EP0171711A2 - Procédé et dispositif de séparation d'argon brut - Google Patents
Procédé et dispositif de séparation d'argon brut Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0171711A2 EP0171711A2 EP85109675A EP85109675A EP0171711A2 EP 0171711 A2 EP0171711 A2 EP 0171711A2 EP 85109675 A EP85109675 A EP 85109675A EP 85109675 A EP85109675 A EP 85109675A EP 0171711 A2 EP0171711 A2 EP 0171711A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- gas mixture
- raw gas
- nitrogen
- argon
- liquefied
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J3/00—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification
- F25J3/02—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream
- F25J3/04—Processes or apparatus for separating the constituents of gaseous or liquefied gaseous mixtures involving the use of liquefaction or solidification by rectification, i.e. by continuous interchange of heat and material between a vapour stream and a liquid stream for air
- F25J3/04642—Recovering noble gases from air
- F25J3/04648—Recovering noble gases from air argon
- F25J3/04721—Producing pure argon, e.g. recovered from a crude argon column
- F25J3/04733—Producing pure argon, e.g. recovered from a crude argon column using a hybrid system, e.g. using adsorption, permeation or catalytic reaction
- F25J3/04739—Producing pure argon, e.g. recovered from a crude argon column using a hybrid system, e.g. using adsorption, permeation or catalytic reaction in combination with an auxiliary pure argon column
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2205/00—Processes or apparatus using other separation and/or other processing means
- F25J2205/82—Processes or apparatus using other separation and/or other processing means using a reactor with combustion or catalytic reaction
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2230/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams
- F25J2230/58—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams the fluid being argon or crude argon
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method and a device for the decomposition of an essentially argon and small amounts of oxygen and possibly nitrogen-containing raw gas mixture, in which the raw gas mixture compresses, the oxygen with the supplied hydrogen is reduced to water and the water formed is separated from the gas mixture, and the remaining The gas mixture is at least partially liquefied and broken down into a liquid argon fraction and a residual gas fraction by rectification.
- crude argon with a composition of, for example, 95% by volume Ar, 3% by volume 0 and 2% by volume N is obtained. Since this purity is not sufficient for many uses, the crude argon is processed further to produce pure argon, i.e. To obtain argon with a purity of more than 99% by volume.
- the crude argon obtained in gaseous form from a crude argon column is mixed with hydrogen and compressed.
- the oxygen contained in the raw argon is reduced to water by the hydrogen.
- the water is separated off by partial condensation and adsorption, while the remaining gas mixture is cooled and partially liquefied.
- the two-phase mixture is introduced into a rectification column in which it is broken down into a liquid pure argon fraction and a gaseous residual gas fraction which essentially contains nitrogen and residual hydrogen.
- the pressure in the crude argon column is only slightly above atmospheric pressure and is, for example, 1.1 bar.
- a higher pressure namely at least about 2 bar, preferably 3-5 bar, for example 4.5 bar, is required, so that the gas mixture has to be compressed. The process is therefore energetically unfavorable.
- the invention has for its object to develop a method of the type mentioned, which has a lower energy consumption while maintaining product purity.
- This object is achieved in that the raw gas mixture is liquefied, brought to the desired pressure in the liquid state using its hydrostatic potential and evaporated.
- a hydrostatic pressure between 2 and 6 bar is set.
- the hydrostatic pressure is preferably between 3 and 5 bar.
- the nitrogen is advantageously removed from the air separation plant if the argon production is operated after an air separation plant by means of low-temperature rectification.
- the evaporation of the raw gas mixture is carried out by heat exchange with air and / or nitrogen. If air is used, it must be dry and free of CO.
- the liquefaction of the raw gas mixture is carried out in a raw argon column.
- the liquefied raw gas mixture is removed from the top of the crude argon column below the top condenser.
- the air or the nitrogen have a pressure of at least 7 or 8.5 bar and a Condensation temperature, which is 1-3 ° above the vaporization temperature of the argon.
- the preferred pressure range is between 8 bar and 10 bar, corresponding to a pressure of 3 to 4 bar of the evaporating argon.
- the pressure can be lower if the air or nitrogen are not liquefied during the heat exchange with the raw gas mixture.
- the air or the nitrogen is brought into heat exchange with the raw gas mixture to be liquefied
- hydrogen is separated from the remaining gas mixture before the rectification and is returned to the raw gas mixture.
- a device for carrying out the method according to the invention comprises a feed line for a raw gas mixture into which a line for hydrogen flows, a so-called “Deoxo” reactor located downstream of the confluence, a drying device, its input with the output of the "Deoxo” reactor and its output is connected to a rectification column, which has removal devices for a top and a bottom fraction, and is characterized in that a condenser and an evaporator are provided in the feed line and the condenser is arranged above the evaporator.
- the height difference between the outlet of the condenser and the inlet of the evaporator is at least 12 m.
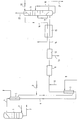
- a rectification column 1 which is connected via a feed line 2 and a discharge line 3 to a rectification column (not shown) for air separation, is used to produce crude argon. That about the
- Line 2 fed mixture has a composition of 88-95% oxygen, 5-12% argon and less than 0.1% nitrogen.
- the crude argon is removed from the top of the crude argon column 1 via a line 4 at a pressure of approximately 1.2 bar and has, for example, a composition of 95% by volume argon, 3% by volume oxygen and 2% by volume nitrogen. Its temperature is, for example, 89 K.
- the raw gas mixture is fed to a liquefier 5, in which the raw gas mixture is liquefied.
- the liquefied raw gas mixture is fed to an evaporator 7 via a line 7 6.
- the liquefier 5 is arranged above the evaporator 7, so that the liquefied raw argon at the inlet of the evaporator has a hydrostatic pressure of 3 to 5, preferably 4 bar. This hydrostatic pressure corresponds to a height difference between the condenser and evaporator of approx. 12 m to 27 m.
- the evaporator 7 is supplied with air or nitrogen or a mixture of air and nitrogen at a pressure of at least 7 or 8.5 bar, preferably 8 or 10 bar, via a line 8.
- the air or the nitrogen or the nitrogen / air mixture is fed to the condenser 5, where it is brought from line 4 into heat exchange with the crude argon to be liquefied.
- the air or the nitrogen or the nitrogen / air mixture is admixed with liquid nitrogen via a line 9.
- hydrogen is mixed into the vaporous crude argon via a line 10.
- the mixture is fed to a reactor 11 by reducing the oxygen contained in the raw gas mixture with the hydrogen to water.
- the outlet of the reactor 11 is followed by a dryer 12 in which the water formed in the reaction is separated off (line 13).
- the dryer 12 contains, for example, a cooler with a subsequent water separator and a subsequent adsorber.
- a gas mixture is withdrawn via a line 14, which essentially contains argon, nitrogen and optionally hydrogen, since it is advisable to supply hydrogen in a stoichiometric ratio upstream of the reactor 11 in order to ensure complete removal of the oxygen.
- This gas mixture is cooled in a heat exchanger 15 by heat exchange with nitrogen (line 16) and at least partially liquefied. It is fed to the bottom heater of a pure argon column 17, where it is brought into heat exchange with the liquid bottom product of this column.
- the liquid portion of the gas mixture is throttled via a line 18 into the pure argon column 17, which is operated at a pressure of approximately 1.6 bar.
- the gaseous fraction of the gas mixture is introduced into the pure argon column 17 via a line 19.
- the head cooling of the pure argon column 17 is carried out by liquid nitrogen, which is supplied via a line 20.
- the pure argon column 17 there is a rectification of the gas mixture, in which a liquid is formed in the sump which contains argon with a purity of approximately 99.999%.
- the liquid argon is removed via a line 21.
- a residual gas which essentially contains nitrogen and optionally hydrogen is removed via a line 22.
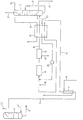
- the raw gas mixture is removed from the raw argon column 1 in the liquefied state. This eliminates the condenser 5.
- This gas stream 23 which essentially contains 0 " N, and Ar, is introduced into the air stream, for example, upstream of the air compressor of the air separation plant (not shown) to which the crude argon column is connected
- FIG. 2 also shows two further differences from the process according to FIG. 1.
- the raw gas mixture is passed through a line 24 through the heat exchanger 15 and heated before it is fed to the reactor 11. This procedure is used when the heat content of the air or nitrogen in line 8 does not ensure sufficient heating of the raw gas mixture.
- the gaseous portion of the gas mixture which is withdrawn via line 19 and which has a high hydrogen content, is instead introduced directly into the pure argon column 17, warmed in the heat exchanger 15 and, after recompression in a blower 26 in front of the reactor 11, returned to the raw gas mixture (line 25). In this way, the hydrogen is used optimally. The amount of residual gas withdrawn via line 22 is reduced accordingly.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Separation By Low-Temperature Treatments (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19843428968 DE3428968A1 (de) | 1984-08-06 | 1984-08-06 | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur zerlegung von rohargon |
| DE3428968 | 1984-08-06 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0171711A2 true EP0171711A2 (fr) | 1986-02-19 |
| EP0171711A3 EP0171711A3 (fr) | 1987-08-26 |
Family
ID=6242459
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP85109675A Withdrawn EP0171711A3 (fr) | 1984-08-06 | 1985-08-01 | Procédé et dispositif de séparation d'argon brut |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0171711A3 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JPS6144279A (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3428968A1 (fr) |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0331028A1 (fr) * | 1988-03-01 | 1989-09-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de purification d'argon brut |
| DE4406051A1 (de) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-08-31 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon |
| DE4406049A1 (de) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-09-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon |
| DE4406069A1 (de) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-09-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon |
| US5590544A (en) * | 1994-02-24 | 1997-01-07 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Process and apparatus for recovery of pure argon |
| US5592833A (en) * | 1994-02-24 | 1997-01-14 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Process and apparatus for the recovery of pure argon |
| US5644934A (en) * | 1994-12-05 | 1997-07-08 | Linde Aktiengesellchaft | Process and device for low-temperature separation of air |
| EP0628778B2 (fr) † | 1993-06-07 | 2001-03-21 | L'air Liquide, Societe Anonyme Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes Georges Claude | Procédé et unité de fourniture d'un gaz sous pression à une installation consommatrice d'un constituant de l'air |
| FR2848652A1 (fr) * | 2002-12-12 | 2004-06-18 | Air Liquide | Procede et installation de production d'argon |
| DE102007035619A1 (de) | 2007-07-30 | 2009-02-05 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Argon durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| EP2026024A1 (fr) | 2007-07-30 | 2009-02-18 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif pour la production d'argon par séparation cryogénique d'air |
| DE102009016043A1 (de) | 2009-04-02 | 2010-10-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Reinargonsäule und Vorrichtung zur Reinargongewinnung |
| WO2014135271A2 (fr) | 2013-03-06 | 2014-09-12 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Installation de séparation d'air, procédé de récupération d'un produit contenant de l'argon et procédé pour créer une installation de séparation d'air |
| DE102013018664A1 (de) | 2013-10-25 | 2015-04-30 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft und Tieftemperatur-Luftzerlegungsanlage |
| EP3040665A1 (fr) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Système de colonne de distillation et installation pour la production d'oxygène par séparation cryogénique de l'air |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3840506A1 (de) * | 1988-12-01 | 1990-06-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur luftzerlegung |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2325422A1 (de) * | 1973-05-18 | 1974-12-05 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur zerlegung von rohargon |
| EP0029656A1 (fr) * | 1979-10-23 | 1981-06-03 | Air Products And Chemicals, Inc. | Procédé et installation cryogénique pour la production de l'oxygène gazeux |
| JPS5697774A (en) * | 1979-12-29 | 1981-08-06 | Nippon Oxygen Co Ltd | Method of sampling argon in air separator |
-
1984
- 1984-08-06 DE DE19843428968 patent/DE3428968A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1985
- 1985-08-01 EP EP85109675A patent/EP0171711A3/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 1985-08-05 JP JP17224385A patent/JPS6144279A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2325422A1 (de) * | 1973-05-18 | 1974-12-05 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur zerlegung von rohargon |
| EP0029656A1 (fr) * | 1979-10-23 | 1981-06-03 | Air Products And Chemicals, Inc. | Procédé et installation cryogénique pour la production de l'oxygène gazeux |
| JPS5697774A (en) * | 1979-12-29 | 1981-08-06 | Nippon Oxygen Co Ltd | Method of sampling argon in air separator |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| CHEMICAL ABSTRACTS OF JAPAN, Band 96, Nr. 10, M{rz 1982, Seite 137, Zusammenfassung Nr. 71221r, Columbus, Ohio, US; & JP-A-56 097 774 (JAPAN OXYGEN CO. LTD) 06-08-1981 * |
| CHEMICAL ABSTRACTS, Band 97, Nr. 4, Juli 1982, Seite 118, Zusammenfassung Nr. 25811f, Columbus, Ohio, US; & JP-A-57 060 165 (JAPAN OXYGEN CO., LTD) 30-09-1980 * |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0331028A1 (fr) * | 1988-03-01 | 1989-09-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé de purification d'argon brut |
| EP0628778B2 (fr) † | 1993-06-07 | 2001-03-21 | L'air Liquide, Societe Anonyme Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes Georges Claude | Procédé et unité de fourniture d'un gaz sous pression à une installation consommatrice d'un constituant de l'air |
| DE4406051A1 (de) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-08-31 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon |
| DE4406049A1 (de) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-09-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon |
| DE4406069A1 (de) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-09-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon |
| US5590544A (en) * | 1994-02-24 | 1997-01-07 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Process and apparatus for recovery of pure argon |
| US5592833A (en) * | 1994-02-24 | 1997-01-14 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Process and apparatus for the recovery of pure argon |
| US5644934A (en) * | 1994-12-05 | 1997-07-08 | Linde Aktiengesellchaft | Process and device for low-temperature separation of air |
| FR2848652A1 (fr) * | 2002-12-12 | 2004-06-18 | Air Liquide | Procede et installation de production d'argon |
| DE102007035619A1 (de) | 2007-07-30 | 2009-02-05 | Linde Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Argon durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft |
| EP2026024A1 (fr) | 2007-07-30 | 2009-02-18 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Procédé et dispositif pour la production d'argon par séparation cryogénique d'air |
| DE102009016043A1 (de) | 2009-04-02 | 2010-10-07 | Linde Ag | Verfahren zum Betreiben einer Reinargonsäule und Vorrichtung zur Reinargongewinnung |
| WO2014135271A2 (fr) | 2013-03-06 | 2014-09-12 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Installation de séparation d'air, procédé de récupération d'un produit contenant de l'argon et procédé pour créer une installation de séparation d'air |
| DE102013018664A1 (de) | 2013-10-25 | 2015-04-30 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren zur Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft und Tieftemperatur-Luftzerlegungsanlage |
| EP3040665A1 (fr) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-06 | Linde Aktiengesellschaft | Système de colonne de distillation et installation pour la production d'oxygène par séparation cryogénique de l'air |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3428968A1 (de) | 1986-02-13 |
| EP0171711A3 (fr) | 1987-08-26 |
| JPS6144279A (ja) | 1986-03-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0299364B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de séparation de l'air par rectification | |
| EP0331028B1 (fr) | Procédé de purification d'argon brut | |
| EP0171711A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de séparation d'argon brut | |
| EP0377117B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de séparation de l'air | |
| DE2535132C3 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Drucksauerstoff durch zweistufige Tieftemperaturrektifikation von Luft | |
| DE2920270C2 (de) | Verfahren zum Erzeugen von Sauerstoff | |
| EP0100923A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour séparer un mélange de gaz | |
| EP1284928B1 (fr) | Procede pour la production d'acide nitrique concentre, ainsi qu'installation pour l'execution de ce procede | |
| EP0948730A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de production d'azote comprime | |
| DE2854508C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Tieftemperaturzerlegung eines Gasgemisches | |
| DE3307181C2 (fr) | ||
| EP0313883B1 (fr) | Procédé de séparation d'un mélange d'hydrogène-monoxyde de carbone en utilisant une condensation partielle à basse température | |
| DE1135935B (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Sauerstoff geringer Reinheit durch Tieftemperatur-Luftzerlegung | |
| DE3035844A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur gewinnung von sauerstoff mittlerer reinheit | |
| DE19725851A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung hochreiner, wässriger Hydroxylaminlösungen | |
| DE19636306A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von Argon durch Tieftemperaturzerlegung von Luft | |
| EP0834711A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour la production d'azote à haute pureté | |
| DE1041989B (de) | Verfahren und Einrichtung zur Gaszerlegung, vorzugsweise Luftzerlegung, mittels Tieftemperaturrektifikation | |
| DE3814187A1 (de) | Verfahren zur luftzerlegung durch tieftemperaturrektifikation | |
| DE602952C (de) | Zweistufiges Verfahren zur Zerlegung von Luft | |
| EP0559117B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour la séparation d'un mélange de gaz | |
| DE702246C (de) | Vorrichtung zum Zerlegen eines Gasgemisches mit tiefliegenden Siedepunkten | |
| EP4189311A1 (fr) | Procédé et installation pour effectuer un processus industriel | |
| DE19743731A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Gewinnung von reinem Argon | |
| DD239580A1 (de) | Verfahren zur gewinnung von reinem krypton und reinem xenon |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19880227 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: SCHOENPFLUG, EUGEN, DIPL.-ING. Inventor name: KOENNING, HEINRICH, ING. GRAD. |