EP0239013A2 - Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil - Google Patents
Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0239013A2 EP0239013A2 EP87104061A EP87104061A EP0239013A2 EP 0239013 A2 EP0239013 A2 EP 0239013A2 EP 87104061 A EP87104061 A EP 87104061A EP 87104061 A EP87104061 A EP 87104061A EP 0239013 A2 EP0239013 A2 EP 0239013A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- shaft rod
- shaft
- heald frame
- heald
- projections
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03C—SHEDDING MECHANISMS; PATTERN CARDS OR CHAINS; PUNCHING OF CARDS; DESIGNING PATTERNS
- D03C9/00—Healds; Heald frames
- D03C9/06—Heald frames
- D03C9/0608—Construction of frame parts
- D03C9/0616—Horizontal upper or lower rods
- D03C9/0625—Composition or used material
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03C—SHEDDING MECHANISMS; PATTERN CARDS OR CHAINS; PUNCHING OF CARDS; DESIGNING PATTERNS
- D03C9/00—Healds; Heald frames
- D03C9/06—Heald frames
- D03C9/0666—Connection of frame parts
- D03C9/0675—Corner connections between horizontal rods and side stays
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03C—SHEDDING MECHANISMS; PATTERN CARDS OR CHAINS; PUNCHING OF CARDS; DESIGNING PATTERNS
- D03C9/00—Healds; Heald frames
- D03C9/06—Heald frames
- D03C9/0683—Arrangements or means for the linking to the drive system
Definitions
- the invention relates to a heald frame with shaft rods made of an aluminum profile and with side supports, wherein the side supports on the end faces of the shaft rod ends each engage with a projection in cavities of the aluminum profile and are anchored therein by means of screws.
- the invention has for its object to form a heald frame with shaft rods made of an aluminum profile so that a secure connection of the side supports to the shaft rods and good power transmission from shaft drive to the shaft rods and the side supports is achieved.
- the object is achieved with a heald frame of the type mentioned at the outset in that the projections of the side supports have the same thickness as the shaft rod at least in the area of the anchoring screws and protrude into matching end-side recesses in the shaft rod and in that the anchoring screw has its head on one each on the narrow side of a shaft rod, the cheeks are placed on the outside and the other end is screwed into the threaded bore of a jaw inserted into a cavity of the shaft rod profile.
- the projections of the side supports can expediently rest at least approximately over their entire circumference on the edges of the matching end recess of the associated shaft rod end.
- the connecting projections of the side supports are thicker than in conventional heald frames, so that they allow the formation of larger through-bores for stronger anchoring screws.
- the projections are no longer on the side walls of the shaft rod hollow profile and on fastening jaws as before, but are supported by the system against the edges of the end recess formed in the shaft rod end over their entire circumference and thus tilt-proof on the shaft rod.
- the jaws placed on the outside of the narrow side of the shaft rod allow a good distribution of the forces transmitted via an anchoring screw to the shaft rod.
- the cheek placed on the outside can also be formed by a shaft drive piece, the anchoring screw also serving to fasten this shaft drive piece.
- the anchoring screw also serving to fasten this shaft drive piece.
- the tilt-proof fit of the projections of the sides & supports in the shaft rods can be increased by an extension of the projections, which has a smaller thickness than the shaft rod and fits into a cavity of the shaft rod 4 profiles. This extension creates additional force transmission surfaces on the inside of the shaft rod.
- connection points of the side supports with the shaft rods of a heald frame designed according to the invention are explained in more detail with reference to the attached drawing.
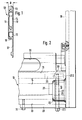
- Fig. 1 shows a shaft rod 10 of a heald frame made of an extruded aluminum profile in cross section.
- the shaft rod 10 has closed side walls 11 and 12, a closed upper narrow side 13 and two continuous cavities 14 and 15 on the inside. It has a maximum thickness B.
- the one side wall 12 is extended beyond a lower narrow side 16 of the shaft rod 10 to a holding part 17 which, according to FIGS. 2 and 3, can have larger cutouts 36.
- shaft rods 10 form the upper and lower frame legs of the heald frame in a known manner and are also connected to one another by suitably profiled but narrower side supports 18.
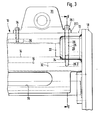
- FIG. 2 shows the lower right corner and FIG. 3 the upper right corner of a heald frame, where a side support 18 is each connected to a shaft rod 10.
- the side support 18 is provided at both ends with a solid web-like lateral projection 19 and 20, which has the same thickness B as the shaft rod 10.
- Both projections 19 and 20 also have an extension 21 and 22, which has a smaller thickness , which corresponds to the clear width of the cavity 14 of the shaft rods 10.
- 3 visible shaft rod 10 of the heald frame are provided with an end-side recess 23 and 24, which are exactly on the corners
- Shape of the projections 19, 20 is adapted so that the projections 19 and 20 can be inserted without tilting into the recesses 23, 24 of the shaft rods 10 formed by milling, the extensions 21 and 22 being immersed in the adjoining cavity 14 of the shaft rods 10.
- the projections 19 and 20 are thus supported almost over their entire circumference at the edges of the cutouts 23 and 24 and thus on the side walls 11 and 12 of the shaft rods 10.
- the projection 20 (and in the same way also the lower projection 19 of the shaft rod 18) is provided with a through hole 25.
- the through hole 25 serves to pass an anchoring screw 26 or 27.
- the other end provided with a thread 27.2 of the anchoring screw 27 is screwed into a threaded bore of a second jaw 29, which is inserted into the cavity 15 of the shaft rod 10 and held there by means of a dowel pin 30 which is through a transverse bore in the jaw 29 and with it aligned holes in the side walls 11 and 12 of the shaft rod 10 protrudes.
- the anchoring screw 26 serves at the same time for fastening a shaft drive piece 31 placed on the upper narrow side 13 of the shaft rod, on which the shaft drive device acts, but whose known structure is of no further interest.
- the base 31.1 of this shaft drive piece 31 here forms the jaws, against which the head 26.1 of the anchoring screw 26 rests, the threaded other end 26.2 of which can be screwed into the threaded bore of a second jaw 32 which is inserted into the cavity 15 of the shaft rod.
- the jaw 28 shown in FIG. 2 is additionally fastened by means of a second screw 33 which is directly in a 3 is anchored by means of a screw 34, which is anchored in a threaded hole of an additional jaw 35 inserted into the shaft rod.
- the side supports 18 can be easily and quickly released from the shaft rods 10.
- the jaws 29 and 32 serving to anchor the clamping screws 26 and 27 with their threaded bores are expediently made of steel. Anchoring of the screws in the relatively soft aluminum material of the shaft rods 10 is thus avoided.
- the jaws are easy to replace if the threads of their holes are damaged.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Looms (AREA)
- Mutual Connection Of Rods And Tubes (AREA)
- Heat Treatment Of Articles (AREA)
- Shafts, Cranks, Connecting Bars, And Related Bearings (AREA)
- Joining Of Building Structures In Genera (AREA)
- Superconductors And Manufacturing Methods Therefor (AREA)
- Woven Fabrics (AREA)
- Tents Or Canopies (AREA)
- Forging (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft einen Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil und mit Seitenstützen, wobei die Seitenstützen an den Stirnseiten der Schaftstabenden jeweils mit einem Vorsprung in Hohlräume des Aluminiumprofils eingreifen und darin mittels Schrauben verankert sind.
- Bei dem Bestreben, Webmaschinen zur Erhöhung der Produktiv vität mit höheren Betriebsgeschwindigkeiten zu betreiben, hat sich unter anderem das Problem ergeben, daß die Webeschäfte herkömmlicher Bauart in ihrer Stabilität nicht mehr ausreichen, um die erhöhte Schwingungsbelastung und den rascheren Bewegungswechsel zu verkraften. Dies gilt insbesondere für Webeschäfte mit aus einem Aluminiumprofil gefertigten Schaftstäben. Es ist zwar grundsätzlich bekannt, bei der Verbindung von Seitenstützen mit hohlen Schaftstäben die Seitenstützen mit einem Vorsprung zu versehen, der in das Hohlprofil des Webeschaftes eintaucht und innerhalb des Hohlprofiles mittels einer Spannbacken und den Vorsprung durchdringenden Schraube einzuspannen und formschlüssig zu halten. Eine solche Verbindung ist aber nicht ausreichend, weil hier nur schwache Verankerungsschrauben verwendet werden können und der Formschluß der Seitenstützen mit den Schaftstabenden zu gering ist, um den erhöhten Belastungen standzuhalten.
- Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, einen Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil so auszubilden, daß eine sichere Verbindung der Seitenstützen mit den Schaftstäben und eine gute Kraftübertragung von Schaftantrieb auf die Schaftstäbe und die Seitenstützen erreicht wird.
- Die gestellte Aufgabe wird mit einem Webeschaft der eingangs genannten Art erfindungsgemäß dadurch gelöst, daß die Vorsprünge der Seitenstützen mindestens im Bereich der Verankerungsschrauben die gleiche Dicke wie der Schaftstab haben und in passende stirnseitige Ausnehmungen des Schaftstabes ragen und daß die Verankerungsschraube mit ihrem Kopf jeweils auf einem auf der Schmalseite eines Schaftstabes außen aufgesetzten Backen aufliegt und mit ihrem anderen Ende jeweils in die Gewindebohrung eines in einen Hohlraum des Schaftstabprofiles eingesetzten Backens eingeschraubt ist. Hierbei können die Vorsprünge der Seitenstützen zweckmäßig jeweils mindestens annähernd über ihren ganzen Umfang an den Rändern der passenden stirnseitigen Ausnehmung des zugeordneten Schaftstabendes anliegen.
- Bei einem erfindungsgemäß ausgebildeten Webeschaft sind die Verbindungsvorsprünge der Seitenstützen dicker als bei herkömmlichen Webeschäften, so daß sie die Ausbildung von größeren Durchgangsbohrungen für stärkere Verankerungsschrauben erlauben. Die Vorsprünge liegen nicht mehr wie bisher nur an Seitenwandungen des Schaftstab-Hohlprofiles und an Befestigungsbacken an, sondern sind durch die Anlage gegen die Ränder der im Schaftstabende ausgebildeten stirnseitigen Ausnehmung über ihren ganzen Umfang und damit verkantungssicher am Schaftstab abgestützt. Der auf die Schmalseite des Schaftstabes außen aufgesetzte Backen erlaubt eine gute Verteilung der über eine Verankerungsschraube übertragenen Kräfte auf den Schaftstab.
- Der außen aufgesetzte Backen kann erfindungsgemäß auch durch ein Schaftantriebsstück gebildet sein, wobei die Verankerungsschraube gleichzeitig zur Befestigung dieses Schaftantriebsstückes dient. Bei dieser Ausführungsform wird über die Verankerungsschraube eine unmittelbare Verteilung der vom Schaftantriebsstück ausgehenden Belastungskräfte auf den Schaftstab und auf die angrenzende Seitenstütze erreicht.
- Der verkantungssichere Sitz der Vorsprünge der Seiten& stützen in den Schaftstäben kann noch durch einen Fortsatz der Vorsprünge erhöht werden, der eine geringere Dicke als der Schaftstab hat und in einen Hohlraum des Schaftstab4 profiles paßt. Durch diesen Fortsatz werden noch zusätzliche Kraftübertragungsflächen an den Innenseiten des Schaftstabes geschaffen.
- Nachfolgend werden Ausführungsbeispiele von Verbindungsstellen der Seitenstützen mit den Schaftstäben eines erfindungsgemäß ausgebildeten Webeschaftes anhand der beiliegenden Zeichnung näher erläutert.
- Im einzelnen zeigen:
- Fig. 1 einen Querschnitt durch einen profilierten Aluminiumschaftstab eines Webeschaftes;
- Fig. 2 eine Darstellung der rechten unteren Ecke eines rechteckigen Webeschaftes mit der Verbindungsstelle der Seitenstütze mit dem Schaftstabende;
- Fig. 3 eine Darstellung der rechten oberen Ecke des Webeschaftes mit der dortigen Verbindungsstelle der Seitenstütze mit dem Schaftstabende;
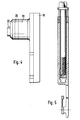
- Fig. 4 eine Einzeldarstellung des Endbereiches der in Fig. 3 verwendeten Seitenstütze;
- Fig. 5 einen Querschnitt durch die Verbindungsstelle von Seitenstütze und Schaftstab entlang der Linie V - V in Fig. 3 in gegenüber Fig. 3 verdoppeltem Maßstab.
- Fig. 1 zeigt einen aus einem Aluminium-Strangpreßprofil hergestellten Schaftstab 10 eines Webeschaftes im Querschnitt. Der Schaftstab 10 weist geschlossene Seitenwandungen 11 und 12, eine geschlossene obere Schmalseite 13 und im Innern zwei durchgehende Hohlräume 14 und 15 auf. Er hat eine maximale Dicke B. Die eine Seitenwandung 12 ist über eine untere Schmalseite 16 des Schaftstabes 10 hinaus zu einem Halteteil 17 verlängert, der gemäß Fig. 2 und 3 größere Aussparungen 36 aufweisen kann.
- Bei den rechteckigen Webeschäften bilden Schaftstäbe 10 in bekannter Weise den oberen und den unteren Rahmenschenkel des Webeschaftes und sind durch zweckmäßig ebenfalls pro4 filierte, aber schmälere Seitenstützen 18 miteinander verbunden. Fig. 2 zeigt die rechte untere und Fig. 3 die rechte obere Ecke eines Webeschaftes, wo eine Seitenstütze 18 jeweils mit einem Schaftstab 10 verbunden ist. Die Seitenstütze 18 ist an ihren beiden Enden mit einem massiven stegartigen seitlichen Vorsprung 19 und 20 versehen, der die gleiche Dicke B wie der Schaftstab 10 aufweist..Beide Vorsprünge 19 und 20 weisen noch einen Fortsatz 21 und 22 auf, der eine kleinere Dicke hat, die der lichten Weite des Hohlraumes 14 der Schaftstäbe 10 entspricht. Zur Aufnahme der Vorsprünge 19 und 20 sind sowohl der untere, aus Fig. 2 ersichtliche, als auch der obere, aus Fig. 3 erL sichtliche Schaftstab 10 des Webeschaftes mit einer stirnseitigen Ausnehmung 23 und 24 versehen, die bis auf die Ecken genau an die Form der Vorsprünge 19, 20 angepaßt ist, so daß sich die Vorsprünge 19 und 20 verkantungsfrei in die durch Ausfräsen gebildeten Ausnehmungen 23, 24 der Schaftstäbe 10 einstecken lassen, wobei die Fortsätze 21 und 22 in den anschließenden Hohlraum 14 der Schaftstäbe 10 eintauchen. Die Vorsprünge 19 und 20 stützen sich also nahezu über ihren ganzen Umfang an den Rändern der Ausfräsungen 23 und 24 und damit an den Seitenwandungen 11 und 12 der Schaftstäbe 10 ab.
- Wie die Einzeldarstellung des oberen Endbereichs der Seitenstütze 18 in Fig. 4 zeigt, ist der Vorsprung 20 (und in gleicher Weise auch der untere Vorsprung 19 des Schaftstabes 18) mit einer Durchgangsbohrung 25 versehen. Die Durchgangsbohrung 25 dient zum Hindurchführen einer Verankerungsschraube 26 oder 27. Der Kopf 27.1 der in Fig. 2 dargestellten Verankerungsschraube 27 liegt gegen einen auf der Schmalseite 13 des Schaftstabes 10 aufliegenden länglichen Backen 28 an, der ebenfalls eine nicht bezeichnete Durchgangsbohrung für die Verankerungsschraube 27 aufweist. Das mit einem Gewinde vesehene andere Ende 27.2 der Verankerungsschraube 27 ist in eine Gewindebohrung eines zweiten Backens 29 eingeschraubt, der in den Hohlraum 15 des Schaftstabes 10 eingeschoben ist und dort mittels eines Spannstiftes 30 gehalten ist, der durch eine Querbohrung des Backens 29 und mit ihr fluchtende Bohrungen in den Seitenwandungen 11 und 12 des Schaftstabes 10 hindurchragt.
- An der aus Fig. 3 ersichtlichen oberen Verbindungsstelle der Seitenstütze 18 mit einem Schaftstab 10 dient die Verankerungsschraube 26 gleichzeitig zum Befestigen eines auf die obere Schmalseite 13 des Schaftstabes aufgesetzten Schaftantriebsstückes 31, an welchem die Schaftantriebsvorrichtung angreift, dessen bekannter Aufbau aber nicht näher interessiert. Der Sockel 31.1 dieses Schaftantriebsstückes 31 bildet hier den Backen, gegen welchen der Kopf 26.1 der Verankerungsschraube 26 anliegt, deren mit einem Gewinde versehenes anderes Ende 26.2 in die Gewindebohrung eines zweiten und in den Hohlraum 15 des Schaftstabes eingeschobenen Backens 32 einschraubbar ist. Während der aus Fig. 2 ersichtliche Backen 28 zusätzlich mittels einer zweiten Schraube 33 befestigt ist, die direkt in einer Gewindebohrung des Schaftstabes 10 verankert ist, ist das aus Fig. 3 ersichtliche Schaftantriebsstück 31 zusätzlich mittels einer Schraube 34 befestigt, die in einer Gewindebohrung eines in den Schaftstab eingeschobenen zusätzlichen Backens 35 verankert ist.
- Durch Entfernen der relativ starken Verankerungsschrauben 26 und 27 lassen sich die Seitenstützen 18 leicht und rasch von den Schaftstäben 10 lösen. Die zur Verankerung der Spannschrauben 26 und 27 dienenden Backen 29 und 32 mit ihren Gewindebohrungen sind zweckmäßig aus Stahl gefertigt. Eine Verankerung der Schrauben in dem relativ weichen Aluminiummaterial der Schaftstäbe 10 ist also vermieden. Die Backen lassen sich leicht auswechseln, wenn die Gewinde ihrer Bohrungen beschädigt sein sollten.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT87104061T ATE54684T1 (de) | 1986-03-25 | 1987-03-19 | Webeschaft mit schaftstaeben aus einem aluminiumprofil. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE3609964 | 1986-03-25 | ||
| DE19863609964 DE3609964A1 (de) | 1986-03-25 | 1986-03-25 | Webeschaft mit schaftstaeben aus einem aluminiumprofil |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0239013A2 true EP0239013A2 (de) | 1987-09-30 |
| EP0239013A3 EP0239013A3 (en) | 1988-02-17 |
| EP0239013B1 EP0239013B1 (de) | 1990-07-18 |
Family
ID=6297187
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP87104061A Expired - Lifetime EP0239013B1 (de) | 1986-03-25 | 1987-03-19 | Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4753273A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0239013B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS62243845A (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE54684T1 (de) |
| CS (1) | CS274613B2 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE3609964A1 (de) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1991010764A1 (de) * | 1990-01-18 | 1991-07-25 | C.C. Egelhaaf Maschinenfabrik Gmbh | Mittelverbinder für insbesondere metallische webeschäfte |
| WO1997025465A1 (de) * | 1996-01-13 | 1997-07-17 | Firma Schmeing Gmbh & Co. | Verfahren zur herstellung eines schaftstabes für webschäfte aus einem metallhohlprofil |
| DE19858013A1 (de) * | 1998-12-01 | 2000-06-08 | Schmeing Gmbh & Co | Verbindung zwischen Schaftstab und Seitenstütze bei Webschäften |
| CN101387030B (zh) * | 2007-09-12 | 2013-12-04 | 格罗兹-贝克特公司 | 用于综框的异型杆和承载器杆 |
| EP3241932A1 (de) * | 2016-05-02 | 2017-11-08 | Groz-Beckert KG | Webschaft und herstellverfahren für einen webschaft |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5056231A (en) * | 1990-06-01 | 1991-10-15 | Bear Automotive Service Equipment Co. | Apparatus for locking wheel unit in automotive wheel alignment system |
| DE19612404A1 (de) * | 1996-03-28 | 1997-10-02 | Grob & Co Ag | Eckverbindung für einen Webschaft |
| DE10325908B4 (de) * | 2003-06-05 | 2005-07-21 | Groz-Beckert Kg | Schaftstab, Webschaft und Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Schaftstabs |
| FR2857987B1 (fr) * | 2003-07-21 | 2005-10-07 | Staubli Sa Ets | Cadre de lisses et metier a tisser equipe d'au moins un tel cadre |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT261503B (de) * | 1965-04-30 | 1968-04-25 | Grob & Co Ag | Webschaft mit einer lösbaren Eckverbindung |
| CH427688A (de) * | 1965-04-30 | 1966-12-31 | Grob & Co Ag | Webschaft mit einer lösbaren Eckverbindung |
| CH538560A (de) * | 1971-05-13 | 1973-06-30 | Grob & Co Ag | Webschaft |
| DE2126074A1 (de) * | 1971-05-26 | 1972-12-07 | Fa. CC. Egelhaaf, 7411 Reutlingen-Betzingen | Litzentragschienenhalter-Verriegelung für Webeschäfte |
| US3949789A (en) * | 1972-06-14 | 1976-04-13 | Grob & Co. Aktiengesellschaft | Heddle frame stave with closed T-rail |
| AT315767B (de) * | 1972-06-28 | 1974-06-10 | Grob & Co Ag | Hohler Schaftstab |
| JPS5514185A (en) * | 1978-07-18 | 1980-01-31 | Sintokogio Ltd | Solvent of facing material for reduced-pressure-molded casting mold |
| DE3017629A1 (de) * | 1980-05-08 | 1981-11-12 | Kabushiki Kaisha Maruyama Seisakusho, Sakai | Webschaft |
-
1986
- 1986-03-25 DE DE19863609964 patent/DE3609964A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1987
- 1987-03-19 AT AT87104061T patent/ATE54684T1/de active
- 1987-03-19 EP EP87104061A patent/EP0239013B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1987-03-19 DE DE8787104061T patent/DE3763713D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1987-03-24 US US07/030,067 patent/US4753273A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1987-03-24 CS CS198287A patent/CS274613B2/cs unknown
- 1987-03-24 JP JP62068176A patent/JPS62243845A/ja active Pending
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1991010764A1 (de) * | 1990-01-18 | 1991-07-25 | C.C. Egelhaaf Maschinenfabrik Gmbh | Mittelverbinder für insbesondere metallische webeschäfte |
| US5332006A (en) * | 1990-01-18 | 1994-07-26 | Grob & Co Ltd. | Center connector, for metallic weaving shafts |
| WO1997025465A1 (de) * | 1996-01-13 | 1997-07-17 | Firma Schmeing Gmbh & Co. | Verfahren zur herstellung eines schaftstabes für webschäfte aus einem metallhohlprofil |
| US6076250A (en) * | 1996-01-13 | 2000-06-20 | Firma Schmeing Gmbh & Co. | Process for producing a heald shaft for weaving shafts out of a metal hollow section |
| DE19858013A1 (de) * | 1998-12-01 | 2000-06-08 | Schmeing Gmbh & Co | Verbindung zwischen Schaftstab und Seitenstütze bei Webschäften |
| DE19858013C2 (de) * | 1998-12-01 | 2001-02-01 | Schmeing Gmbh & Co | Verbindung zwischen Schaftstab und Seitenstütze bei Webschäften mit reiterlosem Schaft-Litzensystem |
| CN101387030B (zh) * | 2007-09-12 | 2013-12-04 | 格罗兹-贝克特公司 | 用于综框的异型杆和承载器杆 |
| EP3241932A1 (de) * | 2016-05-02 | 2017-11-08 | Groz-Beckert KG | Webschaft und herstellverfahren für einen webschaft |
| CN107338549A (zh) * | 2016-05-02 | 2017-11-10 | 格罗兹-贝克特公司 | 综框和用于综框的制造方法 |
| CN107338549B (zh) * | 2016-05-02 | 2021-10-22 | 格罗兹-贝克特公司 | 综框和用于综框的制造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US4753273A (en) | 1988-06-28 |
| ATE54684T1 (de) | 1990-08-15 |
| DE3763713D1 (de) | 1990-08-23 |
| CS198287A2 (en) | 1990-11-14 |
| JPS62243845A (ja) | 1987-10-24 |
| EP0239013B1 (de) | 1990-07-18 |
| CS274613B2 (en) | 1991-09-15 |
| DE3609964A1 (de) | 1987-10-01 |
| EP0239013A3 (en) | 1988-02-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE1535854C2 (de) | Webschaft mit einer losbaren Eckver bindung | |
| AT405757B (de) | Verbindungsstück für die lösbare verbindung zweier profilstäbe, vorzugsweise aus leichtmetall | |
| EP0278252A2 (de) | Ankerschiene | |
| EP0136431A2 (de) | Konstruktion aus Profilstäben | |
| EP0050242A2 (de) | Verbindung für Rahmenteile von Möbeln, insbesondere Büromöbeln | |
| EP0239013B1 (de) | Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil | |
| EP0539687B1 (de) | Querverbindung für Profilstäbe mit hinterschnittenen Längsnuten | |
| DE2218066B2 (de) | Webschaft | |
| EP0004374A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Verbinden von zwei Profilstäben | |
| DE3803292A1 (de) | Verbinder fuer zwei mit ihren offenen seiten einander zugewandte c-profilschienen | |
| EP0616135B1 (de) | Verbindungseinrichtung für Profilteile | |
| DE3604984C2 (de) | ||
| DE9012607U1 (de) | Klemmelement für eine Klemmvorrichtung | |
| EP0423474B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum lösbaren Verbinden von zwei Profilstäben | |
| DE3401468C2 (de) | Tragvorrichtung für elektrische Einrichtungen | |
| DE1634666A1 (de) | Vorgefertigtes Pfostenfundament | |
| DE4124157C2 (de) | Modulplatte, Träger o. dgl. Element zur Verwendung bei Maschinenaufbauten | |
| DE9014882U1 (de) | Einrichtung für die Befestigung eines Tragarms an einer Tischplatte | |
| DE4027935C2 (de) | Klemmvorrichtung oder Klemmverbund | |
| DE1954810C3 (de) | Beschlag zum lösbaren Verbinden zweier senkrecht aufeinanderstoßender plattenförmiger Bauteile, insbesondere Möbelteile | |
| EP0496057B1 (de) | Spreizwerkzeug | |
| DE8608183U1 (de) | Webeschaft mit Schaftstäben aus einem Aluminiumprofil | |
| DE8814964U1 (de) | Bausatz für eine Türzarge | |
| DE3706236A1 (de) | Verbindungselement fuer zwei tragteile | |
| EP4298351B1 (de) | Vorrichtung, insbesondere spannelement und verfahren zur anwendung dieses spannelements |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19880323 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19890830 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 54684 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19900815 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3763713 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19900823 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19910221 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19910222 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19910225 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19910308 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19910326 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19910327 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19910331 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19920319 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19920319 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19920331 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19920331 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19920331 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: C.C. EGELHAAF G.M.B.H. & CO. MASCHINENFABRIK K.G. Effective date: 19920331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19921001 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19921130 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19921201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050319 |