EP0234639B1 - Connecteur à déplacement d'isolant - Google Patents
Connecteur à déplacement d'isolant Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0234639B1 EP0234639B1 EP87200208A EP87200208A EP0234639B1 EP 0234639 B1 EP0234639 B1 EP 0234639B1 EP 87200208 A EP87200208 A EP 87200208A EP 87200208 A EP87200208 A EP 87200208A EP 0234639 B1 EP0234639 B1 EP 0234639B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- housing
- push member
- connection terminal
- cable
- opening
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 title claims description 19
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000012774 insulation material Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R11/00—Individual connecting elements providing two or more spaced connecting locations for conductive members which are, or may be, thereby interconnected, e.g. end pieces for wires or cables supported by the wire or cable and having means for facilitating electrical connection to some other wire, terminal, or conductive member, blocks of binding posts
- H01R11/11—End pieces or tapping pieces for wires, supported by the wire and for facilitating electrical connection to some other wire, terminal or conductive member
- H01R11/20—End pieces terminating in a needle point or analogous contact for penetrating insulation or cable strands
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R4/00—Electrically-conductive connections between two or more conductive members in direct contact, i.e. touching one another; Means for effecting or maintaining such contact; Electrically-conductive connections having two or more spaced connecting locations for conductors and using contact members penetrating insulation
- H01R4/24—Connections using contact members penetrating or cutting insulation or cable strands
- H01R4/2416—Connections using contact members penetrating or cutting insulation or cable strands the contact members having insulation-cutting edges, e.g. of tuning fork type
- H01R4/2445—Connections using contact members penetrating or cutting insulation or cable strands the contact members having insulation-cutting edges, e.g. of tuning fork type the contact members having additional means acting on the insulation or the wire, e.g. additional insulation penetrating means, strain relief means or wire cutting knives
- H01R4/2462—Connections using contact members penetrating or cutting insulation or cable strands the contact members having insulation-cutting edges, e.g. of tuning fork type the contact members having additional means acting on the insulation or the wire, e.g. additional insulation penetrating means, strain relief means or wire cutting knives the contact members being in a slotted bent configuration, e.g. slotted bight
Definitions
- Insulation-displacement connector
- the invention relates to an insulation-displacement connector adapted to be connected to a cable having a conductor with an insulation layer covering thereon, which connector displaces the insulation layer and pinches the conductor in a slot of a connection terminal in order to asure an electrical connection between the conductor and the connection terminal such as is further indicated in the heading of the main claim.
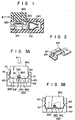
- FIG. 1 An example of a conventional insulation-displacement connector is shown in Fig. 1, and includes housing 100 with connection terminal 200 therewithin. At one end of connection terminal 200, insulation-displacement contact section 210 is formed, and is brought into contact with a conductor in a cable (not shown). At the other end of connection terminal 200, receptacle section 220 is formed, and is connected to a plug pin (not shown. At insulation-displacement contact section 210 of connection terminal 200, opening 211 and slot 212 communicating with opening are formed, as is shown in Fig. 2.
- Push member 300 made of an insulation material is snap-fitted into housing 100 such that projections 311, 312, formed on the side surfaces of push member 300, engage first grooves 110, shown in Fig. 3A, which are formed on the inner surfaces of the housing.
- Cable 400 is inserted, with cable insulation 410, through insertion hole 500 located between recess 320 of push member 300 and opening 211 of terminal 200, as is shown in Fig. 3A.
- a suitable tool such as a pair of pliers
- the cable insulation is displaced, so that conductor 420 of the cable is exposed and pinched in slot 212 of contact section 210, as is shown in Fig. 3B.
- projections 311, 312 of push member 300 abut against second grooves 120, as is shown in Fig. 3B.
- cable 400 is fixedly connected to connection terminal 200, via the exposed conductor 420.
- This conventional insulation-displacement connector comprises a housing in which three connection terminals are arranged in parallel relationship in order to receive a set of three parallel conductors each having an insulation layer. Each connection terminal has a downwardly-directed slot.
- the space within the housing is divided into three channels with the aid of two inner walls parallel to the opposite side walls. In said channels between said opposite side walls of the housing and the two inner walls respectively said three connection terminals are positioned on the bottom of the housing.
- the push member made of insulation material has a closed top and two opposite sides insertable into the housing. Within the space formed by the closed top and opposite sides a push element is located having three recesses evenly divided opposite the slots of the connection terminals of the three channels to receive the conductors. The three recesses each substantially have a shallow half circular form.
- the opposite inner surfaces of the side walls of the housing are each provided with a first rib, and a second rib, while the separate sides of the push member are each provided with first and second projections. These ribs cooperate with said projections on the separate sides of the push member when this push member is inserted into the housing.
- One object of the present invention is to provide an insulation-displacement connector which is markedly improved in relation to a conventional insulation-displacement connector.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide an insulation-displacement connector which, even if the cable is thin, assures a positive connection to a cable conductor, without the risk of the cable inadvertently slipping or dropping off the insertion hole.
- the invention aims to obviate the above mentioned problems with an insulation-displacement connector of the above mentioned type according to the invention such that the second engaging means are grooves provided on the opposite inner surfaces of the side walls of the housing near the bottom thereof, that the guide means are guiding grooves formed between the first and second engaging means, being first and second engaging grooves, on the opposite inner surfaces of the side walls of the housing that the guiding grooves are formed as wider guide grooves between first and second engaging grooves, that the recess in the push member opening toward the opening of the connection terminal is formed by two legs, which form said two opposite sides of the push member, and that the opening of the connection terminal is tapered, so that it aligns with the center of the recess, which has an inverted elongated U-shape, thus defining an insertion hole between said recess and said downwardly-directed opening, and that said projections are placed at the bottom of the sides of the push member.
- the cable is placed over the tapered opening of the connection terminal.
- the push member is pushed down over the cable so that the projections of the push member may be moved along the guide grooves.
- the cable is forced into the tapered opening of the connection terminal and is held there by the push member.
- the push member is further pushed with extra force, so that the cable is pushed into the slot of the connection terminal and the insulation layer of the cable is displaced to permit the exposed conductor to be connected to the connection terminal.
- the cable is temporarily held at the tapered opening of the connection terminal before it can be further pushed into the slot. This prevents the cable from inadvertently slipping or dropping off a connection terminal due to an impact.
- the push member is preferably made of an elastic insulation material, such as a plastic type, so that the pair of legs of the push member can be elastically deformed toward and away from each other.
- the projections of the legs may effectively be sharp-tipped in order to properly engage with the minute grooves which are formed as a knurled portion on the inner surfaces of the side wall of the housing.
- Figs. 4 and 5 show an insulation-displacement connector according to one embodiment of the present invention.
- the connector includes housing 10, connection terminals 20 located within the housing and push member 30 to be inserted into the housing through the open top of the housing.
- Inverted U-shaped recess 32 is formed on front surface 31 of push member 30.
- U-shaped recess 32 is so formed that its center aligns with tapered opening 21 of connection terminal 20.
- Projections 33, 34 are formed on either side of push member 30 such that they can engage with first engaging grooves 11 formed on the inner surface of the side walls 101 of housing 10, with insertion hole 50 defined between tapered opening 21 of connection terminal 20 and U-shaped recess 32 of push member 30.
- the size of insertion hole 50 is selected to allow the ready insertion of not only a thin cable but also a thick one.
- first grooves 11 of the housing Formed below first grooves 11 of the housing are guide grooves 12 which guide projections 33, 34. Guide grooves 12 allow the push member to be moved within a range of the width of the guide groove, when it is forced downward and its projections move beyond first engaging grooves 11.
- Push member 30 has a pair of legs 35, 36 with U-shaped recess 32 defined therebetween.
- the push member is preferably formed of plastic material so that the pair of legs can elastically deform inwardly or outwardly.
- the resultant push member allows its projections 33, 34 to be effectively snap-fitted into first grooves 11 and then into guide grooves 12 beyond the first grooves. With projections 33, 34 located in guide grooves 12, they are pushed firmly against the inner surface of guide grooves 12, by the elastic force of leg sections 35, 36, to allow push member 30 to be held in any desired position.
- Second engaging grooves 13 are formed adjacent to guide grooves 12, and are used to hold the cable in place, as is set forth below.
- the first grooves, second grooves and guide grooves extend in direction perpendicular to that in which push member is pushed into the housing.
- push member 30 is so set that its projections 33, 34 fit into first grooves 11, as is shown in Fig. 4.
- cable 40 is inserted into insertion hole 50 and placed on tapered opening 21.
- Push member 30 is pushed, for example, by hand, into guide grooves 12, as indicated by I in Fig. 6, with its projections clear of the first engaging groove, so that cable 40 is compressed over tapered opening 21 of connection terminal 20 and stopped at that position. Since projections 33, 34 abut against the inner surface of guide grooves 12, with a greater frictional force, there is no risk, even if the pushing force (such as hand grip force) is released from push member 30, that the push member will slip upwardly due to the elastic recovery force exerted by insulation layer 41.
- the pushing force such as hand grip force
- push member 30 With cable 40 so held, push member 30 is forcibly pushed by, for example, a pair of pliers, in the direction indicated by arrow P so that, as indicated by II in Fig. 6, projections 33, 34 snap-fit into second engaging grooves 13, to allow conductor 42 to be pinched in contact with slot 22 of connection terminal 20, with insulation layer 41 displaced.
- the cable Before this step, the cable is already in contact with push member 30 and, for this reason, the cable will assuredly be guided into the slot of connection terminal 20, by the push member.
- Fig. 7 shows an insulation-displacement connector according another embodiment of this invention.
- a number of minute grooves 14a, 14b, ... are formed, as a knurled portion, over a range of the width of guide grooves 12.
- Sharp-tipped projections 33, 34 may effectively be formed on push member 30 so as to allow them to be hooked onto the respective minute grooves.
Landscapes
- Connections By Means Of Piercing Elements, Nuts, Or Screws (AREA)
- Multi-Conductor Connections (AREA)
- Connector Housings Or Holding Contact Members (AREA)
Claims (1)
- Connecteur à déplacement d'isolant apte à être connecté à un câble (40) comportant un conducteur (42) sur lequel se trouve une couche isolante de couverture (41), comprenant:(A) un boîtier (10) en matériau isolant présentant deux parois latérales opposées (101), une partie supérieure ouverte et une partie avant ouverte;(B) une borne de connexion (20) disposée à l'intérieur du boîtier (10) et présentant une ouverture (21) dirigée vers le bas avec une fente (22) qui communique avec elle;(C) un élément poussoir (30) en matériau isolant présentant une partie supérieure fermée et deux parois opposées, insérable dans le boîtier, et présentant une cavité (32) disposée vis-à-vis de l'ouverture (21) de la borne de connexion et des saillies (33,34) formées sur les côtés respectifs vis-à-vis des surfaces intérieures des parois latérales (101) du boîtier, et qui est inséré dans le boîtier à partir de la partie supérieure ouverte du boîtier, l'élément poussoir étant capable avec sa cavité (32) de pousser le câble (40) placé sur l'ouverture (21) de la borne de connexion (20) de telle manière que le câble soit poussé dans la fente (22) afin de mettre à nu le conducteur (42) en vue de sa connexion à la borne de connexion;
le boîtier comportant:(a) des premiers moyens de prise (11) prévus sur les surfaces intérieures opposées des parois latérales (101) du boîtier et aptes se mettre en prise avec les saillies (33,34) de l'élément poussoir (30), le câble (40) étant placé sur l'ouverture (21) de la borne de connexion de manière à tenir l'élément poussoir par rapport au boîtier;
des deuxièmes moyens de prise (13); et
des moyens de guidage (12) aptes à guider l'élément poussoir (30) vers une position où le câble est tenu entre l'ouverture de la borne de connexion (21,20) et la cavité (32) de l'élément poussoir (30) avant que le conducteur dénudé ne soit connecté à la borne de connexion (20);
caractérisé en ce que
les deuxièmes moyens de prise (13) sont des gorges prévues sur les surfaces intérieures opposées des parois latérales du boîtier (10) près du fond de celui-ci,
les moyens de guidage sont des gorges de guidage (12) formées sur les surfaces intérieures opposées des parois latérales (101) du boîtier entre les premiers et deuxièmes moyens de prise, lesquels sont des premières (11) et deuxièmes (13) gorges de prise, les gorges de guidage étant formées entre les premières (11) et deuxièmes (13) gorges de prise comme des gorges de guidage (12) plus larges, et
la cavité (32) pratiquée dans l'élément poussoir et qui s'ouvre vers l'ouverture (21) de la borne de connexion est formée de deux jambages (35,36) qui forment les deux côtés opposés de l'élément poussoir (30), et l'ouverture (21) de la borne de connexion se rétrécit de façon à s'aligner avec le centre de la cavité (32), laquelle a une forme allongée en U inversé (voir fig. 4), ce qui définit entre cette cavité (32) et l'ouverture (21) dirigée vers le bas un trou d'insertion (50), les saillies (33,34) étant disposées au bas des côtés de l'élément poussoir.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP1986019970U JPS62131368U (fr) | 1986-02-14 | 1986-02-14 | |
| JP19970/86U | 1986-02-14 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0234639A1 EP0234639A1 (fr) | 1987-09-02 |
| EP0234639B1 true EP0234639B1 (fr) | 1994-10-26 |
Family
ID=12014051
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP87200208A Expired - Lifetime EP0234639B1 (fr) | 1986-02-14 | 1987-02-11 | Connecteur à déplacement d'isolant |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0234639B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPS62131368U (fr) |
| KR (1) | KR920000714B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3750678T2 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2691846B1 (fr) * | 1992-05-26 | 1995-12-22 | Jacques Nozick | Prise de courant electrique a contact auto-denudant. |
| US5547391A (en) * | 1993-03-11 | 1996-08-20 | Molex Incorporated | Commoning electrical connector |
| JPH08508607A (ja) * | 1993-04-13 | 1996-09-10 | シーメンス アクチエンゲゼルシヤフト | バス線に接続するためのアクチュエータまたはセンサ |
| EP0695468B1 (fr) * | 1993-04-14 | 1996-10-09 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Module pour raccorder des actionneurs et/ou des detecteurs |
| CA2135578A1 (fr) * | 1993-11-17 | 1995-05-18 | Julio F. Rodrigues | Connecteur electrique avec bloc d'ancrage du conducteur |
| DE4442673A1 (de) * | 1994-11-30 | 1996-06-05 | Siemens Ag | Elektrischer Potentialverteiler in Schneidklemmtechnik |
| JP5026884B2 (ja) | 2007-08-04 | 2012-09-19 | 株式会社森精機製作所 | 自動工具交換装置を有する工作機械 |
| HUP1400211A2 (en) | 2014-04-24 | 2015-11-30 | Jozsef Laszlo Baran | Method for manufacturing insulation displacement connector device and insulation displacement connector device |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT312726B (de) * | 1970-11-27 | 1974-01-10 | Assmann Geb | Lötfreier Drahtverbinder |
| GB1554103A (en) * | 1975-07-22 | 1979-10-17 | Bicc Ltd | Electrical connectors |
| ZA80400B (en) * | 1979-03-12 | 1981-05-27 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Wire cutting electrical connector |
| JPS603743B2 (ja) * | 1980-07-05 | 1985-01-30 | モレックス・インコ−ポレ−テッド | リボンケ−ブル用電気コネクタ− |
-
1986
- 1986-02-14 JP JP1986019970U patent/JPS62131368U/ja active Pending
-
1987
- 1987-02-11 EP EP87200208A patent/EP0234639B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1987-02-11 DE DE3750678T patent/DE3750678T2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1987-02-13 KR KR1019870001203A patent/KR920000714B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3750678D1 (de) | 1994-12-01 |
| EP0234639A1 (fr) | 1987-09-02 |
| KR870008410A (ko) | 1987-09-26 |
| KR920000714B1 (ko) | 1992-01-20 |
| DE3750678T2 (de) | 1995-06-01 |
| JPS62131368U (fr) | 1987-08-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4834677A (en) | Male and/or female electrical connectors | |
| US4897041A (en) | Electrical connector having a cable terminating cover retention system and a strain relief therefor | |
| EP0001159B1 (fr) | Connecteur électrique | |
| EP0021731B1 (fr) | Elément de contact électrique et connecteur incorporant de tels éléments de contact | |
| EP0239422A1 (fr) | Connecteur électrique pour câble plat flexible | |
| EP0817313B1 (fr) | Assemblage de connecteur éléctrique à déplacement d'isolant avec dispositif de serrage de câble | |
| US4527852A (en) | Multigauge insulation displacement connector and contacts therefor | |
| US4713020A (en) | Connector unit | |
| EP0650218B1 (fr) | Connecteur de serrage | |
| US4722699A (en) | Embedded wire-stripping connector for electrical equipment | |
| US4508410A (en) | Electrical termination system and connector member | |
| EP0234639B1 (fr) | Connecteur à déplacement d'isolant | |
| EP0720258B1 (fr) | Connecteur à déplacement d'isolant | |
| GB2080032A (en) | A plug for masking switching contacts | |
| JPH059905B2 (fr) | ||
| US4478470A (en) | Electrical contact | |
| JPH0689748A (ja) | 電気コネクタ | |
| US4090770A (en) | Connector cover construction | |
| JP3340325B2 (ja) | 複数段にケーブル列を配する電気コネクタ | |
| USRE32898E (en) | Multigauge insulation displacement connector and contacts therefor | |
| EP0446220B1 (fr) | Contact electrique | |
| JPH0315180A (ja) | ツーピースコネクタ | |
| US4360242A (en) | Self-fastening electrical connector | |
| EP0443264A1 (fr) | Connecteur pour au moins une paire de conducteurs isolés | |
| CN114520421B (zh) | 连接器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19880302 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19910319 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3750678 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19941201 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CD Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CA |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19990108 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19990204 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19990226 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000211 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20000211 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20001031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20001201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050211 |