EP0145979A2 - Hängematte - Google Patents
Hängematte Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0145979A2 EP0145979A2 EP84113887A EP84113887A EP0145979A2 EP 0145979 A2 EP0145979 A2 EP 0145979A2 EP 84113887 A EP84113887 A EP 84113887A EP 84113887 A EP84113887 A EP 84113887A EP 0145979 A2 EP0145979 A2 EP 0145979A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- mat
- hammock
- head
- textile fabric
- foam sheet
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A45—HAND OR TRAVELLING ARTICLES
- A45F—TRAVELLING OR CAMP EQUIPMENT: SACKS OR PACKS CARRIED ON THE BODY
- A45F3/00—Travelling or camp articles; Sacks or packs carried on the body
- A45F3/22—Hammocks; Hammock spreaders
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/2419—Fold at edge
- Y10T428/24215—Acute or reverse fold of exterior component
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/2419—Fold at edge
- Y10T428/24215—Acute or reverse fold of exterior component
- Y10T428/24231—At opposed marginal edges
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/249921—Web or sheet containing structurally defined element or component
- Y10T428/249953—Composite having voids in a component [e.g., porous, cellular, etc.]
Definitions
- the innovation relates to a hammock with a mat and a loop-shaped design at the head and foot end for receiving fastening rods.
- Hammocks for example made of knotted nets, are known and, in addition to the strength requirements for absorbing the weight of a person, must also be weatherproof, since they are mainly used outdoors.
- the innovation is based on the task of creating a new type of hammock with the greatest possible comfort, easy handling and low weight.
- a hammock is proposed according to the innovation, in which the mat or the like from a with a textile fabric made of organic and / or inorganic fibers, threads, tapes.
- Reinforced elastic cross-linked foam sheet with a tensile strength of at least 0.20 N / mm 2 and a tear resistance of at least 1.0 N / mm and an elongation at break of at least 80 to 120% at a bulk density of about 30 to 130, preferably 30 to 80 kg / m 3 is built up.
- Suitable elastic cross-linked foams are, for example, the closed-cell, chemically cross-linked polyolefin foams, which are water-repellent and have good light stability, and at the same time are still cushioning and insulating.
- the textile reinforcement can preferably be a coarse reinforcing fabric or knitted fabric, which is either applied on one side or is laminated as an intermediate layer between two foam webs.
- a non-bulky textile fabric that can be used advantageously consists of a fabric, in particular a ribbon fabric based on plastics such as polyolefins, such as polyethylene tapes.
- the head and foot ends of the foam sheet are preferably turned over to form loops and the envelope is in particular welded, glued or sewn to the mat.
- a fastening rod can then be inserted into the loop thus formed, to which the ropes for hanging the hammock are then attached.
- sew, weld or glue on the head and foot ends of the mat in particular a woven or knitted or laid textile fabric made of plastic to form a loop on the top and / or bottom of the mat.
- the loop can be attached to the head and foot ends throughout the entire width of the mat, but it is also possible to attach only loop sections in sections.
- the material for the loops can also consist of a plastic film, for example, a material selection is advantageous which enables a homogeneous connection, for example by welding with the material of the mat.
- the surface of the foam web forming the mat can be laminated with a film made of plastic, for example a polyolefin film if the foam consists of polyolefins.
- a film made of plastic for example a polyolefin film if the foam consists of polyolefins.
- Such a thin film of approximately 30 to 50 ⁇ m can also be colored or printed in a colorful manner, and it is also possible to emboss it in a simple manner in order to improve the surface grip of the mat.
- the foam sheets of selected raw densities provided in accordance with the innovation are used, which do not allow the weight of the mat to become too large and yet have sufficient strength properties, hammocks with a lying surface of approximately 2 m length to 1 m width can be produced, the mat having a thickness between Can have 5 to 20 mm.
- the mat can consist of a foam sheet or two foam sheets laminated together. It is also possible to combine two foam sheets with different densities, for example that the foam sheet with the lower density is set softer and forms the top of the mat, while a foam sheet with a higher density and thus stiffer forms the underside of the mat and in combination with the textile reinforcement ensures a sufficient absorption of the loading forces.
- a particular advantage of the hammock according to the innovation can be seen in the fact that it is very durable and long-lasting due to the rot-resistant materials used and, moreover, it ensures a high level of comfort due to the elastic foam sheets used. If the mat stays outdoors for a long time, it is also conceivable to perforate it in the middle area, to ensure easy water drainage. The hat can also be perforated at intervals for reasons of higher air circulation.
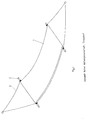
- Figure 1 the principle of a hammock is shown, which essentially serves to accommodate a person from the mat 1, the mat 1 being connected at its head and foot ends to the rod 2, on which the tether 3 for hanging the mat attack.
- the rods 2 are preferably inserted through a loop-like design of the head and foot ends of the mat and held therein.
- the design of the mat 1 is shown schematically.
- the mat 1 consists, for example, of a foam sheet made of chemically crosslinked polyethylene foam, a thickness of 10 mm and a length of the mat of 1.70 to 2.50 m, preferably about 2 m and a width of about 0.6 to 1.0 m .
- the foam has, for example, a bulk density of 50 kg / m 3 , a tensile strength measured according to DIN 53571 of 0.4 N / mm 2 , elongation at break measured according to DIN 53571 of 90%, tear propagation resistance measured according to DIN 53577 of 1.9 N / mm , a compressive stress at 25% deformation measured according to DIN 53577 of 70 KN / m 2 , an impact elasticity measured according to DIN 53512 of 45% and a water absorption after 28 days measured according to DIN 53428 less than 3.0% by volume and a water vapor diffusion - Resistance factor f measured according to DIN 53429 of 3000.
- the top 10 of the foam sheet forming the mat 1, which forms the lying side, can be embossed, for example, or, if necessary, laminated and embossed with a plastic film, for example a 30 to 50 ⁇ m thick polyethylene film.
- the underside 11 of the foam web forming the mat is reinforced with a fabric 7, not shown, which is laminated in, for example made of polyester threads or polyamide threads or polypropylene threads or a fabric made of polyethylene ribbon fabric.
- the foam sheet for the mat 1 is folded over at the front ends, ie at the ends forming the head and foot ends, and the folded over edge 12 is glued or welded to the mat in the region 6, for example, or sewn along one or more seams 5.
- the mat according to the innovation is flexible and can be easily folded up and transported by rolling it up. It is very easy to clean and gives a comfortable feeling of comfort due to the cushioning effect of the foam sheet used.
- FIG. 3 shows a further possibility of designing the hammock according to the invention.
- the mat 1 is formed by two foam webs 1a, 1b, between which the textile reinforcement layer 7 is laminated.
- the two foam sheets 1a, 1b directly to one another and to attach the textile reinforcement layer 7 on the underside, as shown in FIG. 2.
- the two outer sides of the foam sheets 1a, 1b, namely the top 10 and the bottom 11 are either embossed or laminated with a cover layer, for example a plastic film, which may can be embossed or also provided with a fabric-like cover, for example based on plastic and / or natural fibers.
- loops 4 are formed, for example, on the end faces of the mat by welding or gluing or sewing, if necessary in addition to an adhesive connection of tapes 8, which can also consist, for example, of a textile woven fabric made of plastic fibers, such as, for example, polyethylene tape fabric .
- tapes 8 can also consist, for example, of a textile woven fabric made of plastic fibers, such as, for example, polyethylene tape fabric .
- a riveting of the straps 8 forming the loops to the mat 1 is also conceivable.
- Polyester fabric or polyamide fabric or fabrics additionally coated with PVC or polyethylene can also be used, for example, as reinforcing textile fabrics.
Landscapes
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Aiming, Guidance, Guns With A Light Source, Armor, Camouflage, And Targets (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die Neuerung bezieht sich auf eine Hängematte mit einer Matte und am Kopf- und Fußende schlaufenförmige Ausbildung zur Aufnahme von Befestigungsstäben.
- Hängematten beispielsweise aus geknüpften Netzen sind bekannt und müssen neben den Festigkeitsanforderungen zur Aufnahme des Gewichtes einer Person auch noch witterungsbeständig sein, da sie überwiegend im Freien verwendet werden.
- Der Neuerung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine neuartige Hängematte mit möglichst hohem Liegekomfort, einfache Handhabung und geringem Gewicht zu schaffen. Zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe wird neuerungsgemäß eine Hängematte vorgeschlagen, bei der die Matte aus einer mit einem textilen Flächengebilde aus organischen und/oder anorganischen Fasern, Fäden, Bändern o.dgl. verstärkten elastischen vernetzten Schaumstoffbahn mit einer Zugfestigkeit von mindestens 0,20 N/mm2 und einem Weiterreißwiderstand von mindestens 1,0 N/mm und einer Bruchdehnung von mindestens 80 bis 120 %bei einer Rohdichte von etwa 30 bis 130, vorzugsweise 30 bis 80 kg/m3 aufgebaut ist. Geeignete elastische vernetzte Schaumstoffe sind beispielsweise die geschlossenzelligen chemisch vernetzten Polyolefinschaumstoffe, die wasserabweisend sind und eine gute Lichtstabilität aufweisen und zugleich noch polsternd und isolierend sind. Die textile Verstärkung kann vorzugsweise ein grobes Verstärkungsgewebe oder Gewirke sein, das entweder einseitig aufgebracht ist oder als Zwischenlage zwischen zwei Schaumstoffbahnen einkaschiert ist. Ein nicht auftragendes textiles Flächengebilde das vorteilhaft eingesetzt werden kann, besteht aus einem Gewebe, insbesondere Bändchengewebe auf Basis von Kunststoffen wie Polyolefinen, wie beispielsweise Polyethylenbändchen. Um die Matte aufnängen zu können, sind bevorzugt die Kopf-und Fußenden der Schaumstoffbahn zur Schlaufenbildung umgeschlagen und der Umschlag mit der Matte insbesondere verschweißt, verklebt oder vernäht. In die so gebildete Schlaufe kann dann ein Befestigungsstab eingeschoben werden, an dem dann die Seile zum Aufhängen der Hängematte befestigt sind. Es ist jedoch auch möglich, an den Kopf-und Fußenden der Matte insbesondere ein gewebtes oder gewirktes oder gelegtes textiles Flächengebilde aus Kunststoff unter Bildung einer Schlaufe auf der Ober- und/oder Unterseite der Matte anzunähen, anzuschweißen oder anzukleben. Die Schlaufe kann durchgehend über die gesamte Breite der Matte an den Kopf- und Fußenden angebracht sein, es ist jedoch auch möglich, nur Schlaufenabschnitte abschnittsweise anzubringen. Das Material für die Schlaufen kann neben einem textilen Flächengebilde auch aus einer Kunststoffolie beispielsweise bestehen, vorteilhaft ist eine Materialauswahl, die eine homogene Verbindbarkeit beispielsweise durch Schweißen mit dem Material der Matte ermöglicht.
- Zur Verbesserung der Oberfläche der Matte und ggf. auch ästhetischen Wirkung kann die Oberfläche der die Matte bildenden Schaumstoffbahn mit einer Folie aus Kunststoff, beispielsweise einer Polyolefinfolie wenn der Schaumstoff aus Polyolefinen besteht, kaschiert sein. Eine solche dünne Folie von etwa 30 bis 50 µ kann auch bunt eingefärbt oder bedruckt sein, darüber hinaus ist es in einfacher Weise möglich, sie zu prägen, um die Oberflächengriffigkei der Matte zu verbessern.
- Bei Einsatz der neuerungsgemä3.vorgesehenen Schaumstoffbahnen ausgewählter Rohdichten, die das Gewicht der Matte nicht zu groß werden lassen, und dennoch genügende Festigkeitseigenschaften aufweisen, können Hängematten mit einer Liegefläche von etwa 2 m Länge bis 1 m Breite gefertigt werden, wobei die Matte eine Dicke zwischen 5 bis 20 mm aufweisen kann. Die Matte kann hierbei aus einer Schaumstoffbahn bestehen oder aus zwei miteinander kaschierten Schaumstoffbahnen. Es ist auch möglich, zwei Schaumstoffbahnen unterschiedlicher Raumdichte miteinander zu kombinieren, wobei beispielsweise das die Schaumstoffbahn mit dem niedrigeren Raumgewicht weicher eingestellt ist und die Oberseite der Matte bildet, während eine Schaumstoffbahn mit einem höheren Raumgewicht und damit steifer die Unterseite der Matte bildet und im Verbund mit der textilen Verstärkung für eine ausreichende Aufnahme der Belastungskräfte sorgt.
- Ein besonderer Vorteil der neuerungsgemäßen Hängematte ist darin zu sehen, daß sie aufgrund der verwendeten verrottungsfesten Werkstoffe sehr dauerhaft und langlebig ist und darüber hinaus einen hohen Liegekomfort durch die eingesetzten elastischen Schaumstoffbahnen gewährleistet. Falls die Matte für längere Zeit im Freien bleibt, ist es auch denkbar, sie im mittleren Bereich zu perforieren, um auf diese Weise für einen einfachen Wasserabfluß zu sorgen. Im übrigen kann die Hatte auch aus Gründen einer höheren Luftzirkulation in Abständen perforiert sein.
- In der Zeichnung ist die Neuerung anhand von Ausführungsbeispielen erläutert.
- Es zeigen
- Figur 1 schematisch die Ansicht einer Hängematte,
- Figur 2 schematisch die Ansicht einer Matte,
- Figur 3 einen auszugsweisen Querschnitt durch eine Matte.
- In Figur 1 ist das Prinzip einer Hängematte dargestellt, die im wesentlichen aus der Matte 1 zur Aufnahme einer Person dient, wobei die Matte 1 an ihren Kopf- und Fußenden jeweils mit der Stange 2 verbunden ist, an der die Halteseile 3 zum Aufhängen der Matte angreifen. Die Stangen 2 sind bevorzugt durch eine schlaufenartige Ausbildung der Kopf- und Fußenden der Matte gesteckt und darin gehalten.
- Im Figur 2 ist schematisch die Ausbildung der Matte 1 dargestellt. Hierbei besteht die Matte 1 beispielsweise aus einer Schaumstoffbahn aus chemisch vernetztem Polyethylenschaumstoff, einer Dicke von 10 mm bei einer Länge der Matte von 1,70 bis 2,50 m vorzugsweise etwa 2 m und einer Breite von etwa 0,6 bis 1,0 m. Der Schaumstoff hat beispielsweise eine Rohdichte von 50 kg/m3, eine Zugfestig keit gemessen nach DIN 53571 von 0,4 N/mm2, Bruchdehnung gemessen nach DIN 53571 von 90 %, Weiterreißwiderstand gemessen nach DIN 53577 von 1,9 N/mm, eine Druckspannung bei 25 % Verformung gemessen nach DIN 53577 von 70 KN/m2, eine Stoßelastizität gemessen nach DIN 53512 von 45 % und eine Wasseraufnahme nach 28 Tagen gemessen nach DIN 53428 kleiner 3,0 Vol.-% und einen Wasserdampf-Diffusions-Widerstandfaktor f gemessen nach DIN 53429 von 3000. Die Oberseite 10 der die Matte 1 bildenden Schaumstoffbahn, die die Liegeseite bildet, kann beispielsweise geprägt sein oder ggf. mit einer Kunststoffolie beispielsweise einer 30 bis 50 µ dicken Polyethylenfolie kaschiert und geprägt sein. Die Unterseite 11 der die Matte bildenden Schaumstoffbahn ist mit einem nicht näher dargestellten Gewebe 7 verstärkt, das einkaschiert ist, beispielsweise aus Polyesterfäden oder Polyamidfäden oder Polypropylenfäden oder einem Gewebe aus Polyethylen-Bändchen-Gewebe. Die Schaumstoffbahn für die Matte 1 ist an den stirnseitigen Enden d.h. an dem das Kopf- und das Fußende bildenden Enden umgeschlagen und der umgeschlagene Rand 12 ist im Bereich 6 mit der Matte beispielsweise verklebt oder verschweißt bzw. entlang einer oder mehrerer Nähte 5 genäht. Durch die auf diese Weise gebildete Schlaufe 4 können dann die Stäbe zum Aufhängen der Matte durchgesteckt werden. Die neuerungsgemäße Matte ist biegsam und kann leicht durch Aufrollen zusammengelegt und transportiert werden. Sie ist sehr leicht zu reinigen und vermittelt ein angenehmes Liegegefühl aufgrund der polsternden Wirkung der verwendeten Schaumstoffbahn.
- In der Figur 3 ist eine weitere Möglichkeit der Ausbildung der neuerungsgemäßen Hängematte dargestellt. Hierbei wird die Matte 1 von zwei Schaumstoffbahnen 1a, 1b gebildet, zwischen denen die textile Verstärkungsschicht 7 einkaschiert ist. Es ist aber auch möglich, die beiden Schaumstoffbahnen 1a, 1b direkt miteinander zu kaschieren und die textile Verstärkungsschicht 7 unterseitig wie in Figur 2 dargestellt, anzubringen. Bei der Matte nach Fig. 3 sind die beiden außenliegenden Seiten der Schaumstoffbahnen 1a, 1b, nämlich die Oberseite 10 und die Unterseite 11 entweder geprägt oder mit einer Deckschicht beispielsweise einer Kunststoffolie kaschiert, die ggf. geprägt sein kann oder auch mit einem stoffartigen Bezug beispielsweise auf Basis von Kunststoff- und/oder natürlichen Fasern versehen. Für die Aufnahme der Befestigungsstäbe sind beispielsweise an den Stirnseiten der Matte Schlaufen 4 durch Anschweißen oder Ankleben oder Annähen, ggf. zusätzlich zu einer Klebeverbindung von Bändern 8 gebildet, die beispielsweise auch aus einem textilen gewebten Flächgengebilde aus Kunststoffasern, wie beispielsweise Polyethylenbändchen-Gewebe bestehen können. Auch ein Annieten der die Schlaufen bildenden Bänder 8 an die Matte 1 ist denkbar.
- Als verstärkendes textiles Flächengebilde können beispielsweise auch Polyestergewebe oder Polyamidgewebe eingesetzt werden oder mit PVC oder Polyethylen zusätzlich beschichtete Gewebe. Darüber hinaus ist es möglich, Ober-und Unterseite der Matte unterschiedlich einzufärben, wobei eine gemäß Fig. 3 ausgebildete Matte beidseitig als Liegefläche benutzt werden kann.
Claims (7)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE8336302U | 1983-12-17 | ||
| DE19838336302U DE8336302U1 (de) | 1983-12-17 | 1983-12-17 | Haengematte |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0145979A2 true EP0145979A2 (de) | 1985-06-26 |
| EP0145979A3 EP0145979A3 (de) | 1986-07-30 |
Family
ID=6759969
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19840113887 Withdrawn EP0145979A3 (de) | 1983-12-17 | 1984-11-16 | Hängematte |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4542057A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0145979A3 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE8336302U1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5007674A (en) * | 1987-06-15 | 1991-04-16 | John Franc | Infant shade apparatus |
| US7008890B1 (en) * | 1995-04-19 | 2006-03-07 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Der Angewandten Forschung E.V. | Vapor barrier for use in the thermal insulation of buildings |
| US5655235A (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 1997-08-12 | Death; Sam | Hammock with collapsible spreader bars and sheltering enclosure |
| JP3542975B2 (ja) * | 2001-03-21 | 2004-07-14 | アイエスティー株式会社 | 積層シート |
| US20090165205A1 (en) * | 2007-05-15 | 2009-07-02 | Hennessy Holdings, Ltd. | Hammock Having Insulation Retaining Panels |
| RU2413443C1 (ru) * | 2010-01-11 | 2011-03-10 | Закрытое акционерное общество "Научно-производственное объединение специальных материалов" | Устройство подвесное |
| GB2589469B (en) * | 2018-05-10 | 2022-02-16 | Cocam Int Enterprises Ltd | Portable self-standing hammock frame with shortened hammock and method for suspending shortened hammock on frame |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR10890E (fr) * | 1908-08-31 | 1909-10-21 | Jean Leon Bouley | Dossier portatif |
| US996644A (en) * | 1909-09-02 | 1911-07-04 | Herman L Hohlfeld | Hammock-couch. |
| US1748501A (en) * | 1928-05-10 | 1930-02-25 | Esmond Mills | Convertible blanket |
| US3328225A (en) * | 1964-01-20 | 1967-06-27 | Gen Tire & Rubber Co | Dry-cleanable expanded plastic laminates and methods of making the same |
| US3336180A (en) * | 1964-02-14 | 1967-08-15 | Uniroyal Inc | Dry-cleanable vinyl foam-fabric laminate |
| GB1431263A (en) * | 1972-01-19 | 1976-04-07 | Caligen Foam Ltd | Foam laminates |
| CH616802GA3 (de) * | 1977-07-25 | 1980-04-30 | ||
| US4474840A (en) * | 1981-08-27 | 1984-10-02 | The Gates Corporation | Method of selective bonding of textile materials |
-
1983
- 1983-12-17 DE DE19838336302U patent/DE8336302U1/de not_active Expired
-
1984
- 1984-11-16 EP EP19840113887 patent/EP0145979A3/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1984-12-04 US US06/678,045 patent/US4542057A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0145979A3 (de) | 1986-07-30 |
| DE8336302U1 (de) | 1984-05-10 |
| US4542057A (en) | 1985-09-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69716563T2 (de) | TEXTILVERBUNDSTOFF, INSBESONDERE FüR HANDGEPäCK UND BEKLEIDUNG | |
| DE4208600A1 (de) | Sitzpolster, insbesondere fuer ein fahrzeug | |
| DE3524491A1 (de) | Pappschachtel fuer gesichtstuecher | |
| DE4423741A1 (de) | Seitenaufprallschutz für die Tür eines Fahrzeuges | |
| EP0145979A2 (de) | Hängematte | |
| DE112007000721T5 (de) | Verstärkungsmittel und Dachstabilisierungssystem zur Verhinderung von Verformungen an Fracht-Lastkraftwagen | |
| DE4017539A1 (de) | Ski mit einem zumindest im obergurt integrierten sandwichgurt | |
| DE3320346C2 (de) | Kernschicht für eine Aufsprungmatte | |
| DE102017010376B3 (de) | Textiles Schlitzband mit Öffnungen | |
| DE102011119320A1 (de) | Halteprofil zum Positionieren einer zweiDekorschichten verbindenden Naht sowieVerbundteil mit einem Halteprofil | |
| DE202006002470U1 (de) | Schutzdecke | |
| DE10119807A1 (de) | Sitzelement | |
| DE2006240A1 (de) | Dachabdeckung aus flexiblem Material | |
| AT248306B (de) | Ski, Gleitkufe, Schlittenkufe od. dgl. sowie Verfahren und Vorrichtung zu seiner Herstellung | |
| DE102021117447A1 (de) | Anbindungsband zum Anbinden eines Beschattungsmaterials an eine Führung und Verfahren | |
| DE102009006732B4 (de) | Band zum Verstärken einer Naht | |
| DE3311273C2 (de) | Kameratasche | |
| DE202010009716U1 (de) | Schutzmanschette für Bäume | |
| DE9004625U1 (de) | Polsterteil für einen Sitz in öffentlichen Verkehrsmitteln | |
| DE3825049C2 (de) | ||
| DE2837109C3 (de) | Ölschlengel mit einem aufblasbaren Schlauch | |
| DE2229661A1 (de) | Streifenfoermiger griff | |
| DE1943449C3 (de) | Sitzpolsterung | |
| EP0290709A1 (de) | Biegsames Verbundmaterial, insbesondere zur Erzeugung von Schutzbekleidung | |
| DE202022105954U1 (de) | Sportmatte, insbesondere ausgeführt als Fallschutzmatte oder als Gymnastikmatte |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19861129 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: HUELS TROISDORF AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19880531 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: JANSHEN, WALTER Inventor name: KAUTZ, RUDOLF Inventor name: BREITSCHEIDEL, HANS-ULRICH |