WO2024257571A1 - 絶縁電着塗料の製造方法及び絶縁電着塗料 - Google Patents
絶縁電着塗料の製造方法及び絶縁電着塗料 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024257571A1 WO2024257571A1 PCT/JP2024/018863 JP2024018863W WO2024257571A1 WO 2024257571 A1 WO2024257571 A1 WO 2024257571A1 JP 2024018863 W JP2024018863 W JP 2024018863W WO 2024257571 A1 WO2024257571 A1 WO 2024257571A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- silica particles
- insulating
- mass
- resin
- polyimide resin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D179/00—Coating compositions based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing nitrogen, with or without oxygen, or carbon only, not provided for in groups C09D161/00 - C09D177/00
- C09D179/04—Polycondensates having nitrogen-containing heterocyclic rings in the main chain; Polyhydrazides; Polyamide acids or similar polyimide precursors
- C09D179/08—Polyimides; Polyester-imides; Polyamide-imides; Polyamide acids or similar polyimide precursors
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D5/00—Coating compositions, e.g. paints, varnishes or lacquers, characterised by their physical nature or the effects produced; Filling pastes
- C09D5/44—Coating compositions, e.g. paints, varnishes or lacquers, characterised by their physical nature or the effects produced; Filling pastes for electrophoretic applications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D7/00—Features of coating compositions, not provided for in group C09D5/00; Processes for incorporating ingredients in coating compositions
- C09D7/20—Diluents or solvents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D7/00—Features of coating compositions, not provided for in group C09D5/00; Processes for incorporating ingredients in coating compositions
- C09D7/40—Additives
- C09D7/60—Additives non-macromolecular
- C09D7/61—Additives non-macromolecular inorganic
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B3/00—Insulators or insulating bodies characterised by the insulating materials; Selection of materials for their insulating or dielectric properties
- H01B3/18—Insulators or insulating bodies characterised by the insulating materials; Selection of materials for their insulating or dielectric properties mainly consisting of organic substances
- H01B3/30—Insulators or insulating bodies characterised by the insulating materials; Selection of materials for their insulating or dielectric properties mainly consisting of organic substances plastics; resins; waxes
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to a method for producing insulating electrocoating paint and insulating electrocoating paint.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a suspension (electrodeposition liquid) in which resin particles and heat-resistant particles are dispersed in a dispersion medium.
- the present disclosure has been made in consideration of the above circumstances, and aims to provide a method for producing an insulating electrocoating for forming a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent long-term insulating stability.
- the present disclosure also aims to provide an insulating electrocoating produced by the method.
- a method for producing an insulating electrocoating comprising the step of preparing an insulating electrocoating by mixing a resin liquid containing a polyimide resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent with a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property.
- the present disclosure it is possible to provide a manufacturing method for insulating electrocoating for forming a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent long-term insulating stability.
- One aspect of the present disclosure provides a method for producing an insulating electrodeposition paint, comprising a step of mixing a resin liquid containing a polyimide-based resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent with a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property to prepare an insulating electrodeposition paint.
- a resin liquid containing a polyimide-based resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent with a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property to prepare an insulating electrodeposition paint.
- the organic solvent may contain N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 1-methoxy-2-propanol. This makes it easier to maintain good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles.
- the insulating electrodeposition paint may contain 0.01 to 22 parts by mass of silica particles per 100 parts by mass of polyimide resin. This makes it easier to maintain the dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles.
- the silica sol may contain at least one of NaOH and NH 4 OH, which makes it easier to maintain the dispersibility of the polyimide resin and the silica particles.
- the average particle size of the silica particles may be 1 to 60 nm. This makes it easier to maintain the dispersibility of the silica particles.
- the pH of the silica sol may be 2.0 to 10.0. This makes it easier to maintain the dispersibility of the silica particles and to form a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent insulation stability over the long term.
- the liquid medium may contain 70 to 95% by mass of an organic solvent. This makes it easier to maintain the dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles.
- an insulating electrodeposition paint comprising a mixture of a resin liquid containing a polyimide-based resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent, and a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property.
- the insulating electrodeposition paint can form a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent insulating stability over a long period of time.
- the method for producing an insulating electrodeposition paint according to the present disclosure includes a step of mixing a resin liquid containing a polyimide-based resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent with a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property to prepare an insulating electrodeposition paint.
- an insulating electrodeposition paint (hereinafter, sometimes simply referred to as a "paint")
- a coating film that has heat resistance and excellent insulation stability over a long period of time.
- the inventors speculate that it is because the polyimide resin and silica particles are suitably dispersed in the paint prepared as described above, resulting in the formation of a homogeneous coating film.
- the resin liquid and silica sol are mixed so that the paint contains preferably 0.01 parts by mass or more of silica particles, more preferably 0.05 parts by mass or more, and even more preferably 1 part by mass or more, per 100 parts by mass of polyimide resin. Also, from the viewpoint of easily forming a coating film having heat resistance and excellent long-term insulation stability, the resin liquid and silica sol are mixed so that the paint contains preferably 22 parts by mass or less of silica particles, more preferably 15 parts by mass or less, and even more preferably 8 parts by mass or less, per 100 parts by mass of polyimide resin.
- the resin liquid and silica sol in advance and mixing the two, preferably by adding silica sol to the resin liquid and mixing them, it is easy to obtain a paint in which the polyimide resin and silica particles are suitably dispersed.
- a paint in which the polyimide resin and silica particles are suitably dispersed There are no particular restrictions on the method of mixing the two, but for example, if the amount is small, it can be mixed in a beaker while stirring with a magnetic stirrer, and if the amount is large, it can be mixed by stirring with an emulsifier such as a homodisper.
- polyimide resins examples include polyimide resins, polyamideimide resins, polyetherimide resins, polyesterimide resins, etc. Among these, polyimide resins may be used from the viewpoints of dispersibility in the coating material, long-term stability of the coating material, etc.
- the polyimide resin may be present in the coating material as polyimide resin particles.
- the average particle size of the polyimide resin is preferably 10 nm or more, more preferably 100 nm or more, from the viewpoint of facilitating the formation of a homogeneous coating film.
- the average particle size is preferably 1000 nm or less, more preferably 900 nm or less, from the viewpoint of facilitating the formation of a homogeneous coating film.
- the average particle size referred to here is the median size (D50), and can be measured, for example, by using a laser diffraction/scattering type particle size distribution measuring device.
- the content of polyimide resin based on the total amount of resin liquid is preferably 1% by mass or more, and more preferably 5% by mass or more, from the viewpoint of easily forming a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent insulation stability over a long period of time.
- the content is preferably 25% by mass or less, and more preferably 10% by mass or less, from the viewpoint of easily forming a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent insulation stability over a long period of time.
- the organic solvent is not particularly limited as long as it is used in a coating material for electrodeposition containing a polyimide resin, but examples thereof include N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, N,N-dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, etc., and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone may be used from the viewpoint of good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles.
- N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone or the like in combination with an alcohol-based solvent as the organic solvent, it is easy to maintain good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles.
- the alcohol-based solvent examples include methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, t-butyl alcohol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, 1-methoxy-2-propanol, etc., and 1-methoxy-2-propanol is preferred from the viewpoint of good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles.
- the organic solvent preferably contains water, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 1-methoxy-2-propanol, and more preferably consists essentially of these.
- the liquid medium may mainly contain an organic solvent, that is, the content of the organic solvent may be greater than the content of water.
- the liquid medium preferably contains 70 to 95 mass % of the organic solvent, and more preferably contains 75 to 90 mass %.
- the resin liquid may contain a dispersant such as pyridine as an additive.
- Silica sol Silica particles are heat-resistant particles themselves, and when present together with the resin component in the coating film, they can suppress the deterioration of the resin component. It is presumed that this is because the dehydration and endothermic reaction on the surface of the silica particles caused by discharge in the coating film suppresses the deterioration of the resin component caused by discharge.
- polyimide resin the inventors' studies have shown that silica particles have superior properties in this respect compared to metal oxide particles such as alumina and zirconia, which also have heat resistance.
- the silica particles can be used without any particular restrictions, and examples thereof include amorphous (non-crystalline) silica particles.
- amorphous silica particles include fused silica particles, fumed silica particles, and colloidal silica particles. Of these, colloidal silica particles have high monodispersity and are easy to suppress from agglomerating in the paint.
- the shape of the silica particles is not particularly limited, and examples include spherical, cocoon-shaped, and association-shaped. Among these, the use of spherical silica particles makes it easier to suppress aggregation in the paint.
- the silica particles may be particles having a hollow structure, a porous structure, etc.
- the average particle size of the silica particles is preferably 1 nm or more, more preferably 5 nm or more, from the viewpoint of more easily maintaining good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and the silica particles, and is preferably 60 nm or less, more preferably 30 nm or less, from the viewpoint of more easily maintaining good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and the silica particles.
- the average particle size referred to here is the median size (D50), and can be measured, for example, by using a laser diffraction/scattering type particle size distribution measuring device.
- the content of silica particles based on the total amount of silica sol is preferably 5.0% by mass or more, and more preferably 10.0% by mass or more, from the viewpoint of easily forming a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent insulation stability over a long period of time.
- the content is preferably 30% by mass or less, and more preferably 20% by mass or less, from the viewpoint of easily forming a coating film that is heat resistant and has excellent insulation stability over a long period of time.
- the liquid property of the silica sol is acidic to weakly alkaline.
- the pH of the silica sol is preferably 2.0 or more, more preferably 2.5 or more, from the viewpoint of more easily maintaining the good dispersibility of the polyimide resin and silica particles in the paint.
- the pH is preferably 10.0 or less, more preferably 9.6 or less, from the viewpoint of maintaining the dispersibility of silica particles when used as a paint.
- the pH here is a value measured at 25° C. using a pH meter in accordance with JIS Z 8802.
- the silica sol may contain an alkali or acid as a stabilizer for the silica particles.
- the alkali include NaOH, ammonia (NH 4 OH), etc.
- the acid include organic acids such as lactic acid and acetic acid, and inorganic acids such as nitric acid.
- the silica sol contains NaOH, ammonia (NH 4 OH), etc., from the viewpoint of more easily maintaining good dispersibility of the silica particles due to electrical mutual repulsion with the polyimide resin in the coating material.
- the insulating electrodeposition paint according to the present disclosure is obtained by mixing the above-mentioned resin liquid containing a polyimide resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent with the above-mentioned silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property.
- a coating film having heat resistance and excellent insulation stability over a long period of time can be formed.
- the liquid properties of the silica sol affect the expression of the characteristics of the coating film (preparation of the desired paint), but there is a risk that the liquid properties may not be properly reflected as the characteristics of the paint obtained by mixing the silica sol with the resin liquid.
- the insulating electrodeposition paint is said to be a mixture of the resin liquid and the silica sol.
- the coating preferably contains 0.01 to 22 parts by mass of silica particles per 100 parts by mass of polyimide resin, more preferably 0.05 to 15 parts by mass, and even more preferably 1 to 8 parts by mass.
- a heat-resistant coating film (insulating film) can be formed on the surface of the object.
- the coating conditions can be, for example, an applied voltage of 10 to 200 kV and a voltage application time of 1 second or more, and the thickness of the coating film formed can be, for example, 1 to 200 ⁇ m.
- the target object is not particularly limited as long as it is an object that is generally subjected to insulating electrodeposition coating, but examples thereof include electric high-power density motor stators, power semiconductors, transistors, and other electronic components that require heat resistance and insulating reliability over a long period of time.
- a method for producing an insulating electrodeposition paint comprising a step of mixing a resin liquid containing a polyimide resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent with a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property to prepare an insulating electrodeposition paint.
- the organic solvent comprises N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and 1-methoxy-2-propanol.
- the insulating electrodeposition paint contains 0.01 to 22 parts by mass of the silica particles per 100 parts by mass of the polyimide resin.
- An insulating electrodeposition paint comprising a mixture of a resin liquid containing a polyimide resin and a liquid medium containing water and an organic solvent, and a silica sol containing silica particles and water and having an acidic to weakly alkaline liquid property.
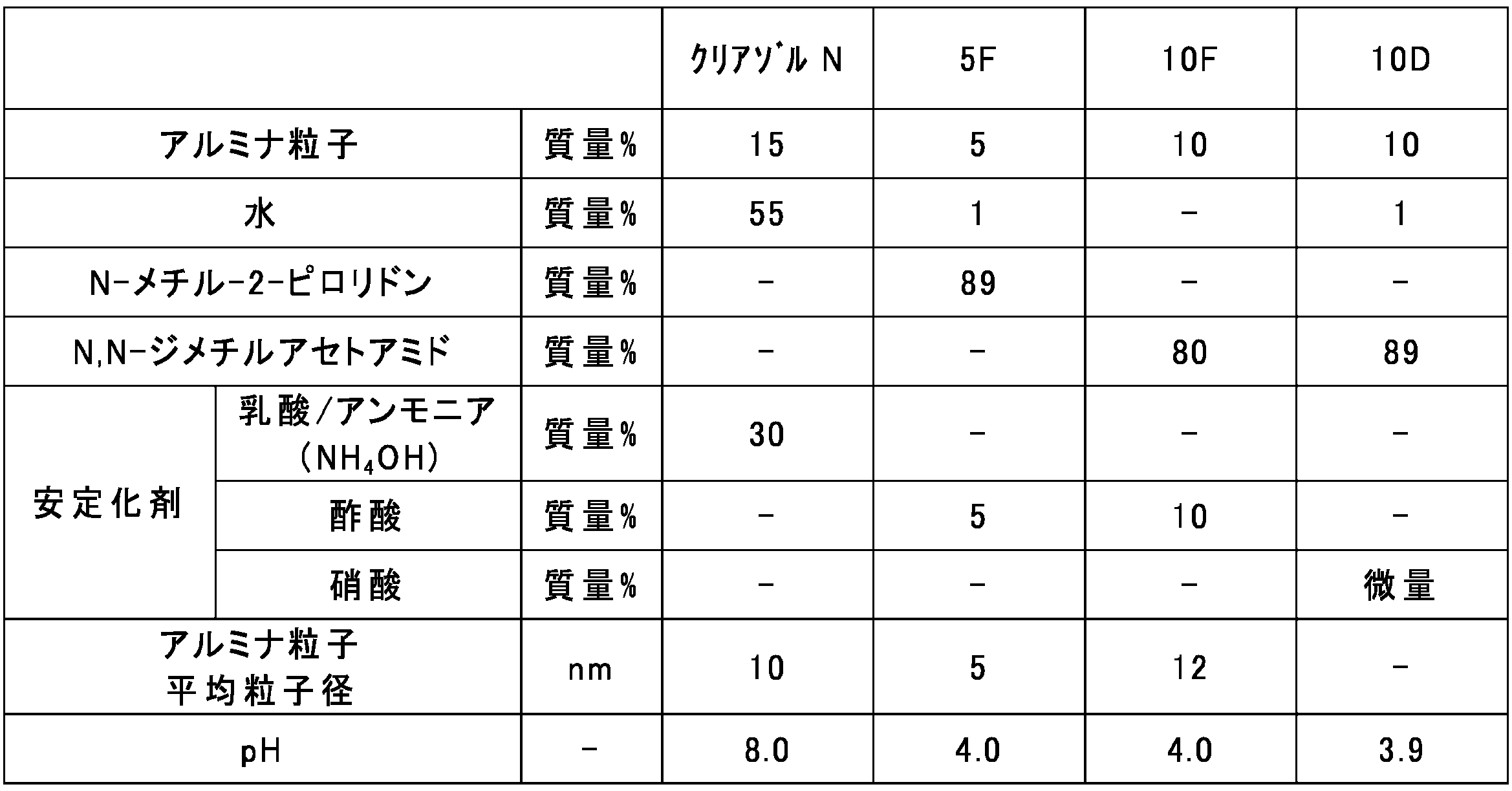
- alumina sol (Preparation of alumina sol) The alumina sols shown in Table 3 were prepared. Clearsol N: Manufactured by Kawaken Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd. Aluminasol-5F: manufactured by Kawaken Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. Aluminasol-10F: manufactured by Kawaken Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. Alumina sol-10D: manufactured by Kawaken Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Test pieces with the coating film obtained as described above were placed in a drying furnace at 300° C. and taken out after 100 hours. When the appearance of the test pieces with the coating film after taking them out was visually observed, no defects such as cracks or peeling were found in the coating of any of the test pieces.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Paints Or Removers (AREA)
Abstract
ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法。
Description
本開示は、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法及び絶縁電着塗料に関する。
電着塗装により対象物に絶縁膜を形成するための絶縁電着塗料が知られている。特許文献1には、樹脂粒子及び耐熱性粒子が分散媒中に分散した懸濁液(電着液)が開示されている。
発明者らが鋭意検討を進めたところ、特許文献1等の従来技術に基づき調製された塗料を用いて形成された塗膜には、耐熱性及び長期に亘る絶縁安定性の両立の点において、依然改善の余地があることが分かった。
本開示は上記事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成するための絶縁電着塗料の製造方法を提供することを目的とする。また、本開示は、当該製造方法から製造される絶縁電着塗料を提供することを目的とする。
ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法。
本開示によれば、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成するための絶縁電着塗料の製造方法を提供することができる。また、本開示によれば、当該製造方法から製造される絶縁電着塗料を提供することができる。
以下、本開示の実施形態について詳細に説明する。ただし、本開示は以下の実施形態に限定されない。
本開示の一側面は、ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法を提供する。
上記製造方法によれば、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成するための絶縁電着塗料を提供することができる。
上記製造方法によれば、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成するための絶縁電着塗料を提供することができる。
一態様において、有機溶媒はN-メチル-2-ピロリドン及び1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールを含んでいてよい。これにより、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性をより維持し易い。
一態様において、絶縁電着塗料は、ポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、シリカ粒子を0.01~22質量部含んでいてよい。これにより、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の分散性をより維持し易い。
一態様において、シリカゾルはNaOH及びNH4OHの少なくともいずれかを含んでいてよい。これにより、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の分散性をより維持し易い。
一態様において、シリカ粒子の平均粒子径は1~60nmであってよい。これにより、シリカ粒子の分散性をより維持し易い。
一態様において、シリカゾルのpHは2.0~10.0であってよい。これにより、シリカ粒子の分散性をより維持し易く、また、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い。
一態様において、液状媒体は、有機溶媒を70~95質量%含んでいてよい。これにより、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の分散性をより維持し易い。
本開示の他の側面は、ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルを混合してなる絶縁電着塗料を提供する。
上記絶縁電着塗料によれば、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成することができる。
上記絶縁電着塗料によれば、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成することができる。
<絶縁電着塗料の製造方法>
本開示に係る絶縁電着塗料の製造方法は、ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える。
液状媒体として水及び有機溶媒を併用した系にポリイミド系樹脂を分散させ、これを液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと混合して絶縁電着塗料(以下、単に「塗料」という場合がある)とすることで、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜(絶縁膜)を形成することができる。この理由は定かではないが、上記のとおり調製された塗料においてはポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子が好適に分散しており、その結果均質な塗膜が形成されるためであると、発明者らは推察している。
本開示に係る絶縁電着塗料の製造方法は、ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える。
液状媒体として水及び有機溶媒を併用した系にポリイミド系樹脂を分散させ、これを液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと混合して絶縁電着塗料(以下、単に「塗料」という場合がある)とすることで、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜(絶縁膜)を形成することができる。この理由は定かではないが、上記のとおり調製された塗料においてはポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子が好適に分散しており、その結果均質な塗膜が形成されるためであると、発明者らは推察している。
上記調製する工程では、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い観点から、塗料が、ポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、好ましくはシリカ粒子を0.01質量部以上、より好ましくは0.05質量部以上、さらに好ましくは1質量部以上含むように、樹脂液とシリカゾルとが混合される。また、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い観点から、塗料が、ポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、好ましくはシリカ粒子を22質量部以下、より好ましくは15質量部以下、さらに好ましくは8質量部以下含むように、樹脂液とシリカゾルとが混合される。
上記のとおり予め樹脂液とシリカゾルとを準備して両者を混合すること、好ましくは樹脂液にシリカゾルを添加して混合することにより、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子が好適に分散した塗料が得易い。両者の混合方法は特に制限されないが、例えば少量であればマグネチックスターラー等で攪拌しながらビーカー内で行うことができ、大量であればホモディスパー等の乳化機での攪拌により行うことができる。
(樹脂液)
ポリイミド系樹脂としては、ポリイミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂、ポリエーテルイミド樹脂、ポリエステルイミド樹脂等が挙げられる。これらのうち、上記塗料中での分散性、塗料の長期安定性等の観点から、ポリイミド樹脂を用いても良い。
ポリイミド系樹脂としては、ポリイミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂、ポリエーテルイミド樹脂、ポリエステルイミド樹脂等が挙げられる。これらのうち、上記塗料中での分散性、塗料の長期安定性等の観点から、ポリイミド樹脂を用いても良い。
ポリイミド系樹脂は塗料中でポリイミド系樹脂粒子として存在していてよい。ポリイミド系樹脂の平均粒子径は、均質な塗膜形成をし易い観点から10nm以上であることが好ましく、100nm以上であることがより好ましい。当該平均粒子径は、均質な塗膜形成をし易い観点から1000nm以下であることが好ましく、900nm以下であることがより好ましい。
ここでいう平均粒子径とはメジアン径(D50)であり、例えばレーザ回折/散乱式粒子径分布測定装置を用いて測定することができる。
ここでいう平均粒子径とはメジアン径(D50)であり、例えばレーザ回折/散乱式粒子径分布測定装置を用いて測定することができる。
樹脂液の全量を基準とするポリイミド系樹脂の含有量は、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い観点から1質量%以上であることが好ましく、5質量%以上であることがより好ましい。当該含有量は、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い観点から25質量%以下であることが好ましく、10質量%以下であることがより好ましい。
液状媒体として水及び有機溶媒を併用することで、塗液としたときのポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性を維持することができる。
有機溶媒としては、ポリイミド系樹脂を含む電着用の塗料に用いられるものであれば特に限定されないが、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン、N,Nジメチルホルムアミド、ジメチルスルホキシド等が挙げられ、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性の観点からはN-メチル-2-ピロリドンを用いても良い。また、有機溶媒として、これらN-メチル-2-ピロリドン等とアルコール系溶媒とを併用することで、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性を維持し易い。アルコール系溶媒としては、メタノール、エタノール、1-プロパノール、2-プロパノール、t-ブチルアルコール、エチレングリコール、プロピレングリコール、1-メトキシ-2-プロパノール等が挙げられ、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性の観点からは1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールが好ましい。
ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の分散性の観点から、有機溶媒として、水、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン及び1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールを含むものが好ましく、実質的にこれらからなるものがより好ましい。
有機溶媒としては、ポリイミド系樹脂を含む電着用の塗料に用いられるものであれば特に限定されないが、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン、N,Nジメチルホルムアミド、ジメチルスルホキシド等が挙げられ、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性の観点からはN-メチル-2-ピロリドンを用いても良い。また、有機溶媒として、これらN-メチル-2-ピロリドン等とアルコール系溶媒とを併用することで、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性を維持し易い。アルコール系溶媒としては、メタノール、エタノール、1-プロパノール、2-プロパノール、t-ブチルアルコール、エチレングリコール、プロピレングリコール、1-メトキシ-2-プロパノール等が挙げられ、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性の観点からは1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールが好ましい。
ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の分散性の観点から、有機溶媒として、水、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン及び1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールを含むものが好ましく、実質的にこれらからなるものがより好ましい。
液状媒体は、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性の観点から、有機溶媒を主として含むこと、すなわち水の含有量よりも有機溶媒の含有量の方が多くても良い。例えば、液状媒体は有機溶媒を70~95質量%含むことが好ましく、75~90質量%含むことがより好ましい。
樹脂液には、ポリイミド系樹脂の他に、添加剤としてピリジン等の分散剤が含まれていてよい。
(シリカゾル)
シリカ粒子は、それ自体が耐熱性を有する粒子であると共に、塗膜中で樹脂成分と共に存在させることで樹脂成分の劣化を抑制することができる。これは、塗膜における放電により生じるシリカ粒子表面での脱水・吸熱反応が、放電による樹脂成分の劣化を抑制するためであると推察している。ポリイミド系樹脂を用いる場合、発明者らの検討によると、同じく耐熱性を有するアルミナ、ジルコニア等の金属酸化物粒子に比して、シリカ粒子はこの特性に優れている。
シリカ粒子は、それ自体が耐熱性を有する粒子であると共に、塗膜中で樹脂成分と共に存在させることで樹脂成分の劣化を抑制することができる。これは、塗膜における放電により生じるシリカ粒子表面での脱水・吸熱反応が、放電による樹脂成分の劣化を抑制するためであると推察している。ポリイミド系樹脂を用いる場合、発明者らの検討によると、同じく耐熱性を有するアルミナ、ジルコニア等の金属酸化物粒子に比して、シリカ粒子はこの特性に優れている。
シリカ粒子としては、特に制限なく用いることができ、例えばアモルファス(非晶質)シリカ粒子が挙げられる。アモルファスシリカ粒子としては、例えば、溶融シリカ粒子、ヒュームドシリカ粒子、コロイダルシリカ粒子等が挙げられる。このうちコロイダルシリカ粒子は、単分散性が高く、塗料中での凝集を抑制し易い。
シリカ粒子の形状は特に制限されず、球状、繭型、会合型等が挙げられる。これらのうち、シリカ粒子として球状の粒子を用いることにより、塗料中での凝集を抑制し易くなる。また、シリカ粒子は、中空構造、多孔質構造等を有する粒子であってもよい。
シリカ粒子の平均粒子径は、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性をより維持し易い観点から1nm以上であることが好ましく、5nm以上であることがより好ましい。当該平均粒子径は、ポリイミド系樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性をより維持し易い観点から60nm以下であることが好ましく、30nm以下であることがより好ましい。
ここでいう平均粒子径とはメジアン径(D50)であり、例えばレーザ回折/散乱式粒子径分布測定装置を用いて測定することができる。
ここでいう平均粒子径とはメジアン径(D50)であり、例えばレーザ回折/散乱式粒子径分布測定装置を用いて測定することができる。
シリカゾルの全量を基準とするシリカ粒子の含有量は、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い観点から5.0質量%以上であることが好ましく、10.0質量%以上であることがより好ましい。当該含有量は、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成し易い観点から30質量%以下であることが好ましく、20質量%以下であることがより好ましい。
均質な塗膜形成の観点、及び塗料としたときのシリカ粒子の分散性を維持する観点から、シリカゾルの液性は酸性~弱アルカリ性である。具体的にはシリカゾルのpHは、塗料中のポリイミド樹脂及びシリカ粒子の良好な分散性をより維持し易い観点から2.0以上であることが好ましく、2.5以上であることがより好ましい。当該pHは、塗料としたときのシリカ粒子の分散性を維持する観点から10.0以下であることが好ましく、9.6以下であることがより好ましい。
ここでいうpHとは、pH計を用いてJIS Z 8802に準じて25℃で測定される値である。
ここでいうpHとは、pH計を用いてJIS Z 8802に準じて25℃で測定される値である。
シリカゾルは、シリカ粒子の安定化剤としてアルカリ又は酸を含むことができる。アルカリとしてはNaOH、アンモニア(NH4OH)等が挙げられ、酸としては乳酸、酢酸等の有機酸、硝酸等の無機酸などが挙げられる。これらのうち、塗料中のポリイミド樹脂との電気的な相互反発によるシリカ粒子の良好な分散性をより維持し易い観点から、シリカゾルはNaOH、アンモニア(NH4OH)等を含むことが好ましい。
<絶縁電着塗料>
本開示に係る絶縁電着塗料は、ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む上述の樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性である上述のシリカゾルと、を混合してなるものである。このような塗料を用いることで、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成することができる。
なお、シリカゾルの液性は塗膜の当該特性の発現(所望の塗料を調製すること)に影響すると考えているが、シリカゾルと樹脂液とを混合して得られる塗料の特徴としてその液性が正しく反映されない虞がある。このことに鑑み、上記絶縁電着塗料は樹脂液とシリカゾルとを混合してなるものであるとしている。
本開示に係る絶縁電着塗料は、ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む上述の樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性である上述のシリカゾルと、を混合してなるものである。このような塗料を用いることで、耐熱性を有すると共に長期に亘る絶縁安定性に優れる塗膜を形成することができる。
なお、シリカゾルの液性は塗膜の当該特性の発現(所望の塗料を調製すること)に影響すると考えているが、シリカゾルと樹脂液とを混合して得られる塗料の特徴としてその液性が正しく反映されない虞がある。このことに鑑み、上記絶縁電着塗料は樹脂液とシリカゾルとを混合してなるものであるとしている。
塗料は、上記のとおりポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、好ましくはシリカ粒子を0.01~22質量部、より好ましくは0.05~15質量部、さらに好ましくは1~8質量部含む。
この塗料を用いて、電着塗装装置にて対象物に塗装を施すことにより、対象物表面に耐熱性を有する塗膜(絶縁膜)を形成することができる。塗装条件は、例えば印加電圧10~200kv、電圧印加時間1秒以上とすることができ、形成される塗膜の厚さは、例えば1~200μmとすることができる。
対象物としては、一般に絶縁電着塗装が施される物であれば特に制限されないが、例えば、長期に亘って耐熱性及び絶縁信頼性が求められる、電動化高出力密度型モータステータ;パワー半導体、トランジスタ等の電子部品などが挙げられる。
対象物としては、一般に絶縁電着塗装が施される物であれば特に制限されないが、例えば、長期に亘って耐熱性及び絶縁信頼性が求められる、電動化高出力密度型モータステータ;パワー半導体、トランジスタ等の電子部品などが挙げられる。
<本実施形態の概要>
[1] ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法。
[2] 有機溶媒が、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン及び1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールを含む、[1]に記載の製造方法。
[3] 前記絶縁電着塗料は、前記ポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、前記シリカ粒子を0.01~22質量部含む、[1]又は[2]に記載の製造方法。
[4] 前記シリカゾルがNaOH及びNH4OHの少なくともいずれかを含む、[1]~[3]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[5] 前記シリカ粒子の平均粒子径が1~60nmである、[1]~[4]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[6] 前記シリカゾルのpHが2.0~10.0である、[1]~[5]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[7] 前記液状媒体が、前記有機溶媒を70~95質量%含む、[1]~[6]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[8] ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合してなる絶縁電着塗料。
[1] ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法。
[2] 有機溶媒が、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン及び1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールを含む、[1]に記載の製造方法。
[3] 前記絶縁電着塗料は、前記ポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、前記シリカ粒子を0.01~22質量部含む、[1]又は[2]に記載の製造方法。
[4] 前記シリカゾルがNaOH及びNH4OHの少なくともいずれかを含む、[1]~[3]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[5] 前記シリカ粒子の平均粒子径が1~60nmである、[1]~[4]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[6] 前記シリカゾルのpHが2.0~10.0である、[1]~[5]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[7] 前記液状媒体が、前記有機溶媒を70~95質量%含む、[1]~[6]のいずれか一に記載の製造方法。
[8] ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合してなる絶縁電着塗料。
本開示を以下の実施例によりさらに詳細に説明するが、本開示はこれらの例に限定されるものではない。
(樹脂液の準備)
表1に示す組成を有する樹脂液を準備した。
表1に示す組成を有する樹脂液を準備した。
(シリカゾルの準備)
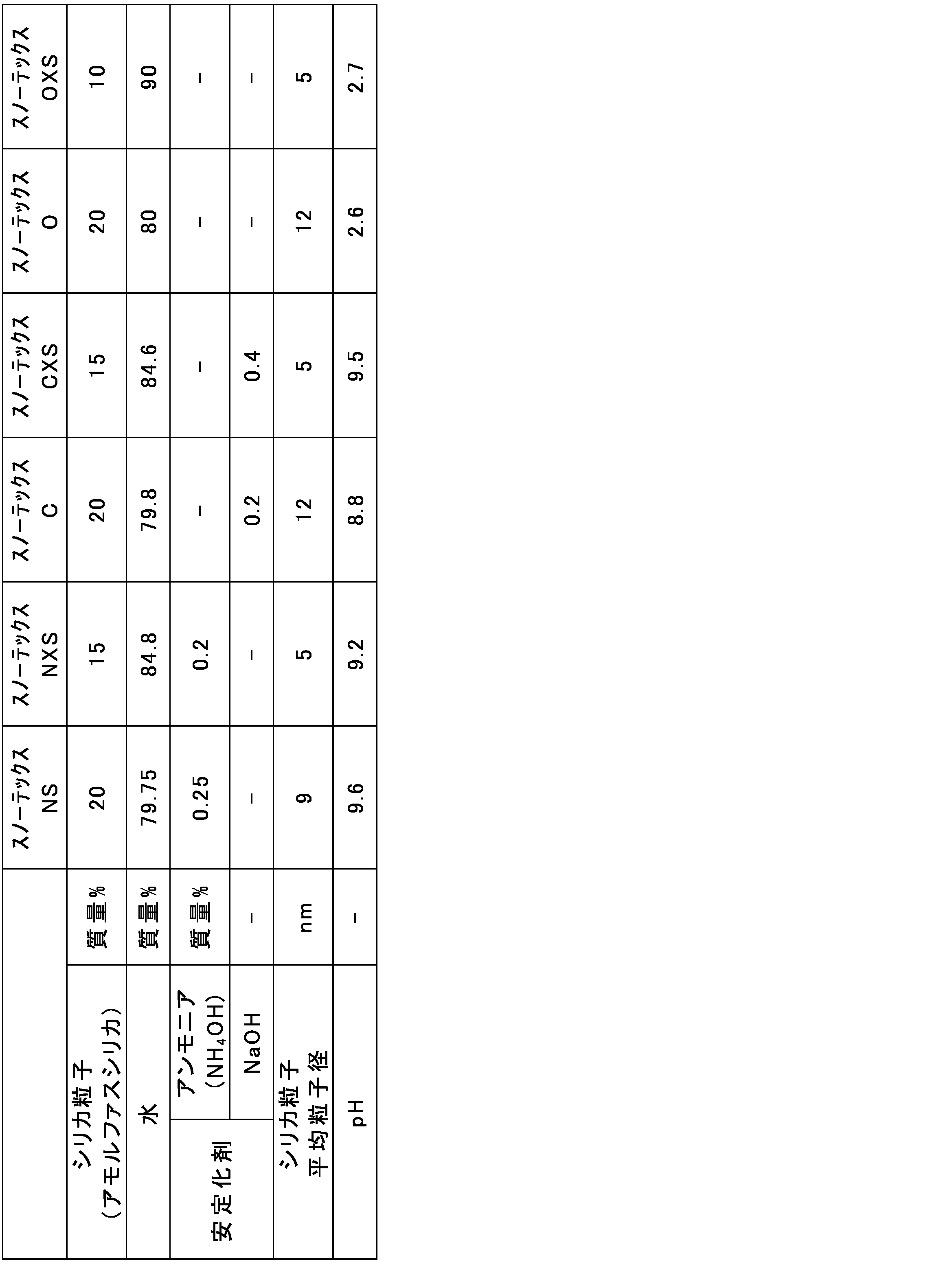
表2に示すシリカゾル(日産化学株式会社製のスノーテックスシリーズ)を準備した。
表2に示すシリカゾル(日産化学株式会社製のスノーテックスシリーズ)を準備した。
(アルミナゾルの準備)
表3に示すアルミナゾルを準備した。
クリアゾルN:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
アルミナゾル-5F:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
アルミナゾル-10F:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
アルミナゾル-10D:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
表3に示すアルミナゾルを準備した。
クリアゾルN:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
アルミナゾル-5F:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
アルミナゾル-10F:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
アルミナゾル-10D:川研ファインケミカル株式会社製。
(電着塗料の調製)
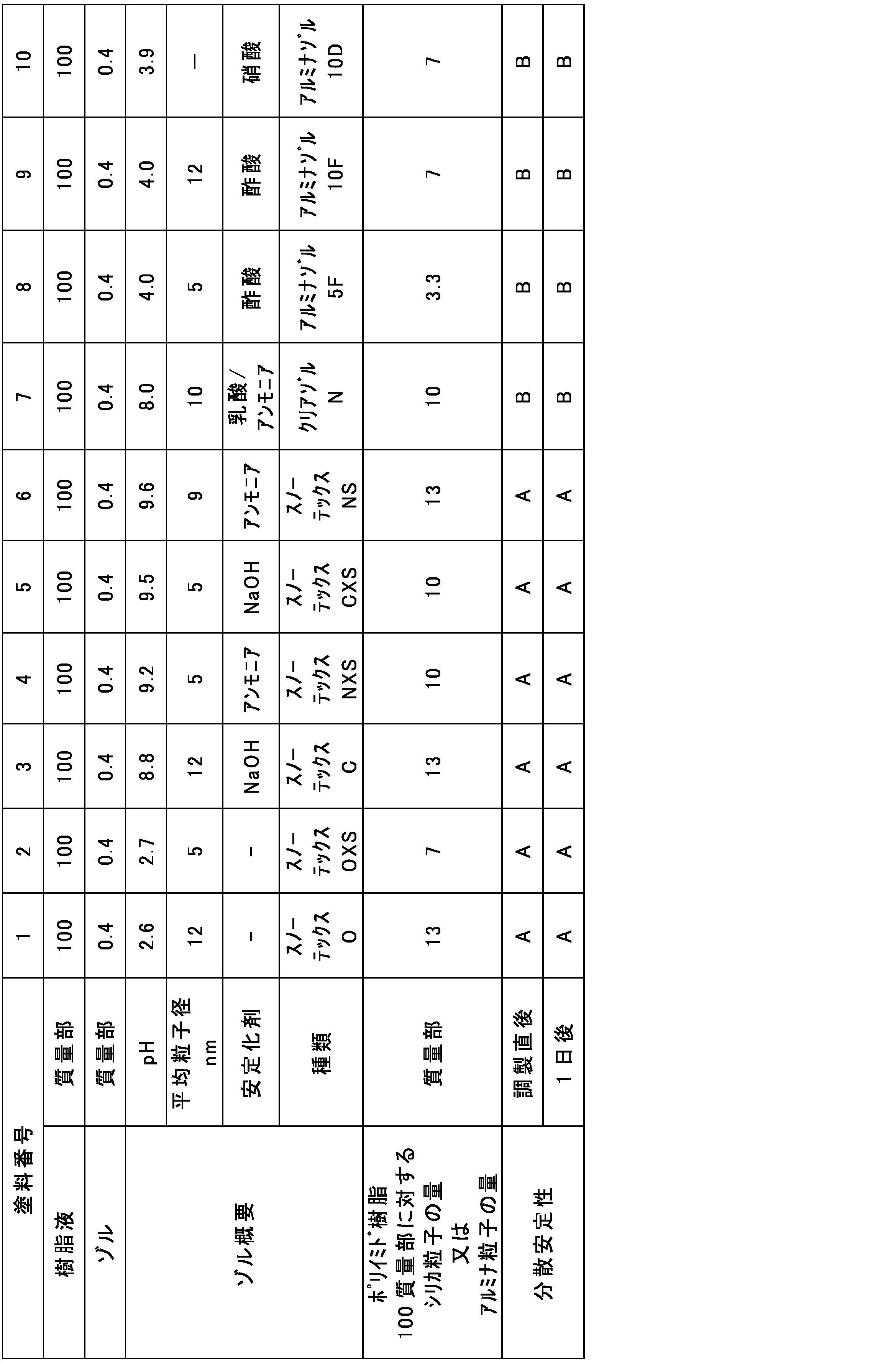
上記樹脂液をビーカーに入れてホモディスパーで攪拌しながら、樹脂液100質量部に対し、上記シリカゾル又はアルミナゾルを表4に示すとおり0.4質量部添加した。攪拌時間は5分以上とした。
上記樹脂液をビーカーに入れてホモディスパーで攪拌しながら、樹脂液100質量部に対し、上記シリカゾル又はアルミナゾルを表4に示すとおり0.4質量部添加した。攪拌時間は5分以上とした。
(電着塗料の分散性評価)
上記のとおり調製した塗料の分散性を以下のとおり評価した。具体的には、上記方法にて調整した電着塗料を100mlのガラス瓶に入れ、調整直後及び1日後にそれぞれの電着塗料の状態を目視観察した。結果を表4に示す。
A:沈降物及び凝集物がなく、電着塗装が可能な状態であった。
B:沈降物及び凝集物があり、電着塗装が不可能な状態であった。
上記のとおり調製した塗料の分散性を以下のとおり評価した。具体的には、上記方法にて調整した電着塗料を100mlのガラス瓶に入れ、調整直後及び1日後にそれぞれの電着塗料の状態を目視観察した。結果を表4に示す。
A:沈降物及び凝集物がなく、電着塗装が可能な状態であった。
B:沈降物及び凝集物があり、電着塗装が不可能な状態であった。
(塗膜付き試験片の作製)
分散安定性がA評価であった塗料番号1~6の塗料を、それぞれ500gずつビーカーに入れた。マグネチックスターラーで300rpmの条件で塗料を攪拌しながら、ビーカー内にて陽極(めっき銅試験片)、陰極(SUS対極片)を対向させて設置し、株式会社高砂製作所社製の電着塗装装置SD-EC-800-Mを用いて試験片表面に電着塗膜(絶縁膜)を形成した。電着塗装条件は、印加電圧60kv、電圧印加時間300秒とした。その後、塗膜が形成された試験片を乾燥器で乾燥させた。塗膜の厚さは50μmであった。
分散安定性がA評価であった塗料番号1~6の塗料を、それぞれ500gずつビーカーに入れた。マグネチックスターラーで300rpmの条件で塗料を攪拌しながら、ビーカー内にて陽極(めっき銅試験片)、陰極(SUS対極片)を対向させて設置し、株式会社高砂製作所社製の電着塗装装置SD-EC-800-Mを用いて試験片表面に電着塗膜(絶縁膜)を形成した。電着塗装条件は、印加電圧60kv、電圧印加時間300秒とした。その後、塗膜が形成された試験片を乾燥器で乾燥させた。塗膜の厚さは50μmであった。
(耐熱性評価)
上記のとおり得られた塗膜付き試験片を300℃の乾燥炉に入れ、100時間経過後に取り出した。取り出した後の塗膜付き試験片外観を目視にて観察したところ、いずれの試験片の塗膜にも割れ、剥がれ等の不具合は認められなかった。
上記のとおり得られた塗膜付き試験片を300℃の乾燥炉に入れ、100時間経過後に取り出した。取り出した後の塗膜付き試験片外観を目視にて観察したところ、いずれの試験片の塗膜にも割れ、剥がれ等の不具合は認められなかった。
(絶縁破壊時間測定)
塗料番号5の塗料を用いて得られた塗膜付き試験片(長さ180mm×幅9mm×厚さ5mm、塗膜が形成された部分の長さ60mm)を2本準備した。各試験片を、塗膜が形成された部分同士が対向するように重ねて配置し、カプトンテープで固定した。そして、各試験片の塗膜が形成されていない端部に電源を接続してV-t試験(試験条件:クロック周波数1kHz、電圧±1500V、気圧1.0atm)を行ったところ、約71時間経過後にようやく塗膜が絶縁破壊した。これは、上記のとおり得られた塗膜が長期に亘り絶縁安定性に優れることを示すものである。
塗料番号5の塗料を用いて得られた塗膜付き試験片(長さ180mm×幅9mm×厚さ5mm、塗膜が形成された部分の長さ60mm)を2本準備した。各試験片を、塗膜が形成された部分同士が対向するように重ねて配置し、カプトンテープで固定した。そして、各試験片の塗膜が形成されていない端部に電源を接続してV-t試験(試験条件:クロック周波数1kHz、電圧±1500V、気圧1.0atm)を行ったところ、約71時間経過後にようやく塗膜が絶縁破壊した。これは、上記のとおり得られた塗膜が長期に亘り絶縁安定性に優れることを示すものである。
Claims (8)
- ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合して絶縁電着塗料を調製する工程を備える、絶縁電着塗料の製造方法。
- 有機溶媒が、N-メチル-2-ピロリドン及び1-メトキシ-2-プロパノールを含む、請求項1に記載の製造方法。
- 前記絶縁電着塗料が、前記ポリイミド系樹脂100質量部に対し、前記シリカ粒子を0.01~22質量部含む、請求項1又は2に記載の製造方法。
- 前記シリカゾルが、NaOH及びNH4OHの少なくともいずれかを含む、請求項1又は2に記載の製造方法。
- 前記シリカ粒子の平均粒子径が1~60nmである、請求項1又は2に記載の製造方法。
- 前記シリカゾルのpHが2.0~10.0である、請求項1又は2に記載の製造方法。
- 前記液状媒体が、前記有機溶媒を70~95質量%含む、請求項1又は2に記載の製造方法。
- ポリイミド系樹脂並びに水及び有機溶媒を含む液状媒体を含む樹脂液と、シリカ粒子及び水を含み液性が酸性~弱アルカリ性であるシリカゾルと、を混合してなる絶縁電着塗料。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2025527607A JPWO2024257571A1 (ja) | 2023-06-13 | 2024-05-22 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023-096804 | 2023-06-13 | ||
| JP2023096804 | 2023-06-13 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024257571A1 true WO2024257571A1 (ja) | 2024-12-19 |
Family
ID=93851774
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2024/018863 Pending WO2024257571A1 (ja) | 2023-06-13 | 2024-05-22 | 絶縁電着塗料の製造方法及び絶縁電着塗料 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPWO2024257571A1 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2024257571A1 (ja) |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004515558A (ja) * | 1999-03-26 | 2004-05-27 | エー. ラポイント,デイビッド | 耐摩耗コーティング組成物、それらの製造方法及びそれにより被覆された物品 |
| JP2008137876A (ja) * | 2006-12-05 | 2008-06-19 | Catalysts & Chem Ind Co Ltd | シリカゾルおよびこれを含む塗料組成物 |
| JP2016015295A (ja) * | 2014-07-03 | 2016-01-28 | 三菱マテリアル株式会社 | 耐熱性絶縁電線とその絶縁層の形成に用いる電着液 |
| WO2017006999A1 (ja) * | 2015-07-09 | 2017-01-12 | 住友精化株式会社 | 耐部分放電用電気絶縁樹脂組成物 |
| WO2017007000A1 (ja) * | 2015-07-09 | 2017-01-12 | 住友精化株式会社 | 耐部分放電用電気絶縁樹脂組成物 |
| WO2020059689A1 (ja) * | 2018-09-20 | 2020-03-26 | 住友精化株式会社 | 電着塗料及び絶縁被膜 |
| JP2022164467A (ja) * | 2021-04-16 | 2022-10-27 | 合同会社Hide Technology | 電着塗装用塗料、電着塗装用塗料の製造方法、及び絶縁材の製造方法 |
| JP2023168150A (ja) * | 2022-05-13 | 2023-11-24 | 株式会社リグノマテリア | 電着塗装用塗料、電着塗装用塗料の製造方法及び絶縁材の製造方法 |
-
2024
- 2024-05-22 WO PCT/JP2024/018863 patent/WO2024257571A1/ja active Pending
- 2024-05-22 JP JP2025527607A patent/JPWO2024257571A1/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004515558A (ja) * | 1999-03-26 | 2004-05-27 | エー. ラポイント,デイビッド | 耐摩耗コーティング組成物、それらの製造方法及びそれにより被覆された物品 |
| JP2008137876A (ja) * | 2006-12-05 | 2008-06-19 | Catalysts & Chem Ind Co Ltd | シリカゾルおよびこれを含む塗料組成物 |
| JP2016015295A (ja) * | 2014-07-03 | 2016-01-28 | 三菱マテリアル株式会社 | 耐熱性絶縁電線とその絶縁層の形成に用いる電着液 |
| WO2017006999A1 (ja) * | 2015-07-09 | 2017-01-12 | 住友精化株式会社 | 耐部分放電用電気絶縁樹脂組成物 |
| WO2017007000A1 (ja) * | 2015-07-09 | 2017-01-12 | 住友精化株式会社 | 耐部分放電用電気絶縁樹脂組成物 |
| WO2020059689A1 (ja) * | 2018-09-20 | 2020-03-26 | 住友精化株式会社 | 電着塗料及び絶縁被膜 |
| JP2022164467A (ja) * | 2021-04-16 | 2022-10-27 | 合同会社Hide Technology | 電着塗装用塗料、電着塗装用塗料の製造方法、及び絶縁材の製造方法 |
| JP2023168150A (ja) * | 2022-05-13 | 2023-11-24 | 株式会社リグノマテリア | 電着塗装用塗料、電着塗装用塗料の製造方法及び絶縁材の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2024257571A1 (ja) | 2024-12-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2305402B1 (en) | Method for producing silver-containing powder and conductive paste using the same | |
| JP4868716B2 (ja) | フレーク銅粉及び導電性ペースト | |
| EP4116375A1 (en) | Ptfe composite powder, preparation method, and composite material containing ptfe composite powder | |
| CN100465241C (zh) | 耐局部放电性绝缘涂料、绝缘电线及它们的制造方法 | |
| JPH0140070B2 (ja) | ||
| CN112640011B (zh) | 导体与绝缘被膜的层叠体、线圈、旋转电机、绝缘涂料和绝缘膜 | |
| CN108473813A (zh) | 水分散型绝缘覆膜形成用电沉积液 | |
| JP2020029392A (ja) | 銅酸化物粒子組成物、導電性ペースト及び導電性インク | |
| JP2017095547A (ja) | 耐部分放電性塗料および絶縁電線 | |
| JP2010013312A (ja) | カーボンナノチューブ分散剤、カーボンナノチューブ分散液およびその製造方法 | |
| CN1238144C (zh) | 一种结晶铜粉的制备方法 | |
| WO2024257571A1 (ja) | 絶縁電着塗料の製造方法及び絶縁電着塗料 | |
| EP3493223A1 (en) | Insulating film | |
| TWI712560B (zh) | 矽烷處理鎂橄欖石微粒子及其製造方法、以及矽烷處理鎂橄欖石微粒子之有機溶劑分散液及其製造方法 | |
| JP2007177103A (ja) | 導電性塗料および導電性塗料の製造方法 | |
| CN110235531A (zh) | 散热电路基板 | |
| JP4131168B2 (ja) | 耐部分放電性絶縁塗料及び絶縁電線 | |
| JP4009191B2 (ja) | オルガノシリカゾル | |
| KR102635572B1 (ko) | 절연 및 방열 기능을 갖는 필름 코팅용 조성물 및 그 제조방법 | |
| CN117924858A (zh) | 一种聚四氟乙烯薄膜、聚四氟乙烯基高频覆铜板及其制备方法 | |
| CN106128543B (zh) | 一种防沉降效果好的导电银浆及其制备方法 | |
| JP2017066014A (ja) | 樹脂コート窒化ホウ素粉末及びその分散液 | |
| CN113773541B (zh) | 一种高击穿、低介损的ktn/pi复合薄膜的制备方法 | |
| CN107057466B (zh) | 一种用于纸塑基的喷墨打印用纳米银墨水 | |
| TW201946070A (zh) | 導電膜形成劑 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 24823193 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2025527607 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2025527607 Country of ref document: JP |