EP0028792A2 - Multi-deck screening machine - Google Patents
Multi-deck screening machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0028792A2 EP0028792A2 EP80106751A EP80106751A EP0028792A2 EP 0028792 A2 EP0028792 A2 EP 0028792A2 EP 80106751 A EP80106751 A EP 80106751A EP 80106751 A EP80106751 A EP 80106751A EP 0028792 A2 EP0028792 A2 EP 0028792A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- deck
- return
- sieve
- stack
- channels
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 40
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007873 sieving Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 abstract description 14
- 239000003082 abrasive agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000013590 bulk material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005422 blasting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003746 feather Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B07—SEPARATING SOLIDS FROM SOLIDS; SORTING
- B07B—SEPARATING SOLIDS FROM SOLIDS BY SIEVING, SCREENING, SIFTING OR BY USING GAS CURRENTS; SEPARATING BY OTHER DRY METHODS APPLICABLE TO BULK MATERIAL, e.g. LOOSE ARTICLES FIT TO BE HANDLED LIKE BULK MATERIAL
- B07B1/00—Sieving, screening, sifting, or sorting solid materials using networks, gratings, grids, or the like
- B07B1/46—Constructional details of screens in general; Cleaning or heating of screens
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B07—SEPARATING SOLIDS FROM SOLIDS; SORTING
- B07B—SEPARATING SOLIDS FROM SOLIDS BY SIEVING, SCREENING, SIFTING OR BY USING GAS CURRENTS; SEPARATING BY OTHER DRY METHODS APPLICABLE TO BULK MATERIAL, e.g. LOOSE ARTICLES FIT TO BE HANDLED LIKE BULK MATERIAL
- B07B1/00—Sieving, screening, sifting, or sorting solid materials using networks, gratings, grids, or the like
- B07B1/28—Moving screens not otherwise provided for, e.g. swinging, reciprocating, rocking, tilting or wobbling screens
- B07B1/34—Moving screens not otherwise provided for, e.g. swinging, reciprocating, rocking, tilting or wobbling screens jigging or moving to-and-fro perpendicularly or approximately perpendiculary to the plane of the screen
Definitions
- the invention relates to a multi-deck sieve machine designed as a throwing sieve with sieve, blind and return decks clamped in the frame and a vibration exciter arranged on the sieve stack for classifying dry, free-flowing bulk goods of small grain size, such as abrasives and blasting media, with which a large number of grain size classes are carried out in one operation can be classified.
- Multi-deck screening machines designed as throwing screens are already known.
- Such a known multi-deck screening machine consists of several screen decks arranged one above the other on a base frame, which are inclined by 30 ° to 40 ° to the horizontal. Vibrating heads are arranged on the sieve housing.
- Multi-deck screening machines designed as throwing screens with return of the screened material against its transport direction, with which a large number of particle sizes can be classified in one continuous continuous operation, are not known.
- a multi-deck screening machine operating as a flat screen which consists of screen, blind and return decks which are clamped in a frame and in which the screen stack thus formed is excited as a whole.
- the inclination of the sieve stack can be adjusted depending on the required dwell time of the material to be sieved on the sieve bottom and its flowability.
- the drive takes place by means of an eccentric acting in the horizontal direction (company lettering "Regula-Siebmaschinen" from J. Engelsmann AG, 67 Ludwigshafen / Rh. FRG).
- This multi-deck screening machine allows the material to be returned, it is also possible to classify up to six grain size classes in one operation using such multi-deck screening machines.
- Plane screening machines generally have the disadvantage that the screen floor is only moved in the screen plane and thus only the gravity, which causes the movement through the screen floor, acts on the undersize.
- the reason for the necessary parallel and series operation when solving screening tasks that require the bulk material to be classified into a large number of grain size classes is that the known multi-deck screening machines designed as throwing screens do not allow the screenings to be returned and the multi-deck screening machines designed as plane screens in the Fine grain area does not work with sufficient selectivity, so that with such multi-deck screening machines only up to a maximum of six grain size classes can be classified in one operation. It is therefore the object of the invention to develop, for the first time, a multi-deck sieve machine designed as a throwing sieve, in which it is possible to return the material to be screened against the direction of transport and which works with a high degree of selectivity in all grain size classes.
- this object is achieved in that a vibration exciter known per se is arranged so displaceably and rotatably on a sieve stack that its line of action acts at an angle of 45 ° ... 85 ° to a horizontal on the sieve stack and vertically free-swinging in a return deck and inclined at 0 ° ... 30 ° to the horizontal and articulated to a frame of the return deck. It is also characteristic that the channels end at the ends in vertical channels in the sieve stack and several channels are coupled to one another at their ends.
- the multi-deck screening machine consists of a screen stack, a vibration exciter and the grain removal.
- blind and return decks are firmly clamped using a clamping frame and a clamping device.
- a vibration exciter is slidably and rotatably fastened so that a throw angle and the line of action of the vibration exciter can be adjusted from 45 ° to 85 ° to a horizontal.
- channels are suspended from springs in a vertically swinging manner. They have an inclination of 0 ° ... 30 ° to the horizontal and are articulated at the ends to the frame of the return deck. Several channels can be coupled together at the ends.
- the sieve stack is excited as a whole by the vibration exciter.
- the multi-deck screening machine according to the invention is preferably suitable for solving screening tasks in which the bulk material can be classified into a large number of grain size classes in one operation. It is particularly suitable for classifying abrasives and abrasives, but is not restricted to this area of application. With the solution according to the invention, it was possible for the first time to secure the return of the material to be screened against the throwing and transport direction of the material to be screened on the screen and blind decks in the case of a multi-deck screening machine designed as a screening screen.
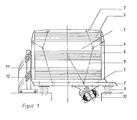
- FIG. 1 a side view of the multi-deck screening machine
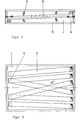
- FIG. 2 a section through the return deck
- Figure 3 a top view of the return deck.
- the multi-deck sieving machine consists of the sieve stack 1, which is arranged on the oscillating frame 2.
- the sieve and blind decks 3 and the return decks 4 are arranged one above the other in the sieve stack 1.
- the screen and blind decks 3 and the return decks 4 are clamped together by the base frame 5, side frame 6, cover frame 7 and the tensioning device 8.
- the sieve stack 1 seated on the oscillating frame 2 is supported on springs 9.
- the vibration exciter 10 is slidably and rotatably arranged. This makes it possible, 11 1 to adjust the line of action of the excitation force of the vibration generator 10 to the stack of sieves as to form a roll angle of 45 0 ⁇ 85 ° with the horizontal.
- the screened-out grits are discharged via the grit discharges 12.
- several channels 13 are provided in the return deck 4, which are inclined 5 ° from the horizontal against the tranapor direction A of the material to be screened. These channels are suspended on the springs 14 in a vertically free-swinging manner and are connected at their ends to the frame 15 of the return deck 4 in an articulated manner 16. A plurality of channels 13 can be coupled to one another at their ends 17 in order to bring together material flows.
- the screen stack 1 rigidly arranged on the oscillating frame 2 is excited as a whole by the vibration exciter 10.
- the vibrations can act on the sieve stack 1 in accordance with the sieving task to be solved.
- the return of the material to be screened against the transport direction A of the same to the screen base is ensured by the vertical oscillating movements of the channels 13, which are caused by the excitation of the screen stack 1.
Landscapes
- Combined Means For Separation Of Solids (AREA)
- Bakery Products And Manufacturing Methods Therefor (AREA)
- Seasonings (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf eine als Wurfsieb ausgebildete Mehrdecksiebmaschine mit im Rahmen verspannten Sieb-, Blind-und Rückführdecks und einem am Siebstapel angeordneten Schwingungserreger zur Klassierung trockener rieselfähiger Schüttgüter kleiner Korngröße, wie Schleif- und Strahlmittel, mit der in einem Arbeitsgang eine Vielzahl von Korngrößenklassen klassiert werden können. Es sind bereits als Wurfsieb ausgebildete Mehrdecksiebmaschinen bekannt. Eine solche bekannte Mehrdecksiebmaschine besteht aus mehreren auf einem Grundrahmen übereinander angeordneten Siebdecks, die um 30° bis 40° zur Waagerechten geneigt sind. Am Siebgehäuse sind Schwingköpfe angeordnet. Unter dem Siebgewebe sind mit Schlagleisten versehene Wellen vorgesehen, die dem Siebgewebe über die Stößel und Stößelköpfe die Schwingungen aufzwingen (Firmenschrift "Hochleistungs-Schallsiebmaschinen" des Rhewum Rheinische Werkzeug- und Maschinenfabrik GmbH 5630 Remscheid-Lüttringhausen, BRD Liste 8.100-200 11.70/D-3000). Bei einer anderen als Wurfsieb ausgebildeten Mehrdecksiebmaschine erfolgt der Antrieb mittels elektromagnetischer Schwingungserreger, wobei die Schwingungen mittels Stößel direkt auf das Siebgewebe übertragen werden (Firmenschrift "Stößel-Schwingsiebmaschinen" des VEB Chemieanlagenbau Staßfurt, DDR). Diese als Wurfsieb ausgebildeten Mehrdecksiebmaschinen weisen, obwohl sie leistungsfähig sind, den Mangel auf, daß eine Rückführung des Siebgutes nicht möglich ist, so daß sie für Einsatzfälle, bei denen eine Vielzahl von Korngrößenklassen in einem Arbeitsgang zu klassieren sind, nicht geeignet sind, Die Rückführung des Siebgutes wird insbesondere dadurch verhindert, daß die Siebböden in Richtung einer senkrechten Längsebene schwingen, wodurch der Transport in Richtung der Neigung des Siebgutes erfolgt. Eine Rückführung des Siebgutes ist deshalb nicht möglich, weil diese entgegen der Wurfrichtung des Siebgutes erfolgen muß. Dem kann man zwar durch eine starke Neigung des Rückführdeckea begegenen, was jedoch zu großen Baukosten führt, ohne den gewünschten Effekt sicher zu erreichen, da sich das Siebgut trotz der starken Neigung im Rückführdeck staut. Ein weiterer Mangel solcher Mehrdecksiebmaschinen besteht darin, daß mit diesen nur bis zu maximal sechs Korngrößenklassen in einem Arbeitsgang klassiert werden können. Bei Einsatzfällen, bei denen eine Vielzahl von Korngrößenklassen klassiert werden müssen, wie z.B. 10 bis 25 Korngrößenklassen bei der Herstellung von Schleif- oder Strahlmitteln, sind deshalb mehrere solcher Mehrdecksiebmaschinen in Parallel- und Reihenschaltung aufzustellen und zu betreiben. Außerdem sind Übergabeeinrichtungen für das Siebgut von einer Maschine zur anderen und Einrichtungen zur Zusammenführung des Siebgutes erforderlich. Deshalb ist bei solchen Einsatzfällen der Aufwand an Ausrüstungen sowie für das Betreiben, Warten und Instandhalten derselben hoch und ein großer Raumbedarf erfor- .derlich. Als Wurfsieb ausgebildete Mehrdecksiebmaschinen mit Rückführung des Siebgutes entgegen seiner Transportrichtung mit der in einem Arbeitsgang im kontinuierlichen Dauerbetrieb eine Vielzahl von Korngrößen klassiert werden können, sind nicht bekannt.The invention relates to a multi-deck sieve machine designed as a throwing sieve with sieve, blind and return decks clamped in the frame and a vibration exciter arranged on the sieve stack for classifying dry, free-flowing bulk goods of small grain size, such as abrasives and blasting media, with which a large number of grain size classes are carried out in one operation can be classified. Multi-deck screening machines designed as throwing screens are already known. Such a known multi-deck screening machine consists of several screen decks arranged one above the other on a base frame, which are inclined by 30 ° to 40 ° to the horizontal. Vibrating heads are arranged on the sieve housing. Shafts provided with blow bars are provided under the sieve cloth, which force the sieve cloth to vibrate via the plunger and plunger heads (company publication "High-Performance Noise Sieving Machines" from Rhewum Rheinische Werkzeug- und Maschinenfabrik GmbH 5630 Remscheid-Lüttringhausen, FRG list 8.100-200 11.70 / D- 3000). In another multi-deck screening machine designed as a throwing screen, the drive is carried out by means of electromagnetic vibration exciters, the vibrations being transmitted directly to the screen fabric by means of a tappet (company name "Tappet vibrating screening machines" from VEB Chemieanlagenbau Staßfurt, GDR). These multi-deck screening machines, which are designed as throwing screens, have the deficiency, despite the fact that they are powerful, that it is not possible to return the screenings, so that they are not suitable for applications in which a large number of grain size classes have to be classified in one operation, the return of the material to be sieved is prevented in particular by the fact that the sieve trays swing in the direction of a vertical longitudinal plane, as a result of which the transport takes place in the direction of the inclination of the material to be sieved. A return of the material to be screened is not possible because this must take place against the direction of the screened material. This can be countered by a strong inclination of the return cover, but this leads to high construction costs without the desired effect can be reached safely because the screenings jam in the return deck despite the strong inclination. Another shortcoming of such multi-deck screening machines is that they can only classify up to a maximum of six grain size classes in one operation. For applications in which a large number of grain size classes have to be classified, such as 10 to 25 grain size classes in the production of abrasives or abrasives, several such multi-deck screening machines must therefore be set up and operated in parallel and in series. In addition, transfer devices for the screenings from one machine to another and facilities for merging the screenings are required. Therefore, in such cases, the outlay on equipment as well as for the operation, maintenance and repair of the same is high and a large space requirement is required. Multi-deck screening machines designed as throwing screens with return of the screened material against its transport direction, with which a large number of particle sizes can be classified in one continuous continuous operation, are not known.
Ferner ist eine als Plansieb arbeitende Mehrdecksiebmaschine bekannt, die aus in einem Rahmen verspannten Sieb-, Blind-und Rückführdecks besteht und bei der der so gebildete Siebstapel als Ganzes erregt wird. Die Neigung des Siebstapels kann je nach der erforderlichen Verweilzeit des Siebgutes auf den Siebboden und dessen Flußfähigkeit eingestellt werden. Der Antrieb erfolgt mittels eines in horizontaler Richtung wirkender Exzenters (Firmenschrift "Regula-Siebmaschinen" der J. Engelsmann AG, 67 Ludwigshafen /Rh. BRD). Obwohl diese Mehrdecksiebmaschine eine Rückführung des Siebgutes gestattet, können mit solchen nach dem Plansiebprinzip arbeitenden Mehrdecksiebmaschinen ebenfalls nur bis zu sechs Korngrößenklassen in einem Arbeitsgang klassiert werden. Plansiebmaschinen haben allgemein den Nachteil, daß der Siebboden nur in der Siebebene bewegt wird und somit wirkt auf das Unterkorn nur dessen Schwerkraft, die die Bewegung durch den Siebboden bewirkt.Furthermore, a multi-deck screening machine operating as a flat screen is known which consists of screen, blind and return decks which are clamped in a frame and in which the screen stack thus formed is excited as a whole. The inclination of the sieve stack can be adjusted depending on the required dwell time of the material to be sieved on the sieve bottom and its flowability. The drive takes place by means of an eccentric acting in the horizontal direction (company lettering "Regula-Siebmaschinen" from J. Engelsmann AG, 67 Ludwigshafen / Rh. FRG). Although this multi-deck screening machine allows the material to be returned, it is also possible to classify up to six grain size classes in one operation using such multi-deck screening machines. Plane screening machines generally have the disadvantage that the screen floor is only moved in the screen plane and thus only the gravity, which causes the movement through the screen floor, acts on the undersize.
Mit zunehmender Feinheit des Siebgutes wirken noch Haftkräfte auf das Unterkorn ein, die so groß sein können, daß die geringe Schwerkraft des Feinstkornes nicht mehr ausreicht, diese Kräfte zu überwinden. Hierdurch wird die Trennschärfe der Siebmaschine im Feinkornbereich beeinträchtigt, was zu Qualitätsminderungen führt. Außerdem können sich auf den Siebböden großflächige Verstopfungen ausbilden, die die Siebleistung verringern. Auf Grund dessen,können auch mit solchen Siebmaschinen Siebaufgaben, bei denen eine Vielzahl Korngrößenklassen zu klassieren sind, nur im aufwendigen Parallel- und Reihenbetrieb mehrer Mehrdecksiebmaschinen gelöst werden. Die Ursache für den notwendigen Parallel- und Reihenbetrieb bei der Lösung von Siebaufgaben, die die Klassierung des Schüttgutes in eine Vielzahl von Korngrößenklassen erfordern, besteht darin, daß die bekannten als Wurfsieb ausgebildeten Mehrdecksiebmaschinen eine Rückführung des Siebgutes nicht gestatten und die als Plansieb ausgebildeten Mehrdecksiebmaschinen im Feinstkornbereich nicht mit ausreichender Trennschärfe arbeiten, so daß mit solchen Mehrdecksiebmaschinen nur bis zu maximal sechs Korngrößenklassen in einem Arbeitsgang klassiert werden können. Es ist deshalb Aufgabe der Erfindung, erstmals eine als Wurfsieb ausgebildete Mehrdecksiebmaschine, bei der die Rückführung des Siebgutes entgegen der Transportrichtung möglich ist und die bei allen Korngrößenklassen mit großer Trennschärfe arbeitet, zu entwickeln. Erfindungsgemäß wird diese Aufgabe dadurch gelöst, daß ein an sich bekannter Schwingungserreger derart verschiebbar und verdrehbar an einem Siebstapel angeordnet ist, daß seine Wirkungslinie in einem Winkel von 45° ... 85° zu einer Waagerechten am Siebstapel angreift und in einem Rückführdeck Rinnen vertikal freischwingend und um 0° ... 30° zur Waagerechten geneigt angeordnet und mit einem Rahmen des Rückführdecks gelenkig verbunden sind. Weiter ist kennzeichnend, daß die Rinnen an den Enden in senkrechte im Siebstapel befindliche Kanäle münden und mehrere Rinnen an ihren Enden miteinander gekoppelt sind. Die Mehrdecksiebmaschine besteht aus einem Siebstapel, einem Schwingungserreger und der Körnungeabführung. Im Siebstapel sind Sieb-, Blind- und Rückführdecks mittels Spannrahmen und einer Spanneinrichtung fest verspannt angeordnet. Am Siebstapel oder an einem separaten Schwingungsrahmen ist ein Schwingungserreger verschiebbar und verdrehbar befestigt, so daß ein Wurfwinkelct sowie die Wirkungslinie des Schwingungserregers von 45° ... 85° zu einer Waagerechten einstellbar ist. Im Rückführdeck sind Rinnen an Federn vertikal freischwingend aufgehängt. Sie weisen eine Neigung von 0° ... 30° zur Waagerechten auf und sind an den Enden mit dem Rahmen des Rückführdecks gelenkig verbunden. Es können mehrere Rinnen an den Enden miteinander gekoppelt sein. Der Siebstapel wird durch den Schwingungserreger als Ganzes erregt. Die Rückführung des Siebgutes entgegen der Transportrichtung wird durch die Übertragung der Schwingungen auf die freischwingende Rinne gesichert. Die erfindungsgemäße Mehrdecksiebmaschine eignet sich vorzugsweise zur Lösung von Siebaufgaben, bei denen das Schüttgut in einem Arbeitsgang in eine Vielzahl von Korngrößenklassen zu klassieren ist. Sie eignet sich besonders zur Klassierung von Schleif- und Strahlmitteln, ist jedoch nicht auf dieses Anwendungsgebiet beschränkt. Durch die erfindungsgemäße Lösung ist es erstmals gelungen bei als Wurfsieb ausgebildeter Mehrdecksiebmaschine die Rückführung des Siebgutes entgegen der Wurf- und Transportrichtung des Siebgutes auf den Sieb- und Blinddecks zu sichern. Durch die Art der Schwingungserregung im Siebstapel kann selbst bei feinstkörnigem Siebgut eine hohe Trennschärfe erreicht werden. Darüber hinaus können bis zu 25 Korngrößenklassen in einem Arbeitsgang in einer derartigen Mehrdecksiebmaschine klassiert werden. Dadurch entfällt bei der Lösung solcher Siebaufgaben der bisherige Parallel- und Reihenbetrieb mehrerer Maschinen. Das führt zur Minderung des Raum- und Platzbedarfes und zur Verringerung des apparativen Aufwandes sowie der Betriebs-, Wartungs- und Instandhaltungskosten. Nachstehend wird die Erfindung anhand eines Ausführungeweges und Zeichnungen näher erläutert. Die Zeichnungen zeigen in Figur 1: eine Seitenansicht der Mehrdecksiebmaschine, Figur 2: einen Schnitt durch das Rückführdeck, Figur 3: eine Draufsicht auf das Rückführdeck.With increasing fineness of the screenings, adhesive forces act on the undersize, which can be so large that the low gravity of the fine grain is no longer sufficient to overcome these forces. This affects the selectivity of the screening machine in the fine grain area, which leads to a reduction in quality. In addition, large blockages can form on the sieve trays, which reduce the sieving capacity. Because of this, even with such screening machines, screening tasks in which a large number of grain size classes can be classified can only be solved in the complex parallel and series operation of multiple multi-deck screening machines. The reason for the necessary parallel and series operation when solving screening tasks that require the bulk material to be classified into a large number of grain size classes is that the known multi-deck screening machines designed as throwing screens do not allow the screenings to be returned and the multi-deck screening machines designed as plane screens in the Fine grain area does not work with sufficient selectivity, so that with such multi-deck screening machines only up to a maximum of six grain size classes can be classified in one operation. It is therefore the object of the invention to develop, for the first time, a multi-deck sieve machine designed as a throwing sieve, in which it is possible to return the material to be screened against the direction of transport and which works with a high degree of selectivity in all grain size classes. According to the invention, this object is achieved in that a vibration exciter known per se is arranged so displaceably and rotatably on a sieve stack that its line of action acts at an angle of 45 ° ... 85 ° to a horizontal on the sieve stack and vertically free-swinging in a return deck and inclined at 0 ° ... 30 ° to the horizontal and articulated to a frame of the return deck. It is also characteristic that the channels end at the ends in vertical channels in the sieve stack and several channels are coupled to one another at their ends. The multi-deck screening machine consists of a screen stack, a vibration exciter and the grain removal. In the stack of seven sieve, blind and return decks are firmly clamped using a clamping frame and a clamping device. On the sieve stack or on a separate vibration frame, a vibration exciter is slidably and rotatably fastened so that a throw angle and the line of action of the vibration exciter can be adjusted from 45 ° to 85 ° to a horizontal. In the return deck, channels are suspended from springs in a vertically swinging manner. They have an inclination of 0 ° ... 30 ° to the horizontal and are articulated at the ends to the frame of the return deck. Several channels can be coupled together at the ends. The sieve stack is excited as a whole by the vibration exciter. The return of the screenings against the transport direction is ensured by the transmission of the vibrations to the free-swinging trough. The multi-deck screening machine according to the invention is preferably suitable for solving screening tasks in which the bulk material can be classified into a large number of grain size classes in one operation. It is particularly suitable for classifying abrasives and abrasives, but is not restricted to this area of application. With the solution according to the invention, it was possible for the first time to secure the return of the material to be screened against the throwing and transport direction of the material to be screened on the screen and blind decks in the case of a multi-deck screening machine designed as a screening screen. Due to the type of vibration excitation in the sieve stack, a high degree of selectivity can be achieved even with very fine-grained screenings. In addition, up to 25 grain size classes can be classified in one operation in such a multi-deck screening machine. This eliminates the previous parallel and series operation of several machines when solving such screening tasks. This leads to a reduction in the space and space required and to a reduction in the outlay on equipment and in operating, maintenance and repair costs. The invention is explained in more detail below with reference to an embodiment and drawings. The drawings show in FIG. 1: a side view of the multi-deck screening machine, FIG. 2: a section through the return deck, Figure 3: a top view of the return deck.
Die Mehrdecksiebmaschine besteht aus dem Siebstapel 1, der auf dem Schwingrahmen 2 angeordnet ist. Im Siebstapel 1 sind die Sieb- und Blinddecks 3 und die Rückführdecks 4 übereinander angeordnet. Die Sieb- und Blinddecks 3 sowie die Rückführdecks 4 sind durch den Grundrahmen 5, Seitenrahmen 6, Deckrahmen 7 und die Spanneinrichtung 8 miteinander verspannt. Der auf dem Schwingrahmen 2 aufsitzende Siebstapel 1 ist auf Federn 9 gelagert. Am Schwingrahmen 2 ist der Schwingungserreger 10 verschiebbar und verdrehbar angeordnet. Dadurch ist es möglich, die Wirkungslinie 11 der Erregerkraft des Schwingungserregers 10 am Siebstapel 1 so einzustellen, daß sie mit der Waagerechten einen Wurfwinkel von 450 ··· 85° bildet. Die ausgesiebten Körnungen werden über die Körnungsabführungen 12 abgeführt. Wie aus den Figuren 2 und 3 zu entnehmen ist, sind im Rückführdeck 4 mehrere Rinnen 13 vorgesehen, die entgegen der Tranaportrichtung A des Siebgutes 5° von der Waagerechten geneigt sind. Diese Rinnen sind an den Federn 14 vertikal freischwingend aufgehängt und an ihren Enden mit dem Rahmen 15 des Rückführdecks 4 gelenkig 16 verbunden. Zur Zusammenführung von Siebgutströmen können mehrere Rinnen 13 an ihren Enden 17 miteinander gekoppelt sein. Der starr auf dem Schwingrahmen 2 angeordnete Siebstapel 1 wird von dem Schwingungserreger 10 als Ganzes erregt. Durch die veränderliche Angriffläche des Schwingungserregers 10 am Schwingrahmen 2 und die Veränderung des Wurfwinkels cL können die Schwingungen entsprechend der zu lösenden Siebaufgabe auf den Siebstapel 1 einwirken. Die Rückführung des Siebgutes entgegen der Transportrichtung A desselben auf den Siebboden wird durch die vertikalen Schwingbewegungen der Rinnen 13, die durch die Erregung des Siebstapels 1 hervorgerufen werden, gewährleistet.The multi-deck sieving machine consists of the
- 1 Siebstapel1 stack of sieves
- 2 Schwingrahmen2 swing frames
- 3 Sieb- und Blinddecks3 screen and blind decks
- 4 Rückführdeck4 return deck
- 5 Grundrahmen5 basic frames
- 6 Seitenrahmen6 side frames
- 7 Deckrahmen7 cover frames
- 8 Spanneinrichtung8 tensioning device
- 9 Federn9 springs
- 10 Schwingungserreger10 vibration exciters
- 11 Wirkungslinie11 line of action
- 12 Körnungsabführungen12 grit discharges
- 13 Rinnen13 channels
- 14 Federn14 feathers
- 15 Rahmen15 frames
- 16 gelenkige Verbindung16 articulated connection
- 17 Kopplung17 coupling
- α Wurfwinkelα throw angle
- A TransportrichtungA direction of transport
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT80106751T ATE19361T1 (en) | 1979-11-08 | 1980-11-03 | MULTI DECK SCREEN. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DD79216758A DD151882A1 (en) | 1979-11-08 | 1979-11-08 | multi deck |
| DD216758 | 1979-11-08 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0028792A2 true EP0028792A2 (en) | 1981-05-20 |
| EP0028792A3 EP0028792A3 (en) | 1983-03-23 |
| EP0028792B1 EP0028792B1 (en) | 1986-04-23 |
Family
ID=5520964
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP80106751A Expired EP0028792B1 (en) | 1979-11-08 | 1980-11-03 | Multi-deck screening machine |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0028792B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE19361T1 (en) |
| DD (1) | DD151882A1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3071571D1 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0208221A3 (en) * | 1985-07-12 | 1988-06-01 | Hein, Lehmann Aktiengesellschaft | Screening machine |
| CN105107718A (en) * | 2015-08-24 | 2015-12-02 | 海安县万力振动机械有限公司 | Closed vibrating screen |
| US20150353290A1 (en) * | 2012-12-20 | 2015-12-10 | Sandvik Mining And Construction Oy | Vibrating equipment and metod of processing material |
| CN105621005A (en) * | 2016-03-07 | 2016-06-01 | 四川江油新川矿山机械有限公司 | Screening and vibrating feeding machine |
| CN107716283A (en) * | 2017-10-27 | 2018-02-23 | 安徽星辉工业科技有限公司 | A kind of steaming utensil type vibration screening mechanism device for conveyer |
| CN110586465A (en) * | 2019-10-11 | 2019-12-20 | 安徽康博特保健食品有限公司 | A screening plant for health products tablet preparation |
| CN113770031A (en) * | 2021-09-30 | 2021-12-10 | 新乡市伟德筛分科技有限公司 | Double-bin multilayer rocking screen |
| CN115921291A (en) * | 2022-11-29 | 2023-04-07 | 合肥市公路桥梁工程有限责任公司 | Vibrating screen with multi-layer screen structure |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD256227A3 (en) * | 1985-09-23 | 1988-05-04 | Akad Wissenschaften Ddr | type of screen |
| CN111014022B (en) * | 2019-12-13 | 2020-12-08 | 通城县百丈潭茶业有限责任公司 | Tea processing equipment |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR646966A (en) * | 1928-01-11 | 1928-11-19 | Anciens Etablissements Lhuilli | Improvements to shaker sieves |
| FR765692A (en) * | 1932-12-15 | 1934-06-14 | Method and devices for adjusting the movements of vibrating apparatus | |
| US2238454A (en) * | 1939-04-03 | 1941-04-15 | Oliver W Steele | Method for sizing corn |
| GB611289A (en) * | 1946-04-26 | 1948-10-27 | Simon Ltd Henry | Improvements in plansifters |
| CH298059A (en) * | 1950-09-15 | 1954-04-30 | Limited Henry Simon Holdings | Crusher for seeds. |
| CH413564A (en) * | 1964-04-02 | 1966-05-15 | Muehlenbau Dresden Veb | Sieve sifter with vibration drive for grain cleaning |
| FR2314776A1 (en) * | 1975-06-16 | 1977-01-14 | Babbitless Sa | DIRECTED ACTION VIBRATING DEVICE |
-
1979
- 1979-11-08 DD DD79216758A patent/DD151882A1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
1980
- 1980-11-03 EP EP80106751A patent/EP0028792B1/en not_active Expired
- 1980-11-03 DE DE8080106751T patent/DE3071571D1/en not_active Expired
- 1980-11-03 AT AT80106751T patent/ATE19361T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0208221A3 (en) * | 1985-07-12 | 1988-06-01 | Hein, Lehmann Aktiengesellschaft | Screening machine |
| US20150353290A1 (en) * | 2012-12-20 | 2015-12-10 | Sandvik Mining And Construction Oy | Vibrating equipment and metod of processing material |
| US9649665B2 (en) * | 2012-12-20 | 2017-05-16 | Sandvik Mining And Construction Oy | Vibrating equipment and method of processing material |
| CN105107718A (en) * | 2015-08-24 | 2015-12-02 | 海安县万力振动机械有限公司 | Closed vibrating screen |
| CN105621005A (en) * | 2016-03-07 | 2016-06-01 | 四川江油新川矿山机械有限公司 | Screening and vibrating feeding machine |
| CN107716283A (en) * | 2017-10-27 | 2018-02-23 | 安徽星辉工业科技有限公司 | A kind of steaming utensil type vibration screening mechanism device for conveyer |
| CN110586465A (en) * | 2019-10-11 | 2019-12-20 | 安徽康博特保健食品有限公司 | A screening plant for health products tablet preparation |
| CN110586465B (en) * | 2019-10-11 | 2024-04-02 | 安徽康博特保健食品有限公司 | Screening device for manufacturing health-care product tablets |
| CN113770031A (en) * | 2021-09-30 | 2021-12-10 | 新乡市伟德筛分科技有限公司 | Double-bin multilayer rocking screen |
| CN115921291A (en) * | 2022-11-29 | 2023-04-07 | 合肥市公路桥梁工程有限责任公司 | Vibrating screen with multi-layer screen structure |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0028792A3 (en) | 1983-03-23 |
| ATE19361T1 (en) | 1986-05-15 |
| EP0028792B1 (en) | 1986-04-23 |
| DD151882A1 (en) | 1981-11-11 |
| DE3071571D1 (en) | 1986-05-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AT6073U1 (en) | multi deck | |
| DE69426524T2 (en) | VIBRATING SCREEN | |
| DE69017835T2 (en) | Twin-screen grain classifier and method. | |
| DE60026345T2 (en) | screening | |
| DE102006041989B4 (en) | Sieving machine especially for difficult to separate mixtures, such as heavy oil-sand mixtures | |
| DE3826996A1 (en) | VIBRATION SCREENER | |
| EP0028792A2 (en) | Multi-deck screening machine | |
| DE202016103754U1 (en) | screening machine | |
| WO2003045587A1 (en) | Sifting device | |
| DE3741966C2 (en) | ||
| EP3090817A1 (en) | Device for separating coarse particles from smaller particles | |
| DE2923662C2 (en) | Vibrating screen, especially circular vibrating screen | |
| DE102020125280B3 (en) | Vibrating screening machine | |
| DE3221344C1 (en) | Screening machine | |
| DE1201160B (en) | Sieving line made up of several two-mass vibrating sieves coupled to one another | |
| DE2701341A1 (en) | Screening machine for difficult material - with beater strips on oscillating frame with unbalanced mass drive | |
| DD151882B1 (en) | multi deck | |
| DE69119228T2 (en) | Method and device for screening granular materials | |
| EP0073319A2 (en) | Method of highly uniformly tensioning a fine-meshed screen-cloth mounted on a frame | |
| DE2135323A1 (en) | VIBRATING SCREEN, IN PARTICULAR VIBRATING SCREEN FOR FINE SCREENING | |
| DE3132140C1 (en) | Sieving machine | |
| DD215943A5 (en) | SIEVE SHAKER | |
| DE3344035C2 (en) | ||
| DE4012802A1 (en) | Operating system for multi-deck sieve - has superimposed vibrations to ensure sieving of lump-forming materials | |
| DE3330196C1 (en) | Sieving machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH GB LI SE |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19830831 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE GB LI SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 19361 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19860515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3071571 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19860528 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19921016 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19921021 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19921022 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19921022 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19921027 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19930126 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19931103 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19931103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19931104 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19931130 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19931130 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19931130 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: AKADEMIE DER WISSENSCHAFTEN DER DDR Effective date: 19931130 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19931103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19940802 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 80106751.3 Effective date: 19940610 |