EP0446822A1 - Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen - Google Patents
Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0446822A1 EP0446822A1 EP19910103645 EP91103645A EP0446822A1 EP 0446822 A1 EP0446822 A1 EP 0446822A1 EP 19910103645 EP19910103645 EP 19910103645 EP 91103645 A EP91103645 A EP 91103645A EP 0446822 A1 EP0446822 A1 EP 0446822A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- carrier web
- filaments
- web according
- melting point
- binder
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 13
- 239000010426 asphalt Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- -1 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007596 consolidation process Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 abstract description 6
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004049 embossing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006264 polyurethane film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005871 repellent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010454 slate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/005—Synthetic yarns or filaments
- D04H3/009—Condensation or reaction polymers
- D04H3/011—Polyesters
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/08—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating
- D04H3/14—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating with bonds between thermoplastic yarns or filaments produced by welding
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/08—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating
- D04H3/14—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating with bonds between thermoplastic yarns or filaments produced by welding
- D04H3/153—Mixed yarns or filaments
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/08—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating
- D04H3/16—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating with bonds between thermoplastic filaments produced in association with filament formation, e.g. immediately following extrusion
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06N—WALL, FLOOR, OR LIKE COVERING MATERIALS, e.g. LINOLEUM, OILCLOTH, ARTIFICIAL LEATHER, ROOFING FELT, CONSISTING OF A FIBROUS WEB COATED WITH A LAYER OF MACROMOLECULAR MATERIAL; FLEXIBLE SHEET MATERIAL NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06N5/00—Roofing materials comprising a fibrous web coated with bitumen or another polymer, e.g. pitch
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24355—Continuous and nonuniform or irregular surface on layer or component [e.g., roofing, etc.]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24802—Discontinuous or differential coating, impregnation or bond [e.g., artwork, printing, retouched photograph, etc.]
- Y10T428/24826—Spot bonds connect components
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T442/00—Fabric [woven, knitted, or nonwoven textile or cloth, etc.]
- Y10T442/60—Nonwoven fabric [i.e., nonwoven strand or fiber material]
- Y10T442/681—Spun-bonded nonwoven fabric
Definitions
- the invention relates to a carrier sheet for roofing membranes and a roofing membrane produced with this carrier membrane.
- roofing membranes are known to be installed under the tiles or slate slabs of steep roofs or the like as protection against flying snow, dust etc.
- roofing underlays should on the one hand be impermeable to water and on the other hand should be permeable to air and steam.
- they should have high strength, in particular tear resistance, e.g. to be able to absorb the weight of the roofer in the event of an accident.
- roofing underlays made of grid-reinforced foils are widespread. Although these films have good tear strength; However, the tear resistance and often also the vapor permeability remain unsatisfactory.
- a roofing membrane made of a polyurethane film is known, which is covered with a non-woven layer of e.g. Polyester is covered.
- a sarking membrane is mentioned which consists of highly tear-resistant polyester spunbonded fabric and is provided with a water-repellent and breathable special coating in the form of a paste.
- a sarking membrane which consists of highly tear-resistant polyester spunbonded fabric and is provided with a water-repellent and breathable special coating in the form of a paste.
- EP-PS 0027750 describes a carrier web for a roofing membrane which consists of a non-woven fabric made of polypropylene, polyethylene, polyester or polyvinyl and has a basis weight between 85 and 200 g / m2.
- the fiber fleece is used to manufacture the roofing membrane Provide a bitumen layer on one side by warm coating the nonwoven with the bitumen and then cooling to cause micro-holes or micro-cracks.
- This publication also shows nothing regarding the structure of the nonwoven fabric - apart from the fiber material used and the weight per unit area.
- the invention has for its object to provide a carrier sheet for roofing underlay, which ensures high strength, in particular tear resistance of the roofing underlay and which has good dimensional stability even at high processing temperatures.
- a carrier web for roofing underlays which consists of a spunbond made of polyester, in particular polyethylene terephthalate filaments
- this object is achieved according to the invention in that the spunbonded fabric has a basis weight of 50 to 100 g / m 2 with a single titer of the filaments of 1 to 8 dtex and is solidified by a melt binder.
- the carrier web obtains good dimensional stability even at high processing temperatures due to the structure of the spunbonded fabric according to the invention. This is important for the production of roofing underlays in which the carrier sheet is provided with bitumen. Processing temperatures of 160 to 180 ° C prevail, especially when impregnating the carrier sheet with bitumen. As has been shown, the carrier web designed according to the invention has good dimensional stability even at these high temperatures, which is essential for processing the carrier web. Carrier webs out In contrast, polypropylene, which has a softening point of approx. 156 ° C, is less suitable for bituminization, for example.
- the carrier web is preferably used in connection with bitumen to produce a roofing underlay.
- the carrier web is preferably impregnated with bitumen; instead, the carrier web can also be coated with bitumen, it preferably being coated on both sides with bitumen.
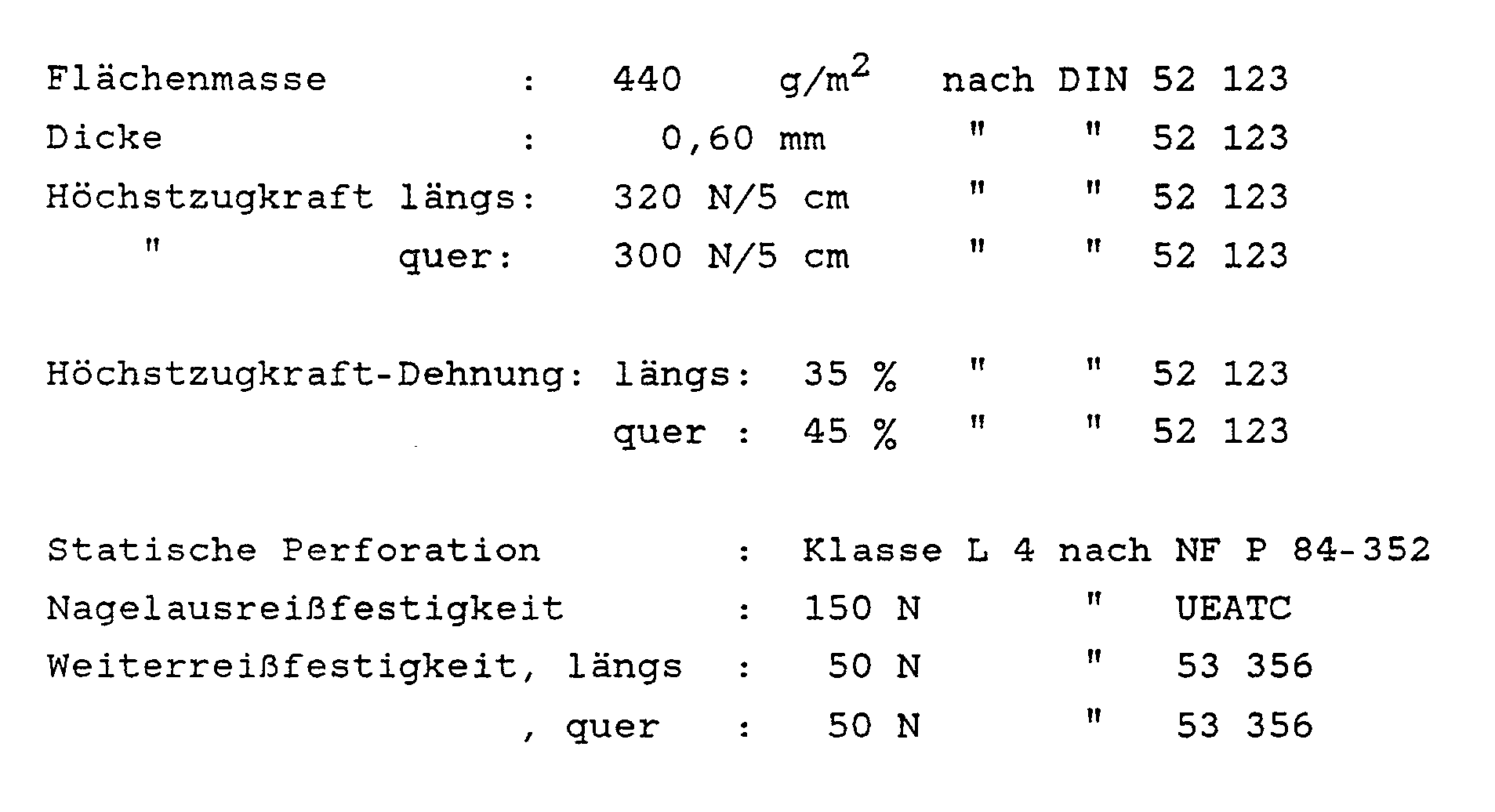
- the carrier web designed according to the invention has a tear resistance of the order of 20 N to 80 N, a nail tear resistance of 50 N to 180 N and a perforation stability of 400 N to 1200 N.
- bitumen instead of bitumen, another material, e.g. Polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride can be used with the spunbonded fabric according to the invention.
- the low basis weight of the spunbonded fabric is advantageous in terms of vapor permeability and material consumption.
- the basis weight of the spunbonded fabric is preferably 70 to 90 g / m 2.
- the fine individual titer of the spunbonded filaments results in good adhesion of the material associated with the spunbonded nonwoven, in particular the bitumen, due to the high specific surface area of the spunbonded nonwoven.
- the individual titer of the spunbonded nonwoven filaments is preferably 2 to 5 dtex, in particular 4 dtex.
- melt binders are polymers whose melting point is lower than the melting point of the the spunbonding - the so-called supporting - filaments.
- the melting point of the melt binder is expediently 10 ° C., preferably 30 ° C. below the melting point of the supporting filaments.
- melt binders consist of polyesters, preferably polybutylene terephthalate or modified polyesters with a correspondingly lowered melting point, preferably modified polyethylene terephthalate.
- the melt binders mentioned above can be used particularly advantageously in the form of binding filaments in the nonwoven during manufacture, i.e. when depositing the filaments on the conveyor belt.
- the binding filaments melt completely or partially and form the desired binding points (binding sail) at the crossing points of the supporting filaments.
- the proportion of binder is advantageously 5 to 25% by weight, preferably 10 to 15% by weight.
- a spunbonded nonwoven made of polyethylene terephthalate filaments with a single titer was used as the carrier web of 4 dtex and binding filaments made of a modified polyester with a share of 9%.
- the spunbonded fabric was thermomechanically pre-consolidated by embossing rollers and then finally consolidated by hot air.
- the basis weight of the support was 100 g / m2.
- the carrier sheet was then bituminized in a roofing membrane system, coated on both sides with bitumen and sanded. An excellent dimensional stability during the processing process was noticed.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
- Synthetic Leather, Interior Materials Or Flexible Sheet Materials (AREA)
- Auxiliary Devices For And Details Of Packaging Control (AREA)
- Supporting Of Heads In Record-Carrier Devices (AREA)
- Particle Accelerators (AREA)
- Treatments For Attaching Organic Compounds To Fibrous Goods (AREA)
- Tents Or Canopies (AREA)
- Separation Using Semi-Permeable Membranes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen sowie eine mit dieser Trägerbahn hergestellte Dachunterspannbahn.
- Dachunterspannbahnen werden bekanntlich unter den Ziegeln oder Schieferplatten von Steildächern oder dergl. als Schutz gegen Flugschnee, Staub usw. angebracht. Dachunterspannbahnen sollen einerseits wasserundurchlässig und andererseits luft- und dampfdurchlässig sein. Außerdem sollen sie eine hohe Festigkeit, insbesondere Weiterreißfestigkeit, haben, um z.B. bei einem Unfall das Gewicht des Dachdeckers aufnehmen zu können.
- Weit verbreitet sind Dachunterspannbahnen aus gitterbewehrten Folien. Diese Folien weisen zwar eine gute Reißfestigkeit auf; unbefriedigend bleibt aber die Weiterreißfestigkeit und häufig auch die Dampfdurchlässigkeit.
- Aus der DE-OS 34 25 794 ist eine Dachunterspannbahn aus einer Polyurethanfolie bekannt, die mit einer Vliesschicht aus z.B. Polyester belegt ist. In der Beschreibungseinleitung dieser Offenlegungsschrift wird eine Unterspannbahn erwähnt, die aus hochreißfestem Polyester-Spinnvlies besteht und mit einer wasserabweisenden und atmungsaktiven Spezialbeschichtung in Form einer Paste versehen ist. Über den Aufbau der verwendeten Polyester-Vliesstoffe läßt sich dieser Veröffentlichung jedoch nichts entnehmen.
- Die EP-PS 0027750 beschreibt eine Trägerbahn für eine Dachunterspannbahn, die aus einem Faservlies aus Polypropylen, Polyethylen, Polyester oder Polyvinyl besteht und ein Flächengewicht zwischen 85 und 200 g/m² aufweist. Zur Herstellung der Dachunterspannbahn wird das Faservlies auf einer Seite mit einer Bitumenschicht versehen, indem das Faservlies mit dem Bitumen warm bestrichen und dann einer Abkühlung unterzogen wird, um Mikrolöcher oder Mikrorisse hervorzurufen. Auch dieser Druckschrift läßt sich jedoch hinsichtlich des Aufbaus des Faservlieses - abgesehen von dem verwendeten Fasermaterial und dem Flächengewicht - nichts entnehmen.
- Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen zu schaffen, die für eine hohe Festigkeit, insbesondere Weiterreißfestigkeit der Dachunterspannbahn sorgt und die eine gute Dimensionsstabilität selbst bei hohen Verarbeitungstemperaturen besitzt.
- Ausgehend von einer Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen, die aus einem Spinnvlies aus Polyester, insbesondere Polyethylenterephthalat-Filamenten besteht, wird diese Aufgabe erfindungsgemäß dadurch gelöst, daß das Spinnvlies ein Flächengewicht von 50 bis 100 g/m² bei einem Einzeltiter der Filamente von 1 bis 8 dtex aufweist und durch einen Schmelzbinder endverfestigt ist.
- Wie in Versuchen festgestellt wurde, erhält die Trägerbahn aufgrund des erfindungsgemäßen Aufbaus des Spinnvlieses eine gute Dimensionsstabilität selbst bei hohen Verarbeitungstemperaturen. Dies ist für die Herstellung von Dachunterspannbahnen von Bedeutung, bei denen die Trägerbahn mit Bitumen versehen wird. Insbesondere beim Tränken der Trägerbahn mit Bitumen herrschen Verarbeitungstemperaturen von 160 bis 180°C. Wie sich gezeigt hat, besitzt die erfindungsgemäß ausgebildete Trägerbahn selbst bei diesen hohen Temperaturen eine gute Dimensionsstabilität, was für die Verarbeitung der Trägerbahn von wesentlicher Bedeutung ist. Trägerbahnen aus Polypropylen, das einen Erweichungspunkt von ca. 156°C hat, sind dagegen beispielsweise für eine Bituminierung weniger geeignet.
- Wie bereits erwähnt, wird die Trägerbahn zur Herstellung einer Dachunterspannbahn vorzugsweise in Verbindung mit Bitumen verwendet. Hierbei wird die Trägerbahn vorzugsweise mit Bitumen getränkt; stattdessen kann die Trägerbahn auch mit Bitumen beschichtet werden, wobei sie vorzugsweise beidseitig mit Bitumen beschichtet wird.
- Bei der erfindungsgemäß ausgebildeten Trägerbahn ergeben sich eine Weiterreißfestigkeit in der Größenordnung von 20 N bis 80 N, eine Nagelausreißfestigkeit von 50 N bis 180 N und eine Perforationsstabilität von 400 N bis 1200 N. Hierbei wird die Weiterreißfestigkeit nach DIN 53356, die Nagelausreißfestigkeit nach UEATC-Norm und die Perforationsstabilität nach DIN 54307 bestimmt.
- Statt Bitumen könnte jedoch auch ein anderes Material, z.B. Polyethylen oder Polyvinylchlorid mit dem erfindungsgemäßen Spinnvlies verwendet werden.
- Das geringe Flächengewicht des Spinnvlieses ist vorteilhaft im Hinblick auf die Dampfdurchlässigkeit sowie den Materialverbrauch. Vorzugsweise beträgt das Flächengewicht des Spinnvlieses 70 bis 90 g/m².
- Der feine Einzeltiter der Spinnvlies-Filamente ergibt eine gute Haftung des mit dem Spinnvlies verbundenen Materials, insbesondere des Bitumens, aufgrund der hohen spezifischen Oberfläche des Spinnvlieses. Vorzugsweise beträgt der Einzeltiter der Spinnvlies-Filamente 2 bis 5 dtex, insbesondere 4 dtex.
- Als Schmelzbinder kommen insbesondere Polymere in Frage, deren Schmelzpunkt niedriger liegt als der Schmelzpunkt der das Spinnvlies bildenden - der sogenannten tragenden - Filamente.
- Zweckmäßigerweise liegt der Schmelzpunkt des Schmelzbinders 10°C, vorzugsweise 30°C unter dem Schmelzpunkt der tragenden Filamente.
- Besonders geeignete Schmelzbinder bestehen aus Polyestern, vorzugsweise Polybutylenterephthalat oder modifizierten Polyestern mit entsprechend abgesenktem Schmelzpunkt, vorzugsweise modifiziertem Polyethylenterephthalat.
- Der Schmelzbinder wird vorzugsweise in Faserform eingebracht. Die Verfestigung erfolgt durch eine Wärmebehandlung des Vlieses, insbesondere mittels Kalander, wobei dieser glatte oder profilierte Walzen, z.B. Prägewalzen mit Gravur, besitzen kann.
Die Verfestigung kann ausschließlich durch den Kalander erfolgen oder mittels Kalander (Vorverfestigung) und nachgeschalteter weiterer Wärmebehandlung, z.B. mittels Heißluft oder Strahlungsenergie. - Die oben genannten Schmelzbinder können besonders vorteilhaft in Form von Bindefilamenten dem Vlies bei der Herstellung, d.h. bei der Ablage der Filamente auf dem Transportband, zugemischt werden. Bei einer nachfolgenden Wärmebehandlung z.B. in Heißkalander, schmelzen die Bindefilamente ganz oder teilweise und bilden an dem Kreuzungspunkten der tragenden Filamente die gewünschten Bindepunkte (Bindesegel) aus.
- Der Binderanteil beträgt zweckmäßigerweise 5 bis 25 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise 10 bis 15 Gew.-%.
- Das folgende Beispiel erläutert die Erfindung:
Als Trägerbahn wurde ein Spinnvlies aus Polyethylenterephthalat-Filamenten mit einem Einzeltiter von 4 dtex und Bindefilamenten aus einem modifizierten Polyester mit einem Anteil von 9 % verwendet. Das Spinnvlies wurde durch Prägewalzen thermomechanisch vorverfestigt und anschließend durch Heißluft endverfestigt. Das Flächengewicht des Trägers betrug 100 g/m². Die Trägerbahn wurde dann in einer Dachbahnanlage bituminiert, beidseitig mit Bitumen beschichtet und besandet. Dabei fiel eine ausgezeichnete Dimensionsstabilität während des Verarbeitungsprozesses auf. -
Claims (12)
- Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen, die aus einem Spinnvlies aus Polyester-, insbesondere Polyethylenterephthalat-Filamenten besteht, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Spinnvlies ein Flächengewicht von 50 bis 100 g/m² bei einem Einzeltiter der Filamente von 1 bis 8 dtex aufweist und durch einen Schmelzbinder verfestigt ist.
- Trägerbahn nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Flächengewicht des Spinnvlieses 70 bis 90 g/m² beträgt.
- Trägerbahn nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Einzeltiter der Spinnvlies-Filamente 2 bis 5 dtex beträgt.
- Trägerbahn nach mindestens einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Schmelzbinder aus einem Polymer mit einem Schmelzpunkt, der niedriger liegt als der Schmelzpunkt der tragenden Filamente, besteht.
- Trägerbahn nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Schmelzpunkt des Schmelzbinders 10°C, vorzugsweise 30°C unter dem Schmelzpunkt der tragenden Filamente liegt.
- Trägerbahn nach mindestens einem der Ansprüche 4 und 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Schmelzbinder aus Polyestern, vorzugsweise Polybutylenterephthalat oder modifizierten Polyestern mit entsprechend abgesenktem Schmelzpunkt, vorzugsweise modifiziertem Polyethylenterephthalat besteht.
- Trägerbahn nach einem der Ansprüche 4 bis 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Schmelzbinder in Form von Bindefilamenten vorliegt.
- Trägerbahn nach mindestens einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Binderanteil 5 bis 25 Gew.-% beträgt.
- Trägerbahn nach Anspruch 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Binderanteil 10 bis 15 Gew.-% beträgt.
- Dachunterspannbahn mit einer Trägerbahn nach mindestens einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Trägerbahn mit Bitumen imprägniert oder beschichtet, insbesondere beidseitig beschichtet ist.
- Verfahren zur Herstellung der Trägerbahn nach Anspruch 1 durch Herstellen eines Spinnvlieses aus Polyester-Filamenten in an sich bekannter Weise, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Schmelzbinder in Faserform eingebracht wird und das Vlies durch eine Wärmebehandlung verfestigt wird.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 11, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Verfestigung mittels Kalander (Vorverfestigung) und nachgeschalteter weiterer Wärmebehandlung erfolgt.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4008043A DE4008043A1 (de) | 1990-03-14 | 1990-03-14 | Traegerbahn fuer dachunterspannbahnen |
| DE4008043 | 1990-03-14 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0446822A1 true EP0446822A1 (de) | 1991-09-18 |
| EP0446822B1 EP0446822B1 (de) | 1995-06-07 |
| EP0446822B2 EP0446822B2 (de) | 1999-06-16 |
Family
ID=6402119
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19910103645 Expired - Lifetime EP0446822B2 (de) | 1990-03-14 | 1991-03-09 | Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5130178A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0446822B2 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP3096311B2 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE123538T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE4008043A1 (de) |
| DK (1) | DK0446822T4 (de) |
| GR (1) | GR3030982T3 (de) |
| IE (1) | IE67658B1 (de) |
| PT (1) | PT97025A (de) |
Cited By (36)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0594892A1 (de) * | 1992-09-25 | 1994-05-04 | CASA BERNARDO Ltda | Verstärkter Werkstoff aus 100% tigem Polyester der als Applikator zur Aufnahme von Schädlingsbekämpfungsmittel verwendet wird und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| WO1996036778A1 (de) * | 1995-05-15 | 1996-11-21 | Paul Bauder Gmbh & Co. | Diffusionsoffene schalungs- und unterspannbahn |
| DE19620361A1 (de) * | 1996-05-10 | 1997-11-13 | Hoechst Trevira Gmbh & Co Kg | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE19618775A1 (de) * | 1996-05-10 | 1997-11-13 | Hoechst Trevira Gmbh & Co Kg | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102006060241A1 (de) * | 2006-12-20 | 2008-06-26 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007008424A1 (de) | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Neue Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007008423A1 (de) | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Neue Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007012651A1 (de) | 2007-03-16 | 2008-09-18 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Direkt-dekorierbare Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE202008010258U1 (de) | 2008-07-30 | 2008-10-30 | Johns Manville, Denver | Trägereinlage und beschichtete Dachbahnen |
| DE102007028531A1 (de) | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-24 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Neue Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007027299A1 (de) | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-24 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Filtermedium |
| DE202009000393U1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2009-03-19 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Betonschalung |
| DE202009000539U1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2009-04-02 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Mineralisch beschichtete textile Flächen für Holzwerkstoffe |
| DE102007060494A1 (de) | 2007-12-14 | 2009-06-18 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102008051430A1 (de) | 2008-10-11 | 2010-04-15 | Trevira Gmbh | Superabsorbierende Bikomponentenfaser |
| DE102008059129A1 (de) | 2008-11-26 | 2010-05-27 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| DE102008059128A1 (de) | 2008-11-26 | 2010-05-27 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| DE102009004573A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-15 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Betonschalung, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102009004970A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-15 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Mineralisch beschichtete textile Flächen für Holzwerkstoffe |
| DE102009005587A1 (de) | 2009-01-21 | 2010-07-22 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Verfahren zur Qualitätssicherung von verstärkten flächigen Gebilden |
| DE102009022120A1 (de) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-11-25 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Filtermedium |
| DE102009023737A1 (de) | 2009-06-03 | 2010-12-09 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Digitales Bedrucken von Vliesstoffen und deren Verwendung in Verbundwerkstoffen |
| EP2269814A1 (de) | 2009-06-03 | 2011-01-05 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Bedrucken von Vliesstoffen und deren Verwendung in Verbundstoffen |
| EP2309046A1 (de) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-13 | Johns Manville | Mehrschichtige Stoffmaterialien für Bedachungsanwendungen |
| WO2011043937A1 (en) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-14 | Johns Manville | Binder composition |
| DE202006021073U1 (de) | 2006-12-20 | 2012-04-30 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Trägereinlage und deren Verwendung |
| EP2604322A2 (de) | 2011-12-15 | 2013-06-19 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Mehrlagiges Filtermedium |
| DE102011121589A1 (de) | 2011-12-20 | 2013-06-20 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| EP2745907A2 (de) | 2012-12-20 | 2014-06-25 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Filtermedium |
| DE102014010332A1 (de) | 2014-07-14 | 2016-01-14 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Verbundwerkstoffe umfassend Wabenkerne auf Basis von thermoplastischen Synthesefaservliesen |
| EP3086384A1 (de) | 2015-04-23 | 2016-10-26 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Röhrenförmige taschen vom patronengurt-typ für blei-säure batterien aus einem textilen flächengebilde textiles flächengebilde |
| DE102016015248A1 (de) | 2016-12-21 | 2018-06-21 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Hocheffizientes Filtermedium |
| EP3771483A1 (de) | 2019-07-31 | 2021-02-03 | Johns Manville | Reinigbares filtermedium |
| EP4303353A1 (de) | 2022-07-05 | 2024-01-10 | Johns Manville | Vliesstoff mit verbessertem mds-cd-verhältnis, verfahren zu seiner herstellung und seine verwendung |
| EP4556214A1 (de) | 2023-11-15 | 2025-05-21 | Johns Manville | Vliesstoff mit neuem thermoplastischem bindemittel |
| EP4574231A1 (de) | 2023-12-18 | 2025-06-25 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Filtermaterial und verfahren zur bereitstellung eines filtermaterials |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE9207367U1 (de) * | 1992-05-30 | 1992-09-10 | Johns Manville International, Inc., Denver, Col. | Schichtstoff aus Vlies und Gelege |
| DK0590629T3 (da) * | 1992-10-02 | 1997-08-18 | Hoechst Ag | Bituminøs undertagsbane og bærerbane dertil |
| US6451409B1 (en) * | 1995-10-17 | 2002-09-17 | Robert F. Lassiter | Roofing material with integrally formed nail tabs |
| US5695373A (en) * | 1996-09-13 | 1997-12-09 | Bay Mills Limited | Preformed unitary composite for reinforcing while suppressing curl in bituminous roofing membranes and process for making such composites |
| GB2340654A (en) | 1997-06-03 | 2000-02-23 | Seagate Technology | Optical disc for optical storage system |
| US9960300B2 (en) * | 2007-11-21 | 2018-05-01 | Arkema Inc. | Photovoltaic module using PVDF based flexible glazing film |
| US8906275B2 (en) | 2012-05-29 | 2014-12-09 | Nike, Inc. | Textured elements incorporating non-woven textile materials and methods for manufacturing the textured elements |
| US20100199406A1 (en) | 2009-02-06 | 2010-08-12 | Nike, Inc. | Thermoplastic Non-Woven Textile Elements |
| US9682512B2 (en) | 2009-02-06 | 2017-06-20 | Nike, Inc. | Methods of joining textiles and other elements incorporating a thermoplastic polymer material |
| US20130255103A1 (en) | 2012-04-03 | 2013-10-03 | Nike, Inc. | Apparel And Other Products Incorporating A Thermoplastic Polymer Material |
| CA3084635C (en) | 2019-06-24 | 2025-04-01 | Owens Corning Intellectual Capital, Llc | LOWER LINING OF A ROOF WITH A HYDROPHOBIC NON-WOVEN CORE |
| CA3084636C (en) | 2019-06-24 | 2024-06-18 | Owens Corning Intellectual Capital, Llc | Roofing underlayment with enhanced walkability and traction |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0042150A1 (de) * | 1980-06-13 | 1981-12-23 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Voluminöser nichtgewebter Stoff aus kontinuierlichen Polybutylenterephthalat-Endlosfäden |
| EP0049732A1 (de) * | 1980-10-13 | 1982-04-21 | Firma Carl Freudenberg | Aufbügelbarer Einlagevliesstoff |
| EP0176847A2 (de) * | 1984-09-28 | 1986-04-09 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Schichtstoff |
| EP0242524A2 (de) * | 1986-02-22 | 1987-10-28 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Genadelter Schichtstoff |
| EP0359165A2 (de) * | 1988-09-14 | 1990-03-21 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2467934A1 (fr) * | 1979-10-18 | 1981-04-30 | Siplast Soc Nouvelle | Materiau de sous-toiture |
| DE3425794A1 (de) * | 1984-07-13 | 1986-01-23 | Ewald Dörken GmbH & Co KG, 5804 Herdecke | Unterspannbahn aus kunststoff |
-
1990
- 1990-03-14 DE DE4008043A patent/DE4008043A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1991
- 1991-03-09 AT AT91103645T patent/ATE123538T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-03-09 DE DE59105638T patent/DE59105638D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1991-03-09 EP EP19910103645 patent/EP0446822B2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-03-09 DK DK91103645T patent/DK0446822T4/da active
- 1991-03-12 US US07/667,888 patent/US5130178A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-03-13 IE IE84491A patent/IE67658B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-03-13 PT PT97025A patent/PT97025A/pt not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1991-03-14 JP JP4935491A patent/JP3096311B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1999
- 1999-08-18 GR GR990402060T patent/GR3030982T3/el unknown
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0042150A1 (de) * | 1980-06-13 | 1981-12-23 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Voluminöser nichtgewebter Stoff aus kontinuierlichen Polybutylenterephthalat-Endlosfäden |
| EP0049732A1 (de) * | 1980-10-13 | 1982-04-21 | Firma Carl Freudenberg | Aufbügelbarer Einlagevliesstoff |
| EP0176847A2 (de) * | 1984-09-28 | 1986-04-09 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Schichtstoff |
| EP0242524A2 (de) * | 1986-02-22 | 1987-10-28 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Genadelter Schichtstoff |
| EP0359165A2 (de) * | 1988-09-14 | 1990-03-21 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen |
Cited By (56)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0594892A1 (de) * | 1992-09-25 | 1994-05-04 | CASA BERNARDO Ltda | Verstärkter Werkstoff aus 100% tigem Polyester der als Applikator zur Aufnahme von Schädlingsbekämpfungsmittel verwendet wird und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| WO1996036778A1 (de) * | 1995-05-15 | 1996-11-21 | Paul Bauder Gmbh & Co. | Diffusionsoffene schalungs- und unterspannbahn |
| DE19620361A1 (de) * | 1996-05-10 | 1997-11-13 | Hoechst Trevira Gmbh & Co Kg | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE19618775A1 (de) * | 1996-05-10 | 1997-11-13 | Hoechst Trevira Gmbh & Co Kg | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE19620361C2 (de) * | 1996-05-10 | 1998-09-10 | Hoechst Trevira Gmbh & Co Kg | Trägereinlage und deren Verwendung |
| DE19620361C5 (de) * | 1996-05-10 | 2004-01-15 | Johns Manville International, Inc., Denver | Trägereinlage und deren Verwendung |
| DE102006060241A1 (de) * | 2006-12-20 | 2008-06-26 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE202006021073U1 (de) | 2006-12-20 | 2012-04-30 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Trägereinlage und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007008423A1 (de) | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Neue Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007008424A1 (de) | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Neue Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007012651A1 (de) | 2007-03-16 | 2008-09-18 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Direkt-dekorierbare Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007027299A1 (de) | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-24 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Filtermedium |
| EP2006009A2 (de) | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-24 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Filtermedium |
| DE102007028531A1 (de) | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-24 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Neue Verbundwerkstoffe, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102007060494A1 (de) | 2007-12-14 | 2009-06-18 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE202008010258U1 (de) | 2008-07-30 | 2008-10-30 | Johns Manville, Denver | Trägereinlage und beschichtete Dachbahnen |
| EP2154281A2 (de) | 2008-07-30 | 2010-02-17 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Basiszwischenschicht und beschichtete Dachmembrane |
| DE202008017741U1 (de) | 2008-10-11 | 2010-05-12 | Trevira Gmbh | Superabsorbierende Bikomponentenfaser |
| DE102008051430A1 (de) | 2008-10-11 | 2010-04-15 | Trevira Gmbh | Superabsorbierende Bikomponentenfaser |
| DE102008059128A1 (de) | 2008-11-26 | 2010-05-27 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| DE102008059129A1 (de) | 2008-11-26 | 2010-05-27 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| EP2192153A2 (de) | 2008-11-26 | 2010-06-02 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Mit Bindemittel verfestigtes Textilgewebe, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| EP2199333A1 (de) | 2008-11-26 | 2010-06-23 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| DE202009000539U1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2009-04-02 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Mineralisch beschichtete textile Flächen für Holzwerkstoffe |
| DE102009004573A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-15 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Betonschalung, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102009004970A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-15 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Mineralisch beschichtete textile Flächen für Holzwerkstoffe |
| EP2208836A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-21 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Betonschalung, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| EP2208614A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2010-07-21 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Mit Mineralien beschichtete Stoffoberflächen für Holzmaterialien |
| DE202009000393U1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2009-03-19 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Betonschalung |
| EP2886743A1 (de) | 2009-01-14 | 2015-06-24 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Betonschalung, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung |
| DE102009005587A1 (de) | 2009-01-21 | 2010-07-22 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Verfahren zur Qualitätssicherung von verstärkten flächigen Gebilden |
| DE102009022120A1 (de) | 2009-05-20 | 2010-11-25 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Filtermedium |
| EP2269706A1 (de) | 2009-05-20 | 2011-01-05 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Filtermedium |
| DE102009022120B4 (de) | 2009-05-20 | 2021-10-21 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Mehrlagiges Filtermedium, Verfahren zur dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung in der Luft/Gas- und Flüssigkeitsfiltration, sowie Filtermodule enthaltend das mehrlagige Filtermedium |
| EP2269814A1 (de) | 2009-06-03 | 2011-01-05 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Bedrucken von Vliesstoffen und deren Verwendung in Verbundstoffen |
| DE102009023737A1 (de) | 2009-06-03 | 2010-12-09 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Digitales Bedrucken von Vliesstoffen und deren Verwendung in Verbundwerkstoffen |
| EP2309046A1 (de) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-13 | Johns Manville | Mehrschichtige Stoffmaterialien für Bedachungsanwendungen |
| WO2011043937A1 (en) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-04-14 | Johns Manville | Binder composition |
| EP2604322A2 (de) | 2011-12-15 | 2013-06-19 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Mehrlagiges Filtermedium |
| DE102011121136A1 (de) | 2011-12-15 | 2013-06-20 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Mehrlagiges Filtermedium |
| DE102011121589A1 (de) | 2011-12-20 | 2013-06-20 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Binderverfestigtes, textiles Flächengebilde, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| EP2607533A2 (de) | 2011-12-20 | 2013-06-26 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Mit Bindemittel verfestigtes Textilgewebe, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und dessen Verwendung |
| EP2745907A2 (de) | 2012-12-20 | 2014-06-25 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Filtermedium |
| US12090432B2 (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2024-09-17 | Johns Manville | Filter medium |
| DE102012025023A1 (de) | 2012-12-20 | 2014-06-26 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Filtermedium |
| DE102014010332A1 (de) | 2014-07-14 | 2016-01-14 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Verbundwerkstoffe umfassend Wabenkerne auf Basis von thermoplastischen Synthesefaservliesen |
| EP2974855A2 (de) | 2014-07-14 | 2016-01-20 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Verbundwerkstoffe umfassend wabenkerne auf basis von thermoplastischen synthesefaserspinnvliesen |
| EP3086384A1 (de) | 2015-04-23 | 2016-10-26 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Röhrenförmige taschen vom patronengurt-typ für blei-säure batterien aus einem textilen flächengebilde textiles flächengebilde |
| WO2018114764A1 (de) | 2016-12-21 | 2018-06-28 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Hocheffizientes filtermedium |
| DE102016015248A1 (de) | 2016-12-21 | 2018-06-21 | Johns Manville Europe Gmbh | Hocheffizientes Filtermedium |
| EP3771483A1 (de) | 2019-07-31 | 2021-02-03 | Johns Manville | Reinigbares filtermedium |
| EP4303353A1 (de) | 2022-07-05 | 2024-01-10 | Johns Manville | Vliesstoff mit verbessertem mds-cd-verhältnis, verfahren zu seiner herstellung und seine verwendung |
| WO2024008660A1 (en) | 2022-07-05 | 2024-01-11 | Johns Manville | Nonwoven material with improved md/cd ratio, method for its manufacture and its use |
| EP4556214A1 (de) | 2023-11-15 | 2025-05-21 | Johns Manville | Vliesstoff mit neuem thermoplastischem bindemittel |
| WO2025103962A1 (en) | 2023-11-15 | 2025-05-22 | Johns Manville | Nonwoven with new thermoplastic binder |
| EP4574231A1 (de) | 2023-12-18 | 2025-06-25 | Johns Manville Europe GmbH | Filtermaterial und verfahren zur bereitstellung eines filtermaterials |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE123538T1 (de) | 1995-06-15 |
| IE67658B1 (en) | 1996-04-17 |
| JPH04214474A (ja) | 1992-08-05 |
| DE4008043A1 (de) | 1991-09-19 |
| DK0446822T4 (da) | 1999-11-22 |
| GR3030982T3 (en) | 1999-12-31 |
| IE910844A1 (en) | 1991-09-25 |
| US5130178A (en) | 1992-07-14 |
| PT97025A (pt) | 1993-03-31 |
| EP0446822B2 (de) | 1999-06-16 |
| JP3096311B2 (ja) | 2000-10-10 |
| DE59105638D1 (de) | 1995-07-13 |
| EP0446822B1 (de) | 1995-06-07 |
| DK0446822T3 (da) | 1995-10-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0446822B1 (de) | Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen | |
| EP0590629B1 (de) | Bituminierte Dachunterspannbahn und Trägerbahn dazu | |
| DE19642252C2 (de) | Diffusionsoffene Dachunterspannbahn und Verfahren zum Herstellen derselben | |
| EP0435001B1 (de) | Schichtstoff | |
| EP0006189B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen einer bituminierten Dachbahn | |
| EP0806509B2 (de) | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung | |
| DE3435643A1 (de) | Schichtstoff | |
| DE9207367U1 (de) | Schichtstoff aus Vlies und Gelege | |
| EP1939342B1 (de) | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung | |
| EP0880628B1 (de) | Diffusionsoffene dachunterspannbahn und verfahren zum herstellen derselben | |
| EP0359165B1 (de) | Trägerbahn für Dachunterspannbahnen | |
| EP0806510A1 (de) | Trägereinlage, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung | |
| DE7739489U1 (de) | Dach- und dichtungsbahn | |
| EP0805752B1 (de) | Flächenartiges verbundisoliermaterialsystem und verfahren zu dessen herstellung | |
| EP0700779A2 (de) | Diffusionsoffene Baufolien und Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung | |
| DE19950057B4 (de) | Zwei- oder Mehrlagenschichtstoffe aus Polyesterfilamentvliesen und Glasfasergeweben oder -gelegen | |
| EP0260494A1 (de) | Bitumenbahn mit Abdeckschicht und Verfahren zu ihrer Verwendung | |
| DE19952432B4 (de) | Schichtstoff | |
| DE19935408B4 (de) | Mehrlagenschichtstoff | |
| EP2052103B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines grundvliesstoffes als beschichtungsträger | |
| DE19935531C2 (de) | Zweilagenschichtstoff | |
| DE9313329U1 (de) | Gerauhtes Spinnvlies aus Synthesefasern | |
| DE9318032U1 (de) | Gerauhtes Spinnvlies aus Synthesefasern | |
| DE29602908U1 (de) | Bituminierte Dachunterspannbahn und Trägerbahn dazu | |
| DE202006021073U1 (de) | Trägereinlage und deren Verwendung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19910906 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19931116 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK FR GB GR LI LU NL SE |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK FR GB GR LI LU NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 123538 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19950615 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59105638 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19950713 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: FG4A Free format text: 3016674 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19950821 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PLBQ | Unpublished change to opponent data |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OPPO |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: AKZO NOBEL N.V. Effective date: 19960306 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: AKZO NOBEL N.V. |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| PLAW | Interlocutory decision in opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IDOP |
|
| PLAW | Interlocutory decision in opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IDOP |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19990323 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Payment date: 19990331 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 19990616 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK FR GB GR LI LU NL SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: AEN Free format text: AUFRECHTERHALTUNG DES PATENTES IN GEAENDERTER FORM |
|
| NLR2 | Nl: decision of opposition | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19990818 |
|
| GBTA | Gb: translation of amended ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(b)/1977) | ||
| ET3 | Fr: translation filed ** decision concerning opposition | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T4 |
|
| NLS | Nl: assignments of ep-patents |
Owner name: JOHNS MANVILLE INTERNATIONAL, INC. |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000309 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: DIPL.-ING. ETH H. R. WERFFELI PATENTANWALT Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PUE Owner name: HOECHST AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT TRANSFER- JOHNS MANVILL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20010323 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020402 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20060216 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20060221 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20060317 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20060329 Year of fee payment: 16 Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20060329 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20060330 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20060427 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20060502 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070310 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070309 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20070309 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20071001 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *JOHNS MANVILLE INTERNATIONAL INC. Effective date: 20070331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20071130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20071001 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20071002 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070331 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070309 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070402 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |