WO2021029199A1 - コネクタ - Google Patents
コネクタ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021029199A1 WO2021029199A1 PCT/JP2020/028468 JP2020028468W WO2021029199A1 WO 2021029199 A1 WO2021029199 A1 WO 2021029199A1 JP 2020028468 W JP2020028468 W JP 2020028468W WO 2021029199 A1 WO2021029199 A1 WO 2021029199A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- outer conductor
- male
- female
- connector
- conductor
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 285
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims description 46
- 238000002788 crimping Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910001111 Fine metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009941 weaving Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/648—Protective earth or shield arrangements on coupling devices, e.g. anti-static shielding
- H01R13/658—High frequency shielding arrangements, e.g. against EMI [Electro-Magnetic Interference] or EMP [Electro-Magnetic Pulse]
- H01R13/6591—Specific features or arrangements of connection of shield to conductive members
- H01R13/6592—Specific features or arrangements of connection of shield to conductive members the conductive member being a shielded cable
- H01R13/6593—Specific features or arrangements of connection of shield to conductive members the conductive member being a shielded cable the shield being composed of different pieces
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/648—Protective earth or shield arrangements on coupling devices, e.g. anti-static shielding
- H01R13/658—High frequency shielding arrangements, e.g. against EMI [Electro-Magnetic Interference] or EMP [Electro-Magnetic Pulse]
- H01R13/6581—Shield structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/02—Contact members
- H01R13/04—Pins or blades for co-operation with sockets
- H01R13/05—Resilient pins or blades
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/62—Means for facilitating engagement or disengagement of coupling parts or for holding them in engagement
- H01R13/629—Additional means for facilitating engagement or disengagement of coupling parts, e.g. aligning or guiding means, levers, gas pressure electrical locking indicators, manufacturing tolerances
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/64—Means for preventing incorrect coupling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/648—Protective earth or shield arrangements on coupling devices, e.g. anti-static shielding
- H01R13/658—High frequency shielding arrangements, e.g. against EMI [Electro-Magnetic Interference] or EMP [Electro-Magnetic Pulse]
- H01R13/6581—Shield structure
- H01R13/6582—Shield structure with resilient means for engaging mating connector
- H01R13/6583—Shield structure with resilient means for engaging mating connector with separate conductive resilient members between mating shield members
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R9/00—Structural associations of a plurality of mutually-insulated electrical connecting elements, e.g. terminal strips or terminal blocks; Terminals or binding posts mounted upon a base or in a case; Bases therefor
- H01R9/03—Connectors arranged to contact a plurality of the conductors of a multiconductor cable, e.g. tapping connections
- H01R9/05—Connectors arranged to contact a plurality of the conductors of a multiconductor cable, e.g. tapping connections for coaxial cables
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/40—Securing contact members in or to a base or case; Insulating of contact members
- H01R13/42—Securing in a demountable manner
- H01R13/428—Securing in a demountable manner by resilient locking means on the contact members; by locking means on resilient contact members
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/46—Bases; Cases
- H01R13/502—Bases; Cases composed of different pieces
- H01R13/506—Bases; Cases composed of different pieces assembled by snap action of the parts
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/648—Protective earth or shield arrangements on coupling devices, e.g. anti-static shielding
- H01R13/658—High frequency shielding arrangements, e.g. against EMI [Electro-Magnetic Interference] or EMP [Electro-Magnetic Pulse]
- H01R13/6591—Specific features or arrangements of connection of shield to conductive members
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R13/00—Details of coupling devices of the kinds covered by groups H01R12/70 or H01R24/00 - H01R33/00
- H01R13/648—Protective earth or shield arrangements on coupling devices, e.g. anti-static shielding
- H01R13/658—High frequency shielding arrangements, e.g. against EMI [Electro-Magnetic Interference] or EMP [Electro-Magnetic Pulse]
- H01R13/6591—Specific features or arrangements of connection of shield to conductive members
- H01R13/6592—Specific features or arrangements of connection of shield to conductive members the conductive member being a shielded cable
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R9/00—Structural associations of a plurality of mutually-insulated electrical connecting elements, e.g. terminal strips or terminal blocks; Terminals or binding posts mounted upon a base or in a case; Bases therefor
- H01R9/03—Connectors arranged to contact a plurality of the conductors of a multiconductor cable, e.g. tapping connections
- H01R9/05—Connectors arranged to contact a plurality of the conductors of a multiconductor cable, e.g. tapping connections for coaxial cables
- H01R9/0512—Connections to an additional grounding conductor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R9/00—Structural associations of a plurality of mutually-insulated electrical connecting elements, e.g. terminal strips or terminal blocks; Terminals or binding posts mounted upon a base or in a case; Bases therefor
- H01R9/03—Connectors arranged to contact a plurality of the conductors of a multiconductor cable, e.g. tapping connections
- H01R9/05—Connectors arranged to contact a plurality of the conductors of a multiconductor cable, e.g. tapping connections for coaxial cables
- H01R9/0518—Connection to outer conductor by crimping or by crimping ferrule
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to connectors.
- a shield connector described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2018-6183 is known as a shield connector connected to a terminal of a cable through which a communication signal is transmitted.
- This shield connector is a male connector, and has a male inner conductor and an outer conductor surrounding the male inner conductor via a dielectric material. Further, the male connector can be fitted with the female connector.
- the female connector has a female inner conductor and a female outer conductor that surrounds the female inner conductor via a female dielectric. When the male connector and the female connector are fitted, the outer conductor is fitted to the outside of the female side outer conductor, and the outer conductor and the female side outer conductor are connected.
- the outer conductor is configured by assembling an upper outer conductor and a lower outer conductor. For this reason, when it takes time to align the upper outer conductor and the lower outer conductor, the efficiency of the work of assembling the upper outer conductor and the lower outer conductor is lowered, and the efficiency of the connector assembling work is lowered as a whole. There is a risk.
- This specification discloses a technique for improving the efficiency of connector assembly work.
- the connector of the present disclosure is a connector connected to the end of a cable whose outer circumference is covered with a shield body, and has a first outer conductor and a second outer conductor assembled to the first outer conductor.
- the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor form a dielectric in which the inner conductor connected to the electric wire is housed.
- One of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor is formed with a positioning convex portion that protrudes toward the other, and the other of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor. Is formed with a positioning recess that engages with the positioning protrusion.
- the efficiency of the connector assembly work can be improved.
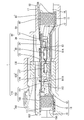
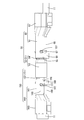
- FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing a connector device according to the first embodiment.
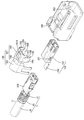
- FIG. 2 is an exploded perspective view showing a female connector.
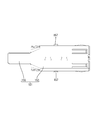
- FIG. 3 is a plan view showing the female first outer conductor.
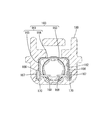
- FIG. 4 is a perspective view in which the male housing and the female housing are omitted in a state where the male connector and the female connector are fitted.
- FIG. 5 is a perspective view seen from an angle different from that of FIG. 4, and is a perspective view in which the male housing and the female housing are omitted in a state where the male connector and the female connector are fitted.
- FIG. 6 is a side view showing a state in which the male connector and the female connector are fitted.
- FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view showing a state in which the female guide groove, the female stabilizer, and the female folded portion are engaged with each other.
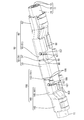
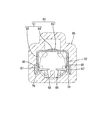
- FIG. 8 is an exploded perspective view showing a male connector.
- FIG. 9 is a plan view showing the male first outer conductor.
- FIG. 10 is a cross-sectional view showing a state in which the male guide groove, the male stabilizer, and the male folded portion are engaged with each other.
- the present disclosure is a connector in which the outer circumference of an electric wire is connected to the end of a cable covered with a shield body, and the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor assembled to the first outer conductor are described.
- the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor are dielectrics in which the inner conductor connected to the electric wire is housed.
- a positioning convex portion is formed on one of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor so as to project toward the other, and of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor.
- a positioning recess that engages with the positioning protrusion is formed.
- the efficiency of the assembling work of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor can be improved by engaging the positioning convex portion and the positioning concave portion.
- the efficiency of the connector assembly work can be improved.
- the second outer conductor is assembled to the outside of the first outer conductor, and the positioning convex portion is formed on the first outer conductor so as to project outward, and the second outer conductor is formed. It is preferable that the positioning recess is formed in the conductor, and the positioning recess is a slit extending along the assembling direction in which the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor are assembled.
- the operator sets the second outer conductor as the first outer conductor by using the positioning convex portion formed so as to project outward as a mark. Can be assembled to a conductor.
- the efficiency of the assembling work of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor can be improved, so that the efficiency of the connector assembling work can be further improved.
- the second outer conductor has a crimping piece to be crimped to the outer periphery of the first outer conductor, and the side edge of the crimping piece forms the mouth edge of the slit.
- the crimping piece can be reliably positioned, so that the assembly accuracy of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor can be improved.
- the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor are housed in the housing in an assembled state, and the second outer conductor has a stabilizer that engages with the housing. It is preferable that the side edge of the stabilizer forms the mouth edge of the slit.
- the stabilizer can be reliably positioned, so that the accuracy of assembling the housing with the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor can be improved.
- the stabilizer has a folded portion in which the tip end portion of the stabilizer is folded back, and the folded portion is inserted into a guide groove formed in the housing.
- FIGS. 1 to 10 The first embodiment in the present disclosure will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 10.
- This embodiment is mounted on, for example, a vehicle (not shown) such as an automobile, and is, for example, between an in-vehicle electrical component (car navigation system, monitor, etc.) and an external device (camera, etc.) in the vehicle, or an in-vehicle electrical component.
- An example is a connector device 1 for communication arranged in a wired communication path between the two.
- the connector device 1 includes a female connector 110 (an example of a connector) and a male connector 10 (an example of a connector) that are connected to a cable 11 and are fitted to each other.
- a female connector 110 an example of a connector
- a male connector 10 an example of a connector
- the cable 11 covers two electric wires 12 (an example of an electric wire), a shield body 15 composed of a braided body that collectively covers the outer circumference of the electric wires 12, and a further outer circumference of the shield body 15. It is configured to include a sheath portion 16 made of an insulating coating.
- the braided body is made by weaving a plurality of fibrous conductors.
- the conductor constituting the braided body may be a fine metal wire or a synthetic resin fiber having a metal bonded to the surface, and any conductor can be selected. A plurality of fine metal wires are woven into the shield body 15 according to the present embodiment.
- the sheath portion 16 and the shield body 15 are peeled off, and the two electric wires 12 exposed from the terminals of the sheath portion 16 and the shield body 15 are exposed. .. Behind the exposed electric wire 12 in the cable 11, the shield body 15 exposed from the terminal of the sheath portion 16 is folded back on the end portion of the sheath portion 16.
- a metal sleeve 17 is arranged inside the shield body 15 folded over the end of the sheath portion 16.
- the sleeve 17 is formed in a cylindrical shape.
- the female connector 110 includes a plurality of female inner conductors 120 (an example of an inner conductor) connected to two exposed electric wires 12 at the front end of the cable 11, and a plurality of females.
- a female dielectric 130 for accommodating the inner conductor 120, a female outer conductor 150 connected to the shield body 15 of the cable 11 while covering the female dielectric 130, and a female housing 180 for accommodating the female outer conductor 150 are provided. It is composed of.
- the female inner conductor 120 is formed by processing a conductive metal plate material. As shown in FIG. 1, the female inner conductor 120 includes a square tubular terminal connecting portion 122 and an electric wire connecting portion 124 connected to the rear of the terminal connecting portion 122.
- the terminal connection portion 122 is electrically connected to the male inner conductor 20 (an example of the inner conductor) of the male connector 10 described later.
- the electric wire connecting portion 124 is crimped to the front end portion of the electric wire 12 and is electrically connected to the electric wire 12.
- the female dielectric 130 is formed of an insulating synthetic resin in a rectangular parallelepiped shape that is long in the front-rear direction. Inside the female dielectric 130, two female inner conductors 120 connected to the electric wire 12 are housed side by side in the left-right direction.
- the female outer conductor 150 includes a female first outer conductor 151 (an example of the first outer conductor) and a female second outer conductor 160 (of the second outer conductor) assembled to the female first outer conductor. An example) and.
- the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 are formed by pressing a conductive metal plate material into a predetermined shape.
- the female second outer conductor 160 is assembled from above with respect to the female first outer conductor 151.
- the female first outer conductor 151 has a tubular connecting portion 152 that can be fitted with the male outer conductor 50 of the male connector 10 described later, and a female shield connected to the shield body 15 of the cable 11. It is provided with a connecting portion 156.
- the tubular connection portion 152 is formed in a square tubular shape that is long in the front-rear direction.
- the female dielectric 130 is accommodated in the tubular connection portion 152 from the rear to the inside.
- the female inner conductor 120 is housed in a state of being electrically insulated from the tubular connection 152 by the female dielectric 130, as shown in FIG. It is supposed to be done.
- female positioning convex portions 157 (an example of the positioning convex portions) projecting outward are formed on the left and right side walls of the tubular connecting portion 152.
- the female positioning convex portion 157 has a substantially cylindrical shape.
- the female shield connecting portion 156 is formed in a plate shape extending rearward from the lower lower end portion of the tubular connecting portion 152.
- the female shield connection portion 156 is arranged below the shield body 15 in the cable 11 as shown in FIG.
- the female second outer conductor 160 is formed by processing a conductive metal plate material by a press or the like. As shown in FIG. 2, the female second outer conductor 160 includes a covering portion 161 that is assembled to the outer periphery of the tubular connecting portion 152, and a female barrel 163 that is crimped to the outer periphery of the shield body 15.
- the covering portion 161 is wound around the outer peripheral surface of the outer peripheral surface of the tubular connecting portion 152.
- the covering portion 161 has an upper wall 164 and a side wall 165 extending downward from the left and right side edges of the upper wall 164.
- a female stabilizer 166 (an example of a stabilizer), a female slit 167 (an example of a positioning recess), and a female crimping piece 168 (an example of a crimping piece) are formed on the side wall 165 in order from the front to the rear. ..
- a female stabilizer 166 extending downward is formed at a position closer to the front end of the lower end of the side wall 165.
- the female stabilizer 166 is formed in a plate shape extending downward and elongated.
- the lower end of the female stabilizer 166 is a female folded portion 169 (an example of the folded portion) that is folded upward so as to overlap the outer surface of the female stabilizer 166.
- a female slit 167 extending upward from the lower end of the side wall 165 is formed behind the female stabilizer 166.
- the posterior edge of the female stabilizer 166 constitutes the anterior rim of the female slit 167.
- a female crimping piece 168 extending from the lower end of the side wall 165 is formed. As shown in FIG. 2, in the state before the female second outer conductor 160 is assembled to the female first outer conductor 151, the female crimping piece 168 extends downward from the lower end portion of the side wall.
- the female second outer conductor 160 and the female first outer conductor 151 are integrally assembled by crimping the female crimping piece 168 so as to wrap around the tubular connecting portion 152. It has become like.
- the front edge of the female crimp piece 168 constitutes the posterior rim of the female slit 167.
- the width dimension of the female slit 167 in the front-rear direction is the same as or slightly larger than the outer diameter dimension of the female positioning convex portion 157. As a result, the female positioning convex portion 157 is accommodated in the female slit 167.
- the female positioning protrusion 157 is inserted into the female slit 167, so that the female second outer conductor 160 and the female first outer conductor 160 are assembled. It is designed to be aligned with. Further, when the female crimping piece 168 is crimped to the tubular connecting portion 152, both or one of the female first outer conductor and the female second outer conductor may extend in the front-rear direction.
- the female positioning convex portion 157 and the rim of the female slit 167 come into contact with each other in the front-rear direction, so that the displacement of the female second outer conductor 160 and the female first outer conductor 151 in the front-rear direction is suppressed. It has become so.
- the female barrel 163 is electrically connected and fixed to the shield body 15 by crimping to the outer circumference of the shield body 15 folded back in the cable 11. That is, the female barrel 163 is crimp-fixed together with the female shield connecting portion 156 so as to be wound around the shield body 15 of the cable 11.
- the female housing 180 is made of synthetic resin and has an accommodating portion 182 for accommodating the female outer conductor 150 from the rear, as shown in FIG.
- the accommodating portion 182 is formed so as to penetrate in the front-rear direction.
- a lance 183 that fits into a lance hole 161A provided in the female outer conductor 150 is provided in the accommodating portion 182.
- the female outer conductor 150 When the female outer conductor 150 is accommodated in the regular accommodating position of the accommodating portion 182, the lance 183 is fitted into the lance hole 161A as shown in FIG. Therefore, the female outer conductor 150 is held in the female housing 180 by locking the lance 183 and the edge of the lance hole 161A.
- a female guide groove 170 (an example of a guide groove) is formed in the accommodating portion 182 at a position corresponding to the female folded portion 169 of the female stabilizer 166 extending in the front-rear direction.
- the inner shape of the female guide groove 170 is formed larger than the outer shape of the female stabilizer 166 including the female folded portion 169.
- the male connector 10 accommodates a plurality of male inner conductors 20 connected to two exposed electric wires 12 at the front end of the cable 11 and a plurality of male inner conductors 20. It is configured to include a male dielectric 30, a male outer conductor 50 connected to the cable 11 with the male dielectric 30 covered, and a male housing 80 accommodating the male outer conductor 50.
- the male inner conductor 20 is formed by processing a conductive metal plate material. As shown in FIG. 1, the male inner conductor 20 includes a pin-shaped male connecting portion 22, a rectangular parallelepiped box portion 23 that is long in the front-rear direction connected to the rear end portion of the male connecting portion 22, and a box portion 23. It is provided with an electric wire connecting portion 24 connected to the rear.
- the male connecting portion 22 is electrically connected to the female inner conductor 120 by entering the terminal connecting portion 122 of the female inner conductor 120 of the female connector 110 from the front.
- the electric wire connecting portion 24 is crimped to the front end portion of the electric wire 12 and is electrically connected to the electric wire 12.
- the male dielectric 30 is formed of an insulating synthetic resin in a rectangular parallelepiped shape that is long in the front-rear direction.
- male inner conductors 20 connected to the electric wire 12 are housed side by side in the left-right direction.
- the male connecting portion 22 protrudes from the front wall of the male dielectric 30.
- the male outer conductor 50 can be fitted with the female outer conductor 150 of the female connector 110.
- the male outer conductor 50 includes a male first outer conductor 51 (an example of the first outer conductor) accommodating the male dielectric 30 inside, and a shield of the male first outer conductor 51 and the cable 11. It is composed of a male second outer conductor 60 (an example of a second outer conductor) assembled to the male first outer conductor 51 so as to cover the outer periphery of the body 15.
- the male first outer conductor 51 is formed by processing a conductive metal plate material. As shown in FIGS. 8 and 9, the male first outer conductor 51 includes a rectangular tubular connecting cylinder portion 52 having a substantially rectangular front view, and a male shield provided on the lower rear end edge of the connecting tubular portion 52. It includes a connecting portion 56.
- the front portion of the connecting cylinder portion 52 is a large-diameter tubular portion 53 into which the tubular connecting portion 152 of the female outer conductor 150 of the female connector 110 fits inside. ing.
- the rear of the large-diameter tubular portion 53 is arranged coaxially with the large-diameter tubular portion 53, and is a small-diameter tubular portion 54 having a smaller diameter that is one size smaller than the large-diameter tubular portion 53.
- the small diameter tubular portion 54 is formed to have the same diameter as the tubular connecting portion 152 of the female outer conductor 150.
- the small diameter tubular portion 54 and the tubular connecting portion 152 have the same diameter when the small diameter tubular portion 54 and the tubular connecting portion 152 have the same diameter, and when the small diameter tubular portion 54 and the tubular connecting portion 152 have the same diameter. Includes cases where even if the diameters are not the same, they can be regarded as having substantially the same diameter. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 9, the connecting cylinder portion 52 is narrower from the central portion to the rear portion as a whole as compared with the front portion.
- Male positioning convex portions 57 (an example of positioning convex portions) projecting outward are formed on the left and right side walls of the small diameter tubular portion 54.
- the male positioning convex portion 57 has a substantially cylindrical shape.
- the male outer conductor 50 can be miniaturized as compared with the case where the male positioning convex portion 57 is formed on the large diameter tubular portion 53. ..
- the male dielectric 30 can be accommodated from the rear to the inside of the connecting cylinder 52.
- the rear portion of the male inner conductor 20 is electrically operated by the male dielectric 30 from the small diameter tubular portion 54.
- the male connecting portion 22 is arranged in the large-diameter tubular portion 53 in a state of protruding from the male dielectric 30 while being housed in an insulated state.
- the male shield connecting portion 56 is formed in a plate shape extending rearward from the lower lower end portion of the connecting cylinder portion 52. As shown in FIG. 1, the male shield connecting portion 56 is arranged below the shield body 15 in the cable 11.
- the male second outer conductor 60 is formed by processing a conductive metal plate material by a press or the like. As shown in FIG. 8, the male second outer conductor 60 includes a covering portion 61 assembled to the outer periphery of the small diameter tubular portion 54, and a male barrel 63 crimped to the outer periphery of the shield body 15.
- the covering portion 61 is wound around the outer peripheral surface of the small diameter tubular portion 54 so as to surround the outer peripheral surface of the small diameter tubular portion 54.
- the covering portion 61 is assembled to the outer peripheral surface of the small diameter tubular portion 54, it is formed to have the same diameter as the large diameter tubular portion 53, as shown in FIGS. 4, 5 and 6.
- the same diameter of the cover portion 61 and the large diameter cylinder portion 53 means that the cover portion 61 and the large diameter cylinder portion 53 have the same diameter, and the cover portion 61 and the large diameter cylinder portion 53 do not have the same diameter. Even in some cases, it includes cases where the diameters can be regarded as substantially the same.
- a through hole 61A into which the terminal locking portion 83 of the male housing 80, which will be described later, is fitted is formed in the upper portion of the covering portion 61 so as to penetrate the covering portion 61 in the vertical direction.
- the covering portion 61 has an upper wall 64 and a side wall 65 extending downward from the left and right side edges of the upper wall 64.
- a male stabilizer 66 (an example of a stabilizer), a male slit 67 (an example of a positioning recess), and a male crimping piece 68 (an example of a crimping piece) are formed on the side wall 65 in order from the front to the rear. ..
- a male stabilizer 66 extending downward is formed at a position closer to the front end of the lower end of the side wall 65.
- the male stabilizer 66 is formed in a plate shape extending downward and elongated.
- the lower end of the male stabilizer 66 is a male folded portion 69 (an example of the folded portion) that is folded upward so as to overlap the outer surface of the male stabilizer 66.
- a male slit 67 extending upward from the lower end of the side wall 65 is formed.
- the posterior edge of the male stabilizer 66 constitutes the anterior rim of the male slit 67.
- a male crimping piece 68 extending from the lower end of the side wall 65 is formed. As shown in FIG. 8, in the state before the male second outer conductor 60 is assembled to the male first outer conductor 51, the male crimping piece 68 extends downward from the lower end portion of the side wall.
- the male second outer conductor 60 and the male first outer conductor 51 are integrally assembled by crimping the male crimping piece 68 so as to wrap around the lower part of the small diameter tubular portion 54. It has become.
- the front edge of the male crimp piece 68 constitutes the posterior rim of the male slit 67.
- the width dimension of the male slit 67 in the front-rear direction is the same as or slightly larger than the outer diameter dimension of the male positioning convex portion 57. As a result, the male positioning convex portion 57 is accommodated in the female slit 167.
- the male positioning convex portion 57 is inserted into the male slit 67, so that the male second outer conductor 60 and the male first outer conductor 60 are assembled. It is designed to be aligned with. Further, when the male crimping piece 68 crimps to the small diameter tubular portion 54, both or one of the male first outer conductor and the male second outer conductor may extend in the front-rear direction.
- the male positioning convex portion 57 and the rim of the male slit 67 come into contact with each other in the front-rear direction, so that the displacement of the male second outer conductor 60 and the male first outer conductor 51 in the front-rear direction is suppressed. It has become so.
- the male barrel 63 is electrically connected and fixed to the shield body 15 by being crimped to the outer circumference of the shield body 15 folded back in the cable 11. That is, the male barrel 63 is connected to the shield body 15 of the cable 11 together with the male shield connecting portion 56.
- the male housing 80 is made of synthetic resin and has a housing portion 82 for accommodating the male outer conductor 50 from the rear. As shown in FIG. 1, the accommodating portion 82 is formed so as to penetrate in the front-rear direction. In the accommodating portion 82, a terminal locking portion 83 that fits into the through hole 61A provided in the covering portion 61 is provided.
- the terminal locking portion 83 is fitted into the through hole 61A as shown in FIG. Therefore, the male outer conductor 50 is held in the male housing 80 by locking the terminal locking portion 83 and the edge portion of the through hole 61A.
- a male guide groove 70 (an example of a guide groove) is formed in the accommodating portion 82 at a position corresponding to the female folded portion 169 of the female stabilizer 166 extending in the front-rear direction.
- the inner shape of the male guide groove 70 is formed larger than the outer shape of the male stabilizer 66 including the male folded portion 69.
- the male connector 10 is a male connector 10 in which the outer periphery of the electric wire 12 is connected to the end of the cable 11 covered with the shield body 15, and is the male first outer conductor 51 and the male first outer conductor 51.
- a male second outer conductor 60 to be assembled to the conductor 51, and a male first outer conductor 51 and a male second outer conductor in a state where the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 are assembled.
- the 60 covers the male dielectric 30 in which the male inner conductor 20 connected to the electric wire 12 is housed, and one of the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 is directed toward the other.
- a protruding male positioning convex portion 57 is formed, and a male slit 67 that engages with the male positioning convex portion 57 is formed on the other side of the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60.
- the female connector 110 is a female connector 110 in which the outer periphery of the electric wire 12 is connected to the end of the cable 11 covered with the shield body 15, and is the female first outer conductor 151 and the female first.
- the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 151 are provided with the female second outer conductor 160 assembled to the outer conductor 151, and the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 are assembled.
- the outer conductor 160 covers the female dielectric in which the female inner conductor connected to the electric wire 12 is housed, and one of the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 is directed toward the other.
- a protruding female positioning convex portion 157 is formed, and a female slit 167 that engages with the female positioning convex portion 157 is formed on the other side of the first outer conductor and the second outer conductor.
- the efficiency of the assembling work of the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 can be improved.
- the efficiency of the assembling work of the male connector 10 can be improved.
- the female positioning convex portion 157 and the female slit 167 it is possible to improve the efficiency of the assembling work of the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160. Thereby, the efficiency of the assembling work of the female connector 110 can be improved.
- the male second outer conductor 60 is assembled to the outside of the male first outer conductor 51, and the male positioning convex portion 57 is outside the male first outer conductor 51. It is formed so as to project in the direction, and the male second outer conductor 60 is formed with a male slit 67 extending along the assembling direction in which the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 are assembled.
- the female second outer conductor 160 is assembled to the outside of the female first outer conductor 151, and the female positioning convex portion 157 is attached to the female first outer conductor 151. It is formed so as to project outward, and the second outer conductor is formed with a female slit 167 extending along the assembling direction in which the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 are assembled.
- the operator uses the male positioning convex portion 57 formed so as to project outward as a mark, and the male number 2
- the outer conductor 60 can be assembled to the male first outer conductor 51.
- the efficiency of the assembling work of the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 can be improved, so that the efficiency of the assembling work of the male connector 10 can be further improved.
- the operator uses the female positioning convex portion 157 formed so as to project outward as a mark, and the female second outer conductor 160 Can be assembled to the female first outer conductor 151.
- the efficiency of the assembling work of the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 can be improved, so that the efficiency of the assembling work of the female connector 110 can be further improved.
- the male second outer conductor 60 has a male crimping piece 68 that crimps to the outer periphery of the male first outer conductor 51, and the side edge of the male crimping piece 68 has a male slit 67. Form the rim.
- the female second outer conductor 160 has a female crimping piece 168 crimping to the outer periphery of the female first outer conductor 151, and the side edge of the female crimping piece 168 is a female slit. Form the rim of 167
- the male crimping piece 68 can be reliably positioned, the assembly accuracy of the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 can be improved.
- the female crimping piece 168 can be reliably positioned, the accuracy of assembling the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 can be improved.
- the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 are housed in the male housing 80 in an assembled state, and the male second outer conductor is accommodated in the male housing 80.
- Reference numeral 60 denotes a male stabilizer 66 that engages with the male housing 80, and the side edges of the male stabilizer 66 form the rim of the male slit 67.
- the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 are housed in the female housing 180 in an assembled state, and the female second outer conductor 110 is accommodated in the female housing 180.
- the outer conductor 160 has a female stabilizer 166 that engages the female housing 180, and the side edges of the female stabilizer 166 form the rim of the female slit 167.
- the male stabilizer 66 can be reliably positioned, the accuracy of assembling the male housing 80 with the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 can be improved.
- the female stabilizer 166 can be reliably positioned, the accuracy of assembling the female housing 180 with the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 can be improved.
- the male stabilizer 66 has a male folded portion 69 in which the tip portion of the male stabilizer 66 is folded back, and the male folded portion 69 is a male guide groove formed in the male housing 80. It is inserted in 70.
- the female stabilizer 166 has a female folded portion 169 in which the tip portion of the female stabilizer 166 is folded back, and the female folded portion 169 is a female formed in the female housing 180. It is inserted into the guide groove 170.
- the assembly accuracy of the male housing 80 and the male first outer conductor 51 and the male second outer conductor 60 can be further improved.
- the engagement allowance between the female stabilizer 166 and the female housing 180 can be increased, the assembly accuracy of the female housing 180 and the female first outer conductor 151 and the female second outer conductor 160 can be further improved. Can be done.
- the male connector 10 is connected to a cable 11 having two electric wires 12.
- the cable 11 may include one electric wire 12 or three or more electric wires 12.
- Connector device 10 Male connector 11: Cable 12: Electric wire 15: Shield body 16: Sheath 17: Sleeve 20: Male inner conductor 22: Male connection 23: Box 24: Electric wire connection 30: Male dielectric 50: Male outer conductor 51: Male first outer conductor 52: Connection cylinder 53: Large diameter cylinder 54: Small diameter cylinder 56: Male shield connection 57: Male positioning convex 60: Male second outer conductor 61: Cover Part 61A: Through hole 63: Male barrel 64: Upper wall 65: Side wall 66: Male stabilizer 67: Male slit 68: Male crimping piece 69: Male folding part 70: Male guide groove 80: Male housing 82: Accommodating part 83: Terminal Locking part 110: Female connector 120: Female inner conductor 122: Terminal connection part 124: Electric wire connection part 130: Female dielectric 150: Female outer conductor 151: Female first outer conductor 152: Cylindrical connection part 156: Female shield connection Part 157: Female positioning convex part 160: Female second outer conductor 161:
Landscapes
- Details Of Connecting Devices For Male And Female Coupling (AREA)
Abstract
雄コネクタ10は、電線12の外周がシールド体15で覆われたケーブル11の端部に接続される雄コネクタ10であって、雄第1外導体51と、雄第1外導体51に組み付けられる雄第2外導体60と、を有し、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60とが組み付けられた状態で、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60が、電線12に接続された雄内導体20が収容される雄誘電体30を覆うようになっており、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60の一方には他方に向かって突出する雄位置決め凸部57が形成されており、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60の他方には雄位置決め凸部57と係合する雄スリット67が形成されている。
Description
本開示は、コネクタに関する。
例えば、通信用の信号が伝送されるケーブルの端末に接続されたシールドコネクタとして、特開2018-6183号公報(下記特許文献1)に記載のものが知られている。このシールドコネクタは、雄コネクタとされており、雄型内導体と、誘電体を介して雄型内導体を囲む外導体とを有している。また、雄コネクタは、雌コネクタと嵌合可能とされている。雌コネクタは、雌型内導体と、雌型誘電体を介して雌側内導体を囲む雌側外導体を有している。雄コネクタと雌コネクタとが嵌合する際には、外導体が雌側外導体の外側に嵌合され、外導体と雌側外導体とが接続される。
特開2018-6183号公報にかかる技術においては、外導体は、上側外導体と下側外導体とが組み付けられて構成されている。このため、上側外導体と下側外導体との位置合わせに手間取る場合には、上側外導体と下側外導体とを組み付ける作業の効率が低下し、全体としてコネクタの組み付け作業の効率が低下するおそれがある。
本明細書では、コネクタの組み付け作業の効率を向上させる技術を開示する。
本開示のコネクタは、電線の外周がシールド体で覆われたケーブルの端部に接続されるコネクタであって、第1外導体と、前記第1外導体に組み付けられる第2外導体と、を有し、前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とが組み付けられた状態で、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体が、前記電線に接続された内導体が収容される誘電体を覆うようになっており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の一方には他方に向かって突出する位置決め凸部が形成されており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の他方には前記位置決め凸部と係合する位置決め凹部が形成されている。
本開示によれば、コネクタの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。
[本開示の実施形態の説明]
最初に本開示の実施形態を列挙して説明する。
(1)本開示は、電線の外周がシールド体で覆われたケーブルの端部に接続されるコネクタであって、第1外導体と、前記第1外導体に組み付けられる第2外導体と、を有し、前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とが組み付けられた状態で、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体が、前記電線に接続された内導体が収容される誘電体を覆うようになっており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の一方には他方に向かって突出する位置決め凸部が形成されており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の他方には前記位置決め凸部と係合する位置決め凹部が形成されている。
最初に本開示の実施形態を列挙して説明する。
(1)本開示は、電線の外周がシールド体で覆われたケーブルの端部に接続されるコネクタであって、第1外導体と、前記第1外導体に組み付けられる第2外導体と、を有し、前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とが組み付けられた状態で、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体が、前記電線に接続された内導体が収容される誘電体を覆うようになっており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の一方には他方に向かって突出する位置決め凸部が形成されており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の他方には前記位置決め凸部と係合する位置決め凹部が形成されている。
上記の構成によれば、位置決め凸部と位置決め凹部とを係合させることにより、第1外導体と第2外導体のとの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。これにより、コネクタの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。
(2)前記第1外導体の外側に前記第2外導体が組み付けられるようになっており、前記第1外導体に前記位置決め凸部が外方に突出して形成されており、前記第2外導体に前記位置決め凹部が形成されており、前記位置決め凹部は、前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とを組み付ける組み付け方向に沿って延びるスリットであることが好ましい。
上記の構成によれば、第1外導体と第2外導体との組み付け作業において、作業者は、外方に突出して形成された位置決め凸部を目印にして、第2外導体を第1外導体に組み付けることができる。これにより、第1外導体と第2外導体のとの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができるので、コネクタの組み付け作業の効率をさらに向上させることができる。
(3)前記第2外導体は、前記第1外導体の外周に圧着する圧着片を有し、前記圧着片の側縁が前記スリットの口縁を形成することが好ましい。
上記の構成によれば、圧着片の位置決めを確実に行うことができるので、第1外導体と第2外導体との組み付け精度を向上させることができる。
(4)前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とが組み付けられた状態でハウジング内に収容されるようになっており、前記第2外導体は前記ハウジングと係合するスタビライザを有し、前記スタビライザの側縁が前記スリットの口縁を形成することが好ましい。
上記の構成によれば、スタビライザの位置決めを確実に行うことができるので、ハウジングと、第1外導体および第2外導体との組み付け精度を向上させることができる。
(5)前記スタビライザは、前記スタビライザの先端部が折り返された折り返し部を有し、前記折り返し部が、前記ハウジングに形成されたガイド溝に挿入されることが好ましい。
スタビライザとハウジングとの係合代を大きくすることができるので、ハウジングと、第1外導体および第2外導体との組み付け精度をさらに向上させることができる。
[本開示の実施形態の詳細]
本開示のコネクタの具体例を、以下の図面を参照しつつ説明する。なお、本開示は、これらの例示に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
本開示のコネクタの具体例を、以下の図面を参照しつつ説明する。なお、本開示は、これらの例示に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
<実施形態1>
本開示における実施形態1について図1から図10を参照して説明する。本実施形態は、例えば、自動車等の車両(図示せず)に搭載され、例えば車両内における車載電装品(カーナビゲーションシステム、モニタ等)と外部機器(カメラ等)との間や、車載電装品間の有線の通信経路に配される通信用のコネクタ装置1を例示している。
本開示における実施形態1について図1から図10を参照して説明する。本実施形態は、例えば、自動車等の車両(図示せず)に搭載され、例えば車両内における車載電装品(カーナビゲーションシステム、モニタ等)と外部機器(カメラ等)との間や、車載電装品間の有線の通信経路に配される通信用のコネクタ装置1を例示している。
[コネクタ装置1]
コネクタ装置1は、図1に示されるように、ケーブル11に接続された状態で互いに嵌合する雌コネクタ110(コネクタの一例)と雄コネクタ10(コネクタの一例)とを備えている。以下の説明においては、上下方向とは図1における上下方向を基準とし、前後方向については雌コネクタ110と雄コネクタ10の嵌合方向を基準として互いに嵌合する側を前側として説明する。
コネクタ装置1は、図1に示されるように、ケーブル11に接続された状態で互いに嵌合する雌コネクタ110(コネクタの一例)と雄コネクタ10(コネクタの一例)とを備えている。以下の説明においては、上下方向とは図1における上下方向を基準とし、前後方向については雌コネクタ110と雄コネクタ10の嵌合方向を基準として互いに嵌合する側を前側として説明する。
[ケーブル11]
ケーブル11は、図2に示されるように、2本の電線12(電線の一例)と、電線12の外周を一括して覆う編組体からなるシールド体15と、シールド体15のさらに外周を覆う絶縁性の被覆からなるシース部16とを備えて構成されている。編組体は、繊維状をなす複数の導体を編み込んでなる。編組体を構成する導体は、金属細線でもよく、合成樹脂製の繊維の表面に金属が貼着されたものでもよく、任意の導体を選択できる。本実施形態にかかるシールド体15は複数の金属細線が編み込まれてなる。
ケーブル11は、図2に示されるように、2本の電線12(電線の一例)と、電線12の外周を一括して覆う編組体からなるシールド体15と、シールド体15のさらに外周を覆う絶縁性の被覆からなるシース部16とを備えて構成されている。編組体は、繊維状をなす複数の導体を編み込んでなる。編組体を構成する導体は、金属細線でもよく、合成樹脂製の繊維の表面に金属が貼着されたものでもよく、任意の導体を選択できる。本実施形態にかかるシールド体15は複数の金属細線が編み込まれてなる。
図2に示されるように、ケーブル11の前端部では、シース部16およびシールド体15が皮剥ぎされて、シース部16およびシールド体15の端末から露出した2本の電線12が露出している。ケーブル11における露出した電線12の後方では、シース部16の端末から露出したシールド体15が、シース部16の端部上に折り返されている。
シース部16の端部上に折り返されたシールド体15の内側には、金属製のスリーブ17が配置されている。スリーブ17は円筒状に形成されている。
[雌コネクタ110]
雌コネクタ110は、図1および図2に示されるように、ケーブル11の前端部において露出した2本の電線12に接続される複数の雌内導体120(内導体の一例)と、複数の雌内導体120を収容する雌誘電体130と、雌誘電体130を覆った状態でケーブル11のシールド体15に接続される雌外導体150と、雌外導体150を収容する雌ハウジング180とを備えて構成されている。
雌コネクタ110は、図1および図2に示されるように、ケーブル11の前端部において露出した2本の電線12に接続される複数の雌内導体120(内導体の一例)と、複数の雌内導体120を収容する雌誘電体130と、雌誘電体130を覆った状態でケーブル11のシールド体15に接続される雌外導体150と、雌外導体150を収容する雌ハウジング180とを備えて構成されている。
[雌内導体120]
雌内導体120は、導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。雌内導体120は、図1に示されるように、角筒状の端子接続部122と、端子接続部122の後方に連なる電線接続部124とを備えている。
雌内導体120は、導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。雌内導体120は、図1に示されるように、角筒状の端子接続部122と、端子接続部122の後方に連なる電線接続部124とを備えている。
端子接続部122は、後述する雄コネクタ10の雄内導体20(内導体の一例)と電気的に接続される。電線接続部124は、電線12の前端部に圧着されて電線12に電気的に接続されている。
[雌誘電体130]
雌誘電体130は、図2に示されるように、絶縁性の合成樹脂によって前後方向に長い直方体状に形成されている。雌誘電体130の内部には、電線12に接続された2つの雌内導体120が左右方向に並んだ状態で収容されている。
雌誘電体130は、図2に示されるように、絶縁性の合成樹脂によって前後方向に長い直方体状に形成されている。雌誘電体130の内部には、電線12に接続された2つの雌内導体120が左右方向に並んだ状態で収容されている。
[雌外導体150]
図2に示されるように、雌外導体150は、雌第1外導体151(第1外導体の一例)と、雌第1外導体に組み付けられる雌第2外導体160(第2外導体の一例)とを有する。雌第1外導体151、および雌第2外導体160は、導電性を有する金属板材が所定の形状にプレス加工されてなる。雌第2外導体160は、雌第1外導体151に対して、上方から組み付けられるようになっている。
図2に示されるように、雌外導体150は、雌第1外導体151(第1外導体の一例)と、雌第1外導体に組み付けられる雌第2外導体160(第2外導体の一例)とを有する。雌第1外導体151、および雌第2外導体160は、導電性を有する金属板材が所定の形状にプレス加工されてなる。雌第2外導体160は、雌第1外導体151に対して、上方から組み付けられるようになっている。
雌第1外導体151は、図3に示されるように、後述する雄コネクタ10の雄外導体50と嵌合可能な筒状接続部152と、ケーブル11のシールド体15に接続される雌シールド接続部156とを備えている。
筒状接続部152は、前後方向に長い角筒状に形成されている。筒状接続部152には、雌誘電体130が後方から内部に収容可能とされている。筒状接続部152内に雌誘電体130が収容されると、図1に示されるように、雌内導体120が雌誘電体130によって筒状接続部152から電気的に絶縁された状態で収容されるようになっている。
図3に示されるように、筒状接続部152の左右両側壁には、外方に突出する雌位置決め凸部157(位置決め凸部の一例)が形成されている。雌位置決め凸部157は略円筒形状をなしている。
雌シールド接続部156は、筒状接続部152の下側下端部から後方に向かって延びる板状に形成されている。雌シールド接続部156は、図1に示されるように、ケーブル11におけるシールド体15の下方に配置される。
[雌第2外導体160]
雌第2外導体160は、導電性を有する金属板材をプレスなどによって加工することによって形成されている。雌第2外導体160は、図2に示されるように、筒状接続部152の外周に組み付けられる覆い部161と、シールド体15の外周に圧着される雌バレル163と、を備えている。
雌第2外導体160は、導電性を有する金属板材をプレスなどによって加工することによって形成されている。雌第2外導体160は、図2に示されるように、筒状接続部152の外周に組み付けられる覆い部161と、シールド体15の外周に圧着される雌バレル163と、を備えている。
図4、図5、および図6に示されるように、覆い部161は、筒状接続部152の外周面の外周面に巻き付けられるようになっている。覆い部161は、上壁164と、上壁164の左右両側縁から下方に延びる側壁165と、を有する。側壁165には、前から後へ向けて順に、雌スタビライザ166(スタビライザの一例)と、雌スリット167(位置決め凹部の一例)と、雌圧着片168(圧着片の一例)とが形成されている。
側壁165の下端部のうち前端部寄りの位置には、下方に延びる雌スタビライザ166が形成されている。雌スタビライザ166は、下方に細長く延びる板状に形成されている。雌スタビライザ166の下端部は、雌スタビライザ166の外面に重なるように、上方に折り返された雌折り返し部169(折り返し部の一例)とされる。
雌スタビライザ166の後方には、側壁165の下端部から上方に延びる雌スリット167が形成されている。雌スタビライザ166の後側縁は、雌スリット167の前側の口縁を構成している。
雌スリット167の後方には、側壁165の下端部から延びる雌圧着片168が形成されている。図2に示されるように、雌第2外導体160が雌第1外導体151に組み付けられる前の状態においては、雌圧着片168は、側壁の下端部から下方に延びている。
図5に示されるように、雌圧着片168が、筒状接続部152の下方に巻き付くように圧着することにより、雌第2外導体160と雌第1外導体151とが一体に組み付けられるようになっている。雌圧着片168の前側縁は、雌スリット167の後側の口縁を構成している。
雌スリット167の前後方向の幅寸法は、雌位置決め凸部157の外径寸法と同じか、やや大きく形成されている。これにより、雌位置決め凸部157は雌スリット167内に収容されるようになっている。
雌第2外導体160が雌第1外導体151の上方から組み付けられる際に、雌位置決め凸部157が雌スリット167内に挿入されることにより、雌第2外導体160と雌第1外導体との位置合わせが行われるようになっている。また、雌圧着片168が筒状接続部152に圧着する際に、雌第1外導体および雌第2外導体の双方または一方が前後方向に延びる場合がある。このとき、雌位置決め凸部157と、雌スリット167の口縁とが前後方向について接触することにより、雌第2外導体160と雌第1外導体151の、前後方向についての位置ずれが抑制されるようになっている。
雌バレル163は、図1に示されるように、ケーブル11において折り返されたシールド体15の外周に圧着することによりシールド体15に電気的に接続固定される。つまり、雌バレル163は、雌シールド接続部156と共に、ケーブル11のシールド体15に巻き付くように圧着固定される。
[雌ハウジング180]
雌ハウジング180は、合成樹脂製であって、図1に示されるように、雌外導体150を後方から収容する収容部182を有している。収容部182は、前後方向に貫通して形成されている。収容部182内には、雌外導体150に設けられたランス孔161Aに嵌まり込むランス183が設けられている。
雌ハウジング180は、合成樹脂製であって、図1に示されるように、雌外導体150を後方から収容する収容部182を有している。収容部182は、前後方向に貫通して形成されている。収容部182内には、雌外導体150に設けられたランス孔161Aに嵌まり込むランス183が設けられている。
ランス183は、雌外導体150が収容部182の正規収容位置に収容されると、図1に示されるように、ランス孔161Aに嵌まり込む。したがって、ランス183とランス孔161Aの縁部とが係止することによって雌外導体150が雌ハウジング180内に保持されている。
図7に示されるように、収容部182には、雌スタビライザ166の雌折り返し部169に対応する位置に、雌ガイド溝170(ガイド溝の一例)が前後方向に延びて形成されている。雌ガイド溝170の内形状は、雌折り返し部169を含む雌スタビライザ166の外形状よりも大きく形成されている。雌折り返し部169が雌ガイド溝170の内面と接触することにより、雌ハウジング180と、雌外導体150との相対的な位置決めがなされるようになっている。
[雄コネクタ10]
雄コネクタ10は、図1および図8に示されるように、ケーブル11の前端部において露出した2本の電線12に接続される複数の雄内導体20と、複数の雄内導体20を収容する雄誘電体30と、雄誘電体30を覆った状態でケーブル11に接続される雄外導体50と、雄外導体50を収容する雄ハウジング80とを備えて構成されている。
雄コネクタ10は、図1および図8に示されるように、ケーブル11の前端部において露出した2本の電線12に接続される複数の雄内導体20と、複数の雄内導体20を収容する雄誘電体30と、雄誘電体30を覆った状態でケーブル11に接続される雄外導体50と、雄外導体50を収容する雄ハウジング80とを備えて構成されている。
[雄内導体20]
雄内導体20は、導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。雄内導体20は、図1に示されるように、ピン型の雄型接続部22と、雄型接続部22の後端部に連なる前後に長い直方体型の箱部23と、箱部23の後方に連なる電線接続部24とを備えている。
雄内導体20は、導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。雄内導体20は、図1に示されるように、ピン型の雄型接続部22と、雄型接続部22の後端部に連なる前後に長い直方体型の箱部23と、箱部23の後方に連なる電線接続部24とを備えている。
雄型接続部22は、図1に示されるように、雌コネクタ110の雌内導体120における端子接続部122内に前方から進入することにより雌内導体120と電気的に接続される。電線接続部24は、電線12の前端部に圧着されて電線12に電気的に接続されている。
[雄誘電体30]
雄誘電体30は、図8に示されるように、絶縁性の合成樹脂によって前後方向に長い直方体状に形成されている。
雄誘電体30は、図8に示されるように、絶縁性の合成樹脂によって前後方向に長い直方体状に形成されている。
雄誘電体30の内部には、電線12に接続された2つの雄内導体20が左右方向に並んだ状態で収容されている。雄誘電体30内に雄内導体20が収容されると、雄誘電体30の前壁から雄型接続部22が突出した状態となる。
[雄外導体50]
図1に示されるように、雄外導体50は、雌コネクタ110の雌外導体150と嵌合可能とされている。雄外導体50は、図8に示されるように、雄誘電体30を内部に収容する雄第1外導体51(第1外導体の一例)と、雄第1外導体51およびケーブル11のシールド体15の外周を覆うように雄第1外導体51に組み付けられる雄第2外導体60(第2外導体の一例)とによって構成されている。
図1に示されるように、雄外導体50は、雌コネクタ110の雌外導体150と嵌合可能とされている。雄外導体50は、図8に示されるように、雄誘電体30を内部に収容する雄第1外導体51(第1外導体の一例)と、雄第1外導体51およびケーブル11のシールド体15の外周を覆うように雄第1外導体51に組み付けられる雄第2外導体60(第2外導体の一例)とによって構成されている。
[雄第1外導体51]
雄第1外導体51は、導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。雄第1外導体51は、図8および図9に示されるように、正面視略矩形の角筒型の接続筒部52と、接続筒部52の下側後端縁に設けられた雄シールド接続部56とを備えている。
雄第1外導体51は、導電性を有する金属板材を加工することによって形成されている。雄第1外導体51は、図8および図9に示されるように、正面視略矩形の角筒型の接続筒部52と、接続筒部52の下側後端縁に設けられた雄シールド接続部56とを備えている。
接続筒部52の前部は、図4、図5および図6に示されるように、雌コネクタ110の雌外導体150における筒状接続部152が内部に嵌合する大径筒部53とされている。大径筒部53の後方は、大径筒部53と同軸に配置されると共に、大径筒部53よりも一回り小さい小径の小径筒部54とされている。
小径筒部54は、図4、図5および図6に示されるように、雌外導体150の筒状接続部152と同径に形成されている。ここで、小径筒部54と筒状接続部152とが同径とは、小径筒部54と筒状接続部152とが同一径である場合と、小径筒部54と筒状接続部152とが同一径でない場合でも実質的に同一径と見なしうる場合を含んでいる。したがって、接続筒部52は、図9に示されるように、中央部から後部が前部に比べて全体的に細くなっている。小径筒部54の左右両側壁には外方に突出する雄位置決め凸部57(位置決め凸部の一例)が形成されている。雄位置決め凸部57はほぼ円筒形状をなしている。
雄位置決め凸部57が小径筒部54に形成されていることにより、雄位置決め凸部57が大径筒部53に形成されている場合に比べて、雄外導体50を小型化することができる。
接続筒部52内には、雄誘電体30が後方から内部に収容可能とされている。接続筒部52内に雄誘電体30が後方から収容されると、図1に示されるように、雄内導体20の箱部23よりも後部が雄誘電体30によって小径筒部54から電気的に絶縁された状態で収容される共に、雄型接続部22が雄誘電体30から突出した状態で大径筒部53内に配置される。
雄シールド接続部56は、接続筒部52の下側下端部から後方に向かって延びる板状に形成されている。雄シールド接続部56は、図1に示されるように、ケーブル11におけるシールド体15の下方に配置される。
[雄第2外導体60]
雄第2外導体60は、導電性を有する金属板材をプレスなどによって加工することによって形成されている。雄第2外導体60は、図8に示されるように、小径筒部54の外周に組み付けられる覆い部61と、シールド体15の外周に圧着される雄バレル63と、を備えている。
雄第2外導体60は、導電性を有する金属板材をプレスなどによって加工することによって形成されている。雄第2外導体60は、図8に示されるように、小径筒部54の外周に組み付けられる覆い部61と、シールド体15の外周に圧着される雄バレル63と、を備えている。
覆い部61は、小径筒部54の外周面を囲うように小径筒部54の外周面に巻き付けられている。覆い部61は、小径筒部54の外周面に組み付けられると、図4、図5および図6に示されるように、大径筒部53と同径の大きさに形成される。ここで、覆い部61と大径筒部53とが同径とは、覆い部61と大径筒部53とが同一径の場合と、覆い部61と大径筒部53とが同一径でない場合でも実質的に同一径と見なしうる場合を含んでいる。覆い部61の上部には、後述する雄ハウジング80の端子係止部83が嵌まり込む貫通孔61Aが覆い部61を上下方向に貫通して形成されている。
図4、図5および図6に示されるように、覆い部61は、上壁64と、上壁64の左右両側縁から下方に延びる側壁65と、を有する。側壁65には、前から後へ向けて順に、雄スタビライザ66(スタビライザの一例)と、雄スリット67(位置決め凹部の一例)と、雄圧着片68(圧着片の一例)とが形成されている。
側壁65の下端部のうち前端部寄りの位置には、下方に延びる雄スタビライザ66が形成されている。雄スタビライザ66は、下方に細長く延びる板状に形成されている。雄スタビライザ66の下端部は、雄スタビライザ66の外面に重なるように、上方に折り返された雄折り返し部69(折り返し部の一例)とされる。
雄スタビライザ66の後方には、側壁65の下端部から上方に延びる雄スリット67が形成されている。雄スタビライザ66の後側縁は、雄スリット67の前側の口縁を構成している。
雄スリット67の後方には、側壁65の下端部から延びる雄圧着片68が形成されている。図8に示されるように、雄第2外導体60が雄第1外導体51に組み付けられる前の状態においては、雄圧着片68は、側壁の下端部から下方に延びている。
図5に示されるように、雄圧着片68が、小径筒部54の下方に巻き付くように圧着することにより、雄第2外導体60と雄第1外導体51とが一体に組み付けられるようになっている。雄圧着片68の前側縁は、雄スリット67の後側の口縁を構成している。
雄スリット67の前後方向の幅寸法は、雄位置決め凸部57の外径寸法と同じか、やや大きく形成されている。これにより、雄位置決め凸部57は雌スリット167内に収容されるようになっている。
雄第2外導体60が雄第1外導体51の上方から組み付けられる際に、雄位置決め凸部57が雄スリット67内に挿入されることにより、雄第2外導体60と雄第1外導体との位置合わせが行われるようになっている。また、雄圧着片68が小径筒部54に圧着する際に、雄第1外導体および雄第2外導体の双方または一方が前後方向に延びる場合がある。このとき、雄位置決め凸部57と、雄スリット67の口縁とが前後方向について接触することにより、雄第2外導体60と雄第1外導体51の、前後方向についての位置ずれが抑制されるようになっている。
雄バレル63は、図1に示されるように、ケーブル11において折り返されたシールド体15の外周に圧着されることによりシールド体15に電気的に接続固定される。つまり、雄バレル63は、雄シールド接続部56と共に、ケーブル11のシールド体15に接続される。
[雄ハウジング80]
雄ハウジング80は、合成樹脂製であって、雄外導体50を後方から収容する収容部82を有している。収容部82は、図1に示されるように、前後方向に貫通して形成されている。収容部82内には、覆い部61に設けられた貫通孔61Aに嵌まり込む端子係止部83が設けられている。
雄ハウジング80は、合成樹脂製であって、雄外導体50を後方から収容する収容部82を有している。収容部82は、図1に示されるように、前後方向に貫通して形成されている。収容部82内には、覆い部61に設けられた貫通孔61Aに嵌まり込む端子係止部83が設けられている。
端子係止部83は、雄外導体50が収容部82の正規収容位置に収容されると、図1に示されるように、貫通孔61Aに嵌まり込む。したがって、端子係止部83と貫通孔61Aの縁部とが係止することによって雄外導体50が雄ハウジング80内に保持されている。
図10に示されるように、収容部82には、雌スタビライザ166の雌折り返し部169に対応する位置に、雄ガイド溝70(ガイド溝の一例)が前後方向に延びて形成されている。雄ガイド溝70の内形状は、雄折り返し部69を含む雄スタビライザ66の外形状よりも大きく形成されている。雄折り返し部69が雄ガイド溝70の内面と接触することにより、雄ハウジング80と、雄外導体50との相対的な位置決めがなされるようになっている。
[本実施形態の作用効果]
続いて、本実施形態の作用効果について説明する。本明細書に開示された技術は、コネクタ装置1を構成する雄コネクタ10と、雌コネクタ110とに適用されている。
続いて、本実施形態の作用効果について説明する。本明細書に開示された技術は、コネクタ装置1を構成する雄コネクタ10と、雌コネクタ110とに適用されている。
本実施形態にかかる雄コネクタ10は、電線12の外周がシールド体15で覆われたケーブル11の端部に接続される雄コネクタ10であって、雄第1外導体51と、雄第1外導体51に組み付けられる雄第2外導体60と、を有し、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60とが組み付けられた状態で、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60が、電線12に接続された雄内導体20が収容される雄誘電体30を覆うようになっており、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60の一方には他方に向かって突出する雄位置決め凸部57が形成されており、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60の他方には雄位置決め凸部57と係合する雄スリット67が形成されている。
また、本実施形態にかかる雌コネクタ110は、電線12の外周がシールド体15で覆われたケーブル11の端部に接続される雌コネクタ110であって、雌第1外導体151と、雌第1外導体151に組み付けられる雌第2外導体160と、を有し、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160とが組み付けられた状態で、雌第1外導体151および雌第2外導体160が、電線12に接続された雌内導体が収容される雌誘電体を覆うようになっており、雌第1外導体151および雌第2外導体160の一方には他方に向かって突出する雌位置決め凸部157が形成されており、第1外導体および第2外導体の他方には雌位置決め凸部157と係合する雌スリット167が形成されている。
上記の構成によれば、雄位置決め凸部57と雄スリット67とを係合させることにより、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60との組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。これにより、雄コネクタ10の組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。同様に、雌位置決め凸部157と雌スリット167を係合させることにより、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160のとの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。これにより、雌コネクタ110の組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができる。
本実施形態にかかる雄コネクタ10においては、雄第1外導体51の外側に雄第2外導体60が組み付けられるようになっており、雄第1外導体51には雄位置決め凸部57が外方に突出して形成されており、雄第2外導体60には雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60とを組み付ける組み付け方向に沿って延びる雄スリット67が形成されている。
また、本実施形態にかかる雌コネクタ110においては、雌第1外導体151の外側に雌第2外導体160が組み付けられるようになっており、雌第1外導体151に雌位置決め凸部157が外方に突出して形成されており、第2外導体には、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160とを組み付ける組み付け方向に沿って延びる雌スリット167が形成されている。
上記の構成によれば、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60との組み付け作業において、作業者は、外方に突出して形成された雄位置決め凸部57を目印にして、雄第2外導体60を雄第1外導体51に組み付けることができる。これにより、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60のとの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができるので、雄コネクタ10の組み付け作業の効率をさらに向上させることができる。同様に、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160との組み付け作業において、作業者は、外方に突出して形成された雌位置決め凸部157を目印にして、雌第2外導体160を雌第1外導体151に組み付けることができる。これにより、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160のとの組み付け作業の効率を向上させることができるので、雌コネクタ110の組み付け作業の効率をさらに向上させることができる。
本実施形態にかかる雄コネクタ10においては、雄第2外導体60は、雄第1外導体51の外周に圧着する雄圧着片68を有し、雄圧着片68の側縁が雄スリット67の口縁を形成する。
また、本実施形態にかかる雌コネクタ110においては、雌第2外導体160は、雌第1外導体151の外周に圧着する雌圧着片168を有し、雌圧着片168の側縁が雌スリット167の口縁を形成する
上記の構成によれば、雄圧着片68の位置決めを確実に行うことができるので、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60との組み付け精度を向上させることができる。同様に、雌圧着片168の位置決めを確実に行うことができるので、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160との組み付け精度を向上させることができる。
本実施形態にかかる雄コネクタ10においては、雄第1外導体51と雄第2外導体60とが組み付けられた状態で雄ハウジング80内に収容されるようになっており、雄第2外導体60は雄ハウジング80と係合する雄スタビライザ66を有し、雄スタビライザ66の側縁が雄スリット67の口縁を形成する。
また、本実施形態にかかる雌コネクタ110においては、雌第1外導体151と雌第2外導体160とが組み付けられた状態で雌ハウジング180内に収容されるようになっており、雌第2外導体160は雌ハウジング180と係合する雌スタビライザ166を有し、雌スタビライザ166の側縁が雌スリット167の口縁を形成する。
上記の構成によれば、雄スタビライザ66の位置決めを確実に行うことができるので、雄ハウジング80と、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60との組み付け精度を向上させることができる。同様に、雌スタビライザ166の位置決めを確実に行うことができるので、雌ハウジング180と、雌第1外導体151および雌第2外導体160との組み付け精度を向上させることができる。
本実施形態にかかる雄コネクタ10においては、雄スタビライザ66は、雄スタビライザ66の先端部が折り返された雄折り返し部69を有し、雄折り返し部69が、雄ハウジング80に形成された雄ガイド溝70に挿入される。
また、本実施形態に係る雌コネクタ110においては、雌スタビライザ166は、雌スタビライザ166の先端部が折り返された雌折り返し部169を有し、雌折り返し部169が、雌ハウジング180に形成された雌ガイド溝170に挿入される。
雄スタビライザ66と雄ハウジング80との係合代を大きくすることができるので、雄ハウジング80と、雄第1外導体51および雄第2外導体60との組み付け精度をさらに向上させることができる。同様に、雌スタビライザ166と雌ハウジング180との係合代を大きくすることができるので、雌ハウジング180と、雌第1外導体151および雌第2外導体160との組み付け精度をさらに向上させることができる。
<他の実施形態>
(1)上記実施形態では、雄コネクタ10は、2本の電線12を有するケーブル11に接続される構成とした。しかしながら、これに限らず、1本の電線12、または3本以上の電線12がケーブル11に含まれる構成としてもよい。
(1)上記実施形態では、雄コネクタ10は、2本の電線12を有するケーブル11に接続される構成とした。しかしながら、これに限らず、1本の電線12、または3本以上の電線12がケーブル11に含まれる構成としてもよい。
1: コネクタ装置
10: 雄コネクタ
11: ケーブル
12: 電線
15: シールド体
16: シース部
17: スリーブ
20: 雄内導体
22: 雄型接続部
23: 箱部
24: 電線接続部
30: 雄誘電体
50: 雄外導体
51: 雄第1外導体
52: 接続筒部
53: 大径筒部
54: 小径筒部
56: 雄シールド接続部
57: 雄位置決め凸部
60: 雄第2外導体
61: 覆い部
61A: 貫通孔
63: 雄バレル
64: 上壁
65: 側壁
66: 雄スタビライザ
67: 雄スリット
68: 雄圧着片
69: 雄折り返し部
70: 雄ガイド溝
80: 雄ハウジング
82: 収容部
83: 端子係止部
110: 雌コネクタ
120: 雌内導体
122: 端子接続部
124: 電線接続部
130: 雌誘電体
150: 雌外導体
151: 雌第1外導体
152: 筒状接続部
156: 雌シールド接続部
157: 雌位置決め凸部
160: 雌第2外導体
161: 覆い部
161A: ランス孔
163: 雌バレル
164: 上壁
165: 側壁
166: 雌スタビライザ
167: 雌スリット
168: 雌圧着片
169: 雌折り返し部
170: 雌ガイド溝
180: 雌ハウジング
182: 収容部
183: ランス
10: 雄コネクタ
11: ケーブル
12: 電線
15: シールド体
16: シース部
17: スリーブ
20: 雄内導体
22: 雄型接続部
23: 箱部
24: 電線接続部
30: 雄誘電体
50: 雄外導体
51: 雄第1外導体
52: 接続筒部
53: 大径筒部
54: 小径筒部
56: 雄シールド接続部
57: 雄位置決め凸部
60: 雄第2外導体
61: 覆い部
61A: 貫通孔
63: 雄バレル
64: 上壁
65: 側壁
66: 雄スタビライザ
67: 雄スリット
68: 雄圧着片
69: 雄折り返し部
70: 雄ガイド溝
80: 雄ハウジング
82: 収容部
83: 端子係止部
110: 雌コネクタ
120: 雌内導体
122: 端子接続部
124: 電線接続部
130: 雌誘電体
150: 雌外導体
151: 雌第1外導体
152: 筒状接続部
156: 雌シールド接続部
157: 雌位置決め凸部
160: 雌第2外導体
161: 覆い部
161A: ランス孔
163: 雌バレル
164: 上壁
165: 側壁
166: 雌スタビライザ
167: 雌スリット
168: 雌圧着片
169: 雌折り返し部
170: 雌ガイド溝
180: 雌ハウジング
182: 収容部
183: ランス
Claims (5)
- 電線の外周がシールド体で覆われたケーブルの端部に接続されるコネクタであって、
第1外導体と、前記第1外導体に組み付けられる第2外導体と、を有し、
前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とが組み付けられた状態で、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体が、前記電線に接続された内導体が収容される誘電体を覆うようになっており、
前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の一方には他方に向かって突出する位置決め凸部が形成されており、前記第1外導体および前記第2外導体の他方には前記位置決め凸部と係合する位置決め凹部が形成されているコネクタ。 - 前記第1外導体の外側に前記第2外導体が組み付けられるようになっており、
前記第1外導体に前記位置決め凸部が外方に突出して形成されており、前記第2外導体に前記位置決め凹部が形成されており、
前記位置決め凹部は、前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とを組み付ける組み付け方向に沿って延びるスリットである請求項1に記載のコネクタ。 - 前記第2外導体は、前記第1外導体の外周に圧着する圧着片を有し、
前記圧着片の側縁が前記スリットの口縁を形成する請求項2に記載のコネクタ。 - 前記第1外導体と前記第2外導体とが組み付けられた状態でハウジング内に収容されるようになっており、
前記第2外導体は前記ハウジングと係合するスタビライザを有し、
前記スタビライザの側縁が前記スリットの口縁を形成する請求項2または請求項3に記載のコネクタ。 - 前記スタビライザは、前記スタビライザの先端部が折り返された折り返し部を有し、前記折り返し部が、前記ハウジングに形成されたガイド溝に挿入される請求項4に記載のコネクタ。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US17/629,613 US20220247133A1 (en) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-07-22 | Connector |
| DE112020003793.2T DE112020003793T5 (de) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-07-22 | Verbinder |
| CN202080054602.9A CN114175413B (zh) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-07-22 | 连接器 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019-147190 | 2019-08-09 | ||
| JP2019147190A JP7211301B2 (ja) | 2019-08-09 | 2019-08-09 | コネクタ |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021029199A1 true WO2021029199A1 (ja) | 2021-02-18 |
Family
ID=74570614
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/028468 WO2021029199A1 (ja) | 2019-08-09 | 2020-07-22 | コネクタ |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20220247133A1 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP7211301B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN114175413B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112020003793T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2021029199A1 (ja) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07254454A (ja) * | 1993-01-15 | 1995-10-03 | Whitaker Corp:The | シールド型電気コネクタ |
| JP2003297493A (ja) * | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-17 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 同軸コネクタ |
| US6783397B2 (en) * | 2002-01-22 | 2004-08-31 | Su-Lan Yang Lee | Connector |
| JP2007280850A (ja) * | 2006-04-10 | 2007-10-25 | Sumitomo Wiring Syst Ltd | 端子金具 |
| JP2016072067A (ja) * | 2014-09-30 | 2016-05-09 | ホシデン株式会社 | コネクタ |
| WO2017122779A1 (ja) * | 2016-01-13 | 2017-07-20 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | コネクタ |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5273459A (en) * | 1992-10-01 | 1993-12-28 | The Whitaker Corporation | Connector feature for improved contact wiping |
| US6210223B1 (en) * | 1998-11-19 | 2001-04-03 | Sumitomo Wiring Systems, Ltd. | Shielded connector, a set of shielded connectors and method for connecting a shielded connector with a shielded cable |
| JP5785011B2 (ja) * | 2011-07-19 | 2015-09-24 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | シールドコネクタ |
| JP5836715B2 (ja) * | 2011-09-07 | 2015-12-24 | 矢崎総業株式会社 | シールドコネクタ |
| JP6708025B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-04 | 2020-06-10 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | シールドコネクタ |
| JP6750525B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-02 | 2020-09-02 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | シールドコネクタ及び雄側シールド端子 |
| JP6863164B2 (ja) | 2017-07-31 | 2021-04-21 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 電線の圧着構造及びシールド導電路 |
| CN107887763B (zh) * | 2017-11-21 | 2023-08-29 | 东莞市卓越鑫汽车电子科技有限公司 | 汽车高速连接器结构和汽车高速连接器组件 |
| JP6920980B2 (ja) * | 2017-12-25 | 2021-08-18 | ヒロセ電機株式会社 | シールド端子ユニットおよびコネクタ |
-
2019
- 2019-08-09 JP JP2019147190A patent/JP7211301B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-07-22 DE DE112020003793.2T patent/DE112020003793T5/de active Pending
- 2020-07-22 WO PCT/JP2020/028468 patent/WO2021029199A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2020-07-22 US US17/629,613 patent/US20220247133A1/en active Pending
- 2020-07-22 CN CN202080054602.9A patent/CN114175413B/zh active Active
-
2023
- 2023-01-11 JP JP2023002256A patent/JP7389957B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07254454A (ja) * | 1993-01-15 | 1995-10-03 | Whitaker Corp:The | シールド型電気コネクタ |
| US6783397B2 (en) * | 2002-01-22 | 2004-08-31 | Su-Lan Yang Lee | Connector |
| JP2003297493A (ja) * | 2002-04-05 | 2003-10-17 | Auto Network Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | 同軸コネクタ |
| JP2007280850A (ja) * | 2006-04-10 | 2007-10-25 | Sumitomo Wiring Syst Ltd | 端子金具 |
| JP2016072067A (ja) * | 2014-09-30 | 2016-05-09 | ホシデン株式会社 | コネクタ |
| WO2017122779A1 (ja) * | 2016-01-13 | 2017-07-20 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | コネクタ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20220247133A1 (en) | 2022-08-04 |
| CN114175413B (zh) | 2024-03-22 |
| CN114175413A (zh) | 2022-03-11 |
| JP7211301B2 (ja) | 2023-01-24 |
| JP7389957B2 (ja) | 2023-12-01 |
| JP2021028871A (ja) | 2021-02-25 |
| JP2023033402A (ja) | 2023-03-10 |
| DE112020003793T5 (de) | 2022-05-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9531132B2 (en) | Connector having shielding structure with shield shell and shield cover | |
| JP6663814B2 (ja) | コネクタ及びワイヤハーネス | |
| JP5751194B2 (ja) | コネクタ及びワイヤハーネス | |
| JP6708025B2 (ja) | シールドコネクタ | |
| US10644414B2 (en) | Terminal fitting and connector | |
| WO2021199945A1 (ja) | シールド端子及びシールドコネクタ | |
| JP2008123913A (ja) | 内導体端子及び同軸コネクタ | |
| WO2021029199A1 (ja) | コネクタ | |
| CN113196581A (zh) | 端子模块及连接器 | |
| JP2017098081A (ja) | シールドコネクタ、及びコネクタ付きシールドケーブル | |
| WO2021029198A1 (ja) | コネクタおよびコネクタ装置 | |
| US11482814B2 (en) | Connector with structure for suppressing rattling of the shield terminal | |
| JP6927447B2 (ja) | 端子モジュールおよびコネクタ | |
| CN111725663B (zh) | 连接器 | |
| JP2021086677A (ja) | シールド電線の接続構造 | |
| CN113228429B (zh) | 带端子电线及连接器 | |
| WO2021029200A1 (ja) | コネクタ | |
| JP7364374B2 (ja) | シールドコネクタ | |
| JP2006107802A (ja) | 電子素子内蔵シールドコネクタ | |
| JP2017010685A (ja) | ツイストペア電線の接続部材及びコネクタ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20853162 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20853162 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |