage de pression (7), et- le deuxième courant partiel (102) est détendu (13, 13′), de manière à produire un travail et envoyé vers l'étage à basse pression (8), où- le travail obtenu lors de la détente (13, 13′) du deuxième courant partiel (102) est utilisé pour la compression (2, 16) d'un courant du procédé, en particulier de l'air de charge,
caractérisé en ce que :- le deuxième courant partiel (102), avant la détente (13, 13′) produisant un travail, est chauffé à une température supérieure à la température ambiante par échange de chaleur indirect (3, 3′) vis-à-vis de l'air de charge comprimé, et en ce que- le courant du procédé qui a été comprimé (2, 16) au moyen du travail obtenu lors de la détente (13, 13′) du deuxième courant partiel (102), n'est pas identique au deuxième courant partiel (102). - Procédé suivant la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce qu'un troisième courant partiel (103) dérive de l'adsorption (4) en aval, est comprimé ultérieurement dans un deuxième étage de compresseur (14), est ensuite refroidi (5), est détendu (15) en produisant un travail et introduit à l'étage à basse pression (8), où le travail obtenu par la détente produisant un travail (15) du troisième courant partiel est utilisé au deuxième étage de compresseur (14).
- Procédé suivant la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que le travail obtenu par la détente produisant un travail (13) du deuxième courant partiel est utilisé pour actionner le premier étage de compresseur (2).
- Procédé suivant la revendication 3, caractérisé en ce que le chauffage léger du deuxième courant partiel est réalisé avant sa détente, par échange de chaleur (3) indirect avec l'air de charge, après le premier étage de compression (2) et avant l'étage de purification (4).
- Procédé suivant la revendication 2, caractérisé en ce que le travail obtenu par la détente produisant un travail (13′) du deuxième courant partiel est utilisé à un troisième étage de compresseur (16) pour une compression ultérieure du troisième courant partiel.
- Procédé suivant l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé en ce qu'un quatrième courant partiel (104) dérive en aval de l'étage de purification (4), est comprimé ultérieurement à un quatrième étage de compresseur, ensuite est refroidi (5), détendu et est introduit à l'étage de pression (7), où le travail obtenu par la détente produisant un travail (13′) du deuxième courant partiel est utilisé à un quatrième étage de compresseur (16) pour une compression ultérieure du quatrième courant partiel.
- Procédé suivant les revendications 5 et 6, caractérisé en ce que les troisième (103) et quatrième (104) courants partiels sont comprimés ultérieurement à un troisième étage commun de compresseur (16).
- Procédé suivant l'une quelconque des revendications 5 à 7, caractérisé en ce que le chauffage léger du deuxième courant partiel (102) est réalisé avant sa détente, par échange de chaleur indirect (3′) avec les troisième et/ou quatrième (104) courants partiels, après la compression ultérieure du troisième (16), respectivement quatrième, étage de compresseur.
- Procédé suivant l'une quelconque des revendications 5 à 8, caractérisé en ce que de l'oxygène liquide est récupéré (9) à l'étage à basse pression (8), mis sous pression (17) et vaporisé dans un échange de chaleur indirect (5) avec le quatrième courant partiel (104) comprimé ultérieurement.
- Procédé suivant la revendication 9, caractérisé en ce que le quatrième courant partiel (104) est au moins partiellement condensé par échange de chaleur indirect (5) avec l'oxygène à vaporiser et ensuite, introduit à l'étage de pression (7), au-dessus du premier courant partiel (101).
- Dispositif de séparation d'air à basse température comprenant :- un premier étage de compresseur (2) pour comprimer l'air de charge (1) à environ la pression de l'étage de pression, dont la sortie est en relation d'écoulement avec l'entrée d'un étage de purification (4) qui présente un dispositif d'adsorption,- un échangeur de chaleur principal (5);- un appareil de rectification (6) constitué d'une colonne sous pression (7) et d'une colonne à basse pression (8);- une première conduite de courant partiel (101) qui va de la sortie de l'étage de purification (4) vers la colonne sous pression (7);- une deuxième conduite de courant partiel (102) qui va de la sortie de l'étage de purification (4) vers la colonne à basse pression (8), par un appareil de détente (13, 13′), et- des moyens de transfert du travail obtenu dans l'appareil de détente (13, 13′) sur un moyen (2, 16) de compression d'un courant du procédé, en particulier de l'air de charge,
caractérisé en ce que :- la deuxième conduite de courant partiel (102) est amenée en amont de l'appareil de détente (13, 13′), par un échangeur de chaleur (3, 3′) pour le réchauffage par échange de chaleur indirect (3, 3′) vis-à-vis d'air de charge comprimé jusqu'à une température supérieure à la température ambiante et en ce que- le moyen (2, 16) de compression d'un courant du procédé et l'appareil de détente (13, 13′) ne sont pas reliés l'un avec l'autre, de sorte que le même courant du procédé traverse les deux appareils. - Utilisation du procédé suivant l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 10 et/ou du dispositif suivant la revendication 11, pour la préparation d'oxygène de faible pureté.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4109945 | 1991-03-26 | ||
| DE4109945A DE4109945A1 (de) | 1991-03-26 | 1991-03-26 | Verfahren zur tieftemperaturzerlegung von luft |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0505812A1 EP0505812A1 (fr) | 1992-09-30 |
| EP0505812B1 true EP0505812B1 (fr) | 1995-10-18 |
Family
ID=6428254
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP92104008A Expired - Lifetime EP0505812B1 (fr) | 1991-03-26 | 1992-03-09 | Procédé de séparation d'air à basse température |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5263328A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0505812B1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN1064125C (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE129336T1 (fr) |
| AU (1) | AU653120B2 (fr) |
| CA (1) | CA2063928C (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE4109945A1 (fr) |
| DK (1) | DK0505812T3 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2077898T3 (fr) |
| ZA (1) | ZA922185B (fr) |
Cited By (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102007031759A1 (de) | 2007-07-07 | 2009-01-08 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung von gasförmigem Druckprodukt durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| DE102007031765A1 (de) | 2007-07-07 | 2009-01-08 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zur Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| DE102009034979A1 (de) | 2009-04-28 | 2010-11-04 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung von gasförmigem Drucksauerstoff |
| EP2312248A1 (fr) | 2009-10-07 | 2011-04-20 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif de production d'oxygène sous pression et de crypton/xénon |
| EP2458311A1 (fr) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-05-30 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif de production d'un produit d'impression gazeux par décomposition à basse température d'air |
| DE102010052544A1 (de) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-05-31 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zur Gewinnung eines gasförmigen Druckprodukts durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| EP2520886A1 (fr) | 2011-05-05 | 2012-11-07 | Linde AG | Procédé et dispositif de production d'un produit comprimé à oxygène gazeux par décomposition à basse température d'air |
| EP2568242A1 (fr) | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-13 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la production d'acier |
| EP2600090A1 (fr) | 2011-12-01 | 2013-06-05 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la production d'oxygène sous pression par décomposition à basse température de l'air |
| DE102011121314A1 (de) | 2011-12-16 | 2013-06-20 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Erzeugung eines gasförmigen Sauerstoff-Druckprodukts durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| DE102013017590A1 (de) | 2013-10-22 | 2014-01-02 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Gewinnung eines Krypton und Xenon enthaltenden Fluids und hierfür eingerichtete Luftzerlegungsanlage |
| DE102012017488A1 (de) | 2012-09-04 | 2014-03-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Erstellung einer Luftzerlegungsanlage, Luftzerlegungsanlage und zugehöriges Betriebsverfahren |
| EP2784420A1 (fr) | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-01 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de séparation de l'air et installation de séparation de l'air |
| WO2014154339A2 (fr) | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-02 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de séparation d'air et installation de séparation d'air |
| EP2801777A1 (fr) | 2013-05-08 | 2014-11-12 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Installation de décomposition de l'air dotée d'un entraînement de compresseur principal |
| CN105135724A (zh) * | 2015-08-21 | 2015-12-09 | 深圳智慧能源技术有限公司 | 节能的制冷机组及压缩膨胀模组 |
| EP2963370A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procede et dispositif cryogeniques de separation d'air |
| EP2963367A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif cryogéniques de séparation d'air avec consommation d'énergie variable |
| EP2963371A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procede et dispositif de production d'un produit de gaz sous pression par decomposition a basse temperature d'air |
| EP2963369A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procede et dispositif cryogeniques de separation d'air |
| WO2017031616A1 (fr) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-03-02 | 深圳智慧能源技术有限公司 | Unité de réfrigération à économie d'énergie et module de compression-détente |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5379598A (en) * | 1993-08-23 | 1995-01-10 | The Boc Group, Inc. | Cryogenic rectification process and apparatus for vaporizing a pumped liquid product |
| FR2728663B1 (fr) | 1994-12-23 | 1997-01-24 | Air Liquide | Procede de separation d'un melange gazeux par distillation cryogenique |
| US5758515A (en) * | 1997-05-08 | 1998-06-02 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic air separation with warm turbine recycle |
| US5802873A (en) * | 1997-05-08 | 1998-09-08 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic rectification system with dual feed air turboexpansion |
| US5924307A (en) * | 1997-05-19 | 1999-07-20 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Turbine/motor (generator) driven booster compressor |
| US5934105A (en) * | 1998-03-04 | 1999-08-10 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic air separation system for dual pressure feed |
| US5901579A (en) * | 1998-04-03 | 1999-05-11 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic air separation system with integrated machine compression |
| US6000239A (en) * | 1998-07-10 | 1999-12-14 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic air separation system with high ratio turboexpansion |
| JP4782380B2 (ja) * | 2003-03-26 | 2011-09-28 | エア・ウォーター株式会社 | 空気分離装置 |
| JP4515225B2 (ja) * | 2004-11-08 | 2010-07-28 | 大陽日酸株式会社 | 窒素製造方法及び装置 |
| US7263859B2 (en) * | 2004-12-27 | 2007-09-04 | L'air Liquide, Societe Anonyme A Directoire Et Conseil De Surveillance Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes Georges Claude | Process and apparatus for cooling a stream of compressed air |
| US7437890B2 (en) * | 2006-01-12 | 2008-10-21 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic air separation system with multi-pressure air liquefaction |
| CN102721263A (zh) * | 2012-07-12 | 2012-10-10 | 杭州杭氧股份有限公司 | 一种利用深冷技术分离空气的系统及方法 |
| US20150168056A1 (en) * | 2013-12-17 | 2015-06-18 | L'air Liquide, Societe Anonyme Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes Georges Claude | Method For Producing Pressurized Gaseous Oxygen Through The Cryogenic Separation Of Air |
| CN103776239B (zh) * | 2014-01-13 | 2016-03-30 | 浙江海天气体有限公司 | 多功能制氮装置 |
| EP3438585A3 (fr) * | 2017-08-03 | 2019-04-17 | L'air Liquide, Societe Anonyme Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes Georges Claude | Procédé de dégivrage d'un appareil de séparation d'air par distillation cryogénique et appareil adapté pour être dégivré par ce procédé |
| CN111693559B (zh) * | 2020-06-22 | 2022-04-01 | 中国核动力研究设计院 | 气相混合物的蒸汽液滴质量流量分离测量装置及测量方法 |
| CN112452095B (zh) * | 2020-11-10 | 2022-11-08 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | 一种改进的尾气精馏方法 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1520103A (en) * | 1977-03-19 | 1978-08-02 | Air Prod & Chem | Production of liquid oxygen and/or liquid nitrogen |
| FR2461906A1 (fr) * | 1979-07-20 | 1981-02-06 | Air Liquide | Procede et installation cryogeniques de separation d'air avec production d'oxygene sous haute pression |
| JPS62102074A (ja) * | 1985-10-30 | 1987-05-12 | 株式会社日立製作所 | ガス分離方法及び装置 |
| US4715873A (en) * | 1986-04-24 | 1987-12-29 | Air Products And Chemicals, Inc. | Liquefied gases using an air recycle liquefier |
| DE3643359C2 (de) * | 1986-12-18 | 1993-11-18 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Luftzerlegung durch zweistufige Rektifikation |
| DE3738559A1 (de) * | 1987-11-13 | 1989-05-24 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zur luftzerlegung durch tieftemperaturrektifikation |
| DE3817244A1 (de) * | 1988-05-20 | 1989-11-23 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zur tieftemperaturzerlegung von luft |
| GB8904275D0 (en) * | 1989-02-24 | 1989-04-12 | Boc Group Plc | Air separation |
| US5114449A (en) * | 1990-08-28 | 1992-05-19 | Air Products And Chemicals, Inc. | Enhanced recovery of argon from cryogenic air separation cycles |
-
1991
- 1991-03-26 DE DE4109945A patent/DE4109945A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1992
- 1992-03-09 AT AT92104008T patent/ATE129336T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1992-03-09 EP EP92104008A patent/EP0505812B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1992-03-09 DK DK92104008.5T patent/DK0505812T3/da active
- 1992-03-09 ES ES92104008T patent/ES2077898T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1992-03-09 DE DE59204027T patent/DE59204027D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1992-03-25 US US07/857,140 patent/US5263328A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1992-03-25 ZA ZA922185A patent/ZA922185B/xx unknown
- 1992-03-25 AU AU13166/92A patent/AU653120B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1992-03-26 CA CA002063928A patent/CA2063928C/fr not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1992-03-26 CN CN92101960A patent/CN1064125C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102007031759A1 (de) | 2007-07-07 | 2009-01-08 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung von gasförmigem Druckprodukt durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| DE102007031765A1 (de) | 2007-07-07 | 2009-01-08 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zur Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| EP2015012A2 (fr) | 2007-07-07 | 2009-01-14 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé pour la séparation cryogénique d'air |
| DE102009034979A1 (de) | 2009-04-28 | 2010-11-04 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung von gasförmigem Drucksauerstoff |
| EP2312248A1 (fr) | 2009-10-07 | 2011-04-20 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif de production d'oxygène sous pression et de crypton/xénon |
| EP2458311A1 (fr) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-05-30 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif de production d'un produit d'impression gazeux par décomposition à basse température d'air |
| DE102010052544A1 (de) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-05-31 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zur Gewinnung eines gasförmigen Druckprodukts durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| DE102010052545A1 (de) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-05-31 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung eines gasförmigen Druckprodukts durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| EP2466236A1 (fr) | 2010-11-25 | 2012-06-20 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de production d'un produit d'impression gazeux par décomposition à basse température de l'air |
| EP2520886A1 (fr) | 2011-05-05 | 2012-11-07 | Linde AG | Procédé et dispositif de production d'un produit comprimé à oxygène gazeux par décomposition à basse température d'air |
| EP2568242A1 (fr) | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-13 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la production d'acier |
| DE102011112909A1 (de) | 2011-09-08 | 2013-03-14 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Stahl |
| EP2600090A1 (fr) | 2011-12-01 | 2013-06-05 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la production d'oxygène sous pression par décomposition à basse température de l'air |
| DE102011121314A1 (de) | 2011-12-16 | 2013-06-20 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Erzeugung eines gasförmigen Sauerstoff-Druckprodukts durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| DE102012017488A1 (de) | 2012-09-04 | 2014-03-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Erstellung einer Luftzerlegungsanlage, Luftzerlegungsanlage und zugehöriges Betriebsverfahren |
| EP2784420A1 (fr) | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-01 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de séparation de l'air et installation de séparation de l'air |
| WO2014154339A2 (fr) | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-02 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de séparation d'air et installation de séparation d'air |
| EP2801777A1 (fr) | 2013-05-08 | 2014-11-12 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Installation de décomposition de l'air dotée d'un entraînement de compresseur principal |
| DE102013017590A1 (de) | 2013-10-22 | 2014-01-02 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Gewinnung eines Krypton und Xenon enthaltenden Fluids und hierfür eingerichtete Luftzerlegungsanlage |
| EP2963371A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procede et dispositif de production d'un produit de gaz sous pression par decomposition a basse temperature d'air |
| EP2963370A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procede et dispositif cryogeniques de separation d'air |
| EP2963367A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif cryogéniques de séparation d'air avec consommation d'énergie variable |
| EP2963369A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procede et dispositif cryogeniques de separation d'air |
| WO2016005031A1 (fr) | 2014-07-05 | 2016-01-14 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif de fractionnement de l'air à basse température à consommation d'énergie variable |
| CN105135724A (zh) * | 2015-08-21 | 2015-12-09 | 深圳智慧能源技术有限公司 | 节能的制冷机组及压缩膨胀模组 |
| WO2017031616A1 (fr) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-03-02 | 深圳智慧能源技术有限公司 | Unité de réfrigération à économie d'énergie et module de compression-détente |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ZA922185B (en) | 1993-09-24 |
| AU653120B2 (en) | 1994-09-15 |
| DK0505812T3 (da) | 1995-12-18 |
| ES2077898T3 (es) | 1995-12-01 |
| CA2063928A1 (fr) | 1992-09-27 |
| AU1316692A (en) | 1992-10-01 |
| EP0505812A1 (fr) | 1992-09-30 |
| CN1064125C (zh) | 2001-04-04 |
| DE59204027D1 (de) | 1995-11-23 |
| CA2063928C (fr) | 2003-05-06 |
| ATE129336T1 (de) | 1995-11-15 |
| CN1065326A (zh) | 1992-10-14 |
| DE4109945A1 (de) | 1992-10-01 |
| US5263328A (en) | 1993-11-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0505812B1 (fr) | Procédé de séparation d'air à basse température | |
| EP0384483B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de rectification d'air | |
| EP0093448B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour obtenir de l'oxygène gazeux sous pression élevée | |
| EP0316768B1 (fr) | Procédé de séparation d'air par rectification à basse température | |
| EP1031804B1 (fr) | Procédé de séparation des gaz de l'air avec recyclage d'azote | |
| EP1074805B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour la production d'oxygène sous pression | |
| EP1994344A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de décomposition de l'air à basse température | |
| EP0758733A2 (fr) | Procédé de séparation d'air par rectification à basse température | |
| EP0342436A2 (fr) | Procédé de séparation de l'air à basse température | |
| WO2010017968A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de séparation de l'air à basse température | |
| DE19908451A1 (de) | Zweisäulensystem zur Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft | |
| EP0989375A1 (fr) | Procédé et liquéfacteur pour produire de l'air liquide | |
| EP0384213A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de rectification d'air | |
| EP1146301A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de production d'azote à haute pression par séparation d'air | |
| EP3059536A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la production d'un produit d'azote pressurisé | |
| DE19951521A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung eines Druckprodukts durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft | |
| DE2854508A1 (de) | Verfahren zur tieftemperaturzerlegung eines gasgemisches | |
| EP0768503B1 (fr) | Procédé de séparation d'air à triple colonne | |
| EP1134524B1 (fr) | Procédé de production d'azote gazeux | |
| DE4030750A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur tieftemperaturzerlegung von luft | |
| DE10045128A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung hoch reinen Stickstoffs durch Tieftemperatur-Luftzerlegung | |
| EP1209431B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de production d'oxygène et d'azote | |
| DE19543953C1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Sauerstoff und Stickstoff unter überatmosphärischem Druck | |
| EP3255366A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de production d'un produit gazeux à base d'oxygène sous pression | |
| DE3216502A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur gewinnung von gasfoermigem sauerstoff unter erhoehtem druck |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE DK ES FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19921217 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19931025 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE DE DK ES FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 129336 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19951115 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed |
Owner name: JACOBACCI & PERANI S.P.A. |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59204027 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19951123 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2077898 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19960105 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20030305 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20030306 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20030310 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20030312 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20030318 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20030320 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20030327 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20030328 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20030516 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040309 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040309 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040310 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040310 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040331 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040331 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *LINDE A.G. Effective date: 20040331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20041001 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20041001 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20041130 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20041001 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050309 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20040310 |